



生物多样性 ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (9): 25082. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2025082 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2025082
李佳璐1( ), 李启研1(
), 李启研1( ), 赵珮杉1(
), 赵珮杉1( ), 高广磊1,2,3,4,5,*(
), 高广磊1,2,3,4,5,*( )(
)( ), 丁国栋1,3,4,5(
), 丁国栋1,3,4,5( ), 张英1,3,4,5(
), 张英1,3,4,5( )
)
收稿日期:2025-03-10
接受日期:2025-07-23
出版日期:2025-09-20
发布日期:2025-10-31
通讯作者:
*E-mail: gaoguanglei@bjfu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Jialu Li1( ), Qiyan Li1(
), Qiyan Li1( ), Peishan Zhao1(
), Peishan Zhao1( ), Guanglei Gao1,2,3,4,5,*(
), Guanglei Gao1,2,3,4,5,*( )(
)( ), Guodong Ding1,3,4,5(
), Guodong Ding1,3,4,5( ), Ying Zhang1,3,4,5(
), Ying Zhang1,3,4,5( )
)
Received:2025-03-10
Accepted:2025-07-23
Online:2025-09-20
Published:2025-10-31
Contact:
*E-mail: gaoguanglei@bjfu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要: 土壤细菌是荒漠生态系统的重要组成部分, 研究不同降水量的荒漠土壤细菌群落多样性和稳定性具有重要意义。本研究以塔里木盆地南缘荒漠为对象, 采集且末县、民丰县、和田县、皮山县、巴楚县荒漠土壤样品, 采用高通量测序技术分析土壤细菌群落组成, 比较降水量对总细菌、共有细菌、特有细菌多样性和稳定性的影响。结果表明: (1)降水量显著影响荒漠土壤细菌组成、多样性和群落结构, 土壤水分和盐碱度是主要环境因素。研究区的土壤细菌以假单胞菌门、放线菌门、拟杆菌门、芽孢杆菌门和芽单胞菌门为优势菌门。总细菌的组成及多样性与共有细菌更为相似, 与相对丰度较高的特有细菌存在显著差异。(2)土壤细菌共现网络以正向边为主, 发现荒漠中的关键种群包括陆地细菌S0134群(S0134_terrestrial_group)、动性球菌属(Planococcus)和芽孢杆菌属(Bacillus)等。降水量与降水频率的升高与细菌共现网络的稳定性相关, 且降水频率的影响比降水量更显著。研究结果有助于理解干旱区荒漠土壤细菌群落多样性和稳定性对环境的响应机制。
李佳璐, 李启研, 赵珮杉, 高广磊, 丁国栋, 张英 (2025) 降水量与塔里木盆地南缘荒漠土壤细菌群落多样性和稳定性的相关性. 生物多样性, 33, 25082. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2025082.
Jialu Li, Qiyan Li, Peishan Zhao, Guanglei Gao, Guodong Ding, Ying Zhang (2025) Correlation between precipitation and the diversity and stability of the desert soil bacterial communities at the southern margin of the Tarim Basin. Biodiversity Science, 33, 25082. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2025082.
| 样地 Plots | 经度 Longitude (E) | 纬度 Latitude (N) | 年平均降水量 Mean annual precipitation (mm) | 年平均气温 Mean annual temperature (℃) | 年平均降水日数 Mean annual precipitation days |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 且末县 QM | 85.76° | 38.58° | 26.26 | 12.17 | 90.2 |
| 民丰县 MF | 82.93° | 37.04° | 53.10 | 13.17 | 53.8 |
| 和田县 HT | 80.36° | 37.56° | 59.77 | 13.96 | 85.8 |
| 皮山县 PS | 79.18° | 37.56° | 69.26 | 14.38 | 102.8 |
| 巴楚县 BC | 79.20° | 39.32° | 91.43 | 13.75 | 170.7 |
表1 塔里木盆地南缘样地地理和气候特性
Table 1 Geographical and climatic properties of plots at the southern margin of the Tarim Basin
| 样地 Plots | 经度 Longitude (E) | 纬度 Latitude (N) | 年平均降水量 Mean annual precipitation (mm) | 年平均气温 Mean annual temperature (℃) | 年平均降水日数 Mean annual precipitation days |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 且末县 QM | 85.76° | 38.58° | 26.26 | 12.17 | 90.2 |
| 民丰县 MF | 82.93° | 37.04° | 53.10 | 13.17 | 53.8 |
| 和田县 HT | 80.36° | 37.56° | 59.77 | 13.96 | 85.8 |
| 皮山县 PS | 79.18° | 37.56° | 69.26 | 14.38 | 102.8 |
| 巴楚县 BC | 79.20° | 39.32° | 91.43 | 13.75 | 170.7 |
| 样地 Plots | 且末县 QM | 民丰县 MF | 和田县 HT | 皮山县 PS | 巴楚县 BC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.98 ± 0.19b | 8.66 ± 0.18c | 9.16 ± 0.07a | 9.07 ± 0.31ab | 8.40 ± 0.05d |
| SWC (%) | 3.72 ± 0.12b | 3.65 ± 0.68b | 6.95 ± 4.00ab | 7.99 ± 7.07a | 9.33 ± 4.24a |
| EC (μs/cm) | 229.07 ± 18.16d | 109.01 ± 8.41e | 1,003.27 ± 83.94a | 812.73 ± 34.46b | 653.07 ± 70.81c |
| TN (g/kg) | 0.16 ± 0.03b | 0.74 ± 0.25a | 0.11 ± 0.05b | 0.71 ± 0.09a | 0.13 ± 0.03b |
| TP (g/kg) | 0.17 ± 0.08e | 0.23 ± 0.04d | 0.39 ± 0.03b | 0.71 ± 0.05a | 0.33 ± 0.06c |
| SOC (g/kg) | 0.36 ± 0.08b | 0.34 ± 0.06b | 0.73 ± 0.33a | 0.33 ± 0.08b | 0.63 ± 0.12a |
| TC (g/kg) | 16.60 ± 3.21ab | 17.34 ± 3.16a | 14.03 ± 3.34bc | 12.61 ± 3.30c | 11.36 ± 2.72c |
表2 塔里木盆地南缘荒漠土壤理化性质
Table 2 Physical and chemical properties of desert soil at the southern margin of the Tarim Basin
| 样地 Plots | 且末县 QM | 民丰县 MF | 和田县 HT | 皮山县 PS | 巴楚县 BC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.98 ± 0.19b | 8.66 ± 0.18c | 9.16 ± 0.07a | 9.07 ± 0.31ab | 8.40 ± 0.05d |
| SWC (%) | 3.72 ± 0.12b | 3.65 ± 0.68b | 6.95 ± 4.00ab | 7.99 ± 7.07a | 9.33 ± 4.24a |
| EC (μs/cm) | 229.07 ± 18.16d | 109.01 ± 8.41e | 1,003.27 ± 83.94a | 812.73 ± 34.46b | 653.07 ± 70.81c |
| TN (g/kg) | 0.16 ± 0.03b | 0.74 ± 0.25a | 0.11 ± 0.05b | 0.71 ± 0.09a | 0.13 ± 0.03b |
| TP (g/kg) | 0.17 ± 0.08e | 0.23 ± 0.04d | 0.39 ± 0.03b | 0.71 ± 0.05a | 0.33 ± 0.06c |
| SOC (g/kg) | 0.36 ± 0.08b | 0.34 ± 0.06b | 0.73 ± 0.33a | 0.33 ± 0.08b | 0.63 ± 0.12a |
| TC (g/kg) | 16.60 ± 3.21ab | 17.34 ± 3.16a | 14.03 ± 3.34bc | 12.61 ± 3.30c | 11.36 ± 2.72c |
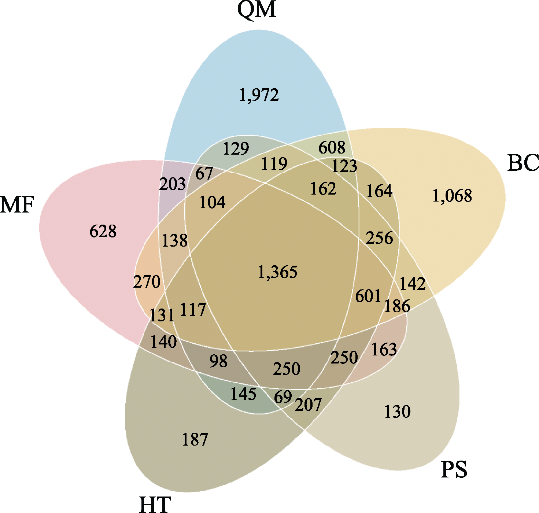
图1 塔里木盆地南缘荒漠土壤细菌Venn图。QM: 且末县; MF: 民丰县; HT: 和田县; PS: 皮山县; BC: 巴楚县。
Fig. 1 Venn of desert soil bacteria at the southern margin of the Tarim Basin. QM, Qiemo County; MF, Minfeng County; HT, Hetian County; PS, Pishan County; BC, Bachu County.
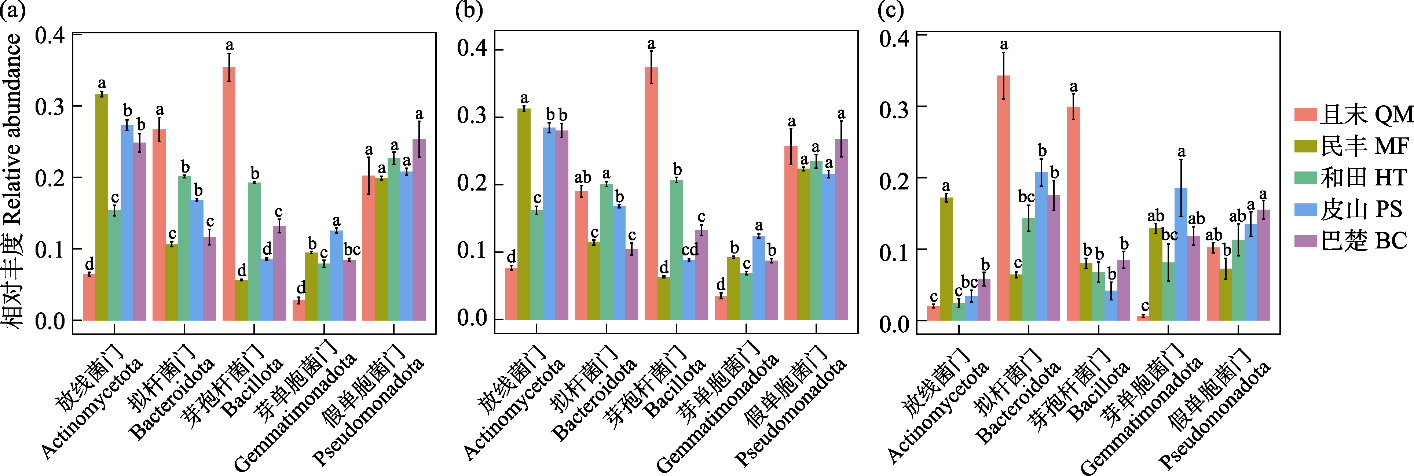
图2 塔里木盆地南缘荒漠土壤细菌优势菌门相对丰度。(a)总细菌; (b)共有细菌; (c)特有细菌。不同小写字母表示不同样地间优势菌门相对丰度存在显著差异(P < 0.05)。QM: 且末县; MF: 民丰县; HT: 和田县; PS: 皮山县; BC: 巴楚县。
Fig. 2 The relative abundance of dominant desert soil bacteria phylum at the southern margin of the Tarim Basin. (a) Whole bacteria; (b) Common bacteria; (c) Specific bacteria. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences in relative abundance of dominant bacterial phyla among the plots (P < 0.05). QM, Qiemo County; MF, Minfeng County; HT, Hetian County; PS, Pishan County; BC, Bachu County.
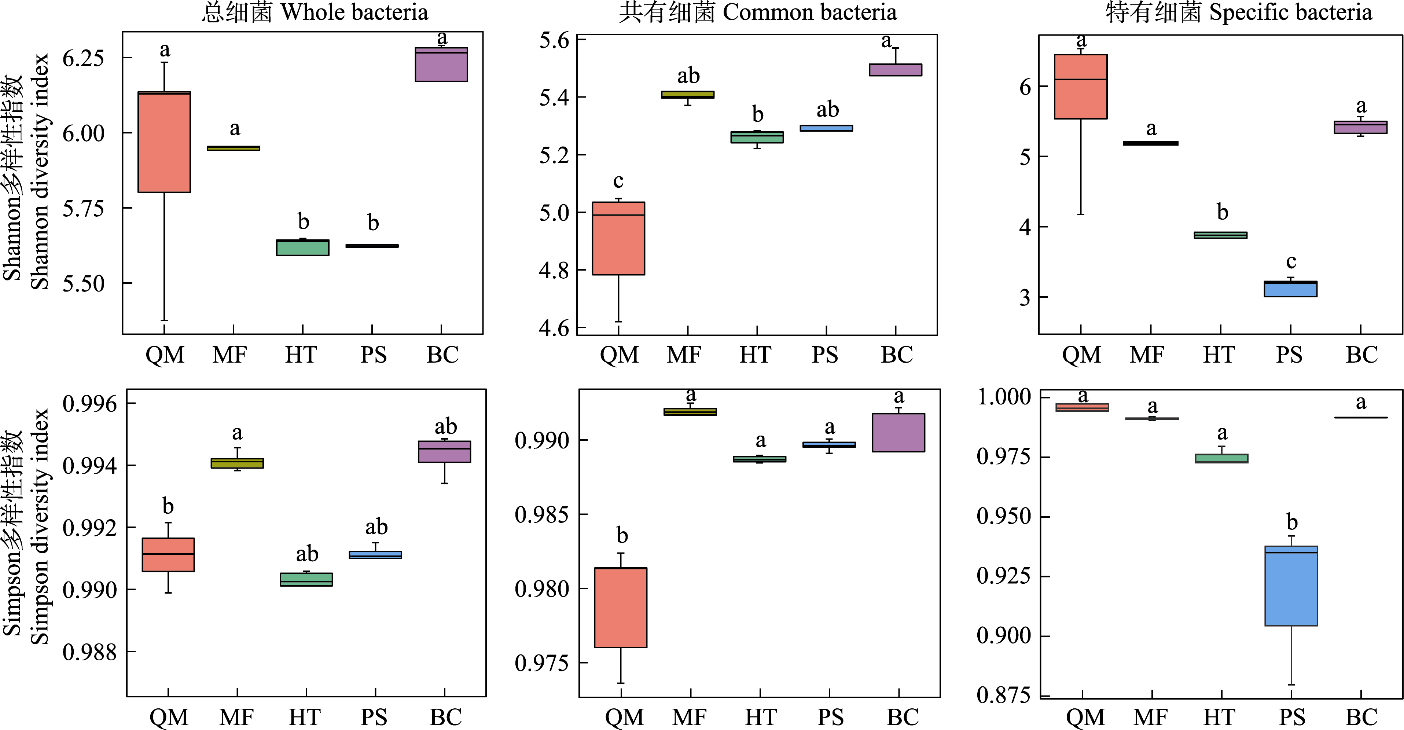
图3 塔里木盆地南缘荒漠土壤细菌群落alpha多样性。不同小写字母表示不同样地间alpha多样性存在显著差异(P < 0.05)。QM: 且末县; MF: 民丰县; HT: 和田县; PS: 皮山县; BC: 巴楚县。
Fig. 3 Alpha diversity of the desert soil bacterial communities at the southern margin of the Tarim Basin. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences in alpha diversity (P < 0.05). QM, Qiemo County; MF, Minfeng County; HT, Hetian County; PS, Pishan County; BC, Bachu County.
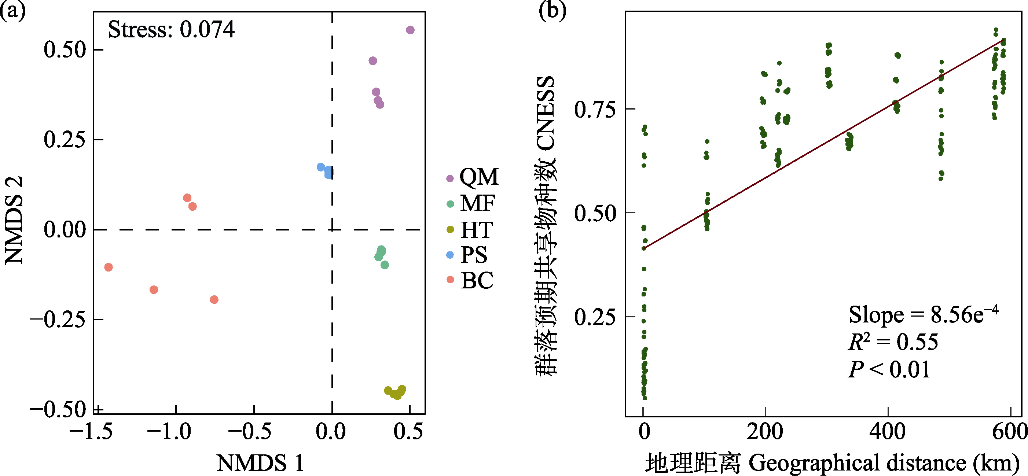
图4 塔里木盆地南缘荒漠土壤细菌群落beta多样性。(a)基于弦标准化的预期共享物种数(CNESS)的细菌群落结构非度量多维尺度排序(NMDS); (b)群落间CNESS与地理距离的关系。QM: 且末县; MF: 民丰县; HT: 和田县; PS: 皮山县; BC: 巴楚县。
Fig. 4 Beta diversity of the desert soil bacterial communities at the southern margin of the Tarim Basin. (a) Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) ordination based on chord-normalized expected species shared (CNESS); (b) Relationship between CNESS and geographical distance. QM, Qiemo County; MF, Minfeng County; HT, Hetian County; PS, Pishan County; BC, Bachu County.
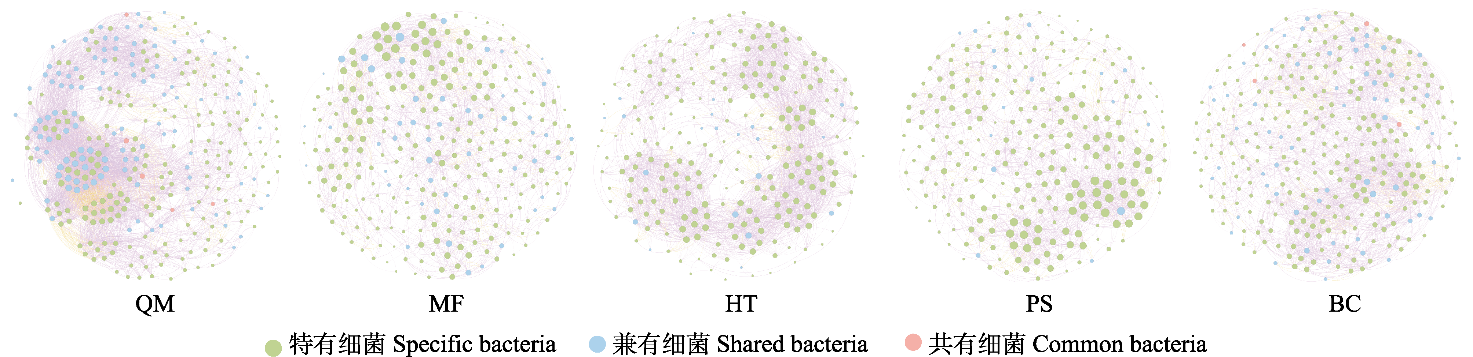
图5 塔里木盆地南缘荒漠土壤细菌共现网络。节点大小表示节点的连接度。紫色边代表正相关性, 黄色边代表负相关性。QM: 且末县; MF: 民丰县; HT: 和田县; PS: 皮山县; BC: 巴楚县。
Fig. 5 Co-occurrence network of the desert soil bacterial communities at the southern margin of the Tarim Basin. Node size represent different degree. Purple edges represent active correlations, and yellow edges represent negative correlations. QM, Qiemo County; MF, Minfeng County; HT, Hetian County; PS, Pishan County; BC, Bachu County.
| 且末县 QM | 民丰县 MF | 和田县 HT | 皮山县 PS | 巴楚县 BC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 节点 Node | 314 | 295 | 253 | 264 | 317 |
| 边 Link | 5,482 | 2,106 | 3,317 | 1,864 | 3,074 |
| 模块化 Modularity | 0.553 | 0.656 | 0.52 | 0.587 | 0.614 |
| 平均度 Average degree | 34.917 | 14.278 | 26.221 | 14.121 | 19.394 |
| 平均路径长度 Average path distance | 3.567 | 4.012 | 3.65 | 3.979 | 3.857 |
| 平均聚类系数 Average clustering coefficient | 0.606 | 0.472 | 0.624 | 0.506 | 0.527 |
| 正向边占比 Proportion of active edges (%) | 85.84 | 85.09 | 94.81 | 90.99 | 90.27 |
| 负向边占比 Proportion of negative edges (%) | 14.16 | 14.91 | 5.19 | 9.01 | 9.73 |
| 共有节点占比 Proportion of common nodes (%) | 1.59 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.26 |
| 兼有节点占比 Proportion of shared nodes (%) | 35.35 | 17.29 | 8.3 | 6.06 | 19.56 |
| 特有节点占比 Proportion of specific nodes (%) | 63.06 | 82.71 | 91.7 | 93.94 | 79.18 |
表3 塔里木盆地南缘荒漠土壤细菌共现网络拓扑特征
Table 3 Topological parameters of desert soil bacterial co-occurrence networks at the southern margin of the Tarim Basin
| 且末县 QM | 民丰县 MF | 和田县 HT | 皮山县 PS | 巴楚县 BC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 节点 Node | 314 | 295 | 253 | 264 | 317 |
| 边 Link | 5,482 | 2,106 | 3,317 | 1,864 | 3,074 |
| 模块化 Modularity | 0.553 | 0.656 | 0.52 | 0.587 | 0.614 |
| 平均度 Average degree | 34.917 | 14.278 | 26.221 | 14.121 | 19.394 |
| 平均路径长度 Average path distance | 3.567 | 4.012 | 3.65 | 3.979 | 3.857 |
| 平均聚类系数 Average clustering coefficient | 0.606 | 0.472 | 0.624 | 0.506 | 0.527 |
| 正向边占比 Proportion of active edges (%) | 85.84 | 85.09 | 94.81 | 90.99 | 90.27 |
| 负向边占比 Proportion of negative edges (%) | 14.16 | 14.91 | 5.19 | 9.01 | 9.73 |
| 共有节点占比 Proportion of common nodes (%) | 1.59 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.26 |
| 兼有节点占比 Proportion of shared nodes (%) | 35.35 | 17.29 | 8.3 | 6.06 | 19.56 |
| 特有节点占比 Proportion of specific nodes (%) | 63.06 | 82.71 | 91.7 | 93.94 | 79.18 |
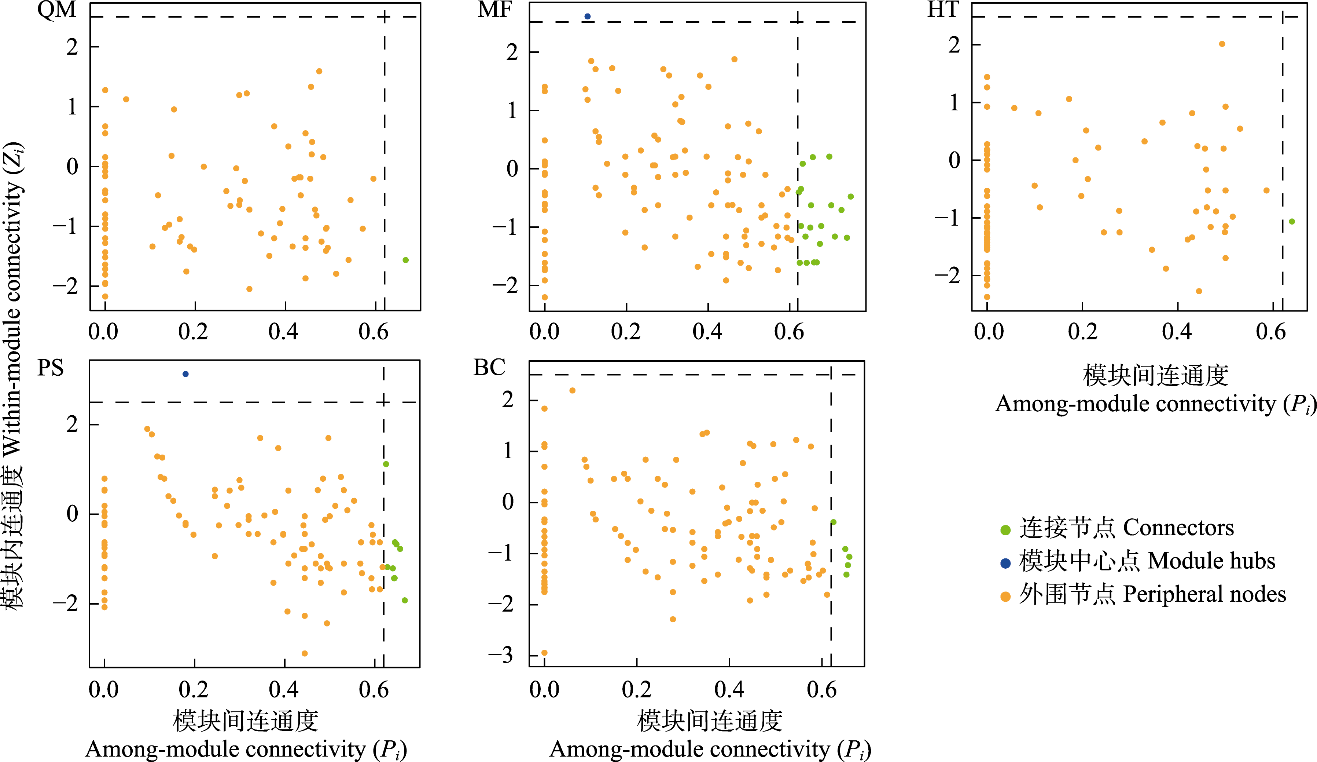
图6 塔里木盆地南缘荒漠土壤细菌共现网络关键节点。QM: 且末县; MF: 民丰县; HT: 和田县; PS: 皮山县; BC: 巴楚县。
Fig. 6 Key nodes of the desert soil bacterial co-occurrence networks at the southern margin of the Tarim Basin. QM, Qiemo County; MF, Minfeng County; HT, Hetian County; PS, Pishan County; BC, Bachu County.
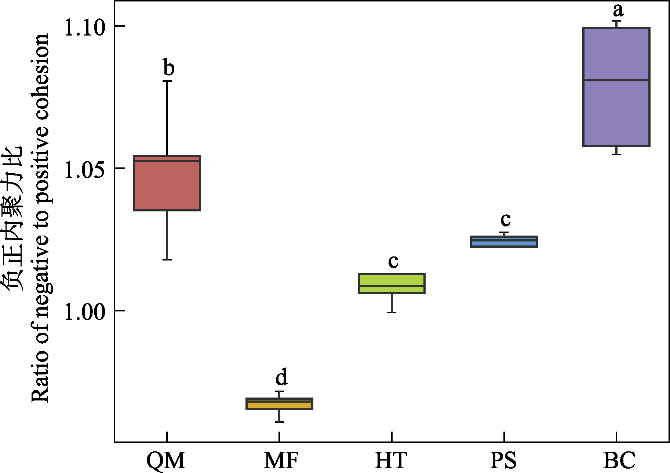
图7 塔里木盆地南缘荒漠土壤细菌共现网络稳定性。QM: 且末县; MF: 民丰县; HT: 和田县; PS: 皮山县; BC: 巴楚县。
Fig. 7 Stability of the desert soil bacteria co-occurrence networks at the southern margin of the Tarim Basin. QM, Qiemo County; MF, Minfeng County; HT, Hetian County; PS, Pishan County; BC, Bachu County.
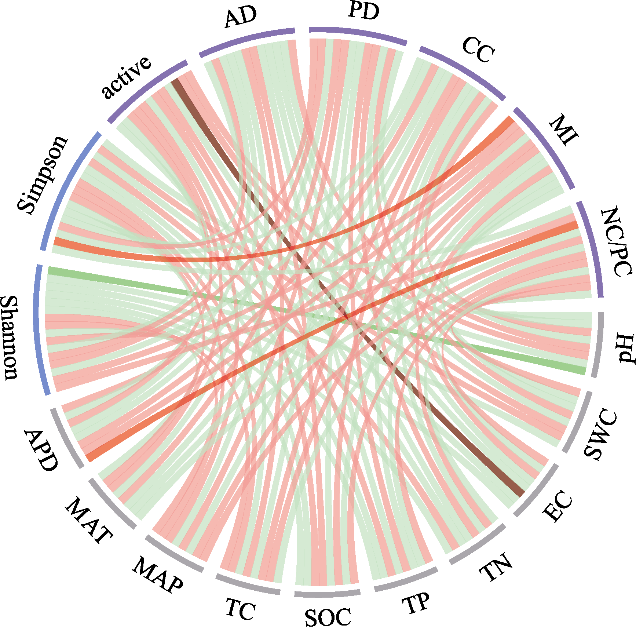
图8 土壤细菌群落特征与环境因子相关性。弦的粗细表示相关性大小, 红色表示正相关关系, 绿色表示负相关关系。颜色深浅表示显著性大小, 深色表明相关性显著。active: 正向边比例; AD: 平均度; PD: 平均路径长度; CC: 平均聚类系数; MI: 模块化指数; NC/PC: 负正内聚力比; SWC: 土壤含水量; EC: 电导率; TN: 全氮; TP: 全磷; SOC: 有机碳; TC: 总碳; MAP: 年平均降水量; MAT: 年平均气温; APD: 年平均降水日数; Shannon: Shannon多样性指数; Simpson: Simpson多样性指数。
Fig. 8 Correlation between soil bacterial community characteristics and environmental factors. Thickness of the chords represents the magnitude of correlations, red indicating positive relationships, green indicating negative relationships. The color of the chords represents the significance level, darker shades indicating higher significance. Active, Fraction of positive edges; AD, Average degree; PD, Average path distance; CC, Average clustering coefficient; MI, Modularity index; NC/PC, Ratio of negative to positive cohesion; SWC, Soil water content; EC, Electrical conductivity; TN, Total nitrogen; TP, Total phosphorus; SOC, Soil organic carbon; TC, Total carbon; MAP, Mean annual precipitation; MAT, Mean annual temperature; APD, Mean annual precipitation days; Shannon, Shannon diversity index; Simpson, Simpson diversity index.
| [1] |
Abbas A, Zhang TX, He Q, Bo L, Jin LL, Zhang JL, Salam A (2022) Variations in different types and levels of daily precipitation in the Tarim Basin, Northwest China. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 149, 1509-1520.
DOI |
| [2] |
Berry D, Widder S (2014) Deciphering microbial interactions and detecting keystone species with co-occurrence networks. Frontiers in Microbiology, 5, 219.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | Burrell AL, Evans JP, De Kauwe MG (2020) Anthropogenic climate change has driven over 5 million km2 of drylands towards desertification. Nature Communications, 11, 3853. |
| [4] |
Cao Y, Li ZY, Du PH, Ji JH, Sun W, Xu JZ, Liang BW (2024) Effects of different dwarfing interstocks on the rhizosphere, endophytic bacteria, and drought resistance of apple trees. Microbiological Research, 283, 127690.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Chen H, Zhao XR, Lin QM, Li GT, Kong WD (2019) Using a combination of PLFA and DNA-based sequencing analyses to detect shifts in the soil microbial community composition after a simulated spring precipitation in a semi-arid grassland in China. Science of the Total Environment, 657, 1237-1245.
DOI |
| [6] |
Coyte KZ, Schluter J, Foster KR (2015) The ecology of the microbiome: Networks, competition, and stability. Science, 350, 663-666.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
Deng Y, Jiang YH, Yang YF, He ZL, Luo F, Zhou JZ (2012) Molecular ecological network analyses. BMC Bioinformatics, 13, 113.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
Du F, Rong XY, Xu P, Yin BF, Zhang YM (2023) Bacterial diversity and community assembly responses to precipitation in the Gurbantunggut Desert. Biodiversity Science, 31, 22492. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[杜芳, 荣晓莹, 徐鹏, 尹本丰, 张元明 (2023) 降水对古尔班通古特沙漠细菌群落多样性和构建过程的影响. 生物多样性, 31, 22492.]
DOI |
|
| [9] | Du QJ (2021) The Patterns and Determinants of Soil Microbial Diversity in China’s Drylands. PhD dissertation, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杜洽军 (2021) 中国干旱区土壤微生物多样性格局及影响因素研究. 博士学位论文, 兰州大学, 兰州.] | |
| [10] |
Fierer N, Wood SA, Bueno de Mesquita CP (2021) How microbes can, and cannot, be used to assess soil health. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 153, 108111.
DOI URL |
| [11] | Gao JP, Zhao RF, Zhang LH, Wang JF, Xie ZK (2021) Effects of precipitation changes on plant community diversity and soil C∶N∶P ecological stoichiometric characteristics in a desert steppe of China. Environmental Science, 42, 977-987. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [高江平, 赵锐锋, 张丽华, 王军锋, 谢忠奎 (2021) 降雨变化对荒漠草原植物群落多样性与土壤C∶N∶P生态化学计量特征的影响. 环境科学, 42, 977-987.] | |
| [12] |
Guimerà R, Nunes Amaral LA (2005) Functional cartography of complex metabolic networks. Nature, 433, 895-900.
DOI |
| [13] |
Guo R, Wu XD, Wang ZJ, Jiang Q, Yu HQ, He J, Liu WJ, Ma K (2023) Responses of soil bacterial and fungal communities to altered precipitation in a desert steppe. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 34, 1500-1508. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[郭蓉, 吴旭东, 王占军, 蒋齐, 俞鸿千, 贺婧, 刘文娟, 马琨 (2023) 荒漠草原土壤细菌和真菌群落对降水变化的响应. 应用生态学报, 34, 1500-1508.]
DOI |
|
| [14] |
Han JY, Miao CY, Gou JJ, Zheng HY, Zhang Q, Guo XY (2023) A new daily gridded precipitation dataset for the Chinese mainland based on gauge observations. Earth System Science Data, 15, 3147-3161.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Hernandez DJ, David AS, Menges ES, Searcy CA, Afkhami ME (2021) Environmental stress destabilizes microbial networks. The ISME Journal, 15, 1722-1734.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Herren CM, McMahon KD (2017) Cohesion: A method for quantifying the connectivity of microbial communities. The ISME Journal, 11, 2426-2438.
DOI URL |
| [17] | Huang Y, Huang MK, Chai LW, Zhao YR (2018) Drivers of the spatial patterns of soil microbial communities in arid and semi-arid regions. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27, 191-198. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[黄艺, 黄木柯, 柴立伟, 赵嫣然 (2018) 干旱半干旱区土壤微生物空间分布格局的成因. 生态环境学报, 27, 191-198.]
DOI |
|
| [18] | Li N, Wang BR, An SS, Jiao F, Huang Q (2020) Response of soil bacterial community structure to precipitation change in grassland of Loess Plateau. Environmental Science, 41, 4284-4293. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李娜, 王宝荣, 安韶山, 焦峰, 黄倩 (2020) 黄土高原草地土壤细菌群落结构对于降水变化的响应. 环境科学, 41, 4284-4293.] | |
| [19] | Li QY, Zhao PS, Gao GL, Ding GD, Zhang Y, Liu MH (2024) Complexity and stability of molecular ecological network of root-associated fungi associated with Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 44, 7226-7237. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李启研, 赵珮杉, 高广磊, 丁国栋, 张英, 刘明慧 (2024) 樟子松根内真菌分子生态网络复杂性与稳定性. 生态学报, 44, 7226-7237.] | |
| [20] |
Li T, Zhang W, Liu GX, Chen T (2018) Advances in the study of microbial ecology in desert soil. Journal of Desert Research, 38, 329-338. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[李婷, 张威, 刘光琇, 陈拓 (2018) 荒漠土壤微生物群落结构特征研究进展. 中国沙漠, 38, 329-338.]
DOI |
|
| [21] | Lin JM, Zheng TT, Yuan HL, Bao XL, Min KK, Jia WN, Zhu XF, Liang C (2024) Effects of ecosystem habitat changes on the response of microbial community structure. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 55, 149-160. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [林佳敏, 郑甜甜, 袁慧兰, 鲍雪莲, 闵凯凯, 贾卫娜, 朱雪峰, 梁超 (2024) 生态系统生境改变对土壤微生物群落结构的影响. 土壤通报, 55, 149-160.] | |
| [22] | Liu KL, Wang JQ, Bu DP, Li D, Yu P, Zhao SG (2010) Current progress in approaches to the study of structure and function diversities of environmental microbial communities. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30, 1074-1080. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘开朗, 王加启, 卜登攀, 李旦, 于萍, 赵圣国 (2010) 环境微生物群落结构与功能多样性研究方法. 生态学报, 30, 1074-1080.] | |
| [23] |
Liu N, Li G, Su Y, Zhao Y, Ma J, Huang GQ (2023) Environmental drivers and interaction mechanisms of heavy metal and antibiotic resistome exposed to amoxicillin during aerobic composting. Frontiers in Microbiology, 13, 1079114.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Liu X, Chu HY, Oscar G, Fan KK, Gao GF, Yang T, Ma YY, Manuel D (2024) Positive associations fuel soil biodiversity and ecological networks worldwide. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 121, e2308769121. |
| [25] |
Na XF, Yu HL, Wang P, Zhu WW, Niu YB, Huang JY (2019) Vegetation biomass and soil moisture coregulate bacterial community succession under altered precipitation regimes in a desert steppe in northwestern China. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 136, 107520.
DOI URL |
| [26] | Niu SQ, Long Y, Li HY, Da WY, Hu S, Li WJ, Zhu XT, Kong WB (2017) Microbial diversity in saline alkali soil from Hexi Corridor analyzed by Illumina MiSeq high-throughput sequencing system. Microbiology China, 44, 2067-2078. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [牛世全, 龙洋, 李海云, 达文燕, 胡山, 李渭娟, 朱学泰, 孔维宝 (2017) 应用Illumina MiSeq高通量测序技术分析河西走廊地区盐碱土壤微生物多样性. 微生物学通报, 44, 2067-2078.] | |
| [27] | Peng SZ (2019) 1-km Monthly Mean Temperature Dataset for China (1901-2023). National Tibetan Plateau/Third Pole Environment Data Center, doi: 10.11888/Meteoro.tpdc.270961; cstr: 18406.11.Meteoro.tpdc.270961. (in Chinese) |
| [彭守璋 (2019) 中国1 km分辨率逐月平均气温数据集(1901-2023). 国家青藏高原科学数据中心, doi: 10.11888/Meteoro.tpdc.270961; cstr: 18406.11.Meteoro.tp dc.270961.] | |
| [28] | Qu Y, Sun XY, Teng XD, Xu L, Jin LM, Wang LJ, Liu XM, Qu JY, Wang XM, Xing ZK (2023) Microbial community diversity of soil in different temperature zones around the world: Based on metagenomic technology. Microbiology China, 50, 1853-1871. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [曲颖, 孙晓玥, 滕新栋, 徐丽, 金黎明, 王丽君, 刘秀梅, 曲江勇, 王绪敏, 邢志凯 (2023) 基于宏基因组技术分析全球不同温度带土壤微生物多样性. 微生物学通报, 50, 1853-1871.] | |
| [29] |
Sala OE, Lauenroth WK (1982) Small rainfall events: An ecological role in semiarid regions. Oecologia, 53, 301-304.
DOI PMID |
| [30] | Su WH, Li HM, Zhang CY, Chen XP, Lang M (2023) Phosphorus gradient fertilization and rhizosphere effect co-determine phoD-harboring bacterial network complexity and stability. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 63, 2776-2790. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [苏卫华, 李昊明, 张春燕, 陈新平, 郎明 (2023) 供磷水平和根际效应协同影响含碱性磷酸酶基因细菌群落的网络复杂性和稳定性. 微生物学报, 63, 2776-2790.] | |
| [31] | Su ZZ, Lu Q, Wu B, Jin HL, Dong GR (2006) Potential impact of climatic change and human activities on desertification in China. Journal of Desert Research, 26, 329-335. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [苏志珠, 卢琦, 吴波, 靳鹤龄, 董光荣 (2006) 气候变化和人类活动对我国荒漠化的可能影响. 中国沙漠, 26, 329-335.] | |
| [32] | Tian R, Kou J, Hu X, Zhang P, Lei J, Wang HL, Lü XD (2025) Effects of warming and precipitation changes on the structure and function of soil bacterial communities in dry-crop farmland. China Environmental Science, 45, 508-518. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [田瑞, 寇谨, 胡啸, 张鹏, 雷俊, 王鹤龄, 吕晓东 (2025) 增温和降水变化对旱作农田土壤细菌群落结构和功能的影响. 中国环境科学, 45, 508-518.] | |
| [33] |
Wang S, Wang XB, Han XG, Deng Y (2018) Higher precipitation strengthens the microbial interactions in semi- arid grassland soils. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 27, 570-580.
DOI URL |
| [34] | Wang X, Zhang Q, Zhang ZJ, Li WJ, Liu WC, Xiao NJ, Liu HY, Wang LY, Li ZX, Ma J, Liu QY, Ren CJ, Yang GH, Zhong ZK, Han XH (2023) Decreased soil multifunctionality is associated with altered microbial network properties under precipitation reduction in a semiarid grassland. iMeta, 2, e106. |
| [35] | Wang YT, Tang LS (2009) Responses of different life-form plants in Garbantunggut Desert to small rainfall events. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 28, 1028-1034. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王亚婷, 唐立松 (2009) 古尔班通古特沙漠不同生活型植物对小雨量降雨的响应. 生态学杂志, 28, 1028-1034.] | |
| [36] |
Wang YY, Ma LB, He J, Liu ZX, Weng SP, Wang LM, He JG, Guo CJ (2021) Whole genome sequencing and comparative genomic analyses of Planococcus alpniumensis MSAK28401T, a new species isolated from Antarctic krill. BMC Microbiology, 21, 288.
DOI |
| [37] | Wu F, Gao ZW, Zhang RB, Shi RX, Liu MJ, Hu J, Wang H, Zhou QP (2025) Effects of warming on soil microbial diversity and functional potential in alpine meadows. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 47, 29-38. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴菲, 高章伟, 张睿博, 时蓉喜, 刘梦洁, 胡健, 汪辉, 周青平 (2025) 增温对高寒草甸土壤微生物多样性及功能潜力的影响. 北京林业大学学报, 47, 29-38.] | |
| [38] |
Wu F, Wang YQ, Wang JT (2023) Asymmetric responses of soil bacterial community and soil respiration to precipitation changes: A global meta-analysis. Land Degradation & Development, 34, 1887-1896.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Wu XF, Yang JJ, Ruan H, Wang SN, Yang YR, Naeem I, Wang L, Liu L, Wang D (2021) The diversity and co-occurrence network of soil bacterial and fungal communities and their implications for a new indicator of grassland degradation. Ecological Indicators, 129, 107989.
DOI URL |
| [40] | Yang G, Zhao DD, Wang DF, Zheng JS, Wan CX, Zhang LL, Luo XX (2024) Diversity of soil bacterial communities in three habitats of the Tarim Basin. Microbiology China, 51, 2030-2048. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨果, 赵迪迪, 王殿付, 郑金水, 万传星, 张利莉, 罗晓霞 (2024) 塔里木盆地3种生境土壤细菌群落多样性. 微生物学通报, 51, 2030-2048.] | |
| [41] | Ye D, Wang R, Wang J, Yan P, Zhuo MJ, Liu D, Lin YH (2024) Response of soil bacterial communities and ecological networks to grazing enclosure and re-grazing in Zoige Alpine Wetland. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 44, 11229-11240. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [叶董, 王瑞, 王京, 言迫, 卓玛姐, 刘丹, 林英华 (2024) 若尔盖高寒湿地土壤细菌群落和生态网络对围封禁牧与恢复放牧的响应. 生态学报, 44, 11229-11240.] | |
| [42] |
Zhai CC, Han LL, Xiong C, Ge AH, Yue XJ, Li Y, Zhou ZX, Feng JY, Ru JY, Song J, Jiang L, Yang YF, Zhang LM, Wan SQ (2024) Soil microbial diversity and network complexity drive the ecosystem multifunctionality of temperate grasslands under changing precipitation. Science of the Total Environment, 906, 167217.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Zhang H, Jiang N, Zhang SY, Zhu XY, Wang H, Xiu WM, Zhao JN, Liu HM, Zhang HF, Yang DL (2024) Soil bacterial community composition is altered more by soil nutrient availability than pH following long-term nutrient addition in a temperate steppe. Frontiers in Microbiology, 15, 1455891.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Zhang LB, He MZ, Zhang KC, An ZS, Wang JG, Hui YX, Jia XL (2022) Effect of preliminary vegetation reconstruction on soil microorganism community structure in arid desert area. Arid Land Geography, 45, 1916-1926. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[张力斌, 何明珠, 张克存, 安志山, 王金国, 惠迎新, 贾小龙 (2022) 干旱风沙区植被重建初期对土壤微生物群落结构的影响. 干旱区地理, 45, 1916-1926.]
DOI |
|
| [45] |
Zhang LH, Gao H, Wang JF, Zhao RF, Wang MM, Hao LY, Guo YF, Jiang XY, Zhong LF (2023) Plant property regulates soil bacterial community structure under altered precipitation regimes in a semi-arid desert grassland, China. Journal of Arid Land, 15, 602-619.
DOI |
| [46] | Zhang Q, Yang JH, Wang PL, Yu HP, Yue P, Liu XY, Lin JJ, Duan XY, Zhu B, Yan XY (2023) Progress and prospect on climate warming and humidification in Northwest China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 68, 1814-1828. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张强, 杨金虎, 王朋岭, 于海鹏, 岳平, 刘晓云, 林婧婧, 段欣妤, 朱飙, 闫昕旸 (2023) 西北地区气候暖湿化的研究进展与展望. 科学通报, 68, 1814-1828.] | |
| [47] | Zhao Y, Li JP, Wang YT, Zhang Y, Zhao YX, Luo X (2025) Effects of short-term precipitation changes on soil microbial communities in desert grasslands. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 45, 64-79. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵莹, 李建平, 王誉陶, 张翼, 赵雅欣, 罗叙 (2025) 短期降水变化对荒漠草原土壤微生物群落的影响. 生态学报, 45, 64-79.] | |
| [48] |
Zhao YX, Liu ZS, Zhang BF, Cai JJ, Yao XW, Zhang M, Deng Y, Hu BL (2023) Inter-bacterial mutualism promoted by public goods in a system characterized by deterministic temperature variation. Nature Communications, 14, 5394.
DOI PMID |
| [49] |
Zhou X, Tahvanainen T, Malard L, Chen L, Pérez-Pérez J, Berninger F (2024) Global analysis of soil bacterial genera and diversity in response to pH. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 198, 109552.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
Zhou ZH, Wang CK, Luo YQ (2020) Meta-analysis of the impacts of global change factors on soil microbial diversity and functionality. Nature Communications, 11, 3072.
DOI PMID |
| [51] |
Zhu GB, Wang SY, Wang C, Zhou LG, Zhao SY, Li YX, Li FB, Jetten MSM, Lu YL, Schwark L (2019) Resuscitation of anammox bacteria after > 10,000 years of dormancy. The ISME Journal, 13, 1098-1109.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
Zou Y, Axmacher JC (2020) The Chord-Normalized Expected Species Shared (CNESS)-distance represents a superior measure of species turnover patterns. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 11, 273-280.
DOI |
| [1] | 冯缨, 宋凤, 金光照, 葛学军. 中亚荒漠区沙拐枣属的分布格局与物种多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(8): 25086-. |
| [2] | 王陈, 徐佳杰, 安瑞志, 卫佩佩, 吴湘君, 巴桑. 环境DNA揭示枯水期雅鲁藏布江中游河段原生动物多样性模式与地理分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(6): 24486-. |
| [3] | 王艺璇, 李浩, 孙蔷, 李紫晶, 李明乐, 史亚博, 郑颖, 李星, 莫宇, 范磊, 郭肖, 苗百岭, 韩瀛, 莎娜, 董雷, 张景慧, 李智勇, 王立新, 赵利清, 梁存柱. 绵刺群落地理分布及分类数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(6): 25095-. |
| [4] | 莫笑梅, 张琪, 杨嘉欣, 郑国, 胡中民, 张晓珂, 梁思维, 崔淑艳. 北方典型草地土壤线虫代谢速率及能量流动对氮沉降和降水模式改变的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24341-. |
| [5] | 魏诗雨, 宋天骄, 罗佳宜, 张燕, 赵子萱, 茹靖雯, 易华, 林雁冰. 秦岭火地塘针叶林土壤细菌群落的海拔分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24180-. |
| [6] | 尹星元, 安慧, 邢彬彬, 苏诗玉, 文志林, 郭建超, 刘小平, 王波. 养分添加和降水变化对荒漠草原地上和地下生物量稳定性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 24073-. |
| [7] | 连佳丽, 陈婧, 杨雪琴, 赵莹, 罗叙, 韩翠, 赵雅欣, 李建平. 荒漠草原植物多样性和微生物多样性对降水变化的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24044-. |
| [8] | 曹可欣, 王敬雯, 郑国, 武鹏峰, 李英滨, 崔淑艳. 降水格局改变及氮沉降对北方典型草原土壤线虫多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23491-. |
| [9] | 任嘉隆, 王永珍, 冯怡琳, 赵文智, 严祺涵, 秦畅, 方静, 辛未冬, 刘继亮. 基于陷阱法采集的河西走廊戈壁荒漠甲虫数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23375-. |
| [10] | 肖媛媛, 冯薇, 乔艳桂, 张宇清, 秦树高. 固沙灌木林地土壤微生物群落特征对土壤多功能性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22585-. |
| [11] | 周欣扬, 王誉陶, 李建平. 黄土高原典型草原植物群落组成对降水变化的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22118-. |
| [12] | 杜芳, 荣晓莹, 徐鹏, 尹本丰, 张元明. 降水对古尔班通古特沙漠细菌群落多样性和构建过程的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22492-. |
| [13] | 王健铭, 雷训, 冯益明, 吴波, 卢琦, 何念鹏, 李景文. 中国温带荒漠植物群落生态特异性格局及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(10): 23144-. |
| [14] | 刘珂, 韩思成, 遇赫, 罗述金. 荒漠猫的演化遗传、分类和保护研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(9): 22396-. |
| [15] | 孔玥峤, 刘炎林, 贺成武, 李天醍, 李全亮, 马存新, 王大军, 李晟. 评估荒漠猫的日活动节律: 基于红外相机与卫星颈圈数据的对比[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(9): 22081-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()