



生物多样性 ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (10): 23144. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023144 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023144
王健铭1, 雷训1, 冯益明2, 吴波2, 卢琦2, 何念鹏3, 李景文1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-05-08
接受日期:2023-08-29
出版日期:2023-10-20
发布日期:2023-11-30
通讯作者:
*E-mail: lijingwenhy@bjfu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Jianming Wang1, Xun Lei1, Yiming Feng2, Bo Wu2, Qi Lu2, Nianpeng He3, Jingwen Li1,*( )
)
Received:2023-05-08
Accepted:2023-08-29
Online:2023-10-20
Published:2023-11-30
Contact:
*E-mail: lijingwenhy@bjfu.edu.cn
摘要:
局域取样单元对beta多样性的贡献可用于测度每个局域群落物种组成的生态特异性(ecological uniqueness)。温带荒漠生态系统广泛分布于全球干旱和极端干旱区域, 极易受到气候变化和人类活动的影响。然而目前温带荒漠植物群落生态特异性大尺度地理分布格局及其形成机制的系统研究还很缺乏, 制约着我们对荒漠植物群落多样性维持机制的认知。本文在温带灌木、矮半乔木及草原化灌木荒漠等6个中国温带荒漠区的主要地带性植被类型中设置了948个样方, 通过开展系统的野外调查采样和室内分析, 以及量化每个取样单元对beta多样性的贡献, 并结合土壤和气候变量等环境数据, 探讨了中国荒漠植物群落生态特异性大尺度地理分布格局及其影响因素。结果表明: (1)温带荒漠植物群落生态特异性存在显著的经度、纬度和海拔分布格局, 随着经度增加显著降低, 但随着纬度或海拔的升高呈现出先下降后增加的变化趋势; (2)土壤、气候、群落特征(植物物种丰富度和群落盖度)对植物群落生态特异性都有着显著的单独影响, 植物群落生态特异性随着物种丰富度增加呈先下降后上升的变化趋势; 经度、土壤、气候和植物群落特征共同解释了温带荒漠植物群落生态特异性33.5%的空间变异, 其中气候因子有着更强的单独解释率。上述结果说明环境过滤和中性过程以及其他未知过程共同调控了温带荒漠植物群落的生态特异性大尺度分布格局的形成, 且气候和土壤因素的过滤作用有着重要影响。
王健铭, 雷训, 冯益明, 吴波, 卢琦, 何念鹏, 李景文 (2023) 中国温带荒漠植物群落生态特异性格局及其影响因素. 生物多样性, 31, 23144. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023144.
Jianming Wang, Xun Lei, Yiming Feng, Bo Wu, Qi Lu, Nianpeng He, Jingwen Li (2023) The ecological uniqueness of plant communities and their determinants across the temperate deserts of China. Biodiversity Science, 31, 23144. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023144.

图2 不同生活型物种对beta多样性贡献的差异性(平均值 ± 标准误)。不同字母表示不同生活型物种之间存在显著差异(P < 0.05)。
Fig. 2 Difference in the species contribution to beta diversity (SCBD) among different life forms (mean ± SE). Different letters indicate significant differences among different life forms (P < 0.05).

图3 中国温带荒漠植物群落生态特异性随经度(a)、纬度(b)和海拔(c)的变化趋势
Fig. 3 Trends of the ecological uniqueness of plant communities across the temperate deserts of China along longitude (a), latitude (b) and altitude (c)
| 变量 Variable | R2 | 斜率 Slope | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| 物种丰富度 Species richness (SR) | 0.044 | US | < 0.0001 |
| 植物群落盖度 Plant community coverage (PCC) | 0.036 | US | < 0.0001 |
| 土壤含水量 Soil moisture (SM) | 0.018 | 0.00002 | < 0.0001 |
| 土壤总氮含量 Soil total nitrogen content (TSN) | 0.039 | 0.00003 | < 0.0001 |
| 土壤pH值 Soil pH (pH) | 0.080 | US | < 0.0001 |
| 年均温 Mean annual temperature (MAT) | 0.037 | US | < 0.0001 |
| 年均降水量 Mean annual precipitation (MAP) | 0.074 | US | < 0.0001 |
| 降水季节性 Precipitation seasonality (PS) | 0.166 | -0.396 | < 0.0001 |
| 太阳辐射强度 Solar radiation (SRAD) | 0.123 | US | < 0.0001 |
表1 单个环境因子与植物群落生态特异性的关系
Table 1 Relationship between the ecological uniqueness of plant communities and single environmental variable
| 变量 Variable | R2 | 斜率 Slope | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| 物种丰富度 Species richness (SR) | 0.044 | US | < 0.0001 |
| 植物群落盖度 Plant community coverage (PCC) | 0.036 | US | < 0.0001 |
| 土壤含水量 Soil moisture (SM) | 0.018 | 0.00002 | < 0.0001 |
| 土壤总氮含量 Soil total nitrogen content (TSN) | 0.039 | 0.00003 | < 0.0001 |
| 土壤pH值 Soil pH (pH) | 0.080 | US | < 0.0001 |
| 年均温 Mean annual temperature (MAT) | 0.037 | US | < 0.0001 |
| 年均降水量 Mean annual precipitation (MAP) | 0.074 | US | < 0.0001 |
| 降水季节性 Precipitation seasonality (PS) | 0.166 | -0.396 | < 0.0001 |
| 太阳辐射强度 Solar radiation (SRAD) | 0.123 | US | < 0.0001 |
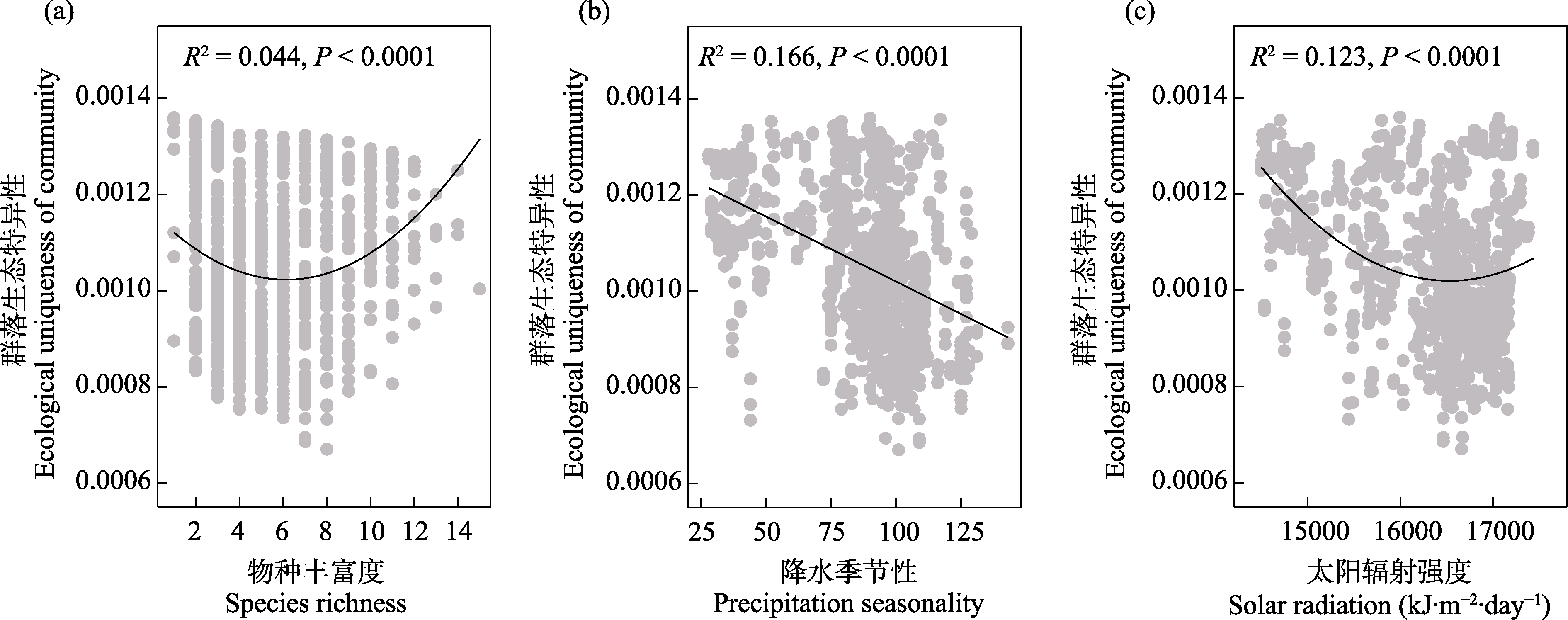
图4 中国温带荒漠植物群落生态特异性随物种丰富度(a)、降水季节性(b)和太阳辐射强度(c)的变化趋势
Fig. 4 Trends of the ecological uniqueness of plant communities across the temperate deserts of China along species richness (a), precipitation seasonality (b) and solar radiation (c)
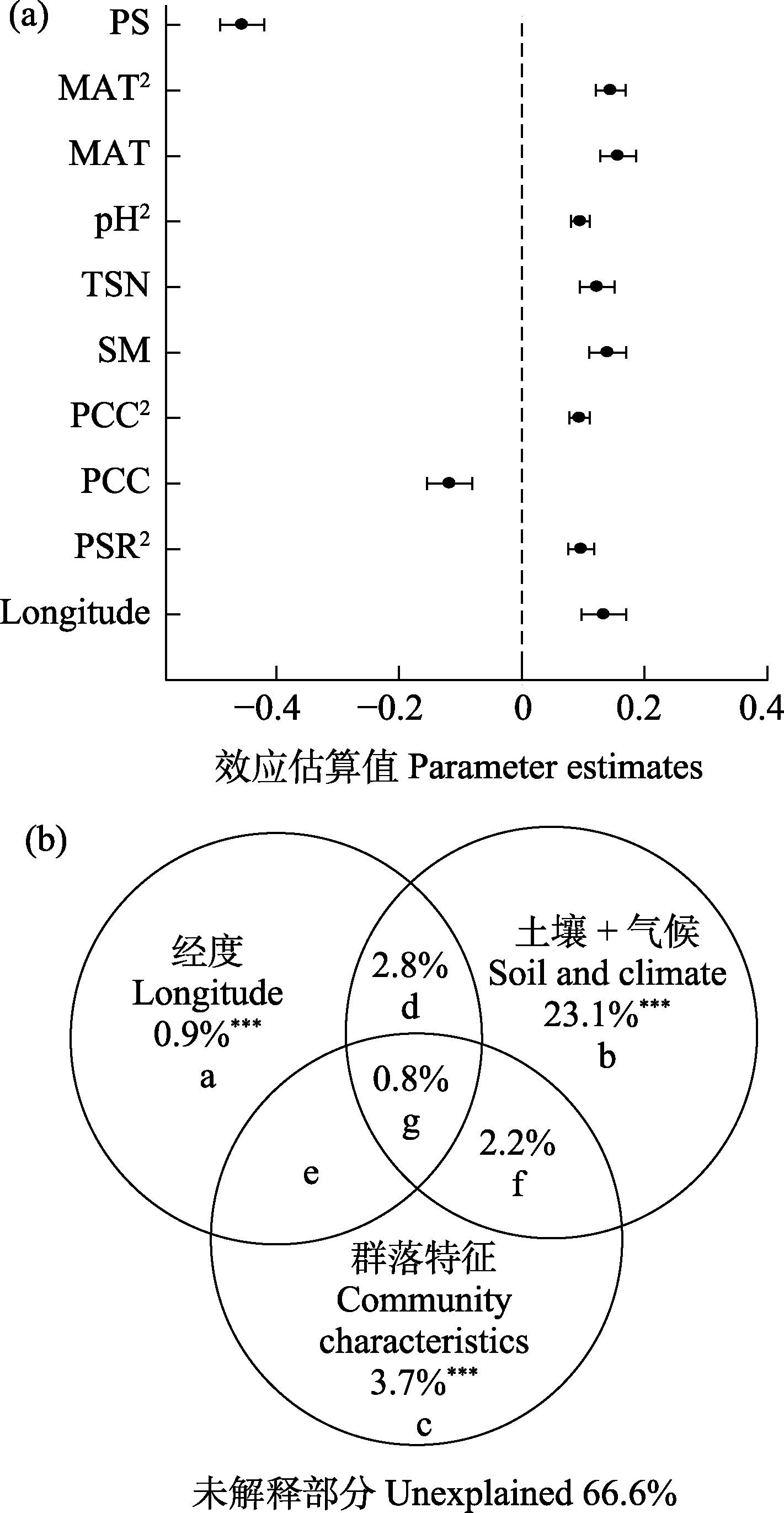
图5 不同变量对植物群落生态特异性的相对影响。(a)进入逐步回归模型中各个变量的效应估计值与95%置信区间; (b)经度、土壤和气候、群落特征(物种丰富度和植物群落盖度)的解释率。Longitude: 经度; SR: 物种丰富度; PCC: 植物群落盖度; SM: 土壤含水量; TSN: 土壤总氮含量; pH: 土壤pH值; MAT: 年均温; PS: 降水季节性。**, P < 0.001。
Fig. 5 Relative influence of different variables on the ecological uniqueness of plant communities. (a) Parameter estimates and the associated 95% confidence interval of each variable that enters into final models; (b) The explanation of longitude, soil and climate, community characteristics (species richness and plant community coverage) to the ecological uniqueness of plant communities. SR, Species richness; PCC, Plant community coverage; SM, Soil moisture; TSN, Soil total nitrogen content; pH, Soil pH; MAT, Mean annual temperature; PS, Precipitation seasonality. ***, P < 0.001.
| [1] |
Anderson MJ, Crist TO, Chase JM, Vellend M, Inouye BD, Freestone AL, Sanders NJ, Cornell HV, Comita LS, Davies KF, Harrison SP, Kraft NJB, Stegen JC, Swenson NG (2011) Navigating the multiple meanings of β diversity: A roadmap for the practicing ecologist. Ecology Letters, 14, 19-28.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
Borcard D, Legendre P, Avois-Jacquet C, Tuomisto H (2004) Dissecting the spatial structure of ecological data at multiple scales. Ecology, 85, 1826-1832.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Burnham KP, Anderson DR (2004) Multimodel inference: Understanding AIC and BIC in model selection. Sociological Methods & Research, 33, 261-304. |
| [4] |
Chase JM, Myers JA (2011) Disentangling the importance of ecological niches from stochastic processes across scales. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 366, 2351-2363.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Chen SB, Ouyang ZY, Xu WH, Xiao Y (2010) A review of beta diversity studies. Biodiversity Science, 18, 323-335. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[陈圣宾, 欧阳志云, 徐卫华, 肖燚 (2010) Beta多样性研究进展. 生物多样性, 18, 323-335.]
DOI |
|
| [6] |
Cook JG, Irwin LL (1992) Climate-vegetation relationships between the Great Plains and Great Basin. American Midland Naturalist, 127, 316.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
da Silva PG, Hernández MIM, Heino J (2018) Disentangling the correlates of species and site contributions to beta diversity in dung beetle assemblages. Diversity and Distributions, 24, 1674-1686.
DOI URL |
| [8] | Dai S, Wang XP, Liu C, Wu X, Li QY, Wang M (2013) Relationship between shrub species richness and climate across central Inner Mongolia, China. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 49, 689-698. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [代爽, 王襄平, 刘超, 武娴, 李巧燕, 王敏 (2013) 内蒙古灌木群落物种丰富度与气候的关系. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 49, 689-698.] | |
| [9] | Dansereau G, Legendre P, Poisot T (2022) Evaluating ecological uniqueness over broad spatial extents using species distribution modelling. Oikos, 2022, e09063. |
| [10] |
Deng HX, Tang QH, Yun XB, Tang Y, Liu XC, Xu XM, Sun S, Zhao G, Zhang YY, Zhang YQ (2022) Wetting trend in Northwest China reversed by warmer temperature and drier air. Journal of Hydrology, 613, 128435.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Dodd MB, Lauenroth WK, Welker JM (1998) Differential water resource use by herbaceous and woody plant life-forms in a shortgrass steppe community. Oecologia, 117, 504-512.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Dubois R, Proulx R, Pellerin S (2020) Ecological uniqueness of plant communities as a conservation criterion in lake-edge wetlands. Biological Conservation, 243, 108491.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Fang JY, Wang XP, Shen ZH, Tang ZY, He JS, Yu D, Jiang Y, Wang ZH, Zheng CY, Zhu JL, Guo ZD (2009) Methods and protocols for plant community inventory. Biodiversity Science, 17, 533-548. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[方精云, 王襄平, 沈泽昊, 唐志尧, 贺金生, 于丹, 江源, 王志恒, 郑成洋, 朱江玲, 郭兆迪 (2009) 植物群落清查的主要内容、方法和技术规范. 生物多样性, 17, 533-548.]
DOI |
|
| [14] |
Gaston KJ (2000) Global patterns in biodiversity. Nature, 405, 220-227.
DOI |
| [15] | Gilbert B, Lechowicz MJ (2004) Neutrality, niches, and dispersal in a temperate forest understory. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 101, 7651-7656 |
| [16] |
Hawkins BA, Porter EE (2004) Water-energy balance and the geographic pattern of species richness of western Palearctic butterflies. Ecological Entomology, 28, 678-686.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Heino J, Grönroos M (2017) Exploring species and site contributions to beta diversity in stream insect assemblages. Oecologia, 183, 151-160.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Heino J, Bini LM, Andersson J, Bergsten J, Bjelke U, Johansson F (2017) Unravelling the correlates of species richness and ecological uniqueness in a metacommunity of urban pond insects. Ecological Indicators, 73, 422-431.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Jiang ZG (2018) Exploring the distribution patterns and conservation approaches of biodiversity on the Qinghai- Tibetan Plateau. Biodiversity Science, 26, 107-110. (in Chinese)
DOI URL |
|
[蒋志刚 (2018) 探索青藏高原生物多样性分布格局与保育途径. 生物多样性, 26, 107-110.]
DOI |
|
| [20] |
Lauenroth WK, Schlaepfer DR, Bradford JB (2014) Ecohydrology of dry regions: Storage versus pulse soil water dynamics. Ecosystems, 17, 1469-1479.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Le Bagousse-Pinguet Y, Gross N, Maestre FT, Maire V, de Bello F, Fonseca CR, Kattge J, Valencia E, Leps J, Liancourt P (2017) Testing the environmental filtering concept in global drylands. Journal of Ecology, 105, 1058-1069.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
Legendre P, De Cáceres M (2013) Beta diversity as the variance of community data: Dissimilarity coefficients and partitioning. Ecology Letters, 16, 951-963.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | Legendre P, Gauthier O (2014) Statistical methods for temporal and space-time analysis of community composition data. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences, 281, 20132728. |
| [24] |
Legendre P, Mi XC, Ren HB, Ma KP, Yu MJ, Sun IF, He FL (2009) Partitioning beta diversity in a subtropical broad-leaved forest of China. Ecology, 90, 663-674.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Li BF, Chen YN, Shi X (2012) Why does the temperature rise faster in the arid region of Northwest China? Journal of Geophysical Research D: Atmospheres, 117, D16115. |
| [26] |
Li LP, Abdusalih N, Wang SP, Wang ZH, Tang ZY (2011) Distribution patterns and climatic explanations of species richness of vascular plants in Xinjiang, China. Arid Zone Research, 28, 25-30. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [李利平, 努尔巴依·阿布都沙力克, 王少鹏, 王志恒, 唐志尧 (2011) 新疆野生维管束植物物种丰富度分布格局的水热解释. 干旱区研究, 28, 25-30.] | |
| [27] | Li XR, Tan HJ, He MZ, Wang XP, Li XJ (2009) The response of shrub species richness and abundance patterns to environmental change in Alxa Plateau: The premise of shrubs diversity conservation in extremely arid gobi regions. Science China: Earth Sciences, 39, 504-515. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李新荣, 谭会娟, 何明珠, 王新平, 李小军 (2009) 阿拉善高原灌木种的丰富度和多度格局对环境因子变化的响应: 极端干旱戈壁地区灌木多样性保育的前提. 中国科学: 地球科学, 39, 504-515.] | |
| [28] |
Myers JA, Chase JM, Jiménez I, Jørgensen PM, Araujo- Murakami A, Paniagua-Zambrana N, Seidel R (2013) Beta-diversity in temperate and tropical forests reflects dissimilar mechanisms of community assembly. Ecology Letters, 16, 151-157.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
O’Brien EM (1998) Water-energy dynamics, climate, and prediction of woody plant species richness: An interim general model. Journal of Biogeography, 25, 379-398.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Qiao XJ, Li QX, Jiang QH, Lu JM, Franklin S, Tang ZY, Wang QG, Zhang JX, Lu ZJ, Bao DC, Guo YL, Liu HB, Xu YZ, Jiang MX (2015) Beta diversity determinants in Badagongshan, a subtropical forest in Central China. Scientific Reports, 5, 17043.
DOI PMID |
| [31] | Scientific Investigation Team of Black Gobi Desert of China (2014) Research on Black Gobi Desert of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [中国黑戈壁地区生态本底科学考察队 (2014) 中国黑戈壁研究. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [32] |
Smith TW, Lundholm JT (2010) Variation partitioning as a tool to distinguish between niche and neutral processes. Ecography, 33, 648-655.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Sor R, Legendre P, Lek S (2018) Uniqueness of sampling site contributions to the total variance of macroinvertebrate communities in the Lower Mekong basin. Ecological Indicators, 84, 425-432.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Svenning JC, Skov F (2005) The relative roles of environment and history as controls of tree species composition and richness in Europe. Journal of Biogeography, 32, 1019-1033.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Ulrich W, Soliveres S, Maestre FT, Gotelli NJ, Quero JL, Delgado-Baquerizo M, Bowker MA, Eldridge DJ, Ochoa V, Gozalo B, Valencia E, Berdugo M, Escolar C, García-Gómez M, Escudero A, Prina A, Alfonso G, Arredondo T, Bran D, Cabrera O, Cea AP, Chaieb M, Contreras J, Derak M, Espinosa CI, Florentino A, Gaitán J, Muro VG, Ghiloufi W, Gómez-González S, Gutiérrez JR, Hernández RM, Huber-Sannwald E, Jankju M, Mau RL, Hughes FM, Miriti M, Monerris J, Muchane M, Naseri K, Pucheta E, Ramírez-Collantes DA, Raveh E, Romão RL, Torres-Díaz C, Val J, Veiga JP, Wang DL, Yuan X, Zaady E (2014) Climate and soil attributes determine plant species turnover in global drylands. Journal of Biogeography, 41, 2307-2319.
DOI PMID |
| [36] |
Vilmi A, Karjalainen SM, Heino J (2017) Ecological uniqueness of stream and lake diatom communities shows different macroecological patterns. Diversity and Distributions, 23, 1042-1053.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Wang H, Zhang R, Cai Y, Yang Q, Lv G (2022) Ecological uniqueness and the determinants in arid desert ecosystems of Northwest China. Global Ecology and Conservation, 34, e02005.
DOI URL |
| [38] | Wang JM, Dong FY, Nasina BH, Li JW, Li JQ, Feng YM, Lu Q (2016) Plant distribution patterns and the factors influencing plant diversity in the Black Gobi Desert of China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36, 3488-3498. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王健铭, 董芳宇, 巴海·那斯拉, 李景文, 李俊清, 冯益明, 卢琦 (2016) 中国黑戈壁植物多样性分布格局及其影响因素. 生态学报, 36, 3488-3498.] | |
| [39] | Wang JM, Chen C, Li JW, Feng YM, Lu Q (2019) Different ecological processes determined the alpha and beta components of taxonomic, functional, and phylogenetic diversity for plant communities in dryland regions of Northwest China. PeerJ, 6, e6220. |
| [40] |
Wang ZH, Fang JY, Tang ZY, Lin X (2012) Relative role of contemporary environment versus history in shaping diversity patterns of China’s woody plants. Ecography, 35, 1124-1133.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Whittaker RH (1960) Vegetation of the Siskiyou Mountains, Oregon and California. Ecological Monographs, 30, 279-338.
DOI URL |
| [42] | Wu ZY (1980) Vegetation of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [吴征镒 (1980) 中国植被. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [43] | Xia YG, Ning Y, Li JW, Li JQ, Feng YM, Wu B, Lu Q (2013) Plant species diversity and floral characters in the Black Gobi Desert of China. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 33, 1906-1915. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [夏延国, 宁宇, 李景文, 李俊清, 冯益民, 吴波, 卢琦 (2013) 中国黑戈壁地区植物区系及其物种多样性研究. 西北植物学报, 33, 1906-1915.] | |
| [44] | Xiao YM, Yang LC, Nie XQ, Li CB, Xiong F, Zhao XH, Zhou GY (2018) Phylogenetic structure of desert shrub community in Qaidam Basin. Acta Botanica Boreali- Occidentalia Sinica, 38, 750-760. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [肖元明, 杨路存, 聂秀青, 李长斌, 熊丰, 赵晓辉, 周国英 (2018) 柴达木盆地荒漠灌丛群落谱系结构研究. 西北植物学报, 38, 750-760.] | |
| [45] |
Yao J, Huang JH, Ding Y, Xu Y, Xu H, Zang RG (2021) Ecological uniqueness of species assemblages and their determinants in forest communities. Diversity and Distributions, 27, 454-462.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Zhang PP, Shao MA, Zhang XC (2017) Spatial pattern of plant species diversity and the influencing factors in a gobi desert within the Heihe River Basin, Northwest China. Journal of Arid Land, 9, 379-393.
DOI |
| [47] | Zhong YM, Wang JM, Zhang TH, Li JW, Feng YM, Lu Q (2017) Composition of seed plant species and floristic features in the gobi area of the northern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau of China. Plant Science Journal, 35, 525-533. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [钟悦鸣, 王健铭, 张天汉, 李景文, 冯益明, 卢琦 (2017) 中国青藏高原北部戈壁区种子植物物种组成及其区系特征. 植物科学学报, 35, 525-533.] |
| [1] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [2] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [3] | 马尚飞, 龚鑫, 上官华媛, 姚海凤, 王滨, 李志鹏, 孙新. 城市化过程中不同用地类型对土壤真核生物多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24540-. |
| [4] | 顾婧婧, 刘宜卓, 苏杨. 基层地方政府在完成《昆蒙框架》中的作用和难点: 基于《联合国气候变化框架公约》任务的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24585-. |
| [5] | 莫笑梅, 张琪, 杨嘉欣, 郑国, 胡中民, 张晓珂, 梁思维, 崔淑艳. 北方典型草地土壤线虫代谢速率及能量流动对氮沉降和降水模式改变的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24341-. |
| [6] | 刘淑琪, 崔东, 江智诚, 刘江慧, 闫江超. 短期氮、水添加和刈割减弱了苦豆子型退化草地土壤生物多样性与生态系统多功能性的联系[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24305-. |
| [7] | 王嘉陈, 徐汤俊, 许唯, 张高季, 尤艺瑾, 阮宏华, 刘宏毅. 城市景观格局对大蚰蜒种群遗传结构的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24251-. |
| [8] | 弋维, 艾鷖, 吴萌, 田黎明, 泽让东科. 青藏高原高寒草甸土壤古菌群落对不同放牧强度的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24339-. |
| [9] | 曲文杰, 王磊, 康文岩, 杨新国, 屈建军, 张雪. 腾格里沙漠东南缘不同年限固沙植被区种子雨和土壤种子库动态与植被更新潜力[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24254-. |
| [10] | 何欣怡, 潘玉梅, 祝燕, 陈佳仪, 张思榕, 张乃莉. 暖温带森林外生菌根树种优势和植物多样性对土壤氮素周转的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24173-. |
| [11] | 魏诗雨, 宋天骄, 罗佳宜, 张燕, 赵子萱, 茹靖雯, 易华, 林雁冰. 秦岭火地塘针叶林土壤细菌群落的海拔分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24180-. |
| [12] | 孙怡欣, 侯春雨, 周磊, 魏雪, 马金豪, 薛娟, 李小涵, 吴鹏飞. 青藏高原盆栽一年生和多年生豆科牧草对土壤线虫群落的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 24040-. |
| [13] | 马骅, 李常青, 余品锋, 陈杰, 贺天耀, 王可洪. 澎溪河消落带大型土壤动物群落分布格局及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 24117-. |
| [14] | 姚祝, 魏雪, 马金豪, 任晓, 王玉英, 胡雷, 吴鹏飞. 气候暖湿化对高寒草甸土壤线虫群落的短期影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23483-. |
| [15] | 吴乐婕, 刘泽康, 田星, 张群, 李博, 吴纪华. 海三棱藨草基因型多样性对种群营养生长和繁殖策略的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23478-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()