



生物多样性 ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (6): 24552. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024552 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024552
所属专题: eDNA技术应用
彭文1( ), 邓泽帅1(
), 邓泽帅1( ), 郑文宝1(
), 郑文宝1( ), 龚凌轩1(
), 龚凌轩1( ), 曾玉枫1(
), 曾玉枫1( ), 孟昊1(
), 孟昊1( ), 陈军2(
), 陈军2( ), 杨道德1,*(
), 杨道德1,*( )(
)( )
)
收稿日期:2024-12-08
接受日期:2025-04-22
出版日期:2025-06-20
发布日期:2025-07-28
通讯作者:
杨道德
基金资助:
Wen Peng1( ), Zeshuai Deng1(
), Zeshuai Deng1( ), Wenbao Zheng1(
), Wenbao Zheng1( ), Lingxuan Gong1(
), Lingxuan Gong1( ), Yufeng Zeng1(
), Yufeng Zeng1( ), Hao Meng1(
), Hao Meng1( ), Jun Chen2(
), Jun Chen2( ), Daode Yang1,*(
), Daode Yang1,*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2024-12-08
Accepted:2025-04-22
Online:2025-06-20
Published:2025-07-28
Contact:
Daode Yang
Supported by:摘要: 野生动物的科学保护和有效管理高度依赖于资源本底数据, 而调查方法的精度直接决定了资源评估结果的客观性与准确性。环境DNA (eDNA)技术已在鱼类等水生生物的物种监测中得到广泛应用, 但在两栖动物资源调查中的应用相对较少, 且多集中于对具体物种的监测。本研究以湖南莽山国家级自然保护区为例, 探究eDNA技术在莽山地区两栖动物资源调查中的检测效率与准确性。本研究利用2023年7-8月在该保护区19个水体采样位点所获取的eDNA检测数据, 与同期采用传统的样线法调查所得数据进行对比分析, 并通过计算α和β多样性对两种方法所得结果进行了详细评估。结果显示: 采用这两种方法记录的两栖动物均为34种, 但相同的物种仅有24种; 在Shannon-Wiener多样性指数、Simpson优势度指数和Pielou均匀度指数上, 这两种方法所获得的两栖动物多样性均存在显著差异(P < 0.05); PCoA和ANOSIM分析的结果也显示, 两种方法记录到的物种组成存在显著差异(P < 0.05), 其原因可能是受到物种习性、采样地点与时间、环境干扰等因素的影响。本研究表明: eDNA技术在两栖动物资源调查方面虽具有较明显的优点, 但目前仍不能完全替代传统的样线法。建议将eDNA技术与传统的调查方法相结合, 以便获得更准确的两栖动物资源本底数据, 促进两栖动物资源的科学保护和管理。
彭文, 邓泽帅, 郑文宝, 龚凌轩, 曾玉枫, 孟昊, 陈军, 杨道德 (2025) eDNA技术在两栖动物调查中的应用: 以湖南莽山国家级自然保护区为例. 生物多样性, 33, 24552. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024552.
Wen Peng, Zeshuai Deng, Wenbao Zheng, Lingxuan Gong, Yufeng Zeng, Hao Meng, Jun Chen, Daode Yang (2025) Application of eDNA technology in amphibian surveys: A case study of Hunan Mangshan National Nature Reserve. Biodiversity Science, 33, 24552. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024552.
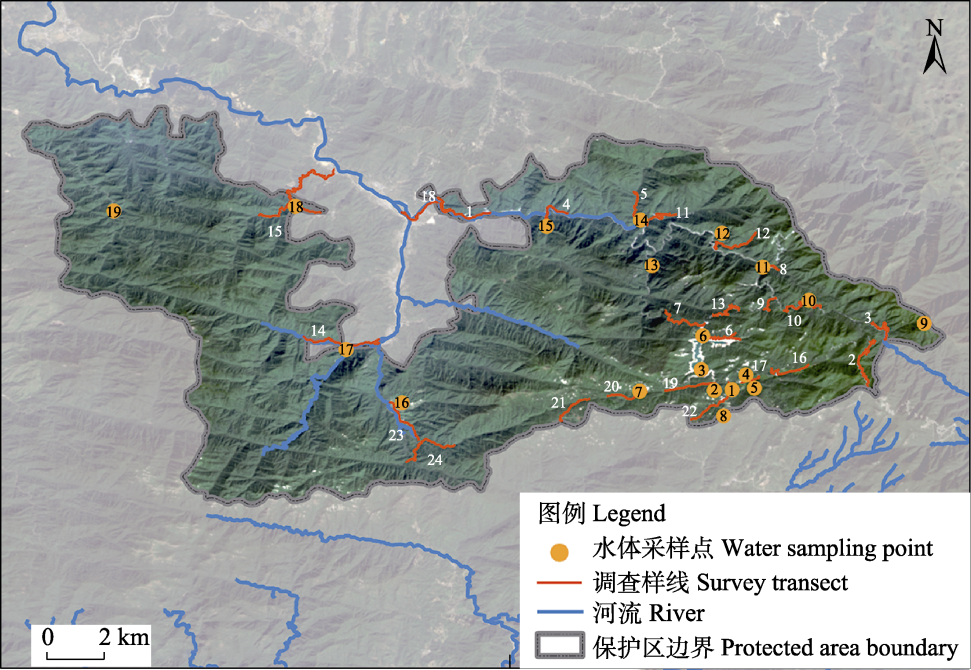
图1 湖南莽山国家级自然保护区两栖动物调查样线及eDNA水体采样点分布图。白色数字代表样线编号。
Fig.1 Distribution map of amphibian survey transects and eDNA water sampling points in Hunan Mangshan National Nature Reserve. White numbers represent the survey transect code.
| 分类地位及物种名 Classification status and species name | 两栖动物名录收录依据 Basis for inclusion in the amphibian directory | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| eDNA技术 eDNA technology | 样线法 Transect method | 水体采样点编号 Water sampling point code | 样线编号 Transect code | |
| I 有尾目 CAUDATA | ||||
| (一) 蝾螈科 Salamandridae | ||||
| 1 黄斑肥螈 Pachytriton xanthospilos* | √ | 5 | 8、10、14 | 2、3、9 |
| 2 莽山疣螈 Tylototriton lizhenchangi* | √ | 5 | 4、9、12 | 16 |
| II 无尾目 ANURA | ||||
| (二) 蟾蜍科 Bufonidae | ||||
| 3 中华蟾蜍 Bufo g. gargarizans | √ | 18 | 4 | 1、6、13、14、16、17、19、22 |
| 4 黑眶蟾蜍 Duttaphrynus melanostictus | - | 7 | 无 None | 1、15、18 |
| (三) 角蟾科 Megophryidae | ||||
| 5 珀普短腿蟾 Brachytarsophrys popei* | √ | 3 | 8、10、14 | 11 |
| 6 九连山角蟾 Boulenophrys jiulianensis* | √ | - | 4、9、16、18 | 无 None |
| 7 南岭角蟾 B. nanlingensis* | √ | 13 | 2、3、14、16、18 | 2、7、20、21、22、24 |
| 8 雨神角蟾 B. ombrophila* | √ | 17 | 2、3、10、14、18 | 7、13 |
| 9 石门台角蟾 B. shimentaina* | √ | 20 | 2、3、4、7、8、10、11、 13、14、16、18 | 2、5、7、22 |
| 10 舜皇角蟾 B. shunhuangensis | √ | - | 14、16 | 无 None |
| 11 莽山掌突蟾 Paramegophrys mangshanensis* | √ | 10 | 14 | 8、10、12、13、20、21 |
| 12 波普拟髭蟾 Leptobrachium bompu | √ | - | 15 | 无 None |
| 13 崇安髭蟾 Leptobrachella liui* | √ | 6 | 10、14 | 3、6、7、21 |
| 14 莽山角蟾 Xenophrys mangshanensis* | √ | 15 | 2、3、10、11、13、14、 16、18 | 2、7、13、15、22、23、24 |
| (四) 蛙科 Ranidae | ||||
| 15 崇安湍蛙 Amolops chunganensis | 3 | 无 None | 3 | |
| 16 戴云湍蛙 A. daiyunensis | √ | - | 6、12、15 | 无 None |
| 17 华南湍蛙 A. ricketti | √ | 66 | 6、12、15、18 | 1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、10、12、13、14、15、20、24 |
| 18 武夷湍蛙 A. wuyiensis | √ | - | 3、5、6、7、9、12、13、 15、16、18、19 | 无 None |
| 19 粤琴蛙 Nidirana guangdongensis* | √ | 8 | 4 | 7、22 |
| 20 湘琴蛙 N. xiangica | √ | 169 | 1、4、6、7、9、10、14 | 1、7、11、16、20、21、23 |
| 21 沼水蛙 Hylarana guentheri | √ | 33 | 13、14 | 4、18、21、22、23 |
| 22 阔褶水蛙 H. latouchi* | √ | 4 | 4、6、7、8、9、10、14 | 14、15、24 |
| 23 大绿臭蛙 Odorrana graminea | - | 57 | 无 None | 1、3、4、5、6、8、10、14、15、19 |
| 24 黄岗臭蛙 O. huanggangensis* | √ | 56 | 1、3、4、5、6、7、8、9、 10、11、12、13、14、15、 16、17、18、19 | 1、4、8、11、12、15、18、24 |
| 25 天目臭蛙 O. tianmuii | √ | - | 5、7、8、10、14、15、 17、18 | 无 None |
| 26 竹叶蛙 O. versabilis | - | 23 | 无 None | 2、6、7、8、10、11、12、14、15、16、18、19、22、23 |
| 27 宜章臭蛙 O. yizhangensis | - | 52 | 无 None | 7、8、9、10、11、13、14、19、22 |
| 28 寒露林蛙 Rana hanluica | - | 7 | 无 None | 10、21、22 |
| 29 长肢林蛙 R. longicrus* | √ | - | 5、7、14、16、18 | 无 None |
| 30 镇海林蛙 R. zhenhaiensis | √ | 23 | 1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、 10、12、13、14、15、16、 17、18、19 | 19、21、22 |
| 31 黑斑侧褶蛙 Pelophyax nigromaculatus | - | 3 | 无 None | 1、6 |
| (五) 树蛙科 Rhacophoridae | ||||
| 32 广东纤树蛙 Gracixalus guangdongensis | √ | 1 | 1、6、9、16、18、19 | 8 |
| 33 布氏泛树蛙 Polypedates braueri | √ | - | 4、9 | 无 None |
| 34 斑腿泛树蛙 P. megacephalus | √ | - | 4、6、9 | 无 None |
| 35 大树蛙 Zhangixalus dennysi | - | 4 | 无 None | 2、8、11、15 |
| 36 峨眉树蛙 Z. omeimontis | 1 | 无 None | 16 | |
| (六) 姬蛙科 Microhylidae | ||||
| 37 粗皮姬蛙 Microhyla butleri | √ | 25 | 2 | 21 |
| 38 小弧斑姬蛙 M. heymonsi | 28 | 无 None | 16、21、22、23 | |
| (七) 叉舌蛙科 Dicroglossidae | ||||
| 39 泽陆蛙 Fejervarya multistriata | √ | 79 | 4、6、9、14 | 1、12、14、18、20、21、23、24 |
| 40 虎纹蛙 Hoplobatrachus chinensis | √ | - | 1、2、4、5、6、8、9、 10、14、15 | 无 None |
| 41 福建大头蛙 Limnonectes fujianensis* | √ | 12 | 7、14 | 4、7、11、12、14、21、22、23、24 |
| 42 棘腹蛙 Quasipaa boulengeri | √ | 7 | 8、10 | 3、6、7、13 |
| 43 小棘蛙 Q. exilispinosa* | √ | 48 | 全部 All | 1、2、4、5、6、8、10、11、12、13、15、17、19、22、24 |
| 44 棘胸蛙 Q. spinosa | √ | 31 | 1、3、6、7、8、9、10、 11、13、14、15、16、17、 18、19 | 3、4、7、10、11、15、16、19、21、24 |
| 合计 Total 44 | 34 | 859 | ||
表1 湖南莽山国家级自然保护区两栖动物名录(2023年7-8月)
Table 1 List of amphibians in Hunan Mangshan National Nature Reserve (July-August 2023)
| 分类地位及物种名 Classification status and species name | 两栖动物名录收录依据 Basis for inclusion in the amphibian directory | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| eDNA技术 eDNA technology | 样线法 Transect method | 水体采样点编号 Water sampling point code | 样线编号 Transect code | |
| I 有尾目 CAUDATA | ||||
| (一) 蝾螈科 Salamandridae | ||||
| 1 黄斑肥螈 Pachytriton xanthospilos* | √ | 5 | 8、10、14 | 2、3、9 |
| 2 莽山疣螈 Tylototriton lizhenchangi* | √ | 5 | 4、9、12 | 16 |
| II 无尾目 ANURA | ||||
| (二) 蟾蜍科 Bufonidae | ||||
| 3 中华蟾蜍 Bufo g. gargarizans | √ | 18 | 4 | 1、6、13、14、16、17、19、22 |
| 4 黑眶蟾蜍 Duttaphrynus melanostictus | - | 7 | 无 None | 1、15、18 |
| (三) 角蟾科 Megophryidae | ||||
| 5 珀普短腿蟾 Brachytarsophrys popei* | √ | 3 | 8、10、14 | 11 |
| 6 九连山角蟾 Boulenophrys jiulianensis* | √ | - | 4、9、16、18 | 无 None |
| 7 南岭角蟾 B. nanlingensis* | √ | 13 | 2、3、14、16、18 | 2、7、20、21、22、24 |
| 8 雨神角蟾 B. ombrophila* | √ | 17 | 2、3、10、14、18 | 7、13 |
| 9 石门台角蟾 B. shimentaina* | √ | 20 | 2、3、4、7、8、10、11、 13、14、16、18 | 2、5、7、22 |
| 10 舜皇角蟾 B. shunhuangensis | √ | - | 14、16 | 无 None |
| 11 莽山掌突蟾 Paramegophrys mangshanensis* | √ | 10 | 14 | 8、10、12、13、20、21 |
| 12 波普拟髭蟾 Leptobrachium bompu | √ | - | 15 | 无 None |
| 13 崇安髭蟾 Leptobrachella liui* | √ | 6 | 10、14 | 3、6、7、21 |
| 14 莽山角蟾 Xenophrys mangshanensis* | √ | 15 | 2、3、10、11、13、14、 16、18 | 2、7、13、15、22、23、24 |
| (四) 蛙科 Ranidae | ||||
| 15 崇安湍蛙 Amolops chunganensis | 3 | 无 None | 3 | |
| 16 戴云湍蛙 A. daiyunensis | √ | - | 6、12、15 | 无 None |
| 17 华南湍蛙 A. ricketti | √ | 66 | 6、12、15、18 | 1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、10、12、13、14、15、20、24 |
| 18 武夷湍蛙 A. wuyiensis | √ | - | 3、5、6、7、9、12、13、 15、16、18、19 | 无 None |
| 19 粤琴蛙 Nidirana guangdongensis* | √ | 8 | 4 | 7、22 |
| 20 湘琴蛙 N. xiangica | √ | 169 | 1、4、6、7、9、10、14 | 1、7、11、16、20、21、23 |
| 21 沼水蛙 Hylarana guentheri | √ | 33 | 13、14 | 4、18、21、22、23 |
| 22 阔褶水蛙 H. latouchi* | √ | 4 | 4、6、7、8、9、10、14 | 14、15、24 |
| 23 大绿臭蛙 Odorrana graminea | - | 57 | 无 None | 1、3、4、5、6、8、10、14、15、19 |
| 24 黄岗臭蛙 O. huanggangensis* | √ | 56 | 1、3、4、5、6、7、8、9、 10、11、12、13、14、15、 16、17、18、19 | 1、4、8、11、12、15、18、24 |
| 25 天目臭蛙 O. tianmuii | √ | - | 5、7、8、10、14、15、 17、18 | 无 None |
| 26 竹叶蛙 O. versabilis | - | 23 | 无 None | 2、6、7、8、10、11、12、14、15、16、18、19、22、23 |
| 27 宜章臭蛙 O. yizhangensis | - | 52 | 无 None | 7、8、9、10、11、13、14、19、22 |
| 28 寒露林蛙 Rana hanluica | - | 7 | 无 None | 10、21、22 |
| 29 长肢林蛙 R. longicrus* | √ | - | 5、7、14、16、18 | 无 None |
| 30 镇海林蛙 R. zhenhaiensis | √ | 23 | 1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、 10、12、13、14、15、16、 17、18、19 | 19、21、22 |
| 31 黑斑侧褶蛙 Pelophyax nigromaculatus | - | 3 | 无 None | 1、6 |
| (五) 树蛙科 Rhacophoridae | ||||
| 32 广东纤树蛙 Gracixalus guangdongensis | √ | 1 | 1、6、9、16、18、19 | 8 |
| 33 布氏泛树蛙 Polypedates braueri | √ | - | 4、9 | 无 None |
| 34 斑腿泛树蛙 P. megacephalus | √ | - | 4、6、9 | 无 None |
| 35 大树蛙 Zhangixalus dennysi | - | 4 | 无 None | 2、8、11、15 |
| 36 峨眉树蛙 Z. omeimontis | 1 | 无 None | 16 | |
| (六) 姬蛙科 Microhylidae | ||||
| 37 粗皮姬蛙 Microhyla butleri | √ | 25 | 2 | 21 |
| 38 小弧斑姬蛙 M. heymonsi | 28 | 无 None | 16、21、22、23 | |
| (七) 叉舌蛙科 Dicroglossidae | ||||
| 39 泽陆蛙 Fejervarya multistriata | √ | 79 | 4、6、9、14 | 1、12、14、18、20、21、23、24 |
| 40 虎纹蛙 Hoplobatrachus chinensis | √ | - | 1、2、4、5、6、8、9、 10、14、15 | 无 None |
| 41 福建大头蛙 Limnonectes fujianensis* | √ | 12 | 7、14 | 4、7、11、12、14、21、22、23、24 |
| 42 棘腹蛙 Quasipaa boulengeri | √ | 7 | 8、10 | 3、6、7、13 |
| 43 小棘蛙 Q. exilispinosa* | √ | 48 | 全部 All | 1、2、4、5、6、8、10、11、12、13、15、17、19、22、24 |
| 44 棘胸蛙 Q. spinosa | √ | 31 | 1、3、6、7、8、9、10、 11、13、14、15、16、17、 18、19 | 3、4、7、10、11、15、16、19、21、24 |
| 合计 Total 44 | 34 | 859 | ||
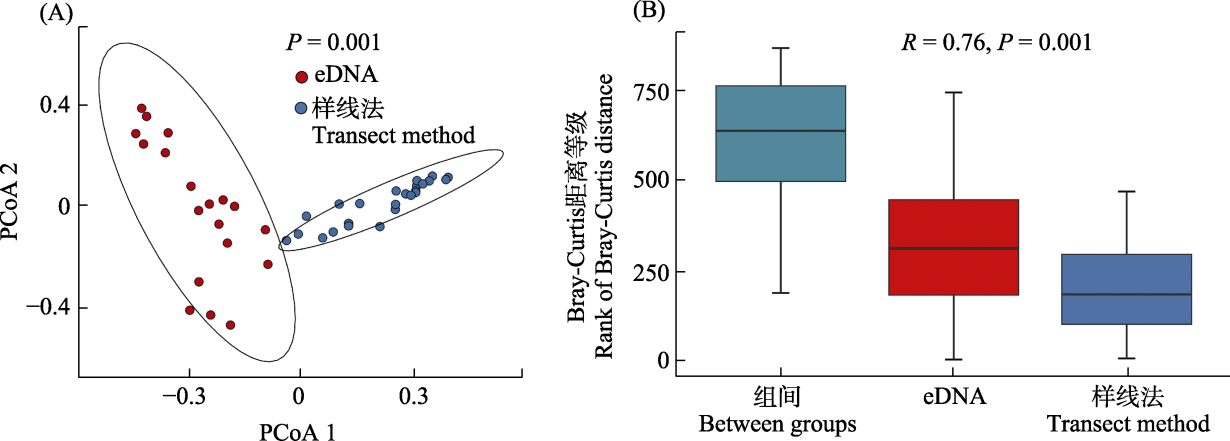
图4 eDNA技术和样线法调查所获两栖动物的β多样性。(A)主坐标分析(PCoA)图; (B)相似性分析(ANOSIM)图。
Fig. 4 The β diversity of amphibians obtained through eDNA technology detection and transect surveys. (A) Principal co-ordinates analysis (PCoA) plot; (B) Analysis of similarities (ANOSIM) plot.
| [1] | Che J, Chen HM, Yang JX, Jin JQ, Jiang K, Yuan ZY, Murphy RW, Zhang YP (2012) Universal COI primers for DNA barcoding amphibians. Molecular Ecology Resources, 12, 247-258. |
| [2] | Chen Z, Song N, Yuan LW, Wu QQ, Gao TX (2020) Establishment of environmental DNA acquisition methods for water samples in the coastal waters of Zhoushan. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 44, 50-58. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈治, 宋娜, 源利文, 邬倩倩, 高天翔 (2020) 舟山近海水样环境DNA获取方法的建立. 水生生物学报, 44, 50-58.] | |
| [3] |
Deiner K, Bik HM, Mächler E, Seymour M, Lacoursière-Roussel A, Altermatt F, Creer S, Bista I, Lodge DM, de Vere N, Pfrender ME, Bernatchez L (2017) Environmental DNA metabarcoding: Transforming how we survey animal and plant communities. Molecular Ecology, 26, 5872-5895.
DOI PMID |
| [4] | Deng ZS, Li Y, Gao ZW, Zhang ZQ, Yang DD (2024) Genetic diversity and haplotype distribution patterns analysis of cytb and RAG2 sequences in Rana hanluica from Southern China. Frontiers in Genetics, 15, 1374263. |
| [5] | Doi H, Katano I, Sakata Y, Souma R, Kosuge T, Nagano M, Ikeda K, Yano K, Tojo K (2017) Detection of an endangered aquatic heteropteran using environmental DNA in a wetland ecosystem. Royal Society Open Science, 4, 170568. |
| [6] | Duarte S, Simões L, Costa FO (2023) Current status and topical issues on the use of eDNA-based targeted detection of rare animal species. Science of the Total Environment, 904, 166675. |
| [7] | Evans NT, Olds BP, Renshaw MA, Turner CR, Li YY, Jerde CL, Mahon AR, Pfrender ME, Lamberti GA, Lodge DM (2016) Quantification of mesocosm fish and amphibian species diversity via environmental DNA metabarcoding. Molecular Ecology Resources, 16, 29-41. |
| [8] | Everts T, Van Driessche C, Neyrinck S, Haegeman A, Ruttink T, Jacquemyn H, Brys R (2024) Phenological mismatches mitigate the ecological impact of a biological invader on amphibian communities. Ecological Applications, 34, e3017. |
| [9] | Fei L, Ye CY, Jiang JP (2012) Color Atlas of Amphibians in China and Their Distribution. Sichuan Science and Technology Press, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [费梁, 叶昌媛, 江建平 (2012) 中国两栖动物及其分布彩色图鉴. 四川科学技术出版社, 成都.] | |
| [10] | Gao EH, Wang ZC, Wang WS, Chen DF, Ma GQ, Tang XP (2014) General Framework of the Second National Terrestrial Wildlife Resources Survey. Chinese Journal of Wildlife, 35, 238-240. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郜二虎, 王志臣, 王维胜, 陈涤非, 马国青, 唐小平 (2014) 全国第二次陆生野生动物资源调查总体思路. 野生动物学报, 35, 238-240.] | |
| [11] |
Gao ZW, Qian TY, Jiang JP, Hou DJ, Deng XJ, Yang DD (2022) Species diversity and distribution of amphibians and reptiles in Hunan Province, China. Biodiversity Science, 30, 21290. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[高志伟, 钱天宇, 江建平, 侯德佳, 邓学建, 杨道德 (2022) 湖南省两栖、爬行动物物种多样性及其地理分布. 生物多样性, 30, 21290.]
DOI |
|
| [12] | Garlapati D, Charankumar B, Ramu K, Madeswaran P, Ramana Murthy MV (2019) A review on the applications and recent advances in environmental DNA (eDNA) metagenomics. Reviews in Environmental Science and Biotechnology, 18, 389-411. |
| [13] | Gu SY, Chen K, Jin XW, Li WP, Chen XF, Xiong J, Tang MZ, Jiang CQ, Xiong J, Li T, Zhang Q, Cui YD, Zeng HH, He SP, Wang YY, Miao W (2024) Development, applications, and standardization of environmental DNA monitoring technology for aquatic organisms. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 48, 1443-1458. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [谷思雨, 陈凯, 金小伟, 李文攀, 陈晓飞, 熊晶, 汤敏喆, 姜传奇, 熊杰, 李涛, 张琪, 崔永德, 曾宏辉, 何舜平, 王业耀, 缪炜 (2024) 水生生物环境DNA监测技术的发展、应用与标准化. 水生生物学报, 48, 1443-1458.] | |
| [14] | Guo NN, Shen M, Xiao NW, Gao XQ, Guo XC, Li JS (2023) Distribution characteristics of autumn fish diversity in the Chishui River based on environmental DNA technology. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 43, 1676-1690. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郭宁宁, 沈梅, 肖能文, 高晓奇, 郭晓晨, 李俊生 (2023) 基于环境DNA技术的赤水河秋季鱼类多样性分布特征. 生态学报, 43, 1676-1690.] | |
| [15] | Harrison JB, Sunday JM, Rogers SM (2019) Predicting the fate of eDNA in the environment and implications for studying biodiversity. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 286, 20191409. |
| [16] | Li B, Zhang W, Shu XX, Mo YM, Pei EL, Yuan X, Wang TH (2017) Distribution characteristic of amphibian in three typical habitats of rural Shanghai. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 26, 824-831. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李贲, 张伟, 束潇潇, 莫英敏, 裴恩乐, 袁晓, 王天厚 (2017) 上海郊区三类典型生境的两栖类分布特征. 长江流域资源与环境, 26, 824-831.] | |
| [17] |
Li C, Jiang JP, Xie F, Zhao T, Che J, Li YM, Du WG, Yang WK, Xu F (2023) Progress and prospect of Chinese biodiversity monitoring of amphibians and reptiles. Biodiversity Science, 31, 23382. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[李成, 江建平, 谢锋, 赵天, 车静, 李义明, 杜卫国, 杨维康, 徐峰 (2023) 中国两栖爬行动物多样性监测进展与展望. 生物多样性, 31, 23382.]
DOI |
|
| [18] | Li CH, Ling LX, Tan J, Lin XL, Wang H, Sun BJ, Li Z (2023) Challenge, breakthrough and future perspectives of environmental DNA technology in monitoring aquatic organisms. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 32, 564-574. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李晨虹, 凌岚馨, 谭娟, 林晓龙, 王辉, 孙冰皎, 李曌 (2023) 环境DNA技术在水生生物监测中的挑战、突破和发展前景. 上海海洋大学学报, 32, 564-574.] | |
| [19] | Li M, Wei TT, Shi BY, Hao XY, Xu HG, Sun HY (2019) Biodiversity monitoring of freshwater benthic macroin- vertebrates using environmental DNA. Biodiversity Science, 27, 480-490. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[李萌, 尉婷婷, 史博洋, 郝希阳, 徐海根, 孙红英 (2019) 环境DNA技术在淡水底栖大型无脊椎动物多样性监测中的应用. 生物多样性, 27, 480-490.]
DOI |
|
| [20] | Li SZ, Liu J, Ke XC, Cheng G, Wang B (2024) A new species of Amolops (Amphibia, Anura, Ranidae) from Guizhou Province, China. ZooKeys, 1189, 33-54. |
| [21] | Li TY, Wu SR, Zhao HL, Tang Y, Liu BX, Fang DA (2025) Fish diversity in the Nanjing section of the Yangtze River by fish larvae survey and eDNA technology. Chinese Journal of Ecology, http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1148.q.20250114.0951.004.html. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李天佑, 吴思燃, 赵华丽, 唐阅, 刘宝兴, 方弟安 (2025) 基于鱼类早期资源调查和eDNA技术揭示长江南京段鱼类资源多样性. 生态学杂志, http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1148.q.20250114.0951.004.html.] | |
| [22] |
Li WH, Hou XL, Xu CX, Qin MS, Wang SP, Wei L, Wang YP, Liu X, Li YM (2021) Validating eDNA measurements of the richness and abundance of anurans at a large scale. Journal of Animal Ecology, 90, 1466-1479.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | Li WH, Hou XL, Zhu YL, Du JC, Xu CX, Yang JY, Li YM (2024) eDNA metabarcoding reveals the species-area relationship of amphibians on the Zhoushan Archipelago. Animals, 14, 1519. |
| [24] | Ling LX, Liang LY, Wang HF, Lin XL, Li CH (2024) Real-time monitoring on the Chinese giant salamander using RPA-LFD. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25, 4946. |
| [25] |
Liu SL, Qiu N, Zhang SY, Zhao ZN, Zhou X (2022) Application of genomics technology in biodiversity conservation research. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22441. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[刘山林, 邱娜, 张纾意, 赵竹楠, 周欣 (2022) 基因组学技术在生物多样性保护研究中的应用. 生物多样性, 30, 22441.]
DOI |
|
| [26] | Liu ZY, Hu C, You WH, Li SX, Wu YS, Liang YY, Chu L, Yan YZ, Zhang C (2024) Comparison between environmental DNA metabarcoding and traditional survey methods to identify community composition and assembly of stream fish. Ecology and Evolution, 14, e70627. |
| [27] | López-de Sancha A, Boix D, Benejam L, Briggs L, Davidson TA, Fahy JC, Frutos-Aragón V, Greaves HM, Lemmens P, Mehner T, Martín L, Oertli B, Sayer C, Brucet S (2025) Amphibian conservation in Europe: The importance of pond condition. Biodiversity and Conservation, 34, 1559-1574. |
| [28] | Luedtke JA, Chanson J, Neam K, Hobin L, Maciel AO, Catenazzi A, Borzée A, Hamidy A, Aowphol A, Jean A, Sosa-Bartuano Á, Fong G A, de Silva A, Fouquet A, Angulo A, Kidov AA, Muñoz Saravia A, Diesmos AC, Tominaga A, Shrestha B, Gratwicke B, Tjaturadi B, Martínez Rivera CC, Vásquez Almazán CR, Señaris C, Chandramouli SR, Strüssmann C, Cortez Fernández CF, Azat C, Hoskin CJ, Hilton-Taylor C, Whyte DL, Gower DJ, Olson DH, Cisneros-Heredia DF, Santana DJ, Nagombi E, Najafi-Majd E, Quah ESH, Bolaños F, Xie F, Brusquetti F, Álvarez FS, Andreone F, Glaw F, Castañeda FE, Kraus F, Parra-Olea G, Chaves G, Medina-Rangel GF, González-Durán G, Ortega-Andrade HM, Machado IF, Das I, Dias IR, Urbina-Cardona JN, Crnobrnja-Isailović J, Yang JH, Jiang JP, Wangyal JT, Rowley JJL, Measey J, Vasudevan K, Chan KO, Gururaja KV, Ovaska K, Warr LC, Canseco-Márquez L, Toledo LF, Díaz LM, Khan MMH, Meegaskumbura M, Acevedo ME, Napoli MF, Ponce MA, Vaira M, Lampo M, Yánez-Muñoz MH, Scherz MD, Rödel MO, Matsui M, Fildor M, Kusrini MD, Ahmed MF, Rais M, Kouamé NG, García N, Gonwouo NL, Burrowes PA, Imbun PY, Wagner P, Kok PJR, Joglar RL, Auguste RJ, Brandão RA, Ibáñez R, May RV, Hedges SB, Biju SD, Ganesh SR, Wren S, Das S, Flechas SV, Ashpole SL, Robleto-Hernández SJ, Loader SP, Incháustegui SJ, Garg S, Phimmachak S, Richards SJ, Slimani T, Osborne-Naikatini T, Abreu-Jardim TPF, Condez TH, De Carvalho TR, Cutajar TP, Pierson TW, Nguyen TQ, Kaya U, Yuan ZY, Long B, Langhammer P, Stuart SN (2023) Ongoing declines for the world’s amphibians in the face of emerging threats. Nature, 622, 308-314. |
| [29] | Lyu ZT, Dai KY, Li Y, Wan H, Liu ZY, Qi S, Lin SM, Wang J, Li YL, Zeng YJ, Li PP, Pang H, Wang YY (2020a) Comprehensive approaches reveal three cryptic species of genus Nidirana (Anura, Ranidae) from China. ZooKeys, 914, 127-159. |
| [30] | Lyu ZT, Li YQ, Zeng ZC, Zhao J, Liu ZY, Guo GX, Wang YY (2020b) Four new species of Asian horned toads (Anura, Megophryidae, Megophrys) from Southern China. ZooKeys, 942, 105-140. |
| [31] | Lyu ZT, Zeng ZC, Wan H, Li Q, Tominaga A, Nishikawa K, Matsui M, Li SZ, Jiang ZW, Liu Y, Wang YY (2024) Contrasting nidification behaviors facilitate diversification and colonization of the Music frogs under a changing paleoclimate. Communications Biology, 7, 638. |
| [32] | Mu YW, Zhang JW, Yang JH, Wu J, Zhang Y, Yu HX, Zhang XW (2024) Enhancing amphibian biomonitoring through eDNA metabarcoding. Molecular Ecology Resources, 24, e13931. |
| [33] | Palumbi S, Martin A, Romano S, McMillan WO, Stice L, Grabowski G (1991) The Simple Fool’s Guide to PCR, version 2.0. Department of Zoology, University of Hawaii, Honolulu. |
| [34] | Quilumbaquin W, Carrera-Gonzalez A, Van der Heyden C, Ortega-Andrade HM (2023) Environmental DNA and visual encounter surveys for amphibian biomonitoring in aquatic environments of the Ecuadorian Amazon. PeerJ, 11, e15455. |
| [35] | Ramli FF, Munian K, Othman N, Hartini Sariyati N, Abdullah-Fauzi NAF, Ilham-Norhakim ML, Abdul-Latiff MAB (2024) A comparative assessment of 16S ribosomal RNA and Cytochrome C Oxidase Subunit I (COI) Primers for Amphibian DNA Barcoding. BIO Web of Conferences, 94, 01003. |
| [36] | Rees HC, Maddison BC, Middleditch DJ, Patmore JRM, Gough KC (2014) The detection of aquatic animal species using environmental DNA—A review of eDNA as a survey tool in ecology. Journal of Applied Ecology, 51, 1450-1459. |
| [37] | Riaz T, Shehzad W, Viari A, Pompanon F, Taberlet P, Coissac E (2011) ecoPrimers: Inference of new DNA barcode markers from whole genome sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Research, 39, e145. |
| [38] |
Saeed M, Rais M, Akram A, Williams MR, Kellner KF, Hashsham SA, Davis DR (2022) Development and validation of an eDNA protocol for monitoring endemic Asian spiny frogs in the Himalayan region of Pakistan. Scientific Reports, 12, 5624.
DOI PMID |
| [39] | Shen YH, Yang DD, Mo XY, Li HH, Chen D (2014) Fauna of Hunan:Amphibia. Hunan Science and Technology Press, Changsha. (in Chinese) |
| [沈猷慧, 杨道德, 莫小阳, 黎红辉, 陈丹 (2014) 湖南动物志·两栖纲. 湖南科学技术出版社, 长沙.] | |
| [40] | Socolar JB, Gilroy JJ, Kunin WE, Edwards DP (2016) How should beta-diversity inform biodiversity conservation? Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 31, 67-80. |
| [41] | Stoeckle BC, Beggel S, Cerwenka AF, Motivans E, Kuehn R, Geist J (2017) A systematic approach to evaluate the influence of environmental conditions on eDNA detection success in aquatic ecosystems. PLoS ONE, 12, e0189119. |
| [42] | Strickler KM, Fremier AK, Goldberg CS (2015) Quantifying effects of UV-B, temperature, and pH on eDNA degradation in aquatic microcosms. Biological Conservation, 183, 85-92. |
| [43] |
Sun XX, Guo NN, Gao JN, Xiao NW (2024) Using eDNA to survey amphibians: Methods, applications, and challenges. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 121, 456-471.
DOI PMID |
| [44] | Sun XX, Xiao NW, Guo NN, Gao XQ, Zhang S, Chu ZS (2024) Exploring diversity and distribution characteristics of amphibians in Chaohu Lake based on environmental DNA. Research of Environmental Sciences, 37, 2310-2323. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孙晓萱, 肖能文, 郭宁宁, 高晓奇, 张硕, 储昭升 (2024) 基于环境DNA方法探究巢湖两栖动物多样性及分布特征. 环境科学研究, 37, 2310-2323.] | |
| [45] | Svenningsen AKN, Pertoldi C, Bruhn D (2022) eDNA metabarcoding benchmarked towards conventional survey methods in amphibian monitoring. Animals, 12, 763. |
| [46] | Wang J, Liu P, Chang J, Li C, Xie F, Jiang JP (2022) Development of an eDNA metabarcoding tool for surveying the world’s largest amphibian. Current Zoology, 68, 608-614. |
| [47] | Wang J, Lyu ZT, Liu ZY, Liao CK, Zeng ZC, Zhao J, Li YL, Wang YY (2019) Description of six new species of the subgenus Panophrys within the genus Megophrys (Anura, Megophryidae) from southeastern China based on molecular and morphological data. ZooKeys, 851, 113-164. |
| [48] | Wang W, Feng CT, Liu FZ, Li JS (2020) Biodiversity conservation in China: A review of recent studies and practices. Environmental Science and Ecotechnology, 2, 100025. |
| [49] | Wu DY, Lee P, Chen HM, Yan F, Huang JY, He YH, Wu RY, Yuan ZY (2024) Validation and development of eDNA metabarcoding primers for comprehensive assessment of Chinese amphibians. Integrative Zoology, 20, 504-519. |
| [50] | Xia X, Li Y, Yang DD, Pi YY (2022) Habitat characteristics and main factors influencing habitat selection of Rana hanluica during breeding period. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 41, 1740-1745. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [夏昕, 李媛, 杨道德, 皮扬焱 (2022) 寒露林蛙繁殖期生境特征及影响其生境选择的主要因子. 生态学杂志, 41, 1740-1745.] | |
| [51] | Xiao ZH, Dong SS, Zhang ZH, Zhang DN, Song ZP (2023) Advances in the application of environmental DNA in amphibians monitoring. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 43, 7861-7873. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [肖泽华, 董姗姗, 张振华, 章嫡妮, 宋志平 (2023) 环境DNA在两栖动物监测中的应用研究进展. 生态学报, 43, 7861-7873.] | |
| [52] | Xu W, Wu YH, Zhou WW, Chen HM, Zhang BL, Chen JM, Xu WH, Rao DQ, Zhao HP, Yan F, Yuan ZY, Jiang K, Jin JQ, Hou M, Zou DH, Wang LJ, Zheng YC, Li JT, Jiang JP, Zeng XM, Chen YH, Liao ZY, Li C, Li XY, Gao W, Wang K, Zhang DR, Lu CQ, Yin TT, Ding ZL, Zhao GG, Chai J, Zhao WG, Zhang YP, Wiens JJ, Che J (2024) Hidden hotspots of amphibian biodiversity in China. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 121, e2320674121. |
| [53] | Yan KC, Li JC, Tian YJ, Liu CL, Zhang YL, Li ZX, Ding ZC (2023) Comparison of fish biodiversity in western south Yellow Sea based on environmental DNA metabarcoding and trawl survey. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 53(5), 71-81. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [言柯程, 李建超, 田永军, 刘纯琳, 张玉磊, 李志新, 丁兆成 (2023) 基于环境DNA metabarcoding和底拖网调查的南黄海西部鱼类多样性比较. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 53(5), 71-81.] | |
| [54] | Yang DD, Ding BZ, Yu XL, Li YH (2023) Biodiversity Research and Conservation in Mangshan National Nature Reserve, Hunan Province. Hunan Science and Technology Press, Changsha. (in Chinese) |
| [杨道德, 丁邦柱, 喻勋林, 李永辉 (2023) 湖南莽山国家级自然保护区生物多样性研究与保护. 湖南科学技术出版社, 长沙.] | |
| [55] |
Yang HL, Du H, Qi HF, Yu LX, Hou XD, Zhang H, Li JY, Wu JM, Wang CY, Zhou Q, Wei QW (2021) Effectiveness assessment of using riverine water eDNA to simultaneously monitor the riverine and riparian biodiversity information. Scientific Reports, 11, 24241.
DOI PMID |
| [56] |
Yang L, Tan ZQ, Wang DR, Xue L, Guan MX, Huang TS, Li RH (2014) Species identification through mitochondrial rRNA genetic analysis. Scientific Reports, 4, 4089.
DOI PMID |
| [57] | Zhang B, Ding XY, Jiang JP, Li LH, Yang DD (2022) Metagenomic analysis of Mangshan pit viper (Protobothrops mangshanensis) gut microbiota reveals differences among wild and captive individuals linked to hibernating behaviors. Asian Herpetological Research, 13, 251-268. |
| [58] | Zhang B, Wu BX, Yang DD, Tao XQ, Zhang M, Hu SS, Chen J, Zheng M (2020) Habitat association in the critically endangered Mangshan pit viper (Protobothrops mangshanensis), a species endemic to China. PeerJ, 8, e9439. |
| [59] | Zhang HB, Wang XY, Zhong LP, Chen Z, Gao TX (2024) Study on fish diversity in the offshore waters of Xixuan Island based on environmental DNA metabarcoding. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 45(2), 173-185. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张浩博, 王晓艳, 钟兰萍, 陈治, 高天翔 (2024) 基于环境DNA metabarcoding的西轩岛近海鱼类多样性研究. 渔业科学进展, 45(2), 173-185.] | |
| [60] | Zhang RZ (2011) Zoogeography of China, 2nd edn. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [张荣祖 (2011) 中国动物地理(第二版). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [61] | Zhang Y, Pavlovska M, Stoica E, Prekrasna I, Yang JH, Slobodnik J, Zhang XW, Dykyi E (2020) Holistic pelagic biodiversity monitoring of the Black Sea via eDNA metabarcoding approach: From bacteria to marine mammals. Environment International, 135, 105307. |
| [62] | Zhou Q, Du H, Wang J, Shao Y, Yan ZG (2024) Distribution characteristics of Chinese sturgeon in the Yangtze River based on environmental DNA. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 14, 71-78. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [周权, 杜浩, 王洁, 邵芸, 闫振广 (2024) 基于环境DNA的长江中华鲟分布特征探究. 环境工程技术学报, 14, 71-78.] | |
| [63] | Zhou Q, Wang C, Zhang MY, Deng ZY, Xie YX, Mao P, Ma J, Xiang HM, Wei Y, Jiang WS (2025) Exploration of an eDNA procedure for surveying Chinese giant salamanders: A comparison with conventional field methods. Biodiversity and Conservation, 34, 841-858. |
| [1] | 贾贞妮, 张意岑, 杜彦君, 任海保. 干扰对中亚热带森林群落物种多样性演替动态的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24078-. |
| [2] | 李华亮, 张明军, 张熙斌, 谭荣, 李诗川, 冯尔辉, 林雪云, 陈珉, 颜文博, 曾治高. 海南东寨港国家级自然保护区两栖类群落组成及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24350-. |
| [3] | 徐伟强, 苏强. 分形模型与一般性物种多度分布关系的检验解析:以贝类和昆虫群落为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23410-. |
| [4] | 何智荣, 吴思雨, 时莹莹, 王雨婷, 江艺欣, 张春娜, 赵娜, 王苏盆. 壶菌感染对两栖动物种群影响的研究现状与挑战[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23274-. |
| [5] | 陈蕾, 许志勇, 苏菩坤, 赖小甜, 赵兆. 依频声学多样性指数用于人类活动区域的适用能力[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(10): 24286-. |
| [6] | 江艺欣, 时莹莹, 高朔, 王苏盆. 人为噪音、夜间人造光和路杀对两栖动物的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22427-. |
| [7] | 侯东敏, 辉洪, 张栋儒, 肖能文, 饶定齐. 云岭山脉云南地区两栖爬行类动物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22316-. |
| [8] | 刘高慧, 崔建国, 王玥, 王洪良, 香宝, 肖能文. 四川省康定市两栖动物多样性及其时空分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(6): 21494-. |
| [9] | 高志伟, 钱天宇, 江建平, 侯德佳, 邓学建, 杨道德. 湖南省两栖、爬行动物物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(2): 21290-. |
| [10] | 卜向丽, 王静, 吴佳忆, 孙太福, 向荣伟, 鲁庆斌, 郝映红, 崔绍朋, 盛岩, 孟秀祥. 太行山东北部哺乳动物区系及多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(3): 331-339. |
| [11] | 尚素琴, 吴兴波, 王召龙, 彭鹤年, 周惠丽, 张红勇, 白映禄. 兴隆山国家级自然保护区不同生境的蝴蝶群落结构与种-多度分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(8): 983-992. |
| [12] | 王存璐,陈浒,肖华,张红梅,李林芝,郭城,陈静,魏强. 黔西北石漠化地区两栖动物多样性及其生境选择[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(4): 485-495. |
| [13] | 王剀, 任金龙, 陈宏满, 吕植桐, 郭宪光, 蒋珂, 陈进民, 李家堂, 郭鹏, 王英永, 车静. 中国两栖、爬行动物更新名录[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(2): 189-218. |
| [14] | 李共国, 李平, 徐杭英, 于海燕, 俞建. 浙江水源地河流浮游动物多样性与环境因子的通径分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(2): 166-175. |
| [15] | 张全建, 杨彪, 付强, 王磊, 龚旭, 张远彬. 邛崃山系水鹿的冬季食性[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(10): 1192-1201. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn