



生物多样性 ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (7): 24493. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024493 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024493
徐进博1,#, 崔雅倩2,#( ), 王渊4(
), 王渊4( ), 王伟波2,3(
), 王伟波2,3( ), 刘锋4, 王广龙4, 扈晶晶4, 普布顿珠4, 边巴多吉4, 旦增4, 胡开4, 王小川4, 宋刚2(
), 刘锋4, 王广龙4, 扈晶晶4, 普布顿珠4, 边巴多吉4, 旦增4, 胡开4, 王小川4, 宋刚2( ), 吕永磊2,3,4,*(
), 吕永磊2,3,4,*( )(
)( ), 温知新2,*(
), 温知新2,*( )(
)( )
)
收稿日期:2024-11-08
接受日期:2025-02-24
出版日期:2025-07-20
发布日期:2025-07-29
通讯作者:
*E-mail: lvyonglei@ioz.ac.cn;wenzx@ioz.ac.cn
作者简介:#共同第一作者
基金资助:
Jinbo Xu1,#, Yaqian Cui2,#( ), Yuan Wang4(
), Yuan Wang4( ), Weibo Wang2,3(
), Weibo Wang2,3( ), Feng Liu4, Guanglong Wang4, Jingjing Hu4, Dunzhu Pubu4, Duoji Bianba4, Zeng Dan4, Kai Hu4, Xiaochuan Wang4, Gang Song2(
), Feng Liu4, Guanglong Wang4, Jingjing Hu4, Dunzhu Pubu4, Duoji Bianba4, Zeng Dan4, Kai Hu4, Xiaochuan Wang4, Gang Song2( ), Yonglei Lü2,3,4,*(
), Yonglei Lü2,3,4,*( )(
)( ), Zhixin Wen2,*(
), Zhixin Wen2,*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2024-11-08
Accepted:2025-02-24
Online:2025-07-20
Published:2025-07-29
Contact:
*E-mail: lvyonglei@ioz.ac.cn;wenzx@ioz.ac.cn
About author:#Co-first authors
Supported by:摘要: 白颊猕猴(Macaca leucogenys)是我国学者于2015年在西藏墨脱地区发现并命名的新哺乳动物物种, 为国家二级重点保护野生动物。白颊猕猴的分布范围有限, 种群数量稀少, 其栖息地适宜性评价方面尚缺乏相关的研究。为了解白颊猕猴的分布格局, 本研究通过红外相机布设与样线调查数据, 结合冠层高度、人类影响指数(human influence index, HII)、归一化植被指数、海拔、坡向、坡度和19个生物气候因子, 使用MaxEnt模型系统分析了白颊猕猴在西藏雅鲁藏布大峡谷国家级自然保护区的栖息地分布现状及影响因素, 并根据未来不同气候变化情景下该区域的生境状况, 预测其栖息地的变化趋势。结果显示: (1)筛选后的影响因素拟合的MaxEnt模型受试者工作特征曲线下的面积为0.924, 表明模型预测结果极为准确; (2)影响白颊猕猴当前分布的关键环境变量为最湿月降水量(bio 13)、人类影响指数、气温年较差(bio 7)、降水季节性(bio 15); (3)当前气候条件下, 白颊猕猴的高适生区大部分集中在西藏雅鲁藏布大峡谷国家级自然保护区的实验区内, 部分高适生区分布于达木核心区。在未来2050s SSP1-2.6气候情景与SSP3-7.0气候情景下, 白颊猕猴的适生区相较于当前气候条件下均有所增加。本研究可为了解白颊猕猴当前及未来的分布情况以及对该珍稀物种实施有效的保护策略提供理论和基础数据支持。
徐进博, 崔雅倩, 王渊, 王伟波, 刘锋, 王广龙, 扈晶晶, 普布顿珠, 边巴多吉, 旦增, 胡开, 王小川, 宋刚, 吕永磊, 温知新 (2025) 西藏雅鲁藏布大峡谷国家级自然保护区内白颊猕猴的栖息地适宜性评价. 生物多样性, 33, 24493. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024493.
Jinbo Xu, Yaqian Cui, Yuan Wang, Weibo Wang, Feng Liu, Guanglong Wang, Jingjing Hu, Dunzhu Pubu, Duoji Bianba, Zeng Dan, Kai Hu, Xiaochuan Wang, Gang Song, Yonglei Lü, Zhixin Wen (2025) Habitat suitability evaluation of Macaca leucogenys in the Xizang Yarlung Zangbo Grand Canyon National Nature Reserve. Biodiversity Science, 33, 24493. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024493.
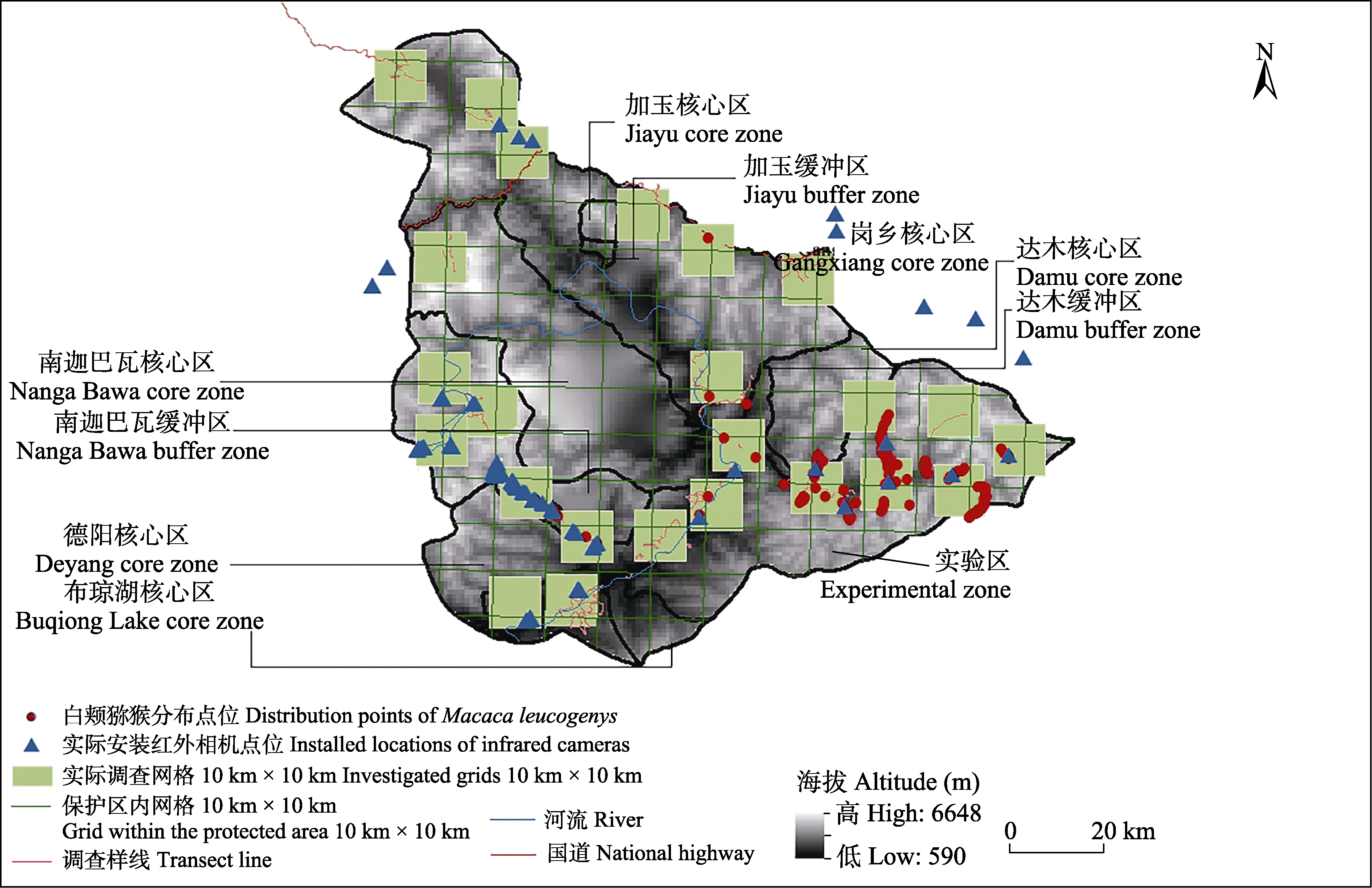
图1 雅鲁藏布大峡谷国家级自然保护区白颊猕猴分布点位、红外相机布置点位和调查样线分布
Fig. 1 Distribution points of Macaca leucogenys, installed locations of infrared cameras, and distribution of transect lines in the Xizang Yarlung Zangbo Grand Canyon National Nature Reserve
| 变量 Variable | 描述 Description | 单位 Unit |
|---|---|---|
| bio 7 | 气温年较差 Temperature annual range | ℃ |
| bio 13 | 最湿月降水量 Precipitation of wettest month | mm |
| bio 15 | 降水季节性 Precipitation seasonality | |
| Altitude | 海拔 Altitude | m |
| Aspect | 坡向 Aspect | ° |
| Slope | 坡度 Slope | ° |
| HII | 人类影响指数 Human influence index | - |
表1 参与建立MaxEnt模型的环境变量
Table 1 The environmental variables used in building MaxEnt model
| 变量 Variable | 描述 Description | 单位 Unit |
|---|---|---|
| bio 7 | 气温年较差 Temperature annual range | ℃ |
| bio 13 | 最湿月降水量 Precipitation of wettest month | mm |
| bio 15 | 降水季节性 Precipitation seasonality | |
| Altitude | 海拔 Altitude | m |
| Aspect | 坡向 Aspect | ° |
| Slope | 坡度 Slope | ° |
| HII | 人类影响指数 Human influence index | - |
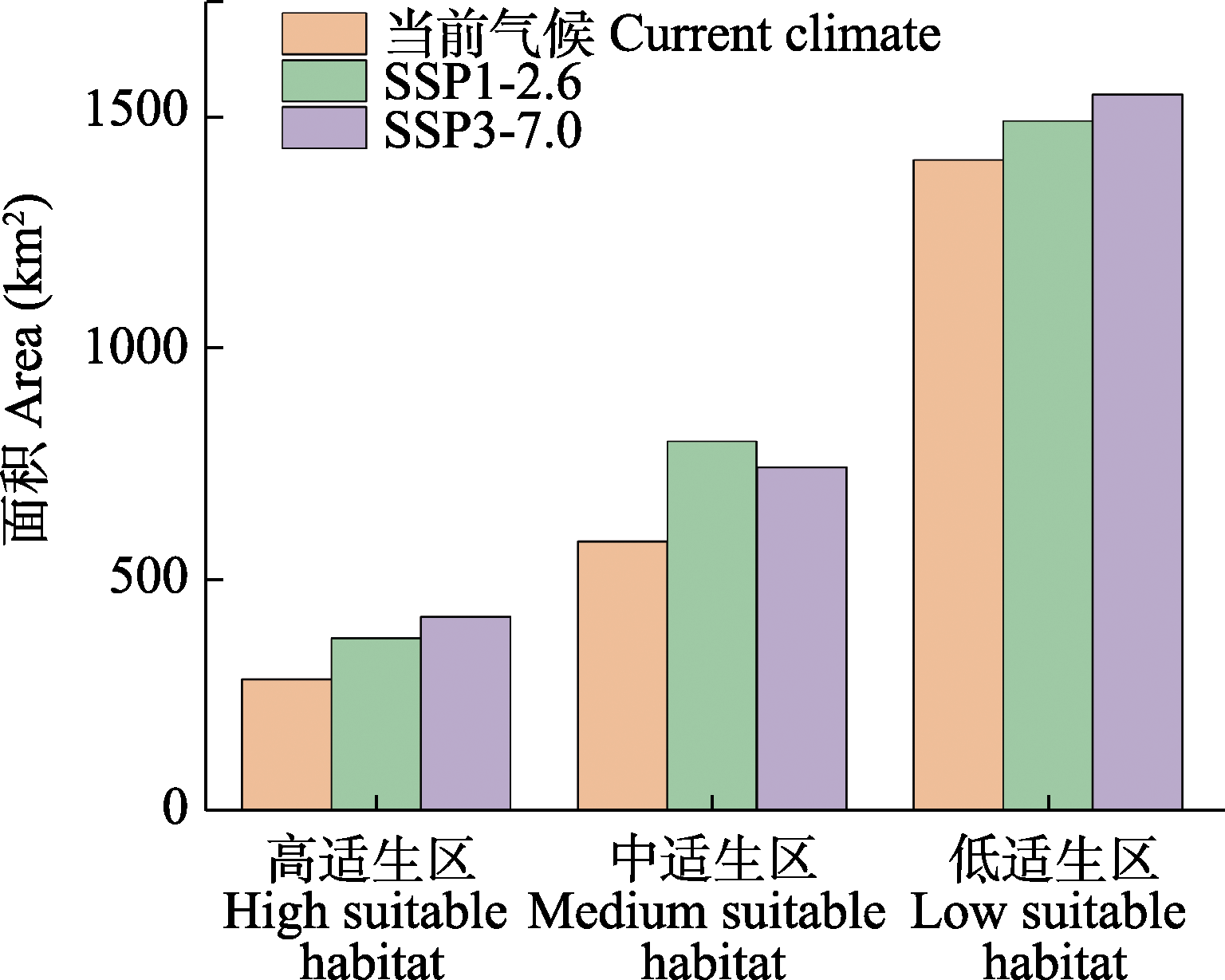
图2 不同气候情景下白颊猕猴在西藏雅鲁藏布大峡谷国家级自然保护区适生区面积
Fig. 2 Suitable areas of Macaca leucogenys under different climate scenarios in the Xizang Yarlung Zangbo Grand Canyon National Nature Reserve
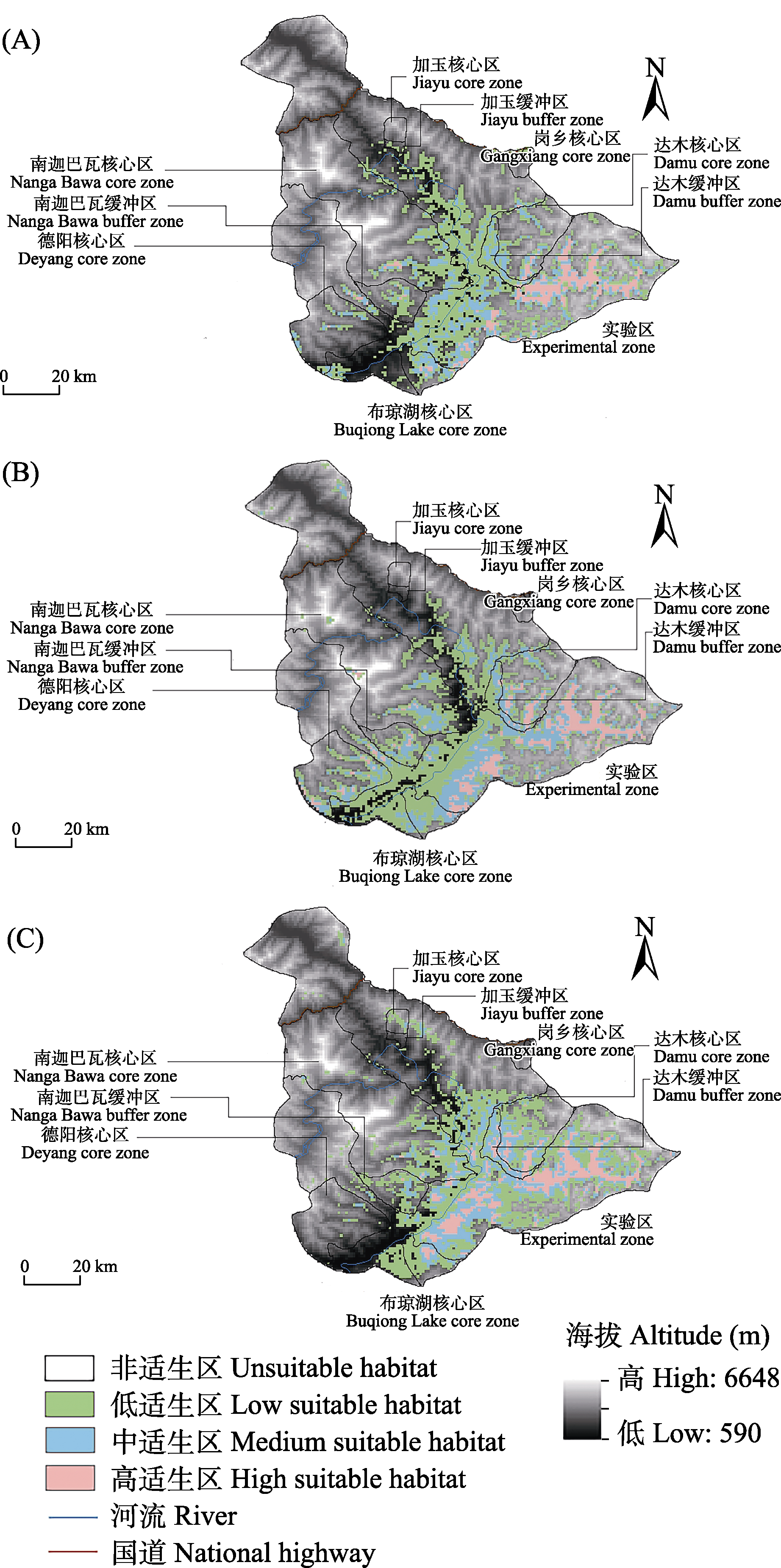
图3 西藏雅鲁藏布大峡谷国家级自然保护区白颊猕猴在当前、未来气候适生区分布预测图。(A)当前气候条件; (B) 2050s SSP1-2.6排放情景; (c) 2050s SSP3-7.0排放情景。
Fig. 3 Current and future suitable habitats for Macaca leucogenys in the Xizang Yarlung Zangbo Grand Canyon National Nature Reserve. (A) Current climate; (B) 2050s SSP1-2.6 scenario; (C) 2050s SSP3-7.0 scenario.
| 气候情景 Climate scenario | 适生区等级 Suitable habitat level | 核心区 Core zone (km2) | 缓冲区 Buffer zone (km2) | 实验区 Experimental zone (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 当前气候 Current climate | 高适生区 High suitable habitat | 24 | 10 | 251 |
| 中适生区 Medium suitable habitat | 149 | 75 | 358 | |
| 低适生区 Low suitable habitat | 362 | 105 | 938 | |
| SSP1-2.6 | 高适生区 High suitable habitat | 58 | 39 | 276 |
| 中适生区 Medium suitable habitat | 161 | 135 | 502 | |
| 低适生区 Low suitable habitat | 447 | 225 | 817 | |
| SSP3-7.0 | 高适生区 High suitable habitat | 74 | 54 | 292 |
| 中适生区 Medium suitable habitat | 171 | 144 | 427 | |
| 低适生区 Low suitable habitat | 405 | 207 | 934 |
表2 西藏雅鲁藏布大峡谷国家级自然保护区不同功能区划内白颊猕猴适生区面积分布
Table 2 Distribution of suitable areas for Macaca leucogenys in different functional divisions of the Xizang Yarlung Zangbo Grand Canyon National Nature Reserve
| 气候情景 Climate scenario | 适生区等级 Suitable habitat level | 核心区 Core zone (km2) | 缓冲区 Buffer zone (km2) | 实验区 Experimental zone (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 当前气候 Current climate | 高适生区 High suitable habitat | 24 | 10 | 251 |
| 中适生区 Medium suitable habitat | 149 | 75 | 358 | |
| 低适生区 Low suitable habitat | 362 | 105 | 938 | |
| SSP1-2.6 | 高适生区 High suitable habitat | 58 | 39 | 276 |
| 中适生区 Medium suitable habitat | 161 | 135 | 502 | |
| 低适生区 Low suitable habitat | 447 | 225 | 817 | |
| SSP3-7.0 | 高适生区 High suitable habitat | 74 | 54 | 292 |
| 中适生区 Medium suitable habitat | 171 | 144 | 427 | |
| 低适生区 Low suitable habitat | 405 | 207 | 934 |
| 环境变量 Environmental variables | 贡献率 Percent contribution (%) | 置换重要性 Permutation importance (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 最湿月降水量 Precipitation of wettest month (bio 13) | 52.4 | 70.5 |
| 人类影响指数 Human influence index (HII) | 30.5 | 14.4 |
| 气温年较差 Temperature annual range (bio 7) | 8 | 4.8 |
| 降水季节性 Precipitation seasonality (bio 15) | 4 | 6.7 |
| 坡向 Aspect | 3.8 | 2.3 |
| 坡度 Slope | 1.2 | 0.8 |
| 海拔 Altitude | 0.1 | 0.5 |
表3 筛选后环境变量的贡献率与置换重要性
Table 3 The contribution rate and permutation importance of the filtered environmental variables
| 环境变量 Environmental variables | 贡献率 Percent contribution (%) | 置换重要性 Permutation importance (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 最湿月降水量 Precipitation of wettest month (bio 13) | 52.4 | 70.5 |
| 人类影响指数 Human influence index (HII) | 30.5 | 14.4 |
| 气温年较差 Temperature annual range (bio 7) | 8 | 4.8 |
| 降水季节性 Precipitation seasonality (bio 15) | 4 | 6.7 |
| 坡向 Aspect | 3.8 | 2.3 |
| 坡度 Slope | 1.2 | 0.8 |
| 海拔 Altitude | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| [1] | Bai DF, Chen PJ, Atzeni L, Cering L, Li Q, Shi K (2018) Assessment of habitat suitability of the snow leopard (Panthera uncia) in Qomolangma National Nature Reserve based on MaxEnt modeling. Zoological Research, 39, 373-386. |
| [2] |
Bai JJ, Hou P, Zhao YH, Xu HT, Zhang B (2022) Research progress of species habitat suitability models and their verification. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 41, 1423-1432. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [白君君, 侯鹏, 赵燕红, 徐海涛, 张兵 (2022) 物种生境适宜性模型及验证的研究进展. 生态学杂志, 41, 1423-1432.] | |
| [3] | Burton AC, Neilson E, Moreira D, Ladle A, Steenweg R, Fisher JT, Bayne E, Boutin S (2015) Review: Wildlife camera trapping: A review and recommendations for linking surveys to ecological processes. Journal of Applied Ecology, 52, 675-685. |
| [4] | Cui ZW (2019) Integrative Studies on Nutritional Ecology of Taihangshan Macaques (Macaca mulatta tcheliensis): Feeding, Nutrition and Gut Microbiota. PhD dissertation, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [崔振伟 (2019) 太行山猕猴营养生态学整合研究: 觅食、营养与肠道菌群. 博士学位论文, 郑州大学, 郑州.] | |
| [5] |
Fan PF, Liu Y, Zhang ZC, Zhao C, Li C, Liu WL, Liu ZJ, Li M (2017) Phylogenetic position of the white-cheeked macaque (Macaca leucogenys), a newly described primate from southeastern Tibet. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 107, 80-89.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | Ghosh A, Dalui S, Mukherjee T, Joshi BD, Singh SK, Maheswaran G, Sharma LK, Chandra K, Thakur M (2022) Serendipitous discovery of white-cheeked macaque (Macaca leucogenys) from “Arunachal Pradesh”. Animal Gene, 23, 200124. |
| [7] | Guo XB, Wang ZL, Tian JD, Lu JQ, Liu JD (2010) Sleeping site selection by Rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta tcheliensis) in Taihangshan National Nature Reserve, Henan Province. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 29, 849-856. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郭相保, 王振龙, 田军东, 路纪琪, 刘金栋 (2010) 河南太行山自然保护区猕猴夜宿地选择研究. 四川动物, 29, 849-856.] | |
| [8] |
Hoffmann S, Irl SDH, Beierkuhnlein C (2019) Predicted climate shifts within terrestrial protected areas worldwide. Nature Communications, 10, 4787.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | Hou N, Dai Q, Ran JH, Jiao YY, Cheng Y, Zhao C (2014) A corridor design for the giant panda in the Niba Mountain of China. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 20, 1039-1045. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [侯宁, 戴强, 冉江洪, 焦迎迎, 程勇, 赵成 (2014) 大相岭山系泥巴山大熊猫生境廊道设计. 应用与环境生物学报, 20, 1039-1045.] | |
| [10] |
Hu WQ, Wang HJ, Li XY, Jiang XL (2024) New records of the white-cheeked macaque provide range extension for the endangered primate in Gaoligong Mountains. Primates, 65, 15-19.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | Huang PZ, Bian K, Huang ZP, Li Q, Dunn DW, Fang G, Liu JH, Wang MY, Yang XF, Pan RL, Gao CL, Si KC, Li BG, Qi XG (2021) Human activities and elevational constraints restrict ranging patterns of snub-nosed monkeys in a mountainous refuge. Integrative Zoology, 16, 202-213. |
| [12] | Jiang N, Zheng YF, Huang Y, Wu LY, He JY, Yang JN, Zhou J, Li CW, Liu ZX (2021) Behavioral time allocation, handedness and human-monkey relationship of Macaca mulatta in Zhangjiajie National Forest Park. International Journal of Ecology, 10(1), 90-99. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [蒋能, 郑义锋, 黄昀, 伍丽艳, 何娇阳, 阳佳宁, 周婧, 李春旺, 刘志霄 (2021) 张家界国家森林公园猕猴行为时间分配、利手性及人猴关系的初步研究. 世界生态学, 10(1), 90-99.] | |
| [13] |
Li C, Zhao C, Fan PF (2015) White-cheeked macaque (Macaca leucogenys): A new macaque species from Medog, southeastern Tibet. American Journal of Primatology, 77, 753-766.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | Li J, Li DQ, Xue YD, Wu B, He XJ, Liu F (2018) Identifying potential refugia and corridors under climate change: A case study of endangered Sichuan golden monkey (Rhinopithecus roxellana) in Qinling Mountains, China. American Journal of Primatology, 80, e22929. |
| [15] | Li WB, Teng Y, Zhang MY, Shen Y, Liu JW, Qi JW, Wang XC, Wu RF, Li JH, Garber PA, Li M (2024) Human activity and climate change accelerate the extinction risk to non-human primates in China. Global Change Biology, 30, e17114. |
| [16] | Li YH, Huang ZH, Zhou QH, Ma GZ, Huang CM (2019) Daily activity pattern in Assamese macaques inhabiting limestone forest, southwest Guangxi, China. Global Ecology and Conservation, 20, e00709. |
| [17] |
Lin HD, Zheng QZ, Shen LQ, Wang G, Liu R, Zhang XY, Qi J, Zhang AP, Meng XX (2024) Assessment of habitat suitability in autumn for wild alpine musk deer in Xinglongshan National Nature Reserve with MaxEnt model. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 43, 299-304. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [林宏东, 郑启泽, 申立泉, 王功, 刘瑞, 张学炎, 祁军, 张爱萍, 孟秀祥 (2024) 基于MaxEnt模型的兴隆山保护区野生马麝秋季生境适宜性评价. 生态学杂志, 43, 299-304.] | |
| [18] | Liu WL (1993) Xizang Nature Reserve. Xizang People’s Publishing House, Lhasa. (in Chinese) |
| [刘务林 (1993) 西藏自然保护区. 西藏人民出版社, 拉萨.] | |
| [19] | Lv YL, Feijó A, Guo KJ, Xie WD, Cheng JL, Ge DY, Xia L, Cui YQ, Song G, Qu YH, Hu JJ, Dan Z, Pubu DZ, Wu EN, He XC, Xu Y, Wang B, Yang QS, Wen ZX (2024) Integrating multiple diversity and socioeconomic criteria in Tibetan felid conservation. Ecosystem Health and Sustainability, 10, 160. |
| [20] | Nautiyal H, Huffman MA (2018) Interspecific feeding association between central Himalayan langurs (Semnopithecus schistaceus) and Himalayan black bears (Ursus thibetanus), in a temperate forest of the western Indian Himalayas. Mammal Study, 43, 1-6. |
| [21] |
Nüchel J, Bøcher PK, Xiao W, Zhu AX, Svenning JC (2018) Snub-nosed monkeys (Rhinopithecus): Potential distribution and its implication for conservation. Biodiversity and Conservation, 27, 1517-1538.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | Shao Q, Cui ZW, Liu CB, Tian JD, Lu JQ (2023) Diets and feeding strategy in Taihangshan macaques (Macaca mulatta tcheliensis) in a temperate forest, North China. International Journal of Primatology, 44, 1074-1090. |
| [23] |
Swets JA (1988) Measuring the accuracy of diagnostic systems. Science, 240, 1285-1293.
DOI PMID |
| [24] | Wang JL, Chen Y (2004) Applications of 3S technology in wildlife habitat researches. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 20(6), 44-47. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王金亮, 陈姚 (2004) 3S技术在野生动物生境研究中的应用. 地理与地理信息科学, 20(6), 44-47.] | |
| [25] |
Wang YS, Xie BY, Wan FH, Xiao QM, Dai LY (2007) Application of ROC curve analysis in evaluating the performance of alien species’ potential distribution models. Biodiversity Science, 15, 365-372. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[王运生, 谢丙炎, 万方浩, 肖启明, 戴良英 (2007) ROC曲线分析在评价入侵物种分布模型中的应用. 生物多样性, 15, 365-372.]
DOI |
|
| [26] | Warren DL, Glor RE, Turelli M (2010) ENMTools: A toolbox for comparative studies of environmental niche models. Ecography, 33, 607-611. |
| [27] | Wei FW, Yang QS, Wu Y, Jiang XL, Liu SY, Hu YB, Ge DY, Li BG, Yang G, Li M, Zhou J, Li S, Li S, Yu WH, Chen BY, Zhang ZJ, Zhou CQ, Wu SB, Zhang L, Chen ZZ, Chen SD, Deng HQ, Jiang TL, Zhang LB, Shi HY, Lu XL, Li Q, Liu Z, Cui YQ, Li YC, He K (2025) Catalogue of mammals in China (2024). Acta Theriologica Sinica, 45, 1-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [魏辅文, 杨奇森, 吴毅, 蒋学龙, 刘少英, 胡义波, 葛德燕, 李保国, 杨光, 李明, 周江, 李松, 李晟, 余文华, 陈炳耀, 张泽钧, 周材权, 吴诗宝, 张立, 陈中正, 陈顺德, 邓怀庆, 江廷磊, 张礼标, 石红艳, 卢学理, 李权, 刘铸, 崔雅倩, 李玉春, 何锴 (2025) 中国兽类名录(2024版). 兽类学报, 45, 1-16.] | |
| [28] | Xiao Q, Liu C, Xu MZ, Zhou XD (2022) Prediction of potential suitable area of Rhinopithecus strykeri based on MaxEnt model. Journal of China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research, 20, 557-564. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [肖祺, 刘成, 徐梦珍, 周雄冬 (2022) 基于MaxEnt模型的怒江金丝猴潜在适生区预测. 中国水利水电科学研究院学报(中英文), 20, 557-564.] | |
| [29] | Yang L, Chen T, Shi KC, Zhang L, Lwin N, Fan PF (2023) Effects of climate and land-cover change on the conservation status of Gibbons. Conservation Biology, 37, e14045. |
| [30] | Zhang DF, Zhang Q, Guo J, Sun CZ, Wu J, Nie X, Xie CX (2017) Research on the global ecological suitability and characteristics of regions with Angelica sinensis based on the MaxEnt model. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 5111-5120. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张东方, 张琴, 郭杰, 孙成忠, 吴杰, 聂祥, 谢彩香 (2017) 基于MaxEnt模型的当归全球生态适宜区和生态特征研究. 生态学报, 37, 5111-5120.] | |
| [31] |
Zhu GP, Liu GQ, Bu WJ, Gao YB (2013) Ecological niche modeling and its applications in biodiversity conservation. Biodiversity Science, 21, 90-98. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[朱耿平, 刘国卿, 卜文俊, 高玉葆 (2013) 生态位模型的基本原理及其在生物多样性保护中的应用. 生物多样性, 21, 90-98.]
DOI |
| [1] | 张彤云, 胡自民. 二裂墨角藻谱系多样性模式显示纽芬兰大浅滩存在一个海洋冰期避难所[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(6): 24416-. |
| [2] | 付梦娣, 朱彦鹏, 任月恒, 李爽, 秦乐, 谢正君, 王清春, 张立博. 新疆野生动物通道空间布局优化[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24346-. |
| [3] | 顾婧婧, 刘宜卓, 苏杨. 基层地方政府在完成《昆蒙框架》中的作用和难点: 基于《联合国气候变化框架公约》任务的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24585-. |
| [4] | 吴琪, 张晓青, 杨雨婷, 周艺博, 马毅, 许大明, 斯幸峰, 王健. 浙江钱江源-百山祖国家公园庆元片区叶附生苔多样性及其时空变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 24010-. |
| [5] | 曹可欣, 王敬雯, 郑国, 武鹏峰, 李英滨, 崔淑艳. 降水格局改变及氮沉降对北方典型草原土壤线虫多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23491-. |
| [6] | 冯莉. 国际法视野下生物多样性和气候变化的协同治理[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 23110-. |
| [7] | 姚雪, 陈星, 戴尊, 宋坤, 邢诗晨, 曹宏彧, 邹璐, 王健. 采集策略对叶附生苔类植物发现概率及物种多样性的重要性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22685-. |
| [8] | 邵雯雯, 范国祯, 何知舟, 宋志平. 多地同质园实验揭示普通野生稻的表型可塑性与本地适应性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22311-. |
| [9] | 张琼悦, 邓卓迪, 胡学斌, 丁志锋, 肖荣波, 修晨, 吴政浩, 汪光, 韩东晖, 张语克, 梁健超, 胡慧建. 粤港澳大湾区城市化进程对区域内鸟类分布及栖息地连通性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22161-. |
| [10] | 桑佳文, 宋创业, 贾宁霞, 贾元, 刘长成, 乔鲜果, 张琳, 袁伟影, 吴冬秀, 李凌浩, 郭柯. 青藏高原植被调查与制图评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22430-. |
| [11] | 王金洲, 徐靖. “基于自然的解决方案”应对生物多样性丧失和气候变化: 进展、挑战和建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22496-. |
| [12] | 李季蔓, 靳楠, 胥毛刚, 霍举颂, 陈小云, 胡锋, 刘满强. 不同干旱水平下蚯蚓对番茄抗旱能力的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21488-. |
| [13] | 朱瑞良, 马晓英, 曹畅, 曹子寅. 中国苔藓植物多样性研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 22378-. |
| [14] | 祖奎玲, 王志恒. 山地物种海拔分布对气候变化响应的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21451-. |
| [15] | 井新, 蒋胜竞, 刘慧颖, 李昱, 贺金生. 气候变化与生物多样性之间的复杂关系和反馈机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22462-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()