



生物多样性 ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (7): 24437. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024437 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024437
时永强1,2,3, 单秀娟1,2,3,*( ), 赵杰1,4, 王一诺1,4, 栾青杉1,2,3, 卞晓东1,2,3, 陈云龙1,2,3, 金显仕1,2,3
), 赵杰1,4, 王一诺1,4, 栾青杉1,2,3, 卞晓东1,2,3, 陈云龙1,2,3, 金显仕1,2,3
收稿日期:2024-10-06
接受日期:2025-05-06
出版日期:2025-07-20
发布日期:2025-08-06
通讯作者:
*E-mail: shanxj@ysfri.ac.cn
基金资助:
Yongqiang Shi1,2,3, Xiujuan Shan1,2,3,*( ), Jie Zhao1,4, Yinuo Wang1,4, Qingshan Luan1,2,3, Xiaodong Bian1,2,3, Yunlong Chen1,2,3, Xianshi Jin1,2,3
), Jie Zhao1,4, Yinuo Wang1,4, Qingshan Luan1,2,3, Xiaodong Bian1,2,3, Yunlong Chen1,2,3, Xianshi Jin1,2,3
Received:2024-10-06
Accepted:2025-05-06
Online:2025-07-20
Published:2025-08-06
Contact:
*E-mail: shanxj@ysfri.ac.cn
Supported by:摘要: 查明生态关键区的生物多样性现状及其演变特征, 是制定有效保护规划及科学管理措施的前提。本文通过整理统计1958‒2020年间101个航次的调查资料, 梳理了黄河口及其邻近海域的浮游动物种类名录, 比较了不同年代间浮游动物种类组成的变化, 分析了优势种及多样性指数年代际的变化情况, 以期为深入推动黄河流域生态保护和高质量发展提供数据支撑。结果显示, 黄河口及其邻近海域共记录浮游动物185种(类), 包括节肢动物94种, 刺胞动物42种, 浮游幼虫35类, 原生动物6种, 尾索动物4种, 栉板动物和毛颚动物各2种。节肢动物中, 桡足类41种, 糠虾类16种, 涟虫类12种, 端足类7种, 枝角类6种, 等足类4种, 十足类3种, 介形类和磷虾类各2种, 无甲类1种。从种类组成来看, 栉板动物在2000年之后开始出现, 刺胞动物和栉板动物等胶质浮游动物呈现暖温种比例降低、暖水种比例升高的变化趋势, 桡足类中, 小型桡足类占比增加。大中型浮游动物优势种组成呈现小型化、胶质化趋势, 并且浮游幼虫占比增加, 夜光虫(Noctiluca scintillans)的大量出现导致Shannon-Wiener多样性指数急剧降低。未来的研究需考虑多重胁迫因子对生物多样性的影响, 确定关键驱动因子及关键影响过程, 并关注极端气候事件的作用。
时永强, 单秀娟, 赵杰, 王一诺, 栾青杉, 卞晓东, 陈云龙, 金显仕 (2025) 1958-2020年黄河口及其邻近海域浮游动物群落组成及多样性演变. 生物多样性, 33, 24437. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024437.
Yongqiang Shi, Xiujuan Shan, Jie Zhao, Yinuo Wang, Qingshan Luan, Xiaodong Bian, Yunlong Chen, Xianshi Jin (2025) Evolution of zooplankton taxa composition and biodiversity in the Yellow River estuary and its adjacent waters from 1958 to 2020. Biodiversity Science, 33, 24437. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024437.
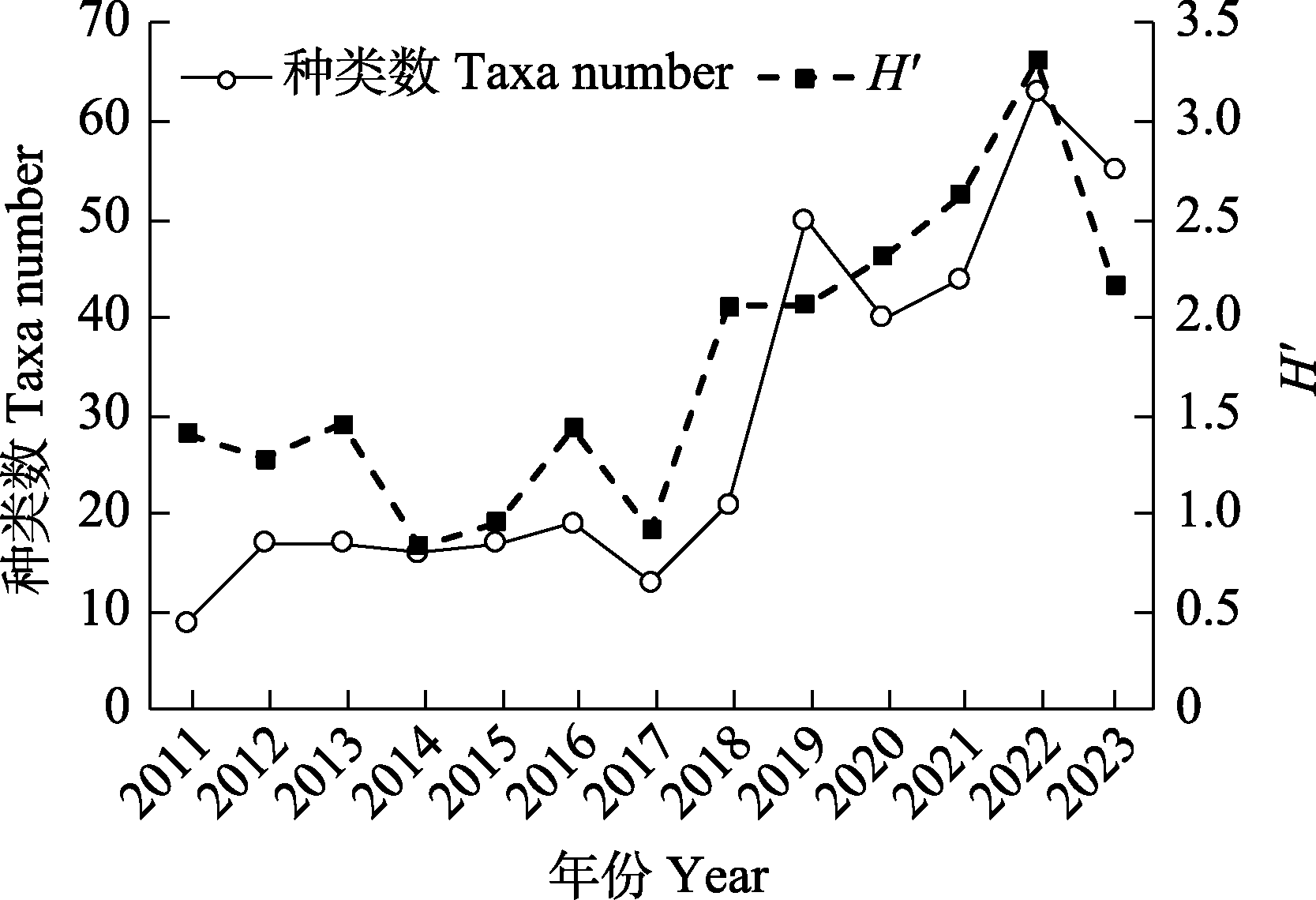
图1 黄河口大型浮游动物种类数及Shannon-Wiener多样性指数(H′)年际变化
Fig. 1 Inter-annual variations in taxa number and Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H′) of macro-zooplankton in the Yellow River estuary
| 年份 Year | 优势种 Dominant species | 年份 Year | 优势种 Dominant species |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 背针胸刺水蚤 Centropages dorsispinatus 强壮滨箭虫 Aidanosagitta crassa | 2018 | 背针胸刺水蚤 Centropages dorsispinatus 强壮滨箭虫 Aidanosagitta crassa |
| 2012 | 强壮滨箭虫 Aidanosagitta crassa 背针胸刺水蚤 Centropages dorsispinatus | 2019 | 球型侧腕水母 Pleurobrachia globosa 锡兰和平水母 Eirene ceylonensis |
| 2013 | 强壮滨箭虫 Aidanosagitta crassa 太平洋纺锤水蚤 Acartia pacifica | 2020 | 强壮滨箭虫 Aidanosagitta crassa 球型侧腕水母 Pleurobrachia globosa |
| 2014 | 强壮滨箭虫 Aidanosagitta crassa 背针胸刺水蚤 Centropages dorsispinatus | 2021 | 球型侧腕水母 Pleurobrachia globosa 拟长腹剑水蚤 Oithona similis |
| 2015 | 强壮滨箭虫 Aidanosagitta crassa 太平洋纺锤水蚤 Acartia pacifica | 2022 | 拟长腹剑水蚤 Oithona similis 强壮滨箭虫 Aidanosagitta crassa |
| 2016 | 背针胸刺水蚤 Centropages dorsispinatus 强壮滨箭虫 Aidanosagitta crassa | 2023 | 球型侧腕水母 Pleurobrachia globosa 强壮滨箭虫 Aidanosagitta crassa |
| 2017 | 背针胸刺水蚤 Centropages dorsispinatus 强壮滨箭虫 Aidanosagitta crassa |
表1 黄河口大型浮游动物优势种年际变化
Table 1 Inter-annual variations in dominant species of macro- zooplankton in the Yellow River estuary
| 年份 Year | 优势种 Dominant species | 年份 Year | 优势种 Dominant species |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 背针胸刺水蚤 Centropages dorsispinatus 强壮滨箭虫 Aidanosagitta crassa | 2018 | 背针胸刺水蚤 Centropages dorsispinatus 强壮滨箭虫 Aidanosagitta crassa |
| 2012 | 强壮滨箭虫 Aidanosagitta crassa 背针胸刺水蚤 Centropages dorsispinatus | 2019 | 球型侧腕水母 Pleurobrachia globosa 锡兰和平水母 Eirene ceylonensis |
| 2013 | 强壮滨箭虫 Aidanosagitta crassa 太平洋纺锤水蚤 Acartia pacifica | 2020 | 强壮滨箭虫 Aidanosagitta crassa 球型侧腕水母 Pleurobrachia globosa |
| 2014 | 强壮滨箭虫 Aidanosagitta crassa 背针胸刺水蚤 Centropages dorsispinatus | 2021 | 球型侧腕水母 Pleurobrachia globosa 拟长腹剑水蚤 Oithona similis |
| 2015 | 强壮滨箭虫 Aidanosagitta crassa 太平洋纺锤水蚤 Acartia pacifica | 2022 | 拟长腹剑水蚤 Oithona similis 强壮滨箭虫 Aidanosagitta crassa |
| 2016 | 背针胸刺水蚤 Centropages dorsispinatus 强壮滨箭虫 Aidanosagitta crassa | 2023 | 球型侧腕水母 Pleurobrachia globosa 强壮滨箭虫 Aidanosagitta crassa |
| 2017 | 背针胸刺水蚤 Centropages dorsispinatus 强壮滨箭虫 Aidanosagitta crassa |
| 年份 Year | 季节 Season | 航次数 No. of surveys | 经纬度 Longitude and latitude | 站位数 No. of stations | 采样网具类型 Type of sampling nets# | 记录种类数 No. of taxa recorded | 文中实际出现的种类数 No. of taxa recorded in the text | 数据来源 Source of data | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1958-1959 | 四季 Four seasons | 16 | 118.4°-120.2° E 37.4°-38.3° N | 14 | 大型网、中型网 Large net, medium net | / | 16 | 中华人民共和国科学技术委员会海洋组海洋综合调查办公室, | |||||
| 1980-1981 | 春、夏、秋 Spring, Summer, Autumn | 5 | 118.0°-119.5° E 37.3°-38.5° N | 30 | 中型网 Medium net | 45 (仅包括3类浮游幼虫 Only include three taxa pelagic larvae) | 18 | 田家怡和李洪彦, | |||||
| 1984 | 春、夏、秋 Spring, Summer, Autumn | 8 | 117.9°-119.7° E 37.2°‒38.5° N | 44 | 浅水I型、浅水II型 Type I net, type II net | 89 | 89 | 山东省科学技术委员会, | |||||
| 1996 | 春、夏、秋 Spring, Summer, Autumn | 4 | 118.0°‒119.5° E 37.2°‒38.4° N | 30 | 大型网、中型网 Large net, medium net | 80 (仅包括1类浮游幼虫 Only include one taxa pelagic larvae) | 80 | 焦玉木和田家怡, | |||||
| 2004 | 春、夏 Spring, Summer | 2 | 118.9°‒119.6° E 37.3°‒38.1° N | / | / | 27 | / | 张达娟等, | |||||
| 2005 | 春*、夏* Spring*, Summer* | 2 | 118.9°‒119.6° E 37.3°‒38.1° N | / | / | 40 | / | 张达娟等, | |||||
| 2006 | 春*、夏* Spring*, Summer* | 2 | 118.9°‒119.6° E 37.3°‒38.1° N | / | / | 43 | / | 张达娟等, | |||||
| 2005-2010 | 春、夏 Spring, Summer | 11 | 119.0°‒119.6° E 37.3°‒38.1° N | 33 | 浅水I型 Type I net | 62 | 62 | 冷宇等, | |||||
| 2006-2007 | 四季 Four seasons | 4 | 118.3°‒120.0° E 37.2°‒38.5° N | 35 | 浅水I型 Type I net | / | / | 杜明敏等, | |||||
| 2007 | 夏 Summer | 1 | 118.6°‒120.4° E 37.4°‒38.6° N | 24 | 浅水I型 Type I net | 72 | 16 | 马静等, | |||||
| 2008 | 春*、夏 Spring*, Summer | 2 | 119.0°‒119.5° E 37.4°‒37.9° N | 14 | / | 31 | / | 孙栋等, | |||||
| 2008-2009 | 春 Spring | 2 | 119.0°‒119.5° E 37.4°‒37.9° N | 14 | 浅水I型、浅水III型 Type I net, Type III net | 45 | 39 | 巩俊霞等, | |||||
| 2009 | 夏 Summer | 1 | 118.9°‒119.6° E 37.5°‒38.2° N | 27 | 浅水I型、浅水II型 Type I net, type II net | 92 | 92 | 马静, 2011①; 王文杰, 2011②; 李浩然等, | |||||
| 2010 | 秋 Autumn | 1 | 119.0°‒119.7° E 37.4°‒38.2° N | 30 | 浅水I型、浅水II型 Type I net, type II net | 83 | 83 | 马静, 2011①; 王文杰, 2011②; 王文杰和刘光兴, | |||||
| 2011 | 春 Spring | 1 | 119.0°‒119.7° E 37.5°‒38.2° N | 29 | 浅水I型、浅水II型 Type I net, type II net | 56 | 56 | 李自尚, 2012③; 葛汝平等, | |||||
| 2011-2020 | 夏 Summer | 18 | 119.0°‒119.7° E 37.6°‒38.2° N | 18 | 浅水I型 Type I net | 82 | 23 | 王秀霞等, | |||||
| 2012-2013 | 四季 Four seasons | 4 | 119.0°‒119.7° E 37.4°‒38.2° N | 29 | 浅水II型 Type II net | 70 | 9 | 董志军等, | |||||
| 2013-2014 | 春、夏*、 秋*、冬* Spring, Summer*, Autumn*, Winter* | 4 | 119.0°‒119.7° E 37.6°‒38.2° N | 18 | 浅水I型 Type I net | 43 | 18 | 刘晓慧等, | |||||
| 2013-2014 | 四季 Four seasons | 6 | 119.0°‒119.7° E 37.6°‒38.2° N | 18 | 浅水I型 Type I net | / | 25 | Liu et al, | |||||
| 2015-2018 | 夏 Summer | 4 | 118.3°‒119.5° E 37.3°‒38.3° N | 18 | 浅水I型、浅水II型 Type I net, type II net | / | 15 | 姜磊, 2020① | |||||
| 2015-2020 | 夏 Summer | 6 | 118.6°‒119.7° E 37.3°‒38.4° N | 10 | 浅水I型 Type I net | 52 | 5 | 张翔和李愫, | |||||
| 2019-2020 | 四季 Four seasons | 6 | 119.0°‒119.7° E 37.3°‒38.1° N | 20 | 浅水II型 Type II net | 16 (仅统计浮游幼虫 Only include pelagic larvae) | 16 | 左涛等, | |||||
| 2020 | 夏* Summer* | 3 | 119.1°‒119.7° E 37.3°‒38.2° N | 23 | 浅水I型 Type I net | 34 | 11 | 王秀霞等, | |||||
表2 黄河口及其邻近海域浮游动物调查航次统计
Table 2 Information of zooplankton sampling surveys in the Yellow River estuary and its adjacent waters
| 年份 Year | 季节 Season | 航次数 No. of surveys | 经纬度 Longitude and latitude | 站位数 No. of stations | 采样网具类型 Type of sampling nets# | 记录种类数 No. of taxa recorded | 文中实际出现的种类数 No. of taxa recorded in the text | 数据来源 Source of data | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1958-1959 | 四季 Four seasons | 16 | 118.4°-120.2° E 37.4°-38.3° N | 14 | 大型网、中型网 Large net, medium net | / | 16 | 中华人民共和国科学技术委员会海洋组海洋综合调查办公室, | |||||
| 1980-1981 | 春、夏、秋 Spring, Summer, Autumn | 5 | 118.0°-119.5° E 37.3°-38.5° N | 30 | 中型网 Medium net | 45 (仅包括3类浮游幼虫 Only include three taxa pelagic larvae) | 18 | 田家怡和李洪彦, | |||||
| 1984 | 春、夏、秋 Spring, Summer, Autumn | 8 | 117.9°-119.7° E 37.2°‒38.5° N | 44 | 浅水I型、浅水II型 Type I net, type II net | 89 | 89 | 山东省科学技术委员会, | |||||
| 1996 | 春、夏、秋 Spring, Summer, Autumn | 4 | 118.0°‒119.5° E 37.2°‒38.4° N | 30 | 大型网、中型网 Large net, medium net | 80 (仅包括1类浮游幼虫 Only include one taxa pelagic larvae) | 80 | 焦玉木和田家怡, | |||||
| 2004 | 春、夏 Spring, Summer | 2 | 118.9°‒119.6° E 37.3°‒38.1° N | / | / | 27 | / | 张达娟等, | |||||
| 2005 | 春*、夏* Spring*, Summer* | 2 | 118.9°‒119.6° E 37.3°‒38.1° N | / | / | 40 | / | 张达娟等, | |||||
| 2006 | 春*、夏* Spring*, Summer* | 2 | 118.9°‒119.6° E 37.3°‒38.1° N | / | / | 43 | / | 张达娟等, | |||||
| 2005-2010 | 春、夏 Spring, Summer | 11 | 119.0°‒119.6° E 37.3°‒38.1° N | 33 | 浅水I型 Type I net | 62 | 62 | 冷宇等, | |||||
| 2006-2007 | 四季 Four seasons | 4 | 118.3°‒120.0° E 37.2°‒38.5° N | 35 | 浅水I型 Type I net | / | / | 杜明敏等, | |||||
| 2007 | 夏 Summer | 1 | 118.6°‒120.4° E 37.4°‒38.6° N | 24 | 浅水I型 Type I net | 72 | 16 | 马静等, | |||||
| 2008 | 春*、夏 Spring*, Summer | 2 | 119.0°‒119.5° E 37.4°‒37.9° N | 14 | / | 31 | / | 孙栋等, | |||||
| 2008-2009 | 春 Spring | 2 | 119.0°‒119.5° E 37.4°‒37.9° N | 14 | 浅水I型、浅水III型 Type I net, Type III net | 45 | 39 | 巩俊霞等, | |||||
| 2009 | 夏 Summer | 1 | 118.9°‒119.6° E 37.5°‒38.2° N | 27 | 浅水I型、浅水II型 Type I net, type II net | 92 | 92 | 马静, 2011①; 王文杰, 2011②; 李浩然等, | |||||
| 2010 | 秋 Autumn | 1 | 119.0°‒119.7° E 37.4°‒38.2° N | 30 | 浅水I型、浅水II型 Type I net, type II net | 83 | 83 | 马静, 2011①; 王文杰, 2011②; 王文杰和刘光兴, | |||||
| 2011 | 春 Spring | 1 | 119.0°‒119.7° E 37.5°‒38.2° N | 29 | 浅水I型、浅水II型 Type I net, type II net | 56 | 56 | 李自尚, 2012③; 葛汝平等, | |||||
| 2011-2020 | 夏 Summer | 18 | 119.0°‒119.7° E 37.6°‒38.2° N | 18 | 浅水I型 Type I net | 82 | 23 | 王秀霞等, | |||||
| 2012-2013 | 四季 Four seasons | 4 | 119.0°‒119.7° E 37.4°‒38.2° N | 29 | 浅水II型 Type II net | 70 | 9 | 董志军等, | |||||
| 2013-2014 | 春、夏*、 秋*、冬* Spring, Summer*, Autumn*, Winter* | 4 | 119.0°‒119.7° E 37.6°‒38.2° N | 18 | 浅水I型 Type I net | 43 | 18 | 刘晓慧等, | |||||
| 2013-2014 | 四季 Four seasons | 6 | 119.0°‒119.7° E 37.6°‒38.2° N | 18 | 浅水I型 Type I net | / | 25 | Liu et al, | |||||
| 2015-2018 | 夏 Summer | 4 | 118.3°‒119.5° E 37.3°‒38.3° N | 18 | 浅水I型、浅水II型 Type I net, type II net | / | 15 | 姜磊, 2020① | |||||
| 2015-2020 | 夏 Summer | 6 | 118.6°‒119.7° E 37.3°‒38.4° N | 10 | 浅水I型 Type I net | 52 | 5 | 张翔和李愫, | |||||
| 2019-2020 | 四季 Four seasons | 6 | 119.0°‒119.7° E 37.3°‒38.1° N | 20 | 浅水II型 Type II net | 16 (仅统计浮游幼虫 Only include pelagic larvae) | 16 | 左涛等, | |||||
| 2020 | 夏* Summer* | 3 | 119.1°‒119.7° E 37.3°‒38.2° N | 23 | 浅水I型 Type I net | 34 | 11 | 王秀霞等, | |||||
| 种类 Taxa | 年代 Decade | 总计 Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1980s | 1990s | 2000s | 2010s | |||
| 原生动物 Protozoa | 1 | 0 | 5 | 4 | 6 | |
| 刺胞动物 Cnidaria | 22 | 21 | 23 | 22 | 42 | |
| 栉板动物 Ctenophora | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
| 节肢动物 Arthropoda | 41 | 56 | 54 | 46 | 94 | |
| 无甲类 Anostraca | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| 枝角类 Cladocera | 3 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 6 | |
| 桡足类 Copepoda | 28 | 31 | 26 | 26 | 41 | |
| 介形类 Ostracoda | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| 糠虾类 Mysida | 8 | 6 | 9 | 9 | 16 | |
| 端足类 Amphipoda | 1 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 7 | |
| 等足类 Isopoda | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 4 | |
| 涟虫类 Cumacea | 0 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 12 | |
| 磷虾类 Euphausiacea | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | |
| 十足类 Decapoda | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 3 | |
| 毛颚动物 Chaetognatha | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | |
| 尾索动物 Urochordata | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
| 浮游幼虫 Pelagic larvae | 22 | / | 28 | 28 | 35 | |
| 总计 Total | 88 | 79* | 116 | 106 | 185 | |
表3 黄河口及其邻近海域浮游动物种类数年代际变化
Table 3 Decadal changes of zooplankton taxa number in the Yellow River estuary and its adjacent waters
| 种类 Taxa | 年代 Decade | 总计 Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1980s | 1990s | 2000s | 2010s | |||
| 原生动物 Protozoa | 1 | 0 | 5 | 4 | 6 | |
| 刺胞动物 Cnidaria | 22 | 21 | 23 | 22 | 42 | |
| 栉板动物 Ctenophora | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
| 节肢动物 Arthropoda | 41 | 56 | 54 | 46 | 94 | |
| 无甲类 Anostraca | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| 枝角类 Cladocera | 3 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 6 | |
| 桡足类 Copepoda | 28 | 31 | 26 | 26 | 41 | |
| 介形类 Ostracoda | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| 糠虾类 Mysida | 8 | 6 | 9 | 9 | 16 | |
| 端足类 Amphipoda | 1 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 7 | |
| 等足类 Isopoda | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 4 | |
| 涟虫类 Cumacea | 0 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 12 | |
| 磷虾类 Euphausiacea | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | |
| 十足类 Decapoda | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 3 | |
| 毛颚动物 Chaetognatha | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | |
| 尾索动物 Urochordata | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
| 浮游幼虫 Pelagic larvae | 22 | / | 28 | 28 | 35 | |
| 总计 Total | 88 | 79* | 116 | 106 | 185 | |
| 调查时间(年-月) Survey time (year-month) | 优势种 Dominant species | 数据来源 Source of data |
|---|---|---|
| 1959-05 | 中华哲水蚤、腹针胸刺水蚤、强壮滨箭虫 Calanus sinicus, Centropages abdominalis, Aidanosagitta crassa | 中华人民共和国科学技术委员会海洋组海洋综合调查办公室, |
| 2005-05 | 强壮滨箭虫、中华哲水蚤、长尾类幼虫、真刺唇角水蚤 Aidanosagitta crassa, Calanus sinicus, Macrura larvae, Labidocera euchaeta | 冷宇等, |
| 2006-05 | 中华哲水蚤、强壮滨箭虫、洪氏纺锤水蚤 Calanus sinicus, Aidanosagitta crassa, Acartia hongi | 冷宇等, |
| 2007-05 | 强壮滨箭虫、中华哲水蚤、洪氏纺锤水蚤、短尾类溞状幼虫 Aidanosagitta crassa, Calanus sinicus, Acartia hongi, Brachyura zoea larvae | 冷宇等, |
| 2008-05 | 中华哲水蚤、强壮滨箭虫、长尾类幼虫、短尾类溞状幼虫 Calanus sinicus, Aidanosagitta crassa, Macrura larvae, Brachyura zoea larvae | 冷宇等, |
| 2009-05 | 洪氏纺锤水蚤、小拟哲水蚤、强壮滨箭虫、腹针胸刺水蚤、中华哲水蚤 Acartia hongi, Paracalanus parvus, Aidanosagitta crassa, Centropages abdominalis, Calanus sinicus | 冷宇等, |
| 2011-05 | 洪氏纺锤水蚤、腹针胸刺水蚤、强壮滨箭虫、中华哲水蚤、短尾类溞状幼虫 Acartia hongi, Centropages abdominalis, Aidanosagitta crassa, Calanus sinicus, Brachyura zoea larvae | 葛汝平等, |
| 2014-05 | 夜光虫、洪氏纺锤水蚤、瘦尾胸刺水蚤、中华哲水蚤 Noctiluca scintillans, Acartia hongi, Centropages tenuiremis, Calanus sinicus | 刘晓慧等, |
表4 春季黄河口及其邻近海域大中型浮游动物优势种年代际变化
Table 4 Decadal changes of macro- and meso-zooplankton dominant species in the Yellow River estuary and its adjacent waters in spring
| 调查时间(年-月) Survey time (year-month) | 优势种 Dominant species | 数据来源 Source of data |
|---|---|---|
| 1959-05 | 中华哲水蚤、腹针胸刺水蚤、强壮滨箭虫 Calanus sinicus, Centropages abdominalis, Aidanosagitta crassa | 中华人民共和国科学技术委员会海洋组海洋综合调查办公室, |
| 2005-05 | 强壮滨箭虫、中华哲水蚤、长尾类幼虫、真刺唇角水蚤 Aidanosagitta crassa, Calanus sinicus, Macrura larvae, Labidocera euchaeta | 冷宇等, |
| 2006-05 | 中华哲水蚤、强壮滨箭虫、洪氏纺锤水蚤 Calanus sinicus, Aidanosagitta crassa, Acartia hongi | 冷宇等, |
| 2007-05 | 强壮滨箭虫、中华哲水蚤、洪氏纺锤水蚤、短尾类溞状幼虫 Aidanosagitta crassa, Calanus sinicus, Acartia hongi, Brachyura zoea larvae | 冷宇等, |
| 2008-05 | 中华哲水蚤、强壮滨箭虫、长尾类幼虫、短尾类溞状幼虫 Calanus sinicus, Aidanosagitta crassa, Macrura larvae, Brachyura zoea larvae | 冷宇等, |
| 2009-05 | 洪氏纺锤水蚤、小拟哲水蚤、强壮滨箭虫、腹针胸刺水蚤、中华哲水蚤 Acartia hongi, Paracalanus parvus, Aidanosagitta crassa, Centropages abdominalis, Calanus sinicus | 冷宇等, |
| 2011-05 | 洪氏纺锤水蚤、腹针胸刺水蚤、强壮滨箭虫、中华哲水蚤、短尾类溞状幼虫 Acartia hongi, Centropages abdominalis, Aidanosagitta crassa, Calanus sinicus, Brachyura zoea larvae | 葛汝平等, |
| 2014-05 | 夜光虫、洪氏纺锤水蚤、瘦尾胸刺水蚤、中华哲水蚤 Noctiluca scintillans, Acartia hongi, Centropages tenuiremis, Calanus sinicus | 刘晓慧等, |
| 调查时间(年-月) Survey time (year-month) | 优势种 Dominant species | 数据来源 Source of data |
|---|---|---|
| 1959-07 | 强壮滨箭虫、瘦尾胸刺水蚤、刺尾歪水蚤、圆唇角水蚤 Aidanosagitta crassa, Centropages tenuiremis, Tortanus spinicaudatus, Labidocera rotunda | 中华人民共和国科学技术委员会海洋组海洋综合调查办公室, |
| 1959-08 | 强壮滨箭虫、圆唇角水蚤、真刺唇角水蚤、刺尾歪水蚤、汤氏长足水蚤 Aidanosagitta crassa, Labidocera rotunda, Labidocera euchaeta, Tortanus spinicaudatus, Calanopia thompsoni | 中华人民共和国科学技术委员会海洋组海洋综合调查办公室, |
| 2005-08 | 强壮滨箭虫、真刺唇角水蚤、异尾类溞状幼虫、小拟哲水蚤、长尾类幼虫 Aidanosagitta crassa, Labidocera euchaeta, Anomura zoea larvae, Paracalanus parvus, Macrura larvae | 冷宇等, |
| 2006-08 | 强壮滨箭虫、太平洋纺锤水蚤、长尾类幼虫、腹足类幼虫、真刺唇角水蚤 Aidanosagitta crassa, Acartia pacifica, Macrura larvae, Gastropoda larvae, Labidocera euchaeta | 冷宇等, |
| 2007-07 | 柱头幼虫、小拟哲水蚤、中华哲水蚤、强壮滨箭虫、洪氏纺锤水蚤 Tornaria larvae, Paracalanus parvus, Calanus sinicus, Aidanosagitta crassa, Acartia hongi | 马静等, |
| 2007-08 | 强壮滨箭虫、小拟哲水蚤、真刺唇角水蚤、长尾类幼虫、太平洋纺锤水蚤 Aidanosagitta crassa, Paracalanus parvus, Labidocera euchaeta, Macrura larvae, Acartia pacifica | 冷宇等, |
| 2008-08 | 强壮滨箭虫、真刺唇角水蚤、长尾类幼虫、小拟哲水蚤 Aidanosagitta crassa, Labidocera euchaeta, Macrura larvae, Paracalanus parvus | 冷宇等, |
| 2009-07 | 强壮滨箭虫、长尾类幼虫、中华哲水蚤、真刺唇角水蚤、小拟哲水蚤 Aidanosagitta crassa, Macrura larvae, Calanus sinicus, Labidocera euchaeta, Paracalanus parvus | 李浩然等, |
| 2009-08 | 强壮滨箭虫、真刺唇角水蚤、异尾类溞状幼虫、长尾类幼虫、背针胸刺水蚤 Aidanosagitta crassa, Labidocera euchaeta, Anomura zoea larvae, Macrura larvae, Centropages dorsispinatus | 冷宇等, |
| 2010-08 | 强壮滨箭虫、长尾类幼虫、背针胸刺水蚤、真刺唇角水蚤 Aidanosagitta crassa, Macrura larvae, Centropages dorsispinatus, Labidocera euchaeta | 冷宇等, |
| 2013-08 | 强壮滨箭虫、背针胸刺水蚤、长尾类幼虫、中华哲水蚤、桡足幼虫 Aidanosagitta crassa, Centropages dorsispinatus, Macrura larvae, Calanus sinicus, Copepodite | 刘晓慧等, |
| 2015-08 | 强壮滨箭虫、洪氏纺锤水蚤、小拟哲水蚤、太平洋纺锤水蚤、真刺唇角水蚤 Aidanosagitta crassa, Acartia hongi, Paracalanus parvus, Acartia pacifica, Labidocera euchaeta | 姜磊, 2020① |
| 2016-08 | 桡足类无节幼虫、桡足幼虫、背针胸刺水蚤、强壮滨箭虫 Copepoda nauplii, Copepodite, Centropages dorsispinatus, Aidanosagitta crassa | 姜磊, 2020① |
| 2017-07 | 短尾类溞状幼虫、强壮滨箭虫、背针胸刺水蚤、细颈和平水母、鱼卵、糠虾幼虫 Brachyura zoea larvae, Aidanosagitta crassa, Centropages dorsispinatus, Eirene menoni, Fish eggs, Mysidae larvae | 王秀霞等, |
| 2017-08 | 背针胸刺水蚤、长尾类幼虫、强壮滨箭虫、短尾类溞状幼虫 Centropages dorsispinatus, Macrura larvae, Aidanosagitta crassa, Brachyura zoea larvae | 姜磊, 2020① |
| 2018-08 | 强壮滨箭虫、背针胸刺水蚤、拟长腹剑水蚤、短尾类溞状幼虫、太平洋纺锤水蚤、长尾类幼虫、桡足幼虫、腹针胸刺水蚤 Aidanosagitta crassa, Centropages dorsispinatus, Oithona similis, Brachyura zoea larvae, Acartia pacifica, Macrura larvae, Copepodite, Centropages abdominalis | 姜磊, 2020① |
| 2020-07 | 强壮滨箭虫、糠虾幼虫、夜光虫、嵊山秀氏水母、圆唇角水蚤 Aidanosagitta crassa, Mysidae larvae, Noctiluca scintillans, Sugiura chengshanense, Labidocera rotunda | 王秀霞等, |
表5 夏季黄河口及其邻近海域大中型浮游动物优势种年代际变化
Table 5 Decadal changes of macro- and meso-zooplankton dominant species in the Yellow River estuary and its adjacent waters in summer
| 调查时间(年-月) Survey time (year-month) | 优势种 Dominant species | 数据来源 Source of data |
|---|---|---|
| 1959-07 | 强壮滨箭虫、瘦尾胸刺水蚤、刺尾歪水蚤、圆唇角水蚤 Aidanosagitta crassa, Centropages tenuiremis, Tortanus spinicaudatus, Labidocera rotunda | 中华人民共和国科学技术委员会海洋组海洋综合调查办公室, |
| 1959-08 | 强壮滨箭虫、圆唇角水蚤、真刺唇角水蚤、刺尾歪水蚤、汤氏长足水蚤 Aidanosagitta crassa, Labidocera rotunda, Labidocera euchaeta, Tortanus spinicaudatus, Calanopia thompsoni | 中华人民共和国科学技术委员会海洋组海洋综合调查办公室, |
| 2005-08 | 强壮滨箭虫、真刺唇角水蚤、异尾类溞状幼虫、小拟哲水蚤、长尾类幼虫 Aidanosagitta crassa, Labidocera euchaeta, Anomura zoea larvae, Paracalanus parvus, Macrura larvae | 冷宇等, |
| 2006-08 | 强壮滨箭虫、太平洋纺锤水蚤、长尾类幼虫、腹足类幼虫、真刺唇角水蚤 Aidanosagitta crassa, Acartia pacifica, Macrura larvae, Gastropoda larvae, Labidocera euchaeta | 冷宇等, |
| 2007-07 | 柱头幼虫、小拟哲水蚤、中华哲水蚤、强壮滨箭虫、洪氏纺锤水蚤 Tornaria larvae, Paracalanus parvus, Calanus sinicus, Aidanosagitta crassa, Acartia hongi | 马静等, |
| 2007-08 | 强壮滨箭虫、小拟哲水蚤、真刺唇角水蚤、长尾类幼虫、太平洋纺锤水蚤 Aidanosagitta crassa, Paracalanus parvus, Labidocera euchaeta, Macrura larvae, Acartia pacifica | 冷宇等, |
| 2008-08 | 强壮滨箭虫、真刺唇角水蚤、长尾类幼虫、小拟哲水蚤 Aidanosagitta crassa, Labidocera euchaeta, Macrura larvae, Paracalanus parvus | 冷宇等, |
| 2009-07 | 强壮滨箭虫、长尾类幼虫、中华哲水蚤、真刺唇角水蚤、小拟哲水蚤 Aidanosagitta crassa, Macrura larvae, Calanus sinicus, Labidocera euchaeta, Paracalanus parvus | 李浩然等, |
| 2009-08 | 强壮滨箭虫、真刺唇角水蚤、异尾类溞状幼虫、长尾类幼虫、背针胸刺水蚤 Aidanosagitta crassa, Labidocera euchaeta, Anomura zoea larvae, Macrura larvae, Centropages dorsispinatus | 冷宇等, |
| 2010-08 | 强壮滨箭虫、长尾类幼虫、背针胸刺水蚤、真刺唇角水蚤 Aidanosagitta crassa, Macrura larvae, Centropages dorsispinatus, Labidocera euchaeta | 冷宇等, |
| 2013-08 | 强壮滨箭虫、背针胸刺水蚤、长尾类幼虫、中华哲水蚤、桡足幼虫 Aidanosagitta crassa, Centropages dorsispinatus, Macrura larvae, Calanus sinicus, Copepodite | 刘晓慧等, |
| 2015-08 | 强壮滨箭虫、洪氏纺锤水蚤、小拟哲水蚤、太平洋纺锤水蚤、真刺唇角水蚤 Aidanosagitta crassa, Acartia hongi, Paracalanus parvus, Acartia pacifica, Labidocera euchaeta | 姜磊, 2020① |
| 2016-08 | 桡足类无节幼虫、桡足幼虫、背针胸刺水蚤、强壮滨箭虫 Copepoda nauplii, Copepodite, Centropages dorsispinatus, Aidanosagitta crassa | 姜磊, 2020① |
| 2017-07 | 短尾类溞状幼虫、强壮滨箭虫、背针胸刺水蚤、细颈和平水母、鱼卵、糠虾幼虫 Brachyura zoea larvae, Aidanosagitta crassa, Centropages dorsispinatus, Eirene menoni, Fish eggs, Mysidae larvae | 王秀霞等, |
| 2017-08 | 背针胸刺水蚤、长尾类幼虫、强壮滨箭虫、短尾类溞状幼虫 Centropages dorsispinatus, Macrura larvae, Aidanosagitta crassa, Brachyura zoea larvae | 姜磊, 2020① |
| 2018-08 | 强壮滨箭虫、背针胸刺水蚤、拟长腹剑水蚤、短尾类溞状幼虫、太平洋纺锤水蚤、长尾类幼虫、桡足幼虫、腹针胸刺水蚤 Aidanosagitta crassa, Centropages dorsispinatus, Oithona similis, Brachyura zoea larvae, Acartia pacifica, Macrura larvae, Copepodite, Centropages abdominalis | 姜磊, 2020① |
| 2020-07 | 强壮滨箭虫、糠虾幼虫、夜光虫、嵊山秀氏水母、圆唇角水蚤 Aidanosagitta crassa, Mysidae larvae, Noctiluca scintillans, Sugiura chengshanense, Labidocera rotunda | 王秀霞等, |
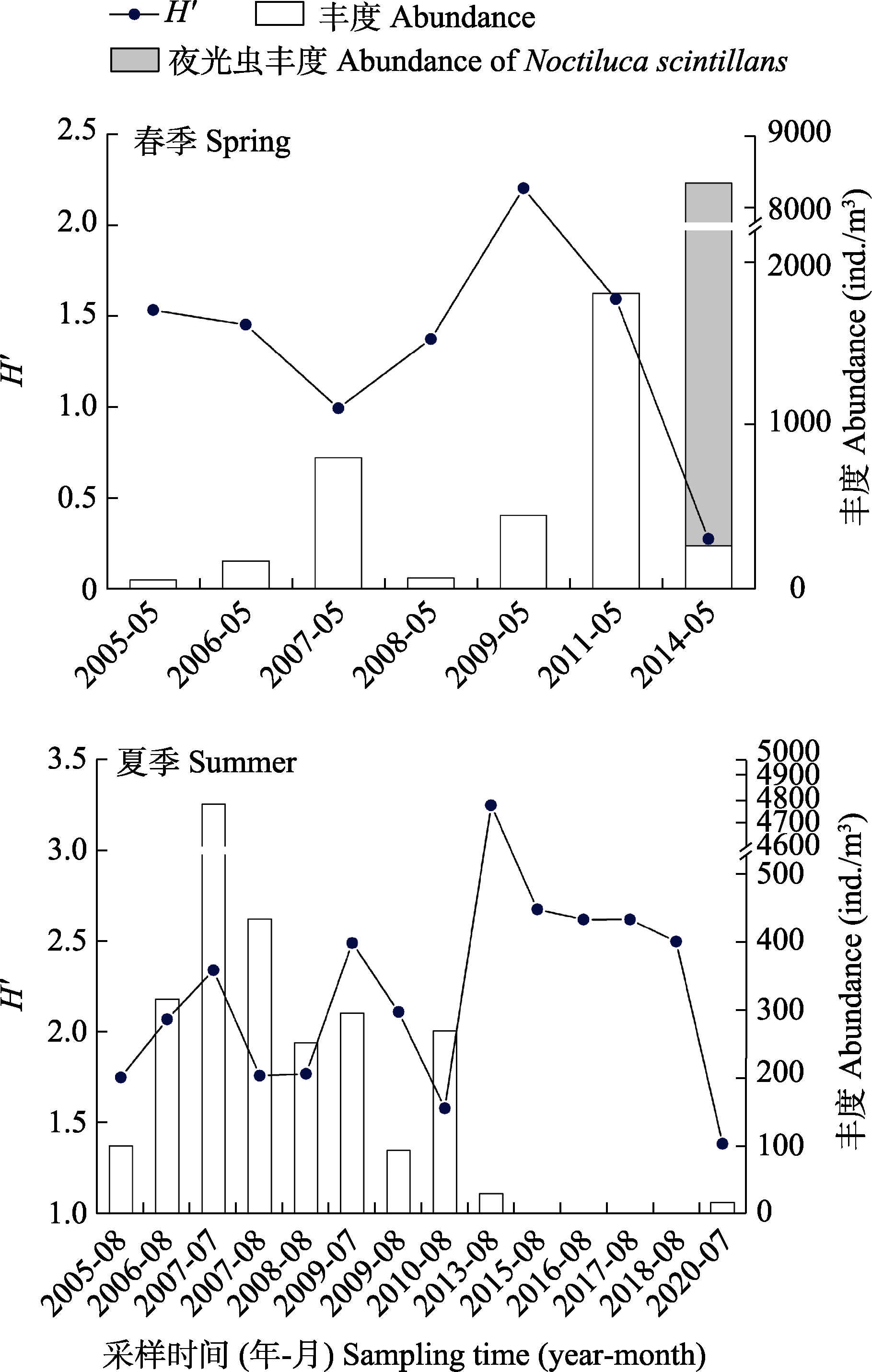
图2 春季和夏季黄河口及其邻近海域大中型浮游动物Shannon-Wiener多样性指数(H′)和丰度年际变化
Fig. 2 Inter-annual variations in Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H′) and abundance of macro- and meso-zooplankton in the Yellow River estuary and its adjacent waters
| [1] | Banse K (1995) Zooplankton: Pivotal role in the control of ocean production. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 52, 265-277. |
| [2] | Beaugrand G, Brander KM, Alistair Lindley J, Souissi S, Reid PC (2003) Plankton effect on cod recruitment in the North Sea. Nature, 426, 661-664. |
| [3] | Bian XD, Wan RJ, Shan XJ, Jin XS (2022) Preliminary analysis on recruitment variation and the exogenous driving factors to early life stages of small pelagic fishes in the Laizhou Bay. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 29, 446-468. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [卞晓东, 万瑞景, 单秀娟, 金显仕 (2022) 莱州湾中上层小型鱼类早期资源量动态及其外在驱动因素. 中国水产科学, 29, 446-468.] | |
| [4] | Brun P, Stamieszkin K, Visser AW, Licandro P, Payne MR, Kiørboe T (2019) Climate change has altered zooplankton-fuelled carbon export in the North Atlantic. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 3, 416-423. |
| [5] | Chang MX, Li P, Sun Y, Wang HJ, Li ZH (2022) Mapping dynamic turbidity maximum zone of the Yellow River estuary from 38 years of landsat imagery. Remote Sensing, 14, 3782. |
| [6] | Dong ZJ, Yang Q, Sun TT, Wang YJ, Jiang HC, Liu DY (2017) Spatial and seasonal variability of the zooplankton community in the Yellow River estuary’s adjacent sea. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 659-667. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [董志军, 杨青, 孙婷婷, 王玉珏, 姜会超, 刘东艳 (2017) 黄河口邻近海域浮游动物群落时空变化特征. 生态学报, 37, 659-667.] | |
| [7] | Du MM, Liu ZS, Wang CS, Zhang DS, Zhang J (2013) The seasonal variation and community structure of zooplankton in China sea. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33, 5407-5418. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杜明敏, 刘镇盛, 王春生, 张东声, 章菁 (2013) 中国近海浮游动物群落结构及季节变化. 生态学报, 33, 5407-5418.] | |
| [8] | Ge RP, Liu GX, Chen HJ, Li ZS, Li HR (2019) Community characteristics of zooplankton sampled with two plankton nets in Yellow River estuary in spring. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 49(4), 62-70. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [葛汝平, 刘光兴, 陈洪举, 李自尚, 李浩然 (2019) 春季黄河口两种网型网采浮游动物的群落特征. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 49(4), 62-70.] | |
| [9] | Gong JX, Yang XL, Duan DX, Wang ZZ, Du XH, Zhang JL, Chen SJ, Liu HC, Chen JP, Sun D (2010) A study on zooplankton community characteristics of Yellow River estuary waters in spring. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University, 30(6), 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [巩俊霞, 杨秀兰, 段登选, 王志忠, 杜兴华, 张金路, 陈述江, 刘红彩, 陈金萍, 孙栋 (2010) 黄河入海口水域春季浮游动物群落特征研究. 广东海洋大学学报, 30(6), 1-6.] | |
| [10] | Hays GC, Richardson AJ, Robinson C (2005) Climate change and marine plankton. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 20, 337-344. |
| [11] | Jiao YM, Tian JY (1999) Zooplankton diversity around the Huanghe River Delta. Marine Environmental Science, 18(4), 33-38. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [焦玉木, 田家怡 (1999) 黄河三角洲附近海域浮游动物多样性研究. 海洋环境科学, 18(4), 33-38.] | |
| [12] | Jin XS, Shan XJ, Li XS, Wang J, Cui Y, Zuo T (2013) Long-term changes in the fishery ecosystem structure of Laizhou Bay, China. Science China: Earth Sciences, 56, 366-374. |
| [13] | Leng Y, Zhang JM, Liu S, Liu XD, Zhang HL, Zhang AJ (2013) Marine Biodiversity in the Yellow River Estuary and Adjacent Waters. China Ocean University Press, Qingdao. (in Chinese) |
| [冷宇, 张继民, 刘霜, 刘旭东, 张洪亮, 张爱君 (2013) 黄河口及邻近海域海洋生物物种多样性. 中国海洋大学出版社, 青岛.] | |
| [14] | Li HR, Liu GX, Ma J, Chen HJ (2018) Community characteristics of zooplankton in the Yellow River estuary and its adjacent area in summer and autumn. Marine Environmental Science, 37, 631-639. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李浩然, 刘光兴, 马静, 陈洪举 (2018) 夏、秋季黄河口及邻近水域浮游动物群落特征. 海洋环境科学, 37, 631-639.] | |
| [15] | Li L (2021) A Century-long Phytoplankton Shift and Environmental Responses in the Adjacent Sea of the Yellow River Estuary. PhD dissertation, East China Normal University, Shanghai. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李磊 (2021) 黄河口邻近海域浮游植物百年演变特征及与环境变化的响应关系. 博士学位论文, 华东师范大学, 上海.] | |
| [16] | Li WJ, Wang ZY, Cui QC, Sun XL, Huang HJ (2024) Coastal ecological disasters triggered by an extreme rainfall event thousands of kilometers inland. Communications Earth & Environment, 5, 238. |
| [17] | Li XZ, Gan ZB (2022) Common Species List of Benthic Animals in China’s Coastal Waters. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [李新正, 甘志彬 (2022) 中国近海底栖动物常见种名录. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [18] | Li Y, Xu ZL, Gao Q (2009) Effects of global warming on Sagitta crassa and Sagitta enflata (Chaetognatha) in the Changjiang Estuary during different years. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 29, 4773-4780. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李云, 徐兆礼, 高倩 (2009) 长江口强壮箭虫和肥胖箭虫的丰度变化对环境变暖的响应. 生态学报, 29, 4773-4780.] | |
| [19] | Lian GS, Sun RX, Wang YG, Huang JX (2022) Species Diversity of Marine Harpacticoid Copepods in China’s Seas and Adjacent Waters. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [连光山, 孙柔鑫, 王彦国, 黄将修 (2022) 中国海及其邻近海域猛水蚤桡足类多样性. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [20] | Lian GS, Wang YG, Sun RX, Huang JX (2018) Species Diversity of Marine Planktonic Copepods in China’s Seas (Vol. I-II). China Ocean Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [连光山, 王彦国, 孙柔鑫, 黄将修 (2018) 中国海洋浮游桡足类多样性(上下册). 海洋出版社, 北京.] | |
| [21] | Liu RY (2008) Checklist of Marine Biota of China Seas. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘瑞玉 (2008) 中国海洋生物名录. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [22] | Liu XH, Song JJ, Ren YP, Zhan DM, Liu T, Liu KK, Wu HY, Xu BD (2023) Spatio-temporal patterns of zooplankton community in the Yellow River estuary: Effects of seasonal variability and water-sediment regulation. Marine Environmental Research, 189, 106060. |
| [23] | Liu XH, Xu BD, Zhang CL, Xue Y, Ren YP, Ji YP (2017) Characteristics of zooplankton community structure and its seasonal variation in the Yellow River estuary and its adjacent waters. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 24, 922-930. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘晓慧, 徐宾铎, 张崇良, 薛莹, 任一平, 纪毓鹏 (2017) 黄河口及其邻近水域浮游动物群落结构特征及其季节变化. 中国水产科学, 24, 922-930.] | |
| [24] | Ma J, Chen HJ, Liu GX (2012) Study on the zooplankton community structure in the Yellow River estuary and its adjacent waters in summer, 2007. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 42(5), 74-80. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [马静, 陈洪举, 刘光兴 (2012) 2007年夏季黄河口及其邻近水域浮游动物的群落特征. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 42(5), 74-80.] | |
| [25] | Ma ZL, Xu ZL, Zhou J (2009) Effect of global warming on the distribution of Lucifer intermedius and L. hanseni (Decapoda) in the Changjiang estuary. Progress in Natural Science, 19, 1389-1395. |
| [26] | Ministry of Ecological Environment (2019-2024) China Maine Eco-Environmental State Bulletin in 2018-2023. Ministry of Ecological Environment, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [生态环境部 (2019-2024) 2018-2023年中国海洋生态环境状况公报. 生态环境部, 北京.] | |
| [27] | Ocean Research Office of Marine Group, Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China (1961) Data of ‘Comprehensive Oceanography Expedition in China Seas’, Vol. 5: Records of Biomass and Distribution of Major Species of Planktonic and Benthic Organisms in the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea, and East China Sea during 1958.9-1959.12. Ocean Research Office of Marine Group, Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China, Tianjin. (in Chinese) |
| [中华人民共和国科学技术委员会海洋组海洋综合调查办公室 (1961) 全国海洋综合调查资料第五册: 渤、黄、东海浮游生物和底栖生物生物量及主要种类分布记录1958.9-1959.12. 中华人民共和国科学技术委员会海洋组海洋综合调查办公室, 天津.] | |
| [28] | Plankton Group in Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (1977) Scientific Reports of ‘Comprehensive Oceanography Expedition in China Seas’, Vol. 8, 1959.1-1960.6: Study on Plankton in China Seas. Ocean Research Office of Marine Group, Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China, Tianjin. (in Chinese) |
| [中国科学院海洋研究所浮游生物组 (1977) 全国海洋综合调查报告第八册1959.1-1960.6: 中国近海浮游生物的研究. 中华人民共和国科学技术委员会海洋组海洋综合调查办公室, 天津.] | |
| [29] | Purcell JE, Uye SI, Lo WT (2007) Anthropogenic causes of jellyfish blooms and their direct consequences for humans: A review. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 350, 153-174. |
| [30] |
Ratnarajah L, Abu-Alhaija R, Atkinson A, Batten S, Bax NJ, Bernard KS, Canonico G, Cornils A, Everett JD, Grigoratou M, Ahmad Ishak NH, Johns D, Lombard F, Muxagata E, Ostle C, Pitois S, Richardson AJ, Schmidt K, Stemmann L, Swadling KM, Yang G, Yebra L (2023) Monitoring and modelling marine zooplankton in a changing climate. Nature Communications, 14, 564.
DOI PMID |
| [31] | Richardson AJ (2008) In hot water: Zooplankton and climate change. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 65, 279-295. |
| [32] | Shandong Provincial Science and Technology Committee (1991) Comprehensive Survey Reports on Coastal Zone and Tidal Flat Resources of Shandong Province:Comprehensive Survey Report of the Yellow River Estuary Survey Area. China Science and Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [山东省科学技术委员会 (1991) 山东省海岸带和海涂资源综合调查报告集: 黄河口调查区综合调查报告. 中国科学技术出版社, 北京.] | |
| [33] | Shannon CE, Weaver W (1949) The Mathematical Theory of Communication. University of Illinois Press, Urbana. |
| [34] | Shi YQ (2015) Interannual Changes of Zooplankton Functional Groups in the Yellow Sea. PhD dissertation, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [时永强 (2015) 黄海浮游动物功能群年际变化研究. 博士学位论文, 中国科学院海洋研究所, 青岛.] | |
| [35] | Song NQ, Wang N, Lu Y, Zhang JR (2016) Temporal and spatial characteristics of harmful algal blooms in the Bohai Sea during 1952-2014. Continental Shelf Research, 122, 77-84. |
| [36] | State Oceanic Administration (2012-2017) China Maine Environmental State Bulletin in 2011-2016. State Oceanic Administration, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [国家海洋局 (2012-2017) 2011-2016年中国海洋环境状况公报. 国家海洋局, 北京.] | |
| [37] | State Oceanic Administration (2018) China Maine Eco-Environmental State Bulletin in 2017. State Oceanic Administration, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [国家海洋局 (2018) 2017年中国海洋生态环境状况公报. 国家海洋局, 北京.] | |
| [38] | Sun D, Duan DX, Liu HC, Zhang JL, Wang ZZ, Chen JP, Chen SJ, Du XH, Gong JX (2010) Investigation and study on fishery aquatic environments in the Yellow River estuary. Advances in Marine Science, 28, 229-236. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孙栋, 段登选, 刘红彩, 张金路, 王志忠, 陈金萍, 陈述江, 杜兴华, 巩俊霞 (2010) 黄河口水域渔业生态水环境调查与研究. 海洋科学进展, 28, 229-236.] | |
| [39] | Sun S, Li YH, Sun XX (2012) Changes in the small-jellyfish community in recent decades in Jiaozhou Bay, China. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 30, 507-518. |
| [40] | Syvitski J, Anthony E, Saito Y, Zăinescu F, Day J, Bhattacharya JP, Giosan L (2022) Large deltas, small deltas: Toward a more rigorous understanding of coastal marine deltas. Global and Planetary Change, 218, 103958. |
| [41] | Tian JY, Jia WZ, Dou HY, Jiao YM, Gao KJ, Cai XJ (1999) Study on Biodiversity in the Yellow River Delta. Qingdao Press, Qingdao. (in Chinese) |
| [田家怡, 贾文泽, 窦洪云, 焦玉木, 高奎江, 蔡学军 (1999) 黄河三角洲生物多样性研究. 青岛出版社, 青岛.] | |
| [42] | Tian JY, Li HY (1985) Distribution characteristics of zooplankton and its relationship with environmental factors in the Yellow River estuary and its adjacent waters. Marine Environmental Science, 4(3), 32-41. (in Chinese) |
| [田家怡, 李洪彦 (1985) 黄河口附近海域浮游动物的分布特征及其与环境因子的关系. 海洋环境科学, 4(3), 32-41.] | |
| [43] | Wang SW, Zhang GT, Zhou KL, Sun S (2020) Long-term population variability and reproductive strategy of a northward expanded ctenophore Pleurobrachia globosa Moser, 1903 in a temperate bay, China. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 533, 151457. |
| [44] | Wang WJ, Liu GX (2013) The characteristics of meso- and micro-zooplankton community in the Yellow River estuary and its adjacent area in autumn, 2010. Marine Sciences, 37(11), 9-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王文杰, 刘光兴 (2013) 2010年秋季黄河口及其邻近海域中小型浮游动物的群落特征. 海洋科学, 37(11), 9-15.] | |
| [45] | Wang XX, Gao YJ, Zuo M, Zhang XM, Li SW, Yang YY, Xu BQ, Li F, Wang YH (2022a) Interannual variation and influencing factors of zooplankton in the Yellow River estuary before and after water and sediment discharge regulation from 2011 to 2020. Marine Sciences, 46(12), 115-127. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王秀霞, 高彦洁, 左明, 张孝民, 李少文, 杨艳艳, 徐炳庆, 李凡, 王育红 (2022a) 2011-2020年调水调沙前后黄河口海域浮游动物年间变化及影响因子. 海洋科学, 46(12), 115-127.] | |
| [46] | Wang XX, Zhang PC, Yang YY, Li F, Li SW, Xu BQ, Zhang XM, Wang YH (2022b) Community structure of zooplankton in the Yellow River estuary during the water and sediment discharge regulation in 2020. Science Technology and Engineering, 22, 9061-9070. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王秀霞, 张培超, 杨艳艳, 李凡, 李少文, 徐炳庆, 张孝民, 王育红 (2022b) 2020年调水调沙工程实施期间黄河口海域浮游动物群落结构特征. 科学技术与工程, 22, 9061-9070.] | |
| [47] |
Xin M, Wang BD, Xie LP, Sun X, Wei QS, Liang SK, Chen K (2019) Long-term changes in nutrient regimes and their ecological effects in the Bohai Sea, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 146, 562-573.
DOI PMID |
| [48] | Xu ZL, Chen YQ (1989) Aggregated intensity of dominant species of zooplankton in autumn in the East China Sea and Yellow Sea. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 8(4), 13-15, 19. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [徐兆礼, 陈亚瞿 (1989) 东黄海秋季浮游动物优势种聚集强度与鲐鲹渔场的关系. 生态学杂志, 8(4), 13-15, 19.] | |
| [49] | Xu ZL, Gao Q (2009) Labidocera euchaeta: Its distribution in Yangtze River estuary and responses to global warming. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 20, 1196-1201. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [徐兆礼, 高倩 (2009) 长江口海域真刺唇角水蚤的分布及其对全球变暖的响应. 应用生态学报, 20, 1196-1201.] | |
| [50] | Xu ZL, Ma ZL, Wu YM (2011) Peaked abundance of Calanus sinicus earlier shifted in the Changjiang River (Yangtze River) estuary: A comparable study between 1959, 2002 and 2005. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 30(3), 84-91. |
| [51] | Xu ZL, Zhang D (2014) Dramatic declines in Euphausia pacifica abundance in the East China Sea: Response to recent regional climate change. Zoological Science, 31, 135-142. |
| [52] | Xu ZZ, Huang JQ, Lin M, Guo DH, Wang CG (2014) The Superclass Hydrozoa of the Phylum Cnidaria in China (Vol. I-II). China Ocean Press, Beijing. (in Chinese with English Abstract) |
| [许振祖, 黄加祺, 林茂, 郭东晖, 王春光 (2014) 中国刺胞动物门水螅虫总纲(上下册). 海洋出版社, 北京.] | |
| [53] | Zhang DJ, Yan QL, Wang ZL (2008) Variation in species number and biomass of zooplankton in typical estuaries of China. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 39, 536-540. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张达娟, 闫启仑, 王真良 (2008) 典型河口浮游动物种类数及生物量变化趋势的研究. 海洋与湖沼, 39, 536-540.] | |
| [54] | Zhang GT, Sun S, Xu ZL, Zhang QL (2010) Unexpected dominance of the subtropical copepod Temora turbinata in the temperate Changjiang River estuary and its possible causes. Zoological Studies, 49, 492-503. |
| [55] | Zhang X, Li S (2022) Monitoring and analysis on ecological environment in near-shore waters of Yellow River estuary during 2015-2020. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 42(3), 139-147. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张翔, 李愫 (2022) 2015-2020年黄河口近岸海域生态环境监测与分析. 水土保持通报, 42(3), 139-147.] | |
| [56] | Zhou J, Xu ZL, Ma ZL (2009) Effect of global warming on abundance variation of Parathemisto gaudichardi (Amphipoda) in the Changjiang Estuary. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 29, 5758-5765. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [周进, 徐兆礼, 马增岭 (2009) 长江口拟长脚虫戎数量变化和对环境变暖的响应. 生态学报, 29, 5758-5765.] | |
| [57] | Zuo T, Li YT, Zuo M, Cheng ZL, Wang J, Wang AD (2022) Seasonal variations of the planktonic larvae community in the Huanghe River estuary adjacent waters. Haiyang Xuebao, 44(4), 47-56. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [左涛, 李永涛, 左明, 程兆龙, 王俊, 王安东 (2022) 黄河口邻近海域浮游幼虫群落结构季节变化. 海洋学报, 44(4), 47-56.] |
| [1] | 韩群力. 关于联合国教科文组织人与生物圈计划及世界生物圈保护区网络未来优先行动的建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(9): 25144-. |
| [2] | 钱嘉宁. 履行就地保护义务的投资仲裁风险及应对[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(7): 24333-. |
| [3] | 陈耀辉, 周梓华, 邱洪, 张敬怀. 广东省海岸带牡蛎礁的分布特征、主要威胁及保护建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(7): 24414-. |
| [4] | 董雪云, 夏富才, 周繇, 张立秋, 何怀江, 刘冰, 姜润华, 王洪峰. 吉林省野生维管植物名录[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(7): 25120-. |
| [5] | 赵富伟. 遗传资源数字序列信息多边机制的谈判进程及我国的对策[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(6): 24559-. |
| [6] | 李云翱, 张文富, 赵桂刚, 杨春燕, 陈向清, 袁盛东, 曹敏, 蔡望, 杨洁. 空气环境DNA在陆生脊椎动物多样性监测上的应用: 以西双版纳20 ha森林动态样地为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(6): 24318-. |
| [7] | 干靓, 刘巷序, 鲁雪茗, 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区中国大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [8] | 曾子轩, 杨锐, 黄越, 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [9] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [10] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [11] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野: 趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [12] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [13] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [14] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [15] | 杨军, 杨旭东, 刘心怡, 周景. 面向《昆蒙框架》目标12的中国城市生物多样性研究展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25104-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()