



生物多样性 ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (3): 23319. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023319 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2023319
陈瑶琪1, 郭晶晶1,2, 蔡国俊1, 葛依立1, 廖宇1, 董正1, 符辉1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-09-04
接受日期:2024-01-25
出版日期:2024-03-20
发布日期:2024-03-06
通讯作者:
*E-mail: huifu367@163.com
基金资助:
Yaoqi Chen1, Jingjing Guo1,2, Guojun Cai1, Yili Ge1, Yu Liao1, Zheng Dong1, Hui Fu1,*( )
)
Received:2023-09-04
Accepted:2024-01-25
Online:2024-03-20
Published:2024-03-06
Contact:
*E-mail: huifu367@163.com
摘要:
沉水植物在维持浅水湖泊生态系统健康和稳定等方面起着重要作用, 掌握其长期动态及驱动因子对湖泊生态系统恢复和富营养化治理具有重要的理论和现实意义。本研究以长江中下游17个湖泊为研究对象, 分析了近70年(1954-2021)来沉水植物的α和β多样性格局及其变化情况, 并基于Sørensen相异性指数将β多样性分解为周转(turnover)和嵌套(nestedness)两个组分, 探讨了湖泊环境异质性变化与沉水植物群落多样性格局的联系。结果表明: (1)在湖泊尺度上, 11个湖泊沉水植物的α多样性呈减小趋势; 而大多数湖泊βtemporal多样性(同一湖泊不同年份之间的群落结构相异性)无显著变化, 且其变异主要由不同物种间的嵌套成分驱动。(2)在流域尺度上, 长江中下游湖泊沉水植物的α多样性在演化过程中呈先增大后减小的趋势, βspatial多样性(同一时期不同湖泊之间的群落结构相异性)在演化过程中呈逐渐减小的趋势, 而湖泊环境异质性呈逐渐增大的趋势。(3)环境异质性越高的湖泊, 其α多样性越小, β多样性越大。这些变化可能是多种因素综合作用的结果, 包括人类活动、水质污染、水文变化和气候变化等。本研究对于长江中下游湖泊生态系统管理和保护具有一定理论价值, 为制定有效的保护策略和措施提供了科学依据。
陈瑶琪, 郭晶晶, 蔡国俊, 葛依立, 廖宇, 董正, 符辉 (2024) 近七十年(1954-2021)长江中下游湖泊沉水植物群落多样性演变特征. 生物多样性, 32, 23319. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023319.
Yaoqi Chen, Jingjing Guo, Guojun Cai, Yili Ge, Yu Liao, Zheng Dong, Hui Fu (2024) Evolution characteristics of submerged macrophyte community diversity in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River in the past seventy years (1954-2021). Biodiversity Science, 32, 23319. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2023319.
| 编号 No. | 科 Family | 物种 Species | 编号 No. | 科 Family | 物种 Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | 眼子菜科 Potamogetonaceae | 菹草 Potamogeton crispus | 21 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 伊乐藻 Elodea nuttallii |
| 02 | 眼子菜科 Potamogetonaceae | 鸡冠眼子菜 P. cristatus | 22 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 光果黑藻 Hydrilla roxburghii |
| 03 | 眼子菜科 Potamogetonaceae | 光叶眼子菜 P. lucens | 23 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 轮叶黑藻 H. verticillata |
| 04 | 眼子菜科 Potamogetonaceae | 微齿眼子菜 P. maackianus | 24 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 弯果茨藻 Najas ancistrocarpa |
| 05 | 眼子菜科 Potamogetonaceae | 八蕊眼子菜 P. octandrus | 25 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 多孔茨藻 N. foveolata |
| 06 | 眼子菜科 Potamogetonaceae | 尖叶眼子菜 P. oxyphyllus | 26 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 纤细茨藻 N. gracillima |
| 07 | 眼子菜科 Potamogetonaceae | 蓼叶眼子菜 P. polygonifolius | 27 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 草茨藻 N. graminea |
| 08 | 眼子菜科 Potamogetonaceae | 小眼子菜 P. pusillus | 28 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 大茨藻 N. marina |
| 09 | 眼子菜科 Potamogetonaceae | 竹叶眼子菜 P. wrightii | 29 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 小茨藻 N. minor |
| 10 | 眼子菜科 Potamogetonaceae | 丝叶眼子菜 Stuckenia filiformis | 30 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 澳古茨藻 N. oguraensis |
| 11 | 眼子菜科 Potamogetonaceae | 篦齿眼子菜 S. pectinata | 31 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 东方茨藻 N. orientalis |
| 12 | 轮藻科 Characeae | 轮藻 Chara vulgaris | 32 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 龙舌草 Ottelia alismoides |
| 13 | 小二仙草科 Haloragaceae | 东方狐尾藻 Myriophyllum oguraense | 33 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 密刺苦草 Vallisneria denseserrulata |
| 14 | 小二仙草科 Haloragaceae | 穗状狐尾藻 M. spicatum | 34 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 苦草 V. natans |
| 15 | 小二仙草科 Haloragaceae | 乌苏里狐尾藻 M. ussuriense | 35 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 刺苦草 V. spinulosa |
| 16 | 小二仙草科 Haloragaceae | 狐尾藻 M. verticillatum | 36 | 毛茛科 Ranunculaceae | 水毛茛 Batrachium bungei |
| 17 | 金鱼藻科 Ceratophyllaceae | 金鱼藻 Ceratophyllum demersum | 37 | 毛茛科 Ranunculaceae | 毛柄水毛茛 B. trichophyllum |
| 18 | 金鱼藻科 Ceratophyllaceae | 粗糙金鱼藻 C. muricatum kossinskyi | 38 | 狸藻科 Lentibulariaceae | 黄花狸藻 Utricularia aurea |
| 19 | 金鱼藻科 Ceratophyllaceae | 五刺金鱼藻 C. oryzetorum | 39 | 狸藻科 Lentibulariaceae | 少花狸藻 U. gibba |
| 20 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 水筛 Blyxa japonica |
表1 长江中下游17个湖泊中出现的沉水植物物种名录
Table 1 Species list of submerged macrophytes appearing in 17 lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River
| 编号 No. | 科 Family | 物种 Species | 编号 No. | 科 Family | 物种 Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | 眼子菜科 Potamogetonaceae | 菹草 Potamogeton crispus | 21 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 伊乐藻 Elodea nuttallii |
| 02 | 眼子菜科 Potamogetonaceae | 鸡冠眼子菜 P. cristatus | 22 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 光果黑藻 Hydrilla roxburghii |
| 03 | 眼子菜科 Potamogetonaceae | 光叶眼子菜 P. lucens | 23 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 轮叶黑藻 H. verticillata |
| 04 | 眼子菜科 Potamogetonaceae | 微齿眼子菜 P. maackianus | 24 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 弯果茨藻 Najas ancistrocarpa |
| 05 | 眼子菜科 Potamogetonaceae | 八蕊眼子菜 P. octandrus | 25 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 多孔茨藻 N. foveolata |
| 06 | 眼子菜科 Potamogetonaceae | 尖叶眼子菜 P. oxyphyllus | 26 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 纤细茨藻 N. gracillima |
| 07 | 眼子菜科 Potamogetonaceae | 蓼叶眼子菜 P. polygonifolius | 27 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 草茨藻 N. graminea |
| 08 | 眼子菜科 Potamogetonaceae | 小眼子菜 P. pusillus | 28 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 大茨藻 N. marina |
| 09 | 眼子菜科 Potamogetonaceae | 竹叶眼子菜 P. wrightii | 29 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 小茨藻 N. minor |
| 10 | 眼子菜科 Potamogetonaceae | 丝叶眼子菜 Stuckenia filiformis | 30 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 澳古茨藻 N. oguraensis |
| 11 | 眼子菜科 Potamogetonaceae | 篦齿眼子菜 S. pectinata | 31 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 东方茨藻 N. orientalis |
| 12 | 轮藻科 Characeae | 轮藻 Chara vulgaris | 32 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 龙舌草 Ottelia alismoides |
| 13 | 小二仙草科 Haloragaceae | 东方狐尾藻 Myriophyllum oguraense | 33 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 密刺苦草 Vallisneria denseserrulata |
| 14 | 小二仙草科 Haloragaceae | 穗状狐尾藻 M. spicatum | 34 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 苦草 V. natans |
| 15 | 小二仙草科 Haloragaceae | 乌苏里狐尾藻 M. ussuriense | 35 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 刺苦草 V. spinulosa |
| 16 | 小二仙草科 Haloragaceae | 狐尾藻 M. verticillatum | 36 | 毛茛科 Ranunculaceae | 水毛茛 Batrachium bungei |
| 17 | 金鱼藻科 Ceratophyllaceae | 金鱼藻 Ceratophyllum demersum | 37 | 毛茛科 Ranunculaceae | 毛柄水毛茛 B. trichophyllum |
| 18 | 金鱼藻科 Ceratophyllaceae | 粗糙金鱼藻 C. muricatum kossinskyi | 38 | 狸藻科 Lentibulariaceae | 黄花狸藻 Utricularia aurea |
| 19 | 金鱼藻科 Ceratophyllaceae | 五刺金鱼藻 C. oryzetorum | 39 | 狸藻科 Lentibulariaceae | 少花狸藻 U. gibba |
| 20 | 水鳖科 Hydrocharitaceae | 水筛 Blyxa japonica |
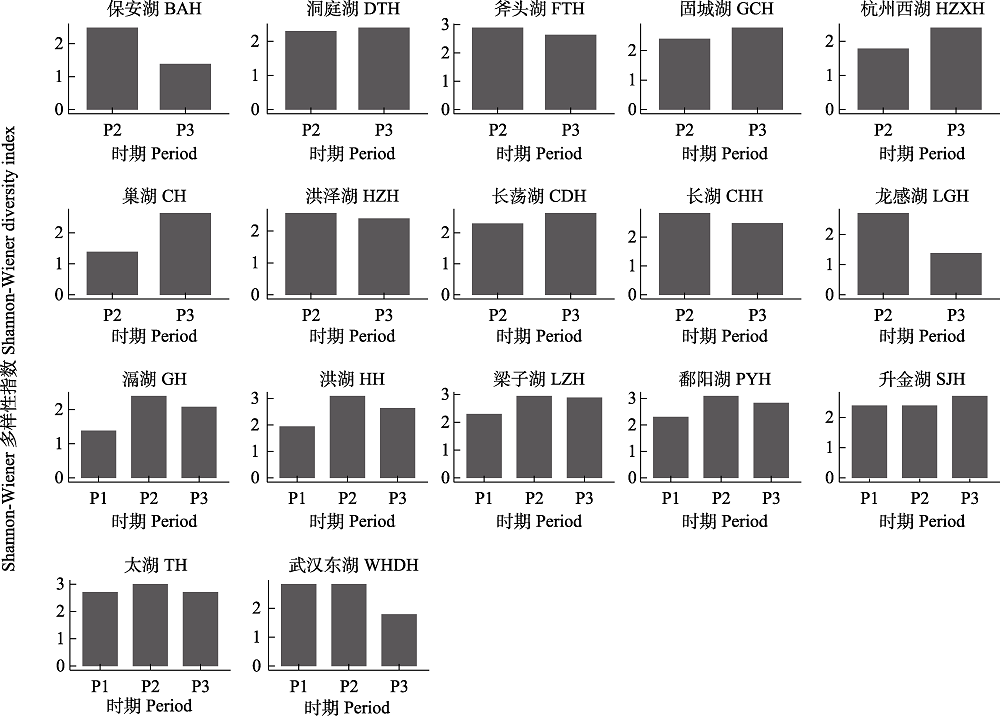
图1 长江中下游17个湖泊不同时期沉水植物群落Shannon-Wiener多样性指数。P1: 1954-1980年; P2: 1981-2006年; P3: 2007-2021年。
Fig. 1 Shannon-Wiener diversity index of submerged macrophytes in 17 lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River at different periods. P1, 1954-1980; P2, 1981-2006; P3, 2007-2021. BAH, Baoan Lake; DTH, Dongting Lake; FTH, Futou Lake; GCH, Gucheng Lake; HZXH, Hangzhou West Lake; CH, Chaohu Lake; HZH, Hongze Lake; CDH, Changdang Lake; CHH, Changhu Lake; LGH, Longgan Lake; GH, Gehu Lake; HH, Honghu Lake; LZH, Liangzi Lake; PYH, Poyang Lake; SJH, Shengjin Lake; TH, Taihu Lake; WHDH, Wuhan East Lake.
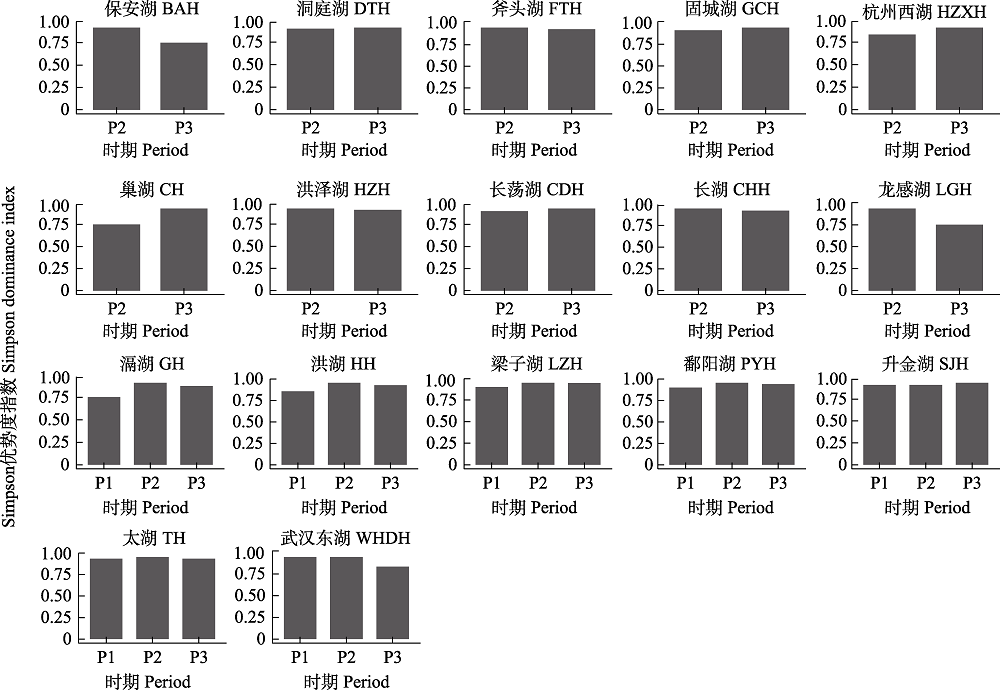
图2 长江中下游17个湖泊不同时期沉水植物群落Simpson优势度指数。缩写含义见图1。
Fig. 2 Simpson dominance index of submerged macrophytes in 17 lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River at different periods. Abbreviations can be found in Fig. 1.
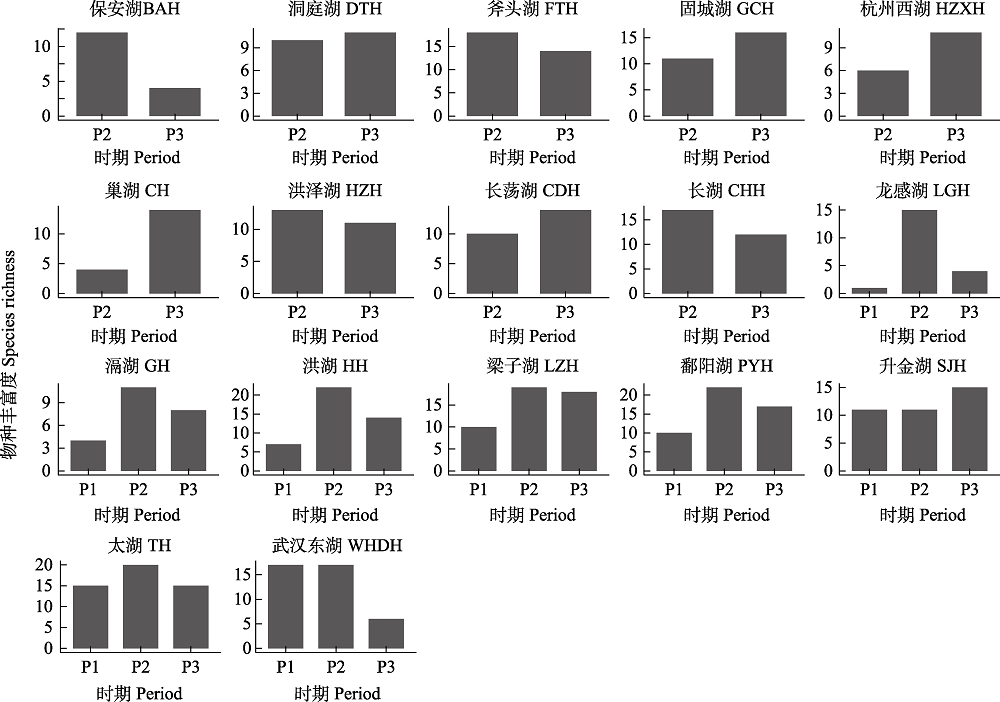
图3 长江中下游17个湖泊不同时期沉水植物群落的物种丰富度指数。缩写含义见图1。
Fig. 3 Species richness index of submerged macrophytes in 17 lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River at different periods. Abbreviations can be found in Fig. 1.
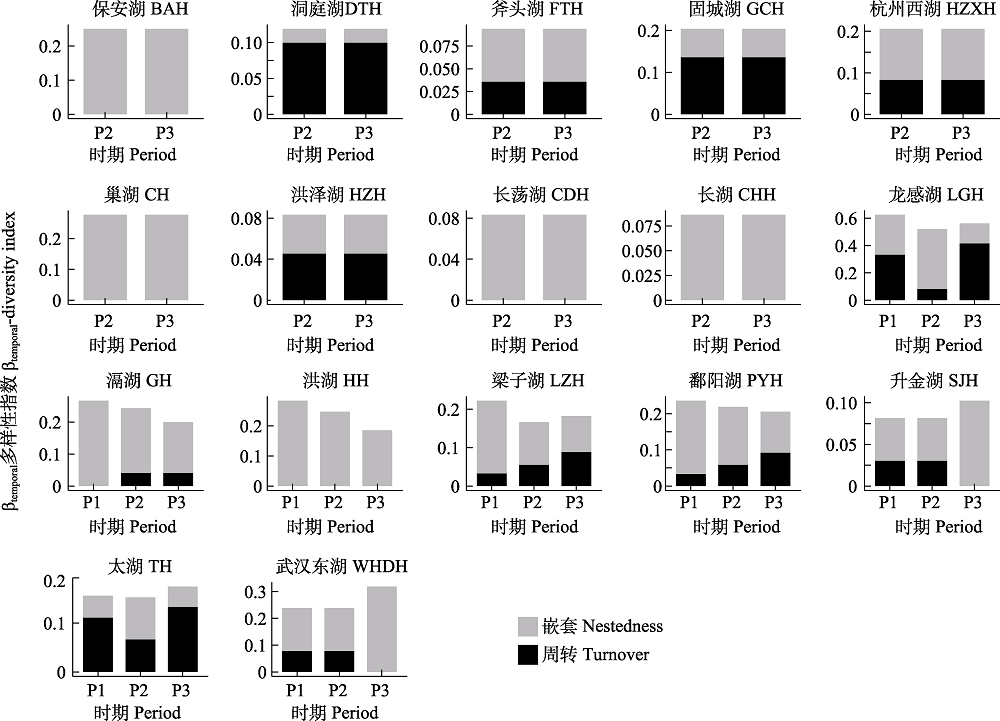
图4 长江中下游17个湖泊不同时期沉水植物群落βtemporal多样性两个组分(嵌套、周转)的分布。缩写含义见图1。
Fig. 4 Distribution of two components of βtemporal-diversity (nestedness and turnover) in submerged macrophytes in 17 lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River at different periods. Abbreviations can be found in Fig. 1.
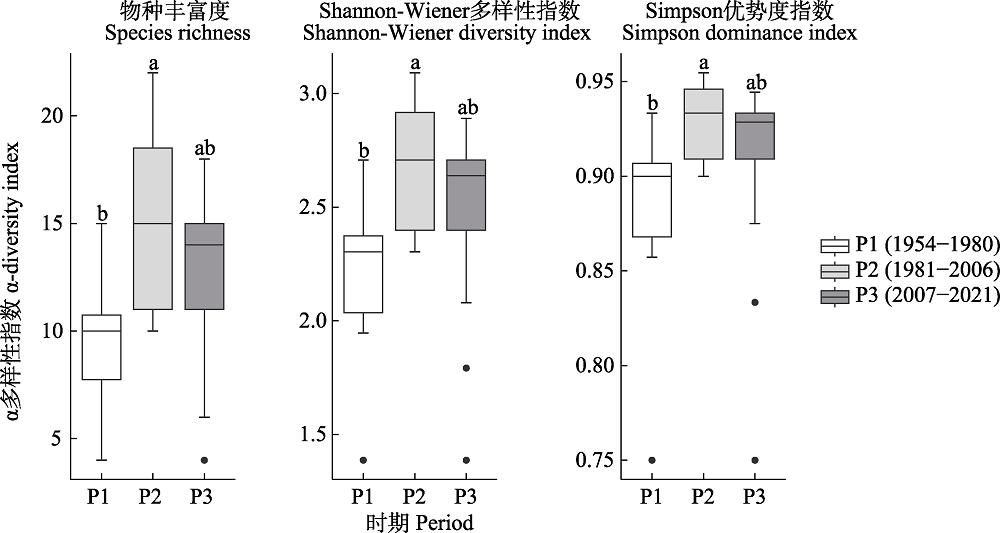
图5 长江中下游17个湖泊不同时期沉水植物群落α多样性指数的差异。图中不同小写字母表示差异显著。不同时期湖泊数: P1 = 8, P2 = 17, P3 = 17。
Fig. 5 Difference of α-diversity index of submerged macrophytes in 17 lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River at different periods. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences. Number of lakes in different periods: P1 = 8, P2 = 17, P3 = 17.
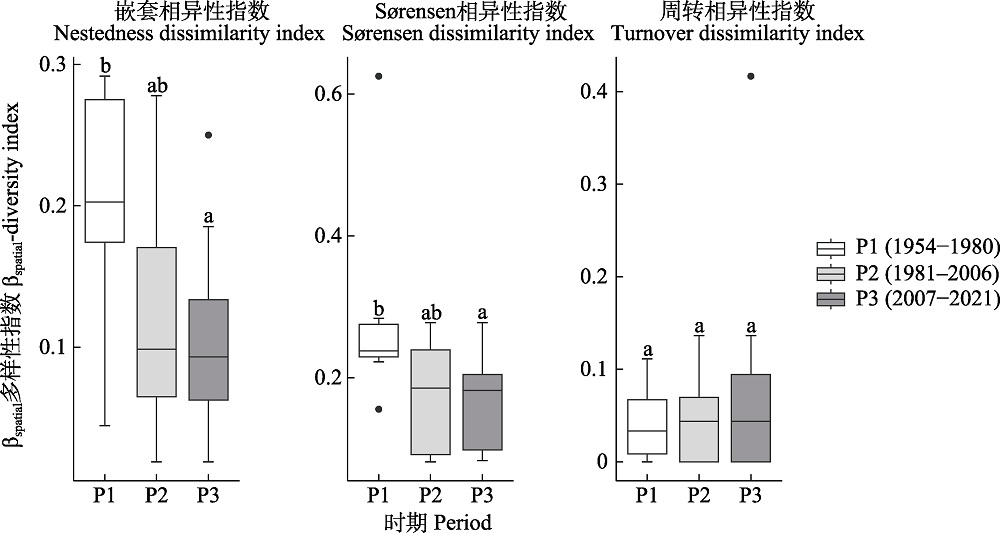
图6 长江中下游17个湖泊不同时期沉水植物群落βspatial多样性指数的差异。图中不同小写字母表示差异显著。不同时期湖泊数: P1 = 8, P2 = 17, P3 = 17。
Fig. 6 Difference of βspatial-diversity index of submerged macrophytes in 17 lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River at different periods. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences. Number of lakes in different periods: P1 = 8, P2 = 17, P3 = 17.
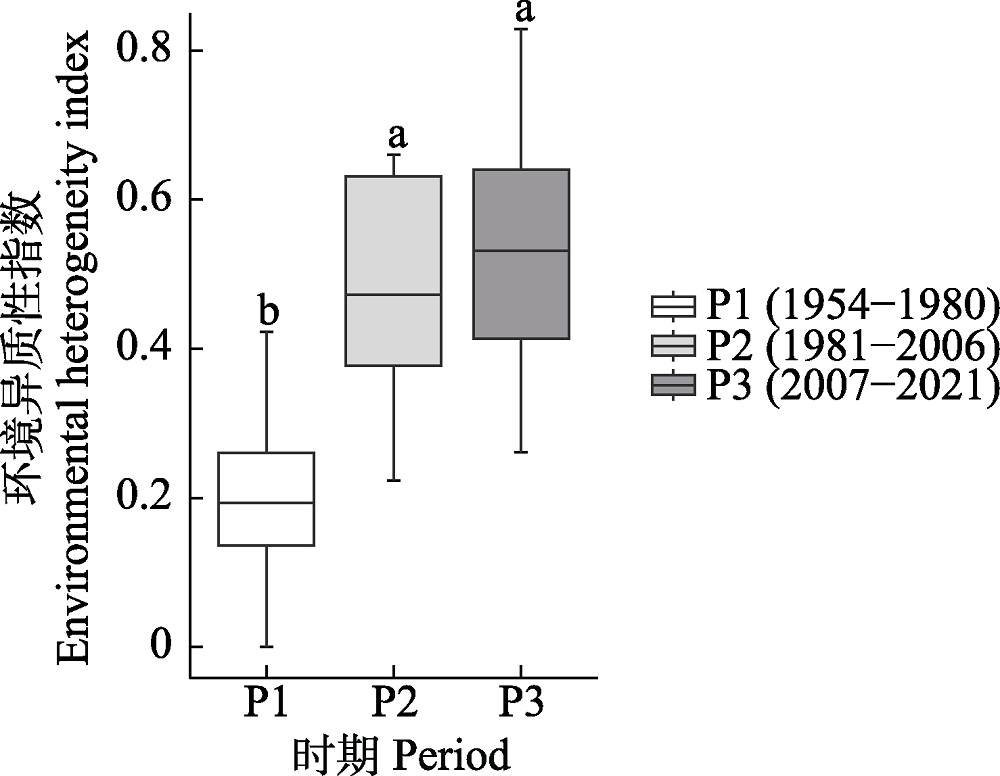
图7 长江中下游17个湖泊不同时期环境异质性的差异。图中不同小写字母表示差异显著。不同时期湖泊数: P1 = 4, P2 = 16, P3 = 17。
Fig. 7 Differences in environmental heterogeneity among 17 lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River during different periods. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences. Number of lakes in different periods: P1 = 4, P2 = 16, P3 = 17.
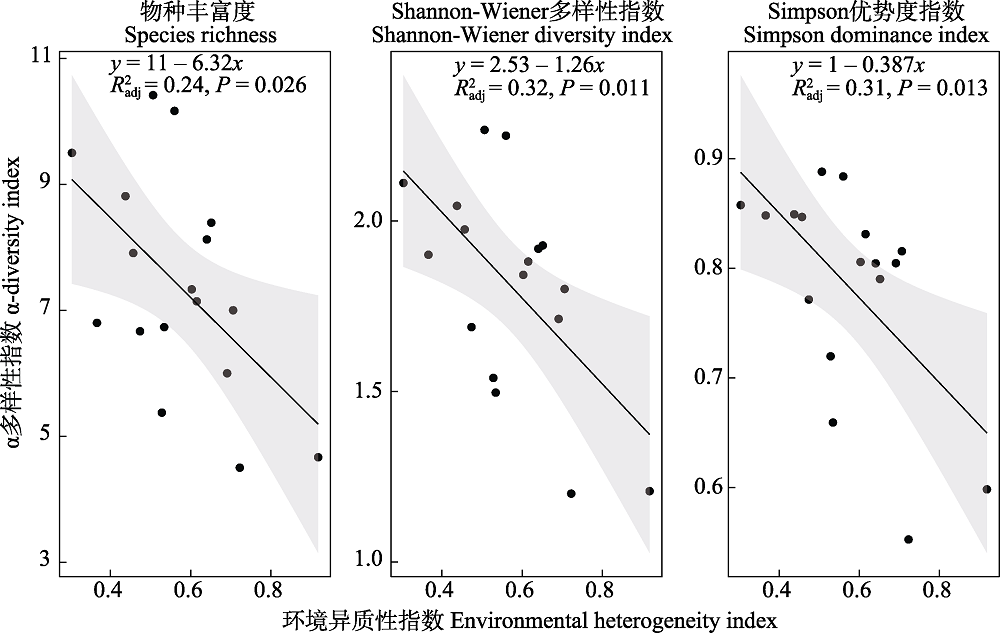
图8 长江中下游17个湖泊沉水植物群落α多样性与环境异质性的关系
Fig. 8 Relationship between α-diversity of submerged macrophytes and environmental heterogeneity in 17 lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River
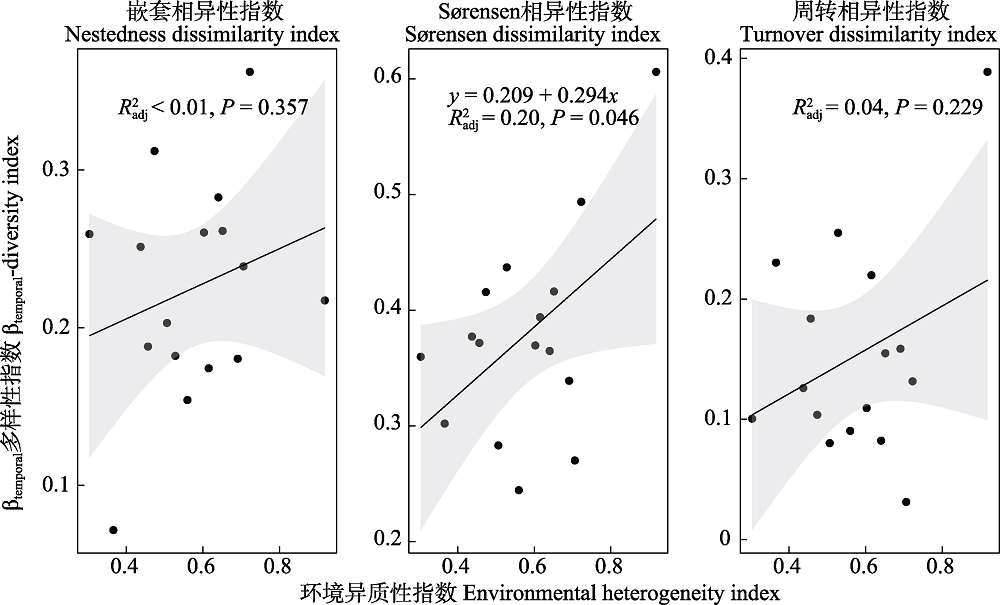
图9 长江中下游17个湖泊沉水植物群落βtemporal多样性与环境异质性的关系
Fig. 9 Relationship between βtemporal-diversity of submerged macrophytes and environmental heterogeneity in 17 lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River
| [1] | Alahuhta J, Kosten S, Akasaka M, Auderset D, Azzella MM, Bolpagni R, Bove CP, Chambers PA, Chappuis E, Clayton J, de Winton M, Ecke F, Gacia E, Gecheva G, Grillas P, Hauxwell J, Hellsten S, Hjort J, Hoyer MV, Ilg C, Kolada A, Kuoppala M, Lauridsen T, Li EH, Lukács BA, Mjelde M, Mikulyuk A, Mormul RP, Nishihiro J, Oertli B, Rhazi L, Rhazi M, Sass L, Schranz C, Søndergaard M, Yamanouchi T, Yu Q, Wang HJ, Willby N, Zhang XK, Heino J (2017) Global variation in the beta diversity of lake macrophytes is driven by environmental heterogeneity rather than latitude. Journal of Biogeography, 44, 1758-1769. |
| [2] | Bakker ES, Sarneel JM, Gulati RD, Liu ZW, van Donk E (2013) Restoring macrophyte diversity in shallow temperate lakes: Biotic versus abiotic constraints. Hydrobiologia, 710, 23-37. |
| [3] | Bennion H, Sayer CD, Clarke SJ, Davidson TA, Rose NL, Goldsmith B, Rawcliffe R, Burgess A, Clarke G, Turner S, Wiik E (2018) Sedimentary macrofossil records reveal ecological change in English lakes: Implications for conservation. Journal of Paleolimnology, 60, 329-348. |
| [4] |
Bertuzzi T, Pires MM, Maltchik L (2019) Drivers of the beta diversity of aquatic plant communities along a latitudinal gradient in southern Brazilian coastal ponds. Journal of Vegetation Science, 30, 281-290.
DOI |
| [5] | Cai XW, Li W, Fan HR, Fang T, Li W, Chang FY, Liu JS, Liao CS (2021) Roles of fish assemblage regulation on ecological restoration in a shallow lake: A case study from the Kuilei Lake, China. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 28, 737-742. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 蔡杏伟, 李为, 樊厚瑞, 方涛, 李伟, 常锋毅, 刘家寿, 廖传松 (2021) 鱼类群落调控在浅水湖泊生态修复中的作用: 以傀儡湖为例. 中国水产科学, 28, 737-742.] | |
| [6] | Cao Y, Liu Y, Ndirangu L, Li W, Xian L, Jiang HS (2019) The analysis of leaf traits of eight Ottelia populations and their potential ecosystem functions in karst freshwaters in China. Frontiers in Plant Science, 9, 1938. |
| [7] | Cardoso P, Rigal F, Carvalho JC, Fortelius M, Borges PAV, Podani J, Schmera D (2014) Partitioning taxon, phylogenetic and functional beta diversity into replacement and richness difference components. Journal of Biogeography, 41, 749-761. |
| [8] | Castaño-Sánchez A, Valencia L, Serrano JM, Delgado JA (2018) Species introduction and taxonomic homogenization of Spanish freshwater fish fauna in relation to basin size, species richness and dam construction. Journal of Freshwater Ecology, 33, 347-360. |
| [9] |
Cui LJ, Gao CJ, Zhao XS, Ma QF, Zhang MY, Li W, Song HT, Wang YF, Li SN, Zhang Y (2013) Dynamics of the lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River Basin, China, since late nineteenth century. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185, 4005-4018.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | Declerck SAJ, Coronel JS, Legendre P, Brendonck L (2011) Scale dependency of processes structuring metacommunities of cladocerans in temporary pools of High-Andes wetlands. Ecography, 34, 296-305. |
| [11] | Ding XQ, Jia YT, Yang JY, An YJ, Yang S (2010) Seed bank in aquaculture area of Honghu Lake and the strategy of aquatic vegetation restoration. Journal of Huazhong Normal University (Natural Sciences), 44, 296-300. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 丁小青, 贾延亭, 杨娇艳, 安彦杰, 杨劭 (2010) 洪湖养殖区水生植物种子库现状及水生植被恢复策略研究. 华中师范大学学报(自然科学版), 44, 296-300.] | |
| [12] | Downing AL, Leibold MA (2002) Ecosystem consequences of species richness and composition in pond food webs. Nature, 416, 837-841. |
| [13] | Fang JY, Wang ZH, Zhao SQ, Li YK, Tang ZY, Yu D, Ni LY, Liu HZ, Xie P, Da LJ, Li ZQ, Zheng CY (2006) Biodiversity changes in the lakes of the Central Yangtze. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 4, 369-377. |
| [14] | Flower RJ, Juggins S, Battarbee RW (1997) Matching diatom assemblages in lake sediment cores and modern surface sediment samples: The implications for lake conservation and restoration with special reference to acidified systems. Hydrobiologia, 344, 27-40. |
| [15] | Fu H, Yuan GX, Jeppesen E, Ge DB, Li W, Zou DS, Huang ZR, Wu AP, Liu QL (2019) Local and regional drivers of turnover and nestedness components of species and functional beta diversity in lake macrophyte communities in China. Science of the Total Environment, 687, 206-217. |
| [16] |
Fu H, Zhong JY, Fang SW, Hu JM, Guo CJ, Lou Q, Yuan GX, Dai TT, Li ZQ, Zhang M, Li W, Xu J, Cao T (2017) Scale-dependent changes in the functional diversity of macrophytes in subtropical freshwater lakes in South China. Scientific Reports, 7, 8294.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | Fu H, Zhong JY, Yuan GX, Xie P, Guo LG, Zhang XL, Xu J, Li Z, Li W, Zhang M, Cao T, Ni LY (2014) Trait-based community assembly of aquatic macrophytes along a water depth gradient in a freshwater lake. Freshwater Biology, 59, 2462-2471. |
| [18] | Gámez-Virués S, Perović DJ, Gossner MM, Börschig C, Blüthgen N, de Jong H, Simons NK, Klein AM, Krauss J, Maier G, Scherber C, Steckel J, Rothenwöhrer C, Steffan-Dewenter I, Weiner CN, Weisser W, Werner M, Tscharntke T, Westphal C (2015) Landscape simplification filters species traits and drives biotic homogenization. Nature Communications, 6, 8568. |
| [19] | García-Girón J, Lindholm M, Heino J, Toivonen H, Alahuhta J (2022) Historical contingency via priority effects counteracts environmental change on metacommunity dynamics across decades. Limnology and Oceanography, 67, S38-S53. |
| [20] |
Gianuca AT, Declerck SAJ, Lemmens P, De Meester L, (2017) Effects of dispersal and environmental heterogeneity on the replacement and nestedness components of β-diversity. Ecology, 98, 525-533.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | Guo KD, Zhang XB, Liu PZ, Lei GC, Lü C, Zeng XF, Zeng WK (2020) The response of submerged plants to different environmental factors and hydrologic regime in West Lake Dongting. Journal of Lake Sciences, 32, 1736-1748. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郭凯迪, 张晓波, 刘培中, 雷光春, 吕偲, 曾喜凡, 曾伟坤 (2020) 西洞庭湖沉水植物分布格局对环境因子及水文情势差异的响应. 湖泊科学, 32, 1736-1748.] | |
| [22] | Gutiérrez-Cánovas C, Millán A, Velasco J, Vaughan IP, Ormerod SJ (2013) Contrasting effects of natural and anthropogenic stressors on beta diversity in river organisms. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 22, 796-805. |
| [23] | Hill MJ, Heino J, Thornhill I, Ryves DB, Wood PJ (2017) Effects of dispersal mode on the environmental and spatial correlates of nestedness and species turnover in pond communities. Oikos, 126, 1575-1585. |
| [24] |
Hillebrand H, Blenckner T (2002) Regional and local impact on species diversity—From pattern to processes. Oecologia, 132, 479-491.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Hu Y, Qian DX, Wang LF (2023) Research progress on the remediation effect of submerged plants on water pollution. South China Agriculture, 17(7), 82-85, 89. (in Chinese) |
| [ 胡昱, 钱德雪, 王利芬 (2023) 沉水植物对水体污染的修复效果研究进展. 南方农业, 17(7), 82-85, 89.] | |
| [26] | Huang FF, Zhang K, Huang SX, Lin Q (2021) Patterns and trajectories of macrophyte change in East China’s shallow lakes over the past one century. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 64, 1735-1745. |
| [27] | Jia YY, Tang XL, Tang FL, Yang Y, Ma K (2020) Research on human activity intensity and its impact on wetland landscape pattern in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River Basin. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 29, 950-963. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 贾艳艳, 唐晓岚, 唐芳林, 杨阳, 马坤 (2020) 长江中下游流域人类活动强度及其对湿地景观格局影响研究. 长江流域资源与环境, 29, 950-963.] | |
| [28] | Kong XH, Xiao LL, Su HJ, Wu Y, Zhang XL, Li ZQ (2015) Status of aquatic plants and its relationship with water environment factors in the lakes along the lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Journal of Lake Sciences, 27, 385-391. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 孔祥虹, 肖兰兰, 苏豪杰, 吴耀, 张霄林, 李中强 (2015) 长江下游湖泊水生植物现状及与水环境因子的关系. 湖泊科学, 27, 385-391.] | |
| [29] | Krynak EM, Lindo Z, Yates AG (2019) Patterns and drivers of stream benthic macroinvertebrate beta diversity in an agricultural landscape. Hydrobiologia, 837, 61-75. |
| [30] |
Kuglerová L, Jansson R, Sponseller RA, Laudon H, Malm-Renöfält B (2015) Local and regional processes determine plant species richness in a river-network metacommunity. Ecology, 96, 381-391.
PMID |
| [31] | Larsen S, Karaus U, Claret C, Sporka F, Hamerlík L, Tockner K (2019) Flooding and hydrologic connectivity modulate community assembly in a dynamic river-floodplain ecosystem. PLoS ONE, 14, e0213227. |
| [32] | Lee DY, Lee DS, Park YS (2023) Taxonomic and functional diversity of benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages in reservoirs of South Korea. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20, 673. |
| [33] | Li MJ, Wu KY, Meng FF, Shen J, Liu YQ, Xiao NW, Wang JJ (2020) Beta diversity of stream bacteria in Hengduan Mountains: The effects of climatic and environmental variables. Biodiversity Science, 28, 1570-1580. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李明家, 吴凯媛, 孟凡凡, 沈吉, 刘勇勤, 肖能文, 王建军 (2020) 西藏横断山区溪流细菌beta多样性组分对气候和水体环境的响应. 生物多样性, 28, 1570-1580.] | |
| [34] | Li N, Yang L, Deng XW, Wang ZX, Li ZQ (2018) Aquatic plant diversity in relation to lake morphology in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Plant Science Journal, 36, 65-72. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李娜, 杨磊, 邓绪伟, 汪正祥, 李中强 (2018) 湖泊形态与水生植物多样性关系——以长江中下游湖群典型湖泊为例. 植物科学学报, 36, 65-72.] | |
| [35] | Lin H, Yin WH, Dong YB, Li B (2019) Advances in response of submerged macrophytes to stress. Environmental Science and Technology, 32(1), 63-67, 73. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 林海, 殷文慧, 董颖博, 李冰 (2019) 沉水植物对逆境胁迫的响应研究进展. 环境科技, 32(1), 63-67, 73.] | |
| [36] | Liu J, Yang XD, Wang SM (2006) Study on the nutrient evolution and its controlling factors of Longgan Lake for the last 200 years. Science in China Series D, 49, 193-202. |
| [37] | Liu Y (2021) Combined Effects of Nutrient Enrichment and Herbivory on Growth of Submerged Macrophytes. PhD dissertation, Nanchang University, Nanchang. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘颖 (2021) 富营养化与牧食作用对沉水植物生长的复合影响研究. 博士学位论文, 南昌大学, 南昌.] | |
| [38] | Liu Y, Fu WL Cao Y, Li W (2017) Study on the functional traits of submerged macrophytes. Plant Science Journal, 35, 444-451. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘洋, 付文龙, 操瑜, 李伟 (2017) 沉水植物功能性状研究的思考. 植物科学学报, 35, 444-451.] | |
| [39] | Lu J, Wang HB, Pan M, Xia J, Xing W, Liu GH (2012) Using sediment seed banks and historical vegetation change data to develop restoration criteria for a eutrophic lake in China. Ecological Engineering, 39, 95-103. |
| [40] | Mäemets H, Palmik K, Haldna M (2016) Eutrophication-driven spatial and temporal changes in macrophyte diversity in Lake Peipsi. Proceedings of the Estonian Academy of Sciences, 65, 394-407. |
| [41] | McGill BJ, Dornelas M, Gotelli NJ, Magurran AE (2015) Fifteen forms of biodiversity trend in the Anthropocene. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 30, 104-113. |
| [42] | Moss B, Kosten S, Meerhoff M, Battarbee RW (2011) Allied attack: Climate change and eutrophication. Inland Waters, 1, 101-105. |
| [43] | O’Hare MT, Aguiar FC, Asaeda T, Bakker ES, Chambers PA, Clayton JS, Elger A, Ferreira TM, Gross EM, Gunn IDM, Gurnell AM, Hellsten S, Hofstra DE, Li W, Mohr S, Puijalon S, Szoszkiewicz K, Willby NJ, Wood KA (2018) Plants in aquatic ecosystems: Current trends and future directions. Hydrobiologia, 812, 1-11. |
| [44] | Olden JD, Rooney TP (2006) On defining and quantifying biotic homogenization. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 15, 113-120. |
| [45] | Phillips G, Willby N, Moss B (2016) Submerged macrophyte decline in shallow lakes: What have we learnt in the last forty years? Aquatic Botany, 135, 37-45. |
| [46] | Pozzobom UM, Landeiro VL, da Silva Brito MT, Alahuhta J, Heino J (2021) Multiple facets of macrophyte beta diversity are shaped by environmental factors, directional spatial processes, and connectivity across tropical floodplain lakes in the dry season. Hydrobiologia, 848, 3587-3602. |
| [47] | Qin BQ (2020) Shallow lake limnology and control of eutrophication in Lake Taihu. Journal of Lake Sciences, 32, 1229-1243. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 秦伯强 (2020) 浅水湖泊湖沼学与太湖富营养化控制研究. 湖泊科学, 32, 1229-1243.] | |
| [48] | Qiu DR, Wu ZB (1997) On the decline and restoration of submerged vegetation in eutrophic shallow lakes. Journal of Lake Sciences, 9, 82-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 邱东茹, 吴振斌 (1997) 富营养化浅水湖泊沉水水生植被的衰退与恢复. 湖泊科学, 9, 82-88.] | |
| [49] | Sachse R, Petzoldt T, Blumstock M, Moreira S, Pätzig M, Rücker J, Janse JH, Mooij WM, Hilt S (2014) Extending one-dimensional models for deep lakes to simulate the impact of submerged macrophytes on water quality. Environmental Modelling and Software, 61, 410-423. |
| [50] | Salgado J, Sayer CD, Brooks SJ, Davidson TA, Goldsmith B, Patmore IR, Baker AG, Okamura B (2018) Eutrophication homogenizes shallow lake macrophyte assemblages over space and time. Ecosphere, 9, e02406. |
| [51] | Sayer CD, Burgess A, Kari K, Davidson TA, Peglar S, Yang HD, Rose NL (2010) Long-term dynamics of submerged macrophytes and algae in a small and shallow, eutrophic lake: Implications for the stability of macrophyte- dominance. Freshwater Biology, 55, 565-583. |
| [52] | Scheffer M, Hosper SH, Meijer ML, Moss B, Jeppesen E (1993) Alternative equilibria in shallow lakes. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 8, 275-279. |
| [53] | Scheffer M, Szabó S, Gragnani A, Van Nes EH, Rinaldi S, Kautsky N, Norberg J, Roijackers RMM, Franken RJM (2003) Floating plant dominance as a stable state. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 100, 4040-4045. |
| [54] | Su GH, Xu J, Akasaka M, Molinos JG (2015) Human impacts on functional and taxonomic homogenization of plateau fish assemblages in Yunnan, China. Global Ecology and Conservation, 4, 470-478. |
| [55] | Tan FX, Luo JB, Gong SS, Zhou WB, Xiang MM, Meng JX, Chai Y (2019) Effects of removal of the breeding seine on aquatic plant diversity in Yuanxinhu area of Chang Lake. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 58(21), 92-96. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 谭凤霞, 罗静波, 龚森森, 周文博, 向苗苗, 孟建雪, 柴毅 (2019) 养殖围网拆除对长湖圆心湖区水生植物多样性的影响. 湖北农业科学, 58(21), 92-96.] | |
| [56] | Tang XD, Zhang Y (2023) Water quality regulation and submerged plant restoration in water ecological remediation. Environmental Ecology, 5(6), 88-92, 98. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 唐旭东, 张扬 (2023) 水生态修复中水质调控与沉水植物恢复探析. 环境生态学, 5(6), 88-92, 98.] | |
| [57] | Tian Q, Wang PF, Ouyang P, Wang C, Zhang WM (2009) Purification of eutrophic water with five submerged hydrophytes. Water Resources Protection, 25(1), 14-17. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 田琦, 王沛芳, 欧阳萍, 王超, 张文明 (2009) 5种沉水植物对富营养化水体的净化能力研究. 水资源保护, 25(1), 14-17.] | |
| [58] | Villéger S, Grenouillet G, Brosse S (2014) Functional homogenization exceeds taxonomic homogenization among European fish assemblages. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 23, 1450-1460. |
| [59] | Wang JL (2023) Study on the effect of aquatic phytoremediation on the aquatic ecological environment of Chaohu Lake. Scientific and Technological Innovation, (5), 77-80. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王锦龙 (2023) 水生植物修复对巢湖水生态环境的影响研究. 科学技术创新, (5), 77-80.] | |
| [60] | Wang XP, Wang YB, Yang GJ, Qin BQ, Yang HW (2016) The effects of different fish species on growth of submerged macrophytes. Journal of Lake Sciences, 28, 1354-1360. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王晓平, 王玉兵, 杨桂军, 秦伯强, 杨宏伟 (2016) 不同鱼类对沉水植物生长的影响. 湖泊科学, 28, 1354-1360.] | |
| [61] | Wu NC, Wang YC, Wang YX, Sun XM, Faber C, Fohrer N (2022) Environment regimes play an important role in structuring trait- and taxonomy-based temporal beta diversity of riverine diatoms. Journal of Ecology, 110, 1442-1454. |
| [62] | Wu YH, Liu EF, Bing HJ, Yang XD, Xue B, Xia WL (2010) Geochronology of recent lake sediments from Longgan Lake, middle reach of the Yangtze River, influenced by disturbance of human activities. Science China: Earth Science, 40, 751-757. (in Chinese) |
| [ 吴艳宏, 刘恩峰, 邴海健, 羊向东, 薛滨, 夏威岚 (2010) 人类活动影响下的长江中游龙感湖近代湖泊沉积年代序列. 中国科学: 地球科学, 40, 751-757.] | |
| [63] | Wu ZG, Xiong W, Hou HW (2019) Biodiversity pattern and conservation of aquatic vascular plants in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 43(Suppl.), 27-41. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吴志刚, 熊文, 侯宏伟 (2019) 长江流域水生植物多样性格局与保护. 水生生物学报, 43(增刊), 27-41.] | |
| [64] | Yao SM, Zhang YC, Chai ZH, Jin ZW, Qu G (2022) Current status and measures of conservation and restoration of rivers and lakes in the lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Technology and Economy of Changjiang, 6(6), 1-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 姚仕明, 章运超, 柴朝晖, 金中武, 渠庚 (2022) 长江下游河湖保护与修复状况及对策建议. 长江技术经济, 6(6), 1-10.] | |
| [65] | Yuan LY (2007) Study on Effects of Environmental Factors on the Life-history Strategies of Submerged Macrophytes. PhD dissertation, Wuhan Botanical Garden, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 袁龙义 (2007) 环境因子对沉水植物生活史对策的影响研究. 博士学位论文, 中国科学院武汉植物园, 武汉.] | |
| [66] |
Zhang M, Molinos JG, Zhang XL, Xu J (2018) Functional and taxonomic differentiation of macrophyte assemblages across the Yangtze River floodplain under human impacts. Frontiers in Plant Science, 9, 387.
DOI PMID |
| [67] |
Zhang PY, Kuramae A, Velthuis M, Donk E, Xu J, Bakker ES (2020) Interactive effects of rising temperature and nutrient enrichment on aquatic plant growth, stoichiometry, and palatability. Frontiers in Plant Science, 11, 58.
DOI PMID |
| [68] | Zhang YL, Jeppesen E, Liu XH, Qin BQ, Shi K, Zhou YQ, Thomaz SM, Deng JM (2017) Global loss of aquatic vegetation in lakes. Earth-Science Reviews, 173, 259-265. |
| [69] | Zhen W, Zhang XM, Guan BH, Yin CY, Yu JL, Jeppesen E, Zhao XF, Liu ZW (2018) Stocking of herbivorous fish in eutrophic shallow clear-water lakes to reduce standing height of submerged macrophytes while maintaining their biomass. Ecological Engineering, 113, 61-64. |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 孙智闲, 田晨, 王鑫, 方雨田, 李博, 赵亚辉. 热带沿海城市土著鱼类面临的威胁: 以海南省三亚市为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 24165-. |
| [3] | 吴琪, 张晓青, 杨雨婷, 周艺博, 马毅, 许大明, 斯幸峰, 王健. 浙江钱江源-百山祖国家公园庆元片区叶附生苔多样性及其时空变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 24010-. |
| [4] | 陈越, 毛子昆, 王绪高. 基于生态独特性的β多样性研究进展与未来展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24199-. |
| [5] | 王巍伟, 米湘成, 王宁宁, 任海保, 唐治喜, 张主宁, 马克平, 陈磊. 2005-2020年浙江古田山24 ha亚热带常绿阔叶林动态监测样地植物多样性数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24417-. |
| [6] | 冯志荣, 陈有城, 彭艳琼, 李莉, 王波. 生态网络分析: 从集合群落到集合网络[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23171-. |
| [7] | 陈晓澄, 张鹏展, 康斌, 刘林山, 赵亮. 基于中国科学院西北高原生物研究所馆藏标本分析青藏高原雀形目鸟类物种和功能多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22638-. |
| [8] | 杨清, 李晓东, 杨胜娴, 巢欣, 刘惠秋, 巴桑. 雅鲁藏布江中游丰水期原生动物群落多样性及其影响因子[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22500-. |
| [9] | 王晓凤, 饶杰生, 杨涛, 刘文聪, 田希, 陈稀, 刘其明, 徐衍潇, 张秋雨, 张洪强, 张旭, 欧晓昆, 沈泽昊. 云南鸡足山半湿润常绿阔叶林群落木本植物多样性格局与环境解释[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23217-. |
| [10] | 薛文凯, 孟华旦尚, 王艳红, 朱攀, 德吉, 郭小芳. 纳木措可培养丝状真菌多样性及其与理化因子关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(6): 21473-. |
| [11] | 李艳辉, 兰天元, 王月, 于洋, 赵常明, 李利华, 徐文婷, 申国珍. 神农架植物物种空间周转的驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(4): 21377-. |
| [12] | 沈国平, 韩睿, 缪增强, 邢江娃, 李永臻, 王嵘, 朱德锐. 青藏高原4类典型水化学特征湖泊的细菌多样性差异及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(4): 21420-. |
| [13] | 曲梦君, 努尔依拉·阿巴拜克, 邹旭阁, 赵航, 朱威霖, 王健铭, 李景文. 地理距离和环境因子对阿拉善戈壁植物群落β多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(11): 22029-. |
| [14] | 孙远, 胡维刚, 姚树冉, 孙颖, 邓建明. 黄河流域被子植物和陆栖脊椎动物丰富度格局及其影响因子[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(12): 1523-1532. |
| [15] | 周昌艳, 王彬, 邓云, 乌俊杰, 曹敏, 林露湘. 林冠结构是局域尺度木本植物功能性状beta多样性形成的重要驱动力[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(12): 1546-1557. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()