



生物多样性 ›› 2018, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (6): 554-563. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018002 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2018002
收稿日期:2018-01-03
接受日期:2018-03-18
出版日期:2018-06-20
发布日期:2018-09-11
通讯作者:
曲波
作者简介:# 共同第一作者
基金资助:
Chenyang Xue1, Yufeng Xu1, Bo Qu1,2,*( )
)
Received:2018-01-03
Accepted:2018-03-18
Online:2018-06-20
Published:2018-09-11
Contact:
Qu Bo
About author:# Co-first authors
摘要:
入侵种与本地种杂交可能会改变其入侵性。为探讨入侵种与本地种杂交是否能促进植物入侵, 我们通过盆栽实验比较了高、中和低3种氮水平下入侵植物瘤突苍耳(Xanthium strumarium)、本地近缘种苍耳(X. sibiricum)及两者杂交种(X. strumarium♀ × X. sibiricum♂)的形态、光合及生长特征的差异。结果表明, 杂交种的总生物量在中氮和高氮水平下显著低于瘤突苍耳而高于苍耳。然而, 杂交种的茎粗在低氮水平下显著高于两个亲本, 叶绿素总含量和蒸腾速率在高氮水平下显著高于瘤突苍耳, 相对生长速率在低氮和高氮水平下显著高于两个亲本。此外, 在3种氮水平下瘤突苍耳的株高均显著小于苍耳, 而杂交种的株高在中氮和高氮水平下均与苍耳无显著差异。这些特性有可能提高了杂交种对资源的捕获和利用能力, 使其不仅能适应贫瘠的养分环境, 还能在有利条件下扩大自身优势。杂交带来较高的生长速率可能与瘤突苍耳的入侵性相关。
薛晨阳, 许玉凤, 曲波 (2018) 不同氮水平下瘤突苍耳、苍耳及其杂交种形态、光合及生长特征比较. 生物多样性, 26, 554-563. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018002.
Chenyang Xue, Yufeng Xu, Bo Qu (2018) Comparison of morphology, photosynthesis, and growth among Xanthium strumarium, X. sibiricum and their hybrid under different nitrogen levels. Biodiversity Science, 26, 554-563. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018002.
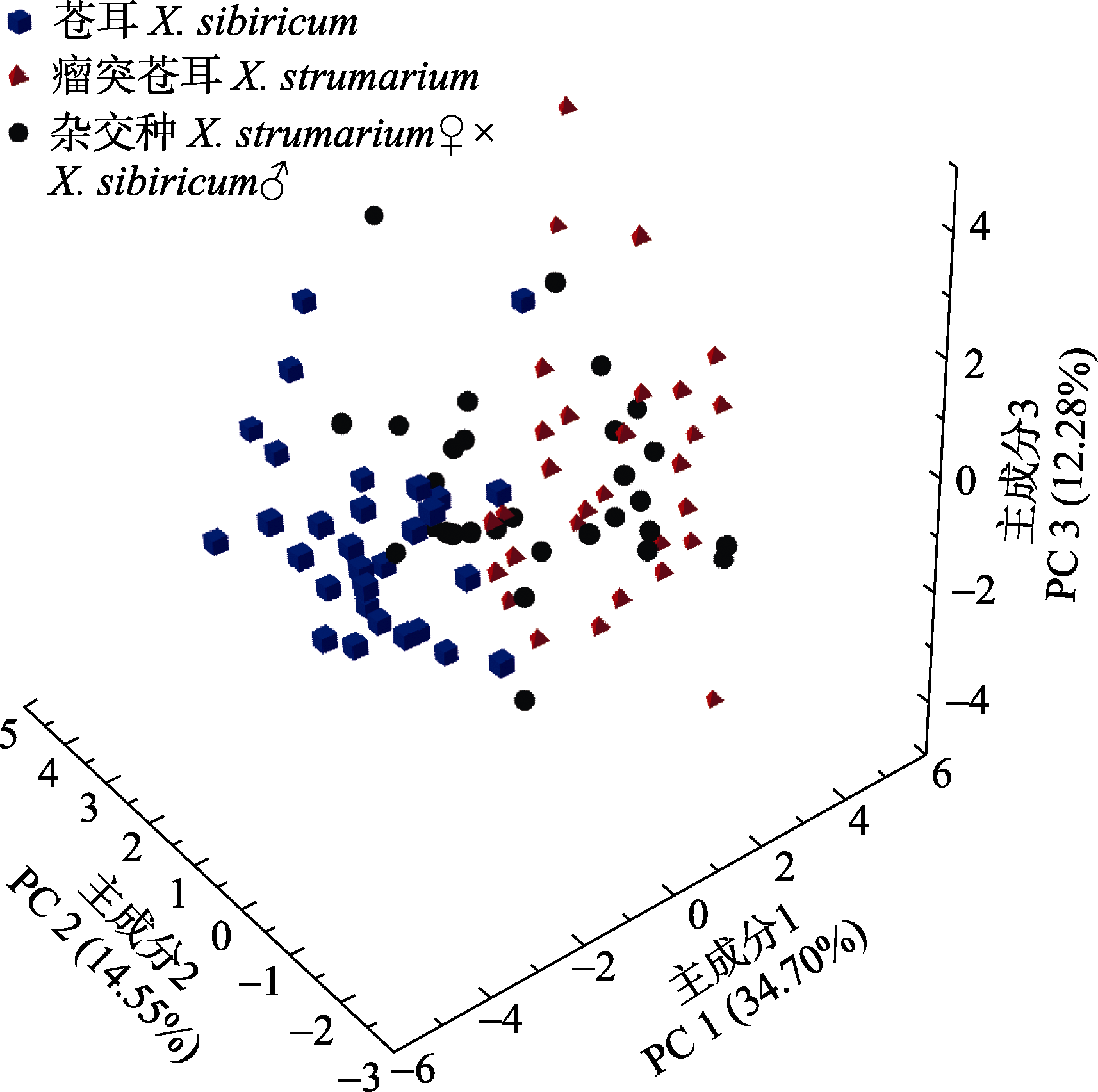
图1 苍耳、瘤突苍耳及其杂交种的主成分分析三维散点排序图
Fig. 1 Three-dimensional ordination scatter plots of Xanthium sibiricum, X. strumarium and X. strumarium♀ × X. sibiricum♂
| 杂交 Hybridization (H) | 养分水平 Nitrogen levels (N) | 交互作用 H × N | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | |
| 株高 Height | 13.698 | 0.001* | 4.093 | 0.022* | 1.849 | 0.167 |
| 茎粗 Diameter | 1.424 | 0.238 | 3.940 | 0.025* | 3.096 | 0.053 |
| 比叶面积 Specific leaf area | 6.593 | 0.013* | 1.286 | 0.285 | 1.745 | 0.184 |
| 根生物量 Root biomass | 5.462 | 0.023* | 5.323 | 0.008* | 0.477 | 0.623 |
| 茎生物量 Stem biomass | 13.334 | 0.001* | 7.818 | 0.001* | 1.539 | 0.224 |
| 叶生物量 Leaf biomass | 4.603 | 0.036* | 0.616 | 0.544 | 1.231 | 0.300 |
| 总生物量 Total biomass | 12.908 | 0.001* | 8.905 | 0.000* | 1.244 | 0.296 |
| 根生物量比 Root biomass ratio | 0.188 | 0.667 | 1.769 | 0.180 | 0.203 | 0.817 |
| 茎生物量比 Stem biomass ratio | 0.007 | 0.934 | 0.598 | 0.553 | 0.155 | 0.857 |
| 叶生物量比 Leaf biomass ratio | 0.907 | 0.345 | 4.829 | 0.012* | 0.207 | 0.814 |
| 根冠比 Root mass/Crown mass | 0.126 | 0.724 | 2.174 | 0.124 | 0.015 | 0.985 |
| 蒸腾速率 Transpiration rate | 0.470 | 0.496 | 2.477 | 0.093 | 9.622 | 0.000* |
| 气孔导度 Stomatal conductance | 0.505 | 0.480 | 2.152 | 0.126 | 6.325 | 0.003* |
| 胞间CO2浓度 Intercellular CO2 concentration | 0.413 | 0.523 | 10.364 | 0.000* | 7.174 | 0.002* |
| 叶绿素含量 Chlorophyll content | 7.019 | 0.011* | 3.719 | 0.031* | 17.131 | 0.000* |
| 最大净光合速率 Maximum net photosynthetic rate | 2.399 | 0.127 | 0.250 | 0.780 | 0.768 | 0.469 |
| 净同化速率 Net assimilation rate | 0.001 | 0.976 | 3.490 | 0.038* | 3.335 | 0.043* |
| 相对生长速率 Relative growth rate | 6.893 | 0.011* | 6.247 | 0.004* | 7.706 | 0.001* |
表1 杂交和养分水平对瘤突苍耳形态、生长和生理生态性状的影响
Tab1 e 1 Effects of hybridization and nitrogen levels on morphology, growth and eco-physiological measures of plants
| 杂交 Hybridization (H) | 养分水平 Nitrogen levels (N) | 交互作用 H × N | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | |
| 株高 Height | 13.698 | 0.001* | 4.093 | 0.022* | 1.849 | 0.167 |
| 茎粗 Diameter | 1.424 | 0.238 | 3.940 | 0.025* | 3.096 | 0.053 |
| 比叶面积 Specific leaf area | 6.593 | 0.013* | 1.286 | 0.285 | 1.745 | 0.184 |
| 根生物量 Root biomass | 5.462 | 0.023* | 5.323 | 0.008* | 0.477 | 0.623 |
| 茎生物量 Stem biomass | 13.334 | 0.001* | 7.818 | 0.001* | 1.539 | 0.224 |
| 叶生物量 Leaf biomass | 4.603 | 0.036* | 0.616 | 0.544 | 1.231 | 0.300 |
| 总生物量 Total biomass | 12.908 | 0.001* | 8.905 | 0.000* | 1.244 | 0.296 |
| 根生物量比 Root biomass ratio | 0.188 | 0.667 | 1.769 | 0.180 | 0.203 | 0.817 |
| 茎生物量比 Stem biomass ratio | 0.007 | 0.934 | 0.598 | 0.553 | 0.155 | 0.857 |
| 叶生物量比 Leaf biomass ratio | 0.907 | 0.345 | 4.829 | 0.012* | 0.207 | 0.814 |
| 根冠比 Root mass/Crown mass | 0.126 | 0.724 | 2.174 | 0.124 | 0.015 | 0.985 |
| 蒸腾速率 Transpiration rate | 0.470 | 0.496 | 2.477 | 0.093 | 9.622 | 0.000* |
| 气孔导度 Stomatal conductance | 0.505 | 0.480 | 2.152 | 0.126 | 6.325 | 0.003* |
| 胞间CO2浓度 Intercellular CO2 concentration | 0.413 | 0.523 | 10.364 | 0.000* | 7.174 | 0.002* |
| 叶绿素含量 Chlorophyll content | 7.019 | 0.011* | 3.719 | 0.031* | 17.131 | 0.000* |
| 最大净光合速率 Maximum net photosynthetic rate | 2.399 | 0.127 | 0.250 | 0.780 | 0.768 | 0.469 |
| 净同化速率 Net assimilation rate | 0.001 | 0.976 | 3.490 | 0.038* | 3.335 | 0.043* |
| 相对生长速率 Relative growth rate | 6.893 | 0.011* | 6.247 | 0.004* | 7.706 | 0.001* |
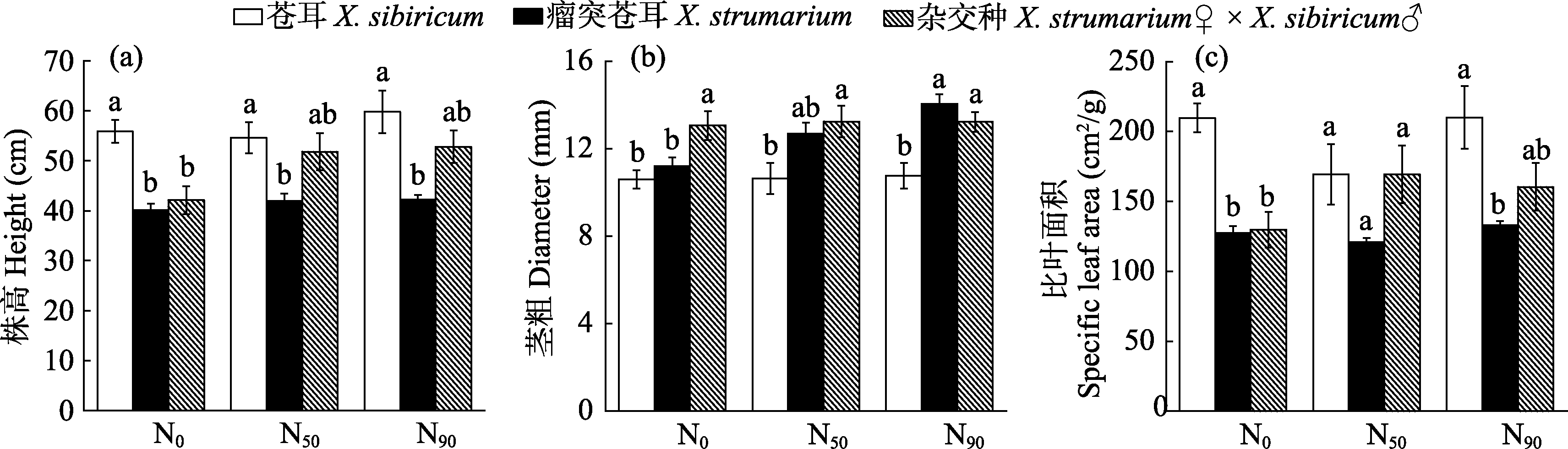
图2 不同氮水平下苍耳、瘤突苍耳及其杂交种的形态特征(平均值±标准误)。同一氮水平下, 不同小写字母代表3个物种存在显著差异(P < 0.05)。N0: 有效氮含量10.34 mg/kg; N50: 有效氮含量50 mg/kg; N90: 有效氮含量90 mg/kg。
Fig. 2 Morphology of Xanthium sibiricum, X. strumarium and X. strumarium♀ × X. sibiricum♂ at different nitrogen levels (mean ± SE). Within the same nitrogen level, different small letters indicate significant differences among the three species (P < 0.05). N0, Effective nitrogen content 10.34 mg/kg; N50, Effective nitrogen content 50 mg/kg; N90, Effective nitrogen content 90 mg/kg.
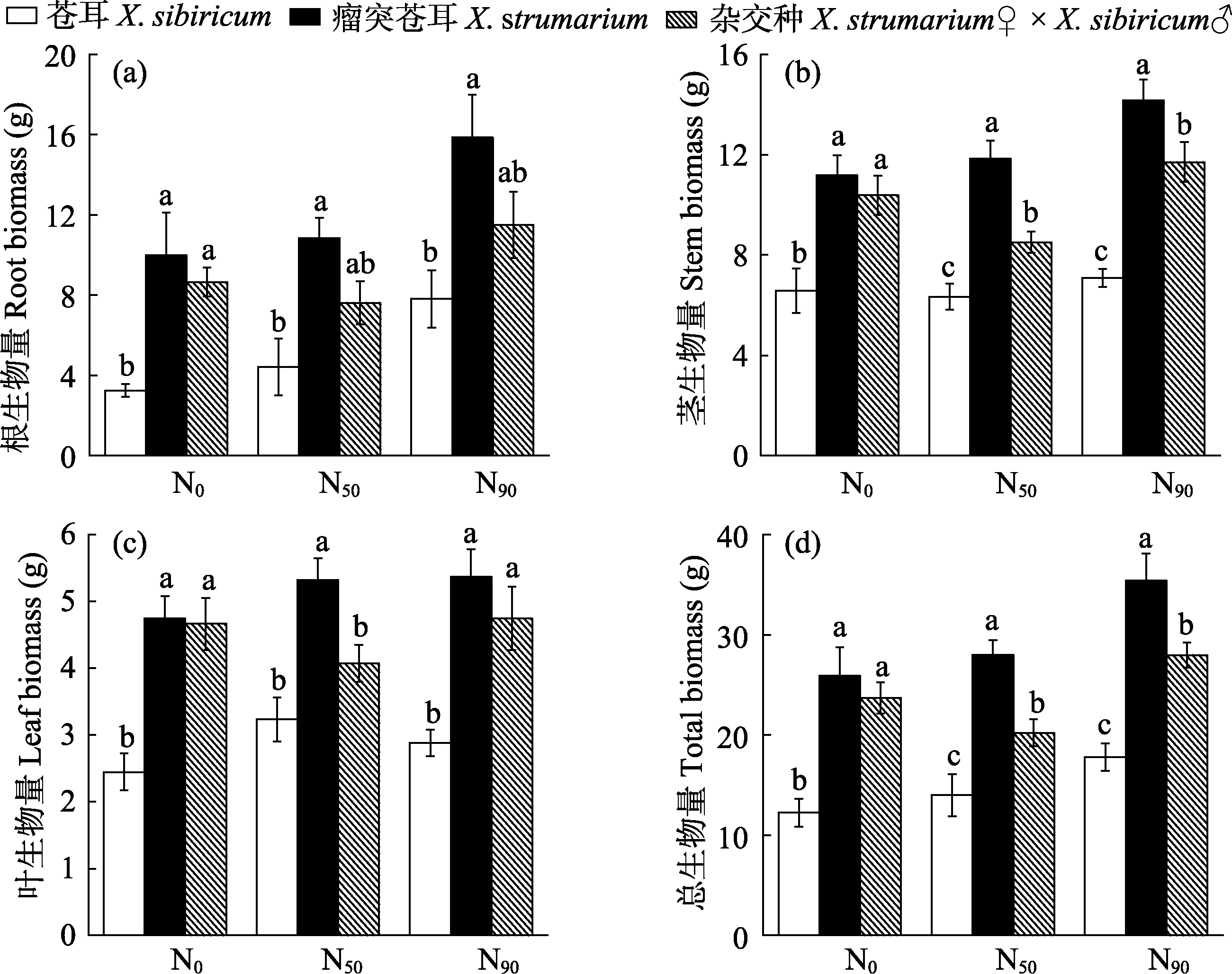
图3 不同氮水平下苍耳、瘤突苍耳及其杂交种的生物量特征(平均值±标准误)。同一氮水平下, 不同小写字母代表3个物种差异显著(P < 0.05)。N0: 有效氮含量10.34 mg/kg; N50: 有效氮含量50 mg/kg; N90: 有效氮含量90 mg/kg。
Fig. 3 Biomass characteristics of Xanthium sibiricum, X. strumarium and X. strumarium♀ × X. sibiricum♂ at different nitrogen levels (mean ± SE). Within the same nitrogen level, different small letters indicate significant differences among the three species (P < 0.05). N0, Effective nitrogen content 10.34 mg/kg; N50, Effective nitrogen content 50 mg/kg; N90, Effective nitrogen content 90 mg/kg.
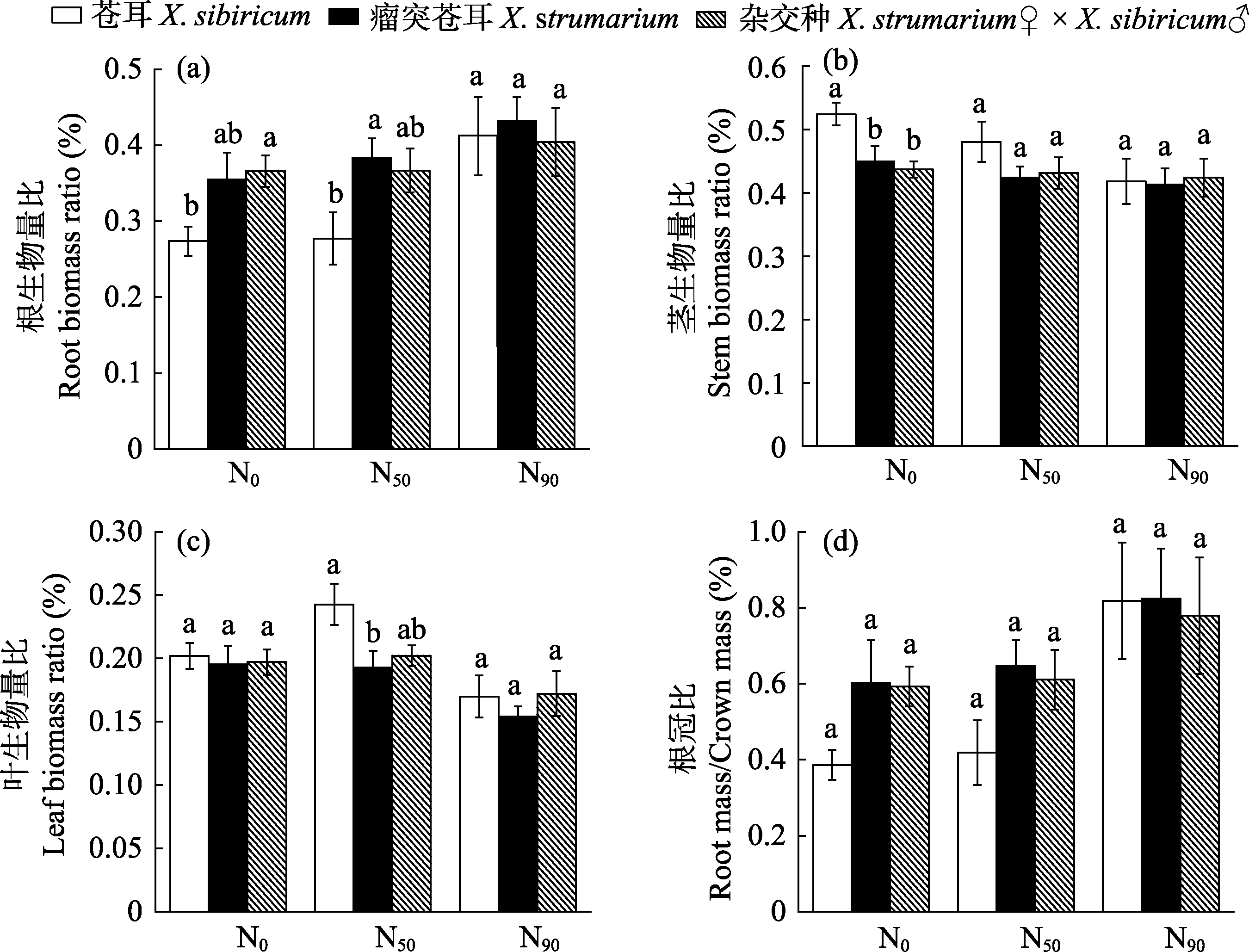
图4 不同养分水平下苍耳、瘤突苍耳及其杂交种的生物量分配特征(平均值±标准误)。同一氮水平下, 不同小写字母代表3个物种差异显著(P < 0.05)。N0: 有效氮含量10.34 mg/kg; N50: 有效氮含量50 mg/kg; N90: 有效氮含量90 mg/kg。
Fig. 4 Biomass allocation of Xanthium sibiricum, X. strumarium and X. strumarium♀ × X. sibiricum♂ at different nitrogent levels (mean ± SE). Within the same nitrogen level, different small letters indicate significant differences among the three species (P < 0.05). N0, Effective nitrogen content 10.34 mg/kg; N50, Effective nitrogen content 50 mg/kg; N90, Effective nitrogen content 90 mg/kg.
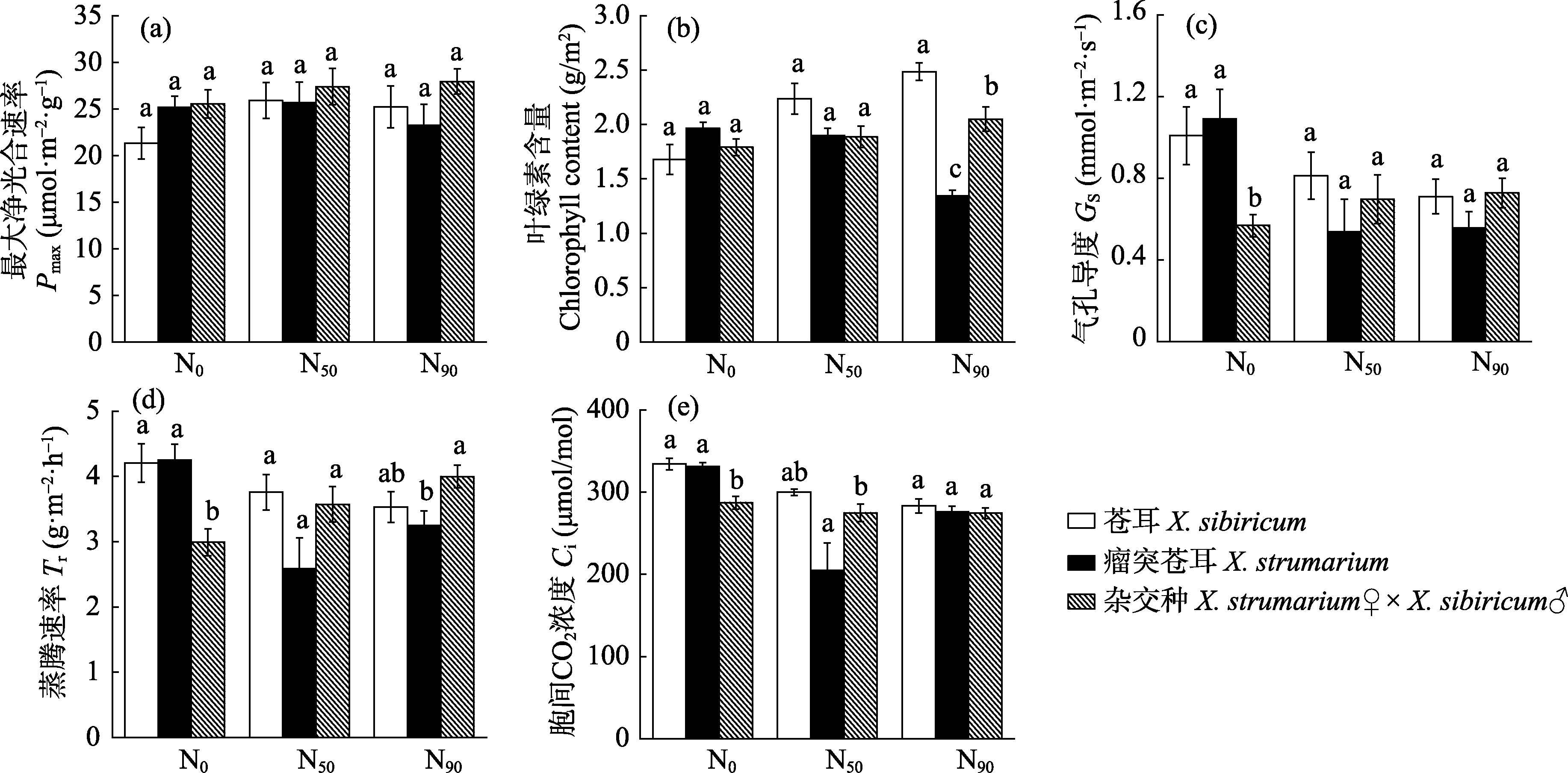
图5 不同养分水平下苍耳、瘤突苍耳及其杂交种的光合特征(平均值±标准误)。同一氮水平下, 不同小写字母分别代表3个物种在相同处理下差异显著(P < 0.05)。N0: 有效氮含量10.34 mg/kg; N50: 有效氮含量50 mg/kg; N90: 有效氮含量90 mg/kg。
Fig. 5 Photosynthetic parameters of Xanthium sibiricum, X. strumarium and X. strumarium♀ × X. sibiricum♂ at different nutrient levels (mean ± SE). Within the same nitrogen level, different small letters indicate significant differences among the three species (P < 0.05). N0, Effective nitrogen content 10.34 mg/kg; N50, Effective nitrogen content 50 mg/kg; N90, Effective nitrogen content 90 mg/kg; Pmax, Maximum net photosynthetic rate; Gs, Stomatal conductance; Tr, Transpiration rate; Ci, Intercellular CO2 concentration.
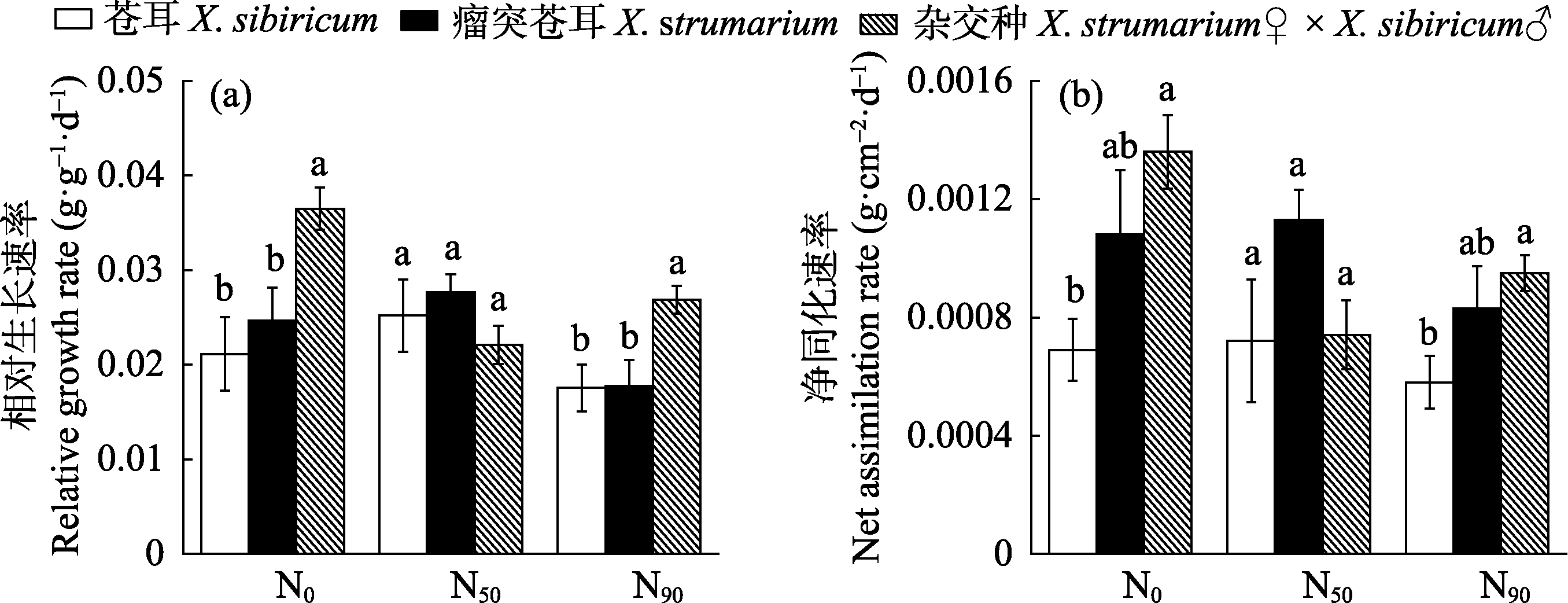
图6 不同氮水平下苍耳、瘤突苍耳及其杂交种的生长特征(平均值±标准误)。同一氮水平下, 不同小写字母代表3个物种差异显著(P < 0.05)。N0: 有效氮含量10.34 mg/kg; N50: 有效氮含量50 mg/kg; N90: 有效氮含量90 mg/kg。
Fig. 6 Growth characteristics of Xanthium sibiricum, X. strumarium and X. strumarium♀ × X. sibiricum♂ at different nitrogen levels (mean ± SE). Within the same nitrogen level, different small letters indicate significant differences among the three species (P < 0.05). N0, Effective nitrogen content 10.34 mg/kg; N50, Effective nitrogen content 50 mg/kg; N90, Effective nitrogen content 90 mg/kg.
| [1] | Abbott RJ (1992) Plant invasions, interspecific hybridization and the evolution of new plant taxa. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 7, 401-405. |
| [2] | Aïnouche ML, Fortune PM, Salmon A, Parisod C, Grandbastien MA, Fukunaga K, Ricou M, Misset MT (2009) Hybridization, polyploidy and invasion: Lessons from Spartina (Poaceae). Biological Invasions, 11, 1159-1173. |
| [3] | Blair AC, Blumenthal D, Hufbauer RA (2012) Hybridization and invasion: An experimental test with diffuse knapweed (Centaurea diffusa Lam.). Evolutionary Applications, 5, 17-28. |
| [4] | Chai WL, Lei YB, Li YP, Xiao HF, Feng YL (2014) Responses of invasive Chromolaena odorata and native Eupatorium heterophyllum to atmospheric CO2 enrichment. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34, 3744-3751. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [柴伟玲, 类延宝, 李扬苹, 肖海峰, 冯玉龙 (2014) 外来入侵植物飞机草和本地植物异叶泽兰对大气 CO2 浓度升高的响应. 生态学报, 34, 3744-3751.] | |
| [5] | Ellstrand NC, Schierenbeck KA (2000) Hybridization as a stimulus for the evolution of invasiveness in plants? Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 97, 7043-7050. |
| [6] | Facon B, Genton BJ, Shykoff J, Jarne P, Estoup A, David P (2006) A general eco-evolutionary framework for understanding bioinvasions. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 21, 130-135. |
| [7] | Funk JL, Vitousek PM (2007) Resource-use efficiency and plant invasion in low-resource systems. Nature, 446, 1079-1081. |
| [8] | Hollingsworth ML, Bailey JP (2000) Hybridisation and clonal diversity in some introduced Fallopia species (Polygonaceae). Watsonia, 23, 111-122. |
| [9] | Lavergne S, Molofsky J (2007) Increased genetic variation and evolutionary potential drive the success of an invasive grass. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 104, 3883-3888. |
| [10] | Leger, EA, Espeland EK, Merrill KR, Meyer SE (2009) Genetic variation and local adaptation at a cheatgrass (Bromus tectorum) invasion edge in western Nevada. Molecular Ecology, 18, 4366-4379. |
| [11] | Lei YB, Xiao HF, Feng YL (2010) Impacts of alien plant invasions on biodiversity and evolutionary responses of native species. Biodiversity Science, 18, 622-630. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [类延宝, 肖海峰, 冯玉龙 (2010) 外来植物入侵对生物多样性的影响及本地生物的进化响应. 生物多样性, 18, 622-630.] | |
| [12] | Leicht Y, Stacey A, John AS, Andrew ML (2007) Comparative performance of invasive and native Celastrus species across environmental gradients. Oecologia, 154, 273-282. |
| [13] | Leimu R, Mutikainen PIA, Koricheva J, Fischer M (2006) How general are positive relationships between plant population size, fitness and genetic variation? Journal of Ecology, 94, 942-952. |
| [14] | Lexer C, Welch ME, Durphy JL, Rieseberg LH (2003) Natural selection for salt tolerance quantitative trait loci (QTLs) in wild sunflower hybrids: Implications for the origin of Helianthus paradoxus, a diploid hybrid species. Molecular Ecology, 12, 1225-1235. |
| [15] | Li B, Chen JK (2002) Ecology of biological invasions: Achievements and challenges. World Science-Technology Research Development, 24(2), 26-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李博, 陈家宽 (2009) 生物入侵生态学: 成就与挑战. 世界科技研究与发展, 24(2), 26-36.] | |
| [16] | Li H, Xu H (2016) Introduction of Invasive Alien Species Science. Science Press, Beijing. |
| (in Chinese) [李宏, 许惠 (2016) 外来物种入侵科学导论. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [17] | Li YL, Zhang AM (2012) Vegetative growth and reproductive growth. Chinese Horticulture Abstracts, 28(2), 36-37. (in Chinese) |
| [李彦连, 张爱民 (2012) 植物营养生长与生殖生长辨证关系解析. 中国园艺文摘, 28(2), 36-37.] | |
| [18] | Liang WB, Nie DL, Wu SZ, Bai WF, Shen SZ (2015) Effects of shading on the growth and photosynthesis of Macropanax rosthornii seedlings. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 34, 413-419. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [梁文斌, 聂东伶, 吴思政, 柏文富, 沈素贞 (2015) 遮荫对短梗大参苗木光合作用及生长的影响. 生态学杂志, 34, 413-419.] | |
| [19] | Linchenthaler HR, Wellburn AR (1983) Determination of total carotenoides and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents. Biochemical Society Transactions, 11, 591-592. |
| [20] | Liu MC, Wei CY, Tang SC, Pan YM (2012) Bionomics of two invasive weeds, Bidens alba and B. pilosa, and their native congeners grown under different nutrient levels. Journal of Biosafety, 21(1), 32-40. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘明超, 韦春强, 唐赛春, 潘玉梅 (2012) 不同土壤养分水平下2种外来鬼针草和近缘本地种的比较研究. 生物安全学报, 21(1), 32-40.] | |
| [21] | Mealor BA, Hild AL (2007) Post-invasion evolution of native plant populations: A test of biological resilience. Oikos, 116, 1493-1500. |
| [22] | Meziane D, Shipley B (1999) Interacting components of interspecific relative growth rate: Constancy and change under differing conditions of light and nutrient supply. Functional Ecology, 13, 611-622. |
| [23] | Murchie EH, Horton P (1998) Contrasting patterns of photosynthetic acclimation to the light environment are dependent on the differential expression of the responses to altered irradiance and spectral quality. Plant Cell and Environment, 21, 139-148. |
| [24] | Parepa M, Fischer M, Bossdorf O (2013) Environmental variability promotes plant invasion. Nature Communications, 4, 1604. |
| [25] | Poorter H, Evans JR (1998) Photosynthetic nitrogen-use efficiency of species that differ inherently in specific leaf area. Oecologia, 116, 26-37. |
| [26] | Poorter L (1999) Growth response of 15 rainforest tree species to a light gradient: The relative importance of morphological and physiological traits. Functional Ecology, 13, 396-410. |
| [27] | Prentis PJ, Wilson JRU, Dormontt EE, Richardson DM, Lowe AJ (2008) Adaptive evolution in invasive species. Trends in Plant Science, 13, 288-294. |
| [28] | Pyšek P, Křivánek M, Jarošík V (2009) Planting intensity, residence time, and species traits determine invasion success of alien woody species. Ecology, 90, 2734-2744. |
| [29] | Quan GM, Mao DJ, Zhang JE, Xie JF (2015) Effects of nutrient level on plant growth and biomass allocation of invasive Chromolaena odorata. Ecological Science, 34(2), 27-33. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [全国明, 毛丹鹃, 章家恩, 谢俊芳 (2015) 不同养分水平对飞机草生长与生物量分配的影响. 生态科学, 34(2), 27-33.] | |
| [30] | Rieseberg LH, Carney SE (1998) Plant hybridization. The New Phytologist, 140, 599-624. |
| [31] | Rieseberg LH, Raymond O, Rosenthal DM, Lai Z, Livingstone K, Nakazato T, Durphy JL, Schwarzbach AE, Donovan LA, Lexer C (2003) Major ecological transitions in wild sunflowers facilitated by hybridization. Science, 301, 1211-1216. |
| [32] | Shipley B (2006) Net assimilation rate, specific leaf area and leaf mass ratio: Which is most closely correlated with relative growth rate? A meta-analysis. Functional Ecology, 20, 565-574. |
| [33] | Sultan SE (2001) Phenotypic plasticity for fitness components in Polygonum species of contrasting ecological breadth. Ecology, 82, 328-343. |
| [34] | Sun JL, Wang CQ, Xiao SH, Gao C, Li LB, Cao QW, Jiao ZG (2017) Effect of low light on photosynthesis and rubisco of cucumber seedlings. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 31, 1200-1209. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孙建磊, 王崇启, 肖守华, 高超, 李利斌, 曹齐卫, 焦自高 (2017) 弱光对黄瓜幼苗光合特性及 Rubisco 酶的影响. 核农学报, 31, 1200-1209.] | |
| [35] | Wan FH, Hou YM, Jiang MX (2015) Invasion Biology. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [万方浩, 侯有明, 蒋明星 (2015) 入侵生物学. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [36] | Wang JP, Dong LJ, Sang WG (2012) Effects of different nitrogen regimes on competition between Ambrosia artemisiifolia, an invasive species, and two native species, Artemisia annua and Artemisia mongolica. Biodiversity Science, 20, 3-11. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王晋萍, 董丽佳, 桑卫国 (2012) 不同氮素水平下入侵种豚草与本地种黄花蒿、蒙古蒿的竞争关系. 生物多样性, 20, 3-11.] | |
| [37] | Wang ML, Feng YL (2005) Effects of soil nitrogen leves on morphology, biomass allocation and photosynthesis in Ageratina adenophora and Chromoleana odorata. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 29, 697-705. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王满莲, 冯玉龙 (2005) 紫茎泽兰和飞机草的形态、生物量分配和光合特性对氮营养的响应. 植物生态学报, 29, 697-705.] | |
| [38] | Wang ML, Feng YL, Li X (2006) Effects of soil phosphorus level on morphological and photosynthetic characteristics of Ageratina adenophora and Chromolaena odorata. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 17, 602-606. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王满莲, 冯玉龙, 李新 (2006) 紫茎泽兰和飞机草的形态和光合特性对磷营养的响应. 应用生态学报, 17, 602-606.] | |
| [39] | Yuan ZG, Liu Y, Shao H, Zhao JY, Zhao Y, Hu YX (2017) The allelopathic effect of the invasive plant Xanthium spinosum L. at different growing stages. Ecological Science, 36(6), 107-113. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [袁着耕, 刘影, 邵华, 赵金雨, 赵玉, 胡云霞 (2017) 不同生长期入侵植物刺苍耳的化感作用. 生态科学, 36(6), 107-113.] | |
| [40] | Zalapa JE, Brunet J, Guries RP (2010) The extent of hybridization and its impact on the genetic diversity and population structure of an invasive tree, Ulmus pumila (Ulmaceae). Evolutionary Applications, 3, 157-168. |
| [41] | Zhang SR, Huang YF, Li BG, Zhang FR, Hu KL (2003) Temporal-spatial variability of soil nitrogen nutrients in Quzhou County, Hebei Province. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 40, 475-479. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张世熔, 黄元仿, 李保国, 张凤荣, 胡克林 (2003) 河北曲周土壤氮素养分的时空变异特征. 土壤学报, 40, 475-479.] | |
| [42] | Zheng YL, Feng YL, Liu WX, Liao ZY (2009) Growth, biomass allocation, morphology, and photosynthesis of invasive Eupatorium adenophorum and its native congeners grown at four irradiances. Plant Ecology, 203, 263-271. |
| [43] | Zhu YL, He LL, Du JS (2006) Studies of physiological adaptation ability of different cucumber varieties under poor light. Journal of Shenyang Aricultural University, 37, 331-334. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [朱艳蕾, 何莉莉, 都基帅 (2006) 弱光下不同黄瓜品种生理适应性的研究. 沈阳农业大学学报, 37, 331-334.] | |
| [44] | Zu YG, Zhang ZH, Wang WJ, Yang FJ, He HS (2006) Different characteristics of photosynthesis in stems and leaves of Mikania micranth. Journal of Plant Ecology (Chinese Version), 30, 998-1004. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [祖元刚, 张衷华, 王文杰, 杨逢建, 贺海升 (2006) 薇甘菊叶和茎的光合特性. 植物生态学报, 30, 998-1004.] |
| [1] | 李勇, 李三青, 王欢. 天津野生维管植物编目及分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23128-. |
| [2] | 肖俞, 李宇然, 段禾祥, 任正涛, 冯圣碧, 姜志诚, 李家华, 张品, 胡金明, 耿宇鹏. 高黎贡山外来植物入侵现状及管控建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 23011-. |
| [3] | 孙尧初, 潘远飞, 刘木, 潘晓云. 专食性-广食性天敌比例影响入侵植物喜旱莲子草生长防御策略[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22632-. |
| [4] | 蒲佳佳, 杨平俊, 戴洋, 陶可欣, 高磊, 杜予州, 曹俊, 俞晓平, 杨倩倩. 长江下游外来生物福寿螺的种类及其种群遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22346-. |
| [5] | 崔夏, 刘全儒, 吴超然, 何宇飞, 马金双. 京津冀外来入侵植物[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(8): 21497-. |
| [6] | 林秦文, 肖翠, 马金双. 中国外来植物数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 22127-. |
| [7] | 郭朝丹, 赵彩云, 李飞飞, 李俊生. 天然林和人工林外来入侵和本地植物对比研究: 以弄岗国家级自然保护区为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(4): 21356-. |
| [8] | 郭朝丹, 朱金方, 柳晓燕, 赵彩云, 李俊生. 贵州典型自然保护区内外外来入侵草本植物的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(5): 596-604. |
| [9] | 范兴科, 燕霞, 冯媛媛, 冉进华, 钱朝菊, 尹晓月, 周姗姗, 房庭舟, 马小飞. 红砂基因组大小变异及物种分化[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(10): 1308-1320. |
| [10] | 王亚, 王玮倩, 王钦克, 李晓霞, 刘延, 黄乔乔. 土壤养分对菊科一年生入侵种和本地种繁殖性状的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(1): 1-9. |
| [11] | 韩雪, 苏锦权, 姚娜娜, 陈宝明. 外来入侵植物的根系觅养行为研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(6): 727-733. |
| [12] | 李媛媛, 刘超男, 王嵘, 罗水兴, 农寿千, 王静雯, 陈小勇. 分子标记在濒危物种保护中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(3): 367-375. |
| [13] | 邓亨宁, 鞠文彬, 高云东, 张君议, 李诗琦, 高信芬, 徐波. 新建川藏铁路(雅安-昌都段)沿线外来入侵植物种类及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(10): 1174-1181. |
| [14] | 黄建峰, 徐睿, 彭艳琼. 榕树种间杂交研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(4): 457-467. |
| [15] | 土艳丽,王力平,王喜龙,王林林,段元文. 利用昆虫携带的花粉初探西藏入侵植物印加孔雀草在当地传粉网络中的地位[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(3): 306-313. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()