



生物多样性 ›› 2017, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (4): 372-381. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016257 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2016257
李瑶1, 肖向明1,2,*( ), 李香萍1, 马俊1, 陈帮乾1, 秦元伟2, 董金玮3, 赵斌1
), 李香萍1, 马俊1, 陈帮乾1, 秦元伟2, 董金玮3, 赵斌1
收稿日期:2016-09-12
接受日期:2017-03-29
出版日期:2017-04-20
发布日期:2017-04-20
通讯作者:
肖向明
基金资助:Yao Li1, Xiangming Xiao1,2,*, Xiangping Li1, Jun Ma1, Bangqian Chen1, Yuanwei Qin2, Jinwei Dong3, Bin Zhao1
Received:2016-09-12
Accepted:2017-03-29
Online:2017-04-20
Published:2017-04-20
Contact:
Xiao Xiangming
摘要:
基于2010年50 m空间分辨率森林分布图, 我们利用森林破碎化模型制作了中国森林6个不同破碎化类型 (内部森林、孔洞森林、边缘森林、斑块森林、过渡森林和未确定森林)的空间分布图。然后结合2010年中国行政区划图, 对比分析了不同尺度行政区域的森林破碎化情况。结果表明: 在国家尺度上, 斑块森林的比例最大(49.05%), 内部森林的比例最小(3.40%); 在区域尺度上, 东北地区森林破碎化程度最低, 西南地区森林破碎化程度次之, 华北平原、华中地区、山东半岛、黄淮海平原的森林破碎化程度最高; 在省级尺度上, 上海市森林破碎化程度最高, 天津市次之, 云南省及黑龙江省森林破碎化程度较低; 在县级尺度上, 陕西省所属的县森林破碎化程度最低。由此可知, 总体上我国森林破碎化情况较为严重, 但不同森林破碎化类型的空间分布存在较大差异。本研究可为各级林业部门管理森林资源以及优化林业生产和森林空间格局中提供数据支持, 提高森林的生态系统服务功能和生物多样性保护功能。
李瑶, 肖向明, 李香萍, 马俊, 陈帮乾, 秦元伟, 董金玮, 赵斌 (2017) 中国森林破碎化多尺度评价. 生物多样性, 25, 372-381. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016257.
Yao Li, Xiangming Xiao, Xiangping Li, Jun Ma, Bangqian Chen, Yuanwei Qin, Jinwei Dong, Bin Zhao (2017) Multi-scale assessments of forest fragmentation in China. Biodiversity Science, 25, 372-381. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016257.
| 类型 Type | 判定标准 Criterion | 说明 Description |
|---|---|---|
| 斑块森林Patch forest | Pf < 0.4 | 森林密度小于40% Forest density is less than 40% |
| 过渡森林Transitional forest | 0.4 < Pf < 0.6 | 森林密度介于40-60%之间 Forest density is between 40% and 60% |
| 孔洞森林Perforated forest | Pf > 0.6, Pf - Pff > 0 | 森林密度大于60%且森林密度大于森林连接度 Forest density is greater than 60%, and forest density is greater than forest connectivity |
| 未确定Undetermined | Pf > 0.6, Pf = Pff | 森林密度大于60%且森林密度等于森林连接度 Forest density is greater than 60%, and forest density is equal to forest connectivity |
| 边缘森林Edge forest | Pf > 0.6, Pf - Pff < 0 | 森林密度大于60%且森林密度小于森林连接度 Forest density is greater than 60%, and forest density is less than forest connectivity |
| 内部森林Interior forest | Pf = 1 | 森林密度为100%, 亦可称作完整森林 Forest density is 100%, and also can be known as complete forest |
表1 各森林破碎化类型判定标准
Table 1 Criteria for forest fragmentation types
| 类型 Type | 判定标准 Criterion | 说明 Description |
|---|---|---|
| 斑块森林Patch forest | Pf < 0.4 | 森林密度小于40% Forest density is less than 40% |
| 过渡森林Transitional forest | 0.4 < Pf < 0.6 | 森林密度介于40-60%之间 Forest density is between 40% and 60% |
| 孔洞森林Perforated forest | Pf > 0.6, Pf - Pff > 0 | 森林密度大于60%且森林密度大于森林连接度 Forest density is greater than 60%, and forest density is greater than forest connectivity |
| 未确定Undetermined | Pf > 0.6, Pf = Pff | 森林密度大于60%且森林密度等于森林连接度 Forest density is greater than 60%, and forest density is equal to forest connectivity |
| 边缘森林Edge forest | Pf > 0.6, Pf - Pff < 0 | 森林密度大于60%且森林密度小于森林连接度 Forest density is greater than 60%, and forest density is less than forest connectivity |
| 内部森林Interior forest | Pf = 1 | 森林密度为100%, 亦可称作完整森林 Forest density is 100%, and also can be known as complete forest |
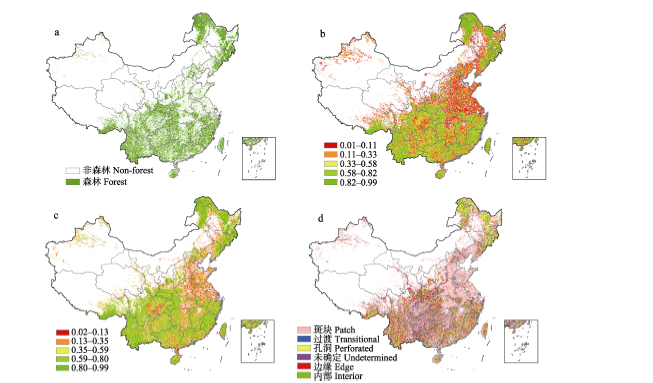
图1 中国森林破碎化分析流程。(a)森林空间分布图; (b)森林密度(Pf)图; (c)森林连接度(Pff)图; (d)森林破碎化分布图。
Fig. 1 The workflow for analyzing forest fragmentation of China. (a) Distribution of forest; (b) Forest density (Pf); (c) Forest connectivity (Pff); (d) Distribution of forest fragmentation.
| 省/区名 Province/region | 森林面积 Forest area (km2) | 斑块 Patch (%) | 过渡 Transitional (%) | 孔洞 Perforated (%) | 未确定 Undetermined (%) | 边缘 Edge (%) | 内部 Interior (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 278,034.73 | 38.37 | 8.75 | 36.66 | 0.03 | 6.72 | 9.47 |
| 四川 Sichuan | 248,583.13 | 44.11 | 17.64 | 16.43 | 0.05 | 19.31 | 2.45 |
| 云南 Yunnan | 230,131.73 | 26.36 | 16.97 | 28.85 | 0.08 | 23.68 | 4.07 |
| 内蒙古 Inner Mongolia | 203,160.96 | 40.83 | 8.23 | 29.78 | 0.03 | 9.31 | 11.82 |
| 广西 Guangxi | 143,319.58 | 35.14 | 21.25 | 23.28 | 0.07 | 19.36 | 0.90 |
| 湖南 Hunan | 129,880.06 | 45.96 | 18.98 | 18.73 | 0.06 | 15.47 | 0.80 |
| 西藏 Tibet | 129,673.51 | 46.02 | 12.04 | 20.13 | 0.05 | 17.61 | 4.16 |
| 湖北 Hubei | 112,266.81 | 48.38 | 14.23 | 19.61 | 0.06 | 16.29 | 1.43 |
| 吉林 Jilin | 110,053.89 | 40.54 | 8.88 | 30.63 | 0.03 | 8.40 | 11.53 |
| 贵州 Guizhou | 108,704.03 | 42.62 | 23.62 | 15.04 | 0.06 | 18.25 | 0.41 |
| 广东 Guangdong | 104,709.11 | 42.96 | 17.26 | 23.52 | 0.05 | 14.57 | 1.64 |
| 河北 Hebei | 100,720.87 | 80.48 | 10.36 | 4.26 | 0.01 | 4.79 | 0.09 |
| 江西 Jiangxi | 99,898.31 | 41.00 | 16.86 | 26.79 | 0.06 | 14.06 | 1.22 |
| 河南 Henan | 94,811.72 | 78.71 | 9.11 | 6.68 | 0.02 | 5.20 | 0.28 |
| 陕西 Shaanxi | 94,132.33 | 37.28 | 15.27 | 23.91 | 0.08 | 21.16 | 2.30 |
| 新疆 Xinjiang | 92,699.24 | 82.77 | 9.09 | 3.21 | 0.01 | 4.69 | 0.23 |
| 辽宁 Liaoning | 92,018.43 | 63.95 | 12.83 | 13.19 | 0.03 | 8.41 | 1.59 |
| 山东 Shandong | 87,139.80 | 86.88 | 8.34 | 2.66 | 0.01 | 1.97 | 0.14 |
| 安徽 Anhui | 82,906.74 | 64.96 | 11.50 | 15.03 | 0.03 | 7.91 | 0.56 |
| 福建 Fujian | 75,164.76 | 23.26 | 17.66 | 34.36 | 0.10 | 22.32 | 2.30 |
| 甘肃 Gansu | 65,808.05 | 64.72 | 11.12 | 10.43 | 0.04 | 12.62 | 1.07 |
| 浙江 Zhejiang | 63,367.31 | 33.64 | 16.58 | 28.96 | 0.09 | 19.58 | 1.15 |
| 山西 Shanxi | 60,692.29 | 69.90 | 10.23 | 9.75 | 0.03 | 9.05 | 1.04 |
| 江苏 Jiangsu | 54,259.88 | 91.24 | 5.78 | 2.08 | 0.00 | 0.80 | 0.09 |
| 重庆 Chongqing | 52,634.41 | 48.84 | 18.81 | 14.60 | 0.06 | 16.83 | 0.86 |
| 青海 Qinghai | 31,309.74 | 88.00 | 5.87 | 1.92 | 0.01 | 4.07 | 0.14 |
| 台湾 Taiwan | 21,229.70 | 29.32 | 12.55 | 32.94 | 0.07 | 19.56 | 5.55 |
| 海南 Hainan | 19,339.76 | 39.06 | 16.26 | 30.83 | 0.05 | 9.98 | 3.81 |
| 北京 Beijing | 11,312.26 | 58.65 | 15.41 | 11.62 | 0.04 | 13.48 | 0.80 |
| 宁夏 Ningxia | 5,206.68 | 89.40 | 4.68 | 2.74 | 0.00 | 2.98 | 0.19 |
| 天津 Tianjin | 4,805.12 | 92.54 | 4.41 | 1.59 | 0.00 | 1.39 | 0.08 |
| 上海 Shanghai | 3,421.85 | 93.68 | 5.66 | 0.63 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.00 |
| 香港 Hong Kong | 627.35 | 38.25 | 16.37 | 18.79 | 0.00 | 20.27 | 6.33 |
表2 各省森林面积及各破碎化类型百分比
Table 2 Forest area and percentage of forest fragmentation types at provincial scale
| 省/区名 Province/region | 森林面积 Forest area (km2) | 斑块 Patch (%) | 过渡 Transitional (%) | 孔洞 Perforated (%) | 未确定 Undetermined (%) | 边缘 Edge (%) | 内部 Interior (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黑龙江 Heilongjiang | 278,034.73 | 38.37 | 8.75 | 36.66 | 0.03 | 6.72 | 9.47 |
| 四川 Sichuan | 248,583.13 | 44.11 | 17.64 | 16.43 | 0.05 | 19.31 | 2.45 |
| 云南 Yunnan | 230,131.73 | 26.36 | 16.97 | 28.85 | 0.08 | 23.68 | 4.07 |
| 内蒙古 Inner Mongolia | 203,160.96 | 40.83 | 8.23 | 29.78 | 0.03 | 9.31 | 11.82 |
| 广西 Guangxi | 143,319.58 | 35.14 | 21.25 | 23.28 | 0.07 | 19.36 | 0.90 |
| 湖南 Hunan | 129,880.06 | 45.96 | 18.98 | 18.73 | 0.06 | 15.47 | 0.80 |
| 西藏 Tibet | 129,673.51 | 46.02 | 12.04 | 20.13 | 0.05 | 17.61 | 4.16 |
| 湖北 Hubei | 112,266.81 | 48.38 | 14.23 | 19.61 | 0.06 | 16.29 | 1.43 |
| 吉林 Jilin | 110,053.89 | 40.54 | 8.88 | 30.63 | 0.03 | 8.40 | 11.53 |
| 贵州 Guizhou | 108,704.03 | 42.62 | 23.62 | 15.04 | 0.06 | 18.25 | 0.41 |
| 广东 Guangdong | 104,709.11 | 42.96 | 17.26 | 23.52 | 0.05 | 14.57 | 1.64 |
| 河北 Hebei | 100,720.87 | 80.48 | 10.36 | 4.26 | 0.01 | 4.79 | 0.09 |
| 江西 Jiangxi | 99,898.31 | 41.00 | 16.86 | 26.79 | 0.06 | 14.06 | 1.22 |
| 河南 Henan | 94,811.72 | 78.71 | 9.11 | 6.68 | 0.02 | 5.20 | 0.28 |
| 陕西 Shaanxi | 94,132.33 | 37.28 | 15.27 | 23.91 | 0.08 | 21.16 | 2.30 |
| 新疆 Xinjiang | 92,699.24 | 82.77 | 9.09 | 3.21 | 0.01 | 4.69 | 0.23 |
| 辽宁 Liaoning | 92,018.43 | 63.95 | 12.83 | 13.19 | 0.03 | 8.41 | 1.59 |
| 山东 Shandong | 87,139.80 | 86.88 | 8.34 | 2.66 | 0.01 | 1.97 | 0.14 |
| 安徽 Anhui | 82,906.74 | 64.96 | 11.50 | 15.03 | 0.03 | 7.91 | 0.56 |
| 福建 Fujian | 75,164.76 | 23.26 | 17.66 | 34.36 | 0.10 | 22.32 | 2.30 |
| 甘肃 Gansu | 65,808.05 | 64.72 | 11.12 | 10.43 | 0.04 | 12.62 | 1.07 |
| 浙江 Zhejiang | 63,367.31 | 33.64 | 16.58 | 28.96 | 0.09 | 19.58 | 1.15 |
| 山西 Shanxi | 60,692.29 | 69.90 | 10.23 | 9.75 | 0.03 | 9.05 | 1.04 |
| 江苏 Jiangsu | 54,259.88 | 91.24 | 5.78 | 2.08 | 0.00 | 0.80 | 0.09 |
| 重庆 Chongqing | 52,634.41 | 48.84 | 18.81 | 14.60 | 0.06 | 16.83 | 0.86 |
| 青海 Qinghai | 31,309.74 | 88.00 | 5.87 | 1.92 | 0.01 | 4.07 | 0.14 |
| 台湾 Taiwan | 21,229.70 | 29.32 | 12.55 | 32.94 | 0.07 | 19.56 | 5.55 |
| 海南 Hainan | 19,339.76 | 39.06 | 16.26 | 30.83 | 0.05 | 9.98 | 3.81 |
| 北京 Beijing | 11,312.26 | 58.65 | 15.41 | 11.62 | 0.04 | 13.48 | 0.80 |
| 宁夏 Ningxia | 5,206.68 | 89.40 | 4.68 | 2.74 | 0.00 | 2.98 | 0.19 |
| 天津 Tianjin | 4,805.12 | 92.54 | 4.41 | 1.59 | 0.00 | 1.39 | 0.08 |
| 上海 Shanghai | 3,421.85 | 93.68 | 5.66 | 0.63 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.00 |
| 香港 Hong Kong | 627.35 | 38.25 | 16.37 | 18.79 | 0.00 | 20.27 | 6.33 |
| 县/市名 County/city | 百分比 % |
|---|---|
| 斑块森林 Patch forest | |
| 陕西省留坝县 Liuba, Shaanxi | 3.80 |
| 陕西省佛坪县 Foping, Shaanxi | 3.93 |
| 海南省琼中黎族苗族自治县 Qiongzhong, Hainan | 4.41 |
| 云南省勐腊县 Mengla, Yunnan | 5.52 |
| 黑龙江省伊春市市辖区 Yichun, Heilongjiang | 5.62 |
| 陕西省宁陕县 Ningshan, Shaanxi | 6.43 |
| 云南省江城哈尼族彝族自治县 Jiangcheng, Yunnan | 6.45 |
| 海南省五指山市 Wuzhishan, Hainan | 6.73 |
| 陕西省镇坪县 Zhenping, Shaanxi | 6.85 |
| 云南省普洱哈尼族彝族自治县 Puer, Yunnan | 7.27 |
| 过渡森林 Transitional forest | |
| 四川省简阳市 Jianyang, Sichuan | 41.01 |
| 四川省乐至县 Lezhi, Sichuan | 40.89 |
| 安徽省砀山县 Dangshan, Anhui | 37.69 |
| 四川省安岳县 Anyue, Sichuan | 37.68 |
| 四川省射洪县 Shehong, Sichuan | 35.99 |
| 四川省盐亭县 Yanting, Sichuan | 35.53 |
| 四川省三台县 Santai, Sichuan | 34.71 |
| 四川省西充县 Xichong, Sichuan | 33.81 |
| 四川省名山县 Mingshan, Sichuan | 32.87 |
| 四川省攀枝花市 Panzhihua, Sichuan | 32.65 |
| 孔洞森林 Perforated forest | |
| 黑龙江省塔河县 Tahe, Heilongjiang | 66.96 |
| 海南省琼中黎族苗族自治县 Qiongzhong, Hainan | 59.68 |
| 黑龙江省伊春市市辖区 Yichun, Heilongjiang | 59.28 |
| 吉林省安图县 Antu, Jilin | 58.32 |
| 黑龙江省逊克县 Xunke, Heilongjiang | 57.18 |
| 黑龙江省呼玛县 Huma, Heilongjiang | 57.04 |
| 黑龙江省漠河县 Mohe, Heilongjiang | 56.98 |
| 吉林省抚松县 Fusong, Jilin | 56.84 |
| 云南省梁河县 Lianghe, Yunnan | 55.34 |
| 广西省昭平县 Zhaoping, Guangxi | 54.01 |
| 边缘森林 Edge forest | |
| 陕西省石泉县 Shiquan, Shaanxi | 36.17 |
| 广西省天峨县 Tiane, Guangxi | 35.51 |
| 陕西省略阳县 Lueyang, Shaanxi | 34.46 |
| 四川省青川县 Qingchuan, Sichuan | 34.45 |
| 陕西省镇安县 zhen’an, Shaanxi | 33.14 |
| 陕西省平利县 Pingli, Shaanxi | 33.06 |
| 湖北省保康县 Baokang, Hubei | 32.86 |
| 云南省绿春县 Lvchun, Yunnan | 32.63 |
| 陕西省留坝县 Liuba, Shaanxi | 32.61 |
| 陕西省镇坪县 Zhenping, Shaanxi | 32.59 |
| 内部森林 Interior forest | |
| 吉林省和龙市 Helong, Jilin | 34.66 |
| 黑龙江省海林市 Hailin, Heilongjiang | 33.62 |
| 黑龙江省铁力市 Tieli, Heilongjiang | 32.27 |
| 吉林省珲春市 Hunchun, Jilin | 30.91 |
| 吉林省敦化市 Dunhua, Jilin | 28.41 |
| 吉林省汪清县 Wangqing, Jilin | 27.92 |
| 黑龙江省伊春市市辖区 Yichun, Heilongjiang | 26.42 |
| 黑龙江省通河县 Tonghe, Heilongjiang | 25.10 |
| 内蒙古额尔古纳市 Argun, Inner Mongolia | 23.09 |
| 吉林省安图县 Antu, Jilin | 19.65 |
表3 县级各森林破碎化类型百分比(排序依据: 斑块森林比例最小的10个县, 其他森林类型比例最大的10个县)
Table 3 Percentage of forest fragmentation types at county scale. The 10 counties with patch forests are ranked by the lowest percentage, while the other 40 counties are ranked by the highest percentage.
| 县/市名 County/city | 百分比 % |
|---|---|
| 斑块森林 Patch forest | |
| 陕西省留坝县 Liuba, Shaanxi | 3.80 |
| 陕西省佛坪县 Foping, Shaanxi | 3.93 |
| 海南省琼中黎族苗族自治县 Qiongzhong, Hainan | 4.41 |
| 云南省勐腊县 Mengla, Yunnan | 5.52 |
| 黑龙江省伊春市市辖区 Yichun, Heilongjiang | 5.62 |
| 陕西省宁陕县 Ningshan, Shaanxi | 6.43 |
| 云南省江城哈尼族彝族自治县 Jiangcheng, Yunnan | 6.45 |
| 海南省五指山市 Wuzhishan, Hainan | 6.73 |
| 陕西省镇坪县 Zhenping, Shaanxi | 6.85 |
| 云南省普洱哈尼族彝族自治县 Puer, Yunnan | 7.27 |
| 过渡森林 Transitional forest | |
| 四川省简阳市 Jianyang, Sichuan | 41.01 |
| 四川省乐至县 Lezhi, Sichuan | 40.89 |
| 安徽省砀山县 Dangshan, Anhui | 37.69 |
| 四川省安岳县 Anyue, Sichuan | 37.68 |
| 四川省射洪县 Shehong, Sichuan | 35.99 |
| 四川省盐亭县 Yanting, Sichuan | 35.53 |
| 四川省三台县 Santai, Sichuan | 34.71 |
| 四川省西充县 Xichong, Sichuan | 33.81 |
| 四川省名山县 Mingshan, Sichuan | 32.87 |
| 四川省攀枝花市 Panzhihua, Sichuan | 32.65 |
| 孔洞森林 Perforated forest | |
| 黑龙江省塔河县 Tahe, Heilongjiang | 66.96 |
| 海南省琼中黎族苗族自治县 Qiongzhong, Hainan | 59.68 |
| 黑龙江省伊春市市辖区 Yichun, Heilongjiang | 59.28 |
| 吉林省安图县 Antu, Jilin | 58.32 |
| 黑龙江省逊克县 Xunke, Heilongjiang | 57.18 |
| 黑龙江省呼玛县 Huma, Heilongjiang | 57.04 |
| 黑龙江省漠河县 Mohe, Heilongjiang | 56.98 |
| 吉林省抚松县 Fusong, Jilin | 56.84 |
| 云南省梁河县 Lianghe, Yunnan | 55.34 |
| 广西省昭平县 Zhaoping, Guangxi | 54.01 |
| 边缘森林 Edge forest | |
| 陕西省石泉县 Shiquan, Shaanxi | 36.17 |
| 广西省天峨县 Tiane, Guangxi | 35.51 |
| 陕西省略阳县 Lueyang, Shaanxi | 34.46 |
| 四川省青川县 Qingchuan, Sichuan | 34.45 |
| 陕西省镇安县 zhen’an, Shaanxi | 33.14 |
| 陕西省平利县 Pingli, Shaanxi | 33.06 |
| 湖北省保康县 Baokang, Hubei | 32.86 |
| 云南省绿春县 Lvchun, Yunnan | 32.63 |
| 陕西省留坝县 Liuba, Shaanxi | 32.61 |
| 陕西省镇坪县 Zhenping, Shaanxi | 32.59 |
| 内部森林 Interior forest | |
| 吉林省和龙市 Helong, Jilin | 34.66 |
| 黑龙江省海林市 Hailin, Heilongjiang | 33.62 |
| 黑龙江省铁力市 Tieli, Heilongjiang | 32.27 |
| 吉林省珲春市 Hunchun, Jilin | 30.91 |
| 吉林省敦化市 Dunhua, Jilin | 28.41 |
| 吉林省汪清县 Wangqing, Jilin | 27.92 |
| 黑龙江省伊春市市辖区 Yichun, Heilongjiang | 26.42 |
| 黑龙江省通河县 Tonghe, Heilongjiang | 25.10 |
| 内蒙古额尔古纳市 Argun, Inner Mongolia | 23.09 |
| 吉林省安图县 Antu, Jilin | 19.65 |
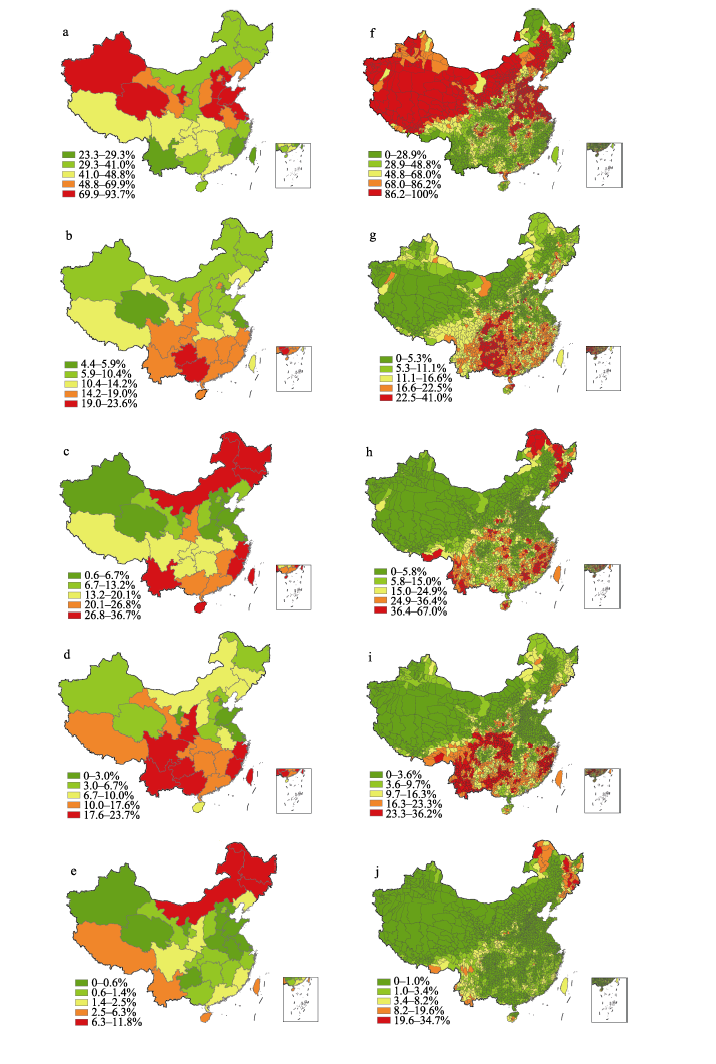
图5 省级县级各破碎化类型百分比空间分布。省级: (a)斑块; (b)过渡; (c)孔洞; (d)边缘; (e)内部。县级: (f)斑块; (g)过渡; (h)孔洞; (i)边缘; (j)内部。
Fig. 5 Percentage distribution of forest fragmentation types at provincial and county scale. Province: (a) Patch; (b) Transitional; (c) Perforated; (d) Edge; (e) Interior. County: (f) Patch; (g) Transitional; (h) Perforated; (i) Edge; (j) Interior.
| 1 | Achard F, Hansen MC (2012) Global Forest Monitoring from Earth Observation. CRC Press, Boca Raton. |
| 2 | Andrén H (1994) Effects of habitat fragmentation on birds and mammals in landscapes with different proportions of suitable habitat: a review. Oikos, 71, 355-366. |
| 3 | Baur B, Erhardt A (1995) Habitat fragmentation and habitat alterations: principal threats to most animal and plant species. GAIA—Ecological Perspectives for Science and Society, 4, 221-226. |
| 4 | Bonan GB (2008) Forests and climate change: forcings, feedbacks, and the climate benefits of forests. Science, 320, 1444-1449. |
| 5 | Chen LD, Liu XH, Fu BJ (1999) Evaluation on giant panda habitat fragmentation in Wolong Nature Reserve. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 19, 291-297. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈利顶, 刘雪华, 傅伯杰 (1999) 卧龙自然保护区大熊猫生境破碎化研究. 生态学报, 19, 291-297.] | |
| 6 | Dong JW, Xiao XM, Sheldon S, Biradar C, Zhang GL, Duong ND, Hazarika M, Wikantika K, Takeuhci W, Moore III B (2014) A 50-m forest cover map in Southeast Asia from ALOS/PALSAR and its application on forest fragmentation assessment. PLoS ONE, 9, e85801. |
| 7 | Fang JY, Guo ZD, Hu HF, Kato T, Muraoka H, Son Y (2014) Forest biomass carbon sinks in East Asia, with special reference to the relative contributions of forest expansion and forest growth. Global Change Biology, 20, 2019-2030. |
| 8 | Fang X, Tang DS, Yang L, Jin WF (2008) Landscape pattern of the experimental forest farm run by Hunan Forestry Academy and its fragmentation analysis. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 28(4), 107-112. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [方晰, 唐代生, 杨乐, 金文芬 (2008) 湖南省林科院试验林场森林植被景观格局及破碎化分析. 中南林业科技大学学报, 28(4), 107-112.] | |
| 9 | Groombridge B, Jenkins MD (2002) World Atlas of Biodiversity. University of California Press, Oakland. |
| 10 | Laurance WF, Lovejoy TE, Vasconcelos HL, Bruna EM, Didham RK, Stouffer PC, Gascon C, Bierregaard RO, Laurance SG, Sampaio E (2002) Ecosystem decay of Amazonian forest fragments: a 22-year investigation. Conservation Biology, 16, 605-618. |
| 11 | Li JC, Liu YF, Li MS (2014) Assessing changes in landscape pattern and forest fragmentation based on landscape mosaic model—a case study from the Purple Mountains of Nanjing. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 29, 226-231. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李金臣, 刘云峰, 李明诗 (2014) 基于景观镶嵌模型的景观格局变化及森林破碎化分析——以南京市紫金山风景区为例. 西北林学院学报, 29, 226-231.] | |
| 12 | Li MS, Ming L, Fan MM, Shen WJ, Sun L (2012) Spatio-temporal patterns and managerial implications of forest fragmentation derived from three national parks in the western United States. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 40(3), 103-107. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李明诗, 明莉, 樊鸣鸣, 沈文娟, 孙力 (2012) 美国西部国有森林破碎化模式及其管理含义. 东北林业大学学报, 40(3), 103-107.] | |
| 13 | Li YM, Li DM (1994) The effect of human activities on large and middle mammals on the Zhoushan Island—analysis on the cause of their endangerment. Chinese Biodiversity, 2, 187-192. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李义明, 李典谟 (1994) 人为活动对舟山群岛大中型兽的影响——大中型兽受威胁原因分析. 生物多样性, 2, 187-192.] | |
| 14 | Liu JF, Xiao WF, Jiang ZP, Feng X, Li XY (2005) A study on the influence of landscape fragmentation on biodiversity. Forest Research, 18, 222-226. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘建锋, 肖文发, 江泽平, 冯霞, 李秀英 (2005) 景观破碎化对生物多样性的影响. 林业科学研究, 18, 222-226.] | |
| 15 | O’Neill RV, Gardner RH, Turner MG (1992) A hierarchical neutral model for landscape analysis. Landscape Ecology, 7, 55-61. |
| 16 | Pan YD, Birdsey RA, Fang JY, Houghton R, Kauppi PE, Kurz WA, Phillips OL, Shvidenko A, Lewis SL, Canadell JG, Ciais P, Jackson RB, Pacala SW, McGuire AD, Piao SL, Rautiainen A, Sitch S, Hayes D (2011) A large and persistent carbon sink in the world’s forests. Science, 333, 988-993. |
| 17 | Pongratz J, Reick CH, Raddatz T, Claussen M (2010) Biogeophysical versus biogeochemical climate response to historical anthropogenic land cover change. Geophysical Research Letters, 37, L08702. |
| 18 | Qin YW, Xiao XM, Dong JW, Zhang GL, Shimada M, Liu JY, Li CG, Kou WL, Moore B (2015) Forest cover maps of China in 2010 from multiple approaches and data sources: PALSAR, Landsat, MODIS, FRA, and NFI. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 109, 1-16. |
| 19 | Qin YW, Dong JW, Xiao XM (2015) Difference and uncertainty of forest coverage estimation in China. Biodiversity Science, 23, 830-834. (in Chinese) |
| [秦元伟, 董金玮, 肖向明 (2015) 中国森林覆盖度产品的差异性及不确定性分析. 生物多样性, 23, 830-834. ] | |
| 20 | Ren Y, Wang DR (2012) Temporal and spatial variations of urban forest fragmentation in Xiamen. Journal of Fujian College of Forestry, 32, 213-219. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [任引, 王大睿 (2012) 厦门城市森林景观破碎化时空演变特征分析. 福建林学院学报, 32, 213-219.] | |
| 21 | Ribon R, Simon JE, Mattos GT (2003) Bird extinctions in Atlantic forest fragments of the Vicosa region, southeastern Brazil. Conservation Biology, 17, 1827-1839. |
| 22 | Riitters KH, Wickham JD, O’Neill RV, Jones KB, Smith ER (2000) Global-scale patterns of forest fragmentation. Conservation Ecology, 4, 1924-1925. |
| 23 | Riitters KH, Wickham JD, O’Neill RV, Jones KB, Smith ER, Coulston JW, Wade TG, Smith JH (2002) Fragmentation of Continental United States Forests. Ecosystems, 5, 815-822. |
| 24 | Robbins C, Dawson D, Dowell B (1989) Habitat area requirements of breeding forest birds of the middle Atlantic States. Wildlife Monographs, 103, 1-34. |
| 25 | Shen WJ, Xu T, Li MS (2013) Spatio-temporal changes in forest fragmentation, disturbance patterns over the three giant forested regions of China. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 37(4), 75-79. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [沈文娟, 徐婷, 李明诗 (2013) 中国三大林区森林破碎化及干扰模式变动分析. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 37(4), 75-79.] | |
| 26 | Shi JJ, Xia CZ, Yan EP, Dang YF (2015) Study on the evolution of forest fragmentation and driving forces in Yunyang County based on MultiMate remote sensing. Forest Resources Management, (4), 59-68. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [史京京, 夏朝宗, 严恩萍, 党永峰 (2015) 基于多期遥感的云阳县域森林景观破碎化演变与驱动力研究. 林业资源管理, (4), 59-68.] | |
| 27 | Stauffer D (1985) Introduction to Percolation Theory. Taylor and Francis, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. |
| 28 | Sun F, Chen MX, Mao LJ, Li MS (2011) Assessment of provincial-scale forest fragmentation in Chinese mainland. Journal of Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 39(1), 43-51. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孙飞, 陈敏学, 毛丽君, 李明诗 (2011) 中国大陆省级尺度森林破碎化特征评价. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 39(1), 43-51.] | |
| 29 | Suo AN, Xiong YC, Wang TM, Kou XJ, Ge JP (2007) Effect of deforestation on watershed hydrological process in Ziwuling on the Loess Plateau. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 43(6), 13-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [索安宁, 熊友才, 王天明, 寇晓军, 葛剑平 (2007) 黄土高原子午岭森林破碎化对流域水文过程的影响. 林业科学, 43(6), 13-19.] | |
| 30 | Wang ZB, Wang DX, Ren GX (2011) Analysis of forest landscape pattern and fragmentation of Qinling Caiziping forest region. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 39(12), 95-100. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王志彬, 王得祥, 任广鑫 (2011) 秦岭菜子坪林区森林景观格局及破碎化分析. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 39(12), 95-100.] | |
| 31 | Yang GJ, Xiao DN (2003) Forest landscape pattern and fragmentation: a case study on Xishui Natural Reserve in Qilian Mountain. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 22(5), 56-61. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨国靖, 肖笃宁 (2003) 森林景观格局分析及破碎化评价——以祁连山西水自然保护区为例. 生态学杂志, 22(5), 56-61.] | |
| 32 | Zhang YX, Yan EP, Xia CZ, Dang YF (2013) Study on evolution of forest landscape fragmentation of Three Gorges Reservoir Area based on multi-remote sensing images. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 33(7), 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张煜星, 严恩萍, 夏朝宗, 党永峰 (2013) 基于多期遥感的三峡库区森林景观破碎化演变研究. 中南林业科技大学学报, 33(7), 1-7.] | |
| 33 | Zhao AJ, Hu TX, Lai CH, Song XB (2006) Comparative study on fragmentation of forest landscapes in different regions. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University, 24(2), 187-193. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵安玖, 胡庭兴, 赖长鸿, 宋小波 (2006) 区域森林景观破碎化对比分析. 四川农业大学学报, 24(2), 187-193.] |
| [1] | 周志华, 金效华, 罗颖, 李迪强, 岳建兵, 刘芳, 何拓, 李希, 董晖, 罗鹏. 中国林草部门落实《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》的机制、成效分析及建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24487-. |
| [2] | 田志奇, 苏杨. 环境相关国际公约的中国履约模式和在《生物多样性公约》中的应用: 从完成《昆蒙框架》目标和发挥国家公园作用的角度[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24593-. |
| [3] | 弋维, 艾鷖, 吴萌, 田黎明, 泽让东科. 青藏高原高寒草甸土壤古菌群落对不同放牧强度的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24339-. |
| [4] | 宋阳, 柳军, 何少林, 徐薇, 程琛, 刘博, 余绩庆. 我国能源企业生物多样性保护主流化管理路径[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24345-. |
| [5] | 耿江天, 王菲, 赵华斌. 城市化对中国蝙蝠影响的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 24109-. |
| [6] | 李邦泽, 张树仁. 中国莎草科最新物种名录和分类纲要[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 24106-. |
| [7] | 胡宗刚. 抗战胜利后中美曾筹划合编《中国植物志》[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24220-. |
| [8] | 池玉杰, 张心甜, 田志炫, 关成帅, 谷新治, 刘智会, 王占斌, 王金杰. 东北亚地区白粉菌的物种多样性与寄主物种多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23443-. |
| [9] | 江建平, 蔡波, 王斌, 陈蔚涛, 温知新, 张德志, 隋璐璐, 马舜, 王伟波. 中国脊椎动物2023年度新增物种报告[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24327-. |
| [10] | 曹焕喜, 周青松, 罗阿蓉, 唐璞, 李廷景, 李泽建, 陈华燕, 牛泽清, 朱朝东. 2023年现生膜翅目新分类单元[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24319-. |
| [11] | 杜诚, 刘军, 叶文, 廖帅. 中国植物新分类群、新名称变化2023年度报告[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24253-. |
| [12] | 徐思远, 连琦琦, 张瑞欣, 赵嘉腾, 周璇, 周露, 陈芹, 白明. 2023年全球鞘翅目现生类群新分类单元[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24307-. |
| [13] | 努日耶·木合太尔, 张秀英, 苏比奴尔·艾力, 李后魂. 中国鳞翅目新物种2023年度报告[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24428-. |
| [14] | 林晨, 杨棋程, 吴艳玲, 侯鹏, 张冰, 杨定. 2023年中国双翅目新分类单元[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24328-. |
| [15] | 邓晶, 李艺, 侯一蕾. 城市生物多样性保护: 基于中欧对比视角下的经验借鉴[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23070-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()