



生物多样性 ›› 2016, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (8): 896-906. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016111 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2016111
刘鸿雁, 杨超杰, 张沛东, 李文涛, 杨晓龙, 张秀梅*( )
)
收稿日期:2016-04-25
接受日期:2016-07-19
出版日期:2016-08-20
发布日期:2016-09-02
通讯作者:
张秀梅
基金资助:
Hongyan Liu, Chaojie Yang, Peidong Zhang, Wentao Li, Xiaolong Yang, Xiumei Zhang*( )
)
Received:2016-04-25
Accepted:2016-07-19
Online:2016-08-20
Published:2016-09-02
Contact:
Zhang Xiumei
摘要:
基于2015年5月至2016年1月在青岛崂山湾人工鱼礁区的调查数据, 采用Margalef种类丰富度指数(d)、Shannon-Wiener多样性指数(H')、Pielou均匀度指数(J)、丰度/生物量曲线、等级聚类分析、SIMPER相似性百分比分析和非度量多维尺度排序(NMDS)分析, 对底层游泳动物群落结构和多样性进行研究。调查期间共捕获游泳动物61种, 隶属34科, 其中鱼类36种, 甲壳类22种, 头足类3种。优势种为日本蟳(Charybdis japonica)、许氏平鲉(Sebastes schlegelii)、大泷六线鱼(Hexagrammus otakii)、斑头鱼(H. agrammus)和星康吉鳗(Conger myriaster), 其中日本蟳(26.91%)和许氏平鲉(26.74%)的生物量占绝对优势。礁区游泳动物的渔获量和渔获种类数均多于对照区, 月平均单位捕捞努力量渔获量(CPUE)最高值出现在5月, 达到735.74 ± 316.59 g·net-1·d-1。游泳动物群落组成的特征值上, 7、8月的多样性指数较高, 但鱼礁区和对照区无显著差异(P>0.05)。丰度/生物量曲线表明, 5、6月游泳动物群落处于严重受干扰状态, 11月和次年1月群落处于相对稳定状态。聚类分析表明, 除1月外, 各月份不同区域的样方相似性都较高, 5、6月三亩前礁区的相似性最高, 达到86.21%。
刘鸿雁, 杨超杰, 张沛东, 李文涛, 杨晓龙, 张秀梅 (2016) 青岛崂山湾人工鱼礁区底层游泳动物群落结构特征. 生物多样性, 24, 896-906. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016111.
Hongyan Liu, Chaojie Yang, Peidong Zhang, Wentao Li, Xiaolong Yang, Xiumei Zhang (2016) Demersal nekton community structure of artificial reef zones in Laoshan Bay, Qingdao. Biodiversity Science, 24, 896-906. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2016111.
| 环境变量 Environment variable | 1月 Jan. | 5月 May | 6月 Jun. | 7月 Jul. | 8月 Aug. | 9月 Sept. | 10月 Oct. | 11月 Nov. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水温 Temperature (℃) | 4.57 ± 0.12a | 11.93 ± 0.23b | 14.09 ± 0.08c | 22.68 ± 0.51d | 25.84 ± 0.11e | 24.70 ± 0.06f | 20.30 ± 0.15g | 14.09 ± 0.05c |
| 溶解氧含量 DO (mg/L) | 8.33 ± 1.45a | 9.18 ± 0.78ab | 7.89 ± 0.84b | 6.04 ± 0.33c | 4.22 ± 0.43d | 4.67 ± 0.03de | 6.71 ± 0.05c | 5.78 ± 0.02dce |
| 盐度 Salinity | 31.29 ± 0.20a | 31.87 ± 0.06b | 31.19 ± 0.07b | 30.96 ± 0.03c | 30.86 ± 0.04c | 30.99 ± 0.03c | 31.16 ± 0.03b | 30.51 ± 0.15d |
| pH | 7.80 ± 0.12a | 7.70 ± 0.03b | 7.85 ± 0.05c | 7.59 ± 0.03a | 7.77 ± 0.08b | 7.73 ± 0.04b | 7.70 ± 0.03ab | 7.89 ± 0.07d |
表1 崂山湾人工鱼礁区底层水域环境特征
Table 1 Environmental conditions of bottom water of the artificial reef zones in Laoshan Bay
| 环境变量 Environment variable | 1月 Jan. | 5月 May | 6月 Jun. | 7月 Jul. | 8月 Aug. | 9月 Sept. | 10月 Oct. | 11月 Nov. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水温 Temperature (℃) | 4.57 ± 0.12a | 11.93 ± 0.23b | 14.09 ± 0.08c | 22.68 ± 0.51d | 25.84 ± 0.11e | 24.70 ± 0.06f | 20.30 ± 0.15g | 14.09 ± 0.05c |
| 溶解氧含量 DO (mg/L) | 8.33 ± 1.45a | 9.18 ± 0.78ab | 7.89 ± 0.84b | 6.04 ± 0.33c | 4.22 ± 0.43d | 4.67 ± 0.03de | 6.71 ± 0.05c | 5.78 ± 0.02dce |
| 盐度 Salinity | 31.29 ± 0.20a | 31.87 ± 0.06b | 31.19 ± 0.07b | 30.96 ± 0.03c | 30.86 ± 0.04c | 30.99 ± 0.03c | 31.16 ± 0.03b | 30.51 ± 0.15d |
| pH | 7.80 ± 0.12a | 7.70 ± 0.03b | 7.85 ± 0.05c | 7.59 ± 0.03a | 7.77 ± 0.08b | 7.73 ± 0.04b | 7.70 ± 0.03ab | 7.89 ± 0.07d |
| 种类 Species | 5月 May | 6月 Jun. | 7月 Jul. | 8月 Aug. | 9月 Sept. | 10月 Oct. | 11月 Nov. | 1月 Jan. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 许氏平鲉 Sebastes schlegelii | 4,665 | 2,671 | 1,829 | 847 | 2,413 | 2,935 | 10,485 | 7,963 |
| 日本蟳 Charybdis japonica | 2,045 | 2,161 | 7,852 | 8,158 | 7,728 | 9,420 | 2,386 | 189 |
| 大泷六线鱼 Hexagrammus otakii | 5,288 | 6,303 | 1,794 | 734 | 1,522 | 1,467 | 1,406 | 2,065 |
| 斑头鱼 Hexagrammus agrammus | 1,601 | 3,168 | 75 | 530 | 350 | 518 | 1,065 | 339 |
| 星康吉鳗 Conger myriaster | 394 | 134 | 1,372 | 807 | 1,290 | 1,103 | 747 | 13 |
| 寄居蟹科 Paguridae | 1,045 | 1,206 | 2,496 | 1,957 | 24 | 46 | - | 642 |
| 褐菖鲉 Sebastiscus mamoratus | 27 | 93 | 31 | 138 | 871 | 2,087 | 1,567 | 199 |
| 朝鲜平鲉 Sebastes koreanus | 691 | 616 | 30 | 10 | 330 | 359 | 225 | 47 |
| 长蛸 Octopus variabilis | 616 | 69 | 45 | - | 159 | 683 | 95 | 191 |
| 厚头平鲉 Sebastes pachycephalus | 281 | 328 | - | 17 | 69 | 195 | 154 | 79 |
| 口虾蛄 Oratosquilla oratoria | 23 | 34 | 398 | 418 | 1,041 | 188 | 158 | - |
| 敖氏长臂虾 Palaemon ortmanni | 53 | 32 | 19 | 150 | 47 | 225 | 61 | - |
| 繸鳚 Chirolophis japonicus | 167 | 4 | - | - | - | - | - | 23 |
| 方氏云鳚 Pholis fangi | 4 | 2 | - | - | 33 | 25 | 503 | - |
| 花鲈 Lateolabrax maculatus | - | - | 10 | - | 588 | 117 | 787 | - |
| 强壮菱蟹 Parthenope validus | - | - | 49 | 185 | 518 | - | - | - |
| 三疣梭子蟹 Portunus trituberculatus | - | - | - | 5 | 1,107 | - | 31 | - |
| 黄姑鱼 Nibea albiflora | - | - | - | 40 | 519 | 34 | - | - |
| 银姑鱼 Pennahia argentata | - | - | - | - | 205 | - | - | - |
| 褐牙鲆 Paralichthys olivaceus | - | - | 16 | 4 | 436 | - | - | - |
表2 2015年5月至2016年1月崂山湾主要游泳动物的Pinkas相对重要性指数(“-”表示未捕获)
Table 2 Index of relative importance (IRI) of the main nektons in Laoshan Bay from May 2015 to January 2016 (“- ” means not catch)
| 种类 Species | 5月 May | 6月 Jun. | 7月 Jul. | 8月 Aug. | 9月 Sept. | 10月 Oct. | 11月 Nov. | 1月 Jan. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 许氏平鲉 Sebastes schlegelii | 4,665 | 2,671 | 1,829 | 847 | 2,413 | 2,935 | 10,485 | 7,963 |
| 日本蟳 Charybdis japonica | 2,045 | 2,161 | 7,852 | 8,158 | 7,728 | 9,420 | 2,386 | 189 |
| 大泷六线鱼 Hexagrammus otakii | 5,288 | 6,303 | 1,794 | 734 | 1,522 | 1,467 | 1,406 | 2,065 |
| 斑头鱼 Hexagrammus agrammus | 1,601 | 3,168 | 75 | 530 | 350 | 518 | 1,065 | 339 |
| 星康吉鳗 Conger myriaster | 394 | 134 | 1,372 | 807 | 1,290 | 1,103 | 747 | 13 |
| 寄居蟹科 Paguridae | 1,045 | 1,206 | 2,496 | 1,957 | 24 | 46 | - | 642 |
| 褐菖鲉 Sebastiscus mamoratus | 27 | 93 | 31 | 138 | 871 | 2,087 | 1,567 | 199 |
| 朝鲜平鲉 Sebastes koreanus | 691 | 616 | 30 | 10 | 330 | 359 | 225 | 47 |
| 长蛸 Octopus variabilis | 616 | 69 | 45 | - | 159 | 683 | 95 | 191 |
| 厚头平鲉 Sebastes pachycephalus | 281 | 328 | - | 17 | 69 | 195 | 154 | 79 |
| 口虾蛄 Oratosquilla oratoria | 23 | 34 | 398 | 418 | 1,041 | 188 | 158 | - |
| 敖氏长臂虾 Palaemon ortmanni | 53 | 32 | 19 | 150 | 47 | 225 | 61 | - |
| 繸鳚 Chirolophis japonicus | 167 | 4 | - | - | - | - | - | 23 |
| 方氏云鳚 Pholis fangi | 4 | 2 | - | - | 33 | 25 | 503 | - |
| 花鲈 Lateolabrax maculatus | - | - | 10 | - | 588 | 117 | 787 | - |
| 强壮菱蟹 Parthenope validus | - | - | 49 | 185 | 518 | - | - | - |
| 三疣梭子蟹 Portunus trituberculatus | - | - | - | 5 | 1,107 | - | 31 | - |
| 黄姑鱼 Nibea albiflora | - | - | - | 40 | 519 | 34 | - | - |
| 银姑鱼 Pennahia argentata | - | - | - | - | 205 | - | - | - |
| 褐牙鲆 Paralichthys olivaceus | - | - | 16 | 4 | 436 | - | - | - |
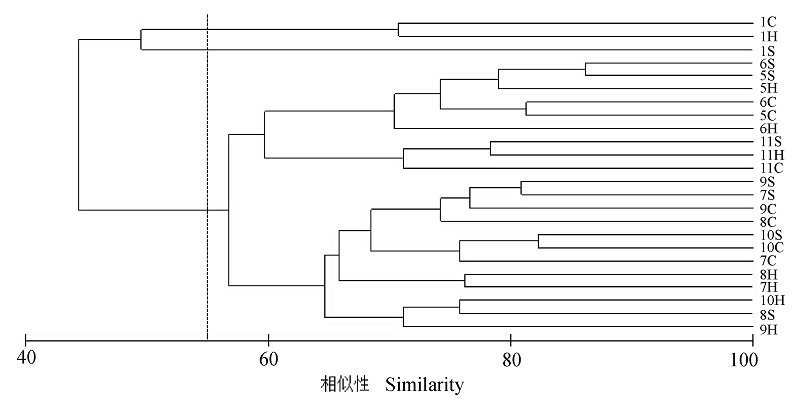
图5 崂山湾不同区域不同月份游泳动物群落聚类分析(数字表示月份, 字母表示区域)
Fig. 5 The cluster analysis of the nekton community in different months and different zones in Laoshan Bay. Digits indicate the month, and letters indicate zones.
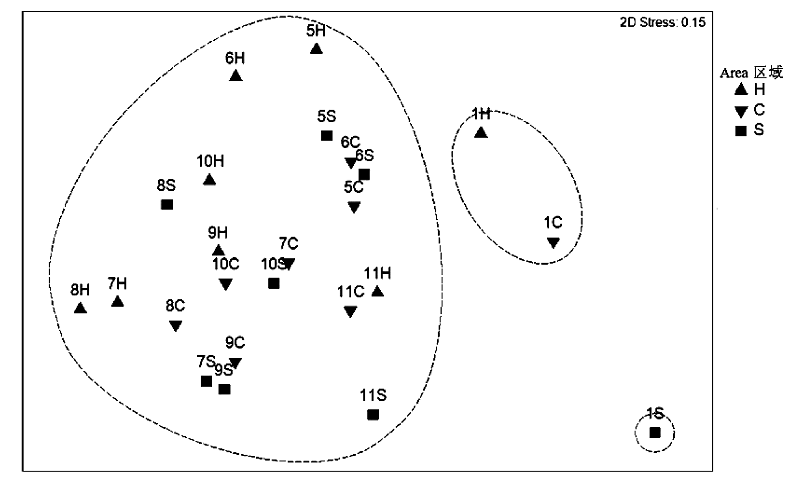
图6 崂山湾不同区域不同月份游泳动物群落NMDS排序分析。数字表示月份, 字母表示区域。
Fig. 6 NMDS analysis of the nekton community in different months and different zones in Laoshan Bay. Digits indicate the month, and letters indicate zones.
| [1] | Agard JBR, Gobin J, Warwick RM (1993) Analysis of marine macrobenthic community structure in relation to pollution, natural oil seepage and seasonal disturbance in a tropical environment (Trinidad, West Indies). Marine Ecology Progress Series, 92, 233-243. |
| [2] | Bray JR, Curtis JT (1957) An ordination of the upland forest communities of southern Wisconsin. Ecological Monographs, 27, 325-349. |
| [3] | Chen Y, Yu CQ, Zhang GS, Zhang S (2002) The environment function and fish gather effect of artificial reefs. Journal of Dalian Fisheries University, 17, 64-69. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈勇, 于长清, 张国胜, 张硕 (2002) 人工鱼礁的环境功能与集鱼效果. 大连水产学院学报, 17, 64-69.] | |
| [4] | Cheng QT, Zheng BS (1987) Systematic Synopsis of Chinese Fishes. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [成庆泰, 郑葆珊 (1987) 中国鱼类系统检索. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [5] | Clarke KR, Warwick RM (2001) Change in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation, 2nd edn. PRIMER-E, Plymouth. |
| [6] | Ji DP, Bian XD, Song N, Gao TX (2014) Feeding ecology of Hexagrammos otakii in Lidao Rongcheng. Journal of Fisheries of China, 38, 1399-1409. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [纪东平, 卞晓东, 宋娜, 高天翔 (2014) 荣成俚岛大泷六线鱼摄食生态研究. 水产学报, 38, 1399-1409.] | |
| [7] | Ji DP, Bian XD, Song N, Gao TX (2015) Feeding ecology of Hexagrammos agrammus in Lidao, Rongcheng, China. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 22, 88-98. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [纪东平, 卞晓东, 宋娜, 高天翔 (2015) 荣成俚岛斑头鱼摄食生态研究. 中国水产科学, 22, 88-98.] | |
| [8] | Jiao JJ, Pan YX, Sun LY, Yang BQ, Qiu SY (2011) Effect of artificial reefs on fish multiplication. Fisheries Science, 30(2), 79-82. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [焦金菊, 潘永玺, 孙利元, 杨宝清, 邱盛尧 (2011) 人工鱼礁区的增殖鱼类资源效果初步探究. 水产科学, 30(2), 79-82.] | |
| [9] | Li F, Zhang HJ, Lü ZB, Xu BQ, Zheng L (2013) Species composition and community diversity of nekton in Laizhou Bay, China. Biodiversity Science, 21, 537-546. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李凡, 张焕君, 吕振波, 徐炳庆, 郑亮 (2013) 莱州湾游泳动物群落种类组成及多样性. 生物多样性, 21, 537-546.] | |
| [10] | Lin J, Zhang SY (2006) Research advances on physicial stability and ecological effects of artificial reef. Marine Fisheries, 28, 257-262. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [林军, 章守宇 (2006) 人工鱼礁物理稳定性及其生态效应的研究进展. 海洋渔业, 28, 257-262.] | |
| [11] | Liu J, Ning P (2011) Species composition and faunal characteristics of fishes in the Yellow Sea. Biodiversity Science, 19, 764-769. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘静, 宁平 (2011) 黄海鱼类组成、区系特征及历史变迁. 生物多样性, 19, 764-769.] | |
| [12] | Liu RY (2008) Checklist of Marine Biota of China Seas. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [刘瑞玉 (2008) 中国海洋生物名录. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [13] | Ludwig JA, Reynolds JF (1988) Statistical Ecology: A Primer on Methods and Computing. John Wiley and Sons, New York. |
| [14] | Ma ZY, Wang HQ (1997) Multivariate analysis of community structure on macrobenthos. China Environmental Science, 17, 297-300. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [马藏允, 王惠卿 (1997) 底栖生物群落结构变化多元变量统计分析. 中国环境科学, 17, 297-300.] | |
| [15] | Margalef R (1968) Perspectives in Ecological Theory. University of Chicago Press, Chicago. |
| [16] | Mei C, Ren YP, Xu BD, Fan YC (2010) Preliminary study on the effect of Penaeus japonicas Bate releasing in the Laoshan Bay. Periodical of Ocean University of China (Natural Science Edition), 40(9), 45-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [梅春, 任一平, 徐宾铎, 范延琛 (2010) 崂山湾日本对虾增殖放流效果的初步研究. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 40(9), 45-50.] | |
| [17] | Palomares MLD, Pauly D (2015) SeaLifeBase.. (accessed on 2015-03-25 |
| [18] | Pielou EC (1966) Species-diversity and pattern-diversity in the study of ecological succession. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 10, 370-383. |
| [19] | Pinkas L, Olphant M, Iverson I (1971) Food habits of albacore, bluefin tuna and bonito in California waters. California Department of Fish and Game: Fish Bulletin, 152, 1-105. |
| [20] | Qi MH, Ma SS, Qu KM, Xin FY (2004) The formation of sulfide in the marine sediments and its relationships to cultivation of shellfish. Marine Fisheries Research, 25(1), 85-89. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [祁铭华, 马绍赛, 曲克明, 辛福言 (2004) 沉积环境中硫化物的形成及其与贝类养殖的关系. 海洋水产研究, 25(1), 85-89.] | |
| [21] | Rounsefell GA (1972) Ecological effects of offshore construction. Journal of Marine Science, 2, 1-119. |
| [22] | Tang YL, Sheng HX, Qi GR, Wu LH, Wan R (2012) The seasonal differences of benthic macroalgae communities in three artificial reefs of Laoshan Bay. Fisheries Modernization, 39(3), 66-71. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [唐衍力, 盛化香, 齐广瑞, 吴连慧, 万荣 (2012) 崂山湾三个人工鱼礁区底栖大型藻类群落的季节性差异. 渔业现代化, 39(3), 66-71.] | |
| [23] | Wang X, Sheng HX, Tang YL, Huang LY, Wan R (2014) Relationship between the structure of phytoplankton community and environmental factors in three artificial reef areas of Laoshan Bay. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 35(4), 7-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王欣, 盛化香, 唐衍力, 黄六一, 万荣 (2014) 崂山湾人工鱼礁区浮游植物群落结构与环境因子的关系. 渔业科学进展, 35(4), 7-12.] | |
| [24] | Wang ZH, Zhang SY, Chen QM, Xu Q, Wang K (2012) Fish community ecology in rocky reef habitat of Ma’an Archipelago. I. Species composition and diversity. Biodiversity Science, 20, 41-50. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [汪振华, 章守宇, 陈清满, 许强, 王凯 (2012) 马鞍列岛岩礁生境鱼类群落生态学. I. 种类组成和多样性. 生物多样性, 20, 41-50.] | |
| [25] | Warwick RM (1986) A new method for detecting pollution effects on marine macrobenthic communities. Marine Biology, 92, 557-562. |
| [26] | Warwick RM, Pearson TH (1987) Detection of pollution effects on marine macrobenthos: further evaluation of the species abundance/biomass method. Marine Biology, 95, 193-200. |
| [27] | Wu ZX, Zhang L, Zhang XM, Zhang PD, Li WT (2012) Nekton community structure and its relationship with main environmental variables in Lidao artificial reef zones of Rongcheng. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32, 6737-6746. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴忠鑫, 张磊, 张秀梅, 张沛东, 李文涛 (2012) 荣成俚岛人工鱼礁区游泳动物群落特征及其与主要环境因子的关系. 生态学报, 32, 6737-6746.] | |
| [28] | Xu BQ, Lü ZB, Li F, Bao JG, Xu WZ (2011) On nekton composition in southern coastal waters off Shandong Peninsula in summer. Marine Fisheries, 33, 59-65. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [徐炳庆, 吕振波, 李凡, 包家国, 徐维柱 (2011) 山东半岛南部近岸海域夏季游泳动物的组成特征. 海洋渔业, 33, 59-65.] | |
| [29] | Xu H, Zeng XQ, Gu YB, Guan LS (2012) The effect of artificial reefs on the community structure and seasonal variation of nektons in Zhuwang Harbor, Laizhou, Shandong. Periodical of Ocean University of China (Natural Science Edition), 42(5), 47-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [徐浩, 曾晓起, 顾炎斌, 关丽莎 (2012) 人工鱼礁对山东莱州朱旺港海区游泳动物的群落结构及季节变化的影响. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 42(5), 47-54.] | |
| [30] | Yang DJ, Wang YL (1989) Invertebrates in North China. Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [杨德渐, 王永良 (1989) 中国北部无脊椎动物. 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| [31] | Yemane D, Field JG, Leslie RW (2005) Exploring the effects of fishing on fish assemblages using Abundance Biomass Comparison (ABC) curves. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 62, 374-379. |
| [32] | Yu Q, Tang YL (2015) Analysis on community structure and diversity of fish and macroinvertebrates in artificial reef area around Xigang, Weihai. Fishery Modernization, 42(3), 65-72. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [于晴, 唐衍力 (2015) 威海西港人工鱼礁区鱼类和大型无脊椎动物群聚特征. 渔业现代化, 42(3), 65-72.] | |
| [33] | Yuan W, Lin Q, Wang J, Sun JQ, Chen RS (2015) Assessment of enhancement effectiveness of Chinese shrimp Fenneropenaeus chinensis stock in the Laoshan Bay. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 36(4), 27-34. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [袁伟, 林群, 王俊, 孙坚强, 陈瑞盛 (2015) 崂山湾中国对虾(Fenneropenaeus chinensis)增殖放流效果评价. 渔业科学进展, 36(4), 27-34.] | |
| [34] | Zhang B, Yuan W, Wang J (2015) Feeding ecology of the dominant fish species in spring in Laoshan Bay. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 22, 820-827. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张波, 袁伟, 王俊 (2015) 崂山湾春季鱼类群落的摄食生态及其主要种类. 中国水产科学, 22, 820-827.] | |
| [35] | Zhang S, Sun MC, Chen Y (2008) The attractive effects of different structural artificial reef models on juvenile Schlegel’s rockfish Sebastes schlegeli and fat greenling Hexagrammos otakii. Journal of Dalian Fisheries University, 23, 13-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张硕, 孙满昌, 陈勇 (2008) 人工鱼礁模型对大泷六线鱼和许氏平鲉幼鱼个体的诱集效果. 大连水产学院学报, 23, 13-19.] | |
| [36] | Zhang YQ (2015) Community Structure, Feeding Ecology and Movement Behaviors of Demersal Fish around Qiansan Islets. PhD dissertation, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张迎秋 (2015) 前三岛海域底层鱼类群落结构、摄食生态和运动行为特征. 博士学位论文, 中国科学院大学, 北京.] | |
| [37] | Zhou YB, Chen PM, Li HQ (2011) Feasibility study on artificial reef construction in planning area around Liuniu of Zhelin Bay in Guangdong Province. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 38(23), 10-13. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [周艳波, 陈丕茂, 李辉权 (2011) 广东省柘林湾海域溜牛礁区建礁可行性研究. 广东农业科学, 38(23), 10-13.] |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [3] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [4] | 周昊, 王茗毅, 张楚格, 肖治术, 欧阳芳. 昆虫旅馆在独栖蜂多样性保护中的现状与挑战[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24472-. |
| [5] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [6] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [7] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [8] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [9] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [10] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [11] | 徐欢, 辛凤飞, 施宏亮, 袁琳, 薄顺奇, 赵欣怡, 邓帅涛, 潘婷婷, 余婧, 孙赛赛, 薛程. 生态修复技术集成应用对长江口北支生境与鸟类多样性提升效果评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24478-. |
| [12] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [13] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [14] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [15] | 张浩斌, 肖路, 刘艳杰. 夜间灯光对外来入侵植物和本地植物群落多样性和生长的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24553-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()