



生物多样性 ›› 2016, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (3): 341-350. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2015260 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2015260
所属专题: 生物入侵
收稿日期:2015-09-23
接受日期:2016-03-11
出版日期:2016-03-20
发布日期:2016-04-05
通讯作者:
俞晓平
基金资助:
Qianqian Yang, Suwen Liu, Weidong Ru, Guangfu Liu, Xiaoping Yu*( )
)
Received:2015-09-23
Accepted:2016-03-11
Online:2016-03-20
Published:2016-04-05
Contact:
Yu Xiaoping
摘要:
外来入侵福寿螺对我国农业生产和水生生态系统平衡等造成严重危害。2010年, 种类鉴定研究首次揭示我国外来入侵福寿螺包括Pomacea canaliculata和P. maculata两个种, 而浙江省仅见P. canaliculata一种报道。P. canaliculata和P. maculata种间形态近似, 且受环境、食物源等因素影响, 同种内外壳形态特征多样, 因而基于形态特征进行种类的准确鉴定极为困难。本研究在采集浙江省7个区县的福寿螺样本的基础上, 利用DNA条形码技术扩增了101个不同个体的COI序列, 并从BOLD数据库下载了“P. canaliculata种团”的5个近缘种的55条COI序列用于分析, 其中包括P. lineata, P. dolioides和P. paludosa所有已发表序列, 以及P. canaliculata和P. maculata的南美洲样品的序列等。序列相似度比对、DNA条形码间隙和系统发育树等分析表明, COI序列可以实现近缘福寿螺的有效鉴别。待测的浙江省福寿螺样品中, 杭州江干区检测到P. canaliculata和P. maculata两种, 而舟山普陀区、绍兴上虞区和新昌县、温州瓯海区及杭州西湖区仅检测到P. canaliculata, 表明P. canaliculata在浙江省具有更广的分布范围。P. canaliculata和P. maculata分别形成4种和2种单倍型, 各区县样点分别包含1-3种单倍型, 浙江省各发生地呈现较低的遗传多样性。依据系统发育关系推测, 浙江省分布的P. canaliculata和P. maculata分别可能来源于阿根廷和巴西。
杨倩倩, 刘苏汶, 茹炜岽, 刘光富, 俞晓平 (2016) 基于DNA条形码技术对浙江省外来入侵福寿螺进行分子鉴定. 生物多样性, 24, 341-350. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2015260.
Qianqian Yang, Suwen Liu, Weidong Ru, Guangfu Liu, Xiaoping Yu (2016) Molecular identification of invasive golden apple snails in Zhejiang Province based on DNA barcoding. Biodiversity Science, 24, 341-350. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2015260.
| 编号 Code | 采集地点 Locality | 采集环境 Habitat | 采集时间 Time | 数量 No. | GenBank注册号 GenBank accession no. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZSPT | 舟山普陀区 Putuo, Zhoushan | 河道 River | 2014年8月 August, 2014 | 31 | KP310330, KP310417, KP310432-KP310435, KP310349- KP310365, KR020946, KR020947, KR020958-KR020961, KR020977, KR020978 |
| SXXC | 绍兴新昌县 Xinchang, Shaoxing | 稻田 Paddy field | 2014年10月 October, 2014 | 10 | KR020982, KR020997, KR021015-KR021020, KP310438, KR106989 |
| SXSY | 绍兴上虞区 Shangyu, Shaoxing | 稻田 Paddy field | 2015年7月 July, 2015 | 7 | KT693024-KT693030 |
| WZOH | 温州瓯海区 Ouhai, Wenzhou | 稻田 Paddy field | 2014年10月 October, 2014 | 13 | KR020970-KR020973, KR020979, KR020981, KR020993, KR021007-KR021010, KR021013, KT692988 |
| NBYY | 宁波余姚市 Yuyao, Ningbo | 稻田 Paddy field | 2014年8月 August, 2014 | 5 | KT852725, KT852726, KT852740-KT852742 |
| HZXH | 杭州西湖区 Xihu, Hangzhou | 荷塘 Lotus pond | 2015年6月 June, 2015 | 15 | KT693009-KT693023 |
| HZACA | 杭州江干区 Jianggan, Hangzhou | 荷塘 Lotus pond | 2015年6月 June, 2015 | 20 | KT692989-KT693008 |
表1 浙江省福寿螺样品采集及COI序列信息表
Table 1 Collection and COI sequence information of apple snail samples from Zhejiang
| 编号 Code | 采集地点 Locality | 采集环境 Habitat | 采集时间 Time | 数量 No. | GenBank注册号 GenBank accession no. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZSPT | 舟山普陀区 Putuo, Zhoushan | 河道 River | 2014年8月 August, 2014 | 31 | KP310330, KP310417, KP310432-KP310435, KP310349- KP310365, KR020946, KR020947, KR020958-KR020961, KR020977, KR020978 |
| SXXC | 绍兴新昌县 Xinchang, Shaoxing | 稻田 Paddy field | 2014年10月 October, 2014 | 10 | KR020982, KR020997, KR021015-KR021020, KP310438, KR106989 |
| SXSY | 绍兴上虞区 Shangyu, Shaoxing | 稻田 Paddy field | 2015年7月 July, 2015 | 7 | KT693024-KT693030 |
| WZOH | 温州瓯海区 Ouhai, Wenzhou | 稻田 Paddy field | 2014年10月 October, 2014 | 13 | KR020970-KR020973, KR020979, KR020981, KR020993, KR021007-KR021010, KR021013, KT692988 |
| NBYY | 宁波余姚市 Yuyao, Ningbo | 稻田 Paddy field | 2014年8月 August, 2014 | 5 | KT852725, KT852726, KT852740-KT852742 |
| HZXH | 杭州西湖区 Xihu, Hangzhou | 荷塘 Lotus pond | 2015年6月 June, 2015 | 15 | KT693009-KT693023 |
| HZACA | 杭州江干区 Jianggan, Hangzhou | 荷塘 Lotus pond | 2015年6月 June, 2015 | 20 | KT692989-KT693008 |
| 编号 Code | Hap1 | Hap2 | Hap3 | Hap4 | Hap5 | Hap6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZSPT | 7 | 24 | ||||
| SXXC | 1 | 9 | ||||
| SXSY | 1 | 6 | ||||
| WZOH | 9 | 2 | 2 | |||
| NBYY | 5 | |||||
| HZXH | 6 | 9 | ||||
| HZACA | 14 | 5 | 1 | |||
| 合计 Total | 43 | 2 | 35 | 15 | 5 | 1 |
表2 福寿螺各单倍型的分布数量
Table 2 Distribution of different haplotypes of two apple snail species
| 编号 Code | Hap1 | Hap2 | Hap3 | Hap4 | Hap5 | Hap6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZSPT | 7 | 24 | ||||
| SXXC | 1 | 9 | ||||
| SXSY | 1 | 6 | ||||
| WZOH | 9 | 2 | 2 | |||
| NBYY | 5 | |||||
| HZXH | 6 | 9 | ||||
| HZACA | 14 | 5 | 1 | |||
| 合计 Total | 43 | 2 | 35 | 15 | 5 | 1 |
| Hap1 | Hap2 | Hap3 | Hap4 | Hap5 | Hap6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hap1 | 27 | 28 | 28 | 60 | 61 | |
| Hap2 | 0.051 | 12 | 1 | 59 | 60 | |
| Hap3 | 0.053 | 0.020 | 13 | 57 | 58 | |
| Hap4 | 0.053 | 0.002 | 0.022 | 58 | 59 | |
| Hap5 | 0.121 | 0.120 | 0.116 | 0.118 | 13 | |
| Hap6 | 0.123 | 0.122 | 0.118 | 0.120 | 0.005 |
表3 两种福寿螺P. canaliculata和P. maculata各单倍型间的K2P遗传距离(下三角)及碱基差异数(上三角)
Table 3 K2P genetic distances (below diagonal) and number of nucleotide divergence (above diagonal) among haplotypes of P. canaliculata and P. maculata
| Hap1 | Hap2 | Hap3 | Hap4 | Hap5 | Hap6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hap1 | 27 | 28 | 28 | 60 | 61 | |
| Hap2 | 0.051 | 12 | 1 | 59 | 60 | |
| Hap3 | 0.053 | 0.020 | 13 | 57 | 58 | |
| Hap4 | 0.053 | 0.002 | 0.022 | 58 | 59 | |
| Hap5 | 0.121 | 0.120 | 0.116 | 0.118 | 13 | |
| Hap6 | 0.123 | 0.122 | 0.118 | 0.120 | 0.005 |
| 查询序列 Query sequences | BOLD比对种 BOLD species | GenBank序列号 GenBank accession no. | 相似度 Similarity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hap1 | P. canaliculata | EF514984 | 100 |
| EF513983 | 100 | ||
| EF514980 | 100 | ||
| Hap2 | P. canaliculata | FJ946822 | 100 |
| AB433759 | 100 | ||
| AB433765 | 100 | ||
| Hap3 | P. canaliculata | AB433771 | 100 |
| FJ946824 | 100 | ||
| FJ946825 | 99.84 | ||
| Hap4 | P. canaliculata | EU528578 | 100 |
| AB433762 | 100 | ||
| AB433770 | 99.85 | ||
| Hap5 | P. maculata* | GU236486 | 100 |
| GU236487 | 100 | ||
| GU236488 | 100 | ||
| Hap6 | P. maculata* | EF514986 | 99.43 |
| EU528502 | 99.43 | ||
| AB433781 | 99.43 |
表4 自测单倍型序列在BOLD中的比对相似度及鉴定结果
Table 4 Similarity of haplotypes blasted in BOLD and the identification results
| 查询序列 Query sequences | BOLD比对种 BOLD species | GenBank序列号 GenBank accession no. | 相似度 Similarity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hap1 | P. canaliculata | EF514984 | 100 |
| EF513983 | 100 | ||
| EF514980 | 100 | ||
| Hap2 | P. canaliculata | FJ946822 | 100 |
| AB433759 | 100 | ||
| AB433765 | 100 | ||
| Hap3 | P. canaliculata | AB433771 | 100 |
| FJ946824 | 100 | ||
| FJ946825 | 99.84 | ||
| Hap4 | P. canaliculata | EU528578 | 100 |
| AB433762 | 100 | ||
| AB433770 | 99.85 | ||
| Hap5 | P. maculata* | GU236486 | 100 |
| GU236487 | 100 | ||
| GU236488 | 100 | ||
| Hap6 | P. maculata* | EF514986 | 99.43 |
| EU528502 | 99.43 | ||
| AB433781 | 99.43 |
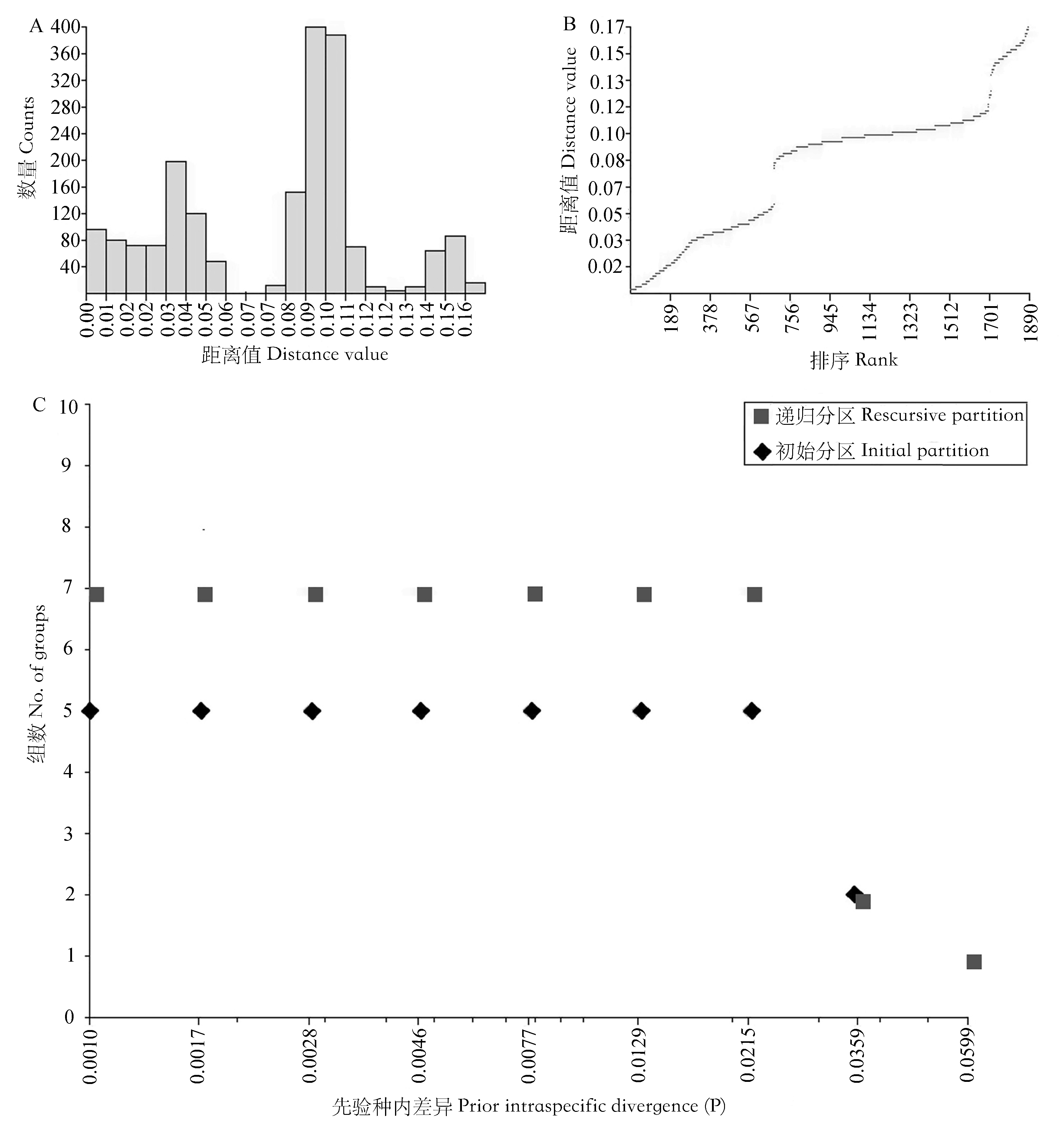
图1 基于ABGD算法计算的DNA条形码间隙及序列分组方案。COI序列两两比对的K2P距离分布的距离直方图(A)、距离排序分布图(B)以及基于先验种内差异的分区结果(C)。
Fig. 1 DNA barcoding gap and partition strategy through ABGD algorithm. Distributions of K2P distances between each pair of COI sequences, histogram of distance (A), ranked distance (B), and number of partitions obtained for each prior intraspecific divergence (C).
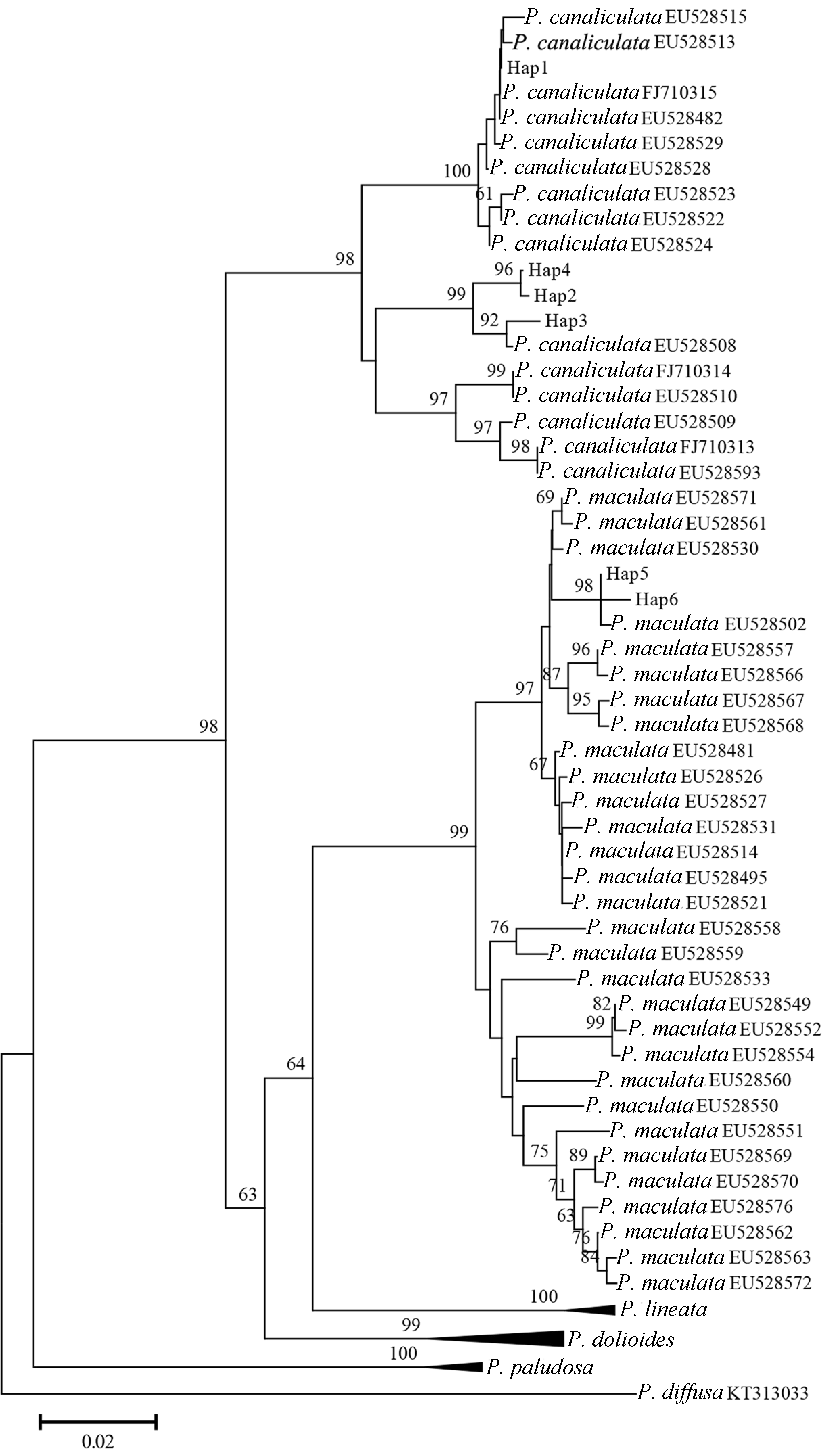
图2 基于福寿螺COI条形码序列的NJ系统发育树(仅显示置信值>60%的序列)
Fig. 2 A neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree based on COI barcode sequences of apple snails. Bootstrap values >60% were showed.
| 16 | Joshi RC, Sebastian LS (2006) Global advances in ecology and management of golden apple snails. Philippine Rice Research Institute, Munoz. |
| 17 | Li HT, Zhang BX, Gao Y, Shi XJ, Zhou P (2015) DNA barcoding in species identification of seashells: a case study in the ecological monitoring zone of Daya Bay, Guangdong. Biodiversity Science, 23, 299-305.(in Chinese) |
| [李海涛, 张保学, 高阳, 时小军, 周鹏 (2015) DNA条形码技术在海洋贝类鉴定中的实践: 以大亚湾生态监控区为例. 生物多样性, 23, 299-305.] | |
| 18 | Li XH, Hu YC, Song HM, Wang PX, Wang XJ, Mou XD, Liu C, Luo JR (2009) Invasion and monitoring methods of Pomacea canaliculata in China. China Agricultural Science Bulletin, 25(14), 229-232.(in Chinese) |
| [李小慧, 胡隐昌, 宋红梅, 王培欣, 汪学杰, 牟希东, 刘超, 罗建仁 (2009) 中国福寿螺的入侵现状及防治方法研究进展. 中国农学通报, 25(14), 229-232.] | |
| 19 | Liu YF, Li YF, Liu WH, Zeng GQ, Su WJ (2011) The distribution situation, damage and early warning on diffusion risk of golden apple snail, Pomacea canaliculata Lamark in Hunan. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 35, 1067-1071.(in Chinese) |
| [刘雨芳, 李玉峰, 刘文海, 曾国强, 苏文杰 (2011) 福寿螺在湖南的分布现状、危害与扩散风险预警. 水生生物学报, 35, 1067-1071.] | |
| 20 | Lv S, Zhang Y, Liu H, Hu L, Liu Q, Wei F, Guo Y, Steinmann P, Hu W, Zhou X, Utzinger J (2013) Phylogenetic evidence for multiple and secondary introductions of invasive snails: Pomacea species in the People’s Republic of China. Diversity and Distributions, 19, 147-156. |
| 21 | Masters BC, Fan V, Ross HA (2011) Species delimitation—a Geneious plugin for the exploration of species boundaries. Molecular Ecology Resources, 11, 154-157. |
| 22 | Matsukura K, Okuda M, Cazzaniga NJ, Wada T (2013) Genetic exchange between two freshwater apple snails, Pomacea canaliculata and Pomacea maculata invading East and Southeast Asia. Biological Invasions, 15, 2039-2048. |
| 23 | Meyer CP, Paulay G (2005) DNA barcoding: error rates based on comprehensive sampling. PLoS Biology, 3, 2229-2238. |
| 24 | Pan YY, Dong SZ, Yu XP (2009) Cloning and phylogenetic analysis of 18S rRNA and 28S rRNA genes of Pomacea canaliculata. Plant Protection, 35(1), 33-36.(in Chinese) |
| [潘颖瑛, 董胜张, 俞晓平 (2009) 福寿螺18S rRNA和28S rRNA基因片段的克隆与进化分析. 植物保护, 35(1), 33-36.] | |
| 25 | Puillandre N, Lambert A, Brouillet S, Achaz G (2012) ABGD, Automatic Barcode Gap Discovery for primary species delimitation. Molecular Ecology, 21, 1864-1877. |
| 26 | Ratnasingham S, Hebert PD (2007) BOLD: the barcode of life data system (). Molecular Ecology Notes, 7, 355-364. |
| 27 | Rawlings TA, Hayes KA, Cowie RH, Collins TM (2007) The identity, distribution, and impacts of non-native apple snails in the continental United States. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 7, 97. |
| 28 | Rubinoff D (2006) Utility of mitochondrial DNA barcodes in species conservation. Conservation Biology, 20, 1026-1033. |
| 29 | Song HM, Hu YC, Wang PH, Mou XD, Li XH, Wang XJ, Luo JR (2010) Sequencing cytochrome oxidase subunit I of mitochondrial DNA and the taxonomic status of apple snails. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 45(1), 1-7.(in Chinese) |
| [宋红梅, 胡隐昌, 王培欣, 牟希东, 李小慧, 汪学杰, 罗建仁 (2010) 福寿螺线粒体DNA COI基因序列测定及分类地位. 动物学杂志, 45(1), 1-7.] | |
| 30 | Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 28, 2731-2739. |
| 31 | Wan FH, Guo JY, Zhang F (2009) Research on Biological Invasions in China. Science Press, Beijing.(in Chinese) |
| [万方浩, 郭建英, 张峰 (2009) 中国生物入侵研究. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 32 | Wang T, Zhang YP, Guan LH, Du YY, Lou ZY, Jiao WL (2015) Current freshwater fish resources and the application of DNA barcoding in species identification in Gansu Province. Biodiversity Science, 23, 306-313.(in Chinese) |
| [王太, 张艳萍, 管丽红, 杜岩岩, 娄忠玉, 焦文龙 (2015) 甘肃省鱼类资源现状及DNA条形码在鱼类物种鉴定中的应用. 生物多样性, 23, 306-313.] | |
| 33 | Xu JR, Han XL, Li N, Yu JF, Qian CH, Bao ZM (2009) Analysis of genetic diversity of three geographic populations of Pomacea canaliculata by AFLP. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 29, 4119-4126.(in Chinese) |
| [徐建荣, 韩晓磊, 李宁, 郁建锋, 钱春花, 包振民 (2009) 福寿螺3个地理群体遗传多样性的AFLP分析. 生态学报, 29, 4119-4126.] | |
| 34 | Xu Y, Zheng G, Dong S, Liu G, Yu X (2014) Molecular cloning, characterization and expression analysis of HSP60, HSP70 and HSP90 in the golden apple snail, Pomacea canaliculata. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 41, 643-653. |
| 35 | Yang TB, Wu ZD, Lun ZR (2013) The apple snail Pomacea canaliculata, a novel vector of the rat lungworm, Angiostrongylus cantonensis: its introduction, spread, and control in China. Hawai’i Journal of Medicine & Public Health, 72, 23. |
| 36 | Yang QQ, Wang ZL, Liu GF, Yu XP (2014) Advance of molecular biology of invasive golden apple snail species in China. Journal of China University of Metrology, 25, 122-128.(in Chinese) |
| 1 | Cowie RH (2002) Apple snails (Ampullariidae) as agricultural pests: their biology, impacts and management. In: Molluscs as Crop Pests (ed. Barker G), pp. 145-192. CABI Publishing, Wallingford. |
| 2 | Dong S, Shentu X, Pan Y, Bai Y, Yu X, Wang H (2013) Evaluation of genetic diversity in the golden apple snail, Pomacea canaliculata (Lamarck), from different geographical populations in China by inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR). African Journal of Biotechnology, 10, 1777-1783. |
| 36 | [杨倩倩, 王正亮, 刘光富, 俞晓平 (2014) 我国外来入侵种福寿螺分子生物学研究进展. 中国计量学院学报, 25, 122-128.] |
| 37 | Yang YX, Hu YC, Li XH, Wang XJ, Mou XD, Song HM, Wang PX, Liu C, Luo JR (2010) Historical invasion, expansion process and harm investigation of Pomacea canaliculata in China. China Agricultural Science Bulletin, 26(5), 245-250.(in Chinese) |
| 3 | Dong S, Zheng G, Yu X, Fu C (2012) Biological control of golden apple snail, Pomacea canaliculata by Chinese soft-shelled turtle, Pelodiscus sinensis in the wild rice, Zizania latifolia field. Scientia Agricola, 69, 142-146. |
| 4 | Folmer O, Black M, Hoeh W, Lutz R, Vrijenhoek R (1994) DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Molecular Marine Biology and Biotechnology, 3, 294-299. |
| 37 | [杨叶欣, 胡隐昌, 李小慧, 汪学杰, 牟希东, 宋红梅, 王培欣, 刘超, 罗建仁 (2010) 福寿螺在中国的入侵历史、扩散规律和危害的调查分析. 中国农学通报, 26(5), 245-250.] |
| 38 | Yu XP, Wada T, Li ZF, Lv ZX, Sun LP, Zhu YH, Chen JM, Zheng XS, Xu HX (2001) Occurrence of golden apple snail, Pomacea canaliculata (Lamarck), in paddy fields and its management. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 13, 247-252.(in Chinese) |
| 5 | Frézal L, Leblois R (2008) Four years of DNA barcoding: current advances and prospects. Infection, Genetics and Evolution, 8, 727-736. |
| 6 | Funk DJ, Omland KE (2003) Species-level paraphyly and polyphyly: frequency, causes, and consequences, with insights from animal mitochondrial DNA. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 34, 397-423. |
| 38 | [俞晓平, 和田节, 李中方, 吕仲贤, 孙乐平, 朱亚红, 陈建明, 郑许松, 徐红星 (2001) 稻田福寿螺的发生和治理. 浙江农业学报, 13, 247-252. ] |
| 39 | Yusa Y, Wada T (1999) Impact of the introduction of apple snails and their control in Japan, Naga. The ICLARM Quarterly, 22, 9-13. |
| 7 | Gao LM (2015) Applications of DNA barcoding in biodiversity inventory and assessment. Biodiversity Science, 23, 286-287.(in Chinese) |
| [高连明 (2015) DNA条形码在生物多样性编目与评价中的应用. 生物多样性, 23, 286-287.] | |
| 8 | Halwart M (1994) The golden apple snail Pomacea canaliculata in Asian rice farming systems: present impact and future threat. International Journal of Pest Management, 40, 199-206. |
| 9 | Hayes KA, Joshi RC, Thiengo SC, Cowie RH (2008) Out of South America: multiple origins of non-native apple snails in Asia. Diversity and Distributions, 14, 701-712. |
| 10 | Hayes KA, Burks RL, Castro-Vazquez A, Darby PC, Heras H, Martín PR, Qiu JW, Thiengo SC, Vega IA, Wada T (2015) Insights from an integrated view of the biology of apple snails (Caenogastropoda: Ampullariidae). Malacologia, 58, 245-302. |
| 11 | Hayes KA, Cowie RH, Thiengo SC (2009) A global phylogeny of apple snails: gondwanan origin, generic relationships, and the influence of outgroup choice (Caenogastropoda: Ampullariidae). Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 98, 61-76. |
| 12 | Hayes KA, Cowie RH, Thiengo SC, Strong EE (2012) Comparing apples with apples: clarifying the identities of two highly invasive Neotropical Ampullariidae (Caenogastropoda). Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, 166, 723-753. |
| 13 | Hebert PD, Cywinska A, Ball SL (2003) Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences, 270, 313-321. |
| 14 | Hebert PD, Stoeckle MY, Zemlak TS, Francis CM (2004) Identification of birds through DNA barcodes. PLoS Biology, 2, 1657-1663. |
| 15 | Hu Y, Mu X, Luo D, Xu M, Yang Y, Gu D, Luo J, Zhang J (2014) Genetic variability of the invasive snail Pomacea canaliculata in South China based on mitochondrial 16S rDNA sequences. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology, 57, 203-209. |
| [1] | 范平, 温知新, 宋刚. 气候因子和人类活动对两栖及哺乳动物不同遗传多样性指标的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(8): 25022-. |
| [2] | 薛瑞翔, 马雪蓉, 吴炯文, 刘爱君, 张细权, 季从亮, 殷颖珊, 朱炜健, 罗庆斌. 中山麻鸭群体遗传多样性与遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(8): 24592-. |
| [3] | 范平, 王欢, 温知新, 宋刚, 雷富民. 气候因子对鸟类遗传多样性与物种分布面积关系的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(8): 25072-. |
| [4] | 周智成, 曹天玲, 刘如垚, 丁琪琪, 马轲, 杨丽萍, 周传江, 聂国兴, 汤永涛. 基于线粒体COI基因的黄河流域麦穗鱼种群遗传多样性与遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(8): 24501-. |
| [5] | 王儒晓, 史博洋, 潘达, 孙红英. 中国特有华溪蟹属淡水蟹多样性格局及其保护空缺[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(8): 25123-. |
| [6] | 王嘉陈, 徐汤俊, 许唯, 张高季, 尤艺瑾, 阮宏华, 刘宏毅. 城市景观格局对大蚰蜒种群遗传结构的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24251-. |
| [7] | 龙诗怡, 张博博, 夏宇辰, 费杨帆, 孟亚妮, 吕冰薇, 宋月青, 郑普, 郭陶然, 张健, 黎绍鹏. 本地群落多样性和时间稳定性对加拿大一枝黄花生物量的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24263-. |
| [8] | 冯晨, 张洁, 黄宏文. 统筹植物就地保护与迁地保护的解决方案: 植物并地保护(parallel situ conservation)[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23184-. |
| [9] | 李庆多, 栗冬梅. 全球蝙蝠巴尔通体流行状况分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23166-. |
| [10] | 齐海玲, 樊鹏振, 王跃华, 刘杰. 中国北方六省区胡桃的遗传多样性和群体结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23120-. |
| [11] | 熊飞, 刘红艳, 翟东东, 段辛斌, 田辉伍, 陈大庆. 基于基因组重测序的长江上游瓦氏黄颡鱼群体遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22391-. |
| [12] | 蒲佳佳, 杨平俊, 戴洋, 陶可欣, 高磊, 杜予州, 曹俊, 俞晓平, 杨倩倩. 长江下游外来生物福寿螺的种类及其种群遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22346-. |
| [13] | 何艺玥, 刘玉莹, 张富斌, 秦强, 曾燏, 吕振宇, 杨坤. 梯级水利工程背景下的嘉陵江干流蛇鮈群体遗传多样性和遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23160-. |
| [14] | 孙维悦, 舒江平, 顾钰峰, 莫日根高娃, 杜夏瑾, 刘保东, 严岳鸿. 基于保护基因组学揭示荷叶铁线蕨的濒危机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21508-. |
| [15] | 陶克涛, 白东义, 图格琴, 赵若阳, 安塔娜, 铁木齐尔·阿尔腾齐米克, 宝音德力格尔, 哈斯, 芒来, 韩海格. 基于基因组SNPs对东亚家马不同群体遗传多样性的评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21031-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()