



Biodiv Sci ›› 2012, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (1): 51-58. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2012.08168 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2012.08168
• Original Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Hui Wang1, Baowei Zhang1,*( ), Wenbo Shi1, Xia Luo1, Lizhi Zhou1, Demin Han1, Qing Chang2
), Wenbo Shi1, Xia Luo1, Lizhi Zhou1, Demin Han1, Qing Chang2
Received:2011-09-02
Accepted:2011-10-16
Online:2012-01-20
Published:2012-02-14
Contact:
Baowei Zhang
Hui Wang, Baowei Zhang, Wenbo Shi, Xia Luo, Lizhi Zhou, Demin Han, Qing Chang. Structural characteristics of di-nucleotide/tetra-nucleotide repeat microsatellite DNA in Pachyhynobius shangchengensisgenomes and its effect on isolation[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2012, 20(1): 51-58.
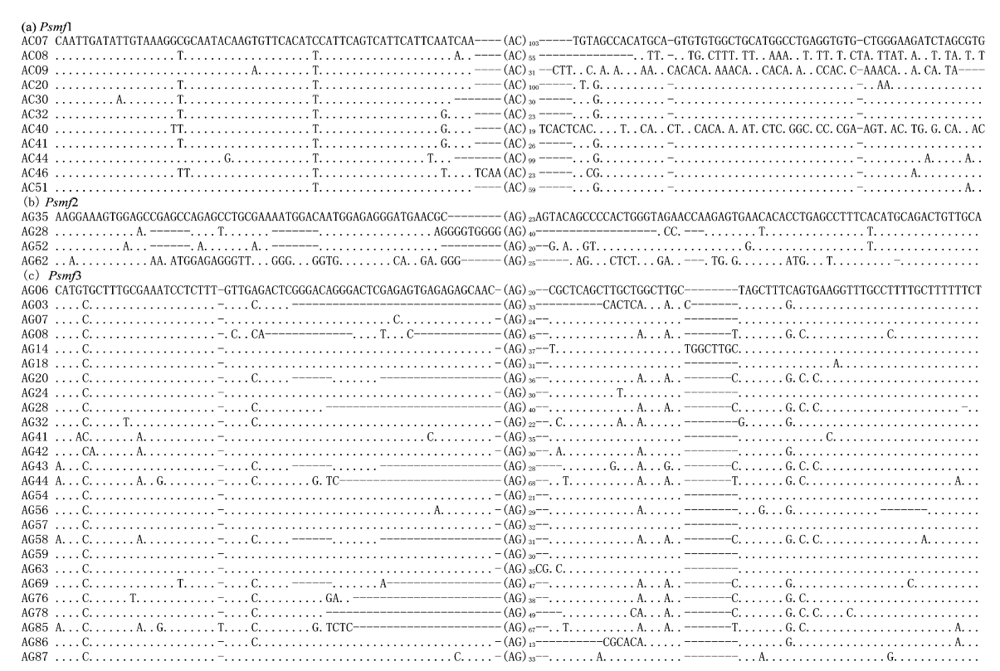
Fig. 1 Structure of three microsatellite DNA families in the present study. Only core region and partial homologous flanking sequences were shown. The dots indicate the nucleotide identical to those in first sequence, and the short strings (-) are the alignment gaps.
| 序列组 Sequence set | 包含的序列数目 Sequence number | 长度范围 Size range | 序列间的遗传距离范围 Range of genetic distance among sequence | 序列间平均的遗传距离 Average genetic distance among sequence | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Psmf1上游侧翼序列 Upstream flanking sequence ofPsmf1 | 11 | 165-438 | 0.016-0.084 | 0.042 | |||
| Psmf1下游侧翼序列 Downstream flanking sequence ofPsmf1 | 11 | 52-482 | - | - | |||
| Psmf2上游侧翼序列 Upstream flanking sequence ofPsmf2 | 4 | 277-297 | 0.109-0.253 | 0.174 | |||
| Psmf2下游侧翼序列 Downstream flanking sequence ofPsmf2 | 4 | 79-140 | 0.090-0.295 | 0.159 | |||
| Psmf3上游侧翼序列 Upstream flanking sequence ofPsmf3 | 26 | 314-500 | 0.021-0.416 | 0.168 | |||
| Psmf3下游侧翼序列 Downstream flanking sequence ofPsmf3 | 26 | 60-85 | 0-0.210 | 0.091 | |||
Table 1 The genetic variation of flanking sequence sets from three microsatellite DNA families in the present study
| 序列组 Sequence set | 包含的序列数目 Sequence number | 长度范围 Size range | 序列间的遗传距离范围 Range of genetic distance among sequence | 序列间平均的遗传距离 Average genetic distance among sequence | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Psmf1上游侧翼序列 Upstream flanking sequence ofPsmf1 | 11 | 165-438 | 0.016-0.084 | 0.042 | |||
| Psmf1下游侧翼序列 Downstream flanking sequence ofPsmf1 | 11 | 52-482 | - | - | |||
| Psmf2上游侧翼序列 Upstream flanking sequence ofPsmf2 | 4 | 277-297 | 0.109-0.253 | 0.174 | |||
| Psmf2下游侧翼序列 Downstream flanking sequence ofPsmf2 | 4 | 79-140 | 0.090-0.295 | 0.159 | |||
| Psmf3上游侧翼序列 Upstream flanking sequence ofPsmf3 | 26 | 314-500 | 0.021-0.416 | 0.168 | |||
| Psmf3下游侧翼序列 Downstream flanking sequence ofPsmf3 | 26 | 60-85 | 0-0.210 | 0.091 | |||
| 位点名称 Loci | 核心序列重复单元 Repeated core units | 引物序列(上游/下游) Primer sequence (Upper primer/down primer) | 扩增结果 PCR result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Psh110 | AC16 | 5′-CACCGCTGACCTGGACACTT-3′ ∕ 5′-GTGACTGACAGCTAGGGAAG-3′ | 单带 Single band |
| Psh116 | AC21 | 5′-CAAGAGGCAATGAATGTGAG-3′ ∕ 5′-TACTATGTCCCATCTTC-3′ | 单带 Single band |
| Psh118 | AC12 | 5′-GGTGGTTCTCTGGAGTGTTG-3′ ∕ 5′-TGGTCCTCCAGTCTCACAGC-3′ | 单带 Single band |
| Psh124 | AC15 | 5′-CACGGATCTCGGAAGCT-3′ ∕ 5′-AGAATAAAGTAACCTCAATG-3′ | 单带 Single band |
| Psh131 | AC16 | 5′-TATTCCCTTTCCTACTCCT-3′ ∕ 5′-AACAGACCCATGATAAGAGC-3′ | 单带 Single band |
| Psh135 | AC22 | 5′-AGGAAAGAGCTCCACCAAG-3′ ∕ 5′-GTGAAAGAAGAGAAGCAGAG-3′ | 单带 Single band |
| Psh138 | AC29 | 5′-CTCCTATTTCCTCCTCAGAC-3′ ∕ 5′-AAGGGTGTAGGCTGAGAG-3′ | 弥散带 Smear |
| Psh143 | AC21 | 5′-TGTGTGGGCTCTGCATTTAC-3′ ∕ 5′-CAGGATGGGGGAAAATATAC-3′ | 单带 Single band |
| Psh209 | AG19 | 5′-CACATTTATACGGACACCAC-3′ ∕ 5′-TCCACATTTTTACAGCCAGG-3′ | 单带 Single band |
| Psh211 | AG28 | 5′-TGAGGAGTTCCCCTAAGCAC-3′ ∕ 5′-GGTGAACGGAAAAGGATTAC-3′ | 多带 Multi-band |
| Psh216 | AG27 | 5′-AACAGAGGCAATGTCCACAC-3′ ∕ 5′-CAACAGTCTGCATGTGAAAG-3′ | 单带 Single band |
| Psh229 | AG43 | 5′-TTTTTGGGACTCTGCCTCTC-3′ ∕ 5′-CTATAGGGCTATGAAG-3′ | 无法扩增 No band |
| Psh230 | AG27 | 5′-ACAGGGTAGGAAGGCAGTAG-3′ ∕ 5′-AGTAAGGGAGAGAAAAAAGC-3′ | 弥散带 Smear |
| Psh238 | AG28 | 5′-TCGCTCGCTCACCCATTCAC-3′ ∕ 5′-GCAGGGGATTGAGATAGTTG-3′ | 多带 Single band |
| Psh245 | AG53 | 5′-CTGTTTCTTTAGAGTGAGTG-3′ ∕ 5′-GGTAGCAAGTTTGATAAGTG-3′ | 单带 Single band |
| Psh246 | AG34 | 5′-TAGGCATCAACTAAGGGGAC-3′ ∕ 5′-TGTTCCATATTTGGGACTGG-3′ | 单带 Single band |
| Psh248 | AG37 | 5′-AGGTATTGTGCGGAACGATC-3′ ∕ 5′-TGGACTGTTTTTGCCACCAG-3′ | 单带 Single band |
| Psh228 | AG40 | 5′-GAAAATGGAGAGGGATGAAC-3′ ∕ 5′-ACAGTCTGCATGAGAAAGGC-3′ | 单带 Single band |
| Psh150 | AC30 | 5′-TAAATGTGAGTCCAGCAAAC-3′ ∕ 5′-CGATTTGAGTATTTGGGTAG-3′ | 单带 Single band |
| Psh274 | AG52 | 5′-GGTGAGCCCTTGAGTTTGAG-3′ ∕ 5′-GCCGCTTCACATTAGTTTTC-3′ | 无法扩增 No band |
| Psh207 | AG24 | 5′-TCTTTGTTGAGACTCGGGAC-3′ ∕ 5′-AAAGCAAAAGGCAAACC-3′ | 弥散带 Smear |
Table 2 The core repeat units in different microsatellite loci, designed primer sequences and their PCR results
| 位点名称 Loci | 核心序列重复单元 Repeated core units | 引物序列(上游/下游) Primer sequence (Upper primer/down primer) | 扩增结果 PCR result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Psh110 | AC16 | 5′-CACCGCTGACCTGGACACTT-3′ ∕ 5′-GTGACTGACAGCTAGGGAAG-3′ | 单带 Single band |
| Psh116 | AC21 | 5′-CAAGAGGCAATGAATGTGAG-3′ ∕ 5′-TACTATGTCCCATCTTC-3′ | 单带 Single band |
| Psh118 | AC12 | 5′-GGTGGTTCTCTGGAGTGTTG-3′ ∕ 5′-TGGTCCTCCAGTCTCACAGC-3′ | 单带 Single band |
| Psh124 | AC15 | 5′-CACGGATCTCGGAAGCT-3′ ∕ 5′-AGAATAAAGTAACCTCAATG-3′ | 单带 Single band |
| Psh131 | AC16 | 5′-TATTCCCTTTCCTACTCCT-3′ ∕ 5′-AACAGACCCATGATAAGAGC-3′ | 单带 Single band |
| Psh135 | AC22 | 5′-AGGAAAGAGCTCCACCAAG-3′ ∕ 5′-GTGAAAGAAGAGAAGCAGAG-3′ | 单带 Single band |
| Psh138 | AC29 | 5′-CTCCTATTTCCTCCTCAGAC-3′ ∕ 5′-AAGGGTGTAGGCTGAGAG-3′ | 弥散带 Smear |
| Psh143 | AC21 | 5′-TGTGTGGGCTCTGCATTTAC-3′ ∕ 5′-CAGGATGGGGGAAAATATAC-3′ | 单带 Single band |
| Psh209 | AG19 | 5′-CACATTTATACGGACACCAC-3′ ∕ 5′-TCCACATTTTTACAGCCAGG-3′ | 单带 Single band |
| Psh211 | AG28 | 5′-TGAGGAGTTCCCCTAAGCAC-3′ ∕ 5′-GGTGAACGGAAAAGGATTAC-3′ | 多带 Multi-band |
| Psh216 | AG27 | 5′-AACAGAGGCAATGTCCACAC-3′ ∕ 5′-CAACAGTCTGCATGTGAAAG-3′ | 单带 Single band |
| Psh229 | AG43 | 5′-TTTTTGGGACTCTGCCTCTC-3′ ∕ 5′-CTATAGGGCTATGAAG-3′ | 无法扩增 No band |
| Psh230 | AG27 | 5′-ACAGGGTAGGAAGGCAGTAG-3′ ∕ 5′-AGTAAGGGAGAGAAAAAAGC-3′ | 弥散带 Smear |
| Psh238 | AG28 | 5′-TCGCTCGCTCACCCATTCAC-3′ ∕ 5′-GCAGGGGATTGAGATAGTTG-3′ | 多带 Single band |
| Psh245 | AG53 | 5′-CTGTTTCTTTAGAGTGAGTG-3′ ∕ 5′-GGTAGCAAGTTTGATAAGTG-3′ | 单带 Single band |
| Psh246 | AG34 | 5′-TAGGCATCAACTAAGGGGAC-3′ ∕ 5′-TGTTCCATATTTGGGACTGG-3′ | 单带 Single band |
| Psh248 | AG37 | 5′-AGGTATTGTGCGGAACGATC-3′ ∕ 5′-TGGACTGTTTTTGCCACCAG-3′ | 单带 Single band |
| Psh228 | AG40 | 5′-GAAAATGGAGAGGGATGAAC-3′ ∕ 5′-ACAGTCTGCATGAGAAAGGC-3′ | 单带 Single band |
| Psh150 | AC30 | 5′-TAAATGTGAGTCCAGCAAAC-3′ ∕ 5′-CGATTTGAGTATTTGGGTAG-3′ | 单带 Single band |
| Psh274 | AG52 | 5′-GGTGAGCCCTTGAGTTTGAG-3′ ∕ 5′-GCCGCTTCACATTAGTTTTC-3′ | 无法扩增 No band |
| Psh207 | AG24 | 5′-TCTTTGTTGAGACTCGGGAC-3′ ∕ 5′-AAAGCAAAAGGCAAACC-3′ | 弥散带 Smear |
| [1] |
Benson G (1999) Tandem repeats finder: a program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Research, 27,573-580.
DOI URL PMID |
| [2] |
Bruford MW, Wayne RK (1993) Microsatellites and their application to population genetic studies. Current Opinion in Genetics and Development, 3,939-943.
URL PMID |
| [3] | Chen BH (陈壁辉) (1991) The Amphibian and Reptilian Fauna of Anhui (安徽两栖爬行动物志), pp.34-36. Anhui Science and Technology Publishing House, Hefei. (in Chinese) |
| [4] |
Devitt TJ, Pereira R, Jakkula L, Alexandrino J, Bardeleben C, Moritz C (2009) Isolation and characterization of 15 polymorphic microsatellites in the Plethodontid salamander Ensatina eschscholtzii. Molecular Ecology Resources, 9,966-969.
URL PMID |
| [5] | Fei L (费梁), Qu WY (瞿文元), Wu SH (吴淑辉) (1985) Description of a new genus and species of Hynobiidae of China. Zoological Research (动物学研究), 6,389-404. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [6] | Fei L (费梁), Ye CY (叶昌媛), Huang YS (黄永韶) (2005) An Illustrated Key to Chinese Amphibians (中国两栖动物检索及图解), p. 23. Sichuan Publishing House of Science and Technology, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [7] |
Garner TWJ (2002) Genome size and microsatellites: the effect of nuclear size on amplification potential. Genome, 45,212-215.
URL PMID |
| [8] | Gonser RA, Collura RV (1996) Waste not, want not: toe-clips as a source of DNA. Journal of Herpetology, 30,445-447. |
| [9] | Gregory TR, Nicol JA, Tamm H, Kullman B, Kullman K, Leitch IJ, Murray BG, Kapraun DF, Greilhuber J, Bennett MD (2007) Eukaryotic genome size databases. Nucleic Acids Research, 35,D332-D338. |
| [10] |
Jarne P, Lagoda PJL (1996) Microsatellites, from molecules to populations and back. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 11,424-429.
URL PMID |
| [11] | Ji YJ (吉亚杰), Zhang DX (张德兴) (2004) Characteristics of microsatellite DNA in lepidopteran genomes and implications for their isolation. Acta Zoologica Sinica (动物学报), 50,608-614. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [12] |
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (2004) MEGA: integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 5,150-163.
DOI URL PMID |
| [13] | Lalitha S (2000) Primer Premier 5. Biotech Software and Internet Report, 1,270-272. |
| [14] |
Purrenhage JL, Niewiarowski PH, Moore FBG (2009) Population structure of spotted salamanders ( Ambystoma maculatum) in a fragmented landscape. Molecular Ecology, 18,235-247.
URL PMID |
| [15] | Rowe G, Beebee TJC, Burke T (2000) A microsatellite analysis of natterjack toad (Bufo calamita), metapopulations. Oikos, 88,641-651. |
| [16] | Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1999) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd edn, pp.463-469. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York. |
| [17] |
Schuler GD, Boguski MS, Stewart EA, Stein LD, Gyapay G, Rice K, White RE, Rodriguez-Tomé P, Aggarwal A, Bajorek E, Bentolila S, Birren BB, Butler A, Castle AB, Chiannilkulchai N, Chu A, Clee C, Cowles S, Day PJR, Dibling T, Drouot N, Dunham I, Duprat S, East C, Edwards C, Fan JB, Fang N, Fizames C, Garrett C, Green L, Hadley D, Harris M, Harrison P, Brady S, Hicks A, Holloway E, Hui L, Hussain S, Louis-Dit-Sully C, Ma J, MacGilvery A, Mader C, Maratukulam A, Matise TC, McKusick KB, Morissette J, Mungall A, Muselet D, Nusbaum HC, Page DC, Peck A, Perkins S, Piercy M, Qin F, Quackenbush J, Ranby S, Reif T, Rozen S, Sanders C, She X, Silva J, Slonim DK, Soderlund C, Sun WL, Tabar P, Thangarajah T, Vega-Czarny N, Vollrath D, Voyticky S, Wilmer T, Wu X, Adams MD, Auffray C, Walter NAR, Brandon R, Dehejia A, Goodfellow PN, Houlgatte R, Hudson JR Jr, Ide SE, Iorio KR, Lee WY, Seki N, Nagase T, Ishikawa K, Nomura N, Phillips C, Polymeropoulos MH, Sandusky M, Schmitt K, Berry R, Swanson K, Torres R, Venter JC, Sikela JM, Beckmann JS, Weissenbach J, Myers RM, Cox DR, James MR, Bentley D, Deloukas P, Lander ES, Hudson TJ (1996) A gene map of the human genome. Science, 274,540-546.
URL PMID |
| [18] | Sequeira F, Rocha S, Ferrand N, Weiss S (2005) Isolation and characterization of seven microsatellite loci in Chioglossa lusitanica (Urodela: Salamandridae). Molecular Ecology Notes, 5,212-214. |
| [19] |
Singh VK, Mangalam AK, Dwivedi S, Naik S (1998) Primer premier: program for design of degenerate primers from a protein sequence. Biotechniques, 24,318-319.
URL PMID |
| [20] |
Tay WT, Behere GT, Batterham P, Heckel DG (2010) Generation of microsatellite repeat families by RTE retrotransposons in lepidopteran genomes. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 10,144.
DOI URL PMID |
| [21] |
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Research, 25,4876-4882.
URL PMID |
| [22] |
Tóth G, Gáspári Z, Jurka J (2000) Microsatellites in different eukaryotic genomes: survey and analysis. Genome Research, 10,967-981.
URL PMID |
| [23] | van de Vliet MS, Diekmann OE, Serrão ETA, Beja P (2009) Isolation of highly polymorphic microsatellite loci for a species with a large genome size: sharp-ribbed salamander (Pleurodeles waltl). Molecular Ecology Resources, 9,425-428. |
| [24] | van Dongen S, Backeljau T, Matthysen E, Dhondt AA (1998) Genetic population structure of the winter moth ( Operophtera brumata L.) (Lepidoptera, Geometridae) in a fragmented landscape. Heredity, 80,92-100. |
| [25] |
Wang IJ, Savage WK, Shaffer HB (2009) Landscape genetics and least-cost path analysis reveal unexpected dispersal routes in the California tiger salamander (Ambystoma californiense). Molecular Ecology, 18,1365-1374.
DOI URL PMID |
| [26] |
Zane L, Bargelloni L, Patarnello T (2002) Strategies for microsatellite isolation: a review. Molecular Ecology, 11,1-16.
URL PMID |
| [27] | Zhang DX (2004) Lepidopteran microsatellite DNA: redundant but promising. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 19,507-509. |
| [28] | Zhang P, Chen YQ, Zhou H, Liu YF, Wang XL, Papenfuss TJ, Wake DB, Qu LH (2006) Phylogeny, evolution, and biogeography of Asiatic salamanders (Hynobiidae). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 103,7360-7365. |
| [1] | Hailing Qi, Pengzhen Fan, Yuehua Wang, Jie Liu. Genetic diversity and population structure of Juglans regia from six provinces in northern China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(8): 23120-. |
| [2] | Xiaofeng Niu, Xiaomei Wang, Yan Zhang, Zhipeng Zhao, Enyuan Fan. Integration and application of sturgeon identification methods [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(6): 22034-. |
| [3] | Junwei Ye, Bin Tian. Genetic structure and its causes of an important woody oil plant in Southwest China, Prinsepia utilis (Rosaceae) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(12): 1629-1637. |
| [4] | Chao Li,Jinjin Jin,Jinzhen Luo,Chunhui Wang,Junjie Wang,Jun Zhao. Genetic relationships of hatchery populations and wild populations of Tanichthys albonubes near Guangzhou [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(4): 474-484. |
| [5] | Jianhua Xue, Li Jiang, Xiaolin Ma, Yanhong Bing, Sichen Zhao, Keping Ma. Identification of lotus cultivars using DNA fingerprinting [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(1): 3-11. |
| [6] | Changhuan He, Yu Zhou, Lifan Wang, Li Zhang. Estimating population size and genetic diversity of Asian elephant in the Shangyong Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2015, 23(2): 202-209. |
| [7] | Min Xiong, Shuang Tian, Zhirong Zhang, Dengmei Fan, Zhiyong Zhang. Population genetic structure and conservation units of Sinomanglietia glauca (Magnoliaceae) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2014, 22(4): 476-484. |
| [8] | Deyun Wang,Jie Peng,Yajing Chen,Guosheng Lü,Xiaoping Zhang,Jianwen Shao. Genetic diversity and genetic structure of the rare and endangered species, Primula ranunculoides [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2013, 21(5): 601-609. |
| [9] | Yafeng Wen,Kentaro Uchiyama,Wenjun Han,Saneyoshi Ueno,Weidong Xie,Gangbiao Xu,Yoshihiko Tsumura. Null alleles in microsatellite markers [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2013, 21(1): 117-126. |
| [10] | Xia Wang, Jing Wang, Jinghu Jiang, Ming Kang. Genetic diversity and the mating system in a fragmented population of Tsoongiodendron odorum [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2012, 20(6): 676-684. |
| [11] | Xiaohong He, Xiuli Han, Weijun Guan, Kechuan Tian, Wenbin Zhang, Yuehui Ma. Genetic variability and relationship of 10 Bactrian camel populations revealed by microsatellite markers [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2012, 20(2): 199-206. |
| [12] | Zhenzhen Liu, Xiuying Guo, Baoyu Li, Ming Wang, Xi Wang, Keliang Wu. An assessment of the Central-China pig genetic diversity using Weitzman approach [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2010, 18(4): 408-413. |
| [13] | Lingliang Cao, Lizhi Zhou, Baowei Zhang. Genetic patterns of an invasive Procambarus clarkii population in the three river basins of Anhui Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2010, 18(4): 398-407. |
| [14] | Changzhong Wang, Zhong Li, Hongwei Liang, Guangfu Hu, Qinchao Wu, Guiwei Zou, Xiangzhong Luo. Genetic diversity in fourProcambarus clarkii populations in the lower reaches of the Yangtze River [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2009, 17(5): 518-523. |
| [15] | Hua Tian, Ming Kang, Li Li, Xiaohong Yao, Hongwen Huang. Genetic diversity in natural populations of Castanea mollissima inferred from nuclear SSR markers [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2009, 17(3): 296-302. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()