



生物多样性 ›› 2020, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (3): 296-302. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019099 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019099
陈俊,姚兰( ),艾训儒,朱江,吴漫玲,黄小,陈思艺,王进,朱强
),艾训儒,朱江,吴漫玲,黄小,陈思艺,王进,朱强
收稿日期:2019-03-24
接受日期:2019-05-16
出版日期:2020-03-20
发布日期:2019-09-27
通讯作者:
姚兰
基金资助:
Jun Chen,Lan Yao( ),Xunru Ai,Jiang Zhu,Manling Wu,Xiao Huang,Siyi Chen,Jin Wang,Qiang Zhu
),Xunru Ai,Jiang Zhu,Manling Wu,Xiao Huang,Siyi Chen,Jin Wang,Qiang Zhu
Received:2019-03-24
Accepted:2019-05-16
Online:2020-03-20
Published:2019-09-27
Contact:
Lan Yao
摘要:
植物的功能性状变异和表型可塑性是其应对异质生境的主要机制, 对植物的生长和分布有重要贡献。本文以湖北星斗山国家级自然保护区的水杉(Metasequoia glyptostroboides)原生母树为研究对象, 分析了母树种群功能性状对树木形态、地形因子及人为干扰的响应机制。结果表明: 水杉原生母树叶面积、叶干重和比叶面积的变异幅度大, 可塑性较强, 而枝和叶的干物质含量稳定性最高。人为干扰和4个地形因子均对每个功能性状变异方差有5%-20%的解释度, 冠幅对枝、叶干物质含量的变异方差有高达38%和76%的解释度。5个功能性状主要受海拔、坡位和人为干扰影响, 其中, 比叶面积对环境因子和干扰的响应规律不明显, 叶面积和叶干重在强烈人为干扰的环境中普遍增大, 枝和叶的干物质含量对坡向的变化最敏感。总之, 水杉原生母树种群通过功能性状变异对环境能产生一定的可塑性响应, 但人为干扰对母树生长影响较大, 建议人工辅助更新, 并适度减少农业和建筑对现存母树的影响。
陈俊, 姚兰, 艾训儒, 朱江, 吴漫玲, 黄小, 陈思艺, 王进, 朱强 (2020) 基于功能性状的水杉原生母树种群生境适应策略. 生物多样性, 28, 296-302. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019099.
Jun Chen, Lan Yao, Xunru Ai, Jiang Zhu, Manling Wu, Xiao Huang, Siyi Chen, Jin Wang, Qiang Zhu (2020) Adaptive strategies of functional traits of Metasequoia glyptostroboides parent trees to changing habitats. Biodiversity Science, 28, 296-302. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019099.
| 性状 Trait | 平均值 ± 标准差 Mean ± SD | 最小值 Minimum | 最大值 Maximum | 中值 Median | 偏度 Sewness | 峰度 Kurtosis | 变异系数 Coefficient of variation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶干重 Leaf dry weight (g) | 0.229 ± 0.085 | 0.096 | 0.889 | 0.210 | 17,406.545 | 11.361 | 37.172 |
| 叶面积 Leaf area (cm2) | 28.316 ± 5.813 | 5.419 | 61.215 | 28.903 | 6,389.909 | 2.264 | 20.389 |
| 比叶面积 Specific leaf area (cm2/g) | 11.6 ± 3.735 | 1.915 | 32.454 | 11.322 | 4,838.621 | 0.983 | 32.121 |
| 叶干物质含量 Leaf dry matter content (g/g) | 0.242 ± 0.045 | 0.129 | 0.430 | 0.237 | 4,740.165 | 0.902 | 18.358 |
| 枝干物质含量 Twig dry matter content (g/g) | 0.415 ± 0.038 | 0.283 | 0.618 | 0.415 | 5,497.453 | 1.527 | 9.059 |
表1 水杉原生母树功能性状及其变异
Table 1 Functional trait and its variance of Metasequoia glyptostroboides parent trees
| 性状 Trait | 平均值 ± 标准差 Mean ± SD | 最小值 Minimum | 最大值 Maximum | 中值 Median | 偏度 Sewness | 峰度 Kurtosis | 变异系数 Coefficient of variation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶干重 Leaf dry weight (g) | 0.229 ± 0.085 | 0.096 | 0.889 | 0.210 | 17,406.545 | 11.361 | 37.172 |
| 叶面积 Leaf area (cm2) | 28.316 ± 5.813 | 5.419 | 61.215 | 28.903 | 6,389.909 | 2.264 | 20.389 |
| 比叶面积 Specific leaf area (cm2/g) | 11.6 ± 3.735 | 1.915 | 32.454 | 11.322 | 4,838.621 | 0.983 | 32.121 |
| 叶干物质含量 Leaf dry matter content (g/g) | 0.242 ± 0.045 | 0.129 | 0.430 | 0.237 | 4,740.165 | 0.902 | 18.358 |
| 枝干物质含量 Twig dry matter content (g/g) | 0.415 ± 0.038 | 0.283 | 0.618 | 0.415 | 5,497.453 | 1.527 | 9.059 |
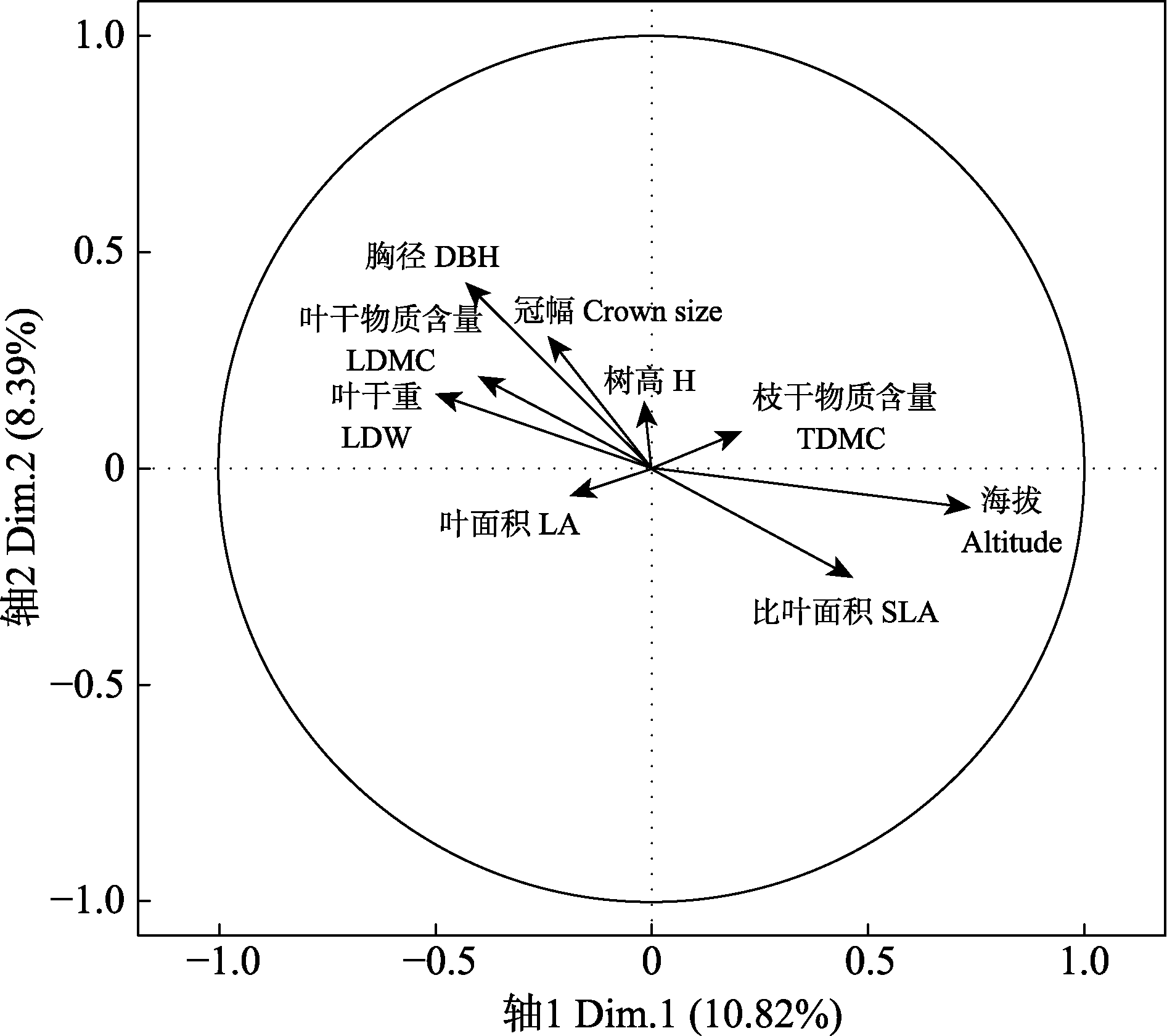
图1 功能性状、形态因子与地形因子的多元因子分析
Fig. 1 Multiple factor analysis of functional traits, tree forms, and topographical factors. LA, Leaf area; SLA, Specific leaf area; LDW, Leaf dry weight; LDMC, Leaf dry matter content; TDMC, Twig dry matter content; DBH, Diameter at breast height; H, Height.
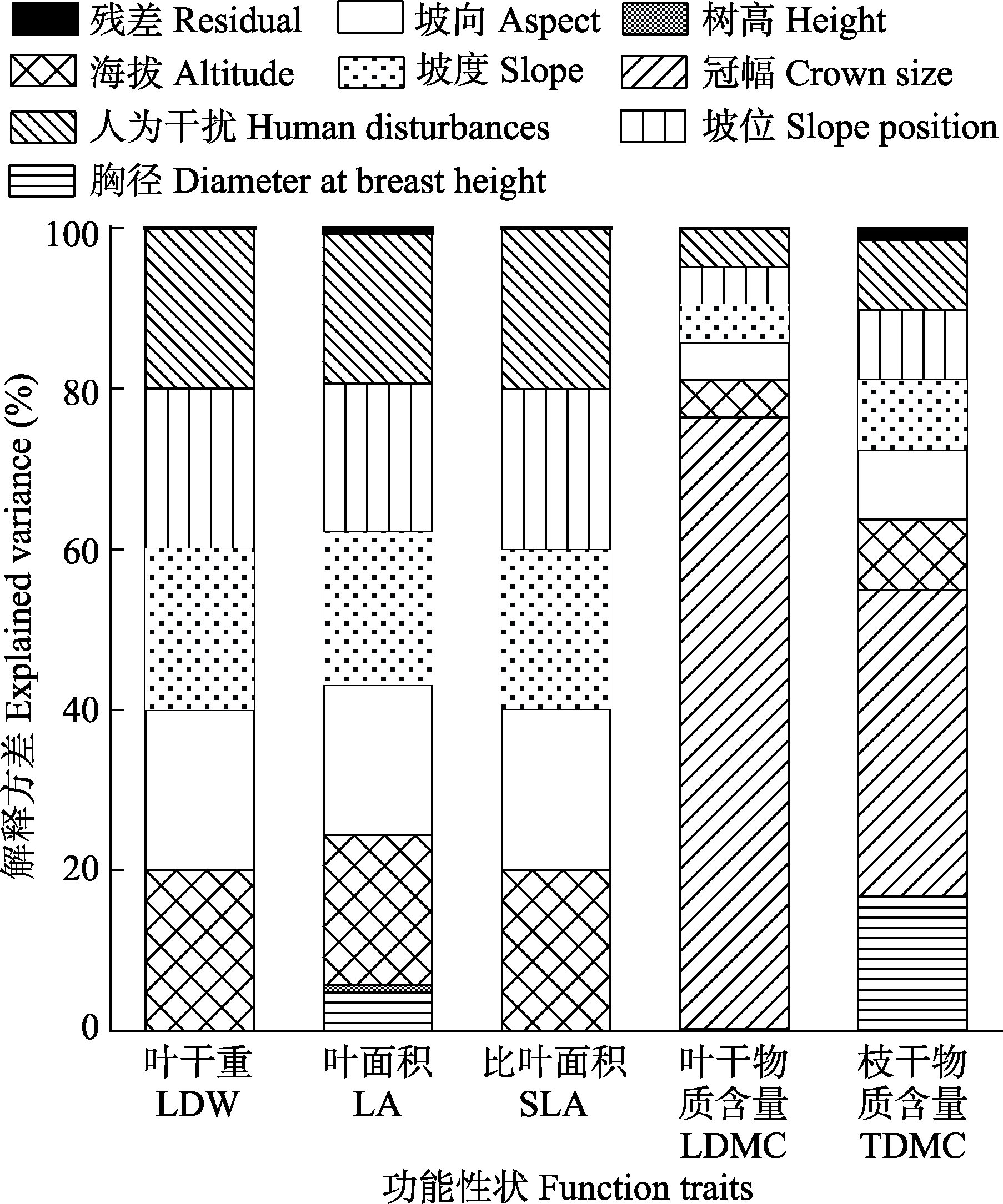
图2 不同因子对功能性状影响的方差分解
Fig. 2 Variance partitioning for function traits by different factors. LA, Leaf area; SLA, Specific leaf area; LDW, Leaf dry weight; LDMC, Leaf dry matter content; TDMC, Twig dry matter content.
| 性状 Trait | 海拔 Altitude | 坡向 Aspect | 坡度 Slope | 坡位 Slope position |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶干重 Leaf dry weight | 0.788 | 0.724 | 0.653 | 0.542 |
| 叶面积 Leaf area | 0.719 | 0.620 | 0.632 | 0.499 |
| 比叶面积 Specific leaf area | 0.875 | 0.774 | 0.762 | 0.601 |
| 叶干物质含量 Leaf dry matter content | 0.786 | 0.616 | 0.606 | 0.506 |
| 枝干物质含量 Twig dry matter content | 0.770 | 0.567 | 0.626 | 0.480 |
表2 功能性状与地形因子灰色关联度分析
Table 2 Grey relational grade analysis between functional traits and topographic factors
| 性状 Trait | 海拔 Altitude | 坡向 Aspect | 坡度 Slope | 坡位 Slope position |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 叶干重 Leaf dry weight | 0.788 | 0.724 | 0.653 | 0.542 |
| 叶面积 Leaf area | 0.719 | 0.620 | 0.632 | 0.499 |
| 比叶面积 Specific leaf area | 0.875 | 0.774 | 0.762 | 0.601 |
| 叶干物质含量 Leaf dry matter content | 0.786 | 0.616 | 0.606 | 0.506 |
| 枝干物质含量 Twig dry matter content | 0.770 | 0.567 | 0.626 | 0.480 |
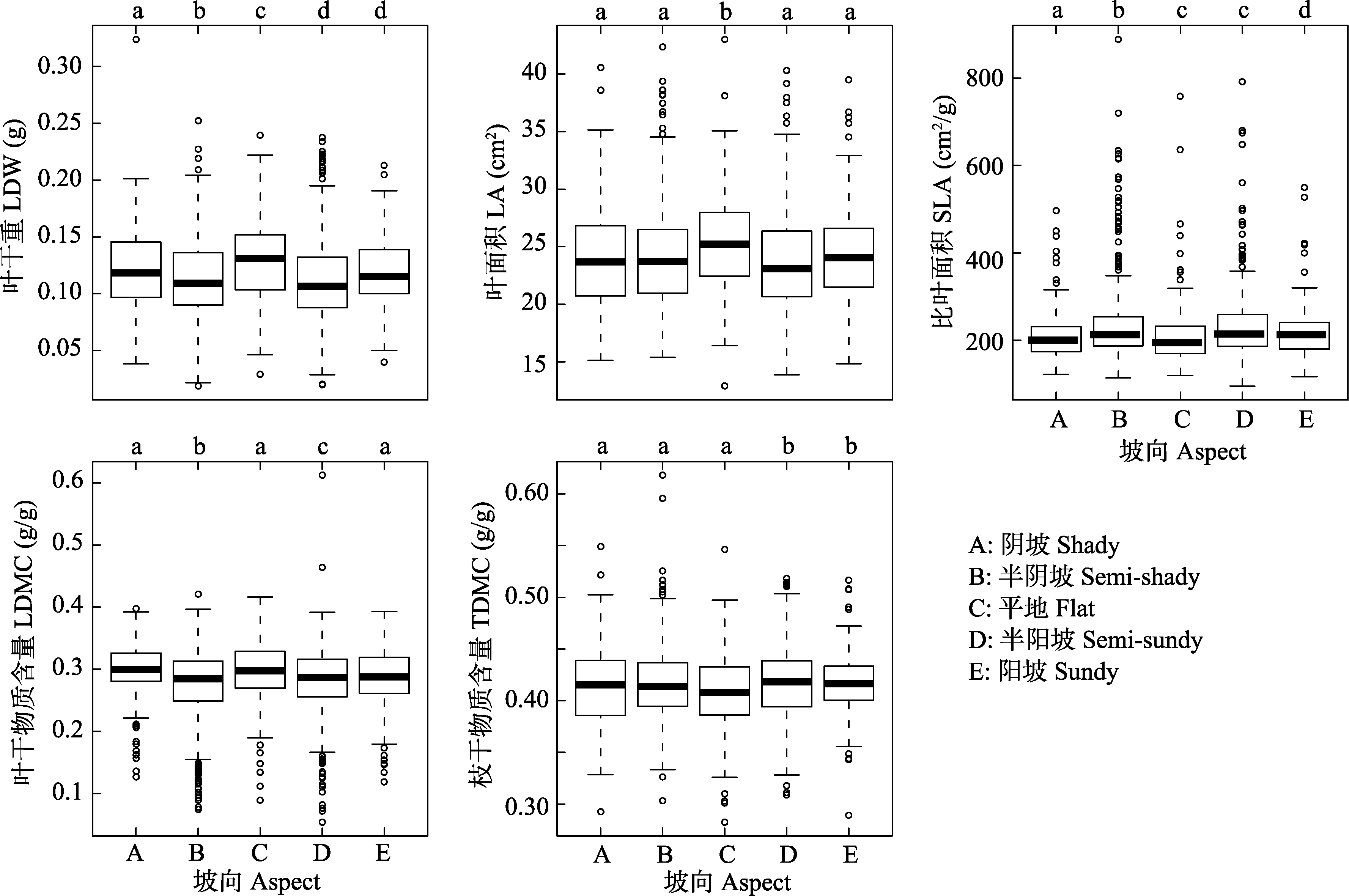
图3 功能性状值在坡向梯度上的变化
Fig. 3 Changes of functional trait values on the gradient of slope aspects. LA, Leaf area; SLA, Specific leaf area; LDW, Leaf dry weight; LDMC, Leaf dry matter content; TDMC, Twig dry matter content.
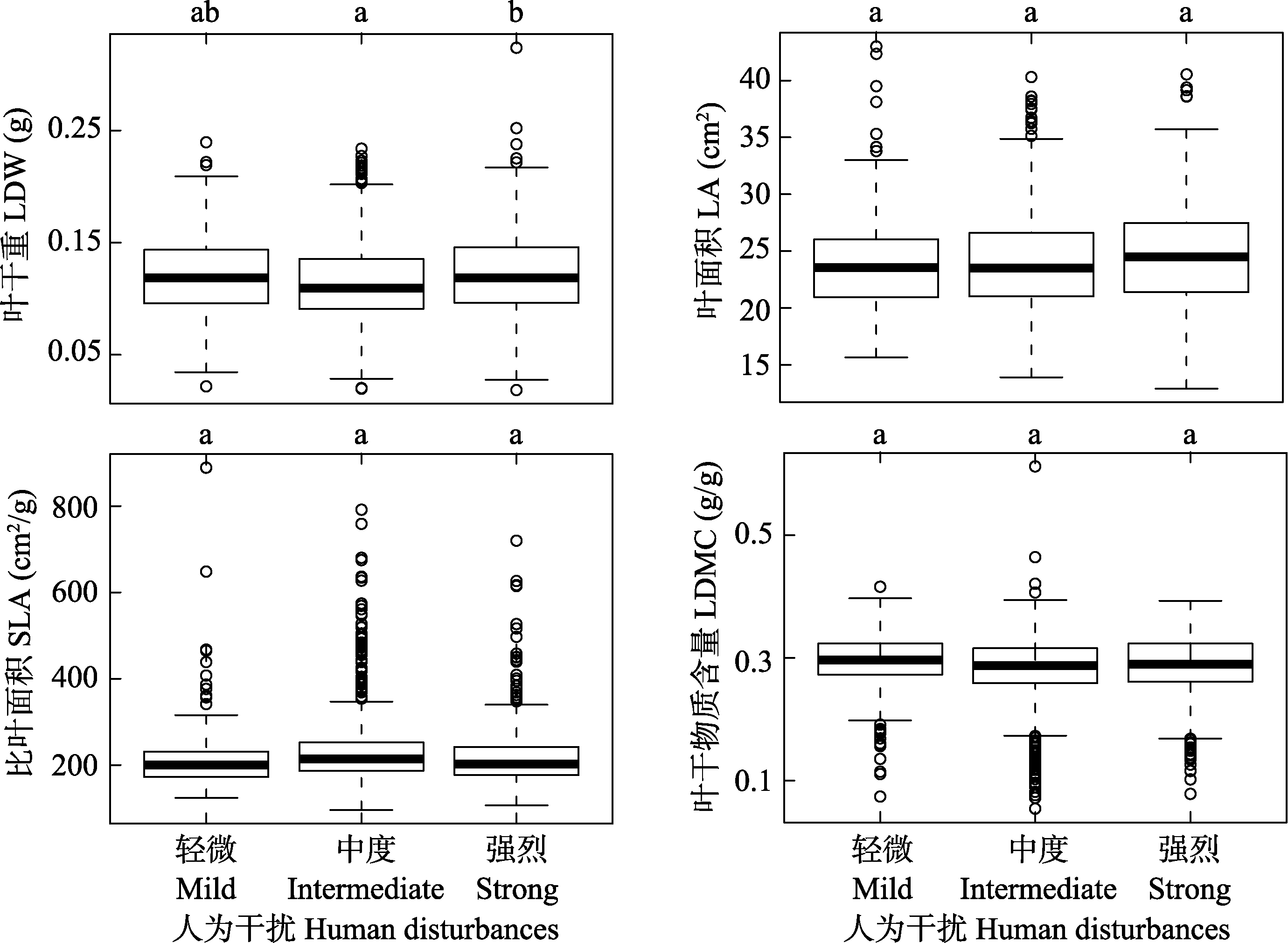
图4 人为干扰下功能性状值的分布
Fig. 4 Distribution of function trait values under human disturbances. LA, Leaf area; SLA, Specific leaf area; LDW, Leaf dry weight; LDMC, Leaf dry matter content.
| 1 |
Ackerly DD, Cornwell WK ( 2007) A trait-based approach to community assembly: Partitioning of species trait values into within- and among-community components. Ecology Letters, 10, 135-145.
DOI URL PMID |
| 2 |
Albert CH, Thuiller W, Yoccoz NG, Soudant A, Boucher F, Saccone P, Lavorel S ( 2010) Intraspecific functional variability: Extent, structure and sources of variation. Journal of Ecology, 98, 604-613.
DOI URL |
| 3 |
Auger S, Shipley B ( 2013) Inter-specific and intra-specific trait variation along short environmental gradients in an old-growth temperate forest. Journal of Vegetation Science, 24, 419-428.
DOI URL |
| 4 | Borcard D, Gillet F, Legendre P ( 2011) Numerical Ecology with R. Springer Science & Business Media, New York. |
| 5 | Chen L, Mi XC, Ma KP ( 2014) Niche differentiation and its consequence on biodiversity maintenance in forest communities. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 26, 112-117. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈磊, 米湘成, 马克平 ( 2014) 生态位分化与森林群落物种多样性维持研究展望. 生命科学, 26, 112-117.] | |
| 6 |
Cornelissen JHC, Lavorel S, Garnier E, Díaz S, Buchmann N, Gurvich DE, Reich PB, ter Steege H, Morgan HD, van der Heijden MGA, Pausas JG, Poorter H ( 2003) A handbook of protocols for standardised and easy measurement of plant functional traits worldwide. Australian Journal of Botany, 51, 335-380.
DOI URL |
| 7 | Duan N, Xu J, Chen HL, Gao JL, Liu YT, Jia YK ( 2018) Effects of drought stress on phenotypic plasticity of Cerasus humilis. Guihaia, 39, 1159-1165. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 段娜, 徐军, 陈海玲, 高君亮, 刘禹廷, 贾玉奎 ( 2018) 干旱胁迫对欧李幼苗表型可塑性的影响. 广西植物, 39, 1159-1165.] | |
| 8 |
Gao L, Li B, Liu WY, Shen YX, Liu WJ ( 2013) Inhibition effects of daughter ramets on parent of clonal plant Eichhornia crassipes. Aquatic Botany, 107, 47-53.
DOI URL |
| 9 |
Jung V, Muller S ( 2010) Intraspecific variability and trait-based community assembly. Journal of Ecology, 98, 1134-1140.
DOI URL |
| 10 |
Kraft NJB, Adler PB, Godoy O, James EC, Fuller S, Levine JM ( 2015) Community assembly, coexistence and the environmental filtering metaphor. Functional Ecology, 29, 592-599.
DOI URL PMID |
| 11 |
Laforest-Lapointe I, Martínez-Vilalta J, Retana J ( 2014) Intraspecific variability in functional traits matters: Case study of Scots pine. Oecologia, 175, 1337-1348.
DOI URL |
| 12 | Liu XJ, Ma KP ( 2015) Plant functional traits—Concepts, applications and future directions. Scienta Sinica Vitae, 45, 325-339. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘晓娟, 马克平 ( 2015) 植物功能性状研究进展. 中国科学: 生命科学, 45, 325-339.] | |
| 13 |
Li XL, Hou XY, Wu XH, Sarula, Ji L, Chen HJ, Liu ZY, Ding Y ( 2014) Plastic responses of stem and leaf functional traits in Leymus chinensis to long-term grazing in a meadow steppe. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 38, 440-451. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 李西良, 侯向阳, 吴新宏, 萨茹拉, 纪磊, 陈海军, 刘志英, 丁勇 ( 2014) 草甸草原羊草茎叶功能性状对长期过度放牧的可塑性响应. 植物生态学报, 38, 440-451.]
DOI URL |
|
| 14 | Li XL, Wen HR, Wang XS, Yang J, Huang CM ( 2018) Phenotypic plasticity of Distylium chinense leaves in relation to soil environmental factors in heterogeneous habitats in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 3581-3591. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李晓玲, 温浩然, 王雪松, 杨进, 黄成名 ( 2018) 三峡库区不同生境下中华蚊母树叶片表型可塑性及其与土壤环境因子的关系. 生态学报, 38, 3581-3591.] | |
| 15 | Lin Y, Ai XR, Yao L, Guo QJ, Zhang MX, Chen J ( 2017) Population structure and dynamics of Metasequoia glyptostroboides parent trees. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 36, 1531-1538. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 林勇, 艾训儒, 姚兰, 郭秋菊, 张敏霞, 陈俊 ( 2017) 水杉原生母树种群结构与动态. 生态学杂志, 36, 1531-1538.] | |
| 16 | Luo Q, Liu H, Wu GL, He PC, Hua L, Zhu LW, Zhang H, Liu N, Jian SG, Ye Q ( 2018) Using functional traits to evaluate the adaptability of five plant species on tropical coral islands. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 1256-1263. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 罗琦, 刘慧, 吴桂林, 贺鹏程, 华雷, 朱丽薇, 张辉, 刘楠, 简曙光, 叶清 ( 2018) 基于功能性状评价5种植物对热带珊瑚岛环境的适应性. 生态学报, 38, 1256-1263.] | |
| 17 |
Pérez-Harguindeguy N, Díaz S, Garnier E, Lavorel S, Poorter H, Jaureguiberry P, Bret-Harte MS, Cornwell WK, Craine JM, Gurvich DE, Urcelay C, Veneklaas EJ, Reich PB, Poorter L, Wright IJ, Ray P, Enrico L, Pausas JG, de Vos AC, Buchmann N, Funes G, Quétier F, Hodgson JG, Thompson K, Morgan HD, ter Steege H, Heijden MGAVD, Sack L, Blonder B, Poschlod P, Vaieretti MV, Conti G, Staver AC, Aquino S, Cornelissen JHC ( 2013) New handbook for standardised measurement of plant functional traits worldwide. Australian Journal of Botany, 61, 167-234.
DOI URL |
| 18 |
Siefert A, Violle C, Chalmandrier L, Albert CH, Taudiere A, Fajardo A, Aarssen LW, Baraloto C, Carlucci MB, Cianciaruso MV, de L Dantas V, de Bello F, Duarte LDS, Fonseca CR, Freschet GT, Gaucherand S, Gross N, Hikosaka K, Jackson B, Jung V, Kamiyama C, Katabuchi M, Kembel SW, Kichenin E, Kraft NJB, Lagerström A, Bagousse-Pinguet YL, Li Y, Mason N, Messier J, Nakashizuka T, Overton JM, Peltzer DA, Pérez-Ramos IM, Pillar VD, Prentice HC, Richardson S, Sasaki T, Schamp BS, Schöb C, Shipley B, Sundqvist M, Sykes MT, Vandewalle M, Wardle DA ( 2015) A global meta-analysis of the relative extent of intraspecific trait variation in plant communities. Ecology Letters, 18, 1406-1419.
DOI URL PMID |
| 19 | Shi JM, Ye XH, Chen FS, Yang QP, Li ZY, Fang K, Yang GY ( 2014) Adaptation of bamboo to heterogeneous habitat: Phenotypic plasticity. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34, 5687-5695. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 施建敏, 叶学华, 陈伏生, 杨清培, 黎祖尧, 方楷, 杨光耀 ( 2014) 竹类植物对异质生境的适应——表型可塑性. 生态学报, 34, 5687-5695.] | |
| 20 |
Tang QQ, Huang YT, Ding Y, Zang RG ( 2016) Interspecific and intraspecific variation in functional traits of subtropical evergreen and deciduous broad-leaved mixed forests. Biodiversity Science, 24, 262-270. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 唐青青, 黄永涛, 丁易, 臧润国 ( 2016) 亚热带常绿落叶阔叶混交林植物功能性状的种间和种内变异. 生物多样性, 24, 262-270.]
DOI URL |
|
| 21 | Wang S, Zhou DW ( 2017) Research on phenotypic plasticity in plants: An overview of history, current status, and development trends. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 8161-8169. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王姝, 周道玮 ( 2017) 植物表型可塑性研究进展. 生态学报, 37, 8161-8169.] | |
| 22 | Xiong B, Yao L, Yi YM, Wang BQ, Fan SH ( 2009) Research on growth of the Metasequoia glyptostroboides mother trees. Journal of Hubei University for Nationalities (Natural Science Edition), 27, 439-442. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 熊彪, 姚兰, 易咏梅, 王柏泉, 范深厚 ( 2009) 水杉原生母树生长势调查研究. 湖北民族学院学报(自然科学版), 27, 439-442.] | |
| 23 | Zhai SH, Wang P, Sheng LX ( 2017) Phenotypic plasticity of plant functional traits in competition environments. Journal of Beihua University (Natural Science), 18, 538-546. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 翟偲涵, 王平, 盛连喜 ( 2017) 竞争条件下植物功能性状的表型可塑性研究进展. 北华大学学报(自然科学版), 18, 538-546.] |
| [1] | 罗敏, 杨永川, 靳程, 周礼华, 龙宇潇. 城市森林兽类组成特征及人类活动的影响——以重庆中心城区为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24402-. |
| [2] | 王战. 我是怎样发现水杉的?[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 25045-. |
| [3] | 靳川, 张子嘉, 底凯, 张卫荣, 乔栋, 程思源, 胡中民. 海南热带雨林植物光合荧光气体交换和叶功能性状数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24139-. |
| [4] | 李艳朋, 盘李军, 陈洁, 许涵, 杨立新. 亚热带人工混交林叶功能性状对森林演替的响应规律及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 24049-. |
| [5] | 任嘉隆, 王永珍, 冯怡琳, 赵文智, 严祺涵, 秦畅, 方静, 辛未冬, 刘继亮. 基于陷阱法采集的河西走廊戈壁荒漠甲虫数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23375-. |
| [6] | 冯嘉谊, 练琚愉, 冯瑜莙, 张东旭, 曹洪麟, 叶万辉. 鼎湖山南亚热带常绿阔叶林群落垂直分层对群落结构及功能的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24306-. |
| [7] | 程继铭, 何慧敏, 牛红玉, 张洪茂. 鼠类种内个性差异对种子传播影响的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22446-. |
| [8] | 邵雯雯, 范国祯, 何知舟, 宋志平. 多地同质园实验揭示普通野生稻的表型可塑性与本地适应性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22311-. |
| [9] | 薛玉洁, 程安鹏, 李珊, 刘晓娟, 李景文. 亚热带森林中环境和物种多样性对灌木存活的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22443-. |
| [10] | 罗彩访, 杨涛, 张秋雨, 王馨培, 沈泽昊. 滇中半湿润常绿阔叶林木本植物的功能特征和功能多样性及其影响因子[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23215-. |
| [11] | 王健铭, 曲梦君, 王寅, 冯益明, 吴波, 卢琦, 何念鹏, 李景文. 青藏高原北部戈壁植物群落物种、功能与系统发育β多样性分布格局及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(6): 21503-. |
| [12] | 付飞, 魏慧玉, 常育腾, 王备新, 陈凯. 澜沧江中游水生昆虫生活史和生态学性状多样性的海拔格局: 气候和土地利用的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21332-. |
| [13] | 罗恬, 俞方圆, 练琚愉, 王俊杰, 申健, 吴志峰, 叶万辉. 冠层垂直高度对植物叶片功能性状的影响: 以鼎湖山南亚热带常绿阔叶林为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21414-. |
| [14] | 林永一, 王永珍, 冯怡琳, 赵文智, 高俊伟, 刘继亮. 河西走廊中部戈壁地表甲虫群落动态变化及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22343-. |
| [15] | 雍青措姆, 习新强, 牛克昌. 高寒草甸植物物种丧失对草原毛虫的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(11): 22069-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn