



生物多样性 ›› 2016, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (4): 421-430. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2015300 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2015300
所属专题: 中国西南干旱河谷的植物多样性
收稿日期:2015-11-01
接受日期:2016-02-02
出版日期:2016-04-20
发布日期:2016-05-11
通讯作者:
沈泽昊
基金资助:
Jie Han1, Zehao Shen1,*( ), Songlin Shi2,3, Peihao Peng2
), Songlin Shi2,3, Peihao Peng2
Received:2015-11-01
Accepted:2016-02-02
Online:2016-04-20
Published:2016-05-11
Contact:
Shen Zehao
摘要:
干旱河谷植被是我国西南横断山区的一类特殊的隐域性生态系统, 影响不同河谷之间植物群落差异的因素与作用大小尚不清楚。本研究调查了四川省雅砻江和大渡河流域干旱河谷段植被组成, 并比较了两个地区在植物多样性上的差别。结果表明: (1)影响两个地区植被类型的主要因素不同, 雅砻江干旱河谷植被主要受海拔和地形(坡度和坡向)影响, 大渡河干旱河谷植被主要受年平均降水量影响。(2)雅砻江和大渡河干旱河谷植物物种丰富度均随着年均温升高而降低。(3)坡向由北至南, 雅砻江干旱河谷灌木、草本物种丰富度减小, 而大渡河干旱河谷灌木、草本丰富度增加。(4)坡度越大, 雅砻江和大渡河干旱河谷灌木的丰富度越高。(5)雅砻江、大渡河干旱河谷植物β多样性受环境距离影响大, 受地理距离影响小。两条江植被间地理隔离效应约为地理距离产生差异的5倍。本研究弥补了干旱河谷研究中对于雅砻江和大渡河干旱河谷植物多样性研究的空白, 为相关区域植被保护提供了参考信息, 同时还为定量估计地理隔离效应对区域间生物多样性差异的影响提供了可行方法。
韩杰, 沈泽昊, 石松林, 彭培好 (2016) 雅砻江和大渡河干旱河谷植被物种多样性比较:气候、地形与空间的影响. 生物多样性, 24, 421-430. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2015300.
Jie Han, Zehao Shen, Songlin Shi, Peihao Peng (2016) Comparison of plant species diversity and composition in the dry valleys of Yalong River and Dadu River: evaluating the effects of climate, topography and space. Biodiversity Science, 24, 421-430. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2015300.
| 年均温 Mean annual temperature | 坡向 Aspect | 坡度 Slope | 河流解释 River explanation | 限制性最大似然估计 REML criterion | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 灌木层 Shrub layer | 雅砻江 The Yalong River | -0.202** | -0.747** | 0.020* | 92.10% | 76.1 |
| 大渡河 The Dadu River | -0.432** | 1.005** | 0.016* | |||
| 草本层 Herb layer | 雅砻江 The Yalong River | -0.537** | -0.687** | - | 92.20% | 104.9 |
| 大渡河 The Dadu River | -0.969** | 1.451** | - | |||
表1 雅砻江和大渡河干旱河谷植物丰富度的混合效应模型模拟结果
Table 1 The mixed-effect model estimated for plant richness in dry valleys of the Yalong River and the Dadu River
| 年均温 Mean annual temperature | 坡向 Aspect | 坡度 Slope | 河流解释 River explanation | 限制性最大似然估计 REML criterion | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 灌木层 Shrub layer | 雅砻江 The Yalong River | -0.202** | -0.747** | 0.020* | 92.10% | 76.1 |
| 大渡河 The Dadu River | -0.432** | 1.005** | 0.016* | |||
| 草本层 Herb layer | 雅砻江 The Yalong River | -0.537** | -0.687** | - | 92.20% | 104.9 |
| 大渡河 The Dadu River | -0.969** | 1.451** | - | |||
| 群落类型 Community type | 河流 River | 海拔 Elevation (m) | 灌木密度 Shrub density (/100 m2) | 草本密度 Herb density (/100 m2) | 植被型 Vegetation type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 类型A Type A | 大渡河 The Dadu River | 1,200 | 9 ± 4 | 41 ± 10 | 亚热带针阔叶混交林Coniferous and broadleaved mixed forest in subtropical |
| 类型B Type B | 大渡河-雅砻江 The Dadu River-the Yalong River | 1,400 | 3 ± 1 | 19 ± 3 | 暖性落叶阔叶灌丛 Warm deciduous broadleaved shrub |
| 类型C Type C | 雅砻江 The Yalong River | 2,600 | 4 ± 2 | 21 ± 4 | 暖性落叶阔叶灌丛 Warm deciduous broadleaved shrub |
| 类型D Type D | 雅砻江 The Yalong River | 2,700 | 6 ± 3 | 26 ± 6 | 暖性落叶阔叶灌丛 Warm deciduous broadleaved shrub |
| 类型E Type E | 雅砻江 The Yalong River | 2,500 | 4 ± 1 | 25 ± 7 | 暖性落叶阔叶灌丛 Warm deciduous broadleaved shrub |
表2 雅砻江和大渡河干旱河谷植物群落类型特征(平均值±标准差)
Table 2 The features of community types in dry valleys of the Yalong River and the Dadu River (mean ± SD)
| 群落类型 Community type | 河流 River | 海拔 Elevation (m) | 灌木密度 Shrub density (/100 m2) | 草本密度 Herb density (/100 m2) | 植被型 Vegetation type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 类型A Type A | 大渡河 The Dadu River | 1,200 | 9 ± 4 | 41 ± 10 | 亚热带针阔叶混交林Coniferous and broadleaved mixed forest in subtropical |
| 类型B Type B | 大渡河-雅砻江 The Dadu River-the Yalong River | 1,400 | 3 ± 1 | 19 ± 3 | 暖性落叶阔叶灌丛 Warm deciduous broadleaved shrub |
| 类型C Type C | 雅砻江 The Yalong River | 2,600 | 4 ± 2 | 21 ± 4 | 暖性落叶阔叶灌丛 Warm deciduous broadleaved shrub |
| 类型D Type D | 雅砻江 The Yalong River | 2,700 | 6 ± 3 | 26 ± 6 | 暖性落叶阔叶灌丛 Warm deciduous broadleaved shrub |
| 类型E Type E | 雅砻江 The Yalong River | 2,500 | 4 ± 1 | 25 ± 7 | 暖性落叶阔叶灌丛 Warm deciduous broadleaved shrub |
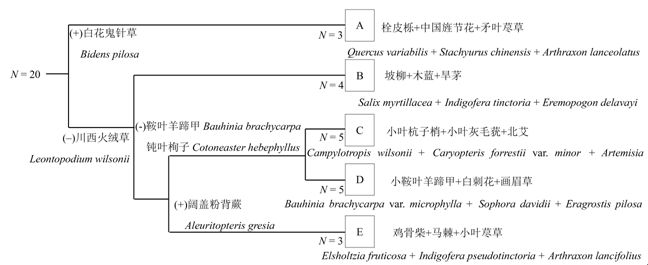
图3 雅砻江和大渡河干旱河谷植物TWINSPAN群落分类图。(+)表示与分类聚组正相关,(-)表示与分类聚组负相关。
Fig. 3 Diagram of TWINSPAN for community classification in dry valleys of the Yalong River and the Dadu River. (+) means it is positive relation with classification, (-) means it is negative relation with classification.
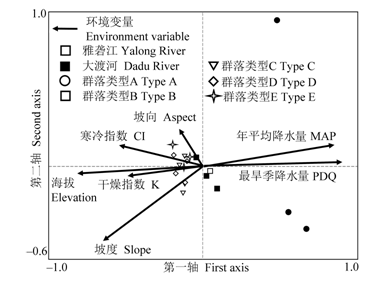
图4 雅砻江和大渡河干旱河谷植物群落的CCA排序。群落类型A、B、C、D、E含义同图3。
Fig. 4 The CCA ordination for plant communities in dry valleys of the Yalong River and the Dadu River. MAP, Mean annual precipitation; PDQ, Precipitation in driest quarter. The meaning of Type A, B, C, D and E are the same as in Fig. 3.
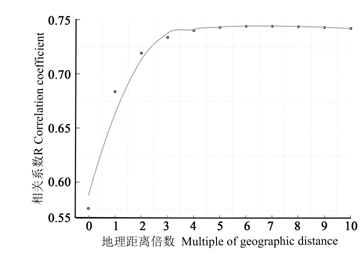
图5 雅砻江和大渡河干旱河谷地理隔离效应曲线。相关系数指的是Jaccard相似性系数矩阵与地理距离矩阵的相关系数。
Fig. 5 The geographical isolation curve in dry valleys of the Yalong River and the Dadu River. R means the correlation coefficient between Jaccard similarity index matrix and geography distance matrix.
| 距离矩阵 Distance matrices | R | P |
|---|---|---|
| 环境 Environmental | -0.727 | 0.001 |
| 环境|地理距离 Environmental | Geographical distance | -0.543 | 0.001 |
| 环境|5倍地理距离 Environments | 5 × Geographical distance | -0.401 | 0.002 |
| 地理距离 Geographical distance | -0.576 | 0.001 |
| 地理距离|环境 Geographical distance | Environments | -0.013 | 0.513 |
| 5 ×地理距离|环境 5 × Geographical distance | Environments | -0.451 | 0.001 |
表3 雅砻江和大渡河干旱河谷植物物种构成相似性Mantel检验及偏Mantel检验
Table 3 The results of Mantel test and partial Mantel test for similarities of plant species composition between dry valleys of the Yalong River and the Dadu River
| 距离矩阵 Distance matrices | R | P |
|---|---|---|
| 环境 Environmental | -0.727 | 0.001 |
| 环境|地理距离 Environmental | Geographical distance | -0.543 | 0.001 |
| 环境|5倍地理距离 Environments | 5 × Geographical distance | -0.401 | 0.002 |
| 地理距离 Geographical distance | -0.576 | 0.001 |
| 地理距离|环境 Geographical distance | Environments | -0.013 | 0.513 |
| 5 ×地理距离|环境 5 × Geographical distance | Environments | -0.451 | 0.001 |
| 1 | Antillensis E, Barker BS, Rodríguez-Robles JA, Aran VS, Waide RB, Cook JA (2012) Sea level, topography and island diversity: phylogeography of the Puerto Rican Red-eyed Coquí. Molecular Ecology, 21, 6033-6052. |
| 2 | Bai WQ, Zhang YL, Bao WK (2003) Landscape patterns and dynamics in the upper reaches of Dadu River. Journal of Natural Resources, 18(1), 75-80.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [摆万奇, 张镱锂, 包维楷 (2003) 大渡河上游地区景观格局与动态. 自然资源学报,18(1), 75-80.] | |
| 3 | Bates D, Maechler M, Bolker B, Walker S (2015) Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software, 67, 1-48. |
| 4 | Brown JH, Stevens GC, Kaufman DM (1996) The geographic range: size, shape, boundaries, and internal structure. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 27, 597-623. |
| 5 | Cao M, Jin ZZ (1989) Classification of vegetation in Qiao Jia dry-hot river valley of Jinsha River, Yunnan. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 11, 324-336.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [曹敏, 金振洲 (1989) 云南巧家金沙江干热河谷的植被分类. 云南植物研究, 11, 324-336.] | |
| 6 | Fang JY, Song YC, Liu HY, Piao SL (2002) Vegetation-climate relationship and its application in the division of vegetation zone in China. Acta Botanica Sinica, 44, 1105-1122. |
| 7 | Fjeldså J, Bowie RCK, Rahbek C (2012) The role of mountain ranges in the diversification of birds. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 43, 249-265. |
| 8 | Guan WB, Yan MS, Ma KM, Liu GH, Wang XL, Tang H (2004) The relationships between plant community species turnover rates and environmental factors in the arid valley of Minjiang River. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 24, 2367-2373.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [关文彬, 冶民生, 马克明, 刘国华, 汪西林, 谭辉 (2004) 岷江干旱河谷植物群落物种周转速率与环境因子的关系. 生态学报, 24, 2367-2373.] | |
| 9 | He F, Xie W, Liu XL, Ma QY, He YP, Chen JH, Cai XH, Long TL (2008) Pteridophytic flora of the upper reaches of the Yalong River in western Sichuan Province. Journal of Chengdu University (Natural Science Edition), 27, 276-280.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [何飞, 谢伟, 刘兴良, 马钦彦, 何亚平, 陈俊华, 蔡小虎, 隆廷伦 (2008) 川西雅砻江上游地区蕨类植物区系研究. 成都大学学报(自然科学版), 27, 276-280.] | |
| 10 | Hawkins BA, Field R, Cornell HV, Currie DJ, Guegan JF, Kaufman DM, Kerr JT, Mittelbach GG, Oberdorff T, O’Brien EM, Porter EE, Turner JRG (2003) Energy, water, and broad-scale geographic patterns of species richness. Ecology, 84, 3105-3117. |
| 11 | Hill MO (1979) TWINSPAN—A Fortran Program for Arranging Multivariate Data in an Ordered Two-way Table by Classification of the Individuals and Attributes. Cornell University Press, Ithaca. |
| 12 | Jaccard P (1912) The distribution of the flora in the alpine zone. New Phytologist, 11, 37-50. |
| 13 | Jacquemyn H, Butaye J, Hermy M (2001) Forest plant species richness in small, fragmented mixed deciduous forest patches: the role of area, time and dispersal limitation. Journal of Biogeography, 28, 801-812. |
| 14 | Jenkins DG, Carey M, Czerniewska J, Fletcher J, Hether T, Jones A, Knight S, Knox J, Long T, Mannino M, McGuire M, Riffle A, Segelsky S, Shappell L, Sterner A, Strickler T, Tursi R (2010) A meta-analysis of isolation by distance: relic or reference standard for landscape genetics? Ecography, 33, 315-320. |
| 15 | Jin ZZ (1998) Study on the floristic elements of seed plant in the dry-warm valleys of Yunnan and Sichuan. Guihaia, 18, 313-321.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [金振洲 (1998) 滇川干暖河谷种子植物区系成分研究. 广西植物,18, 313-321.] | |
| 16 | Jin ZZ (1999a) The floristic study on seed plants in the dry-hot valleys, Yunnan and Sichuan. Guihaia, 19, 1-14.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [金振洲 (1999a) 滇川干热河谷种子植物区系成分研究. 广西植物, 19, 1-14.] | |
| 17 | Jin ZZ (1999b) A phytosociological study on the semi-savanna vegetation in the dry-hot valleys of Yuanjiang River, Yunnan. Guihaia, 19, 289-302.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [金振洲 (1999b) 云南元江干热河谷半萨王纳植被的植物群落学研究. 广西植物, 19, 289-302.] | |
| 18 | Jin ZZ (2002) Floristic Features of Dry-hot and Dry-warm Valleys in Yunnan and Sichuan Provinces. Yunnan Science & Technology Press, Kunming.(in Chinese) |
| [金振洲 (2002) 滇川干热河谷与干暖河谷植物区系特征. 云南科技出版社, 昆明.] | |
| 19 | Jin ZZ, Ou XK (2000) Yuanjiang, Nujiang, Jinshajiang, Lancangjiang Vegetation of Dry-Hot Valley. Yunnan University Press, Yunnan Science & Technology Press, Kunming.(in Chinese) |
| [金振洲, 欧晓昆 (2000) 元江、怒江、金沙江、澜沧江干热河谷植被. 云南大学出版社, 云南科技出版社, 昆明.] | |
| 20 | Keddy PA (1992) Assembly and response rules: two goals for predictive community ecology. Journal of Vegetation Science, 3, 157-164. |
| 21 | Kudoh H (2001) Gene flow among plant populations in ecological landscape. Japanese Journal of Ecology, 84, 1285-1293. |
| 22 | Legendre P, Legendre L (1998) Numerical Ecology, pp. 139-141, 247-258, 279. Elsevier, Amsterdam. |
| 23 | Lomolino MV (2000) Ecology’s most general, yet protean pattern: the species-area relationship. Journal of Biogeography, 27, 17-26. |
| 24 | Liu LH (1989) Vegetational types of the valleys in the Hengduan Mountains region. Mountain Research, 7, 175-182.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘伦辉 (1989) 横断山区干旱河谷植被类型. 山地研究, 7, 175-182.] | |
| 25 | Liu XL, Mu CL, Xiang CH, Su YM (2001) Natural features of arid river valleys in western Sichuan and their vegetation restoring and reestablishing ways. Journal of Sichuan Forestry Science and Technology, 22(2), 10-17.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘兴良, 慕长龙, 向成华, 宿以明 (2001) 四川西部干旱河谷自然特征及植被恢复与重建途径. 四川林业科技, 22(2), 10-17.] | |
| 26 | Liu Y (2015) Plant Diversity and Biogeography of the Arid Valleys in Southwest China. PhD dissertation, Peking University, Beijing.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘晔 (2015) 中国西南干旱河谷植物多样性与生物地理. 博士学位论文, 北京大学, 北京.] | |
| 27 | Liu ZZ, Peng PH, Zhou ZK (2013) Application of 3S techniques in vegetation type investigation in Yajiang. Geospatial Information, 11(2), 78-79.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘中正, 彭培好, 周正坤(2013) 基于3S技术的雅江县植被类型调查与分析. 地理空间信息, 11(2) 78-79.] | |
| 28 | Little RC, Milliken GA, Stroup WW (1996) SAS System for Mixed Models. SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC. |
| 29 | Manel S, Schwartz MK, Luikart G, Taberlet P (2003) Landscape genetics: combining landscape ecology and population genetics. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 18, 189-197. |
| 30 | Manel S, Segelbacher G (2009) Perspectives and challenges in landscape genetics. Molecular Ecology, 18, 1821-1822. |
| 31 | Mantel N (1967) The detection of disease clustering and a generalized regression approach. Cancer Research, 27, 209-220. |
| 32 | McCune B, Mefford M (1999) PC-ORD. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data, version 4.0. MjM Software Design, Gleneden Beach, OR, USA. |
| 33 | Niu KC, Liu YN, Shen ZH, He FL, Fang JY (2009) Community assembly: the relative importance of neutral theory and niche theory. Biodiversity Science, 17, 579-593.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [牛克昌, 刘怿宁, 沈泽昊, 何芳良, 方精云 (2009) 群落构建的中性理论和生态位理论. 生物多样性, 17, 579-593.] | |
| 34 | Ohsawa T, Saito Y, Sawada H, Ide Y (2008) Impact of altitude and topography on the genetic diversity of Quercus serrata populations in the Chichibu Mountains, central Japan. Flora, 203, 187-196. |
| 35 | Ou XK (1988) The study of flora in Yuanmou dry-hot river valley. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 10, 11-18.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [欧晓昆 (1988) 元谋干热河谷植物区系研究. 云南植物研究, 10, 11-18.] | |
| 36 | Ou XK, Jin ZZ (1996) A preliminary study on the flora and ecological diversity in Jinsha River dry-hot valley. Journal of Wuhan Botanical Research, 14, 318-322.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [欧晓昆, 金振洲 (1996) 金沙江干热河谷植物区系和生态多样性的初步研究. 武汉植物学研究, 14, 318-322.] | |
| 37 | Preston FW (1962) The canonical distribution of commonness and rarity. Ecology, 43, 185-215. |
| 38 | Rahbek C, Gotelli NJ, Colwell RK, Entsminger GL, Rangel, TFL, Graves GR (2007) Predicting continental-scale patterns of bird species richness with spatially explicit models. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B. Biological Sciences, 274, 165-174. |
| 39 | Siefert A, Razvenscroft C, Weiser MD, Swenson NG (2013) Functional beta-diversity patterns reveal deterministic community assembly processes in eastern North American trees. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 22, 682-691. |
| 40 | Shen R, Zhang JL, He B, Li F, Zhang ZM, Zhou R, Ou XK (2010) The structure characteristic and analysis on similarity of grassland community in dry-hot valley of Yuanjiang River. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 19, 2821-2825.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [沈蕊, 张建利, 何彪, 李峰, 张志明, 周睿, 欧晓昆 (2010) 元江流域干热河谷草地植物群落结构特征与相似性分析. 生态环境学报, 19, 2821-2821.] | |
| 41 | Shen ZH, Fang JY, Liu ZL, Wu J (2001) Patterns of biodiversity along the vertical vegetation spectrum of the east aspect of Gongga Mountains. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica 25, 721-732.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [沈泽昊, 方精云, 刘增力, 伍杰 (2001) 贡嘎山东坡植被垂直带谱的物种多样性格局分析. 植物生态学报, 25, 721-732.] | |
| 42 | Shen ZH, Fei SL, Feng JM, Liu YN, Liu ZL, Tang ZY, Wang XP, Wu XP, Zheng CY, Zhu B, Fang JY (2012) Geographical patterns of community-based tree species richness in Chinese mountain forests: the effects of contemporary climate and regional history. Ecography, 35, 1134-1146. |
| 43 | Shen ZH, Ji CJ (2010) Landscape genetics: principles and its applications for the genetic effects of habitat fragmentation. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30, 5066-5076.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [沈泽昊, 吉成均 (2010) 景观遗传学原理及其在生境片断化遗传效应研究中的应用. 生态学报, 30, 5066-5076.] | |
| 44 | Shen ZH, Jin YX, Zhao ZE, Wu JQ, Huang HD (2000) A study on the quantitative classification of forest communities of Dalaoling region at the Three Gorges. Journal of Wuhan Botanical Research, 18, 99-107.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [沈泽昊, 金义兴, 赵子恩, 吴金清, 黄汉东(2000) 三峡大老岭地区森林群落的数量分类研究. 武汉植物学研究, 18, 99-107.] | |
| 45 | Slatkin M, Maddison W (1990) Detecting isolation by distance using phylogenies of genes. Genetics, 126, 249-260. |
| 46 | Slatkin M (1993) Isolation by distance in equilibrium and nonequilibrium populations. Evolution, 47, 264-279. |
| 47 | Sork VL, Nason J, Campbell DR, Fernendez JF (1999) Landscape approaches to historical and contemporary gene flow in plants. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 14, 219-224. |
| 48 | Storfer A, Murphy MA, Evans JS, Goldberg CS, Robinson S, Spear SF (2007) Putting the “landscape” in landscape genetics. Heredity, 98, 128-142. |
| 49 | Tang ZY, Fang JY, Chi XL, Feng JM, Liu YN, Shen ZH, Wang XP, Wang ZH, Wu XP, Zheng CY, Gaston KJ (2012) Patterns of plant beta-diversity along elevational and latitudinal gradients in mountain forests of China. Ecography, 35, 1083-1091. |
| 50 | Thomas K, Anna MH, Thomas W (2004) Rarefaction method for assessing plant species diversity on a regional scale. Ecography, 27, 532-544. |
| 51 | Wan DH, Xia J, Song XF, Liu SX (2008) Evaluation of ecological water requirement based on hydrological cycle analysis. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 39, 994-1000.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [万东辉, 夏军, 宋献方, 刘苏峡 (2008) 基于水文循环分析的雅砻江流域生态需水量计算. 水利学报, 39, 994-1000.] | |
| 52 | Wang IJ (2012) Environmental and topographic variables shape genetic structure and effective population sizes in the endan- |
| 53 | gered Yosemite toad. Diversity and Distributions, 18, 1033-1041. |
| 54 | Wang YJ, Huang CD, Zhang J, Yang WQ, Wang XS (2010) Species diversity, biomass and their relationship of shrubberies in an arid valley of the Minjiang River. Arid Zone Research, 27, 567-572.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王勇军, 黄从德, 张健, 杨万勤, 王宪帅 (2010) 岷江干旱河谷灌丛物种多样性. 生物量及其关系. 干旱区研究, 27, 567-572.] | |
| 55 | Wright S (1943) Isolation by distance. Genetics, 28, 114-138. |
| 56 | Ye MS, Guan WB, Tan H, Ma KM, Liu GH, Wang XL (2004) The α diversity of shrubs community in the arid valley of the Minjiang River. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 24, 1123-1130.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [冶民生, 关文彬, 谭辉, 马克明, 刘国华, 汪西林 (2004) 岷江干旱河谷灌丛α多样性分析. 生态学报, 6, 1123-1130.] | |
| 57 | Ye MS, Guan WB, Wu B, Ma KM, Liu GH, Wang XL, Chen JY (2006) Plant community complexity in the arid valley of Minjiang River. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 26, 3159-3165.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [冶民生, 关文彬, 吴斌, 马克明, 刘国华, 汪西林, 陈箐妍 (2006) 岷江干旱河谷植物群落的复杂性. 生态学报, 26, 3159-3165.] | |
| 58 | Yang QZ (2007) Study on the arid-valley scrubs in the upper reaches of Minjing River. Journal of Mountain Research, 25(1), 1-32.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨钦周(2007) 岷江上游干旱河谷灌丛研究. 山地学报, 25(1), 1-32.] | |
| 59 | Yu X, Feng L, Yan DH, Jia YW, Yang SH, Hu DL, Zhang MZ (2008) Development of distributed hydrological model for Yalongjiang River Basin. Journal of China Hydrology, 28(3), 49-53.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [俞烜, 冯琳, 严登华, 贾仰文, 杨舒媛, 胡东来, 张明珠 (2008) 雅砻江流域分布式水文模型开发研究.水文, 28(3), 49-53.] | |
| 60 | Zhang JT, Li S, Li M (2010) A comparison of self-organizing feature map clustering with twinspan and fuzzy C-means clustering in the analysis of woodland communities in the Guancen Mts, China. Community Ecology, 11, 120-126. |
| 61 | Zhang RZ (1992) The Dry Valleys of the Hengduan Mountains Region. Science Press, Beijing.(in Chinese) |
| [张荣祖 (1992) 横断山区干旱河谷. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 62 | Zhang WH, Lu T, Zhou JY, Kang YX, Ma KM, Liu GH (2003) A floristic study on seed plants in the upper reaches of Minjiang River. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 23, 888-894.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张文辉, 卢涛, 周建云, 康永祥, 马克明, 刘国华 (2003) 岷江上游流域种子植物区系研究. 西北植物学报, 23, 888-894.] |
| [1] | 张浩斌, 肖路, 刘艳杰. 夜间灯光对外来入侵植物和本地植物群落多样性和生长的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24553-. |
| [2] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [3] | 连佳丽, 陈婧, 杨雪琴, 赵莹, 罗叙, 韩翠, 赵雅欣, 李建平. 荒漠草原植物多样性和微生物多样性对降水变化的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24044-. |
| [4] | 郑梦瑶, 李媛, 王雪蓉, 张越, 贾彤. 芦芽山不同植被类型土壤原生动物群落构建机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23419-. |
| [5] | 万凤鸣, 万华伟, 张志如, 高吉喜, 孙晨曦, 王永财. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的应用潜力[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23381-. |
| [6] | 张乃鹏, 梁洪儒, 张焱, 孙超, 陈勇, 王路路, 夏江宝, 高芳磊. 土壤类型和地下水埋深对黄河三角洲典型盐沼植物群落空间分异的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23370-. |
| [7] | 蒋陈焜, 郁文彬, 饶广远, 黎怀成, Julien B. Bachelier, Hartmut H. Hilger, Theodor C. H. Cole. 植物系统发生海报——以演化视角介绍植物多样性的科教资料项目[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24210-. |
| [8] | 杨舒涵, 王贺, 陈磊, 廖蓥飞, 严光, 伍一宁, 邹红菲. 松嫩平原异质生境对土壤线虫群落特征的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23295-. |
| [9] | 韩赟, 迟晓峰, 余静雅, 丁旭洁, 陈世龙, 张发起. 青海野生维管植物名录[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23280-. |
| [10] | 陈又生, 宋柱秋, 卫然, 罗艳, 陈文俐, 杨福生, 高连明, 徐源, 张卓欣, 付鹏程, 向春雷, 王焕冲, 郝加琛, 孟世勇, 吴磊, 李波, 于胜祥, 张树仁, 何理, 郭信强, 王文广, 童毅华, 高乞, 费文群, 曾佑派, 白琳, 金梓超, 钟星杰, 张步云, 杜思怡. 西藏维管植物多样性编目和分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23188-. |
| [11] | 宋柱秋, 叶文, 董仕勇, 金梓超, 钟星杰, 王震, 张步云, 徐晔春, 陈文俐, 李世晋, 姚纲, 徐洲锋, 廖帅, 童毅华, 曾佑派, 曾云保, 陈又生. 广东省高等植物多样性编目和分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23177-. |
| [12] | 梁彩群, 陈玉凯, 杨小波, 张凯, 李东海, 江悦馨, 李婧涵, 王重阳, 张顺卫, 朱子丞. 海南省野生维管植物编目和分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 23067-. |
| [13] | 李仕裕, 张奕奇, 邹璞, 宁祖林, 廖景平. 广东省植物园植物多样性迁地保护现状及发展建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22647-. |
| [14] | 桑佳文, 宋创业, 贾宁霞, 贾元, 刘长成, 乔鲜果, 张琳, 袁伟影, 吴冬秀, 李凌浩, 郭柯. 青藏高原植被调查与制图评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22430-. |
| [15] | 吴浩, 余玉蓉, 王佳钰, 赵媛博, 高娅菲, 李小玲, 卜贵军, 薛丹, 吴林. 低水位增加灌木多样性和生物量但降低土壤有机碳含量: 以鄂西南贫营养泥炭地为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22600-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn