



Biodiv Sci ›› 2010, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (6): 615-621. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.2010.615 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.2010.615
Special Issue: 外来物种入侵:机制、影响与防控; 生物入侵
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Kun Wang, Ji Yang, Jiakuan Chen*( )
)
Received:2010-04-22
Accepted:2010-09-26
Online:2010-11-20
Published:2011-01-31
Contact:
Jiakuan Chen
Kun Wang, Ji Yang, Jiakuan Chen. Comparison of morphological traits between alligator weed and two congeners under different water and nutrient conditions[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2010, 18(6): 615-621.
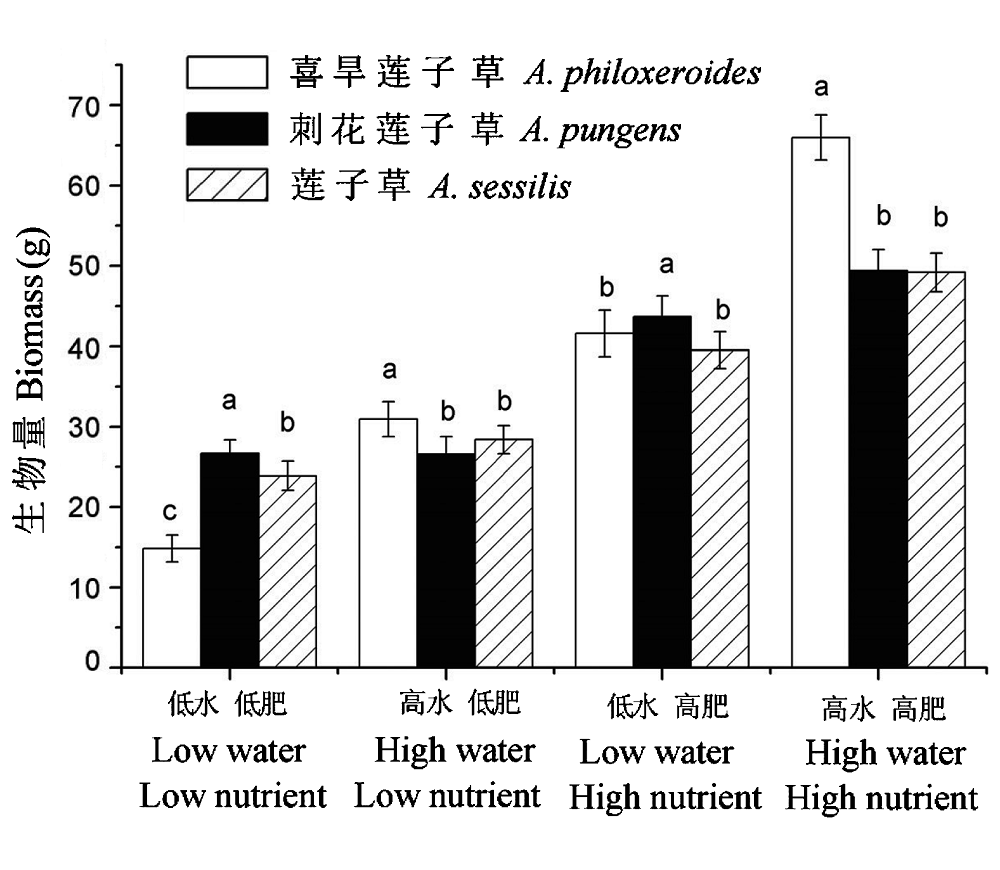
Fig. 1 Effects of environmental factors on biomass of three studied species, Alternanthera philoxeroides, A. pungens and A. sessilis. Different small letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05) among species in the same soil condition.
| 性状 Traits | 数据 转换 Data trans | 物种 Species | 水分 Water availability | 营养 Nutrient level | 物种×水分 Species×water | 物种×营养 Species×nutrient | 水分×营养 Water×nutrient | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | |||||||
| 生物量 Biomass | -- | 21.089 | 0.000 | 658.408 | 0.000 | 3451.420 | 0.000 | 179.623 | 0.000 | 103.106 | 0.000 | 67.504 | 0.000 | |||||
| 比叶面积 SLA | -- | 87.535 | 0.000 | 3.208 | 0.000 | 13.020 | 0.000 | 2.971 | 0.000 | 0.151 | 0.000 | 5.727 | 0.018 | |||||
| 叶面积 Leaf area | -- | 20.714 | 0.000 | 382.271 | 0.000 | 1236.911 | 0.000 | 13.553 | 0.000 | 15.485 | 0.000 | 0.483 | 0.489 | |||||
| 叶质量 Leaf mass | $\sqrt{x}$ | 87.931 | 0.000 | 180.221 | 0.000 | 503.897 | 0.000 | 0.881 | 0.418 | 6.235 | 0.000 | 0.389 | 0.534 | |||||
| 节间长 Internode length | log(x) | 404.691 | 0.000 | 205.384 | 0.000 | 219.201 | 0.000 | 44.146 | 0.000 | 14.689 | 0.000 | 3.376 | 0.069 | |||||
| 茎直径 Stem diameter | Log(x) | 508.679 | 0.000 | 237.240 | 0.000 | 260.662 | 0.000 | 51.080 | 0.000 | 19.651 | 0.003 | 3.685 | 0.058 | |||||
Table 1 Effects of species (n = 3), water availability (n = 2) and nutrient levels (n = 2) on traits of three Alternanthera species (Three-way ANOVA)
| 性状 Traits | 数据 转换 Data trans | 物种 Species | 水分 Water availability | 营养 Nutrient level | 物种×水分 Species×water | 物种×营养 Species×nutrient | 水分×营养 Water×nutrient | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | |||||||
| 生物量 Biomass | -- | 21.089 | 0.000 | 658.408 | 0.000 | 3451.420 | 0.000 | 179.623 | 0.000 | 103.106 | 0.000 | 67.504 | 0.000 | |||||
| 比叶面积 SLA | -- | 87.535 | 0.000 | 3.208 | 0.000 | 13.020 | 0.000 | 2.971 | 0.000 | 0.151 | 0.000 | 5.727 | 0.018 | |||||
| 叶面积 Leaf area | -- | 20.714 | 0.000 | 382.271 | 0.000 | 1236.911 | 0.000 | 13.553 | 0.000 | 15.485 | 0.000 | 0.483 | 0.489 | |||||
| 叶质量 Leaf mass | $\sqrt{x}$ | 87.931 | 0.000 | 180.221 | 0.000 | 503.897 | 0.000 | 0.881 | 0.418 | 6.235 | 0.000 | 0.389 | 0.534 | |||||
| 节间长 Internode length | log(x) | 404.691 | 0.000 | 205.384 | 0.000 | 219.201 | 0.000 | 44.146 | 0.000 | 14.689 | 0.000 | 3.376 | 0.069 | |||||
| 茎直径 Stem diameter | Log(x) | 508.679 | 0.000 | 237.240 | 0.000 | 260.662 | 0.000 | 51.080 | 0.000 | 19.651 | 0.003 | 3.685 | 0.058 | |||||
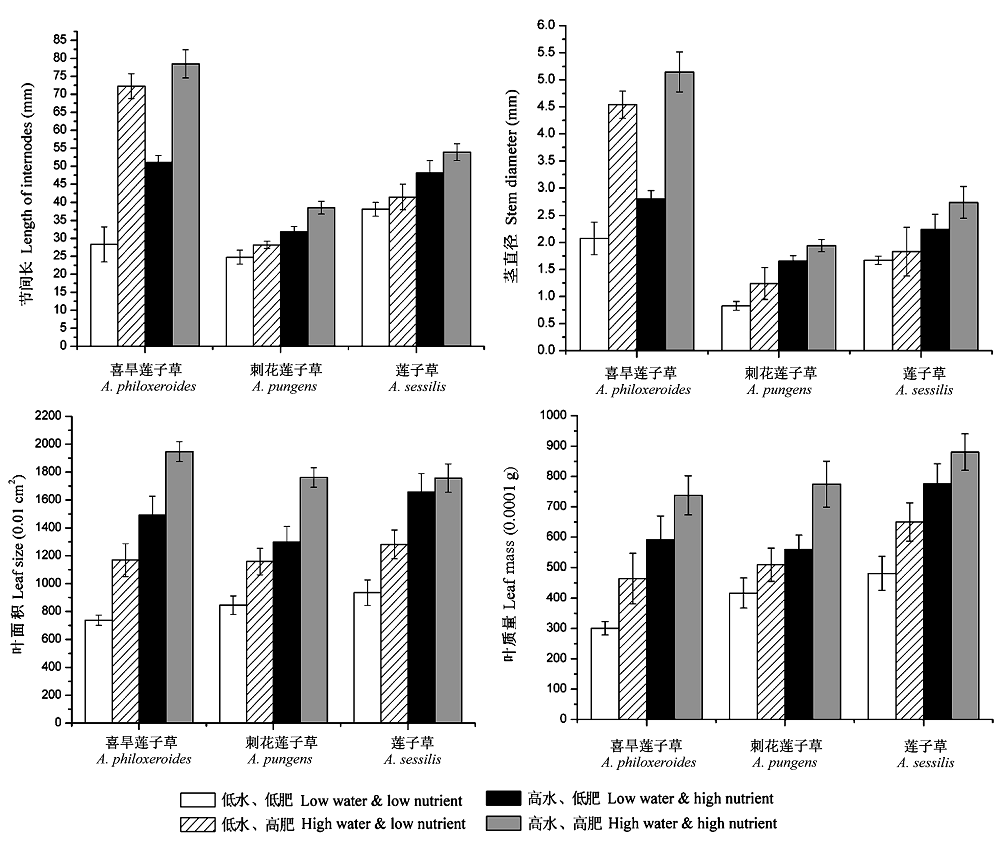
Fig. 2 Difference in leaf size, leaf weight, length of internodes and stem diameter of Alternanthera philoxeroides, A. pungens and A. sessilis among different environmental conditions.
| 喜旱莲子草 A. philoxeroides | 刺花莲子草 A. pungens | 莲子草 A. sessilis | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 叶面积 Leaf area | 0.621 | 0.519 | 0.468 |
| 叶质量 Leaf mass | 0.592 | 0.462 | 0.454 |
| 节间长 Internode length | 0.639 | 0.357 | 0.293 |
| 茎直径 Stem diameter | 0.597 | 0.573 | 0.389 |
Table 2 Values of phenotypic plasticity of three species, Alternanthera philoxeroides, A. pungens and A. sessilis
| 喜旱莲子草 A. philoxeroides | 刺花莲子草 A. pungens | 莲子草 A. sessilis | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 叶面积 Leaf area | 0.621 | 0.519 | 0.468 |
| 叶质量 Leaf mass | 0.592 | 0.462 | 0.454 |
| 节间长 Internode length | 0.639 | 0.357 | 0.293 |
| 茎直径 Stem diameter | 0.597 | 0.573 | 0.389 |
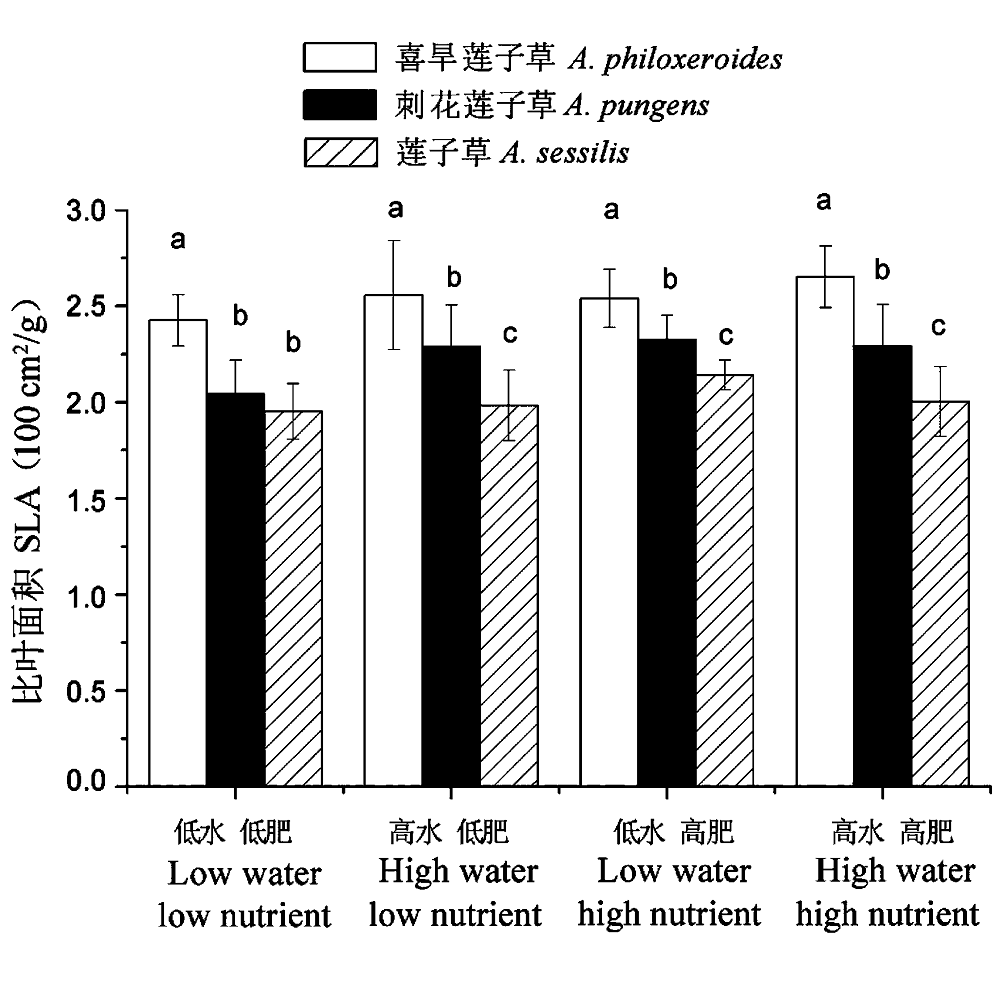
Fig. 3 Specific leaf area (SLA) of three studied species in different soil conditions. Different small letters indicate significant differences (P< 0.05) among species in the same soil condition, Alternanthera philoxeroides, A. pungens and A. sessilis.
| [1] | Agrawal AA, Kotanen PM (2003) Herbivores and the success of exotic plants: a phylogenetically controlled experiment. Ecology Letters, 6, 712-715. |
| [2] | Baret S, Maurice S, Le Bourgeois T, Strasberg D (2004) Altitudinal variation in fertility and vegetative growth in the invasive plant Rubus alceifolius Poiret (Rosaceae), on Reunion Island. Plant Ecology, 172, 265-273. |
| [3] | Bellingham PJ, Duncan RP, Lee WG, Buxton RP (2004) Seedling growth rate and survival do not predict invasiveness in naturalized woody plants in New Zealand. Oikos, 106, 308-316. |
| [4] |
Burns JH (2004) A comparison of invasive and non-invasive dayflowers (Commelinaceae) across experimental nutrient and water gradients. Diversity and Distributions, 10, 387-397.
DOI URL |
| [5] | Burns JH (2006) Relatedness and environment affect traits associated with invasive and non-invasive introduced Commelinaceae. Ecological Applications, 16, 1367-1376. |
| [6] | Daehler CC (2003) Performance comparisons of co-occurring native and alien invasive plants: implications for conservation and restoration. Annual Review of Ecology Evolution and Systematics, 34, 183-211. |
| [7] |
Feng YL (2008) Photosynthesis, nitrogen allocation and specific leaf area in invasive Eupatorium adenophorum and native Eupatorium japonicum grown at different irradiances. Physiologia Plantarum, 133, 318-326.
URL PMID |
| [8] |
Feng YL, Fu GL, Zheng YL (2008) Specific leaf area relates to the differences in leaf construction cost, photosynthesis, nitrogen allocation, and use efficiencies between invasive and noninvasive alien congeners. Planta, 228, 383-390.
DOI URL PMID |
| [9] | Garland T, Adolph SC (1994) Why not to do two-species comparative studies: limitations on inferring adaptation. Physiological Zoology, 67, 797-828. |
| [10] | Geng YP, Pan XY, Xu CY, Zhang WJ, Li B, Chen JK (2006) Phenotypic plasticity of invasive Alternanthera philoxeroides in relation to different water availability, compared to its native congener. Acta Oecologica, 30, 380-385. |
| [11] | Geng YP, Pan XY, Xu CY, Zhang WJ, Li B, Chen JK (2007) Plasticity and ontogenetic drift of biomass allocation in response to above- and below-ground resource availabilities in perennial herbs: a case study of Alternanthera philoxeroides. Ecological Research, 22, 255-260. |
| [12] | Gerlach JD, Rice KJ (2003) Testing life history correlates of invasiveness using congenetic plant species. Ecological Applications, 13, 167-179. |
| [13] |
Grotkopp E, Rejmanek M, Rost TL (2002) Toward a causal explanation of plant invasiveness: seedling growth and life-history strategies of 29 pine ( Pinus) species. The American Naturalist, 159, 396-419.
URL PMID |
| [14] | Grotkopp E, Rejmanek M (2007) High seedling relative growth rate and specific leaf area are traits of invasive species: phylogenetically independent contrasts of woody angiosperms. American Journal of Botany, 94, 526-532. |
| [15] | Hwang BC, Lauenroth WK (2008) Effect of nitrogen, water and neighbor density on the growth of Hesperis matronalis and two native perennials. Biological Invasions, 10, 771-779. |
| [16] | Julien M, Skarratt B, Maywald GF (1995) Potential geographical distribution of alligator weed and its biological control by Agasicles hygrophila. Journal of Aquatic Plant Management, 33, 55-60. |
| [17] | Kong XW (孔宪武), Jian ZP (简焯坡) (1979) Chenopodiaceae and Amaranthaceae. In: Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae, Tomus 25(2) (中国植物志第25卷第2分册) (ed. Delectis Florae Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae Agendae Academicae Sinicae Edita (中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会), pp. 234-236. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [18] | Leicht-Young SA, Silander JA, Latimer AM (2007) Comparative performance of invasive and native Celastrus species across environmental gradients. Oecologia, 154, 273-282. |
| [19] | Li B (李博), Chen JK (陈家宽) (2002) Ecology of biological invasions: achievements and challenges. World Science- Technology Research & Development (世界科技研究与发展), 24(2), 26-36. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [20] | Li MC (李明财), Zhu JJ (朱教君), Sun YR (孙一荣) (2009) Responses of specific leaf area of dominant tree species in Northeast China secondary forests to light intensity. Chinese Journal of Ecology (生态学杂志), 28, 1437-1442. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [21] | Mack RN, Simberloff D, Lonsdale WM, Evans H, Clout M, Bazzaz FA (2000) Biotic invasions: causes, epidemiology, global consequences, and control. Ecological Applications, 10, 689-710. |
| [22] | Pan XY, Geng YP, Xu CY, Zhang WJ, Li B, Chen JK (2006) The influence of abiotic stress and phenotypic plasticity on the distribution of invasive Alternanthera philoxeroides along a riparian zone. Acta Oecologica, 30, 333-341. |
| [23] | Pan XY (潘晓云), Geng YP (耿宇鹏), Sosa AJ, Zhang WJ (张文驹), Li B (李博), Chen JK (陈家宽) (2007) Invasive Alternanthera philoxeroides: biology, ecology and management. Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica (植物分类学报), 45, 884-900. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [24] | Rejmanek M, Richardson DV (1996) What attributes make some plant species more invasive? Ecology, 77, 1655-1661. |
| [25] |
Thompson JD (1991) The biology of an invasive plant: what makes Spartina anglica so successful. BioScience, 41, 393-401.
DOI URL |
| [26] | Valladares F, Wright SJ, Lasso E, Kitajima K, Pearcy RW (2000) Plastic phenotypic response to light of 16 congeneric shrubs from a Panamanian rainforest. Ecology, 81, 1925-1936. |
| [27] | Wang K (王坤), Yang J (杨继), Chen JK (陈家宽) (2009) The applications of congeneric comparisons in plant invasion ecology. Biodiversity Science (生物多样性), 17, 353-361. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [28] | Williams DG, Mack RN, Black RA (1995) Ecophysiology of introduced Pennisetum setaceum on Hawaii: the role of phenotypic plasticity. Ecology, 6, 1569-1580. |
| [29] | Wright IJ, Westoby M, Reich PB (2002) Convergence towards higher leaf mass per area in dry and nutrient-poor habitats has different consequences for leaf life span. Journal of Ecology, 90, 534-543. |
| [30] | Wu XC (吴晓成), Zhang QL (张秋良), Zang RG (臧润国), Lei QZ (雷庆哲) (2009) Leaf area index and specific leaf area of natural poplars in Ergis Basin. Journal of Northwest Forestry University (西北林业大学学报), 24, 10-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [31] |
Zheng YL, Feng YL, Liu WX, Liao ZY (2009) Growth, biomass allocation, morphology, and photosynthesis of invasive Eupatorium adenophorum and its native congeners grown at four irradiances. Plant Ecology, 203, 263-271.
DOI URL |
| [1] | Xiao-Qing Wu Meihui Zhang Suting Ge Manshu Li Kun Song Guochun Shen Jian Zhang. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Woody Plant Species Diversity and Aboveground Biomass during Near-Natural Forest Reconstruction in Shanghai: A Case Study from the Eco-Island in Minhang District [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | Gan Xie, Jing Xuan, Qidi Fu, Ze Wei, Kai Xue, Hairui Luo, Jixi Gao, Min Li. Establishing an intelligent identification model for unmanned aerial vehicle surveys of grassland plant diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [3] | Jingjing Zhang, Wenbin Huang, Yiting Chen, Zepeng Yang, Weiye Ke, Zhaojie Peng, Shichao Wei, Zhiwei Zhang, Yisi Hu, Wenhua Yu, Wenliang Zhou. Reef-building coral diversity and distribution characteristics in the National Nature Reserve for Marine Ecology of Guangdong Nanpeng Islands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [4] | Zhou Zhihua, Jin Xiaohua, Luo Ying, Li Diqiang, Yue Jianbing, Liu Fang, He Tuo, Li Xi, Dong Hui, Luo Peng. Analyses and suggestions on mechanisms of forestry and grassland administrations in China to achieve targets of Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24487-. |
| [5] | Wu Yuxuan, Wang Ping, Hu Xiaosheng, Ding Yi, Peng Tiantian, Zhi Qiuying, Bademu Qiqige, Li Wenjie, Guan Xiao, Li Junsheng. Evaluation of grassland degradation status and vegetation characteristics changes in Hulunbuir [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [6] | Donghong Li, Yuanyuan Hao, Huilin Gan, Hang Zhang, Yaomeng Liu, Fuyuan Ta, Guixin Hu. Distribution of grasshoppers (Orthoptera: Acridoidea) in different grassland types across the middle zone of the northern Qilian Mountains, western China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24119-. |
| [7] | Yixin Sun, Chunyu Hou, Lei Zhou, Xue Wei, Jinhao Ma, Juan Xue, Xiaohan Li, Pengfei Wu. Effects of annual and perennial potted legume forages on soil nematode communities in the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 24040-. |
| [8] | Xingyuan Yin, Hui An, Binbin Xing, Shiyu Su, Zhilin Wen, Jianchao Guo, Xiaoping Liu, Bo Wang. Effects of nutrient addition and precipitation changes on the stability of aboveground and belowground biomass in desert grassland [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 24073-. |
| [9] | Jiali Lian, Jing Chen, Xueqin Yang, Ying Zhao, Xu Luo, Cui Han, Yaxin Zhao, Jianping Li. Responses of desert steppe plant diversity and microbial diversity to precipitation change [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(6): 24044-. |
| [10] | Jianwei Cheng, Manhou Xu, Yongjing Dou, Yadong Wang, Yanan Wang, Xinmin Liu, Frank Yonghong Li. Seasonal dynamics of arthropod communities during horse dung decomposition in Inner Mongolian grasslands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(6): 24018-. |
| [11] | Teng Wang, Chunhou Li, Guanghua Wang, Jinfa Zhao, Juan Shi, Hongyu Xie, Yong Liu, Yu Liu. Species composition and succession of coral reef fishes on Qilianyu Island, Xisha Islands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(6): 23481-. |
| [12] | Fuwei Zhao, Yingshuo Li, Hui Chen. Reflections on biodiversity legislation in China’s new era [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 24027-. |
| [13] | Lejie Wu, Zekang Liu, Xing Tian, Qun Zhang, Bo Li, Jihua Wu. Effects of genotypic diversity on vegetative growth and reproductive strategies of Scirpus mariqueter population [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 23478-. |
| [14] | Yongcai Wang, Huawei Wan, Jixi Gao, Zhuowei Hu, Chenxi Sun, Na Lü, Zhiru Zhang. Identification of common native grassland plants in northern China using deep learning [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 23435-. |
| [15] | Fengming Wan, Huawei Wan, Zhiru Zhang, Jixi Gao, Chenxi Sun, Yongcai Wang. The application potential of unmanned aerial vehicle surveys in grassland plant diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(3): 23381-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()