



Biodiv Sci ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (5): 24444. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024444 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024444
Special Issue: 昆蒙框架目标12下的中国城市生物多样性研究专辑
• Original Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xiaoqing Wu1( ), Meihui Zhang1, Suting Ge1(
), Meihui Zhang1, Suting Ge1( ), Manshu Li1, Liangjun Da2, Kun Song1(
), Manshu Li1, Liangjun Da2, Kun Song1( ), Guochun Shen1(
), Guochun Shen1( ), Jian Zhang3,*(
), Jian Zhang3,*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2024-10-11
Accepted:2024-12-18
Online:2025-05-20
Published:2025-03-11
Contact:
Jian Zhang
Supported by:Xiaoqing Wu, Meihui Zhang, Suting Ge, Manshu Li, Liangjun Da, Kun Song, Guochun Shen, Jian Zhang. Spatiotemporal dynamics of woody plant species diversity and aboveground biomass during near-nature forest reconstruction in Shanghai: A case study from the eco-island in Minhang District[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24444.
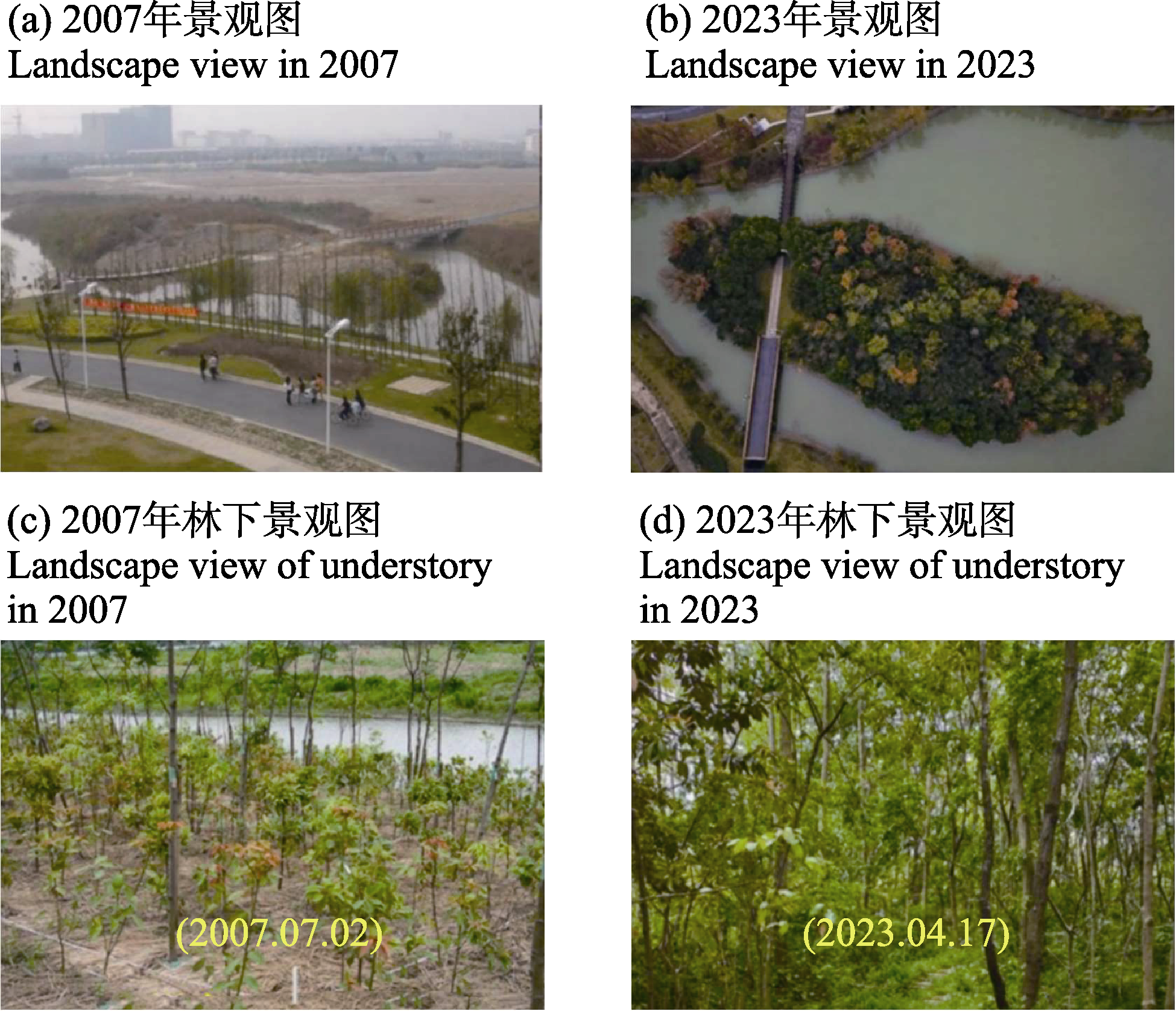
Fig. 1 Comparisons between the near-nature forest in 2007 and 2023 in Minhang District, Shanghai. Photos provider: (a) Liangjun Da; (b) Guochun Shen; (c) Liangjun Da; (d) Xiaoqing Wu.
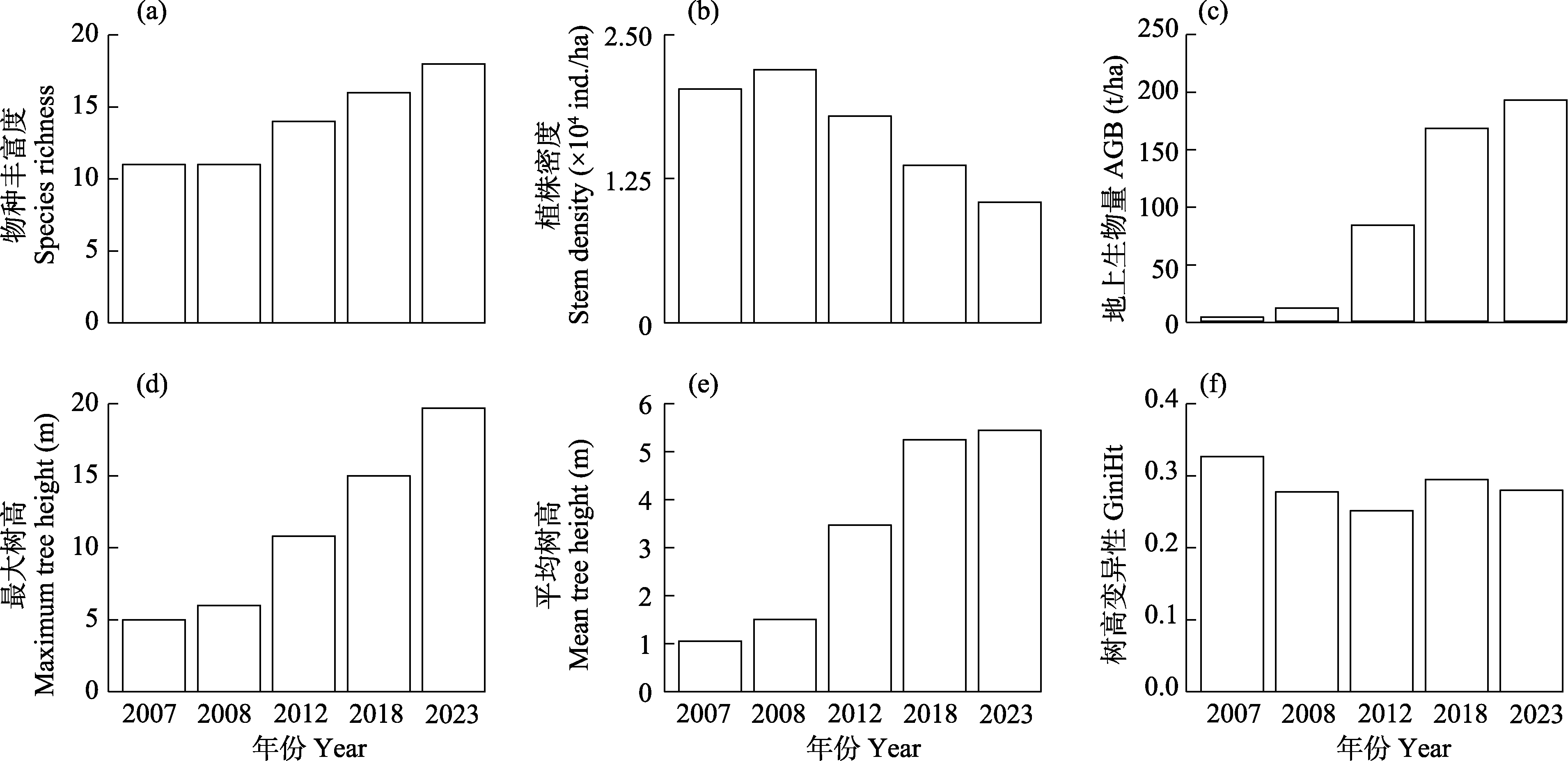
Fig. 2 Dynamics of plant community structural characteristics of near-nature forest from 2007 to 2023 in Minhang District, Shanghai. AGB, Aboveground biomass; GiniHt, Gini coefficient of tree height.
| 树种 Tree species | 地上生物量(地上生物量占比%) AGB (t/ha) (AGB percentage, %) | 平均树高 Mean tree height (m) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2007 | 2008 | 2012 | 2018 | 2023 | 2007 | 2008 | 2012 | 2018 | 2023 | |
| 楝 Melia azedarach | 1.22 (34.72) | 4.58 (37.45) | 16.80 (18.56) | 3.29 | 4.16 | 6.42 | ||||
| 朴树 Celtis sinensis | 0.92 (26.14) | 3.24 (26.48) | 11.62 (6.37) | 3.63 | 5.33 | 6.31 | ||||
| 珊瑚朴 Celtis julianae | 0.38 (10.87) | 1.50 (12.30) | 3.54 | 4.16 | ||||||
| 枫杨 Pterocarya stenoptera | 0.25 (7.14) | 1.03 (8.39) | 13.22 (14.60) | 41.44 (22.72) | 32.44 (15.53) | 3.33 | 4.53 | 8.31 | 11.62 | 11.70 |
| 红楠 Machilus thunbergii | 0.23 (6.46) | 0.67 (5.45) | 0.96 | 4.08 | ||||||
| 合欢 Albizia julibrissin | 16.61 (18.35) | 26.79 (14.69) | 10.91 (5.23) | 10.80 | 11.56 | 11.07 | ||||
| 樟 Camphora officinarum | 15.04 (16.62) | 39.16 (21.47) | 30.49 (14.60) | 8.20 | 7.00 | 12.04 | ||||
| 舟山新木姜子 Neolitsea sericea | 5.79 (6.40) | 3.31 | ||||||||
| 青冈 Quercus glauca | 5.06 (5.59) | 3.96 | ||||||||
| 女贞 Ligustrum lucidum | 12.76 (7.00) | 6.79 | ||||||||
| 小叶青冈 Quercus myrsinifolia | 12.36 (6.78) | 13.71 (6.57) | 4.89 | 5.14 | ||||||
| 麻栎 Quercus acutissima | 11.73 (6.43) | 9.10 | ||||||||
| 无患子 Sapindus saponaria | 45.72 (21.89) | 9.63 | ||||||||
| 复羽叶栾树 Koelreuteria bipinnata | 13.47 (6.45) | 12.40 | ||||||||
| 栾树 Koelreuteria paniculata | 11.89 (5.69) | 11.47 | ||||||||
Table 1 Temporal dynamics of aboveground biomass (AGB) and their mean tree heights in near-nature forest from 2007 to 2023 in Minhang District, Shanghai
| 树种 Tree species | 地上生物量(地上生物量占比%) AGB (t/ha) (AGB percentage, %) | 平均树高 Mean tree height (m) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2007 | 2008 | 2012 | 2018 | 2023 | 2007 | 2008 | 2012 | 2018 | 2023 | |
| 楝 Melia azedarach | 1.22 (34.72) | 4.58 (37.45) | 16.80 (18.56) | 3.29 | 4.16 | 6.42 | ||||
| 朴树 Celtis sinensis | 0.92 (26.14) | 3.24 (26.48) | 11.62 (6.37) | 3.63 | 5.33 | 6.31 | ||||
| 珊瑚朴 Celtis julianae | 0.38 (10.87) | 1.50 (12.30) | 3.54 | 4.16 | ||||||
| 枫杨 Pterocarya stenoptera | 0.25 (7.14) | 1.03 (8.39) | 13.22 (14.60) | 41.44 (22.72) | 32.44 (15.53) | 3.33 | 4.53 | 8.31 | 11.62 | 11.70 |
| 红楠 Machilus thunbergii | 0.23 (6.46) | 0.67 (5.45) | 0.96 | 4.08 | ||||||
| 合欢 Albizia julibrissin | 16.61 (18.35) | 26.79 (14.69) | 10.91 (5.23) | 10.80 | 11.56 | 11.07 | ||||
| 樟 Camphora officinarum | 15.04 (16.62) | 39.16 (21.47) | 30.49 (14.60) | 8.20 | 7.00 | 12.04 | ||||
| 舟山新木姜子 Neolitsea sericea | 5.79 (6.40) | 3.31 | ||||||||
| 青冈 Quercus glauca | 5.06 (5.59) | 3.96 | ||||||||
| 女贞 Ligustrum lucidum | 12.76 (7.00) | 6.79 | ||||||||
| 小叶青冈 Quercus myrsinifolia | 12.36 (6.78) | 13.71 (6.57) | 4.89 | 5.14 | ||||||
| 麻栎 Quercus acutissima | 11.73 (6.43) | 9.10 | ||||||||
| 无患子 Sapindus saponaria | 45.72 (21.89) | 9.63 | ||||||||
| 复羽叶栾树 Koelreuteria bipinnata | 13.47 (6.45) | 12.40 | ||||||||
| 栾树 Koelreuteria paniculata | 11.89 (5.69) | 11.47 | ||||||||
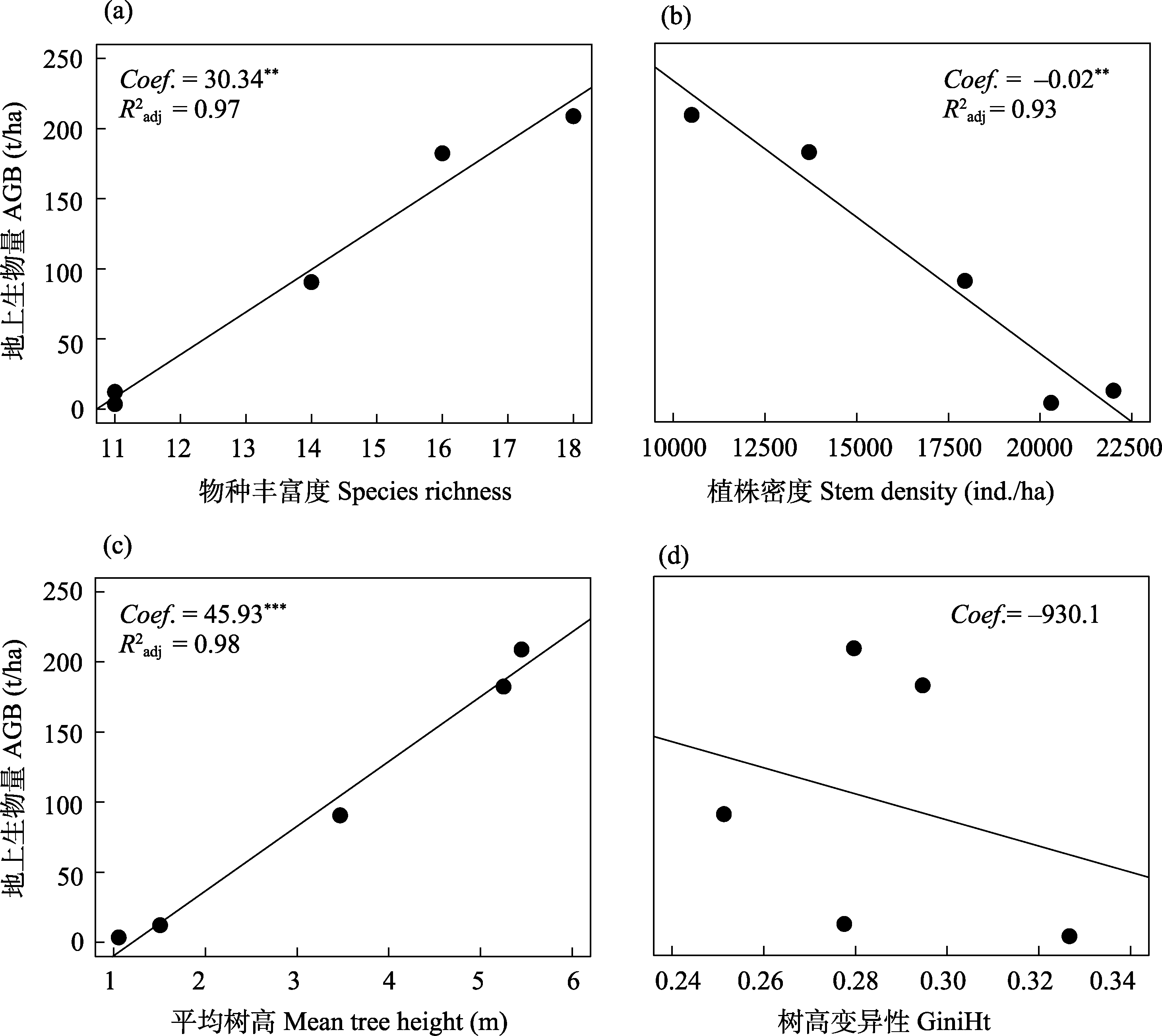
Fig. 3 Relations between aboveground biomass (AGB) and species richness (a), stem density (b), mean tree height (c), and Gini coefficient of tree height (GiniHt) (d) in near-nature forest in Minhang District, Shanghai. ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001.
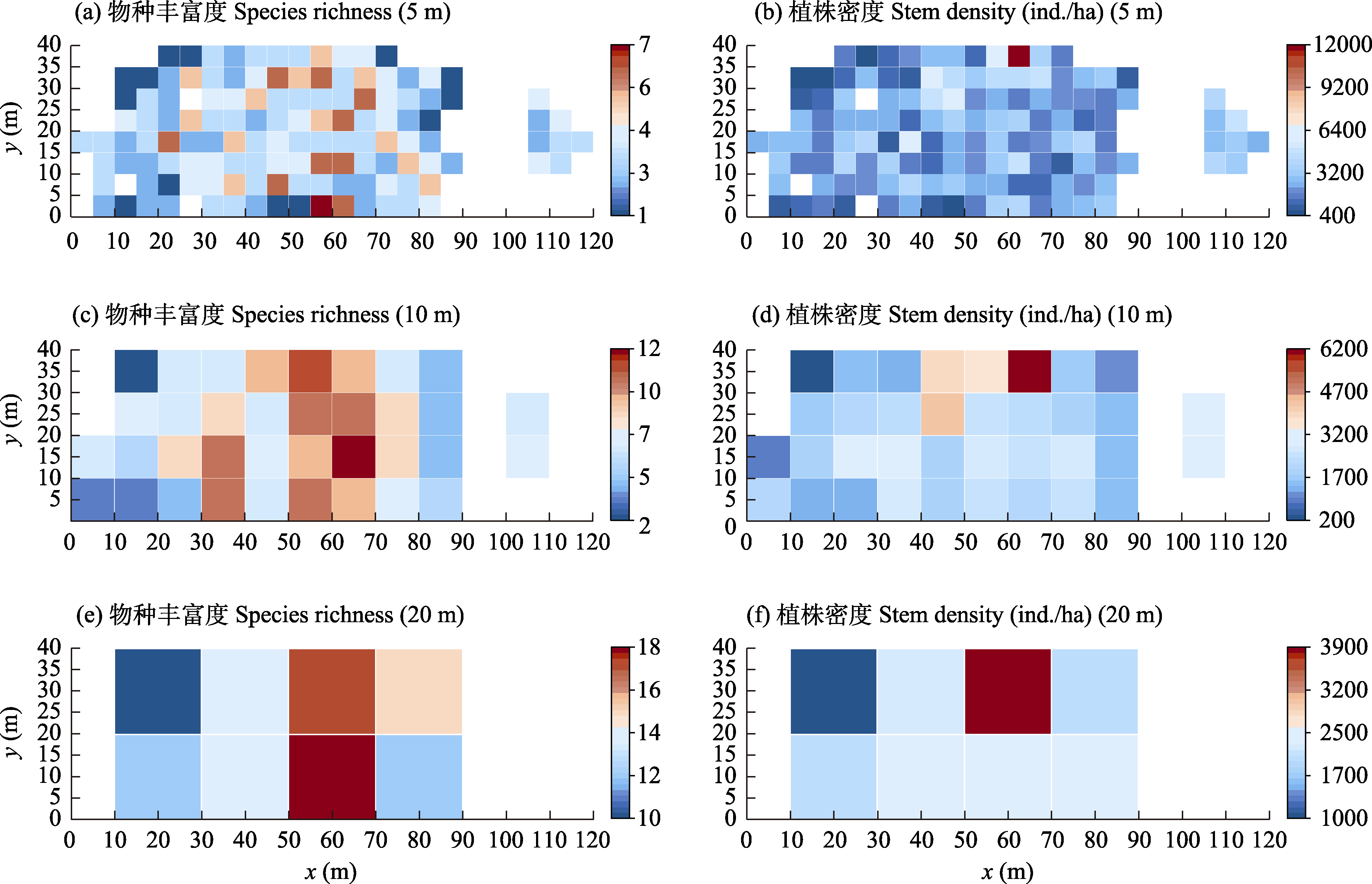
Fig. 4 Spatial distribution of species richness (a, c, e) and stem density (b, d, f) at three scales in near-nature forest in Minhang District, Shanghai. The horizontal and vertical coordinates represent the distances eastward and northward from the origin at the southwest corner in the landscape view, respectively.
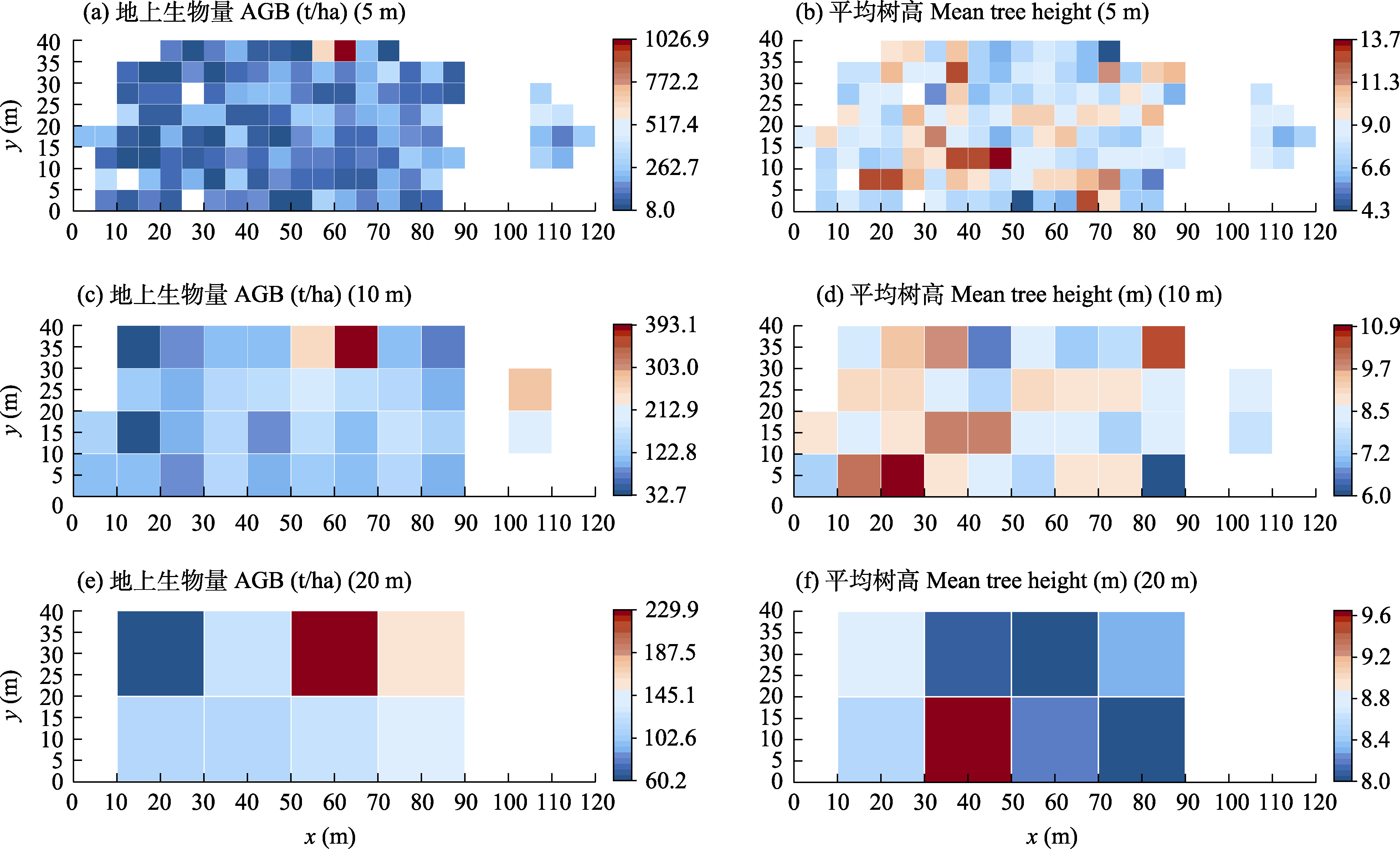
Fig. 5 Spatial distributions of plant aboveground biomass (AGB) (a, c, e) and mean tree height (b, d, f) at three scales in near-nature forest in Minhang District, Shanghai. The horizontal and vertical coordinates represent the distances eastward and northward from the origin at the southwest corner in the landscape view, respectively.
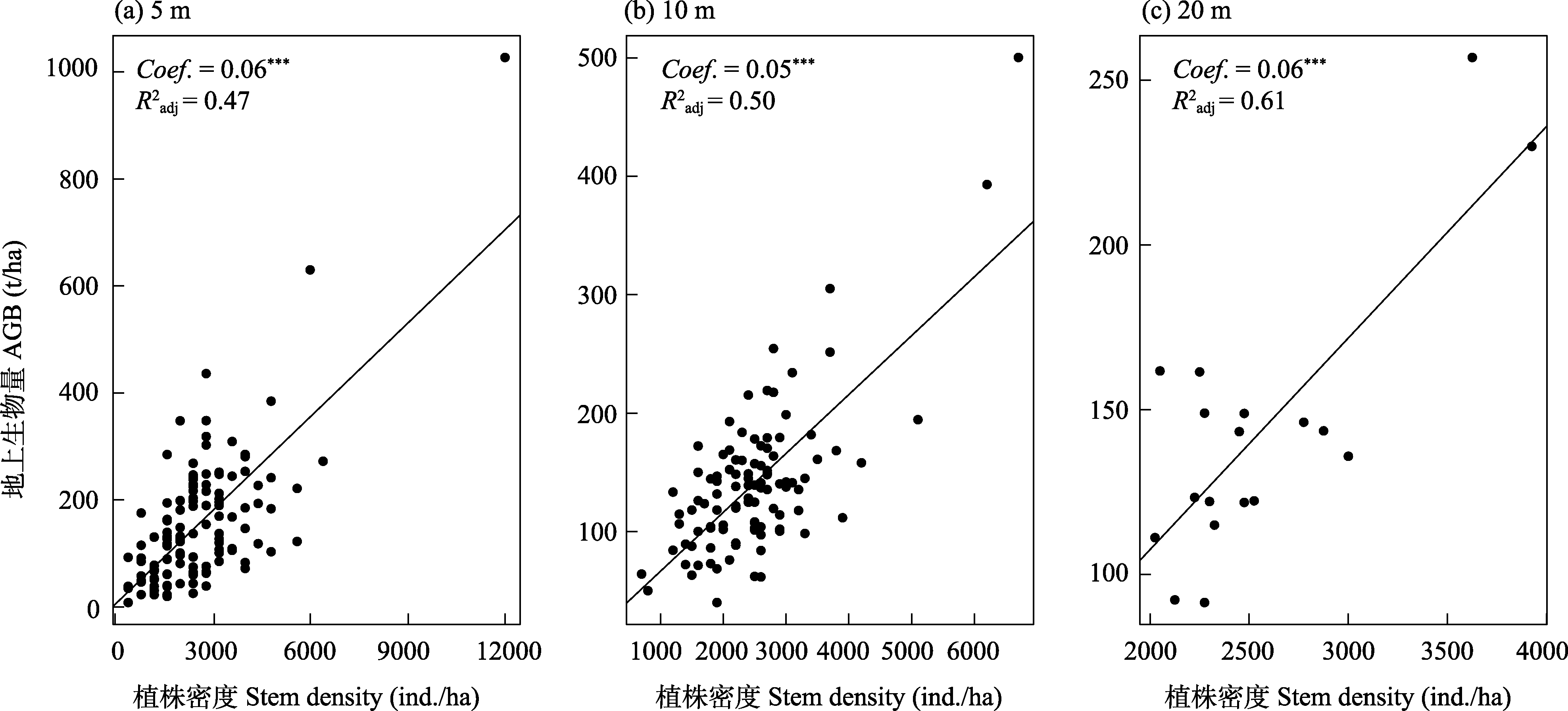
Fig. 6 Correlations between aboveground biomass (AGB) and stem density at three spatial scale in near-nature forest in Minhang District, Shanghai. *** P < 0.001.
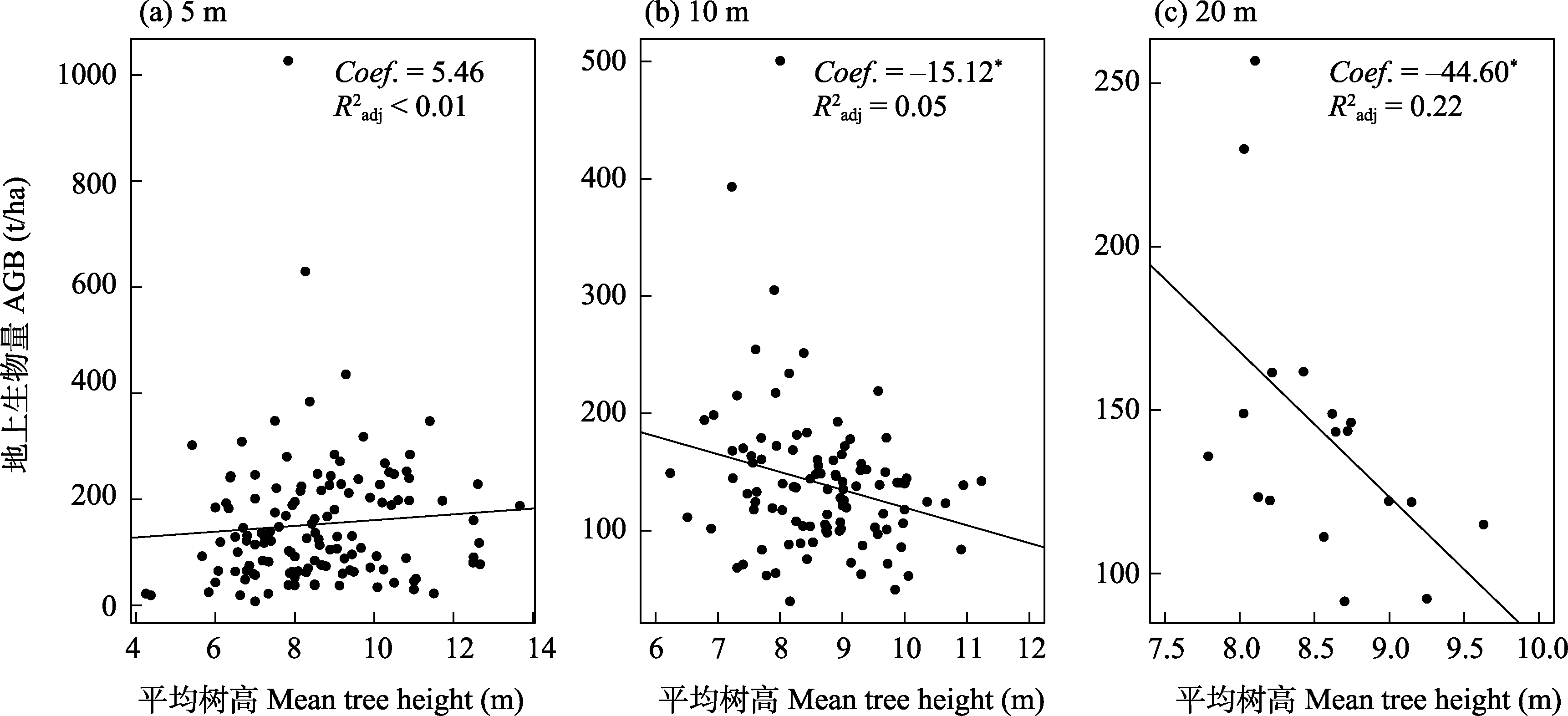
Fig. 7 Correlations between aboveground biomass (AGB) and mean height at three spatial scales in near-nature forest in Minhang District, Shanghai. * P < 0.05
| [1] |
Ammer C (2019) Diversity and forest productivity in a changing climate. New Phytologist, 221, 50-66.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | Aryal DR, De Jong BHJ, Sánchez-Silva S, Haas-Ek A, Esparza-Olguin L, Ochoa-Gaona S, Ghimire R, Morales-Ruiz DE (2024) Biomass recovery along a tropical forest succession: Trends on tree diversity, wood traits and stand structure. Forest Ecology and Management, 555, 121709. |
| [3] | Barrufol M, Schmid B, Bruelheide H, Chi XL, Hector A, Ma KP, Michalski S, Tang ZY, Niklaus PA (2013) Biodiversity promotes tree growth during succession in subtropical forest. PLoS ONE, 8, e81246. |
| [4] | Battles JJ, Shlisky AJ, Barrett RH, Heald RC, Allen-Diaz BH (2001) The effects of forest management on plant species diversity in a Sierran conifer forest. Forest Ecology and Management, 146, 211-222. |
| [5] | Bu WS, Zang RG, Ding Y (2014) Field observed relationships between biodiversity and ecosystem functioning during secondary succession in a tropical lowland rainforest. Acta Oecologica, 55, 1-7. |
| [6] |
Cardinale BJ, Matulich KL, Hooper DU, Byrnes JE, Duffy E, Gamfeldt L, Balvanera P, O’Connor MI, Gonzalez A (2011) The functional role of producer diversity in ecosystems. American Journal of Botany, 98, 572-592.
DOI PMID |
| [7] | Cardinale BJ, Wright JP, Cadotte MW, Carroll IT, Hector A, Srivastava DS, Loreau M, Weis JJ (2007) Impacts of plant diversity on biomass production increase through time because of species complementarity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 104, 18123-18128. |
| [8] | Carrus G, Scopelliti M, Lafortezza R, Colangelo G, Ferrini F, Salbitano F, Agrimi M, Portoghesi L, Semenzato P, Sanesi G (2015) Go greener, feel better? The positive effects of biodiversity on the well-being of individuals visiting urban and peri-urban green areas. Landscape and Urban Planning, 134, 221-228. |
| [9] | Chisholm RA, Muller-Landau HC, Abdul Rahman K, Bebber DP, Bin Y, Bohlman SA, Bourg NA, Brinks J, Bunyavejchewin S, Butt N, Cao H, Cao M, Cárdenas D, Chang L, Chiang J, Chuyong G, Condit R, Dattaraja HS, Davies S, Duque A, Fletcher C, Gunatilleke N, Gunatilleke S, Hao Z, Harrison RD, Howe R, Hsieh C, Hubbell SP, Itoh A, Kenfack D, Kiratiprayoon S, Larson AJ, Lian JY, Lin D, Liu HF, Lutz JA, Ma K, Malhi Y, McMahon S, McShea W, Meegaskumbura M, Mohd Razman S, Morecroft MD, Nytch CJ, Oliveira A, Parker GG, Pulla S, Punchi-Manage R, Romero-Saltos H, Sang WG, Schurman J, Su SH, Sukumar R, Sun IF, Suresh HS, Tan S, Thomas D, Thomas S, Thompson J, Valencia R, Wolf A, Yap S, Ye WH, Yuan ZQ, Zimmerman JK (2013) Scale-dependent relationships between tree species richness and ecosystem function in forests. Journal of Ecology, 101, 1214-1224. |
| [10] | Clements FE (1936) Nature and structure of the climax. Journal of Ecology, 24, 252-284. |
| [11] | Da LJ, Xu DX (2003) An attempt to build a “close-to-nature forest” in Shanghai. Journal of Chinese Urban Forestry, 1(2), 17-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [达良俊, 许东新 (2003) 上海城市“近自然森林”建设的尝试. 中国城市林业, 1(2), 17-20.] | |
| [12] | Da LJ, Yang YC, Chen YP (2004) The diversity of plant community on Dajinshan Island, Shanghai. Journal of Chinese Urban Forestry, 2(3), 22-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [达良俊, 杨永川, 陈燕萍 (2004) 上海大金山岛的自然植物群落多样性. 中国城市林业, 2(3), 22-25.] | |
| [13] | Guo Q (2003) Temporal species richness-biomass relationships along successional gradients. Journal of Vegetation Science, 14, 121-128. |
| [14] | Hooper DU, Chapin FS, Ewel JJ, Hector A, Inchausti P, Lavorel S, Lawton JH, Lodge DM, Loreau M, Naeem S, Schmid B, Setälä H, Symstad AJ, Vandermeer J, Wardle DA (2005) Effects of biodiversity on ecosystem functioning: A consensus of current knowledge. Ecological Monographs, 75, 3-35. |
| [15] | Justine MF, Yang W, Wu F, Tan B, Khan MN, Zhao Y (2015) Biomass stock and carbon sequestration in a chronosequence of Pinus massoniana plantations in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River. Forests, 6, 3665-3682. |
| [16] | Lasky JR, Uriarte M, Boukili VK, Erickson DL, Kress WJ, Chazdon RL, Vila M (2014) Relationship between tree biodiversity and biomass dynamics changes with tropical forest succession. Ecology Letters, 17, 1158-1167. |
| [17] | Levin SA (1992) The problem of pattern and scale in ecology. Ecology, 73, 1943-1967. |
| [18] | Li WJ, Li JH, Liu SS, Zhang RL, Qi W, Zhang RY, Knops JMH, Lu JF (2017) Magnitude of species diversity effect on aboveground plant biomass increases through successional time of abandoned farmlands on the eastern Tibetan Plateau of China. Land Degradation & Development, 28, 370-378. |
| [19] | Liu BB, Lou LH, Liu GN, Zhang DB, Ye Q (2013) Growth of Cyclobalanopsis myrsinaefolia in Zhejiang, China. Journal of Zhejiang Agriculture & Forest University, 30, 517-522. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘彬彬, 楼炉焕, 刘广宁, 张东北, 叶青 (2013) 浙江省小叶青冈生长过程的研究. 浙江农林大学学报, 30, 517-522.] | |
| [20] | Liu J, Wang D, Yan X, Jia L, Chen N, Liu J, Zhao P, Zhou L, Cao Q (2024) Effect of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilization management on soil properties and leaf traits and yield of Sapindus mukorossi. Frontiers in Plant Science, 15, 1300683. |
| [21] | Loreau M, Hector A (2001) Partitioning selection and complementarity in biodiversity experiments. Nature, 412, 72-76. |
| [22] | MacArthur RH, Wilson EO (1967) The Theory of Island Biogeography. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [23] | Miyawaki A (1999) Creative ecology: Restoration of native forests by native trees. Plant Biotechnology, 16, 15-25. |
| [24] | Ouyang S, Xiang W, Wang X, Zeng Y, Lei P, Deng X, Peng C (2016) Significant effects of biodiversity on forest biomass during the succession of subtropical forest in south China. Forest Ecology and Management, 372, 291-302. |
| [25] | Pesola L, Cheng X, Sanesi G, Colangelo G, Elia M, Lafortezza R (2017) Linking above-ground biomass and biodiversity to stand development in urban forest areas: A case study in Northern Italy. Landscape and Urban Planning, 157, 90-97. |
| [26] | Poorter L, van der Sande MT, Thompson J, Arets EJMM, Alarcón A, Álvarez-Sánchez J, Ascarrunz N, Balvanera P, Barajas-Guzmán G, Boit A, Bongers F, Carvalho FA, Casanoves F, Cornejo-Tenorio G, Costa FRC, de Castilho CV, Duivenvoorden JF, Dutrieux LP, Enquist BJ, Fernández-Méndez F, Finegan B, Gormley LHL, Healey JR, Hoosbeek MR, Ibarra-Manríquez G, Junqueira AB, Levis C, Licona JC, Lisboa LS, Magnusson WE, Martínez-Ramos M, Martínez-Yrizar A, Martorano LG, Maskell LC, Mazzei L, Meave JA, Mora F, Muñoz R, Nytch C, Pansonato MP, Parr TW, Paz H, Pérez-García EA, Rentería LY, Rodríguez-Velazquez J, Rozendaal DMA, Ruschel AR, Sakschewski B, Salgado-Negret B, Schietti J, Simões M, Sinclair FL, Souza PF, Souza FC, Stropp J ter Steege H, Swenson NG, Thonicke K, Toledo M, Uriarte M, van ter Hout P, Walker P, Zamora N, Peña-Claros M (2015) Diversity enhances carbon storage in tropical forests. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 24, 1314-1328. |
| [27] | Preston FW (1960) Time and space and the variation of species. Ecology, 41, 785-790. |
| [28] |
Qi ZY (2023) Urban forest construction and vertical greening development under climate change. Landscape Architecture Frontiers, 11(1), 58-64. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [戚智勇 (2023) 气候变化背景下的城市森林构建与立体绿化发展. 景观设计学(中英文), 11(1), 58-64.] | |
| [29] | R Core Team (2022) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. |
| [30] | Song K, Guo XY, Wang ZY, Huang SS, Yan JY, Ye JH, Le Y, Yan M, Wu M, Da LJ (2020) Restoration dynamics of near-to-nature forests in Shanghai. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 39, 1075-1081. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [宋坤, 郭雪艳, 王泽英, 黄莎莎, 严佳瑜, 叶建华, 乐莺, 严明, 吴梅, 达良俊 (2020) 上海城市近自然森林的重建动态. 生态学杂志, 39, 1075-1081.] | |
| [31] |
Trogisch S, Liu X, Rutten G, Xue K, Bauhus J, Brose U, Bu W, Cesarz S, Chesters D, Connolly J, Cui X, Eisenhauer N, Guo L, Haider S, Härdtle W, Kunz M, Liu L, Ma Z, Neumann S, Sang W, Schuldt A, Tang Z, van Dam NM, von Oheimb G, Wang M, Wang S, Weinhold A, Wirth C, Wubet T, Xu X, Yang B, Zhang N, Zhu C, Ma K, Wang Y, Bruelheide H (2021) The significance of tree-tree interactions for forest ecosystem functioning. Basic and Applied Ecology, 55, 33-52.
DOI |
| [32] | Wasof S, Lenoir J, Hattab T, Jamoneau A, Gallet-Moron E, Ampoorter E, Saguez R, Bennsadek L, Bertrand R, Valdès A, Verheyen K, Decocq G (2018) Dominance of individual plant species is more important than diversity in explaining plant biomass in the forest understory. Journal of Vegetation Science, 29, 521-531. |
| [33] | Williams LJ, Paquette A, Cavender-Bares J, Messier C, Reich PB (2017) Spatial complementarity in tree crowns explains overyielding in species mixtures. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 1, 63. |
| [34] | Xia YJ, Zhang J, Zou S, Tang XL, Li F (2018) Dynamics of structural diversity and carbon storage along a successional gradient in south subtropical forest. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27, 424-431. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[夏艳菊, 张静, 邹顺, 唐旭利, 李凤 (2018) 南亚热带森林群落演替过程中结构多样性与碳储量的变化. 生态环境学报, 27, 424-431.]
DOI |
|
| [35] |
Xie L, Chen H, Wei L, Chen S, Wang L, Xu B, Yi X, Wang X, Ding H, Fang Y (2023) Scale-dependent effects of species diversity on aboveground biomass and productivity in a subtropical broadleaved forest on Mt. Huangshan. Ecology and Evolution, 13, e9786.
DOI PMID |
| [36] | Yao Z, Liu J, Zhao X, Long D, Wang L (2015) Spatial dynamics of aboveground carbon stock in urban green space: A case study of Xi’an, China. Journal of Arid Land, 7(1), 350-360. |
| [37] | Zeng WS, Tang SZ (2012) A new general biomass allometric model. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 48(1), 48-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [曾伟生, 唐守正 (2012) 一个新的通用性相对生长生物量模型. 林业科学, 48(1), 48-52.] | |
| [38] | Zhao ZH, Hui GY (2020) Advances in structural diversity of stand structure. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 56(9), 143-152. |
| [赵中华, 惠刚盈 (2020) 林分结构多样性研究进展. 林业科学, 56(9), 143-152.] |
| [1] | Zhengdong Pan, Xirong Lin, Hua Xue, Zhiying Hu, Hongyi Guo, Ya Zhang, Enuo Wu, Wenqiao Tang. Fish species diversity background and community structure in the main inland water bodies of Shanghai [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(6): 24290-. |
| [2] | Wen Peng, Zeshuai Deng, Wenbao Zheng, Lingxuan Gong, Yufeng Zeng, Hao Meng, Jun Chen, Daode Yang. Application of eDNA technology in amphibian surveys: A case study of Hunan Mangshan National Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(6): 24552-. |
| [3] | Lulu Zhang, Zhaojie Ren, Ningning Yu, Fengxi Zhao, Zuntian Zhao. List of bryophytes in Gansu Province, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(6): 24451-. |
| [4] | Liu Yonghua, Tong Guangrong, Yu Hangyuan, Wang Ningning, Ren Haibao, Chen Lei, Ma Keping, Mi Xiangcheng. Responses of canopy three-dimensional structural and spectral characteristics to anthropogenic disturbance in the Qianjiangyuan section of the Qianjiangyuan- Baishanzu National Park candidate area [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24174-. |
| [5] | Wang Tai, Song Fujun, Zhang Yongsheng, Lou Zhongyu, Zhang Yanping, Du Yanyan. Fish diversity and resource status in interior drainage systems of Hexi Corridor [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [6] | Zhang Jingjing, Huang Wenbin, Chen Yiting, Yang Zepeng, Ke Weiye, Peng Zhaojie, Wei Shichao, Zhang Zhiwei, Hu Yisi, Yu Wenhua, Zhou Wenliang. Reef-building coral diversity and distribution characteristics in the National Nature Reserve for Marine Ecology of Guangdong Nanpeng Islands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [7] | Shang Huadan, Zhang Chuqing, Wang Mei, Pei Wenya, Li Guohong, Wang Hongbin. Species diversity and geographic distribution of poplar pests in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [8] | Wu Yuxuan, Wang Ping, Hu Xiaosheng, Ding Yi, Peng Tiantian, Zhi Qiuying, Bademu Qiqige, Li Wenjie, Guan Xiao, Li Junsheng. Evaluation of grassland degradation status and vegetation characteristics changes in Hulunbuir [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [9] | Zihong Chen, Yifei Zhang, Kai Chen, Jianying Chen, Ling Xu. Species diversity of entomopathogenic fungi and the influencing factors in the Southern Gaoligong Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [10] | Ke Tan, Yao Ning, Renfen Wang, Qing Wang, Danping Liang, Zibing Xin, Fang Wen. A dataset on the checklist and geographical distribution of Gesneriaceae in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [11] | Jianan Han, Yang Su, Fei Li, Junyan Liu, Yilin Zhao, Lin Li, Jiancheng Zhao, Hongzhu Liang, Min Li. Bryophytes diversity of Hebei Province, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [12] | Hongyu Niu, Lu Chen, Hengyue Zhao, Gulzar Abdukirim, Hongmao Zhang. Effects of urbanization on animals: From community to individual level [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [13] | Xue Bai, Zhengfei Li, Yang Liu, Junqian Zhang, Duopeng Zhang, Xin Luo, Jiali Yang, Lina Du, Xuankong Jiang, Ruiwen Wu, Zhicai Xie. Species diversity and maintenance mechanisms of benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages in the Xijiang River [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| [14] | Jia Xu, Xiaojuan Cui, Yifei Zhang, Chang Wu, Yuandong Sun. Fish diversity and distribution in the Nanling region [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [15] | Qiyu Kuang, Liang Hu. Species diversity and geographical distribution of marine benthic shell-bearing mollusks around Donghai Island and Naozhou Island, Guangdong Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 24065-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()