



Biodiv Sci ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (6): 24018. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024018 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024018
• Original Papers: Animal Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jianwei Cheng1,2( ), Manhou Xu1(
), Manhou Xu1( ), Yongjing Dou1, Yadong Wang2(
), Yongjing Dou1, Yadong Wang2( ), Yanan Wang2(
), Yanan Wang2( ), Xinmin Liu3, Frank Yonghong Li2,*(
), Xinmin Liu3, Frank Yonghong Li2,*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2024-01-18
Accepted:2024-04-16
Online:2024-06-20
Published:2024-06-12
Contact:
* E-mail: lifyhong@126.comJianwei Cheng, Manhou Xu, Yongjing Dou, Yadong Wang, Yanan Wang, Xinmin Liu, Frank Yonghong Li. Seasonal dynamics of arthropod communities during horse dung decomposition in Inner Mongolian grasslands[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(6): 24018.
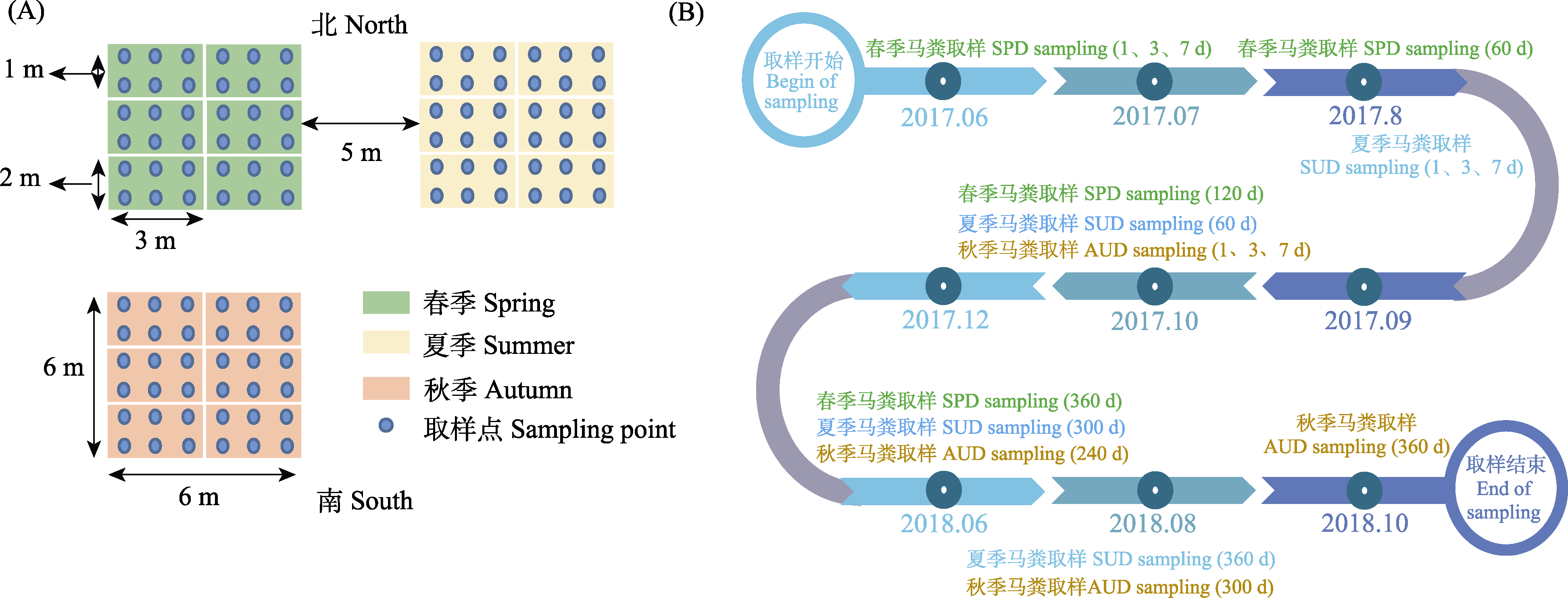
Fig. 1 Field arrangement (A) and sampling scheme (B) of the horse dung decomposition experiment in different seasons. SPD, Horse dung in spring; SUD, Horse dung in summer; AUD, Horse dung in autumn.
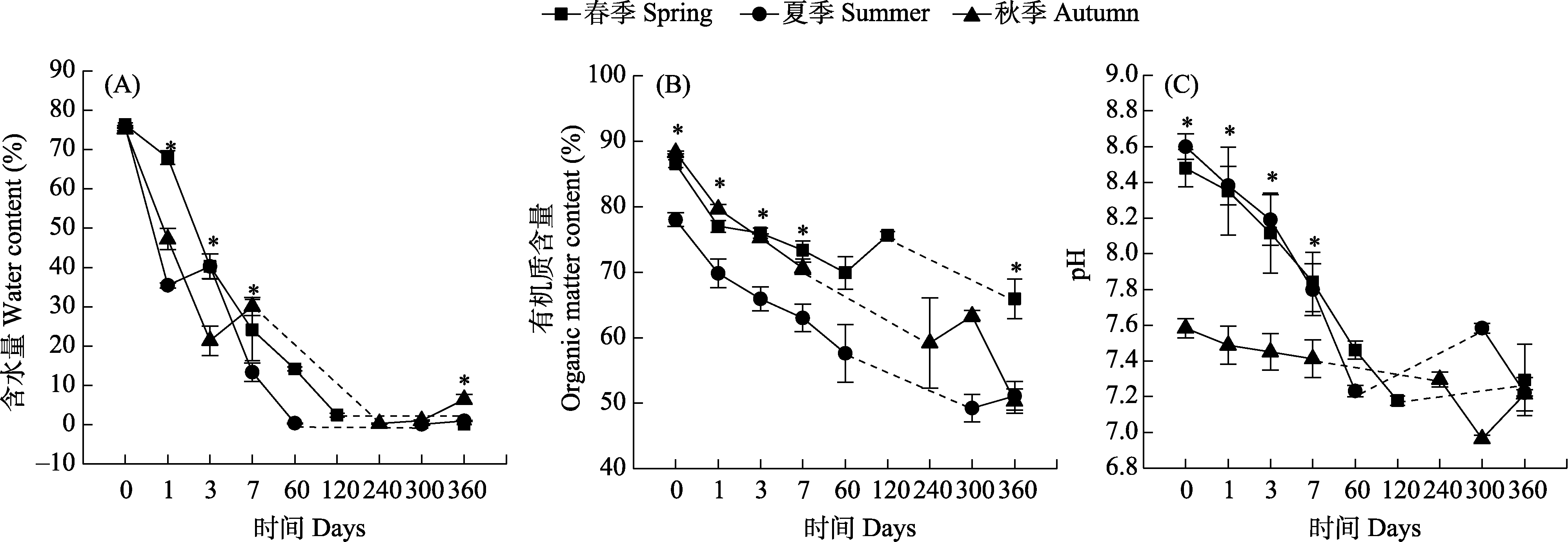
Fig. 3 Changes in the physical and chemical properties of horse dung in different seasons. The dashed line indicates no sampling at the time period. The significant differences between seasons at P < 0.05 are denoted using * (one-way ANOVA with Duncan’s multiple-range tests for post hoc comparisons).
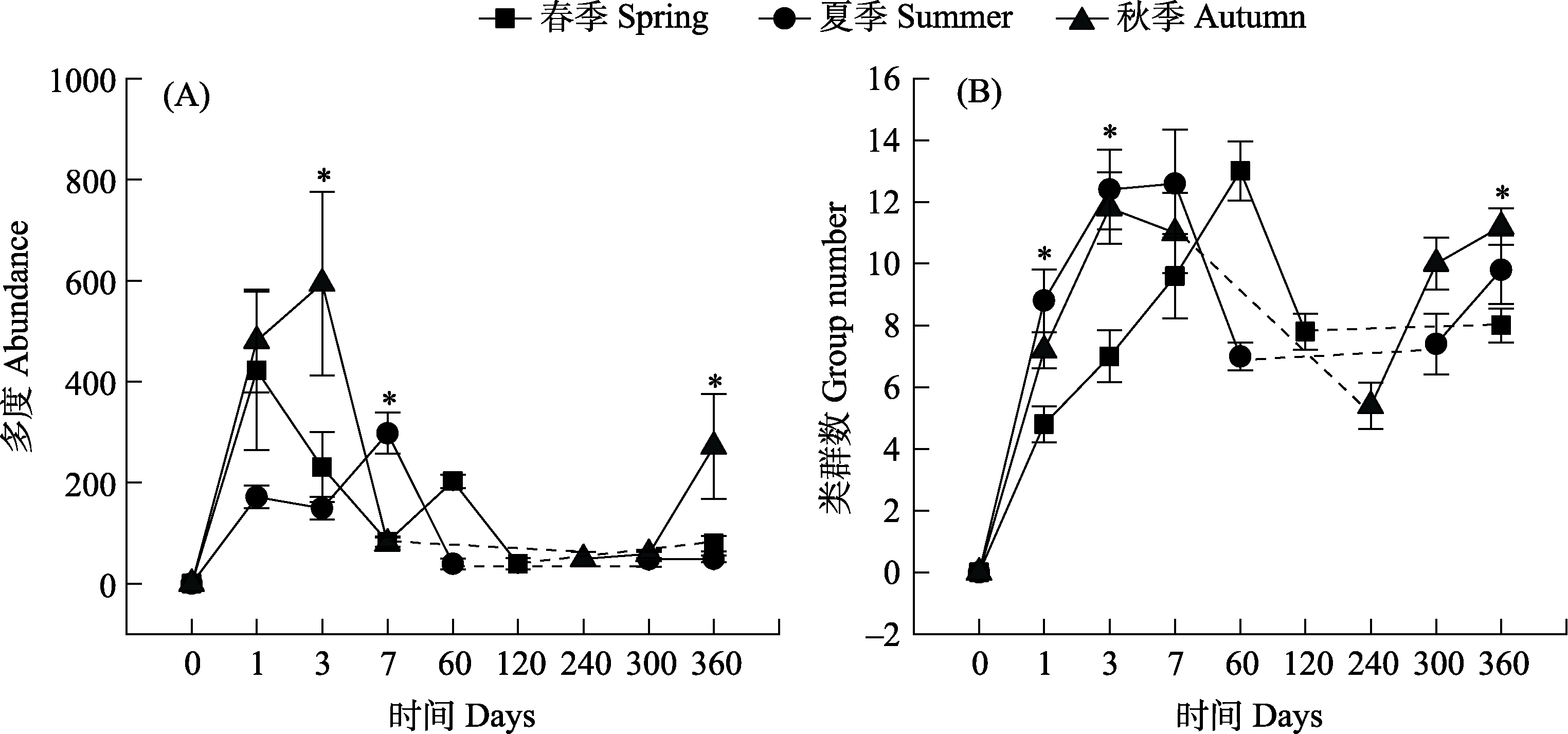
Fig. 4 Changes in the abundance (A) and group number (B) of arthropod communities in horse dung in different seasons. The dashed line indicates no sampling at the time period. The significant differences between seasons at P < 0.05 are denoted using * (one-way ANOVA with Duncan’s multiple-range tests for post hoc comparisons).
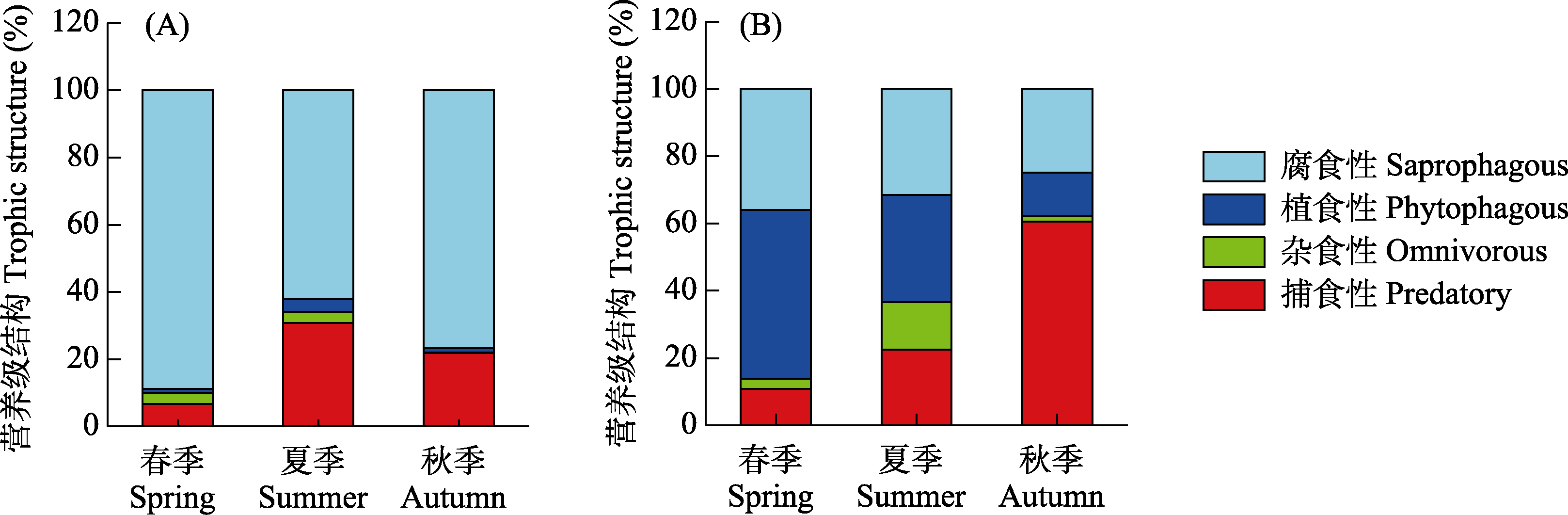
Fig. 5 Relative proportions of abundance of functional groups of arthropods in horse dung in different seasons during the early (A) and late stages (B) of decomposition
| 物种 Species | 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer | 秋季 Autumn | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 多度 Abundance (N) | 优势度 Dominance (%) | 多度 Abundance (N) | 优势度 Dominance (%) | 多度 Abundance (N) | 优势度 Dominance (%) | |
| 双顶嗡蜣螂 Onthophagus bivertex | 6 | 0.19 | 1 | 0.14 | 7 | 0.18 |
| 小驼嗡蜣螂 Onthophagus gibbulus | 2 | 0.06 | 42 | 5.80 | 173 | 4.33 |
| 黑缘嗡蜣螂 Onthophagus marginalis nigrimargo | 4 | 0.13 | 1 | 0.03 | ||
| 立叉嗡蜣螂 Onthophagus olsoufieffi | 4 | 0.09 | ||||
| 游荡蜉金龟 Aphodius erraticus | 1 | 0.03 | ||||
| 直蜉金龟 Aphodius rectus | 3,733 | 93.38 | ||||
| 马粪蜉金龟 Aphodius subterraneus | 1 | 0.03 | 1 | 0.03 | ||
| 泥蜉金龟 Aphodius sordescens | 2,647 | 85.41 | 672 | 93.79 | 3 | 0.08 |
| 符号蜉金龟 Aphodius comma | 435 | 14.04 | ||||
| 布尔蜉金龟 Aphodius burgaltaicus | 76 | 1.89 | ||||
| 甫拉蜉金龟 Aphodius praeustus | 1 | 0.14 | ||||
| Aphodius insularis | 1 | 0.14 | ||||
| Aphodius corallifer | 1 | 0.03 | ||||
| Aphodius chinensis | 2 | 0.06 | ||||
| 个体数 No. of individuals | 3,099 | 717 | 3,998 | |||
| 物种数 Species richness | 9 | 5 | 8 | |||
Table 1 Composition of dung beetle communities in the horse dung in different seasons
| 物种 Species | 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer | 秋季 Autumn | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 多度 Abundance (N) | 优势度 Dominance (%) | 多度 Abundance (N) | 优势度 Dominance (%) | 多度 Abundance (N) | 优势度 Dominance (%) | |
| 双顶嗡蜣螂 Onthophagus bivertex | 6 | 0.19 | 1 | 0.14 | 7 | 0.18 |
| 小驼嗡蜣螂 Onthophagus gibbulus | 2 | 0.06 | 42 | 5.80 | 173 | 4.33 |
| 黑缘嗡蜣螂 Onthophagus marginalis nigrimargo | 4 | 0.13 | 1 | 0.03 | ||
| 立叉嗡蜣螂 Onthophagus olsoufieffi | 4 | 0.09 | ||||
| 游荡蜉金龟 Aphodius erraticus | 1 | 0.03 | ||||
| 直蜉金龟 Aphodius rectus | 3,733 | 93.38 | ||||
| 马粪蜉金龟 Aphodius subterraneus | 1 | 0.03 | 1 | 0.03 | ||
| 泥蜉金龟 Aphodius sordescens | 2,647 | 85.41 | 672 | 93.79 | 3 | 0.08 |
| 符号蜉金龟 Aphodius comma | 435 | 14.04 | ||||
| 布尔蜉金龟 Aphodius burgaltaicus | 76 | 1.89 | ||||
| 甫拉蜉金龟 Aphodius praeustus | 1 | 0.14 | ||||
| Aphodius insularis | 1 | 0.14 | ||||
| Aphodius corallifer | 1 | 0.03 | ||||
| Aphodius chinensis | 2 | 0.06 | ||||
| 个体数 No. of individuals | 3,099 | 717 | 3,998 | |||
| 物种数 Species richness | 9 | 5 | 8 | |||
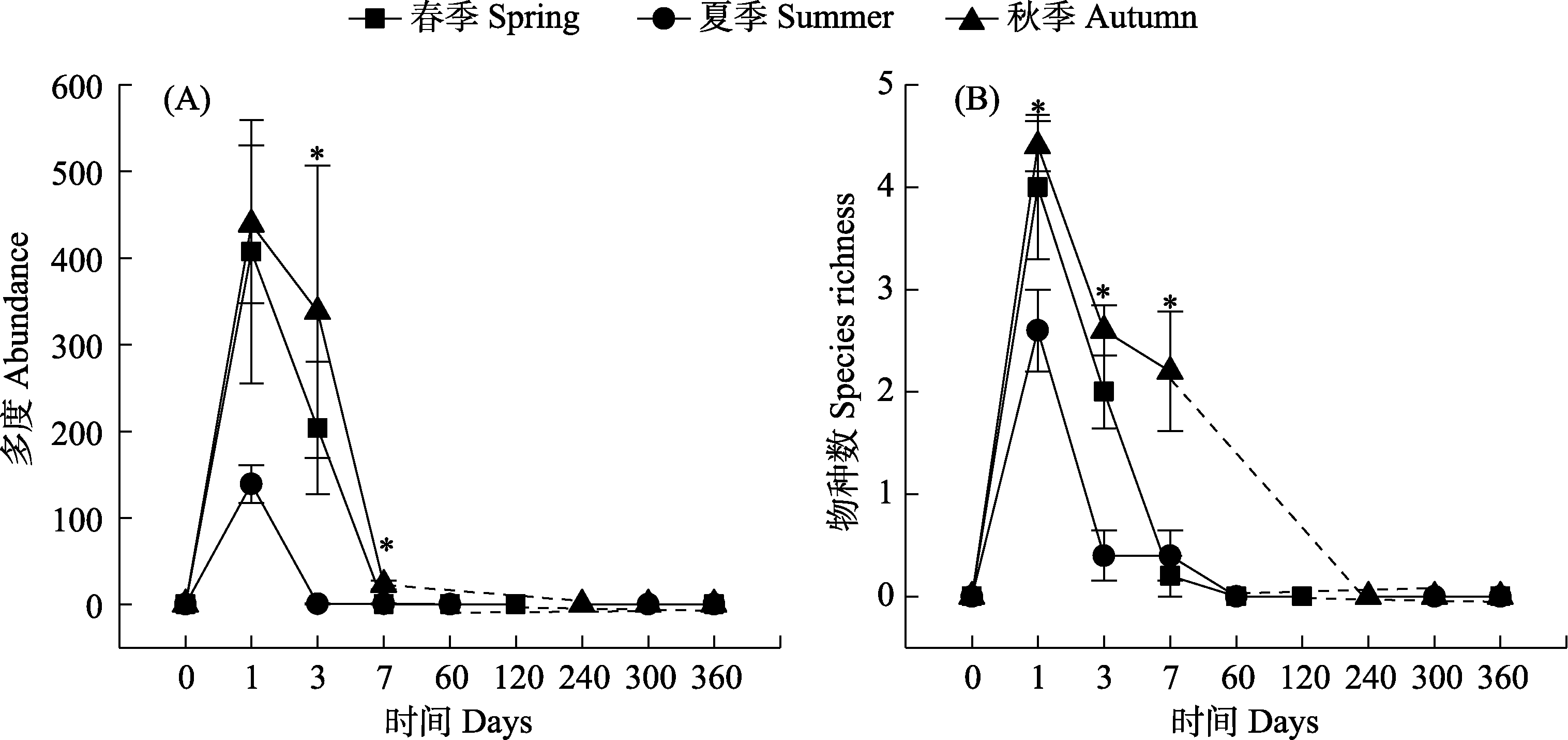
Fig. 6 Changes in the abundance (A) and species richness (B) of dung beetle communities in the horse dung in different seasons. The dashed line indicates no sampling at the time period. The significant differences between seasons at P < 0.05 are denoted using * (one-way ANOVA with Duncan’s multiple-range tests for post hoc comparisons).
| 亚科 Subfamily | 属 Genus | 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer | 秋季 Autumn | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 多度 Abundance (N) | 优势度 Dominance (%) | 多度 Abundance (N) | 优势度 Dominance (%) | 多度 Abundance (N) | 优势度 Dominance (%) | ||
| 前角隐翅虫亚科 Aleocharinae | Ocalea | 15 | 22.39 | 16 | 6.11 | ||
| Oxypoda | 9 | 13.43 | 5 | 5.33 | 81 | 31.19 | |
| Parapimela | 6 | 8.96 | 68 | 26.18 | |||
| Silusa | 45 | 48.04 | 71 | 27.34 | |||
| Aleachara | 6 | 8.96 | 6 | 6.40 | 1 | 0.51 | |
| 胸片隐翅虫亚科 Xantholininae | Saurohypnus | 5 | 5.05 | ||||
| 异形隐翅虫亚科 Oxytelinae | Neoxus | 3 | 4.48 | ||||
| Oncoparia | 3 | 4.48 | |||||
| Oxytelopsis | 9 | 13.43 | |||||
| 背筋隐翅虫属 Oxytelus | 13 | 19.40 | 24 | 25.59 | 21 | 7.90 | |
| Sartallus | 1 | 0.39 | |||||
| 粪隐翅虫属 Coprophilus | 3 | 4.48 | 9 | 9.59 | |||
| 隐翅虫亚科 Staphylinidae | Staphylinaus | 1 | 0.39 | ||||
| 个体数 No. of individuals | 67 | 94 | 260 | ||||
| 属数 No. of genus | 9 | 6 | 8 | ||||
Table 2 Composition of Staphylinidae community in horse dung in different seasons
| 亚科 Subfamily | 属 Genus | 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer | 秋季 Autumn | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 多度 Abundance (N) | 优势度 Dominance (%) | 多度 Abundance (N) | 优势度 Dominance (%) | 多度 Abundance (N) | 优势度 Dominance (%) | ||
| 前角隐翅虫亚科 Aleocharinae | Ocalea | 15 | 22.39 | 16 | 6.11 | ||
| Oxypoda | 9 | 13.43 | 5 | 5.33 | 81 | 31.19 | |
| Parapimela | 6 | 8.96 | 68 | 26.18 | |||
| Silusa | 45 | 48.04 | 71 | 27.34 | |||
| Aleachara | 6 | 8.96 | 6 | 6.40 | 1 | 0.51 | |
| 胸片隐翅虫亚科 Xantholininae | Saurohypnus | 5 | 5.05 | ||||
| 异形隐翅虫亚科 Oxytelinae | Neoxus | 3 | 4.48 | ||||
| Oncoparia | 3 | 4.48 | |||||
| Oxytelopsis | 9 | 13.43 | |||||
| 背筋隐翅虫属 Oxytelus | 13 | 19.40 | 24 | 25.59 | 21 | 7.90 | |
| Sartallus | 1 | 0.39 | |||||
| 粪隐翅虫属 Coprophilus | 3 | 4.48 | 9 | 9.59 | |||
| 隐翅虫亚科 Staphylinidae | Staphylinaus | 1 | 0.39 | ||||
| 个体数 No. of individuals | 67 | 94 | 260 | ||||
| 属数 No. of genus | 9 | 6 | 8 | ||||
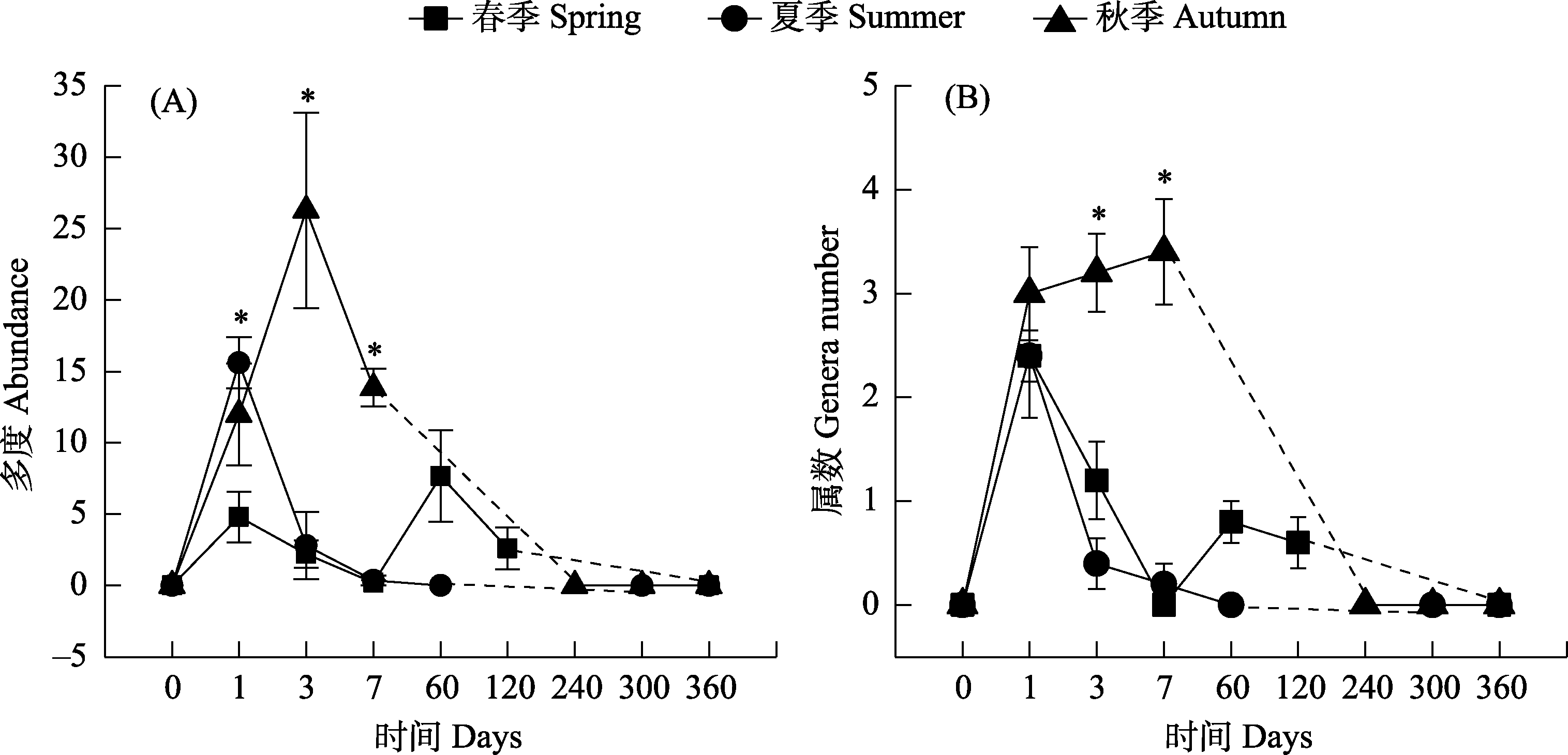
Fig. 7 Changes in the abundance (A) and genera number (B) of Staphylinidae community in the horse dung in different seasons. The dashed line indicates no sampling at the time period. The significant differences between seasons at P < 0.05 are denoted using * (one-way ANOVA with Duncan’s multiple-range tests for post hoc comparisons).
| 分解阶段 Decomposition stage | 变量 Variable | 贡献率 Contribution (%) | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 早期 Early stage | 粪有机质含量 Dung organic matter content | 29.8 | 18.249 | 0.002 |
| 粪含水量 Dung water content | 17.6 | 9.181 | 0.006 | |
| 土壤温度 Soil temperature | 8.1 | 3.787 | 0.062 | |
| 土壤湿度 Soil moisture content | 3.6 | 1.611 | 0.212 | |
| 粪的pH值 Dung pH | 0.7 | 0.283 | 0.686 | |
| 第一排序轴显著性蒙特卡洛置换检验 Monte-Carlo permutation test for significance of the first ordinal axis | F = 22.32, P = 0.002 | |||
| 所有排序轴显著性蒙特卡洛置换检验 Monte-Carlo permutation test for significance of all ordinal axes | F = 4.93, P = 0.002 | |||
| 后期 Late stage | 粪有机质含量 Dung organic matter content | 6.5 | 2.98 | 0.066 |
| 粪含水量 Dung water content | 6.2 | 2.83 | 0.102 | |
| 土壤温度 Soil temperature | 9.5 | 4.53 | 0.014 | |
| 土壤湿度 Soil moisture content | 12.5 | 6.15 | 0.002 | |
| 粪的pH值 Dung pH | 0.9 | 0.397 | 0.592 | |
| 第一排序轴显著性蒙特卡洛置换检验 Monte-Carlo permutation test for significance of the first ordinal axis | F = 13.39, P = 0.026 | |||
| 所有排序轴显著性蒙特卡洛置换检验 Monte-Carlo permutation test for significance of all ordinal axes | F = 3.762, P = 0.004 | |||
Table 3 Relative contribution of partial redundancy analysis of environmental factors to composition of arthropods community
| 分解阶段 Decomposition stage | 变量 Variable | 贡献率 Contribution (%) | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 早期 Early stage | 粪有机质含量 Dung organic matter content | 29.8 | 18.249 | 0.002 |
| 粪含水量 Dung water content | 17.6 | 9.181 | 0.006 | |
| 土壤温度 Soil temperature | 8.1 | 3.787 | 0.062 | |
| 土壤湿度 Soil moisture content | 3.6 | 1.611 | 0.212 | |
| 粪的pH值 Dung pH | 0.7 | 0.283 | 0.686 | |
| 第一排序轴显著性蒙特卡洛置换检验 Monte-Carlo permutation test for significance of the first ordinal axis | F = 22.32, P = 0.002 | |||
| 所有排序轴显著性蒙特卡洛置换检验 Monte-Carlo permutation test for significance of all ordinal axes | F = 4.93, P = 0.002 | |||
| 后期 Late stage | 粪有机质含量 Dung organic matter content | 6.5 | 2.98 | 0.066 |
| 粪含水量 Dung water content | 6.2 | 2.83 | 0.102 | |
| 土壤温度 Soil temperature | 9.5 | 4.53 | 0.014 | |
| 土壤湿度 Soil moisture content | 12.5 | 6.15 | 0.002 | |
| 粪的pH值 Dung pH | 0.9 | 0.397 | 0.592 | |
| 第一排序轴显著性蒙特卡洛置换检验 Monte-Carlo permutation test for significance of the first ordinal axis | F = 13.39, P = 0.026 | |||
| 所有排序轴显著性蒙特卡洛置换检验 Monte-Carlo permutation test for significance of all ordinal axes | F = 3.762, P = 0.004 | |||
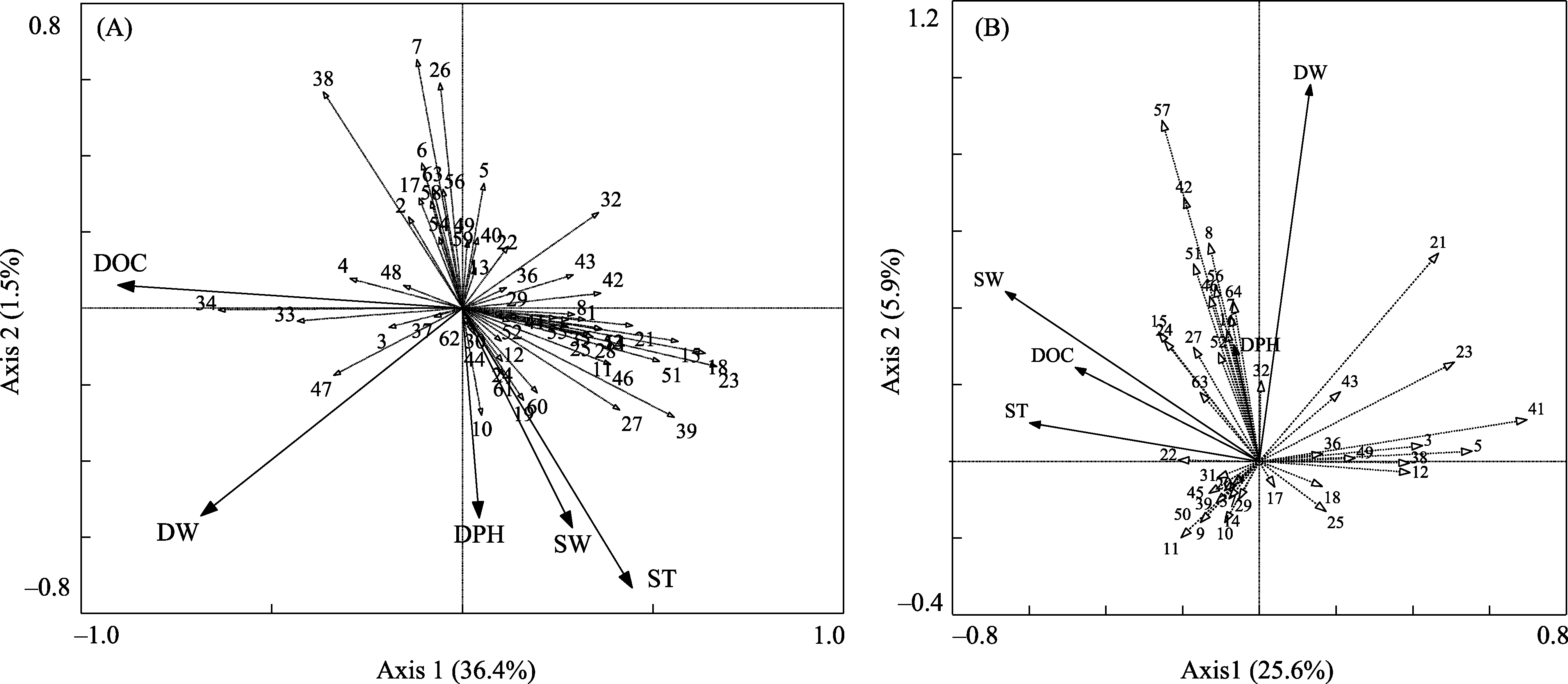
Fig. 8 RDA two-dimensional diagram of the relationship between arthropods and environmental factors at early (A) and late (B) decomposition of horse dung. DOC, Dung organic matter content; DW, Dung water content; ST, Soil temperature; SW, Soil moisture content; DPH, Dung pH; 1, Enchytraeidae; 2, Geophilidae; 3, Scutacaridae; 4, Parholaspidae; 5, Laelapidae; 6, Uropodoidea; 7, Gamasida; 8, Nanorchestidae; 9, Cryptognathidae; 10, Bdellidae; 11, Trombidiidae; 12, Erythraeidae; 13, Actinedida; 14, Oppidae; 15, Ceratozetidae; 16, Zetorchestidae; 17, Thomisidae; 18, Gnaphosidae; 19, Lycosidae; 20, Liocranidae; 21, Entomobryidae; 22, Sminthuridae; 23, Hypogastruridae; 24, Isotomidae; 25, Phlaeothripidae; 26, Thysanoptera; 27, Formicidae; 28, Eulophidae; 29, Bethylidae; 30, Hymenoptera; 31, Chalcidoidea; 32, Liposcelidae; 33, Scarabaeidae; 34, Aphodiidae; 35, Melolonthidae; 36, Tenebrionidae; 37, Oedemeridae; 38, Staphylinidae; 39, Anthicidae; 40, Ptiliidae; 41, Histeridae; 42, Hydrophilidae; 43, Lathridiidae; 44, Carabidae; 45, Ostomatidae; 46, Lygaeidae; 47, Calliphoridae; 48, Cyclorrhapha; 49, Coccoidea; 50, Noctuidae larvae; 51, Carabidae larvae; 52, Staphylinidae larvae; 53, Melolonthidae larvae; 54, Rutelidae larvae; 55, Aphodiidae larvae; 56, Tenebrionidae larvae; 57, Chrysomelidae larvae; 58, Elateridae larvae; 59, Muscidae larvae; 60, Calliphoridae larvae; 61, Syrphidae larvae; 62, Cecidomyiidae larvae; 63, Therevidae larvae; 64, Diptera larvae.
| [1] | Cheng JW, Li FY, Liu XM, Wang XY, Zhao D, Feng XC, Baoyin T (2021) Seasonal patterns of the abundance of ground-dwelling arthropod guilds and their responses to livestock grazing in a semi-arid steppe. Pedobiologia, 85, 150711. |
| [2] | Cheng JW, Li FY, Wang YD, Wang YN, Liu XM, Zhang JZ, Wang ZY, Li YL, Wang H, Yang ZP, Potter MA (2022) Dweller and tunneler dung beetles synergistically accelerate decomposition of cattle and horse dung in a semi-arid steppe. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 329, 107873. |
| [3] |
Cheng JW, Wang YD, Wang YN, Li Y, Guo Y, Bai Z, Liu XM, Li FY (2022) Effects of soil macro- and meso-fauna on the decomposition of cattle and horse dung pats in a semi-arid steppe. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22575. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[程建伟, 王亚东, 王桠楠, 李莹, 郭颖, 白正, 刘新民, 李永宏 (2022) 半干旱草原大中型土壤动物在畜粪分解中的作用. 生物多样性, 30, 22575.]
DOI |
|
| [4] | Du ZY, Cai YJ, Wang XD, Zhang B, Du Z (2019) Research progress on grazing livestock dung decomposition and its influence on the dynamics of grassland soil nutrients. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39, 4627-4637. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杜子银, 蔡延江, 王小丹, 张斌, 杜忠 (2019) 放牧牲畜粪便降解及其对草地土壤养分动态的影响研究进展. 生态学报, 39, 4627-4637.] | |
| [5] | Duddigan S, Fraser T, Green I, Diaz A, Sizmur T, Tibbett M (2021) Plant, soil and faunal responses to a contrived pH gradient. Plant and Soil, 462, 505-524. |
| [6] | Englmeier J, Mitesser O, Benbow ME, Hothorn T, von Hoermann C, Benjamin C, Fricke U, Ganuza C, Haensel M, Redlich S, Riebl R, Rojas Botero S, Rummler T, Steffan-Dewenter I, Stengel E, Tobisch C, Uhler J, Uphus L, Zhang J, Müller J (2023) Diverse effects of climate, land use, and insects on dung and carrion decomposition. Ecosystems, 26, 397-411. |
| [7] | Frouz J (2018) Effects of soil macro- and mesofauna on litter decomposition and soil organic matter stabilization. Geoderma, 332, 161-172. |
| [8] |
He JJ (2012) Precipitation variation characteristics of Xilinhot City for 50 years. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 28(29), 271-278. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [贺俊杰 (2012) 锡林浩特市50年降水量变化特征分析. 中国农学通报, 28(29), 271-278.] | |
| [9] | Jiang SC, Zhou DW (2005) Composition and seasonal variations of macro arthropod fauna associated with cattle dung pats in Songnen Grassland, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 25, 2983-2991. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [姜世成, 周道玮 (2005) 松嫩草地牛粪中大型节肢动物种类组成及种群动态变化. 生态学报, 25, 2983-2991.] | |
| [10] | Li LS, Li YR (1989) Acarology. Chongqing Press, Chongqing. (in Chinese) |
| [李隆术, 李云瑞 (1989) 蜱螨学. 重庆出版社, 重庆.] | |
| [11] | Liang JY, Jiao T, Wu JP, Gong XY, Du WH, Liu HB, Xiao YM (2015) The relationship between seasonal forage digestibility and forage nutritive value in different grazing pastures. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 24(6), 108-115. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[梁建勇, 焦婷, 吴建平, 宫旭胤, 杜文华, 刘海波, 肖元明 (2015) 不同类型草地牧草消化率季节动态与营养品质的关系研究. 草业学报, 24(6), 108-115.]
DOI |
|
| [12] | Liu RT, Steinberger Y (2018) Seasonal distribution and diversity of ground-active arthropods between shrub microhabitats in the Negev Desert, Israel. Arid Land Research and Management, 32, 91-110. |
| [13] |
Liu X, Zhao D, Cheng JW, Chen HY, Liu XM, Baoyin T, Li FY (2017) Effects of grazing and mowing on macrofauna communities in a typical steppe of Inner Mongolia, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 28, 1869-1878. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[刘霞, 赵东, 程建伟, 陈海燕, 刘新民, 宝音陶格涛, 李永宏 (2017) 放牧和刈割对内蒙古典型草原大型土壤动物的影响. 应用生态学报, 28, 1869-1878.]
DOI |
|
| [14] | Liu XM (2011) Assemblage characteristics of dung beetles in livestock dung in Inner Mongolian typical steppe. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 30, 24-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘新民 (2011) 内蒙古典型草原家畜粪中的粪金龟子群落特征. 生态学杂志, 30, 24-29.] | |
| [15] | Liu XM, Hai Y (2011) Dung beetle species composition and decomposition function in horse dung in desert steppe of Inner Mongolia. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 30, 2269-2276. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘新民, 海英 (2011) 荒漠草原马粪中粪金龟子组成及分解作用. 生态学杂志, 30, 2269-2276.] | |
| [16] | Lu RK (1999) Methods of Soil Agrochemical Analysis. China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [鲁如坤 (1999) 土壤农化分析方法. 中国农业科技出版社, 北京.] | |
| [17] | Menéndez R, Webb P, Orwin KH (2016) Complementarity of dung beetle species with different functional behaviours influence dung-soil carbon cycling. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 92, 142-148. |
| [18] | Njoroge DM, Chen SC, Zuo J, Dossa G, Cornelissen J (2022) Soil fauna accelerate litter mixture decomposition globally, especially in dry environments. Journal of Ecology, 110, 659-672. |
| [19] | Peng SS, Piao SL, Shen ZH, Ciais P, Sun ZZ, Chen SP, Bacour C, Peylin P, Chen AP (2013) Precipitation amount, seasonality and frequency regulate carbon cycling of a semi-arid grassland ecosystem in Inner Mongolia, China: A modeling analysis. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 178, 46-55. |
| [20] | Seibold S, Rammer W, Hothorn T, Seidl R, Ulyshen MD, Lorz J, Cadotte MW, Lindenmayer DB, Adhikari YP, Aragón R, Bae S, Baldrian P, Varandi HB, Barlow J, Bässler C, Beauchêne J, Berenguer E, Bergamin RS, Birkemoe T, Boros G, Brandl R, Brustel H, Burton PJ, Cakpo-Tossou YT, Castro J, Cateau E, Cobb TP, Farwig N, Fernández RD, Firn J, Gan KS, González G, Gossner MM, Habel JC, Hébert C, Heibl C, Heikkala O, Hemp A, Hemp C, Hjältén J, Hotes S, Kouki J, Lachat T, Liu J, Liu Y, Luo YH, Macandog DM, Martina PE, Mukul SA, Nachin B, Nisbet K, O’Halloran J, Oxbrough A, Pandey JN, Pavlíček T, Pawson SM, Rakotondranary JS, Ramanamanjato JB, Rossi L, Schmidl J, Schulze M, Seaton S, Stone MJ, Stork NE, Suran B, Sverdrup-Thygeson A, Thorn S, Thyagarajan G, Wardlaw TJ, Weisser WW, Yoon S, Zhang NL, Müller J (2021) The contribution of insects to global forest deadwood decomposition. Nature, 597, 77-81. |
| [21] |
Sladecek FXJ, Dötterl S, Schäffler I, Segar ST, Konvicka M (2021) Succession of dung-inhabiting beetles and flies reflects the succession of dung-emitted volatile compounds. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 47, 433-443.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | Wagg C, Bender SF, Widmer F, van der Heijden MGA (2014) Soil biodiversity and soil community composition determine ecosystem multifunctionality. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 111, 5266-5270. |
| [23] | Wu XW, Duffy JE, Reich PB, Sun SC (2011) A brown-world cascade in the dung decomposer food web of an alpine meadow: Effects of predator interactions and warming. Ecological Monographs, 81, 313-328. |
| [24] |
Wu XW, Niklas KJ, Sun SC (2021) Climate change affects detritus decomposition rates by modifying arthropod performance and species interactions. Current Opinion in Insect Science, 47, 62-66.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Xiang J, Gu J, Wang GM, Bol R, Yao L, Fang YM, Zhang HC (2024) Soil pH controls the structure and diversity of bacterial communities along elevational gradients on Huangshan, China. European Journal of Soil Biology, 120, 103586. |
| [26] | Xu GL, Schleppi P, Li MH, Fu SL (2009) Negative responses of Collembola in a forest soil (Alptal, Switzerland) under experimentally increased N deposition. Environmental Pollution, 157, 2030-2036. |
| [27] | Yang ZM, Ha S, Liu XM (2016) Effects of grazing on the composition of soil animals and their decomposition function to Stipa grandis litter in Inner Mongolia typical steppe, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 27, 2864-2874. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[杨志敏, 哈斯塔米尔, 刘新民 (2016) 放牧对内蒙古典型草原大针茅凋落物中土壤动物组成及其分解功能的影响. 应用生态学报, 27, 2864-2874.]
DOI |
|
| [28] | Yin WY (1998) Pictorical Keys to Soil Animals of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [尹文英 (1998) 中国土壤动物检索图鉴. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [29] | Zhai N, Alatenbagen, Liu XM (2018) Feeding preferences and daily activity rhythms of dung beetles on the Inner Mongolian steppe. Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology, 55, 428-437. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [翟娜, 阿拉腾巴根, 刘新民 (2018) 内蒙古典型草原粪食性金龟的取食偏好和日活动节律特征. 应用昆虫学报, 55, 428-437.] | |
| [30] | Zhang JE (2006) Common Experimental Research Methods and Techniques in Ecology. Chemical Industry Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [章家恩 (2006) 生态学常用实验研究方法与技术. 化学工业出版社, 北京.] |
| [1] | Yongjie Niu, Quanhui Ma, Yu Zhu, Hairong Liu, Jiale Lü, Yuanchun Zou, Ming Jiang. Research progress on the impact of nitrogen deposition on grassland insect diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(9): 23130-. |
| [2] | Jianwei Cheng, Yadong Wang, Yanan Wang, Ying Li, Ying Guo, Zheng Bai, Xinmin Liu, Frank Yonghong Li. Effects of soil macro- and meso-fauna on the decomposition of cattle and horse dung pats in a semi-arid steppe [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(12): 22575-. |
| [3] | Yongyi Lin, Yongzhen Wang, Yilin Feng, Wenzhi Zhao, Junwei Gao, Jiliang Liu. Dynamic change of ground-dwelling beetle community in a gobi desert of the middle of Hexi Corridor and its influencing factors [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(12): 22343-. |
| [4] | Yanjie Ma, Haopeng He, Wenjing Shen, Biao Liu, Kun Xue. Effects of transgenic maize on arthropod diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(4): 419-432. |
| [5] | Xiaozhi Lin, Dongmei Li, Huanzhang Liu, Hongsheng Lin, Shaorong Yang, Hanjin Fan, Rushu Wen. Fish species diversity and its seasonal variations in the Chaozhou section of Hanjiang River, Guangdong Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(2): 185-194. |
| [6] | Jing Yan, Guoliang Zhang, Ruihai Zhang, Zhen Song, Xiaohong Zhao, Yusheng Liu, Weidong Fu. The effect of Flaveria bidentis litter decomposition on the structure of arthropod communities [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(11): 1288-1295. |
| [7] | Yiru Wu, Xingfeng Si, Chuanwu Chen, Di Zeng, Yuhao Zhao, Jiaqi Li, Ping Ding. Effects of dispersal abilities on community dynamics of breeding birds on the land-bridge islands in the Thousand Island Lake, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(10): 1135-1145. |
| [8] | Yi Jin, Jianhua Chen, Xiangcheng Mi, Haibao Ren, Keping Ma, Mingjian Yu. Impacts of the 2008 ice storm on structure and composition of an evergreen broad-leaved forest community in eastern China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2015, 23(5): 610-618. |
| [9] | Zhenguo Liu, Zhenqing Li, Ming Dong. Model analysis of plant community dynamics [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2005, 13(3): 269-277. |
| [10] | WANG Fa-Yuan, LIU Run-Jin. A preliminary survey of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in saline alkaline soil of the Yellow River Delta [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2001, 09(4): 389-392. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()