



Biodiv Sci ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (12): 25212. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2025212 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2025212
• Original Papers:Plant Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xingda Yao1,2,3,#, Kaiyuan Zhu1,#, Yihan Lan4, Shuxia Zhan1, Tana Wuyun1, Jian Li2,3,*( ), Wenting Xu1,*(
), Wenting Xu1,*( )
)
Received:2025-06-09
Accepted:2025-11-16
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2026-01-09
About author:#Co-first author
Supported by:Xingda Yao, Kaiyuan Zhu, Yihan Lan, Shuxia Zhan, Tana Wuyun, Jian Li, Wenting Xu. Effects of alien invasive plants on spontaneous plant communities in Hangzhou Xixi National Wetland Park[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(12): 25212.
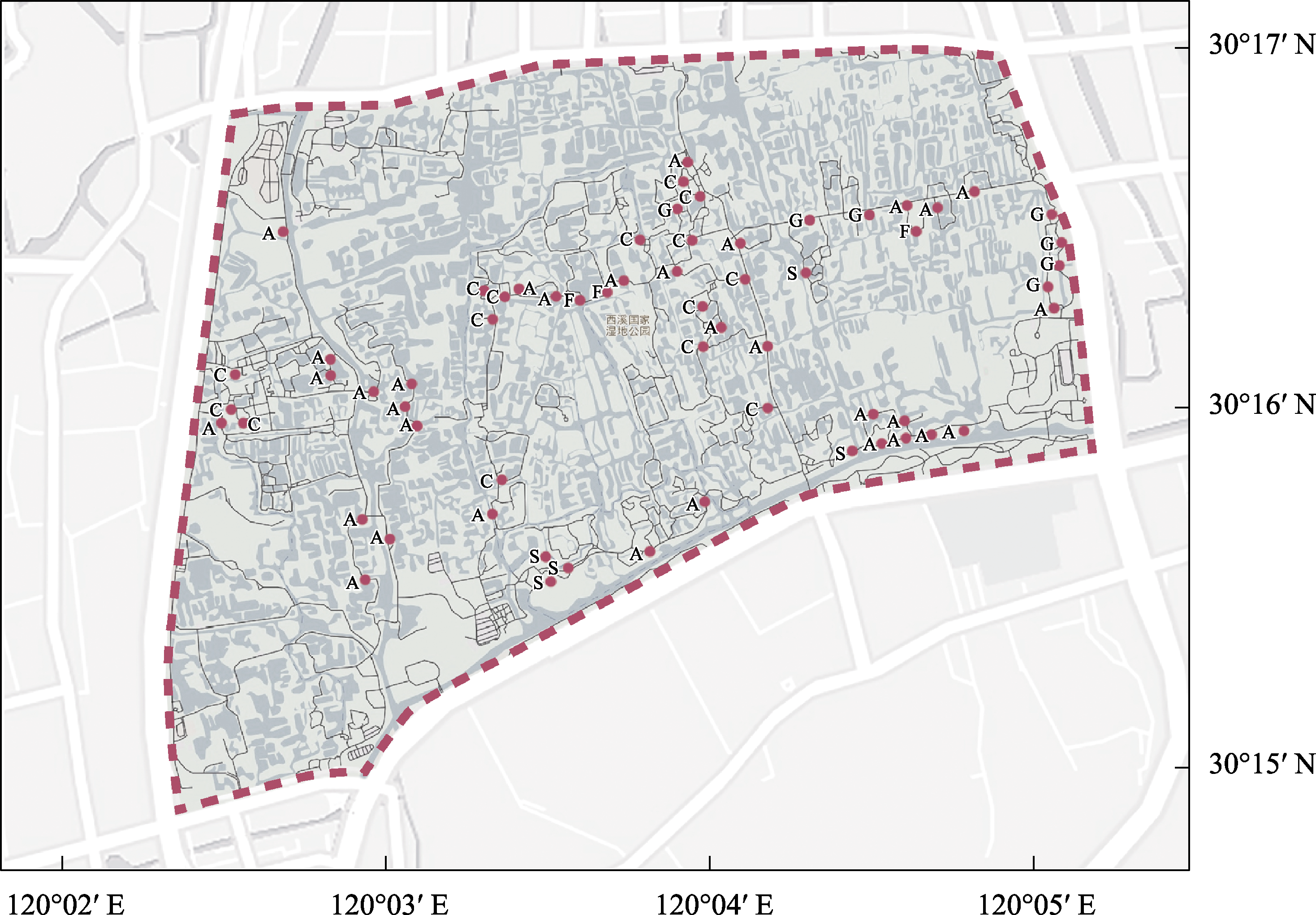
Fig. 1 Study area and sample distribution in Hangzhou Xixi National Wetland Park. A, Arbor woodland; C, Construction land; F, Farmland; G, Grassland; S, Shrub land.
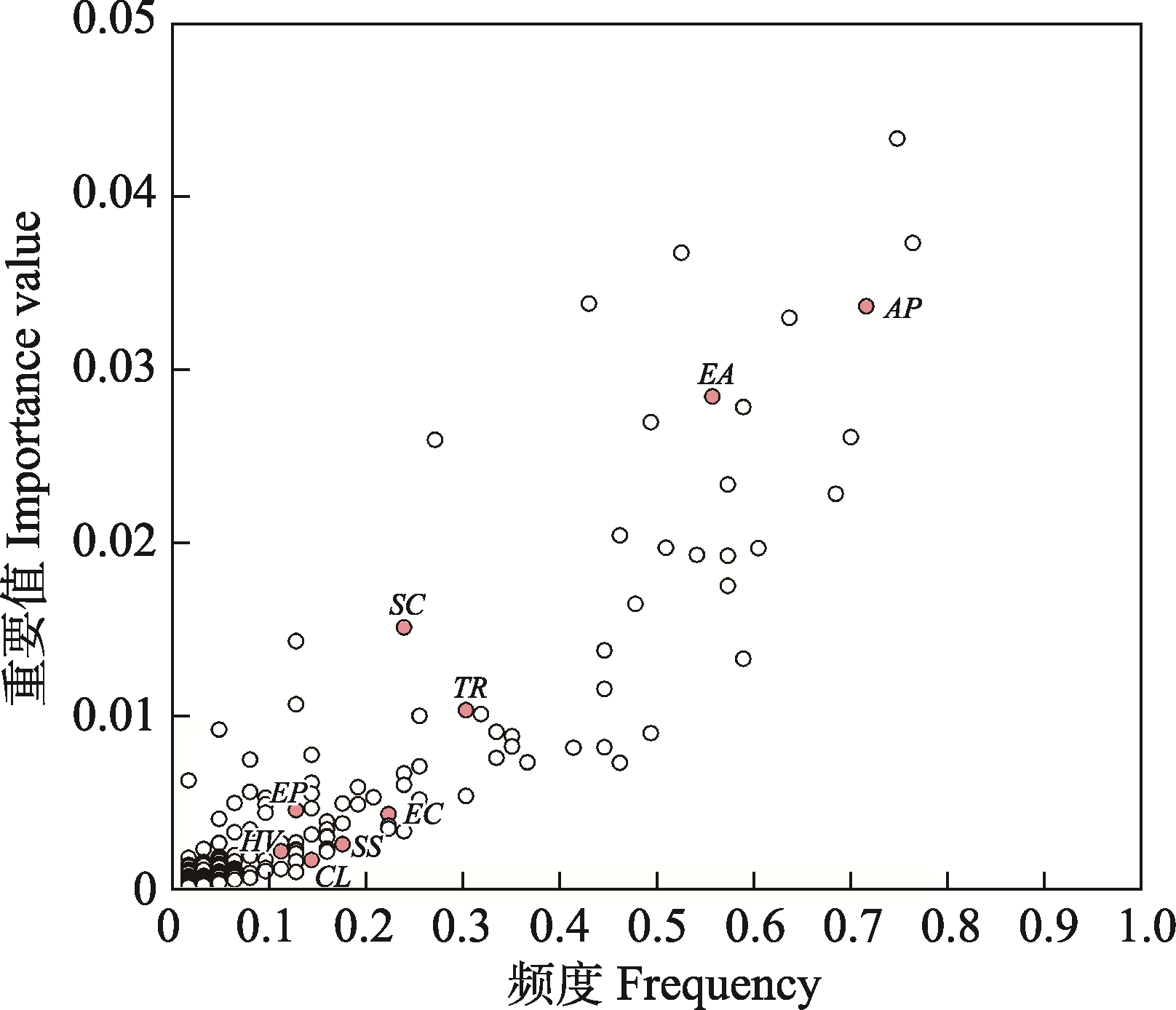
Fig. 2 Relative dominance of the 9 dominant invasive plants in Hangzhou Xixi National Wetland Park. AP, Alternanthera philoxeroides; EA, Erigeron annuus; SC, Solidago canadensis; TR, Trifolium repens; EC, Erigeron canadensis; SS, Symphyotrichum subulatum; CL, Cyclospermum leptophyllum; EP, Erigeron philadelphicus; HV, Hydrocotyle verticillata.
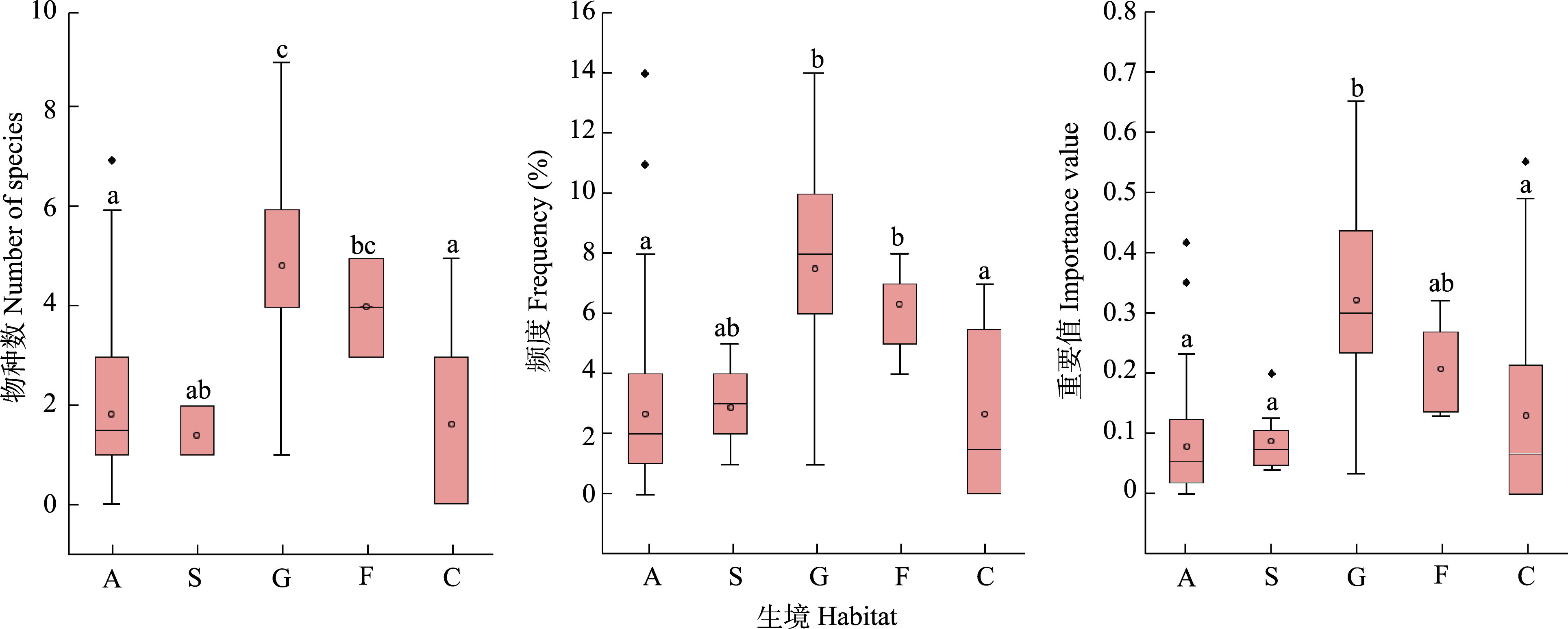
Fig. 3 Differences in the number, frequency and importance value of invasive plant species in different habitats of Hangzhou Xixi National Wetland Park. A, Arbor woodland; S, Shrub land; G, Grassland; F, Farmland; C: Construction land. Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference (P < 0.05).
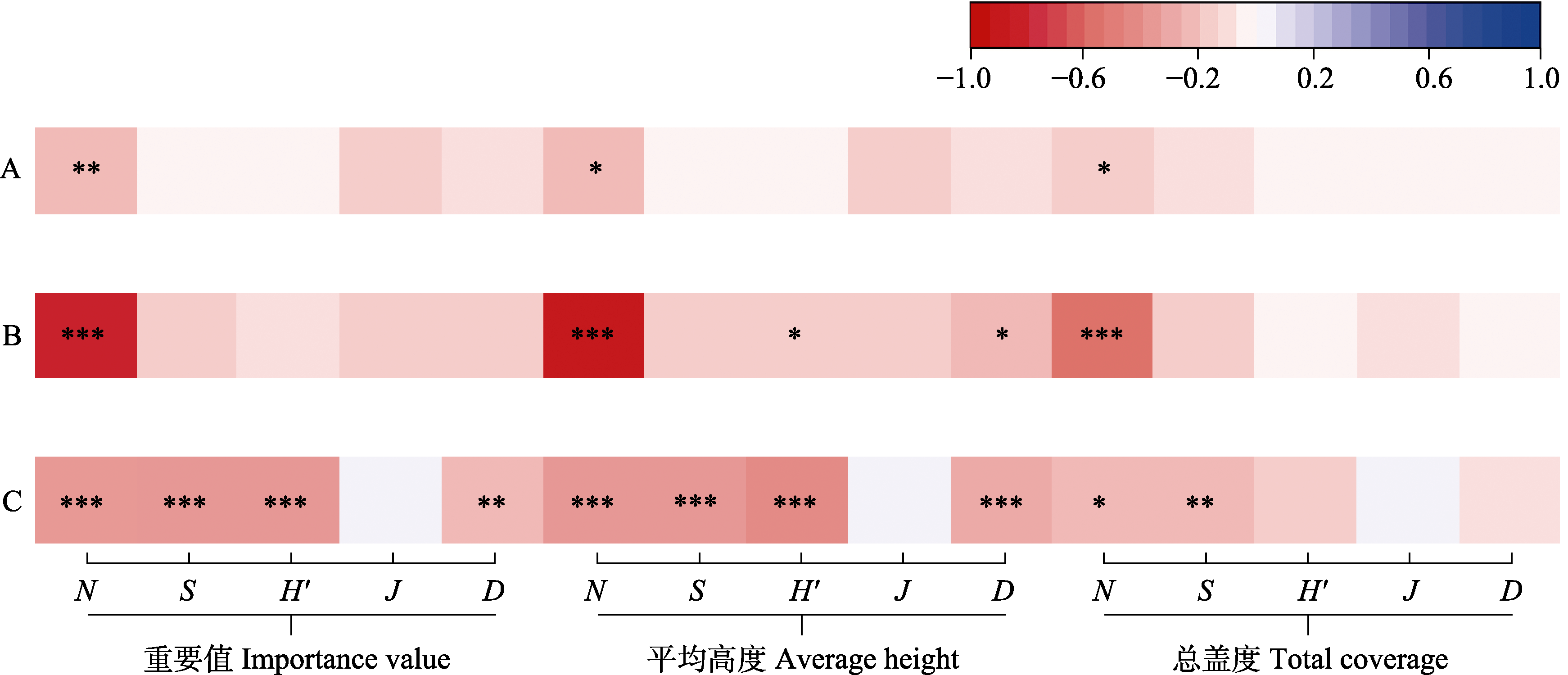
Fig. 4 Correlation between invasive plants and community diversity in Hangzhou Xixi National Wetland Park. N, Number of native plant species; S, Species richness index; H′, Shannon-Wiener diversity index; J, Pielou evenness index; D, Simpson diversity index. Control items for partial correlation analysis: A, Average height × total coverage of artificial ground cover; B, Average height × total coverage of artificial ground cover and total number of species in each belt transect; C, Average height × total coverage of artificial ground cover and number of invasive plant species in each belt transect. The color of the squares represents the correlation coefficient, corresponding to the color of the color band. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001.
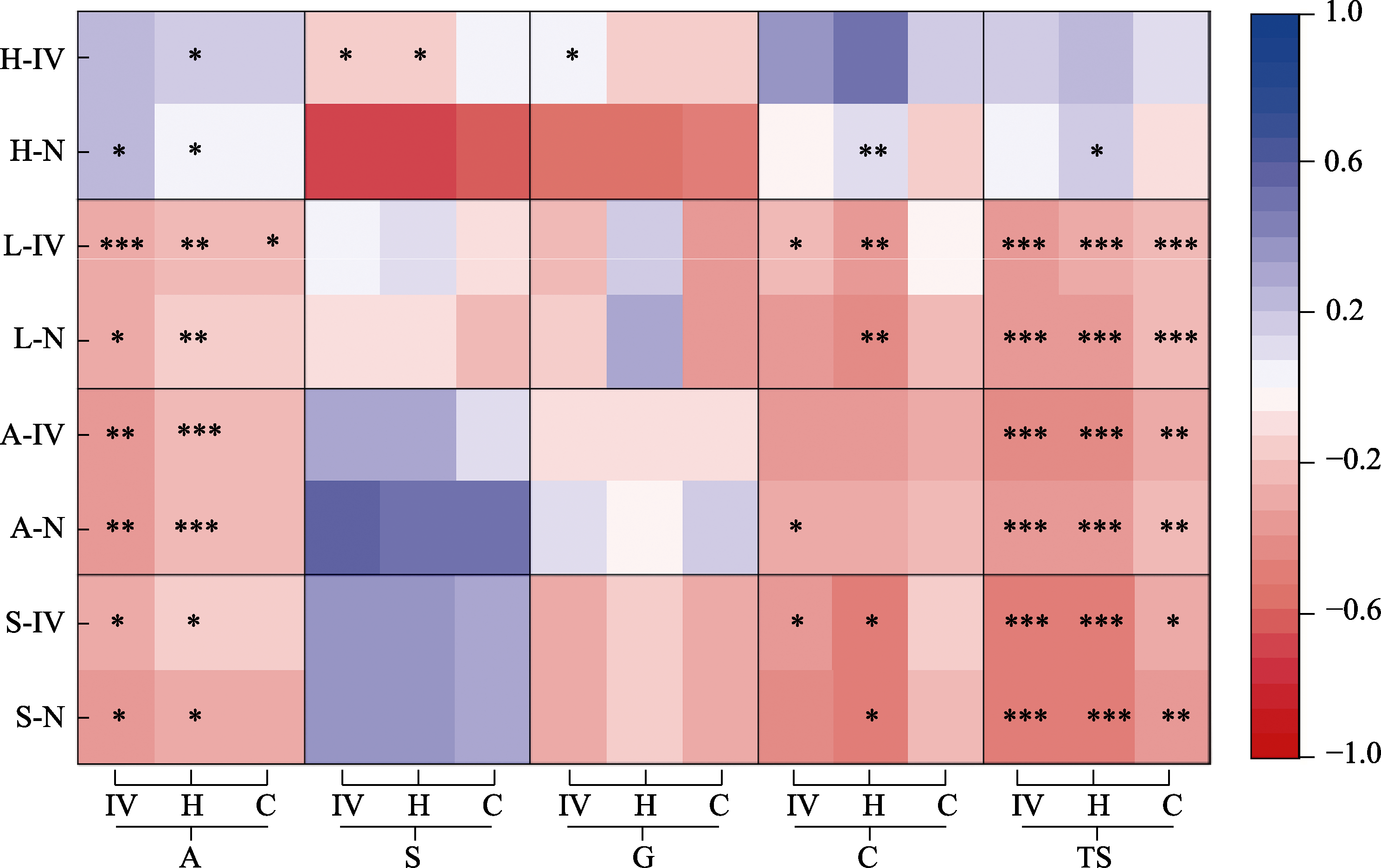
Fig. 5 Correlation between invasive plants and community structure in Hangzhou Xixi National Wetland Park. The ordinate is the parameters of community structure: H-IV, Importance value of herb; H-N, Number of herb; L-IV, Importance value of lianas; L-N, Number of lianas; A-IV, Importnce value of arbor seedling; A-N, Number of arbor seedling species; S-IV, Importance value of shrub seedling; S-N, Number of shrub seedling species. The abscissa is the parameters of the invasive plants: IV, Importance value of invasive plants; H, Average height of invasive plants; C, Total coverage of invasive plants. A, Arbor woodland; S, Shrub land; G, Grassland; C, Construction land; TS represents all types of habit. The color of the squares represents the correlation coefficient, corresponding to the color of the color band. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001.
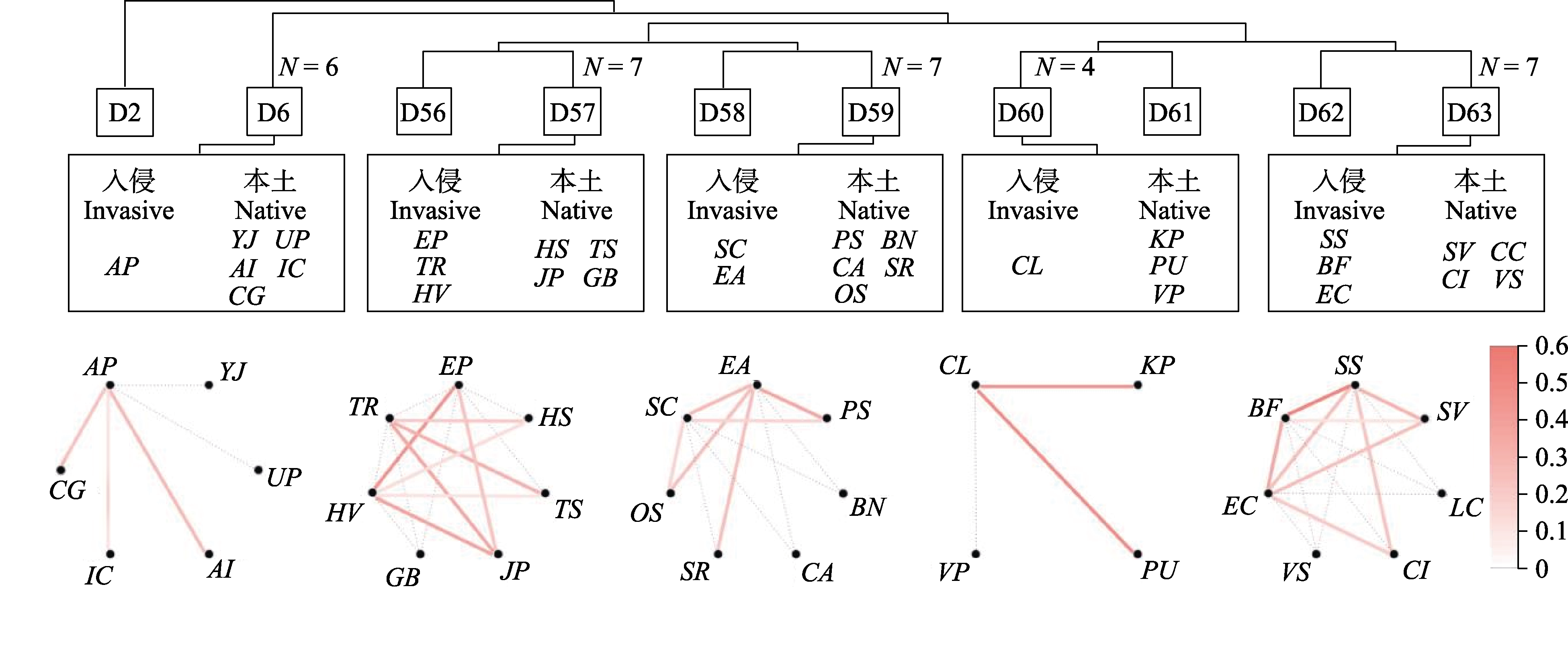
Fig. 6 Companion species of invasive plants under species classification and their competitive relationships. The colors of the lines between species represent niche overlap values, corresponding to the color of the color band on the right side. AP, Alternanthera philoxeroides; YJ, Youngia japonica; UP, Ulmus pumila; AI, Aster indicus; IC, Imperata cylindrica; CG, Clinopodium gracile; EP, Erigeron philadelphicus; TR, Trifolium repens; HV, Hydrocotyle verticillata; HS, Hydrocotyle sibthorpioides; TS, Triadica sebifera; JP, Justicia procumbens; GB, Galium bungei; SC, Solidago canadensis; EA, Erigeron annuus; PS, Pterocarya stenoptera; BN, Boehmeria nivea; CA, Carpesium abrotanoides; SR, Salix rosthornii; OS, Oxalis stricta; CL, Cyclospermum leptophyllum; KP, Kyllinga polyphylla; PU, Phyllanthus urinaria; VP, Veronica polita; SS, Symphyotrichum subulatum; BF, Bidens frondosa; EC, Erigeron canadensis; SV, Setaria viridis; LC, Lindernia crustacea; CI, Cyperus iria; VS, Vicia sativa.
| 群落组 Community group | 包含群落数 No. of communities | 群落 Community | 生境 Habitat |
|---|---|---|---|
| 络石群落组 Trachelospermum jasminoides community group | 7 | 柔毛路边青和一年蓬优势群落 Geum japonicum var. chinense and Erigeron annuus dominant community | 乔木林地 Arbor woodland |
| 求米草群落组 Oplismenus undulatifolius community group | 6 | 一年蓬和求米草优势群落 Erigeron annuus and Oplismenus undulatifolius dominant community | 乔木林地 Arbor woodland |
| 酢浆草群落组 Oxalis corniculata community group | 2 | 酢浆草和一年蓬优势群落 Oxalis corniculata and Erigeron annuus dominant community | 草地 Grassland |
| 细叶旱芹群落组 Cyclospermum leptophyllum community group | 1 | 细叶旱芹单优势群落 Cyclospermum leptophyllum single dominant community | 草地 Grassland |
| 直酢浆草群落组 Oxalis stricta community group | 3 | 直酢浆草和钻叶紫菀优势群落 Oxalis stricta and Symphyotrichum subulatum dominant community | 草地 Grassland |
| 空心莲子草群落组 Alternanthera philoxeroides community group | 6 | 空心莲子草和春飞蓬优势群落 A. philoxeroides and Erigeron philadelphicus dominant community | 草地 Grassland |
| 空心莲子草和狗牙根优势群落 A. philoxeroides and Cynodon dactylon dominant community | 草地 Grassland | ||
| 空心莲子草、乌蔹莓和蛇葡萄优势群落 A. philoxeroides, Causonis japonica and Ampelopsis glandulosa dominant community | 灌木林地 Shrub land | ||
| 空心莲子草单优势群落 A. philoxeroides single dominant community | 草地 Grassland | ||
| 乌蔹莓、三叶地锦和空心莲子草优势群落 Causonis japonica, Parthenocissus semicordata and Alternanthera philoxeroides dominant community | 建筑用地 Construction land | ||
| 鳢肠和空心莲子草优势群落 Eclipta prostrata and Alternanthera philoxeroides dominant community | 建筑用地 Construction land | ||
| 一年蓬群落组 Erigeron annuus community group | 3 | 一年蓬单优势群落 Erigeron annuus single dominant community | 农用地 Farmland |
| 天胡荽群落组 Hydrocotyle sibthorpioides community group | 6 | 空心莲子草和天胡荽优势群落 A. philoxeroides and Hydrocotyle sibthorpioides dominant community | 农用地 Farmland |
| 白车轴草群落组 Trifolium repens community group | 4 | 白车轴草和空心莲子草优势群落 Trifolium repens and Alternanthera philoxeroides dominant community | 草地 Grassland |
| 翅果菊和白车轴草优势群落 Lactuca indica and Trifolium repens dominant community | 建筑用地 Construction land | ||
| 白茅群落组 Imperata cylindrica community group | 6 | 白茅和一年蓬优势群落 Imperata cylindrica and Erigeron annuus dominant community | 草地 Grassland |
| 白茅和加拿大一枝黄花优势群落 Imperata cylindrica and Solidago canadensis dominant community | 草地 Grassland | ||
| 马蹄金群落组 Dichondra micrantha community group | 2 | 马蹄金和加拿大一枝黄花优势群落 Dichondra micrantha and Solidago canadensis dominant community | 乔木林地 Arbor woodland |
Table 1 Community groups and community types dominated by invasive plants based on community clustering
| 群落组 Community group | 包含群落数 No. of communities | 群落 Community | 生境 Habitat |
|---|---|---|---|
| 络石群落组 Trachelospermum jasminoides community group | 7 | 柔毛路边青和一年蓬优势群落 Geum japonicum var. chinense and Erigeron annuus dominant community | 乔木林地 Arbor woodland |
| 求米草群落组 Oplismenus undulatifolius community group | 6 | 一年蓬和求米草优势群落 Erigeron annuus and Oplismenus undulatifolius dominant community | 乔木林地 Arbor woodland |
| 酢浆草群落组 Oxalis corniculata community group | 2 | 酢浆草和一年蓬优势群落 Oxalis corniculata and Erigeron annuus dominant community | 草地 Grassland |
| 细叶旱芹群落组 Cyclospermum leptophyllum community group | 1 | 细叶旱芹单优势群落 Cyclospermum leptophyllum single dominant community | 草地 Grassland |
| 直酢浆草群落组 Oxalis stricta community group | 3 | 直酢浆草和钻叶紫菀优势群落 Oxalis stricta and Symphyotrichum subulatum dominant community | 草地 Grassland |
| 空心莲子草群落组 Alternanthera philoxeroides community group | 6 | 空心莲子草和春飞蓬优势群落 A. philoxeroides and Erigeron philadelphicus dominant community | 草地 Grassland |
| 空心莲子草和狗牙根优势群落 A. philoxeroides and Cynodon dactylon dominant community | 草地 Grassland | ||
| 空心莲子草、乌蔹莓和蛇葡萄优势群落 A. philoxeroides, Causonis japonica and Ampelopsis glandulosa dominant community | 灌木林地 Shrub land | ||
| 空心莲子草单优势群落 A. philoxeroides single dominant community | 草地 Grassland | ||
| 乌蔹莓、三叶地锦和空心莲子草优势群落 Causonis japonica, Parthenocissus semicordata and Alternanthera philoxeroides dominant community | 建筑用地 Construction land | ||
| 鳢肠和空心莲子草优势群落 Eclipta prostrata and Alternanthera philoxeroides dominant community | 建筑用地 Construction land | ||
| 一年蓬群落组 Erigeron annuus community group | 3 | 一年蓬单优势群落 Erigeron annuus single dominant community | 农用地 Farmland |
| 天胡荽群落组 Hydrocotyle sibthorpioides community group | 6 | 空心莲子草和天胡荽优势群落 A. philoxeroides and Hydrocotyle sibthorpioides dominant community | 农用地 Farmland |
| 白车轴草群落组 Trifolium repens community group | 4 | 白车轴草和空心莲子草优势群落 Trifolium repens and Alternanthera philoxeroides dominant community | 草地 Grassland |
| 翅果菊和白车轴草优势群落 Lactuca indica and Trifolium repens dominant community | 建筑用地 Construction land | ||
| 白茅群落组 Imperata cylindrica community group | 6 | 白茅和一年蓬优势群落 Imperata cylindrica and Erigeron annuus dominant community | 草地 Grassland |
| 白茅和加拿大一枝黄花优势群落 Imperata cylindrica and Solidago canadensis dominant community | 草地 Grassland | ||
| 马蹄金群落组 Dichondra micrantha community group | 2 | 马蹄金和加拿大一枝黄花优势群落 Dichondra micrantha and Solidago canadensis dominant community | 乔木林地 Arbor woodland |
| [1] | Bao X, Liu H, Zou ZC, An T, Pei JW (2024) Research on landscape design approach of spontaneous community: Exploration on the improvement design of urban spontaneous ground cover plant community based on CSR theory. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 40(6), 104-109. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [鲍璇, 刘晖, 邹子辰, 安婷, 裴进文 (2024) 基于自生植物群落的景观设计途径研究——CSR理论介入城市自生地被植物群落改良设计的探索. 中国园林, 40(6), 104-109.] | |
| [2] |
Bonthoux S, Voisin L, Bouché-Pillon S, Chollet S (2019) More than weeds: Spontaneous vegetation in streets as a neglected element of urban biodiversity. Landscape and Urban Planning, 185, 163-172.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Cervelli EW, Lundholm JT, Du X (2013) Spontaneous urban vegetation and habitat heterogeneity in Xi’an, China. Landscape & Urban Planning, 120, 25-33. |
| [4] | Chang M, Li XP, Zhang T, Wu XC, Lu SY, Mao W (2025) Spread characteristics of urban spontaneous plants and their coexistence with the cultivars along Chengdu ring road greenway. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 45, 9052-9065. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [常满, 李晓鹏, 张彤, 伍先成, 陆思羽, 毛薇 (2025) 成都绕城绿道自生植物扩散特征及其与栽培植物的共存. 生态学报, 45, 9052-9065.] | |
| [5] |
Del Tredici P (2010) Spontaneous urban vegetation: Reflections of change in a globalized world. Nature and Culture, 5, 299-315.
DOI URL |
| [6] | Delectis Florae Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae Agendae Academiae Sinicae (1959-2004) Florae Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae, Tomus 1-80. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会 (1959-2004) 中国植物志(第1-80卷). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [7] | Editorial Committee of Alien Invasive Flora of China (2020) Alien Invasive Flora of China. Shanghai Jiao Tong University Press, Shanghai. (in Chinese) |
| [ 中国外来入侵植物志编辑委员会 (2020) 中国外来入侵植物志. 上海交通大学出版社, 上海.] | |
| [8] | Editorial Committee of Encyclopedic Dictionary of Landscape and Urban Planning (2010) Encyclopedic Dictionary of Landscape and Urban Planning. Springer, Berlin. |
| [9] | Fan JJ, Yi YM, Zhu XZ (2020) Advances on the invasive weed, Erigeron annuus. Journal of Weed Science, 38(2), 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [范建军, 乙杨敏, 朱珣之 (2020) 入侵杂草一年蓬研究进展. 杂草学报, 38(2), 1-8.] | |
| [10] |
Guo CD, Zhao CY, Li FF, Li JS (2022) Comparative study of invasive and native herbs in natural forests and plantation forests: With Nonggang National Nature Reserve as an example. Biodiversity Science, 30, 21356. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[郭朝丹, 赵彩云, 李飞飞, 李俊生 (2022) 天然林和人工林外来入侵和本地植物对比研究: 以弄岗国家级自然保护区为例. 生物多样性, 30, 21356.]
DOI |
|
| [11] | Hang Y (2017) Development and application of herbaceous vegetation in new naturalistic ecological planting design. Landscape Architecture, 24(5), 16-21. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杭烨 (2017) 新自然主义生态种植设计理念下的草本植物景观的发展与应用. 风景园林, 24(5), 16-21.] | |
| [12] | Li CS, Liu H, Cheng AY, Li MK (2018) Respect for natural forces inspired urban spontaneous community improvement design experiment. Landscape Architecture, 25(6), 58-63. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李仓拴, 刘晖, 程爱云, 李梦珂 (2018) 尊重自然力启示下的城市自生群落改良设计实验. 风景园林, 25(6), 58-63.] | |
| [13] |
Li J (2021) Impact of tourists’ perceived value on brand loyalty: A case study of Xixi National Wetland Park. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research, 26, 262-276.
DOI URL |
| [14] | Li SH, Wang Y, Kang N (2017) From afforestation to ecological restoration and then to natural rehabilitation: The development of the principles of ecological rehabilitation in the practice of plant landscaping. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 33(11), 5-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李树华, 王勇, 康宁 (2017) 从植树种草, 到生态修复, 再到自然再生——基于绿地营造视点的风景园林环境生态修复发展历程探讨. 中国园林, 33(11), 5-12.] | |
| [15] | Li XL, Zhang MY, Fan SX, Luo QY, Li YT, Dong L (2024) Study on distribution characteristics of spontaneous plants in urban park green spaces in different habitats in Beijing. Research of Environmental Sciences, 37, 2118-2125. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李晓璐, 张梦园, 范舒欣, 骆沁宇, 李一彤, 董丽 (2024) 基于不同生境的北京城市公园绿地自生植物分布特征研究. 环境科学研究, 37, 2118-2125.] | |
| [16] | Li XP, Dong L, Guan JH, Zhao F, Wu SJ (2018) Temporal and spatial characteristics of spontaneous plant composition and diversity in a Beijing urban park. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 581-594. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李晓鹏, 董丽, 关军洪, 赵凡, 吴思佳 (2018) 北京城市公园环境下自生植物物种组成及多样性时空特征. 生态学报, 38, 581-594.] | |
| [17] |
Li XP, Fan SX, Guan JH, Zhao F, Dong L (2019a) Diversity and influencing factors on spontaneous plant distribution in Beijing Olympic Forest Park. Landscape and Urban Planning, 181, 157-168.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Li XP, Fan SX, Kühn N, Dong L, Hao PY (2019b) Residents’ ecological and aesthetical perceptions toward spontaneous vegetation in urban parks in China. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 44, 126397. |
| [19] | Li XP, Feng L, Huang R, Liu BC, Xu SH (2023) Species composition and abundance pattern of spontaneous plants responding to various habitats along urban river corridors in Chengdu. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 39(8), 108-114. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李晓鹏, 冯黎, 黄瑞, 刘百川, 徐思慧 (2023) 成都城区河流廊道自生植物的物种组成及其响应不同生境的多度格局. 中国园林, 39(8), 108-114.] | |
| [20] |
Lin QW, Xiao C, Ma JS (2022) A dataset on catalogue of alien plants in China. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22127. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[林秦文, 肖翠, 马金双 (2022) 中国外来植物数据集. 生物多样性, 30, 22127.]
DOI |
|
| [21] |
Luo WQ, Fu SH, Yang XB, Chen YK, Zhou W, Yang Q, Tao C, Zhou WS (2015) Distribution patterns of alien invasive plants and their influences on native plants of Hainan Island. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 39, 486-500. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[罗文启, 符少怀, 杨小波, 陈玉凯, 周威, 杨琦, 陶楚, 周文嵩 (2015) 海南岛入侵植物的分布特点及其对本地植物的影响. 植物生态学报, 39, 486-500.]
DOI |
|
| [22] | Pan N, Min YT, Zhao JJ, Zhang ML, Bai ZP, Qing C, Li J (2024) Species and functional diversity of spontaneous herb communities in urban built-up areas: A case study of Shenzhen city. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 44, 3759-3774. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [潘妮, 闵钰婷, 赵娟娟, 张曼琳, 白泽鹏, 卿晨, 李建 (2024) 城市建成区自生草本植物群落的物种多样性与功能多样性——以深圳市为例. 生态学报, 44, 3759-3774.] | |
| [23] | Qi XZ, Lin ZS, Liu HY (2016) Dynamic modeling of the interactive effects of competition and landscape patterns on the spread of exotic species. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36, 569-579. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [齐相贞, 林振山, 刘会玉 (2016) 竞争和景观格局相互作用对外来入侵物种传播影响的动态模拟. 生态学报, 36, 569-579.] | |
| [24] | Qian SH, Qin DY, Wu X, Hu SW, Hu LY, Lin DM, Zhao L, Shang KK, Song K, Yang YC (2020) Urban growth and topographical factors shape patterns of spontaneous plant community diversity in a mountainous city in Southwest China. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 55, 126814. |
| [25] | Ren BB, Shang R, Li F, Li W, Wang JH, Li G, Liu Q (2019) Close-to-nature plant community construction in urban greenspace of Beijing. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 38, 2911-2917. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [任斌斌, 商茹, 李芳, 李薇, 王建红, 李广, 刘倩 (2019) 北京城市绿地近自然植物群落构建. 生态学杂志, 38, 2911-2917.] | |
| [26] | Shen Q, Liu K, Li SY, Zhang J, Jiang YP, Ge Y, Chang J (2008) Relationships of plant composition, water level and solar radiation in Xixi Wetland, Hangzhou, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 32, 114-122. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[沈琪, 刘珂, 李世玉, 张骏, 蒋跃平, 葛滢, 常杰 (2008) 杭州西溪湿地植物组成及其与水位光照的关系. 植物生态学报, 32, 114-122.]
DOI |
|
| [27] | Shu MY, Cai JG, Fang BS (2009) Situation and control measures of alien invasive plants in Xixi National Wetland Park, Hangzhou City, Zhejiang Province. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry College, 26, 755-761. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [舒美英, 蔡建国, 方宝生 (2009) 杭州西溪湿地外来入侵植物现状与防治对策. 浙江林学院学报, 26, 755-761.] | |
| [28] | Song K, Guo XY, Wang ZY, Huang SS, Yan JY, Ye JH, Yue Y, Yan M, Wu M, Da LJ (2020) Restoration dynamics of near-to-nature forests in Shanghai. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 39, 1075-1081. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [宋坤, 郭雪艳, 王泽英, 黄莎莎, 严佳瑜, 叶建华, 乐莺, 严明, 吴梅, 达良俊 (2020) 上海城市近自然森林的重建动态. 生态学杂志, 39, 1075-1081.] | |
| [29] |
Song U, Son D, Kang CK, Lee EJ, Lee K, Park JS (2018) Mowing: A cause of invasion, but also a potential solution for management of the invasive, alien plant species Erigeron annuus (L.)Pers . Journal of Environmental Management, 223, 530-536.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Wang CY, Wei M, Wang S, Wu BD, Cheng HY (2020) Erigeron annuus (L.) Pers. and Solidago canadensis (L.) antagonistically affect community stability and community invasibility under the co-invasion condition. Science of the Total Environment, 716, 137128.
DOI URL |
| [31] | Wang M, Liu C, Li XL, Gao JH, Li X, Dong L (2022) Biodiversity characteristics in near-natural community parks: A case study in the central area of Beijing. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42, 8254-8264. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王沫, 刘畅, 李晓璐, 高俊宏, 李霞, 董丽 (2022) 近自然社区公园的生物多样性特征——以北京市中心城区为例. 生态学报, 42, 8254-8264.] | |
| [32] |
Wang SM, Zhang N, Yu LQ, Zhao RH, Hao P, Li JW, Jiang YS, Sha HF, Liu Y, Zhang ZX (2012) Distribution pattern and their influcing factors of invasive alien plants in Beijing. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32, 4618-4629. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [王苏铭, 张楠, 于琳倩, 赵容慧, 郝鹏, 李景文, 姜英淑, 沙海峰, 刘义, 张志翔 (2012) 北京地区外来入侵植物分布特征及其影响因素. 生态学报, 32, 4618-4629.] | |
| [33] | Wang Y, Li WH, Li D, Zhang Z (2015) Research progress on invasion mechanism and prevention strategy of Alternanthera philoxeroides. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 32, 625-634. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王颖, 李为花, 李丹, 张震 (2015) 喜旱莲子草入侵机制及防治策略研究进展. 浙江农林大学学报, 32, 625-634.] | |
| [34] | Xu GY, Li HY, Mo XQ, Meng WQ (2019) Restraining factors on the effectiveness of invasive plants management and control. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 38, 3169-3176. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [许光耀, 李洪远, 莫训强, 孟伟庆 (2019) 外来入侵植物管理与控制成效的制约因素. 生态学杂志, 38, 3169-3176.] | |
| [35] | Yan XL, Shou HY, Ma JS (2014) The alien invasive plants in Zhejiang Province, China. Plant Diversity and Resources, 36, 77-88. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [闫小玲, 寿海洋, 马金双 (2014) 浙江省外来入侵植物研究. 植物分类与资源学报, 36, 77-88.] | |
| [36] | Yang YB, Bian ZH, Ren WJ, Wu JH, Liu JQ, Shrestha N (2023) Spatial patterns and hotspots of plant invasion in China. Global Ecology and Conservation, 43, e02424. |
| [37] | Yao XD, Li HM, Jin YL, Shi Y, Bao ZY (2021a) Study on the diversity and community composition of spontaneous vegetation in herb layer in Hangzhou Xixi National Wetland Park. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 37(10), 123-128. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [姚兴达, 李浩铭, 金亚璐, 史琰, 包志毅 (2021a) 杭州西溪国家湿地公园草本层自生植物多样性及群落组分研究. 中国园林, 37(10), 123-128.] | |
| [38] | Yao XD, Li HM, Shi Y, Bao ZY (2021b) Diversity and characteristics of spontaneous vegetation in shrub-grass layer in Xixi National Wetland Park. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry Science and Technology, 41(4), 24-31. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [姚兴达, 李浩铭, 史琰, 包志毅(2021b) 杭州西溪国家湿地公园灌草层自生植物多样性与群落特征. 浙江林业科技, 41(4), 24-31.] | |
| [39] | Ye YH, Yang ZZ, Li SY, Ni GY, Chen SX, Yu YN, Chen XY (2020) Effects of biological invasion on natural resources assets and its application in natural resources balance sheet compile. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 29, 2465-2472. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[叶有华, 杨智中, 李思怡, 倪广艳, 陈三雄, 虞依娜, 陈晓意 (2020) 生物入侵对自然资源资产的影响及其在自然资源资产负债表编制中的应用. 生态环境学报, 29, 2465-2472.]
DOI |
|
| [40] |
Zhang LL, Hao PY, Dong L, Wang YL (2024) Optimization strategy for maintenance management of herbaceous layer in urban parks based on spontaneous plants: A case study of Xicheng District, Beijing. Landscape Architecture, 31(6), 46-54. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [张丽丽, 郝培尧, 董丽, 王应临 (2024) 基于自生植物的城市公园草本层养护管理优化策略——以北京市西城区为例. 风景园林, 31(6), 46-54.] | |
| [41] |
Zhang LM, Tan X, Dong Z, Zheng J, Yuan ZX, Li CX (2022) Effects of Alternanthera philoxeroides invasion on plant diversity in the riparian zones of downtown Chongqing in the Three Gorges Reservoir area. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 31(9), 13-25. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[张丽苗, 谭雪, 董智, 郑杰, 袁中勋, 李昌晓 (2022) 喜旱莲子草入侵对三峡库区重庆主城河岸带植物多样性的影响. 草业学报, 31(9), 13-25.]
DOI |
|
| [42] | Zhang MJ, Li QQ, Li ZJ (2020) Seed dispersal modes and landscape application strategies of autogenesis herbs in the parks of Nanjing City. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 36(8), 119-123. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张明娟, 李青青, 李竹君 (2020) 南京市公园绿地中自生草本植物的种子传播方式及园林应用策略研究. 中国园林, 36(8), 119-123.] | |
| [43] | Zhang MY, Li K, Xing XY, Fan SX, Xu YD, Hao PY, Dong L (2022) Responses of spontaneous plant diversity to urbanization in Wenyu River-North Canal ecological corridor Beijing. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42, 2582-2592. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张梦园, 李坤, 邢小艺, 范舒欣, 徐一丁, 郝培尧, 董丽 (2022) 北京温榆河-北运河生态廊道自生植物多样性对城市化的响应. 生态学报, 42, 2582-2592.] | |
| [44] | Zhang YF, Zheng ZH, Chen XB, Luo ZR (2022) Niche characteristics of the invasive plant Ageratum conyzoides and its commonly associated weeds. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42, 3727-3737. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张亚芬, 郑子洪, 陈旭波, 骆争荣 (2022) 入侵植物藿香蓟与常见伴生杂草的生态位特征. 生态学报, 42, 3727-3737.] | |
| [45] | Zhao YF, Zhao CY, Zhu JF, Li FF, Yang XQ, Guo CD (2022) Distribution pattern of alien invasive plants in typical parks in Beijing. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42, 3656-3665. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [赵云峰, 赵彩云, 朱金方, 李飞飞, 杨秀清, 郭朝丹 (2022) 北京市典型公园外来入侵植物分布格局. 生态学报, 42, 3656-3665.] |
| [1] | Xiaofan Cheng, Qingyuan Li, Yuanhui Li, Mingxiang Zhang. The Dilemmas and Solutions for Invasive Alien Species Governance Policy Systems [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2026, 34(2): 25332-. |
| [2] | Lulu Chen, Haoting Tang, Hong Leng, Qing Yuan, Xinyue Yang. The Impacts of Urban Block Built Environments on Biodiversity ——A Review and Outlook [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2026, 34(2): 25286-. |
| [3] | Wenqi Gao, Jingrong Xiang, Yao Zhao, Lingshuang Fan, Yuan Gu, Weihan Shao, Gaojun Li, Guangjun Zhao, Mingbin Chen, Xingwei Cai, Kai Chen. Stream fish community characteristics and their response to land use in Limushan and Jianfengling of Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2026, 34(2): 25374-. |
| [4] | Xiaoqiang Lu, Dan Rui, Jiangfeng Zhang, Bingxin Yin, Yulu Wang, Yuting Cen, Yichen Cui, Wanxia Yang. Impacts of nitrogen inputs-driven key ecological processes on biodiversity and their management implications [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2026, 34(2): 25368-. |
| [5] | Tinghong Tan, Fan Gao, Yu Yang, Qunying Gao, Chunfang Wu, Na Qiu, Ningning Zhao, Min Zhou, Gongping Kang, Zhihong Lu, Jianqiang Gao, Hong Yang, Chuandong Yang, Chunying Deng. Macrofungal flora and species diversity in karst areas of southwestern China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2026, 34(2): 25281-. |
| [6] | Jiangjian Xie, Mengkun Zhu, Aiwu Jiang, Zhishu Xiao. The Future of Listening to Biodiversity: Limitations and Development Directions of Soundscape-Based Automatic Assessment Methods [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2026, 34(2): 25296-. |
| [7] | Haiou Liu, Zhiming Hao, Leshan Du, Wenhui Liu, Ziyuan Li, Lei Liu. Progress, Challenges, and Insights on the Operation of the Global Biodiversity Framework Fund [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2026, 34(2): 25463-. |
| [8] | Ye Wang, Qianlu Wang, Jing Guan, Ying Wang. The current financial mechanisms of the Convention on Biological Diversity and its alternatives [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2026, 34(1): 25353-. |
| [9] | Ziling Yan, Xiaoyu Chen, Meng Yao. A comparative evaluation of bioinformatic pipelines for invertebrate biodiversity profiling via environmental DNA metabarcoding [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2026, 34(1): 25369-. |
| [10] | Fangyi Yang, Tong Jin, Xiaoli Shen, Li Zhang, Biao Yang. The contribution of philanthropic funding to China National Biodiversity Conservation Strategy and Action Plan (2023‒2030) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2026, 34(1): 25269-. |
| [11] | Luyao Tian, Hao Yin. The current situation and countermeasures of biodiversity offsetting studies abroad [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2026, 34(1): 25187-. |
| [12] | Renjia Meng, Tao Qin, Xinmeng Tang. The driving path and mode of enterprises’ biodiversity conservation [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2026, 34(1): 25246-. |
| [13] | Yang Qin, Aishan Wumaierjiang, Wentao Wei, Shamushake Diliniga. The impact of biodiversity information disclosure on supply chain resilience of A-share listed companies [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2026, 34(1): 25342-. |
| [14] | Ming Li, Xiangling Qin, Yuru Zhu, Wen Xiong. Theoretical framework and operational mechanisms of value realization in biodiversity offsetting for nature reserves [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2026, 34(1): 25241-. |
| [15] | Chunying Wu, Viorel D. Popescu, Yinqiu Ji. Hierarchical occupancy models as solutions to challenges in biodiversity assessment [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2026, 34(1): 25386-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2026 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn