



Biodiv Sci ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (3): 22493. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022493 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022493
• Original Papers: Animal Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Weiwei Lin1, Chengming Tian1, Dianguang Xiong1, Weihang Liu1,2, Ryhguli Sidike3, Yingmei Liang1,4,*( )
)
Received:2022-08-28
Accepted:2022-12-08
Online:2023-03-20
Published:2023-03-04
Contact:
Yingmei Liang
Weiwei Lin, Chengming Tian, Dianguang Xiong, Weihang Liu, Ryhguli Sidike, Yingmei Liang. Influencing factors of spider community diversity in poplar plantations in Xinjiang, China[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(3): 22493.
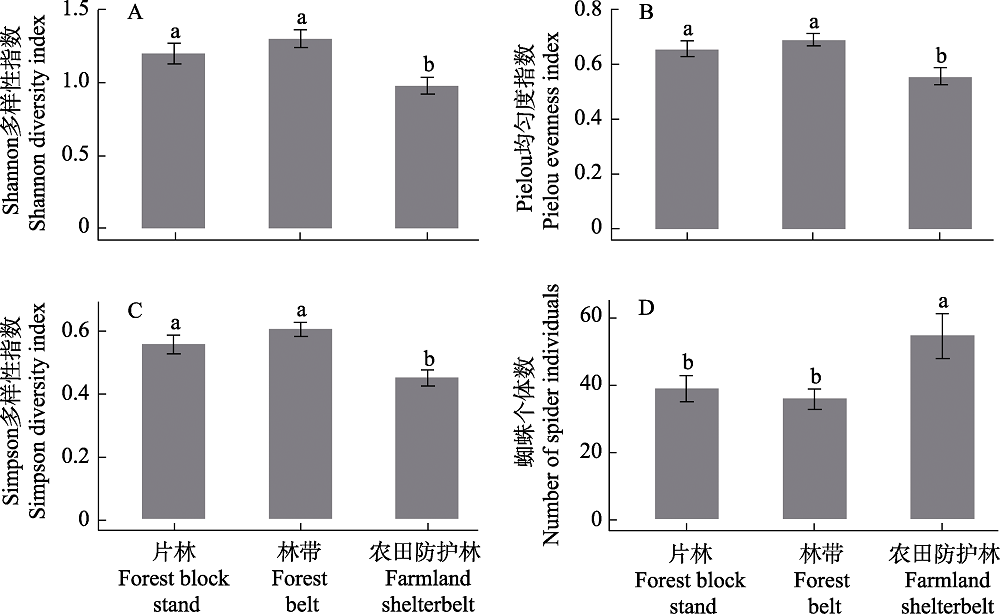
Fig. 2 Differences in the diversity of spiders among different forest types (mean ± SE). Different letters indicate significant differences among different stand types (P < 0.05)
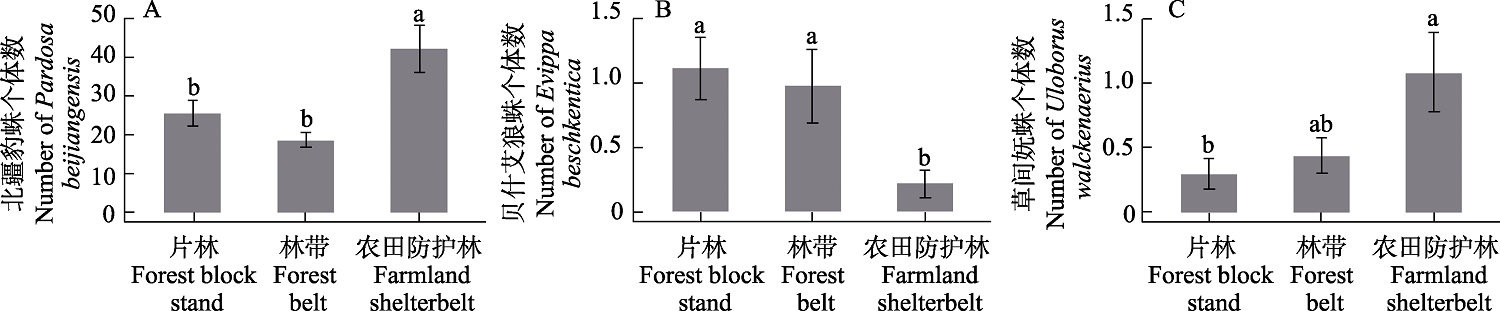
Fig. 3 Differences of dominant species of spiders among different forest types (mean ± SE). Different letters indicate significant differences among different stand types (P < 0.05).
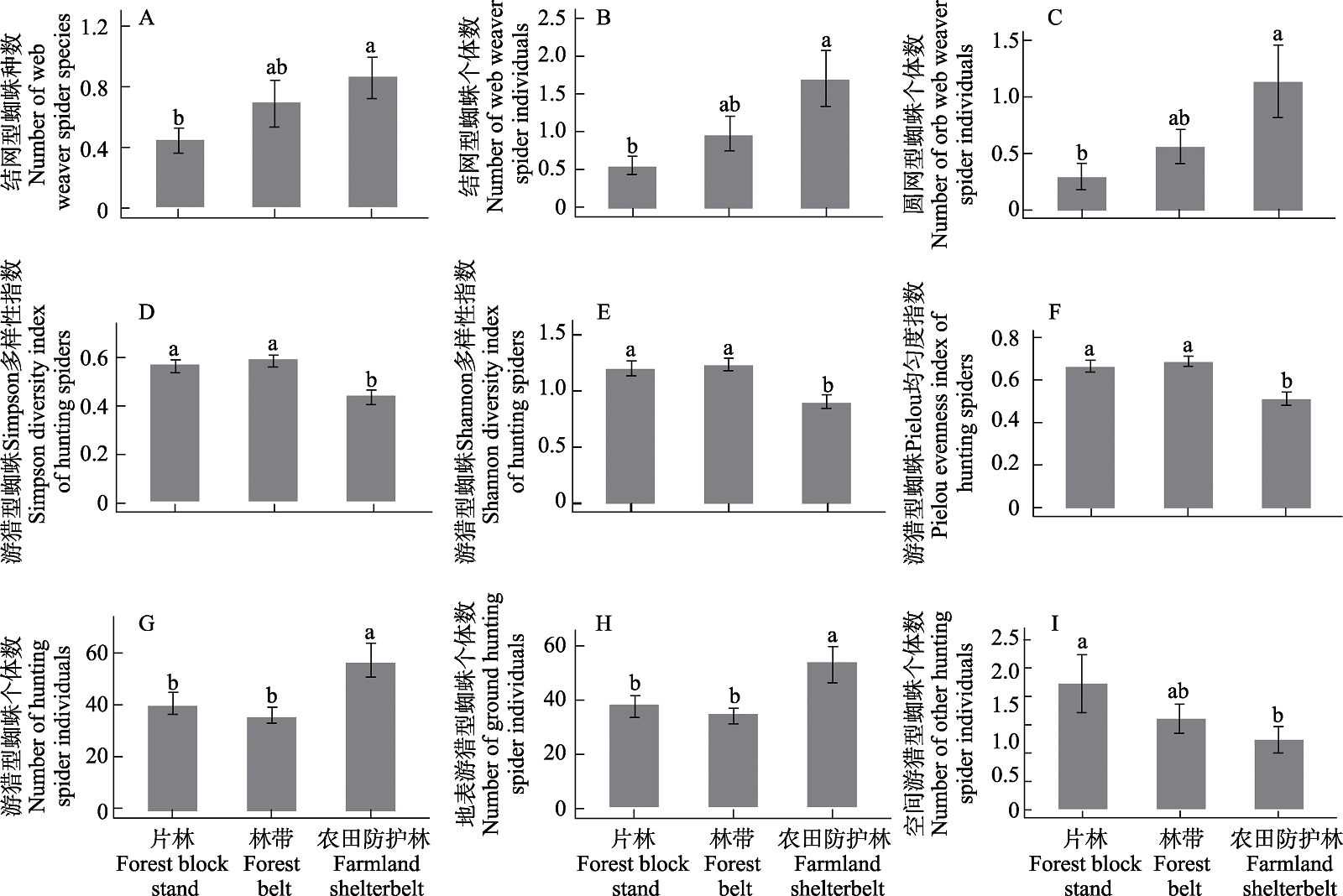
Fig. 4 Differences in the diversity of functional groups of spiders among different forest types (mean ± SE). Different letters indicate significant differences among different stand types (P < 0.05).
| [1] |
Baldissera R, Ganade G, Fontoura SB (2004) Web spider community response along an edge between pasture and Araucaria forest. Biological Conservation, 118, 403-409.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Barbosa P, Hines J, Kaplan I, Martinson H, Szczepaniec A, Szendrei Z (2009) Associational resistance and associational susceptibility: Having right or wrong neighbors. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 40, 1-20.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Barton BT, Schmitz OJ (2009) Experimental warming transforms multiple predator effects in a grassland food web. Ecology Letters, 12, 1317-1325.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
Baskent EZ, Keles S (2005) Spatial forest planning: A review. Ecological Modelling, 188, 145-173.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Bell JR, Bohan DA, Shaw EM, Weyman GS (2005) Ballooning dispersal using silk: World fauna, phylogenies, genetics and models. Bulletin of Entomological Research, 95, 69-114.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
Brierton BM, Allen DC, Jennings DT (2003) Spider fauna of sugar maple and white ash in northern and central New York State. Journal of Arachnology, 31, 350-362.
DOI URL |
| [7] | Cardoso P, Pekár S, Jocqué R, Coddington JA (2011) Global patterns of guild composition and functional diversity of spiders. PLoS ONE, 6, e21710. |
| [8] | Chen JJ, Wang YF, Lei GC, Wang RJ, Xu RM (2004) Impact of habitat quality on metapopulation structure and distribution of two melitaeine butterfly species. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 47, 59-66. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈洁君, 王义飞, 雷光春, 王戎疆, 徐汝梅 (2004) 栖息地质量对两种网蛱蝶集合种群结构和分布的影响. 昆虫学报, 47, 59-66.] | |
| [9] |
Dennis P, Young MR, Bentley C (2001) The effects of varied grazing management on epigeal spiders, harvestmen and pseudoscorpions of Nardus stricta grassland in upland Scotland. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 86, 39-57.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Denno RF, Mitter MS, Langellotto GA, Gratton C, Finke DL (2004) Interactions between a hunting spider and a web-builder: Consequences of intraguild predation and cannibalism for prey suppression. Ecological Entomology, 29, 566-577.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Ding YH, Wang RH, Ning HS (2011) Characteristics of landscape geochemistry in Karamay artificial carbon-sink forests. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 19, 1348-1353. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [丁玉华, 王让会, 宁虎森 (2011) 克拉玛依人工碳汇林区景观地球化学特征与规律. 中国生态农业学报, 19, 1348-1353.] | |
| [12] |
Duan MC, Hu WH, Liu YH, Yu ZR, Li X, Wu PL, Zhang F, Shi HL, Baudry J (2019a) The influence of landscape alterations on changes in ground beetle (Carabidae) and spider (Araneae) functional groups between 1995 and 2013 in an urban fringe of China. Science of the Total Environment, 689, 516-525.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Duan MC, Liu YH, Li X, Wu PL, Hu WH, Zhang F, Shi HL, Yu ZR, Baudry J (2019b) Effect of present and past landscape structures on the species richness and composition of ground beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae) and spiders (Araneae) in a dynamic landscape. Landscape and Urban Planning, 192, 103649.
DOI URL |
| [14] | Fan XY (2013) Thoughts on comprehensive prevention and control of forest pests in Heshuo. Forestry of Xinjiang, (3), 38-39. (in Chinese) |
| [樊秀英 (2013) 和硕县林业有害生物综合防控工作的思考. 新疆林业, (3), 38-39.] | |
| [15] |
Freiberg JA, de Sales Dambros C, Rodrigues ENL, Teixeira RA, Vieira ÂDHN, de Almeida HS, de Faccio Carvalho PC, Jacques RJS (2019) Increased grazing intensity in pastures reduces the abundance and richness of ground spiders in an integrated crop-livestock system. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 40, 1-10.
DOI |
| [16] | Guo HT, Ji XF, Wang C, Zou HL, Wang LY, Jiang J (2022) Spatial variability and influencing factors of plant diversity in the shrub layers of artificial forests in China. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Sciences Edition), 46, 144-152. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郭弘婷, 纪小芳, 汪成, 邹汉鲁, 王丽艳, 姜姜 (2022) 我国人工林林下灌木层植物多样性空间变异及影响要素. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 46, 144-152.] | |
| [17] | Hofer H, Brescovit AD (2001) Species and guild structure of a Neotropical spider assemblage (Araneae; Reserva Ducke, Amazonas, Brazil). Andrias, 15, 99-119. |
| [18] |
Horváth R, Magura T, Szinetár C, Tóthmérész B (2009) Spiders are not less diverse in small and isolated grasslands, but less diverse in overgrazed grasslands: A field study (East Hungary, Nyírség) Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 130, 16-22.
DOI URL |
| [19] | Hu HB, Wang HJ, Lu XZ, Qiu ZJ (2001) A study on effects of protective forest on climate in arid and semi-arid areas of China. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University, 25, 77-82. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [胡海波, 王汉杰, 鲁小珍, 邱志军 (2001) 中国干旱半干旱地区防护林气候效应的分析. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 25, 77-82.] | |
| [20] | Hu WC, Liu JH, He DH (2018) Edge effect of ground-dwelling spiders and spillover effect after alfalfa mowing in alfalfa fields of Yinchuan area. Journal of Plant Protection, 45, 773-781. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [胡文超, 刘军和, 贺达汉 (2018) 苜蓿田地表蜘蛛边缘效应及苜蓿刈割后的溢出效应. 植物保护学报, 45, 773-781.] | |
| [21] | Hu WH, Duan MC, Na SH, Zhang F, Yu ZR (2020) Spider diversity and community characteristics in cropland and two kinds of recovery habitats in Bashang area, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 31, 643-650. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[胡文浩, 段美春, 那书豪, 张锋, 宇振荣 (2020) 坝上地区农田及两种恢复生境中蜘蛛多样性与群落特征. 应用生态学报, 31, 643-650.]
DOI |
|
| [22] |
Jaksić FM (1981) Abuse and misuse of the term “guild” in ecological studies. Oikos, 37, 397-400.
DOI URL |
| [23] | Jiang FQ, Zeng DH, Yu ZY (2006) Decline of protective forest and its prevention strategies from viewpoint of restoration ecology: Taking Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica plantation in Zhanggutai as an example. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 17, 2229-2235. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [姜凤岐, 曾德慧, 于占源 (2006) 从恢复生态学视角透析防护林衰退及其防治对策: 以章古台地区樟子松林为例. 应用生态学报, 17, 2229-2235.] | |
| [24] | Kong TT, Zhang JW, Liu AH (2018) Main diseases and control of poplar in Xinjiang. Protection Forest Science and Technology, (11), 85-87. (in Chinese) |
| [孔婷婷, 张静文, 刘爱华 (2018) 新疆杨树的主要病害及防治. 防护林科技, (11), 85-87.] | |
| [25] | Kong WC, Wang RH, Ning HS, Ji XM, Min SJ, Zhao FS, Wu MH (2010) Stand structure & growth of emission reduction forest in Karamay. Protection Forest Science and Technology, (5), 19-22, 28. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孔维财, 王让会, 宁虎森, 吉小敏, 闵首军, 赵福生, 吴明辉 (2010) 克拉玛依减排林林分结构及生长分析. 防护林科技, (5), 19-22, 28.] | |
| [26] |
Krell FT (2004) Parataxonomy vs. taxonomy in biodiversity studies—Pitfalls and applicability of ‘morphospecies’ sorting. Biodiversity and Conservation, 13, 795-812.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Li R, Li SC, Yang HQ, Tian RJ, Liang J, Zhang JH (2008) Structure, characteristics, spatial and temporal dynamics of dominant species of spider communities in vegetable fields. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 16, 431-435. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [李锐, 李生才, 杨怀卿, 田瑞钧, 梁娟, 张建华 (2008) 菜田蜘蛛群落结构特征及优势种时空动态分析. 中国生态农业学报, 16, 431-435.] | |
| [28] | Li XR, Li XJ, Liu G (2012) Illustration of Common Desert Plants in Cold and Arid Regions of China:Plants in Arid Regions. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [李新荣, 李小军, 刘光 (2012) 中国寒区旱区常见荒漠植物图鉴: 旱区植物卷. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [29] |
Li ZY, Ye XZ, Wang SP (2021) Ecosystem stability and its relationship with biodiversity. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 45, 1127-1139. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[李周园, 叶小洲, 王少鹏 (2021) 生态系统稳定性及其与生物多样性的关系. 植物生态学报, 45, 1127-1139.]
DOI |
|
| [30] | Liang J, Zhang XY (2004) The techniques and practice of forest pest ecological control. Forest Pest and Disease, 23, 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [梁军, 张星耀 (2004) 森林有害生物的生态控制技术与措施. 中国森林病虫, 23, 1-8.] | |
| [31] | Liang JF, Yang JK, Yang Y, Chao QF, Yin YL, Zhao YG (2016) Effect of environmental factors on bacterial community structure in petroleum contaminated soil of Karamay Oil Field. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 56, 1301-1313. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [梁建芳, 杨江科, 杨杨, 晁群芳, 殷亚兰, 赵亚光 (2016) 克拉玛依油田石油污染土壤细菌群落结构与环境因子的关系. 微生物学报, 56, 1301-1313.] | |
| [32] | Liu J, Chen J, Peng Y, Liu FX (2006) Dynamic analysis of distribution patterns of the spiders in a cotton field by pitfall traps. Chinese Bulletin of Entomology, 43, 300-304. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘杰, 陈建, 彭宇, 刘凤想 (2006) 陷阱法调查棉田蜘蛛的分布动态. 昆虫知识, 43, 300-304.] | |
| [33] | Liu MQ, Li SL (1998) The present situation and the prospect for study on poplar resistance. Journal of Henan Agricultural University, 32, 251-257, 267. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘美青, 李淑玲 (1998) 杨树抗性研究的现状及展望. 河南农业大学学报, 32, 251-257, 267.] | |
| [34] |
Liu XP, Zhang WJ, Cao JS, Yang B, Cai YJ (2018) Carbon sequestration of plantation in Beijing-Tianjin sand source areas. Journal of Mountain Science, 15, 2148-2158.
DOI |
| [35] |
Liu YD, Wang XX, He LL, Liu ZY, Zeng XL, Sha HF, He BH, Jin YS, Li J, Chen JM, Guo GF, Duan J (2023) Effects of spatial structure on understory vegetation and soil properties in Pinus tabuliformis plantation of different succession types in Beijing. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 43, doi: 10.5846/stxb202112143542. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[刘亚栋, 王晓霞, 和璐璐, 柳正元, 曾小莉, 沙海峰, 何宝华, 金莹杉, 李杰, 陈建梅, 郭桂凤, 段劼 (2023) 北京地区油松人工林不同演替类型空间结构对林下植被及土壤的影响. 生态学报, 43, doi: 10.5846/stxb202112143542.
DOI |
|
| [36] | Long WC, Li TY, Li C, Xie BY, Ren SP, Jin SQ, Yu ZR, Liu YH, Duan MC (2021) Effects of management measures and soil factors on the diversity of ground spider communities in five agricultural habitat types. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 29, 483-491. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [龙武赐, 李天依, 黎淳, 谢冰一, 任少鹏, 金树权, 宇振荣, 刘云慧, 段美春 (2021) 管理措施及土壤因子对5种农田生境地表蜘蛛群落多样性的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 29, 483-491.] | |
| [37] | Lü GH (2008) Xinjiang Karamay Flora and Fauna List. Xinjiang People’s Publishing House, Urumchi. (in Chinese) |
| [吕光辉 (2008) 新疆克拉玛依动植物名录. 新疆人民出版社, 乌鲁木齐.] | |
| [38] | Lubin YD (1978) Seasonal abundance and diversity of web-building spiders in relation to habitat structure on Barro Colorado Island, Panama. Journal of Arachnology, 6, 31-51. |
| [39] | Ma KM, Fu BJ, Zhou HF (1999) Studies on species and pattern diversities of the forest landscapes of Donglingshan Mountain region, Beijing, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 19, 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [马克明, 傅伯杰, 周华锋 (1999) 北京东灵山地区森林的物种多样性和景观格局多样性研究. 生态学报, 19, 1-7.] | |
| [40] | Ma KP, Huang JH, Yu SL, Chen LZ (1995) Plant community diversity in Dongling Mountain, Beijing, China. II. Species richness, evenness and species diversities. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 15, 268-277. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [马克平, 黄建辉, 于顺利, 陈灵芝 (1995) 北京东灵山地区植物群落多样性的研究. II. 丰富度、均匀度和物种多样性指数. 生态学报, 15, 268-277.] | |
| [41] | Ma LQ (2009) The Study of Sustained Management Development of the Agroforestry System of the Northeast Ulan Buh Desert. PhD dissertation, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Hohhot. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [马利强 (2009) 乌兰布和沙漠东北部农林复合系统持续经营研究. 博士学位论文, 内蒙古农业大学, 呼和浩特.] | |
| [42] | Man JY, Yuan K, Chen BX, Wang ZR, Liu YH (2021) Impact of rice field management on the spider community characteristics in Taihu Lake Basin. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 29, 1467-1479. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [满吉勇, 袁凯, 陈宝雄, 王子睿, 刘云慧 (2021) 太湖流域稻田管理方式对蜘蛛群落特征的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 29, 1467-1479.] | |
| [43] |
McGeoch MA (2007) The selection, testing and application of terrestrial insects as bioindicators. Biological Reviews, 73, 181-201.
DOI URL |
| [44] | Meng XY, Hu Y, Wu TH (1998) Ecogeographic divisions of forest pests and main pests in Xinjiang. Forest Pest and Disease, (1), 19-25. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孟祥永, 胡茵, 吴天虹 (1998) 新疆森林病虫生态地理区划及主要病虫害种类. 森林病虫通讯, (1), 19-25.] | |
| [45] | Meng XY, Zhang H (1996) An individual model for Chinese fir plantations in Fujian Province. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 18(2), 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孟宪宇, 张弘 (1996) 闽北杉木人工林单木模型. 北京林业大学学报, 18(2), 1-8.] | |
| [46] |
Oliver I, Beattie AJ (1993) A possible method for the rapid assessment of biodiversity. Conservation Biology, 7, 562-568.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Pan F, Tian CY, Shao F, Zhou W, Chen F (2011) Evaluation of ecological sensitivity in Karamay, Xinjiang, northwest China. Acta Geographica Sinica, 66, 1497-1507. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [潘峰, 田长彦, 邵峰, 周伟, 陈飞 (2011) 新疆克拉玛依市生态敏感性研究. 地理学报, 66, 1497-1507.] | |
| [48] |
Parnell S, Gottwald TR, Gilligan CA, Cunniffe NJ, van den Bosch F (2010) The effect of landscape pattern on the optimal eradication zone of an invading epidemic. Phytopathology, 100, 638-644.
DOI PMID |
| [49] |
Perkins MJ, Inger R, Bearhop S, Sanders D (2018) Multichannel feeding by spider functional groups is driven by feeding strategies and resource availability. Oikos, 127, 23-33.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
Pfister SC, Schäfer RB, Schirmel J, Entling MH (2015) Effects of hedgerows and riparian margins on aerial web-building spiders in cereal fields. Journal of Arachnology, 43, 400-405.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
Rinaldi IMP, Mendes BP, Cady AB (2002) Distribution and importance of spiders inhabiting a Brazilian sugar cane plantation. Revista Brasileira De Zoologia, 19, 271-279.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
Sanders D, Schaefer M, Platner C, Griffiths GJK (2011) Intraguild interactions among generalist predator functional groups drive impact on herbivore and decomposer prey. Oikos, 120, 418-426.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
Sanders D, Vogel E, Knop E (2015) Individual and species-specific traits explain niche size and functional role in spiders as generalist predators. Journal of Animal Ecology, 84, 134-142.
DOI PMID |
| [54] | Schmidt MH, Thies C, Nentwig W, Tscharntke T (2007) Contrasting responses of arable spiders to the landscape matrix at different spatial scales. Journal of Biogeography, 35, 157-166. |
| [55] |
Schneider G, Krauss J, Steffan-Dewenter I (2013) Predation rates on semi-natural grasslands depend on adjacent habitat type. Basic and Applied Ecology, 14, 614-621.
DOI URL |
| [56] | Shen GF (2001) Science of Forestry Cultivation. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [沈国舫 (2001) 森林培育学. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [57] | Song DX, Zhu MS, Chen J (2001) The Fauna of Hebei Province:Araneae. Hebei Science and Technology Press, Shijiazhuang. (in Chinese) |
| [宋大祥, 朱明生, 陈军 (2001) 河北动物志: 蜘蛛类. 河北科技出版社, 石家庄.] | |
| [58] | Song LN, Zhu JJ, Yan QL (2009) Review on the shelter forest decline. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 28, 1684-1690. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [宋立宁, 朱教君, 闫巧玲 (2009) 防护林衰退研究进展. 生态学杂志, 28, 1684-1690.] | |
| [59] |
Souza ALTD, Martins RP (2004) Distribution of plant- dwelling spiders: Inflorescences versus vegetative branches. Austral Ecology, 29, 342-349.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
Srivastava DS, Cardinale BJ, Downing AL, Duffy JE, Jouseau C, Sankaran M, Wright JP (2009) Diversity has stronger top-down than bottom-up effects on decomposition. Ecology, 90, 1073-1083.
PMID |
| [61] | Su YQ, Zhang Y, Jia XR, Xue YG (2017) Application of several diversity indexes in forest community analysis. Ecological Science, 36, 132-138. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [苏宇乔, 张毅, 贾小容, 薛跃规 (2017) 几种多样性指标在森林群落分析中的应用比较. 生态科学, 36, 132-138.] | |
| [62] |
Turnbull AL (1973) Ecology of the true spiders (Araneomorphae). Annual Review of Entomology, 18, 305-348.
DOI URL |
| [63] | Uetz GW, Halaj J, Cady AB (1999) Guild structure of spiders in major crops. Journal of Arachnology, 27, 270-280. |
| [64] | Wang BH (2010) Multivariate Statistical Analysis and Modeling for R Language. Jinan University Press, Guangzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [王斌会 (2010) 多元统计分析及R语言建模. 暨南大学出版社, 广州.] | |
| [65] | Wang DB, Ji SY, Chen FP (2001) A review on the species diversity of plant community. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 20(4), 55-60. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [汪殿蓓, 暨淑仪, 陈飞鹏 (2001) 植物群落物种多样性研究综述. 生态学杂志, 20(4), 55-60.] | |
| [66] | Wang GH (2002) Further thoughts on diversity and stability in ecosystems, Biodiversity Science, 10, 126-134. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[王国宏 (2002) 再论生物多样性与生态系统的稳定性. 生物多样性, 10, 126-134.]
DOI |
|
| [67] | Xie BY, Cheng XY, Shi J, Zhang QW, Dai SM, Cheng FX, Luo YQ (2009) Formation and expansion mechanism of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus invasive population—Progress of National Key Basic Research and Development Plan “basic research on invasion mechanism and control of agricultural and forestry dangerous organisms”. Science in China, 39, 333-341. (in Chines) |
| [谢丙炎, 成新跃, 石娟, 张青文, 戴素明, 成飞雪, 骆有庆 (2009) 松材线虫入侵种群形成与扩张机制——国家重点基础研究发展计划“农林危险生物入侵机理与控制基础研究”进展. 中国科学, 39, 333-341.] | |
| [68] | Xing SW, Liang XX (2019) Differences in the characteristics of netting and hunting spider community in tea plantations at different altitudes. Journal of Hanshan Normal University, 40, 25-33. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [邢树文, 梁秀霞 (2019) 不同海拔茶园结网型与游猎型蜘蛛亚群落特征差异. 韩山师范学院学报, 40, 25-33.] | |
| [69] | Yan K, Zhang HJ (2011) Atlas of Xinjiang Grassland Plants. China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [闫凯, 张洪江 (2011) 新疆草原植物图册. 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [70] | Yao XR, Pan CD, Li ZH (2009) Dividing of forestation site types and integrated evaluation of soil quality of agricultural development region in Karamay. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 46(1), 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [姚晓蕊, 潘存德, 李兆慧 (2009) 克拉玛依农业开发区造林地立地类型划分及其土壤质量综合评价. 新疆农业科学, 46(1), 1-7.] | |
| [71] | Yao XR, Pan CD, Wang WH (2008) Evaluation on ecological adaptability of the cultivated tree species in agricultural development region of Karamay. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 45(1), 1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [姚晓蕊, 潘存德, 王维翰 (2008) 克拉玛依农业开发区人工栽培树种生态适应性评价. 新疆农业科学, 45(1), 1-6.] | |
| [72] | Yuan FH, Chen LS, Zhou GC, Rao J, Tang X, Hu YY (2017) A comparative study on spider diversities in the Meiling scenic areas of Nanchang City. Biological Disaster Science, 40, 143-150. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [袁凤辉, 陈连水, 周谷春, 饶军, 唐兴, 胡钰颖 (2017) 江西南昌梅岭景区蜘蛛多样性的比较研究. 生物灾害科学, 40, 143-150.] | |
| [73] | Zhang XZ, Zhang X, Song X, Yu ZR, Liu YH (2018) Effects of vegetated field margins on the distribution of epigaeic carabid beetles and spiders and aphid development in adjacent wheat fields. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 8442-8454. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张旭珠, 张鑫, 宋潇, 宇振荣, 刘云慧 (2018) 植被边界带对相邻麦田地表步甲和蜘蛛分布及蚜虫发生的影响. 生态学报, 38, 8442-8454.] | |
| [74] |
Zhang Y, Wang LY, Xiang CL, Duan MC, Zhang ZS (2021) Effects of different grazing intensities on spider diversity in Saihanwula Grassland. Biodiversity Science, 29, 467-476. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[张宇, 王露雨, 向昌林, 段美春, 张志升 (2021) 不同放牧强度对赛罕乌拉草原蜘蛛多样性的影响. 生物多样性, 29, 467-476.]
DOI |
|
| [75] | Zheng SK, Gao RT (1996) Poplar High Production Cultivation and Pest Control. Golden Shield Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [郑世锴, 高瑞桐 (1996) 杨树丰产栽培与病虫害防治. 金盾出版社, 北京.] | |
| [76] | Zhou WJ, Zhong L, Huang JL, Xie YY, Luo YY (2019) Species diversity, functional group structure, and influencing factors of spider community in fragmented landscape of Thousand Island Lake. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39, 2226-2236. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [周文婕, 仲磊, 黄杰灵, 谢央央, 罗媛媛 (2019) 千岛湖片段化景观中蜘蛛群落物种多样性和功能群结构及其影响因素. 生态学报, 39, 2226-2236.] |
| [1] | Mingyi Zhang, Xiaomei Wang, Yanxin Zheng, Nan Wu, Donghao Li, Enyuan Fan, Na Li, Xiujuan Shan, Tao Yu, Chunnuan Zhao, Bo Li, Shuai Xu, Yuping Wu, Liqun Ren. Resource status and habitat function of typical oyster reef areas in the Yellow River Estuary [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [2] | Wei Song, Cai Cheng, Jiawei Wang, Jihua Wu. Soil microbes regulate the relationships between plant diversity and ecosystem functions [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [3] | Tong Miao, Wang Huan, Zhang Wenshuang, Wang Chao, Song Jianxiao. Distribution characteristics of antibiotic resistance genes in soil bacterial communities exposed to heavy metal pollution [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24101-. |
| [4] | Li Yanpeng, Chen Jie, Lu Chunyang, Xu Han. Community characteristics of a 64-ha secondary forest dynamics plot in a tropical montane rainforest in Jianfengling, Hainan [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [5] | Zerong He, Peng Ye, Shuting Wang, Yongxin Guan, Shujun Yan, Xinru Hong. Composition and spatial distribution of dominant weed species in urban lawns of China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24133-. |
| [6] | Shiyu Wei, Tianjiao Song, Jiayi Luo, Yan Zhang, Zixuan Zhao, Jingwen Ru, Hua Yi, Yanbing Lin. Altitudinal distribution patterns of soil bacterial communities in the Huoditang coniferous forests of the Qinling Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24180-. |
| [7] | Yongqiang Shi, Qingshan Luan, Xiujuan Shan, Chao Wei, Yongsong Zhao, Cece Sun, Xianshi Jin. Annual changes in zooplankton biodiversity in the southern waters of Changdao [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23428-. |
| [8] | Yanmei Ni, Li Chen, Zhiyuan Dong, Debin Sun, Baoquan Li, Xumin Wang, Linlin Chen. Community structure of macrobenthos and ecological health evaluation in the restoration area of the Yellow River Delta wetland [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(3): 23303-. |
| [9] | Jiaxin Wei, Zhiguo Jiang, Linsen Yang, Huanhuan Xiong, Jiaojiao Jin, Fanglin Luo, Jiehua Li, Hao Wu, Yaozhan Xu, Xiujuan Qiao, Xinzeng Wei, Hui Yao, Huiliang Yu, Jingyuan Yang, Mingxi Jiang. Community composition and structure in a 25 ha mid-subtropical mountain deciduous broad-leaved forest dynamics plot in Shennongjia, Hubei, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(3): 23338-. |
| [10] | Xiaolin Liu, Yougui Wu, Minhua Zhang, Xiaorong Chen, Zhicheng Zhu, Dingyun Chen, Shu Dong, Buhang Li, Bingyang Ding, Yu Liu. Community composition and structure of a 25-ha forest dynamics plot of subtropical forest in Baishanzu, Zhejiang Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(2): 23294-. |
| [11] | Fangfang Wu, Na Liu, Chunmei He, Zuoqiang Yuan, Zhanqing Hao, Qiulong Yin. Elevational gradient pattern of woody plant community structure and diversity in the Qinling Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24239-. |
| [12] | Hang Shan, Zupei Lei, Fangdong Zheng, Boliang Wei, Lei Zhong, Mingjian Yu. Dynamic changes in the community of a secondary evergreen broad-leaved forest in Wuyanling, Zhejiang Province from 2013 to 2023 [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24372-. |
| [13] | Jia Yao, Congling Zhang, Shixuan Li, Yang Lin, Zhen Wang, Yuhan Zhang, Weilong Zhou, Xinhe Pan, Shan Zhu, Yiqing Wu, Dan Wang, Jinliang Liu, Shanshan Tan, Guochun Shen, Mingjian Yu. Characteristics of plant communities in the Baishanzu continuous elevational transect [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24052-. |
| [14] | Jiayi Feng, Juyu Lian, Yujun Feng, Dongxu Zhang, Honglin Cao, Wanhui Ye. Effects of vertical stratification on community structure and functions in a subtropical, evergreen broad-leaved forest in the Dinghushan National Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24306-. |
| [15] | Xingyu Wang, Jinghui Meng, Siyuan Ren, Yan Zhu. Relationship between biodiversity and aboveground biomass in the warm temperate deciduous broad-leaved forest of Donglingshan, Beijing [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(12): 24230-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()