



Biodiv Sci ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (5): 647-660. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021013 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021013
• Reviews • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yan Xu1, Congling Zhang1, Ruijiao Jiang1, Zifei Wang1, Mengchen Zhu1, Guochun Shen1,*( )
)
Received:2021-01-12
Accepted:2021-03-16
Online:2021-05-20
Published:2021-04-22
Contact:
Guochun Shen
Yan Xu, Congling Zhang, Ruijiao Jiang, Zifei Wang, Mengchen Zhu, Guochun Shen. UAV-based hyperspectral images and monitoring of canopy tree diversity[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(5): 647-660.
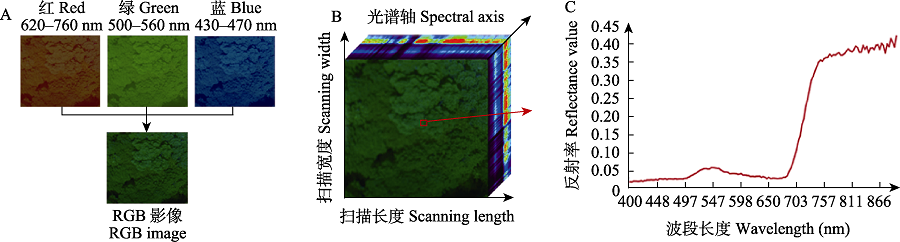
Fig. 1 RGB image and hyperspectral image of typical forest canopy of the subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest in Tiantong, Zhejiang Province. (A) Ordinary RGB images only contain three layers of information: red (620-760 nm), green (500-560 nm) and blue (430-470 nm). Therefore, the canopy of most evergreen tree species is almost the same green in RGB images, which makes it very difficult to identify the canopy species; (B) Three dimensional display of canopy hyperspectral image, x-axis is the scanning length, y-axis is the scanning width, z-axis is the spectral axis; (C) The spectral reflection curve of selected pixel, abscissa represents the wavelength, ordinate represents the band reflectance value, the pixel shows different reflectance values in different bands, forming a nearly continuous spectral curve.
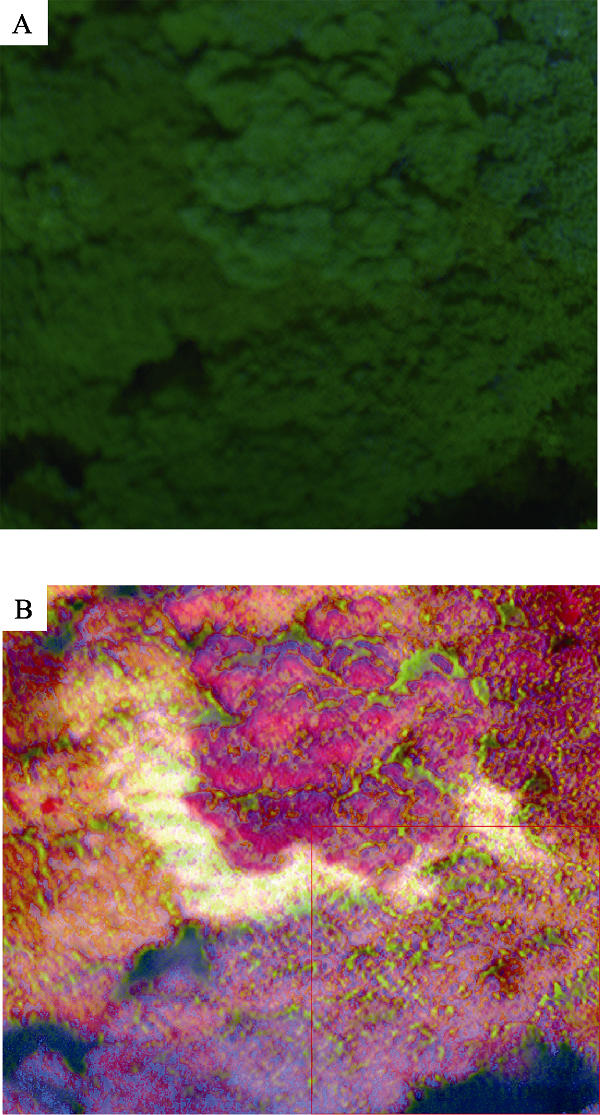
Fig. 2 Comparison of canopy RGB image and canopy hyperspectral image processed by principal component analysis (PCA). (A) The canopy RGB image shows that the canopy of each tree species is similar in green; (B) Through PCA processing of the first three axes of the canopy hyperspectral image, the canopy hyperspectral image of different tree species shows different colors, which means that the hyperspectral images have full potential to reflect the subtle differences between different tree species.
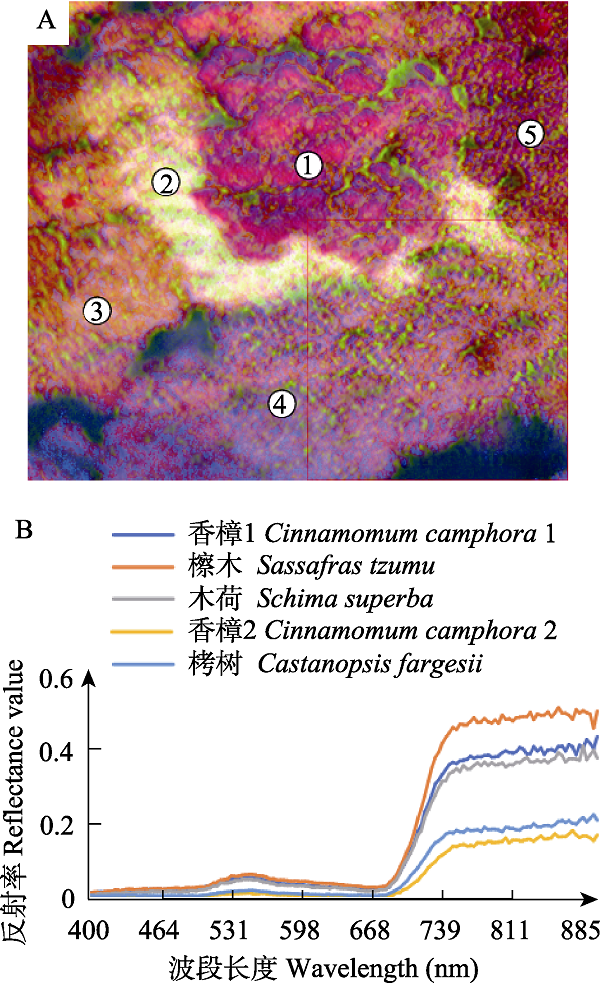
Fig. 3 Individual canopy spectral characteristic curve. (A) In the hyperspectral images of forest canopy processed by principal component analysis (PCA), the numbers ①-⑤ represent different individuals; (B) Spectral reflectance curves of five canopy individuals. Different plants show different spectral reflectance curves because of their different chemical properties and structures, which is the basis of spectral species classification.
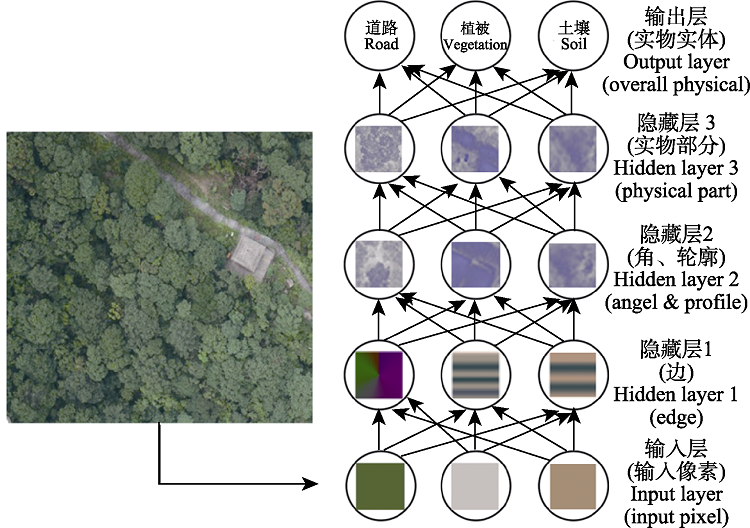
Fig. 4 Classification model based on deep learning network. The model includes input layer, hidden layer and output layer. Hidden layer is used to extract image features. The higher the number of layers is, the higher the features can be extracted by hidden layer.
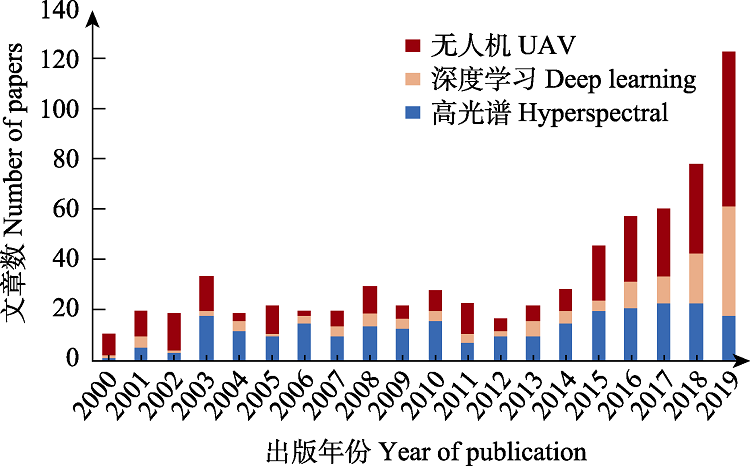
Fig. 5 From 2000 to 2019, the statistical results of articles in the field of ecology using unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), deep learning and hyperspectral, respectively
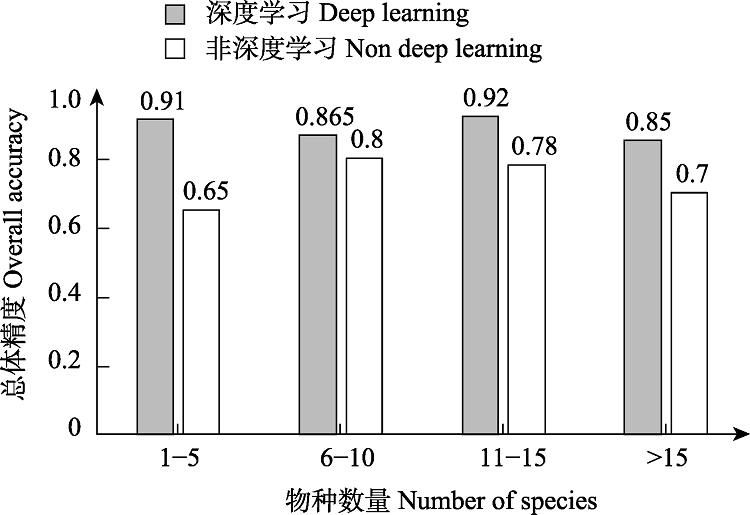
Fig. 6 The performance of deep learning and non deep learning algorithms in hyperspectral tree species classification. The statistical test results show that the deep learning algorithm has obvious advantages in species classification.
| [1] |
Adam E, Mutanga O, Rugege D (2010) Multispectral and hyperspectral remote sensing for identification and mapping of wetland vegetation: A review. Wetlands Ecology and Management, 18, 281-296.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Anderson-Teixeira KJ, Davies SJ, Bennett AC, Gonzalez-Akre EB, Muller-Landau HC, Wright SJ, Salim KA, Almeyda AM, Alfonso A, Baltzer JL, Basset Y, Bourg NA, Broadbent EN, Brockelman WY, Bunyavejchewin S, Burslem DFRP, Butt N, Cao M, Cardenas D, Chuyong GB, Clay K, Cordell S, Dattaraja HS, Deng XB, Detto M, Du XJ, Duque A, Erikson DL, Ewango CEN, Fischer GA, Fletcher C, Foster RB, Giardina CP, Gilbert GS, Gunatilleke N, Gunatilleke S, Hao ZQ, Hargrove WW, Hart TB, Hau BCH, He FL, Hoffman FM, Howe RW, Hubbell SP, Inman-Narahari FM, Jansen PA, Jiang MX, Johnson DJ, Kanzaki M, Kassim AR, Kenfack D, Kibet S, Kinnaird MF, Korte L, Kral K, Kumar J, Larson AJ, Li YD, Li XK, Liu SR, Lum SKY, Lutz JA, Ma KP, Maddalena DM, Makana JR, Malhi Y, Marthews T, Mat Serudin R, McMahon SM, McShea WJ, Memiaghe HR, Mi XC, Mizuno T, Morecroft M, Myers JA, Novotny V, de Oliveira AA, Ong PS, Orwig DA, Ostertag R, den Ouden J, Parker GG, Phillips RP, Sack L, Sainge MN, Sang WG, Sri-Ngernyuang K, Sukumar R, Sun IF, Sungpalee W, Suresh HS, Tan S, Thomas SC, Thomas DW, Thompson J, Turner BL, Uriarte M, Valencia R, Vallejo MI, Vicentini A, Vrška T, Wang XH, Wang XG, Weiblen G, Wolf A, Xu H, Yap S, Zimmerman J (2015) CTFS-ForestGEO: A worldwide network monitoring forests in an era of global change. Global Change Biology, 21, 528-549.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | Asner GP, Vitousek PM (2005) Remote analysis of biological invasion and biogeochemical change. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 102, 4383-4386. |
| [4] |
Asner GP, Martin RE, Ford AJ, Metcalfe DJ, Liddell MJ (2009) Leaf chemical and spectral diversity in Australian tropical forests. Ecological Applications, 19, 236-253.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Asner GP, Martin RE, Anderson CB, Knapp DE (2015) Quantifying forest canopy traits: Imaging spectroscopy versus field survey. Remote Sensing of Environment, 158, 15-27.
DOI URL |
| [6] | Asner GP, Knapp DE, Anderson CB, Martin RE, Vaughn N (2016) Large-scale climatic and geophysical controls on the leaf economics spectrum. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 113, E4043-E4051. |
| [7] |
Asner GP, Martin RE, Knapp DE, Tupayachi R, Anderson CB, Sinca F, Vaughn NR, Llactayo W (2017) Airborne laser-guided imaging spectroscopy to map forest trait diversity and guide conservation. Science, 355, 385-389.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Ballanti L, Blesius L, Hines E, Kruse B (2016) Tree species classification using hyperspectral imagery: A comparison of two classifiers. Remote Sensing, 8, 445.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Bongalov B, Burslem DFRP, Jucker T, Thompson SED, Rosindell J, Swinfield T, Nilus R, Clewley D, Phillips OL, Coomes DA (2019) Reconciling the contribution of environmental and stochastic structuring of tropical forest diversity through the lens of imaging spectroscopy. Ecology Letters, 22, 1608-1619.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
Cayuela L, Benayas JMR, Justel A, Salas-Rey J (2006) Modelling tree diversity in a highly fragmented tropical montane landscape. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 15, 602-613.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Chen YS, Jiang HL, Li CY, Jia XP, Ghamisi P (2016) Deep feature extraction and classification of hyperspectral images based on convolutional neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 54, 6232-6251.
DOI URL |
| [12] | Chesson P, Donahue MJ, Melbourne B, Sears ALW (2005) Scale Transition Theory for Understanding Mechanisms in Metacommunities. University of Chicago Press, Chicago. |
| [13] |
Christin S, Hervet É, Lecomte N (2019) Applications for deep learning in ecology. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 10, 1632-1644.
DOI |
| [14] |
Christin S, Hervet É, Lecomte N (2021) Going further with model verification and deep learning. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 12, 130-134.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Clark ML, Roberts DA (2012) Species-level differences in hyperspectral metrics among tropical rainforest trees as determined by a tree-based classifier. Remote Sensing, 4, 1820-1855.
DOI URL |
| [16] | Crawley MJ (2012) The R Book, 2nd edn. Wiley, New Jersey. |
| [17] |
Dalponte M, Ørka HO, Ene LT, Gobakken T, Næsset E (2014) Tree crown delineation and tree species classification in boreal forests using hyperspectral and ALS data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 140, 306-317.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Dalponte M, Ene LT, Marconcini M, Gobakken T, Næsset E (2015) Semi-supervised SVM for individual tree crown species classification. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 110, 77-87.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Dalponte M, Frizzera L, Gianelle D (2019) Individual tree crown delineation and tree species classification with hyperspectral and LiDAR data. PeerJ, 6, e6227.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Du PJ, Xia JS, Xue ZH, Tan K, Su HJ, Bao R (2016) Review of hyperspectral remote sensing image classification. Journal of Remote Sensing, 20, 236-256. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杜培军, 夏俊士, 薛朝辉, 谭琨, 苏红军, 鲍蕊 (2016) 高光谱遥感影像分类研究进展. 遥感学报, 20, 236-256.] | |
| [21] |
Duro DC, Coops NC, Wulder MA, Han T (2007) Development of a large area biodiversity monitoring system driven by remote sensing. Progress in Physical Geography: Earth and Environment, 31, 235-260.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Fairbanks DHK, McGwire KC (2004) Patterns of floristic richness in vegetation communities of California: Regional scale analysis with multi-temporal NDVI. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 13, 221-235.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Fricker GA, Ventura JD, Wolf JA, North MP, Davis FW, Franklin J (2019) A convolutional neural network classifier identifies tree species in mixed-conifer forest from hyperspectral imagery. Remote Sensing, 11, 2326.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Ghamisi P, Maggiori E, Li ST, Souza R, Tarablaka Y, Moser G, De Giorgi A, Fang LY, Chen YS, Chi MM, Serpico SB, Benediktsson JA (2018) New frontiers in spectral-spatial hyperspectral image classification: The latest advances based on mathematical morphology, Markov random fields, segmentation, sparse representation, and deep learning. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 6(3), 10-43. |
| [25] |
Ghosh A, Fassnacht FE, Joshi PK, Koch B (2014) A framework for mapping tree species combining hyperspectral and LiDAR data: Role of selected classifiers and sensor across three spatial scales. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 26, 49-63.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Graves SJ, Asner GP, Martin RE, Anderson CB, Colgan MS, Kalantari L, Bohlman SA (2016) Tree species abundance predictions in a tropical agricultural landscape with a supervised classification model and imbalanced data. Remote Sensing, 8, 161.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Guo QH, Wu FF, Hu TY, Chen LH, Liu J, Zhao XQ, Gao S, Pang SJ (2016) Perspectives and prospects of unmanned aerial vehicle in remote sensing monitoring of biodiversity. Biodiversity Science, 24, 1267-1278. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 郭庆华, 吴芳芳, 胡天宇, 陈琳海, 刘瑾, 赵晓倩, 高上, 庞树鑫 (2016) 无人机在生物多样性遥感监测中的应用现状与展望. 生物多样性, 24, 1267-1278.] | |
| [28] | Hu JB, Zhang J (2018) Unmanned aerial vehicle remote sensing in ecology: Advances and prospects. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 20-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 胡健波, 张健 (2018) 无人机遥感在生态学中的应用进展. 生态学报, 38, 20-30.] | |
| [29] | Hu W, Huang YY, Wei L, Zhang F, Li HC (2015) Deep convolutional neural networks for hyperspectral image classification. Journal of Sensors, 2015(2), 1-12. |
| [30] | Huang Y, Chen XH, Liu YL, Sun M, Su QC, Li YD (2019) UAV hyperspectral built-in push-scan image fast splicing method. Journal of Geomatics, 44(5), 24-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 黄宇, 陈兴海, 刘业林, 孙梅, 苏秋城, 李艳大 (2019) 基于无人机高光谱影像的引黄灌区水稻叶片全氮含量估测. 测绘地理信息, 44(5), 24-28.] | |
| [31] | Jia W, Pang Y, Ju HB, Li ZY (2018) A BRDF normalization correction method for airborne push broom hyperspectral images in forest areas: China, CN201711429219.3. (in Chinese) |
| [ 荚文, 庞勇, 鞠洪波, 李增元 (2018) 林区机载推扫式高光谱影像的BRDF归一化校正方法: 中国, CN201711429219.3.] | |
| [32] |
Kalacska M, Sanchez-Azofeifa GA, Rivard B, Caelli T, White HP, Calvo-Alvarado JC (2007) Ecological fingerprinting of ecosystem succession: Estimating secondary tropical dry forest structure and diversity using imaging spectroscopy. Remote Sensing of Environment, 108, 82-96.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Kayet N, Pathak K, Chakrabarty A, Kumar S, Singh CP, Chowdary VM (2020) Assessment of mining activities on tree species and diversity in hilltop mining areas using Hyperion and Landsat data. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27, 42750-42766.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Kerr JT, Ostrovsky M (2003) From space to species: Ecological applications for remote sensing. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 18, 299-305.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Kong JX, Zhang ZC, Zhang J (2019) Classification and identification of plant species based on multi-source remote sensing data: Research progress and prospect. Biodiversity Science, 27, 796-812. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 孔嘉鑫, 张昭臣, 张健 (2019) 基于多源遥感数据的植物物种分类与识别: 研究进展与展望. 生物多样性, 27, 796-812.] | |
| [36] |
Luoto M, Virkkala R, Heikkinen RK, Rainio K (2004) Predicting bird species richness using remote sensing in boreal agricultural-forest mosaics. Ecological Applications, 14, 1946-1962.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Nagendra H (2001) Using remote sensing to assess biodiversity. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 22, 2377-2400.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Oindo BO, Skidmore AK (2002) Interannual variability of NDVI and species richness in Kenya. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 23, 285-298.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Pu RL (2009) Broadleaf species recognition with in situ hyperspectral data. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 30, 2759-2779.
DOI URL |
| [40] | Qin ZF, Chang QR, Xie BN, Shen J (2016) Rice leaf nitrogen content estimation based on hysperspectral imagery of UAV in Yellow River diversion irrigation district. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 32(23), 77-85. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 秦占飞, 常庆瑞, 谢宝妮, 申健 (2016) 基于无人机高光谱影像的引黄灌区水稻叶片全氮含量估测. 农业工程学报, 32(23), 77-85.] | |
| [41] | Quan XW (2017) Research on weak sensitive parameters retrieval using vegetation canopy reflectance model. PhD dissertation, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 全兴文 (2017) 植被冠层反射率模型弱敏感参数遥感反演方法. 博士学位论文, 电子科技大学, 成都.] | |
| [42] |
Raczko E, Zagajewski B (2018) Tree species classification of the UNESCO Man and the Biosphere Karkonoski National Park (Poland) using artificial neural networks and APEX hyperspectral images. Remote Sensing, 10, 1111.
DOI URL |
| [43] | Rivard B, Sanchez-Azofeifa GA, Foley S, Calvo-Alvarado J (2008) Species classification of tropical tree leaf reflectance and dependence on selection of spectral bands. In: Hyperspectral Remote Sensing of Tropical and Sub-tropical Forests (eds Kalacska M, Sanchez-Azofeifa GA), pp. 141-157. CRC Press, Florida. |
| [44] |
Shen X, Cao L (2017) Tree-species classification in subtropical forests using airborne hyperspectral and LiDAR data. Remote Sensing, 9, 1180.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Signoroni A, Savardi M, Baronio A, Benini S (2019) Deep learning meets hyperspectral image analysis: A multidisciplinary review. Journal of Imaging, 5, 52.
DOI URL |
| [46] | Song YC (2001) Vegetation Ecology. East China Normal University Press, Shanghai. (in Chinese) |
| [ 宋永昌 (2001) 植被生态学. 华东师范大学出版社, 上海.] | |
| [47] | Tan BX, Li ZY, Chen EX, Pang Y, Wu HG (2008) Research advance in forest information extraction from hyperspectral remote sensing data. Forest Research, 21(A1), 105-111. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 谭炳香, 李增元, 陈尔学, 庞勇, 武红敢 (2008) 高光谱遥感森林信息提取研究进展. 林业科学研究, 21(A1), 105-111.] | |
| [48] |
Tang ZY, Jiang MW, Zhang J, Zhang XY (2018) Applications of satellite and air-borne remote sensing in biodiversity research and conservation. Biodiversity Science, 26, 807-818. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 唐志尧, 蒋旻炜, 张健, 张新悦 (2018) 航空航天遥感在物种多样性研究与保护中的应用. 生物多样性, 26, 807-818.] | |
| [49] | Thenkabail PS, Lyon JG, Huete A (2018) Biophysical and Biochemical Characterization and Plant Species Studies, 2nd edn. 2nd edn. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, Florida. |
| [50] |
Trier ØD, Salberg AB, Kermit M, Rudjord Ø, Gobakken T, Næsset E, Aarsten D (2018) Tree species classification in Norway from airborne hyperspectral and airborne laser scanning data. European Journal of Remote Sensing, 51, 336-351.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
Turner W, Spector S, Gardiner N, Fladeland M, Sterling E, Steininger M (2003) Remote sensing for biodiversity science and conservation. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 18, 306-314.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
Underwood E, Ustin S, DiPietro D (2003) Mapping nonnative plants using hyperspectral imagery. Remote Sensing of Environment, 86, 150-161.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
Vaglio Laurin G, Liesenberg V, Chen Q, Guerriero L, Del Frate F, Bartolini A, Coomes D, Wilebore B, Lindsell J, Valentini R (2013) Optical and SAR sensor synergies for forest and land cover mapping in a tropical site in West Africa. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 21, 7-16.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
Wäldchen J, Mäder P (2018) Machine learning for image based species identification. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 9, 2216-2225.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
Wang BC, Smith TB (2002) Closing the seed dispersal loop. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 17, 379-386.
DOI URL |
| [56] | Wu JG (2007) Landscape Ecology: Pattern, Process, Scale and Hierarchy, 2nd edn. Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 邬建国 (2007) 景观生态学——格局、过程、尺度与等级 (第二版). 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| [57] | Xi XF, Zhou GD (2016) A survey on deep learning for natural language processing. Acta Automatica Sinica, 42, 1445-1465. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 奚雪峰, 周国栋 (2016) 面向自然语言处理的深度学习研究. 自动化学报, 42, 1445-1465.] | |
| [58] |
Xi YB, Ren CY, Wang ZM, Wei SQ, Bai JL, Zhang B, Xiang HX, Chen L (2019) Mapping tree species composition using OHS-1 hyperspectral data and deep learning algorithms in Changbai Mountains, Northeast China. Forests, 10, 818.
DOI URL |
| [59] | Yang C, Wu GF, Li QQ, Wang JL, Qu LQ, Ding K (2018) Research progress on remote sensing classification of vegetation. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 34(4), 24-32. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨超, 邬国锋, 李清泉, 王金亮, 渠立权, 丁凯 (2018) 植被遥感分类方法研究进展. 地理与地理信息科学, 34(4), 24-32. | |
| [60] | Zhang CY, Qiu F (2012) Mapping individual tree species in an urban forest using airborne lidar data and hyperspectral imagery. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing, 78, 1079-1087. |
| [61] |
Zhang J, Chen SB, Chen B, Du YJ, Huang XL, Pan XB, Zhang Q (2013) Citizen science: Integrating scientific research, ecological conservation and public participation. Biodiversity Science, 21, 738-749. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [ 张健, 陈圣宾, 陈彬, 杜彦君, 黄晓磊, 潘绪斌, 张强 (2013) 公众科学: 整合科学研究、生态保护和公众参与. 生物多样性, 21, 738-749.] | |
| [62] | Zhang YJ, Fan CK, Huang K, Liu YJ, Zu JX, Zhu JT (2017) Opportunities and challenges in remote sensing applications to ecosystem ecology. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 36, 809-823. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张扬建, 范春捆, 黄珂, 刘瑶杰, 俎佳星, 朱军涛 (2017) 遥感在生态系统生态学上应用的机遇与挑战. 生态学杂志, 36, 809-823.] | |
| [63] | Zhang ZM, Xu Q, Wang B, Sun H, Geng YP, Tian J (2017) Applications of unmanned aerial vehicles remote sensing technology in landscape ecology. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 4029-4036. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张志明, 徐倩, 王彬, 孙虎, 耿宇鹏, 田冀 (2017) 无人机遥感技术在景观生态学中的应用. 生态学报, 37, 4029-4036.] | |
| [64] | Zhao SD, Zhang YM (2006) Ecosystems and human well-being: The achievements, contributions and prospects of the millennium ecosystem assessment. Advances in Earth Science, 21, 895-902. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 赵士洞, 张永民 (2006) 生态系统与人类福祉——千年生态系统评估的成就、贡献和展望. 地球科学进展, 21, 895-902.] |
| [1] | Qiaoyi Nong, Jun Cao, Wenda Cheng, Yanqiong Peng. Comparative study of monitoring methods for Apoidea resources and diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [2] | Jingyi Yuan, Xu Zhang, Zhenpeng Tian, Zizhe Wang, Yongping Gao, Dizhao Yao, Hongcan Guan, Wenkai Li, Jing Liu, Hong Zhang, Qin Ma. A comparison of methods for extracting tree species composition and quantitative characteristics in urban plant communities using UAV high-resolution RGB imagery and LiDAR point cloud [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24237-. |
| [3] | Yongcai Wang, Huawei Wan, Jixi Gao, Zhuowei Hu, Chenxi Sun, Na Lü, Zhiru Zhang. Identification of common native grassland plants in northern China using deep learning [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(4): 23435-. |
| [4] | Wantao Huang, Zezhou Hao, Zixin Zhang, Zhishu Xiao, Chengyun Zhang. A comparison of bird sound recognition performance among acoustic recorders [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(10): 24273-. |
| [5] | Jiangjian Xie, Chen Shen, Feiyu Zhang, Zhishu Xiao. Cross-regional bird species recognition method integrating audio and ecological niche information [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(10): 24259-. |
| [6] | Jianmin Cai, Peiyu He, Zhipeng Yang, Luying Li, Qijun Zhao, Fan Pan. A deep feature fusion-based method for bird sound recognition and its interpretability analysis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(7): 23087-. |
| [7] | Zhenzhen Li, Mengtian Du, Yuanxin Zhu, Dawei Wang, Zhilin Li, Tianming Wang. A practical guide for estimating the density of unmarked populations using camera traps [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(3): 22422-. |
| [8] | Yufei Huang, Chunyan Lu, Mingming Jia, Zili Wang, Yue Su, Yanlin Su. Plant species classification of coastal wetlands based on UAV images and object- oriented deep learning [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(3): 22411-. |
| [9] | Xiaohu Shen, Xiangyu Zhu, Hongfei Shi, Chuanzhi Wang. Research progress of birdsong recognition algorithms based on machine learning [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(11): 23272-. |
| [10] | Yifei Sun, Shizheng Wang, Jiawei Feng, Tianming Wang. Diel and seasonal variability of the forest soundscape in the Northeast China Tiger and Leopard National Park [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(1): 22523-. |
| [11] | Jian Zhang, Hongzhi Kong, Xiaolei Huang, Shenglei Fu, Liangdong Guo, Qinghua Guo, Fumin Lei, Zhi Lü, Yurong Zhou, Keping Ma. Thirty key questions for biodiversity science in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(10): 22609-. |
| [12] | Xing Chen, Tianpei Guan, Wenle Jiang, Dandan Li, Kong Yang, Sheng Li. Distribution and population status of bovine species in China based on bibliometric analysis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(5): 668-679. |
| [13] | Sheng Li, William J. McShea, Dajun Wang, Xiaoli Shen, Hongliang Bu, Tianpei Guan, Fang Wang, Xiaodong Gu, Xiaofeng Zhang, Haohong Liao. Construction progress of the Camera-trapping Network for the Mountains of Southwest China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(9): 1049-1058. |
| [14] | Tianming Wang, Limin Feng, Haitao Yang, Lei Bao, Hongfang Wang, Jianping Ge. An introduction to Long-term Tiger-Leopard Observation Network based on camera traps in Northeast China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(9): 1059-1066. |
| [15] | Xueyou Li, Wenqiang Hu, Changzhe Pu, Quan Li, Qiupeng Yu, Zhechang Hu, William V. Bleisch, Xuelong Jiang. Camera-trapping monitoring platform for mammals and pheasants in the Longitudinal Range and Gorge Region of Southwest China: Protocol, progress and future outlook [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(9): 1090-1096. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()