



Biodiv Sci ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (1): 22523. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022523 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022523
• Original Papers: Animal Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yifei Sun1,2,3, Shizheng Wang1,2,3, Jiawei Feng1,2,3, Tianming Wang1,2,3,*( )
)
Received:2022-09-13
Accepted:2023-01-08
Online:2023-01-20
Published:2023-01-30
Contact:
*Tianming Wang, E-mail: wangtianming@bnu.edu.cn
Yifei Sun, Shizheng Wang, Jiawei Feng, Tianming Wang. Diel and seasonal variability of the forest soundscape in the Northeast China Tiger and Leopard National Park[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(1): 22523.
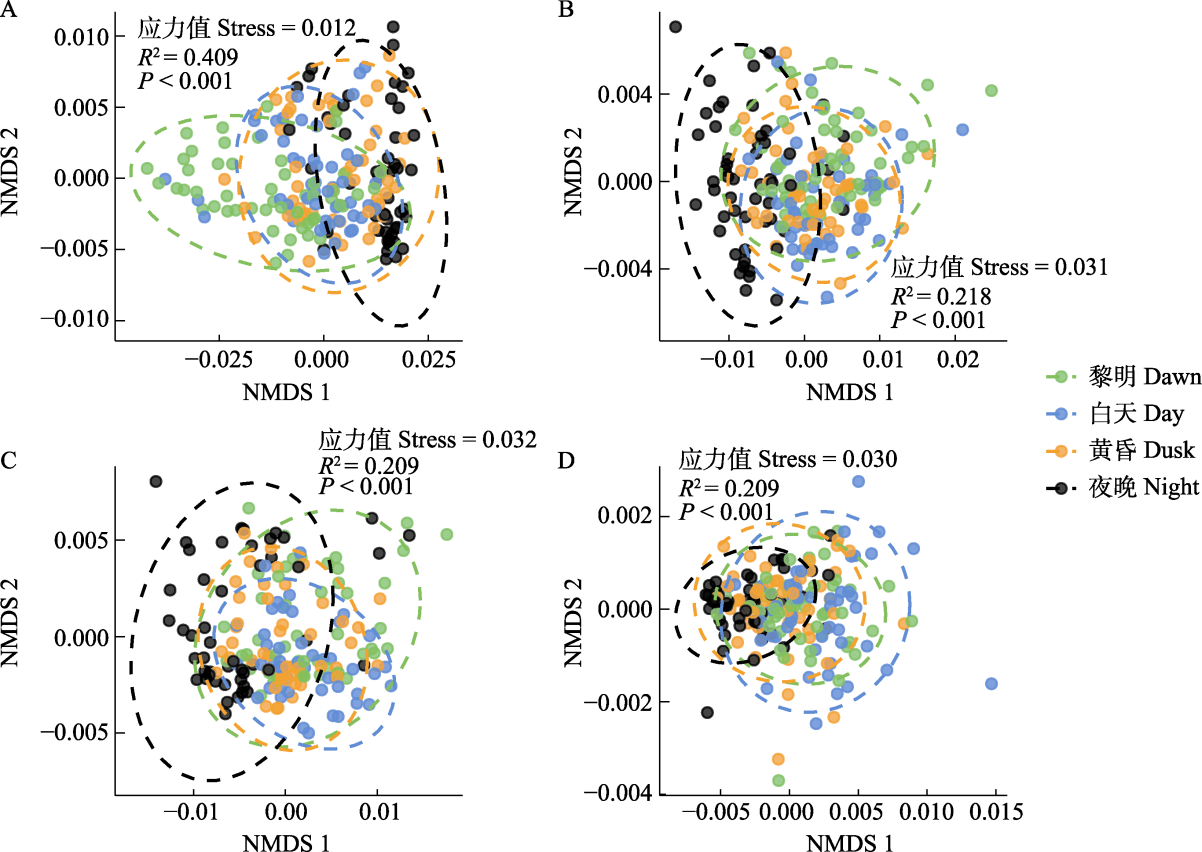
Fig. 3 Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) ordination plots showing the diel divisions between soundscapes in spring (A), summer (B), autumn (C) and winter (D). Group centroids are shown with 95% confidence interval ellipses.
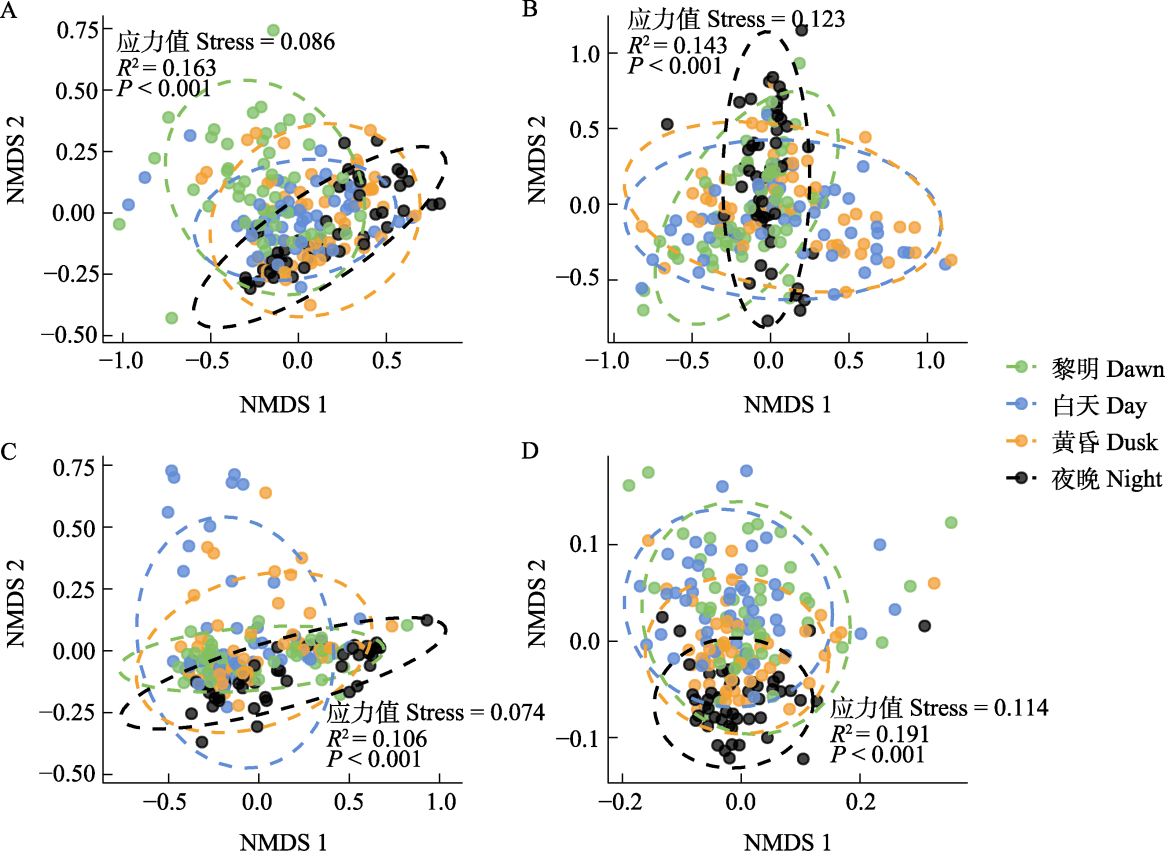
Fig. 4 Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) ordination plots showing the diel divisions between acoustic components using power spectral density (PSD) in spring (A), summer (B), autumn (C) and winter (D). Group centroids are shown with 95% confidence interval ellipses.
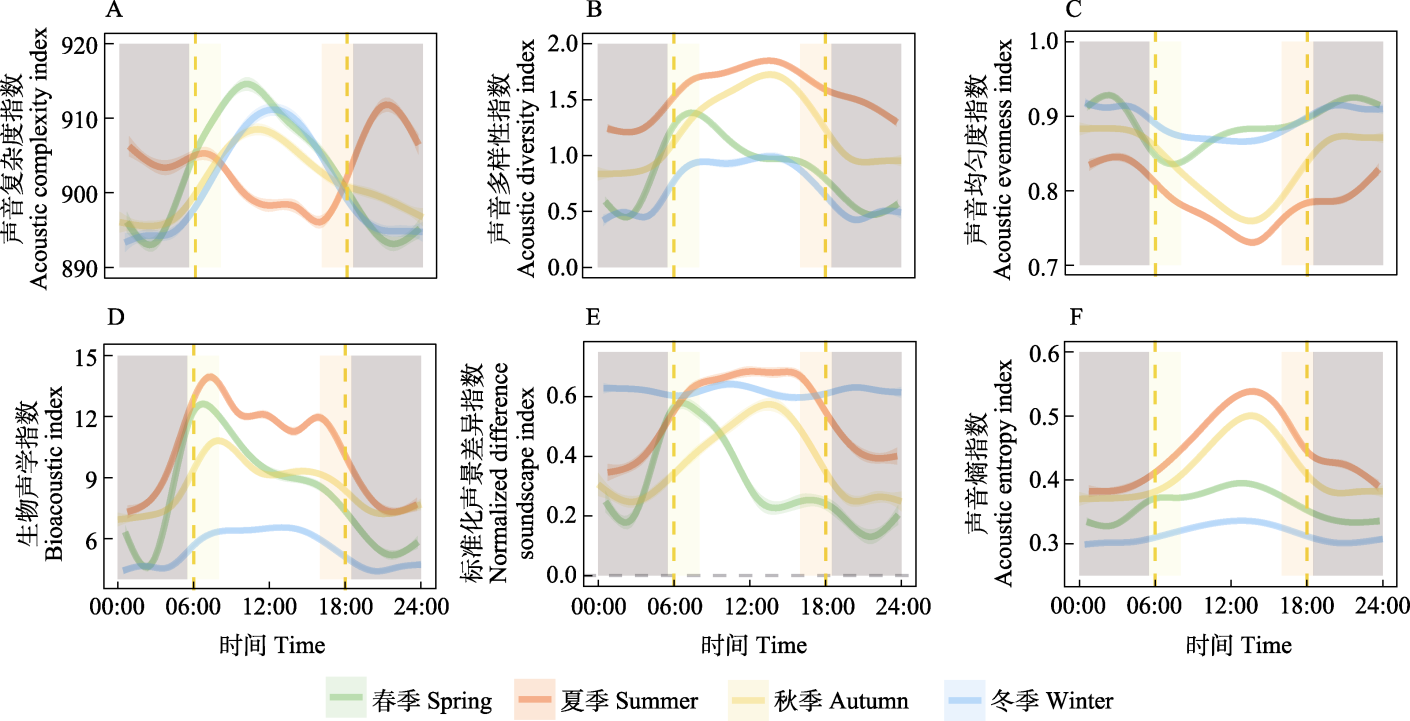
Fig. 5 Fitted curves from generalized additive models (GAMs) showing clear diel patterns of each acoustic index in different seasons. Time of day was converted from clock time to sun time. Dashed lines in orange show sunrise and sunset. Yellow, orange, grey shades and blank represent dawn, dusk, night and day, respectively.
| 季节 Season | 声学指数 Acoustic index | 黎明 Dawn | 白天 Day | 黄昏 Dusk | 夜晚 Night | χ2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春季 Spring | 声音复杂度指数 ACI | 908.99 ± 1.36ab | 912.70 ± 1.02a | 903.49 ± 0.89b | 895.68 ± 1.02c | 97.453 | < 0.001*** |
| 声音多样性指数 ADI | 1.38 ± 0.05a | 1.09 ± 0.04b | 0.93 ± 0.05b | 0.58 ± 0.05c | 80.140 | < 0.001*** | |
| 声音均匀度指数 AEI | 0.84 ± 0.01a | 0.87 ± 0.01b | 0.88 ± 0.01b | 0.91 ± 0.01c | 78.321 | < 0.001*** | |
| 生物声学指数 BIO | 12.79 ± 0.63a | 9.79 ± 0.45ab | 8.38 ± 0.40b | 5.89 ± 0.31c | 78.187 | < 0.001*** | |
| 标准化声景差异指数 NDSI | 0.57 ± 0.03a | 0.39 ± 0.04b | 0.30 ± 0.04b | 0.22 ± 0.05b | 35.158 | < 0.001*** | |
| 声音熵指数 H | 0.37 ± 0.01a | 0.38 ± 0.01a | 0.36 ± 0.01ab | 0.34 ± 0.01b | 15.694 | < 0.001*** | |
| 夏季 Summer | 声音复杂度指数 ACI | 905.12 ± 1.25a | 898.86 ± 0.85b | 897.38 ± 0.61b | 908.09 ± 2.04a | 43.277 | < 0.001*** |
| 声音多样性指数 ADI | 1.61 ± 0.04ab | 1.78 ± 0.05a | 1.64 ± 0.05a | 1.40 ± 0.06b | 27.909 | < 0.001*** | |
| 声音均匀度指数 AEI | 0.80 ± 0.01a | 0.75 ± 0.01b | 0.78 ± 0.01ab | 0.81 ± 0.01a | 25.499 | < 0.001*** | |
| 生物声学指数 BIO | 13.27 ± 0.46a | 12.03 ± 0.36a | 11.64 ± 0.34a | 8.81 ± 0.28b | 79.432 | < 0.001*** | |
| 标准化声景差异指数 NDSI | 0.58 ± 0.04a | 0.67 ± 0.03a | 0.63 ± 0.03a | 0.42 ± 0.05b | 20.688 | < 0.001*** | |
| 声音熵指数 H | 0.42 ± 0.01ab | 0.51 ± 0.01c | 0.47 ± 0.01ac | 0.41 ± 0.01b | 32.107 | < 0.001*** | |
| 秋季 Autumn | 声音复杂度指数 ACI | 902.78 ± 1.06a | 906.87 ± 1.02b | 901.52 ± 0.94a | 897.82 ± 0.86c | 47.306 | < 0.001*** |
| 声音多样性指数 ADI | 1.32 ± 0.05a | 1.58 ± 0.05b | 1.37 ± 0.05ab | 0.95 ± 0.05c | 53.534 | < 0.001*** | |
| 声音均匀度指数 AEI | 0.84 ± 0.01a | 0.79 ± 0.01b | 0.82 ± 0.01ab | 0.87 ± 0.01c | 50.750 | < 0.001*** | |
| 生物声学指数 BIO | 10.65 ± 0.38a | 9.45 ± 0.24ab | 8.81 ± 0.24b | 7.43 ± 0.40c | 44.403 | < 0.001*** | |
| 标准化声景差异指数 NDSI | 0.40 ± 0.04ab | 0.52 ± 0.03a | 0.40 ± 0.04ab | 0.25 ± 0.05b | 14.445 | 0.002** | |
| 声音熵指数 H | 0.40 ± 0.01a | 0.46 ± 0.01b | 0.42 ± 0.01ab | 0.38 ± 0.01a | 21.746 | < 0.001*** | |
| 冬季 Winter | 声音复杂度指数 ACI | 900.38 ± 0.78a | 909.17 ± 1.72b | 901.30 ± 1.12a | 894.93 ± 0.81c | 67.327 | < 0.001*** |
| 声音多样性指数 ADI | 0.87 ± 0.04ab | 0.98 ± 0.05a | 0.74 ± 0.04b | 0.47 ± 0.04c | 57.509 | < 0.001*** | |
| 声音均匀度指数 AEI | 0.88 ± 0.01a | 0.86 ± 0.01a | 0.89 ± 0.01a | 0.91 ± 0.01b | 38.324 | < 0.001*** | |
| 生物声学指数 BIO | 6.05 ± 0.16ab | 6.54 ± 0.19a | 5.49 ± 0.16b | 4.61 ± 0.11c | 64.825 | < 0.001*** | |
| 标准化声景差异指数 NDSI | 0.60 ± 0.02a | 0.63 ± 0.02a | 0.60 ± 0.02a | 0.63 ± 0.02a | 3.510 | 0.320 | |
| 声音熵指数 H | 0.31 ± 0.01ab | 0.34 ± 0.01a | 0.32 ± 0.01ab | 0.30 ± 0.01b | 8.840 | 0.031* |
Table 1 Results of Kruskal-Wallis tests examining significance of acoustic index differences among diel phases in different seasons
| 季节 Season | 声学指数 Acoustic index | 黎明 Dawn | 白天 Day | 黄昏 Dusk | 夜晚 Night | χ2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春季 Spring | 声音复杂度指数 ACI | 908.99 ± 1.36ab | 912.70 ± 1.02a | 903.49 ± 0.89b | 895.68 ± 1.02c | 97.453 | < 0.001*** |
| 声音多样性指数 ADI | 1.38 ± 0.05a | 1.09 ± 0.04b | 0.93 ± 0.05b | 0.58 ± 0.05c | 80.140 | < 0.001*** | |
| 声音均匀度指数 AEI | 0.84 ± 0.01a | 0.87 ± 0.01b | 0.88 ± 0.01b | 0.91 ± 0.01c | 78.321 | < 0.001*** | |
| 生物声学指数 BIO | 12.79 ± 0.63a | 9.79 ± 0.45ab | 8.38 ± 0.40b | 5.89 ± 0.31c | 78.187 | < 0.001*** | |
| 标准化声景差异指数 NDSI | 0.57 ± 0.03a | 0.39 ± 0.04b | 0.30 ± 0.04b | 0.22 ± 0.05b | 35.158 | < 0.001*** | |
| 声音熵指数 H | 0.37 ± 0.01a | 0.38 ± 0.01a | 0.36 ± 0.01ab | 0.34 ± 0.01b | 15.694 | < 0.001*** | |
| 夏季 Summer | 声音复杂度指数 ACI | 905.12 ± 1.25a | 898.86 ± 0.85b | 897.38 ± 0.61b | 908.09 ± 2.04a | 43.277 | < 0.001*** |
| 声音多样性指数 ADI | 1.61 ± 0.04ab | 1.78 ± 0.05a | 1.64 ± 0.05a | 1.40 ± 0.06b | 27.909 | < 0.001*** | |
| 声音均匀度指数 AEI | 0.80 ± 0.01a | 0.75 ± 0.01b | 0.78 ± 0.01ab | 0.81 ± 0.01a | 25.499 | < 0.001*** | |
| 生物声学指数 BIO | 13.27 ± 0.46a | 12.03 ± 0.36a | 11.64 ± 0.34a | 8.81 ± 0.28b | 79.432 | < 0.001*** | |
| 标准化声景差异指数 NDSI | 0.58 ± 0.04a | 0.67 ± 0.03a | 0.63 ± 0.03a | 0.42 ± 0.05b | 20.688 | < 0.001*** | |
| 声音熵指数 H | 0.42 ± 0.01ab | 0.51 ± 0.01c | 0.47 ± 0.01ac | 0.41 ± 0.01b | 32.107 | < 0.001*** | |
| 秋季 Autumn | 声音复杂度指数 ACI | 902.78 ± 1.06a | 906.87 ± 1.02b | 901.52 ± 0.94a | 897.82 ± 0.86c | 47.306 | < 0.001*** |
| 声音多样性指数 ADI | 1.32 ± 0.05a | 1.58 ± 0.05b | 1.37 ± 0.05ab | 0.95 ± 0.05c | 53.534 | < 0.001*** | |
| 声音均匀度指数 AEI | 0.84 ± 0.01a | 0.79 ± 0.01b | 0.82 ± 0.01ab | 0.87 ± 0.01c | 50.750 | < 0.001*** | |
| 生物声学指数 BIO | 10.65 ± 0.38a | 9.45 ± 0.24ab | 8.81 ± 0.24b | 7.43 ± 0.40c | 44.403 | < 0.001*** | |
| 标准化声景差异指数 NDSI | 0.40 ± 0.04ab | 0.52 ± 0.03a | 0.40 ± 0.04ab | 0.25 ± 0.05b | 14.445 | 0.002** | |
| 声音熵指数 H | 0.40 ± 0.01a | 0.46 ± 0.01b | 0.42 ± 0.01ab | 0.38 ± 0.01a | 21.746 | < 0.001*** | |
| 冬季 Winter | 声音复杂度指数 ACI | 900.38 ± 0.78a | 909.17 ± 1.72b | 901.30 ± 1.12a | 894.93 ± 0.81c | 67.327 | < 0.001*** |
| 声音多样性指数 ADI | 0.87 ± 0.04ab | 0.98 ± 0.05a | 0.74 ± 0.04b | 0.47 ± 0.04c | 57.509 | < 0.001*** | |
| 声音均匀度指数 AEI | 0.88 ± 0.01a | 0.86 ± 0.01a | 0.89 ± 0.01a | 0.91 ± 0.01b | 38.324 | < 0.001*** | |
| 生物声学指数 BIO | 6.05 ± 0.16ab | 6.54 ± 0.19a | 5.49 ± 0.16b | 4.61 ± 0.11c | 64.825 | < 0.001*** | |
| 标准化声景差异指数 NDSI | 0.60 ± 0.02a | 0.63 ± 0.02a | 0.60 ± 0.02a | 0.63 ± 0.02a | 3.510 | 0.320 | |
| 声音熵指数 H | 0.31 ± 0.01ab | 0.34 ± 0.01a | 0.32 ± 0.01ab | 0.30 ± 0.01b | 8.840 | 0.031* |
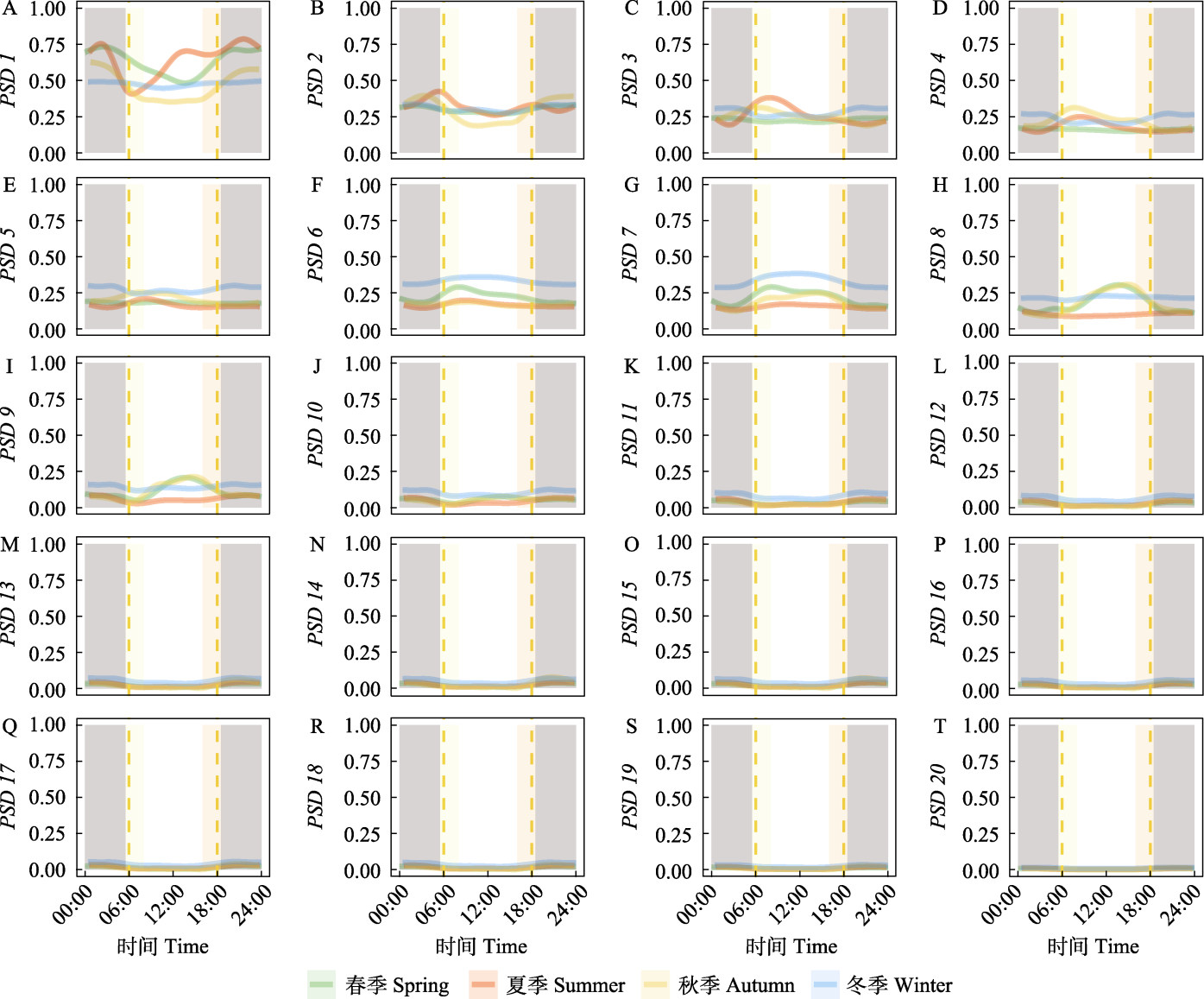
Fig. 6 Fitted curves from generalized additive models (GAMs) showing clear diel patterns of each power spectral density (PSD) in different seasons. Time of day was converted from clock time to sun time. Dashed lines in orange shows sunrise and sunset. Yellow, orange, grey shades and blank represent dawn, dusk, night and day, respectively.
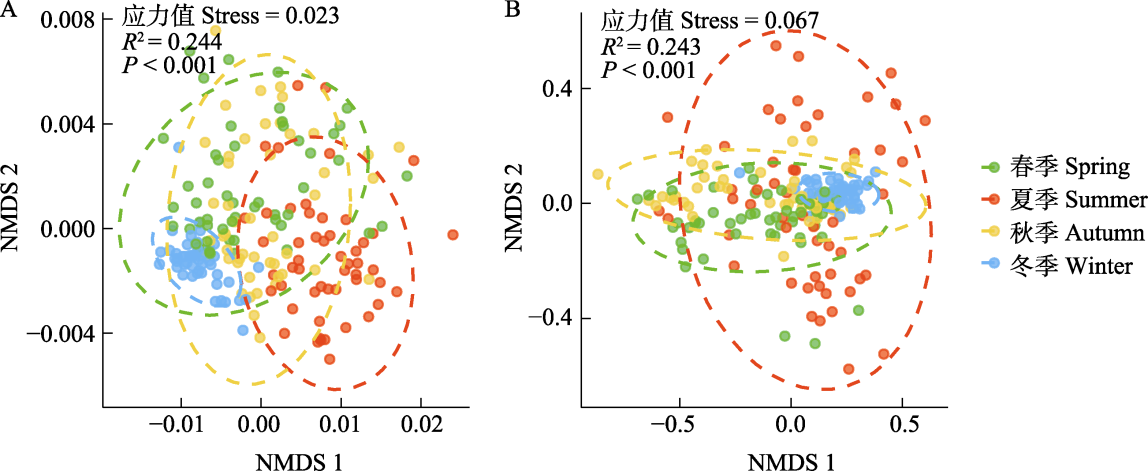
Fig. 7 Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) ordination plots showing the seasonal divisions between soundscapes (A) and acoustic components using power spectral density (PSD) (B). Group centroids are shown with 95% confidence interval ellipses.
| 声学指数 Acoustic index | 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer | 秋季 Autumn | 冬季 Winter | χ2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 声音复杂度指数 ACI | 903.41 ± 0.82a | 902.39 ± 0.85a | 900.74 ± 0.77ab | 898.72 ± 0.94b | 27.325 | < 0.001*** |
| 声音多样性指数 ADI | 0.88 ± 0.04a | 1.61 ± 0.04b | 1.18 ± 0.05c | 0.63 ± 0.04d | 115.990 | < 0.001*** |
| 声音均匀度指数 AEI | 0.89 ± 0.01a | 0.78 ± 0.01b | 0.84 ± 0.01c | 0.90 ± 0.01a | 109.720 | < 0.001*** |
| 生物声学指数 BIO | 8.32 ± 0.40a | 10.77 ± 0.29b | 8.40 ± 0.31a | 5.19 ± 0.11c | 113.100 | < 0.001*** |
| 标准化声景差异指数 NDSI | 0.33 ± 0.04a | 0.57 ± 0.03b | 0.36 ± 0.04a | 0.62 ± 0.01b | 56.311 | < 0.001*** |
| 声音熵指数 H | 0.36 ± 0.01a | 0.46 ± 0.01b | 0.41 ± 0.01b | 0.31 ± 0.01c | 80.463 | < 0.001*** |
Table 2 Results of Kruskal-Wallis tests examining significance of acoustic index differences among seasons
| 声学指数 Acoustic index | 春季 Spring | 夏季 Summer | 秋季 Autumn | 冬季 Winter | χ2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 声音复杂度指数 ACI | 903.41 ± 0.82a | 902.39 ± 0.85a | 900.74 ± 0.77ab | 898.72 ± 0.94b | 27.325 | < 0.001*** |
| 声音多样性指数 ADI | 0.88 ± 0.04a | 1.61 ± 0.04b | 1.18 ± 0.05c | 0.63 ± 0.04d | 115.990 | < 0.001*** |
| 声音均匀度指数 AEI | 0.89 ± 0.01a | 0.78 ± 0.01b | 0.84 ± 0.01c | 0.90 ± 0.01a | 109.720 | < 0.001*** |
| 生物声学指数 BIO | 8.32 ± 0.40a | 10.77 ± 0.29b | 8.40 ± 0.31a | 5.19 ± 0.11c | 113.100 | < 0.001*** |
| 标准化声景差异指数 NDSI | 0.33 ± 0.04a | 0.57 ± 0.03b | 0.36 ± 0.04a | 0.62 ± 0.01b | 56.311 | < 0.001*** |
| 声音熵指数 H | 0.36 ± 0.01a | 0.46 ± 0.01b | 0.41 ± 0.01b | 0.31 ± 0.01c | 80.463 | < 0.001*** |
| [1] |
Alcocer I, Lima H, Sugai LSM, Llusia D (2022) Acoustic indices as proxies for biodiversity: A meta-analysis. Biological Reviews of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 97, 2209-2236.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
Barbaro L, Sourdril A, Froidevaux JSP, Cauchoix M, Calatayud F, Deconchat M, Gasc A (2022) Linking acoustic diversity to compositional and configurational heterogeneity in mosaic landscapes. Landscape Ecology, 37, 1125-1143.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Bertucci F, Parmentier E, Lecellier G, Hawkins AD, Lecchini D (2016) Acoustic indices provide information on the status of coral reefs: An example from Moorea Island in the South Pacific. Scientific Reports, 6, 33326.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
Boelman NT, Asner GP, Hart PJ, Martin RE (2007) Multi-trophic invasion resistance in Hawaii: Bioacoustics, field surveys, and airborne remote sensing. Ecological Applications, 17, 2137-2144.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Bradfer-Lawrence T, Gardner N, Bunnefeld L, Bunnefeld N, Willis SG, Dent DH (2019) Guidelines for the use of acoustic indices in environmental research. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 10, 1796-1807.
DOI |
| [6] | Burivalova Z, Purnomo, Orndorff S, Truskinger A, Roe P, Game ET (2021) The sound of logging: Tropical forest soundscape before, during, and after selective timber extraction. Biological Conservation, 254, 108812. |
| [7] | Butler J, Pagniello CMLS, Jaffe JS, Parnell PE, Širović A (2021) Diel and seasonal variability in kelp forest soundscapes off the southern California coast. Frontiers in Marine Science, 8, 629643. |
| [8] | Buxton RT, Agnihotri S, Robin VV, Goel A, Balakrishnan R (2018) Acoustic indices as rapid indicators of avian diversity in different land-use types in an Indian biodiversity hotspot. Journal of Ecoacoustics, 2, 1-17. |
| [9] | Buxton RT, Pearson AL, Allou C, Fristrup K, Wittemyer G (2021) A synthesis of health benefits of natural sounds and their distribution in national parks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 118, e2013097118. |
| [10] | Chen YF, Luo YH, Mammides C, Cao KF, Zhu SD, Goodale E (2021) The relationship between acoustic indices, elevation, and vegetation, in a forest plot network of Southern China. Ecological Indicators, 129, 107942. |
| [11] |
Depraetere M, Pavoine S, Jiguet F, Gasc A, Duvail S, Sueur J (2012) Monitoring animal diversity using acoustic indices: Implementation in a temperate woodland. Ecological Indicators, 13, 46-54.
DOI URL |
| [12] | Derryberry EP, Phillips JN, Derryberry GE, Blum MJ, Luther D (2020) Singing in a silent spring: Birds respond to a half-century soundscape reversion during the COVID-19 shutdown. Science, 370, 575-579. |
| [13] |
Devi RR, Pugazhenthi D (2016) Ideal sampling rate to reduce distortion in audio steganography. Procedia Computer Science, 85, 418-424.
DOI URL |
| [14] | Diepstraten J, Willie J (2021) Assessing the structure and drivers of biological sounds along a disturbance gradient. Global Ecology and Conservation, 31, e01819. |
| [15] |
Dinerstein E, Loucks C, Wikramanayake E, Ginsberg J, Sanderson E, Seidensticker J, Forrest J, Bryja G, Heydlauff A, Klenzendorf S, Leimgruber P, Mills J, O’Brien TG, Shrestha M, Simons R, Songer M (2007) The fate of wild tigers. BioScience, 57, 508-514.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Dirzo R, Young HS, Galetti M, Ceballos G, Isaac NJB, Collen B (2014) Defaunation in the anthropocene. Science, 345, 401-406.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
Dooley JM, Brown MT (2020) The quantitative relation between ambient soundscapes and landscape development intensity in North Central Florida. Landscape Ecology, 35, 113-127.
DOI |
| [18] | Doser JW, Finley AO, Kasten EP, Gage SH (2020) Assessing soundscape disturbance through hierarchical models and acoustic indices: A case study on a shelterwood logged northern Michigan forest. Ecological Indicators, 113, 106244. |
| [19] |
Eldridge A, Guyot P, Moscoso P, Johnston A, Eyre-Walker Y, Peck M (2018) Sounding out ecoacoustic metrics: Avian species richness is predicted by acoustic indices in temperate but not tropical habitats. Ecological Indicators, 95, 939-952.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Elise S, Urbina-Barreto I, Pinel R, Mahamadaly V, Bureau S, Penin L, Adjeroud M, Kulbicki M, Bruggemann JH (2019) Assessing key ecosystem functions through soundscapes: A new perspective from coral reefs. Ecological Indicators, 107, 105623. |
| [21] | Farina A (2013) Soundscape Ecology: Principles, Patterns, Methods and Applications. Springer, Cham. |
| [22] |
Feng RN, Lü XY, Xiao WH, Feng JW, Sun YF, Guan Y, Feng LM, Smith JLD, Ge JP, Wang TM (2021) Effects of free-ranging livestock on sympatric herbivores at fine spatiotemporal scales. Landscape Ecology, 36, 1441-1457.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Fuller S, Axel AC, Tucker D, Gage SH (2015) Connecting soundscape to landscape: Which acoustic index best describes landscape configuration? Ecological Indicators, 58, 207-215.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Gage SH, Axel AC (2014) Visualization of temporal change in soundscape power of a Michigan lake habitat over a 4-year period. Ecological Informatics, 21, 100-109.
DOI URL |
| [25] | Gage SH, Towsey M, Kasten EP (2017) Analytical methods in ecoacoustics. In: Ecoacoustics: The Ecological Role of Sounds (eds Farina A, Gage SH), pp. 273-296. John Wiley & Sons, Oxford. |
| [26] |
Gasc A, Francomano D, Dunning JB, Pijanowski BC (2017) Future directions for soundscape ecology: The importance of ornithological contributions. The Auk, 134, 215-228.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Gasc A, Sueur J, Jiguet F, Devictor V, Grandcolas P, Burrow C, Depraetere M, Pavoine S (2013) Assessing biodiversity with sound: Do acoustic diversity indices reflect phylogenetic and functional diversities of bird communities? Ecological Indicators, 25, 279-287.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Gibb R, Browning E, Glover-Kapfer P, Jones KE (2019) Emerging opportunities and challenges for passive acoustics in ecological assessment and monitoring. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 10, 169-185.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Gómez WE, Isaza CV, Daza JM (2018) Identifying disturbed habitats: A new method from acoustic indices. Ecological Informatics, 45, 16-25.
DOI URL |
| [30] | Hao ZZ, Wang C, Sun ZK, Zhao DX, Sun BQ, Wang HJ, van den Bosch CK (2021) Vegetation structure and temporality influence the dominance, diversity, and composition of forest acoustic communities. Forest Ecology and Management, 482, 118871. |
| [31] |
Haver SM, Rand Z, Hatch LT, Lipski D, Dziak RP, Gedamke J, Haxel J, Heppell SA, Jahncke J, McKenna MF, Mellinger DK, Oestreich WK, Roche L, Ryan J, Van Parijs SM (2020) Seasonal trends and primary contributors to the low-frequency soundscape of the Cordell Bank National Marine Sanctuary. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 148, 845-858.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Jantz SM, Barker B, Brooks TM, Chini LP, Huang QY, Moore RM, Noel J, Hurtt GC (2015) Future habitat loss and extinctions driven by land-use change in biodiversity hotspots under four scenarios of climate-change mitigation. Conservation Biology, 29, 1122-1131.
DOI PMID |
| [33] | Kasten EP, Gage SH, Fox J, Joo W (2012) The remote environmental assessment laboratory’s acoustic library: An archive for studying soundscape ecology. Ecological Informatics, 12, 50-67. |
| [34] | Lawson J, Whitworth A, Banks-Leite C (2022) Soundscapes show disruption across the diel cycle in human modified tropical landscapes. Ecological Indicators, 144, 109413. |
| [35] |
Li JW, Shi J, Xue Y, Mao HB, Luo YQ (2014) Major physiological adjustments in freezing-tolerant grey tiger longicorn beetle (Xylotrechus rusticus) during overwintering period. Journal of Forestry Research, 25, 653-659.
DOI URL |
| [36] | Li ZW, Wu JG, Kou XJ, Tian Y, Wang TM, Mu P, Ge JP (2009) Land use pattern and its dynamic changes in Amur tiger distribution region. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 20, 713-724. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李钟汶, 邬建国, 寇晓军, 田瑜, 王天明, 牟溥, 葛剑平 (2009) 东北虎分布区土地利用格局与动态. 应用生态学报, 20, 713-724.] | |
| [37] |
Maysenhölder W, Heggli M, Zhou X, Zhang T, Frei E, Schneebeli M (2012) Microstructure and sound absorption of snow. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 83/84, 3-12.
DOI URL |
| [38] | Metcalf OC, Lees AC, Barlow J, Marsden SJ, Devenish C (2020) hardRain: An R package for quick, automated rainfall detection in ecoacoustic datasets using a threshold-based approach. Ecological Indicators, 109, 105793. |
| [39] |
Metcalf OC, Barlow J, Devenish C, Marsden S, Berenguer E, Lees AC (2021) Acoustic indices perform better when applied at ecologically meaningful time and frequency scales. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 12, 421-431.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Morrison CA, Auniņš A, Benkő Z, Brotons L, Chodkiewicz T, Chylarecki P, Escandell V, Eskildsen DP, Gamero A, Herrando S, Jiguet F, Kålås JA, Kamp J, Klvaňová A, Kmecl P, Lehikoinen A, Lindström, Moshøj C, Noble DG, Øien IJ, Paquet JY, Reif J, Sattler T, Seaman BS, Teufelbauer N, Trautmann S, Vořišek P, Butler SJ (2021) Bird population declines and species turnover are changing the acoustic properties of spring soundscapes. Nature Communications, 12, 6217.
DOI PMID |
| [41] |
Mullet TC, Gage SH, Morton JM, Huettmann F (2016) Temporal and spatial variation of a winter soundscape in south-central Alaska. Landscape Ecology, 31, 1117-1137.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Newbold T, Hudson LN, Hill SLL, Contu S, Lysenko I, Senior RA, Börger L, Bennett DJ, Choimes A, Collen B, Day J, De Palma A, Díaz S, Echeverria-Londoño S, Edgar MJ, Feldman A, Garon M, Harrison MLK, Alhusseini T, Ingram DJ, Itescu Y, Kattge J, Kemp V, Kirkpatrick L, Kleyer M, Laginha Pinto Correia D, Martin CD, Shai MR, Novosolov M, Yuan P, Phillips HRP, Purves DW, Robinson A, Simpson J, Tuck SL, Weiher E, White HJ, Ewers RM, Mace GM, Scharlemann JPW, Purvis A (2015) Global effects of land use on local terrestrial biodiversity. Nature, 520, 45-50.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Nouvellet P, Rasmussen GSA, MacDonald DW, Courchamp F (2012) Noisy clocks and silent sunrises: Measurement methods of daily activity pattern. Journal of Zoology, 286, 179-184.
DOI URL |
| [44] | Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Friendly M, Kindt R, Legendre P, McGlinn D, Minchin PR, O’Hara RB, Simpson GL, Solymos P, Stevens MHH, Szoecs E, Wagner H (2020) vegan: Community Ecology Package. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan. (accessed on 2020-12-22) |
| [45] |
Pieretti N, Farina A, Morri D (2011) A new methodology to infer the singing activity of an avian community: The acoustic complexity index (ACI). Ecological Indicators, 11, 868-873.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Pijanowski BC, Farina A, Gage SH, Dumyahn SL, Krause BL (2011a) What is soundscape ecology? An introduction and overview of an emerging new science. Landscape Ecology, 26, 1213-1232.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Pijanowski BC, Villanueva-Rivera LJ, Dumyahn SL, Farina A, Krause BL, Napoletano BM, Gage SH, Pieretti N (2011b) Soundscape Ecology: The science of sound in the landscape. BioScience, 61, 203-216.
DOI URL |
| [48] | Pohlert T (2021) PMCMRplus: Calculate Pairwise Multiple Comparisons of Mean Rank Sums Extended. R package version 1.9.6. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=PMCMRplus. (accessed on 2021-03-16) |
| [49] |
Reed J, Deakin L, Sunderland T (2015) What are ‘Integrated Landscape Approaches’ and how effectively have they been implemented in the tropics: A systematic map protocol. Environmental Evidence, 4, 1-7.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
Ridout MS, Linkie M (2009) Estimating overlap of daily activity patterns from camera trap data. Journal of Agricultural, Biological, and Environmental Statistics, 14, 322-337.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
Rocha PC, Romano PSR (2021) The shape of sound: A new R package that crosses the bridge between Bioacoustics and Geometric Morphometrics. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 12, 1115-1121.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
Roe P, Eichinski P, Fuller RA, McDonald PG, Schwarzkopf L, Towsey M, Truskinger A, Tucker D, Watson DM (2021) The Australian acoustic observatory. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 12, 1802-1808.
DOI URL |
| [53] | Ross SRPJ, Friedman NR, Dudley KL, Yoshimura M, Yoshida T, Economo EP (2018) Listening to ecosystems: Data-rich acoustic monitoring through landscape-scale sensor networks. Ecological Research, 33, 135-147. |
| [54] | Sousa-Lima RS, Ferreira LM, Oliveira EG, Lopes LC, Brito MR, Baumgarten J, Rodrigues FH (2018) What do insects, anurans, birds, and mammals have to say about soundscape indices in a tropical savanna. Journal of Ecoacoustics, 2, PVH6YZ. |
| [55] |
Stowell D, Sueur J (2020) Ecoacoustics: Acoustic sensing for biodiversity monitoring at scale. Remote Sensing in Ecology and Conservation, 6, 217-219.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
Sueur J, Krause B, Farina A (2019) Climate change is breaking earth’s beat. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 34, 971-973.
DOI URL |
| [57] | Sueur J, Pavoine S, Hamerlynck O, Duvail S (2008) Rapid acoustic survey for biodiversity appraisal. PLoS ONE, 3, e4065. |
| [58] |
Sugai LSM, Silva TSF, Ribeiro JW, Llusia D (2019) Terrestrial passive acoustic monitoring: Review and perspectives. BioScience, 69, 15-25.
DOI |
| [59] |
Sun YJ, Yen SC, Lin TH (2022) soundscape_IR: A source separation toolbox for exploring acoustic diversity in soundscapes. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 13, 2347-2355.
DOI URL |
| [60] | van der Lee GH, Desjonquères C, Sueur J, Kraak MHS, Verdonschot PFM (2020) Freshwater ecoacoustics: Listening to the ecological status of multi-stressed lowland waters. Ecological Indicators, 113, 106252. |
| [61] | Villanueva-Rivera LJ, Pijanowski BC (2018) soundecology: Soundscape Ecology. R package version 1.3.3. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=soundecology. (accessed on 2020-09-11) |
| [62] |
Villanueva-Rivera LJ, Pijanowski BC, Doucette J, Pekin B (2011) A primer of acoustic analysis for landscape ecologists. Landscape Ecology, 26, 1233-1246.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
Wang TM, Andrew Royle J, Smith JLD, Zou L, Lü XY, Li T, Yang HT, Li ZL, Feng RN, Bian YJ, Feng LM, Ge JP (2018) Living on the edge: Opportunities for Amur tiger recovery in China. Biological Conservation, 217, 269-279.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
Wang TM, Feng LM, Mou P, Wu JG, Smith JLD, Xiao WH, Yang HT, Dou HL, Zhao XD, Cheng YC, Zhou B, Wu HY, Zhang L, Tian Y, Guo QX, Kou XJ, Han XM, Miquelle DG, Oliver CD, Xu RM, Ge JP (2016) Amur tigers and leopards returning to China: Direct evidence and a landscape conservation plan. Landscape Ecology, 31, 491-503.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
Welch P (1967) The use of fast Fourier transform for the estimation of power spectra: A method based on time averaging over short, modified periodograms. IEEE Transactions on Audio and Electroacoustics, 15, 70-73.
DOI URL |
| [66] | Wickham H (2009) Ggplot2:Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis, 2nd edn. Springer, New York. |
| [67] |
Yang HT, Zhao XD, Han BY, Wang TM, Mou P, Ge JP, Feng LM (2018) Spatiotemporal patterns of Amur leopards in Northeast China: Influence of tigers, prey, and humans. Mammalian Biology, 92, 120-128.
DOI URL |
| [68] |
Yen SC, Shieh BS, Wang YT, Wang Y (2013) Rutting vocalizations of Formosan sika deer Cervus nippon taiouanus—Acoustic structure, seasonal and diurnal variations, and individuality. Zoological Science, 30, 1025-1031.
DOI URL |
| [69] |
Zhao Y, Shen XL, Li S, Zhang YY, Peng RH, Ma KP (2020) Progress and outlook for soundscape ecology. Biodiversity Science, 28, 806-820. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[赵莹, 申小莉, 李晟, 张雁云, 彭任华, 马克平 (2020) 声景生态学研究进展和展望. 生物多样性, 28, 806-820.]
DOI |
|
| [70] | Znidersic E, Towsey M, Roy WK, Darling SE, Truskinger A, Roe P, Watson DM (2020) Using visualization and machine learning methods to monitor low detectability species—The least bittern as a case study. Ecological Informatics, 55, 101014. |
| [1] | Qiaoyi Nong, Jun Cao, Wenda Cheng, Yanqiong Peng. Comparative study of monitoring methods for Apoidea resources and diversity [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [2] | Lei Chen, Zhiyong Xu, Pukun Su, Xiaotian Lai, Zhao Zhao. Exploring the application of frequency-dependent acoustic diversity index in human-dominated areas [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(10): 24286-. |
| [3] | Zezhou Hao, Chengyun Zhang, Le Li, Bingtao Gao, Wei Zeng, Chun Wang, Zixuan Wang, Wantao Huang, Yue Zhang, Nancai Pei, Zhishu Xiao. Applications of passive acoustic monitoring and evaluation in urban bird research [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(10): 24123-. |
| [4] | Wanjun Hu, Zezhou Hao, Canwei Xia, Jiangjian Xie. Wetland soundscape recording scheme and feature selection for soundscape classification [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(10): 24121-. |
| [5] | Yuchen Du, Beimeng Liu, Junfeng Chen, Hao Wang, Yi Xie. Analysis of factors influencing farmers’ protection willingness based on structural equation model: Taking the Hunchun area of Northeast China Tiger and Leopard National Park as an example [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(1): 23155-. |
| [6] | Zhenzhen Li, Mengtian Du, Yuanxin Zhu, Dawei Wang, Zhilin Li, Tianming Wang. A practical guide for estimating the density of unmarked populations using camera traps [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(3): 22422-. |
| [7] | Qi Bian, Cheng Wang, He Cheng, Dan Han, Yilin Zhao, Luqin Yin. Exploring the application of acoustic indices in the assessment of bird diversity in urban forests [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(1): 22080-. |
| [8] | Zhishu Xiao, Jianguo Cui, Daiping Wang, Zhitao Wang, Jinhong Luo, Jie Xie. Interdisciplinary development trends of contemporary bioacoustics and the opportunities for China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(1): 22423-. |
| [9] | Shizheng Wang, Yifei Sun, Zhenzhen Li, Yue Shu, Jiawei Feng, Tianming Wang. Effects of bird migration on the temporal patterns of the wetland soundscape in the downstream region of the Tumen River Basin of China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(1): 22337-. |
| [10] | Jian Zhang, Hongzhi Kong, Xiaolei Huang, Shenglei Fu, Liangdong Guo, Qinghua Guo, Fumin Lei, Zhi Lü, Yurong Zhou, Keping Ma. Thirty key questions for biodiversity science in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(10): 22609-. |
| [11] | Xing Chen, Tianpei Guan, Wenle Jiang, Dandan Li, Kong Yang, Sheng Li. Distribution and population status of bovine species in China based on bibliometric analysis [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(5): 668-679. |
| [12] | Sheng Li, William J. McShea, Dajun Wang, Xiaoli Shen, Hongliang Bu, Tianpei Guan, Fang Wang, Xiaodong Gu, Xiaofeng Zhang, Haohong Liao. Construction progress of the Camera-trapping Network for the Mountains of Southwest China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(9): 1049-1058. |
| [13] | Tianming Wang, Limin Feng, Haitao Yang, Lei Bao, Hongfang Wang, Jianping Ge. An introduction to Long-term Tiger-Leopard Observation Network based on camera traps in Northeast China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(9): 1059-1066. |
| [14] | Xueyou Li, Wenqiang Hu, Changzhe Pu, Quan Li, Qiupeng Yu, Zhechang Hu, William V. Bleisch, Xuelong Jiang. Camera-trapping monitoring platform for mammals and pheasants in the Longitudinal Range and Gorge Region of Southwest China: Protocol, progress and future outlook [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(9): 1090-1096. |
| [15] | Yanlin Liu, Dazhao Song, Beibei Liu, Fan Xia, Yuelong Chen, Yiqing Wang, Qiaowen Huang. Overview of the Camera-trapping Platform for Felid Species in China: Data integration by a conservation NGO [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2020, 28(9): 1067-1074. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2026 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn