



Biodiv Sci ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (8): 873-879. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019060 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019060
Previous Articles Next Articles
Hai-Sheng Yuan1,*( ),Yulian Wei1,Liwei Zhou1,Wenmin Qin1,Baokai Cui2,Shuanghui He2
),Yulian Wei1,Liwei Zhou1,Wenmin Qin1,Baokai Cui2,Shuanghui He2
Received:2019-02-28
Accepted:2019-04-25
Online:2019-08-20
Published:2019-09-25
Contact:
Yuan Hai-Sheng
Hai-Sheng Yuan, Yulian Wei, Liwei Zhou, Wenmin Qin, Baokai Cui, Shuanghui He. Potential distribution and ecological niches of four butt-rot pathogenic fungi in Northeast China[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(8): 873-879.
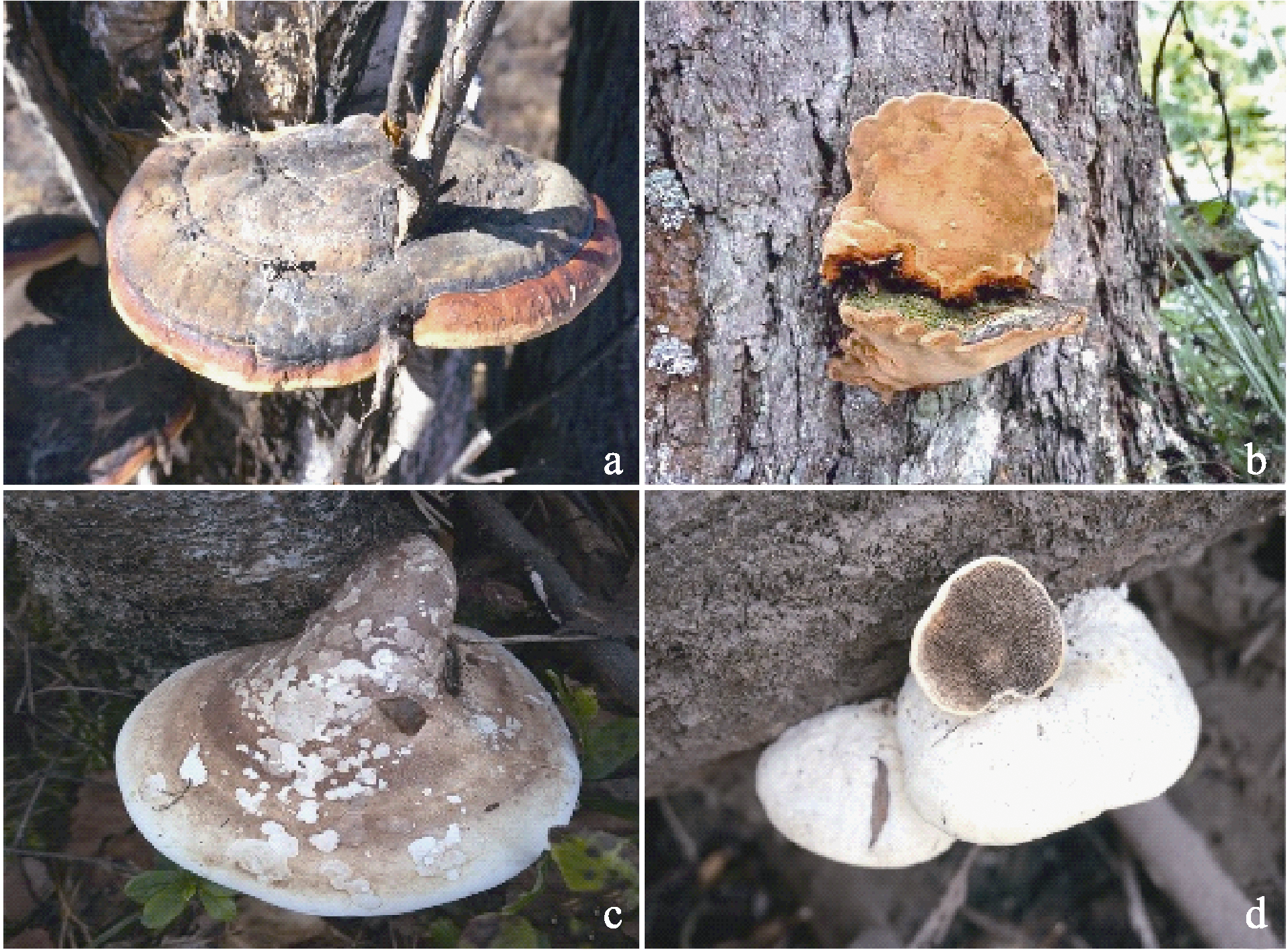

Fig. 1 Basidiocarps of four butt-rot pathogenic fungi. (a) Fomitopsis pinicola; (b) Porodaedalea laricis; (c) Piptoporus betulinus; (d) Trametes suaveolens.
| 物种 Species | 记录点 Registered presence | 训练点数 Number of training points | 训练AUC Training AUC | 测试AUC Test AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 红缘拟层孔菌 Fomitopsis pinicola | 29 | 9 | 0.984 | 0.990 |
| 落叶松锈迷孔菌 Porodaedalea laricis | 9 | 3 | 0.933 | 0.990 |
| 桦剥管孔菌 Piptoporus betulinus | 21 | 7 | 0.984 | 0.989 |
| 香栓孔菌 Trametes suaveolens | 24 | 7 | 0.981 | 0.967 |
Table 1 Training and test AUC values obtained in the models for four butt-rot pathogenic fungi
| 物种 Species | 记录点 Registered presence | 训练点数 Number of training points | 训练AUC Training AUC | 测试AUC Test AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 红缘拟层孔菌 Fomitopsis pinicola | 29 | 9 | 0.984 | 0.990 |
| 落叶松锈迷孔菌 Porodaedalea laricis | 9 | 3 | 0.933 | 0.990 |
| 桦剥管孔菌 Piptoporus betulinus | 21 | 7 | 0.984 | 0.989 |
| 香栓孔菌 Trametes suaveolens | 24 | 7 | 0.981 | 0.967 |
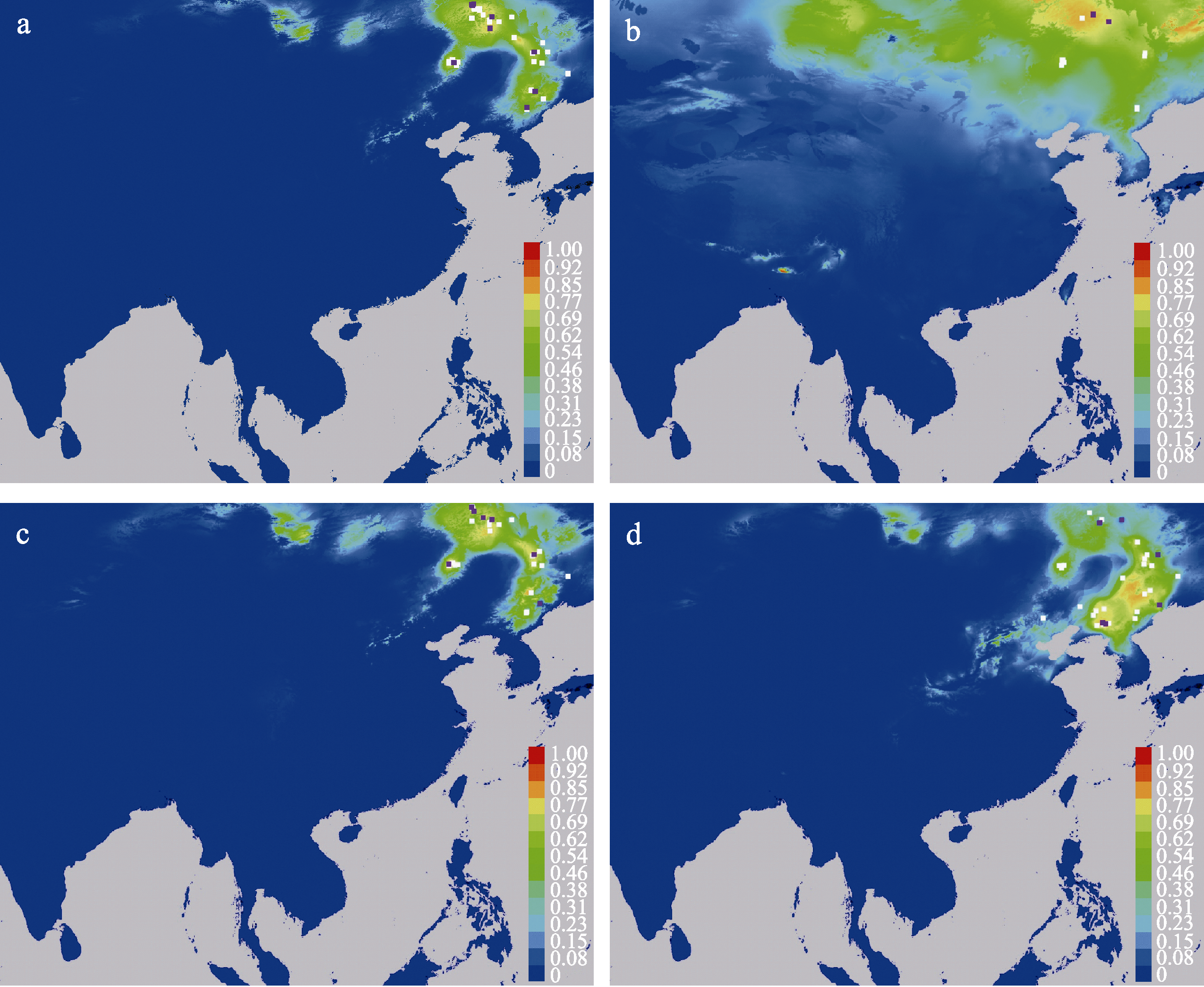
Fig. 3 Potential distributions of four butt-rot pathogenic fungi. (a) Fomitopsis pinicola; (b) Porodaedalea laricis; (c) Piptoporus betulinus; (d) Trametes suaveolens. White squares are training points, purple squares are testing points.
| 编号 Code | 环境变量 Environmental variable | 贡献率 Contribution (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 红缘拟层孔菌 Fomitopsis pinicola | 落叶松锈迷孔菌 Porodaedalea laricis | 桦剥管孔菌 Piptoporus betulinus | 香栓孔菌 Trametes suaveolens | |||
| Bio1 | 年均温 Annual mean temperature (℃) | 6.1 | 0 | 11.8 | 2.9 | |
| Bio2 | 昼夜温差月均值 Mean diurnal range (mean of monthly (max - min temp)) (℃) | 0 | 0.9 | 0 | 0 | |
| Bio3 | 等温性 Isothermality ((Bio2/Bio7) × 100) | 5.2 | 0 | 5.6 | 4.1 | |
| Bio4 | 温度季节性变化标准差 Temperature seasonality (standard deviation × 100) (C of V) | 16.6 | 0 | 6.6 | 34.9 | |
| Bio5 | 最暖月最高温 Maximum temperature of warmest month (℃) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Bio6 | 最冷月最低温 Minimum temperature of coldest month (℃) | 0.5 | 0 | 2.9 | 1.7 | |
| Bio7 | 温度的年较差 Temperature annual range (Bio5 - Bio6) (℃) | 29.9 | 4.3 | 17.6 | 4.2 | |
| Bio8 | 最湿季均温 Mean temperature of wettest quarter (℃) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.3 | |
| Bio9 | 最干季均温 Mean temperature of driest quarter (℃) | 7 | 78.8 | 18.1 | 0 | |
| Bio10 | 最暖季均温 Mean temperature of warmest quarter (℃) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Bio11 | 最冷季均温 Mean temperature of coldest quarter (℃) | 1.5 | 0 | 6.7 | 2.1 | |
| Bio12 | 年降水量 Annual precipitation (mm) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Bio13 | 最湿月降水量 Precipitation of wettest month (mm) | 0 | 0 | 0.6 | 0 | |
| Bio14 | 最干月降水量 Precipitation of driest month (mm) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Bio15 | 降水量季节性变异系数 Precipitation seasonality (coefficient of variation) (C of V) | 0.5 | 1.7 | 0 | 4.4 | |
| Bio16 | 最湿季降水量 Precipitation of wettest quarter (mm) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Bio17 | 最干季降水量 Precipitation of driest quarter (mm) | 5.5 | 0 | 4.9 | 6.9 | |
| Bio18 | 最暖季降水量 Precipitation of warmest quarter (mm) | 25 | 6.2 | 23.5 | 36.3 | |
| Bio19 | 最冷季降水量 Precipitation of coldest quarter (mm) | 0.8 | 0 | 0.4 | 0.2 | |
| ELE | 海拔 Elevation (m) | 1.4 | 8.1 | 1.2 | 1.8 | |
Table 2 Environmental variables used to create the species distribution model and their percentage contribution to model performance
| 编号 Code | 环境变量 Environmental variable | 贡献率 Contribution (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 红缘拟层孔菌 Fomitopsis pinicola | 落叶松锈迷孔菌 Porodaedalea laricis | 桦剥管孔菌 Piptoporus betulinus | 香栓孔菌 Trametes suaveolens | |||
| Bio1 | 年均温 Annual mean temperature (℃) | 6.1 | 0 | 11.8 | 2.9 | |
| Bio2 | 昼夜温差月均值 Mean diurnal range (mean of monthly (max - min temp)) (℃) | 0 | 0.9 | 0 | 0 | |
| Bio3 | 等温性 Isothermality ((Bio2/Bio7) × 100) | 5.2 | 0 | 5.6 | 4.1 | |
| Bio4 | 温度季节性变化标准差 Temperature seasonality (standard deviation × 100) (C of V) | 16.6 | 0 | 6.6 | 34.9 | |
| Bio5 | 最暖月最高温 Maximum temperature of warmest month (℃) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Bio6 | 最冷月最低温 Minimum temperature of coldest month (℃) | 0.5 | 0 | 2.9 | 1.7 | |
| Bio7 | 温度的年较差 Temperature annual range (Bio5 - Bio6) (℃) | 29.9 | 4.3 | 17.6 | 4.2 | |
| Bio8 | 最湿季均温 Mean temperature of wettest quarter (℃) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.3 | |
| Bio9 | 最干季均温 Mean temperature of driest quarter (℃) | 7 | 78.8 | 18.1 | 0 | |
| Bio10 | 最暖季均温 Mean temperature of warmest quarter (℃) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Bio11 | 最冷季均温 Mean temperature of coldest quarter (℃) | 1.5 | 0 | 6.7 | 2.1 | |
| Bio12 | 年降水量 Annual precipitation (mm) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Bio13 | 最湿月降水量 Precipitation of wettest month (mm) | 0 | 0 | 0.6 | 0 | |
| Bio14 | 最干月降水量 Precipitation of driest month (mm) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Bio15 | 降水量季节性变异系数 Precipitation seasonality (coefficient of variation) (C of V) | 0.5 | 1.7 | 0 | 4.4 | |
| Bio16 | 最湿季降水量 Precipitation of wettest quarter (mm) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Bio17 | 最干季降水量 Precipitation of driest quarter (mm) | 5.5 | 0 | 4.9 | 6.9 | |
| Bio18 | 最暖季降水量 Precipitation of warmest quarter (mm) | 25 | 6.2 | 23.5 | 36.3 | |
| Bio19 | 最冷季降水量 Precipitation of coldest quarter (mm) | 0.8 | 0 | 0.4 | 0.2 | |
| ELE | 海拔 Elevation (m) | 1.4 | 8.1 | 1.2 | 1.8 | |
| 1 | Bao QZ, Wei YL, Yuan HS, Li YR (2006) A new butt-rot disease in tropical area from Yunnan Province. Forest Research, 19, 246-247.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 包晴忠, 魏玉莲, 袁海生, 李永儒 ( 2006) 中国云南一种新的阔叶树干基腐朽病. 林业科学研究, 19, 246-247.] | |
| 2 | Dai YC (2005) Illustrations of Pathogenic Wood-decaying Fungi in China. Science Press, Beijing.(in Chinese) |
| [ 戴玉成 ( 2005) 中国林木病原腐朽菌图志. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 3 | Dai YC (2010) Species diversity of wood-decaying fungi in Northeast China. Mycosystema, 29, 801-818.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 戴玉成 ( 2010) 中国东北地区木材腐朽菌的多样性. 菌物学报, 29, 801-818.] | |
| 4 | Dai YC (2012) Pathogenic wood-decaying fungi on woody plants in China. Mycosystema, 31, 493-509.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 戴玉成 (2012) 中国木本植物病原木材腐朽菌研究. 菌物学报, 31, 493-509.] | |
| 5 | Dai YC, Cui BK, Yuan HS, Li BD ( 2007) Pathogenic wood- decaying fungi in China. Forest Pathology, 37, 105-120. |
| 6 | Dai YC, Qin GF, Xu MQ ( 2000) The forest pathogens of root and butt rot in northeast China. Forest Research, 13, 15-22.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 戴玉成, 秦国夫, 徐梅卿 ( 2000) 中国东北地区的立木腐朽菌. 林业科学研究, 13, 15-22.] | |
| 7 | Jiang JQ, Yuan HS ( 2005) Two newly described polypores on Populus in Northeast China. Forest Research, 18, 280-283.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 姜俊清, 袁海生 (2005) 中国东北杨树上多孔菌二新记录. 林业科学研究, 18, 280-283.] | |
| 8 | Marchioro CA, Krechemer FS ( 2018) Potential global distribution of Diabrotica species and the risks for agricultural production. Pest Management Science, 74, 2100-2109. |
| 9 | Pearce JL, Boyce MS ( 2006) Modelling distribution and abundance with presence-only data. Journal of Applied Ecology, 43, 405-412. |
| 10 | Pearce J, Ferrier S (2000) An evaluation of alternative algorithms for fitting species distribution models using logistic regression. Ecological Modelling, 128, 127-147. |
| 11 | Pearson RG, Raxworthy CJ, Nakamura M, Peterson AT ( 2007) Predicting species distributions from small numbers of occurrence records: A test case using cryptic geckos in Madagascar. Journal of Biogeography, 34, 102-117. |
| 12 | Phillips SJ, Dudík M (2008) Modeling of species distributions with MaxEnt: New extensions and a comprehensive evaluation. Ecography, 31, 161-175. |
| 13 | Phillips SJ, Anderson RP, Schapire RE (2006) Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distributions. Ecological Modelling, 190, 231-259. |
| 14 | Shcheglovitova M, Anderson RP (2013) Estimating optimal complexity for ecological niche models: A Jackknife approach for species with small sample sizes. Ecological Modelling, 269, 9-17. |
| 15 | Wei YL, Dai YC ( 2004) The ecological function of wood- inhabiting fungi in forest ecosystem. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 15, 1935-1938.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 魏玉莲, 戴玉成 ( 2004) 木材腐朽菌在森林生态系统中的功能. 应用生态学报, 15, 1935-1938.] | |
| 16 | Wisz MS, Hijmans RJ, Li J, Peterson AT, Graham CH, Guisan A, Elith J, Dudik M, Ferrier S, Huettman F, Leathwick JR, Lehmann A, Lohamnn L, Loiselle BA, Manion G, Moritz C, Nakamura M, Nakazawa Y, Overton JMcC, Phillips SJ, Richardson KS, Scachetti-Pereira R, Schapire RE, Soberón J, Williams SE, Zimmermann NE ( 2008) Effects of sample size on the performance of species distribution models. Diversity and Distributions, 14, 763-773. |
| 17 | Yuan HS, Wang L, Yu CJ, Dai YC (2008) Two new butt-rot pathogens on broad leaved tree in China. Forest Research, 21, 248-252.(in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 袁海生, 王琳, 余长军, 戴玉成 ( 2008) 中国阔叶树干基腐朽两种新病原菌. 林业科学研究, 21, 248-252.] | |
| 18 | Yuan HS, Wei YL, Qin WM, Zhou LW (2009) Lignicolous fungi of eastern Less Hinggan Mts. of Heilongjiang Province. Mycosystema, 28, 36-43. |
| 19 | Yuan HS, Wei YL, Wang XG ( 2015) Maxent modeling for predicting potential distribution of Sanghuang, an important group of medicinal fungi in China. Fungal Ecology, 17, 140-145. |
| [1] | Fu Mengdi, Zhu Yanpeng, Ren Yueheng, Li Shuang, Qin Le, Xie Zhengjun, Wang Qingchun, Zhang Libo. Research on the optimization of wildlife passage spatial layout in Xinjiang [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(3): 24346-. |
| [2] | Tingwei Dong, Meiling Huang, Xu Wei, Shuo Ma, Qu Yue, Wenli Liu, Jiaxin Zheng, Gang Wang, Rui Ma, Youzhong Ding, Shunqi Bo, Zhenghuan Wang. Potential spatial distribution pattern and landscape connectivity of Pelophylax plancyi in Shanghai, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(8): 22692-. |
| [3] | Wei Liu, Ruge Wang, Tianqiao Fan, Nayiman Abudulijiang, Xinhang Song, Shuping Xiao, Ning Guo, Lingying Shuai. Habitat suitability for the Aviceda leuphotes in Mingxi County, Fujian Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(7): 22660-. |
| [4] | Chang Deng, Jiewei Hao, De Gao, Mingxun Ren, Lina Zhang. Identification and protection of suitable habitat hotspots for threatened bryophytes in Hainan [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(4): 22580-. |
| [5] | Qiongyue Zhang, Zhuodi Deng, Xuebin Hu, Zhifeng Ding, Rongbo Xiao, Chen Xiu, Zhenghao Wu, Guang Wang, Donghui Han, Yuke Zhang, Jianchao Liang, Huijian Hu. The impact of urbanization on regional bird distribution and habitat connectivity in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(3): 22161-. |
| [6] | Jirong Teng, Xingming Liu, Liwen He, Junliang Wang, Jian Huang, Jie Feng, Fang Wang, Yue Weng. The spatio-temporal impact of domestic dogs (Canis familiaris) on giant panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca) in Baishuijiang National Nature Reserve [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(1): 21204-. |
| [7] | Chen Zhang, Wei Ma, Chen Chen, Muyang Wang, Wenxuan Xu, Weikang Yang. Changes of habitat pattern for goitered gazelle in the Xinjiang Kalamaili Mountain Ungulate Nature Reserve under the influence of major projects [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(1): 21176-. |
| [8] | Xing Ma, Hao Wang, Wei Yu, Yong Du, Jianchao Liang, Huijian Hu, Shengrong Qiu, Lu Liu. Analysis on the hotspot and conservation gaps of bird biodiversity in Guangdong Province based on MaxEnt model [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(8): 1097-1107. |
| [9] | Run Zhou, Xiuqin Ci, Jianhua Xiao, Guanlong Cao, Jie Li. Effects and conservation assessment of climate change on the dominant group—The genusCinnamomum of subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forests [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(6): 697-711. |
| [10] | Yuhan Shi, Zongxin Ren, Weijia Wang, Xin Xu, Jie Liu, Yanhui Zhao, Hong Wang. Predicting the spatial distribution of three Astragalusspecies and their pollinating bumblebees in the Sino-Himalayas [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(6): 759-769. |
| [11] | Yifeng Hu, Wenhua Yu, Yang Yue, Zhenglanyi Huang, Yuchun Li, Yi Wu. Species diversity and potential distribution of Chiroptera on Hainan Island, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(4): 400-408. |
| [12] | Hongfei Zhuang, Yinbo Zhang, Wei Wang, Yueheng Ren, Fangzheng Liu, Jinhong Du, Yue Zhou. Optimized hot spot analysis for probability of species distribution under different spatial scales based on MaxEnt model: Manglietia insignis case [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2018, 26(9): 931-940. |
| [13] | Bo Wang, Yong Huang, Jiatang Li, Qiang Dai, Yuezhao Wang, Daode Yang. Amphibian species richness patterns in karst regions in Southwest China and its environmental associations [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2018, 26(9): 941-950. |
| [14] | Zhongyi Zhou, Ran Liu, Shuna Shi, Yanjun Su, Wenkai Li, Qinghua Guo. Ecological niche modeling with LiDAR data: A case study of modeling the distribution of fisher in the southern Sierra Nevada Mountains, California [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2018, 26(8): 878-891. |
| [15] | Xiaoyu Wu, Shikui Dong, Shiliang Liu, Quanru Liu, Yuhui Han, Xiaolei Zhang, Xukun Su, Haidi Zhao, Jing Feng. Identifying priority areas for grassland endangered plant species in the Sanjiangyuan Nature Reserve based on the MaxEnt model [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2018, 26(2): 138-148. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2026 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn