



Biodiv Sci ›› 2017, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (7): 758-764. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017145 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2017145
Previous Articles Next Articles
Yong Yang1,*( ), Bing Liu1,2, Dennis M. Njenga2,3,1
), Bing Liu1,2, Dennis M. Njenga2,3,1
Received:2017-05-15
Accepted:2017-07-09
Online:2017-07-20
Published:2017-07-21
Contact:
Yang Yong
Yong Yang, Bing Liu, Dennis M. Njenga. Red list assessment and conservation status of gymnosperms from China[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2017, 25(7): 758-764.
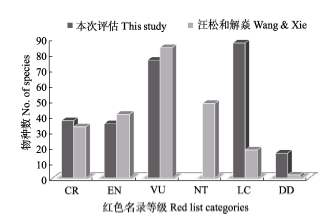
Fig. 1 A comparison of the two red list results of Chinese gymnosperms. CR, Critically Endangered; EN, Endangered; VU, Vulnerable; NT, Near Threatened; LC, Least Concern; DD, Data Deficient.
| 1 | Bellard C, Leroy B, Thuiller W, Rysman JF, Courchamp F (2016) Major drivers of invasion risks throughout the world. Ecosphere, 7, e01241. |
| 2 | Chen YQ, Wang RJ, Zhu SS, Jiang AL, Zhou LX (2016) Population status and conservation strategy of the rare and endangered plant Glyptostrobus pensilis in Guangzhou. Tropical Geography, 36, 944-951. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈雨晴, 王瑞江, 朱双双, 蒋奥林, 周联选 (2016) 广州市珍稀濒危植物水松的种群现状与保护策略. 热带地理, 36, 944-951.] | |
| 3 | Christenhusz MJM, Reveal JL, Farjon A, Gardner MF, Mill RR, Chase MW (2011) A new classification and linear sequence of extant gymnosperms. Phytotaxa, 19, 55-70. |
| 4 | Crisp MD, Cook LG (2011) Cenozoic extinctions account for the low diversity of extant gymnosperms compared with angiosperms. New Phytologist, 192, 997-1009. |
| 5 | Dai JS, Fu QF (2010) Declining reasons of rare plant and protection measures in Meilin Reservoir. China Water Resources, (11), 36-37, 49. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [戴金水, 付奇峰 (2010) 梅林水库珍稀植物衰退原因. 水资源管理, (11), 36-37, 49.] | |
| 6 | Fu DZ, Fu LK, Zuo JB, Peng DW (1998) Status and conservation of angiosperm diversity in China. In: Research and Conservation of Species Diversity (eds Song YL, Yang QE, Huang YQ), pp. 48-78. Zhejiang Science and Technology Press, Hangzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [傅德志, 傅立国, 左家哺, 彭代文 (1998) 中国被子植物物种多样性现状及其保护. 见: 物种多样性研究与保护(宋延龄, 杨亲二, 黄永青主编), 48-78页. 浙江科学技术出版社, 杭州.] | |
| 7 | Gerrienne P, Meyer-Berthaud B, Fairon-Demaret M, Streel M, Steemans P (2004) Runcaria, a Middle Devonian seed plant precursor. Science, 306, 856-858. |
| 8 | Guan ZT, Zhou L (1995) History, present status and conservation significance of Cycas panzhihuaensis. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 12(Suppl.), 59-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [管中天, 周林 (1995) 攀枝花苏铁的历史、现状与保护意义. 植物学通报, 12(增刊), 59-62.] | |
| 9 | Guan ZT, Zhou LJ, Zhou L (1996) The cycad community and flora. I. The cycad community and flora in Jinshajiang Valley. In: Cycads of China (ed. Guan ZT), pp. 47-64. Sichuan Science & Techonology Press, Chengdu. (in Chinese) |
| [管中天, 周立江, 周林 (1996) 苏铁植物群落及植物区系(第一节): 金沙江河谷苏铁植物群落及植物区系. 见: 中国苏铁植物(管中天主编), 47-64页. 四川科学技术出版社, 成都.] | |
| 10 | He YH, Li CL (1999) The ecological geographic distribution, spatial pattern and collecting history of Cycas panzhihuaensis populations. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 23, 23-30. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [何永华, 李朝銮 (1999) 攀枝花苏铁种群生态地理分布、分布格局及采挖历史的研究. 植物生态学报, 23, 23-30.] | |
| 11 | Jian SG, Wei Q, Gao ZZ, Xie ZH, Lin SH, Liu N (2005) Characteristics and conservation of wild populations of Cycas fairylakea newly found in Qujiang of Guangdong Province. Guihaia, 25, 97-101. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [简曙光, 韦强, 高泽正, 谢振华, 林仕洪, 刘念 (2005) 广东省曲江县野生仙湖苏铁新种群及其保护. 广西植物, 25, 97-101.] | |
| 12 | Liu J, Möller M, Gao LM, Zhang DQ, Li DZ (2011) DNA barcoding for the discrimination of Eurasian yews (Taxus L., Taxaceae) and the discovery of cryptic species. Molecular Ecology Resources, 11, 89-100. |
| 13 | Luo ZC, Luo YB (2008) Xinning Plants. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [罗仲春, 罗毅波 (2008) 新宁植物. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| 14 | Maxwell SL, Fuller RA, Brooks TM, Watson JEM (2016) The ravages of guns, nets and bulldozers. Nature, 536, 143-145. |
| 15 | Meng T, Peng RC, Zhong GF, You ZJ, Tan WN, Xu WB (2013) Xanthocyparis Farjon & Hiep, a newly recorded genus of Cupressaceae from China. Guihaia, 33, 388-391. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [蒙涛, 彭日成, 钟国芳, 游旨价, 谭卫宁, 许为斌 (2013) 黄金柏属——中国柏科一新记录属. 广西植物, 33, 388-391.] | |
| 16 | Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (2005) Ecosystems and Human Well-being: Biodiversity Synthesis. World Resources Institute, Washington, DC. |
| 17 | Möller M, Gao LM, Mill RR, Zhang DQ, Roudel RC, Li DZ (2013) A multidisciplinary approach reveals hidden taxonomic diversity in the morphologically challenging Taxus wallichiana complex. Taxon, 62, 1161-1177. |
| 18 | Poudel RC, Möller M, Gao LM, Ahrends A, Baral SR, Liu J, Thomas P, Li DZ (2012) Using morphological, molecular and climatic data to delimitate yews along the Hindu Kush- Himalaya and adjacent regions. PLoS ONE, 7, e46873. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0046873 |
| 19 | Rabasa SG, Granda E, Benavides R, Kunstler G, Romaogaya JME, Penuelas J, Wojciechgil MS, Grodzki W, Ambrozy S, Bergh J, Hodar JA, Zamora R, Valladares F (2013) Disparity in elevational shifts of European trees in response to recent climate warming. Global Change Biology, 19, 2490-2499. |
| 20 | Wang DB, Ji SY, Chen FP (2009) The spatial distribution pattern of main populations in Cycas fairylakea community. Journal of Southwest China Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 34, 93-97. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [汪殿蓓, 暨淑仪, 陈飞鹏 (2009) 仙湖苏铁群落主要种群的空间分布格局. 西南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 34, 93-97.] | |
| 21 | Wang DB, Xing FW, Ji SY, Chen FP (2003) The report on the wild Cycas fairylakea population. Chinese Wild Plant Resources, 22(2), 19-20. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [汪殿蓓, 邢福武, 暨淑仪, 陈飞鹏 (2003) 仙湖苏铁野生种群的报道. 中国野生植物资源, 22(2), 19-20.] | |
| 22 | Wang S, Xie Y (2004) China Species Red List, Vol. 1: Red List. Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese and in English) |
| [汪松, 解焱 (2004) 中国物种红色名录, 第1卷: 红色名录. 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| 23 | Wang XM, Lai YL, Xu XM, Ying ZM, Su YJ, Li YB, Liao WB (2006) Genetic variation in the endemic plant Cycas fairylakea (Cycadaceae) from Meilin Forest Park in Shenzhen on the basis of ISSR analysis. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 45, 82-85. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王晓明, 赖燕玲, 徐向明, 应站明, 苏应娟, 李月波, 廖文波 (2006) 深圳梅林仙湖苏铁野生种群遗传多样性ISSR分析. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 45, 82-85.] | |
| 24 | Wang XQ, Ran JH (2014) Evolution and biogeography of gymnosperms. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 75, 24-40. |
| 25 | Yang Y (2015) Diversity and distribution of gymnosperms in China. Biodiversity Science, 23, 243-246. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨永 (2015) 中国裸子植物的多样性和地理分布. 生物多样性, 23, 243-246.] | |
| 26 | Zheng L, Feng YL (2005) Allelopathic effects of Eupatorium adenophorum Spreng. on seed germination and seedling growth in ten herbaceous species. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 25, 2782-2787. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郑丽, 冯玉龙 (2005) 紫茎泽兰叶片化感作用对10种草本植物种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响. 生态学报, 25, 2782-2787.] | |
| 27 | Zhou LJ, Guan ZT (1985) Studies on the natural Cycas community in the valley of Jinsha River. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 7, 153-168. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [周立江, 管中天 (1985) 金沙江河谷苏铁天然植物群落的研究. 云南植物研究, 7, 153-168.] | |
| 28 | Zhou W, Guang MM, Gong X (2015) Cycas chenii (Cycadaceae), a new species from China, and its phylogenetic position. Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 53, 489-498. |
| [1] | Wu Yuxuan, Wang Ping, Hu Xiaosheng, Ding Yi, Peng Tiantian, Zhi Qiuying, Bademu Qiqige, Li Wenjie, Guan Xiao, Li Junsheng. Evaluation of grassland degradation status and vegetation characteristics changes in Hulunbuir [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [2] | Yanli Wang, Ying Zhang, Chunlin Qi, Changda Zhang, Youhai Shi, Yanjun Du, Qiong Ding. Identifying biodiversity hotspots and conservation gaps in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park based on macrofungi and plants perspectives [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 24081-. |
| [3] | Yiyun Gu, Jiaqi Xue, Jinhui Gao, Xinyi Xie, Ming Wei, Jinyu Lei, Cheng Wen. A public science data-based regional bird diversity assessment method [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 24080-. |
| [4] | Jia Xu, Xiaojuan Cui, Yifei Zhang, Chang Wu, Yuandong Sun. Fish diversity and distribution in the Nanling region [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [5] | Siqi Tao, Feiling Yang, Chaolang Hua, Ruidong Wu. Priority assessment for natural vegetation conservation in Yunnan Province by integrating threatened status and conservation value [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(3): 23324-. |
| [6] | Lei Chen, Zhiyong Xu, Pukun Su, Xiaotian Lai, Zhao Zhao. Exploring the application of frequency-dependent acoustic diversity index in human-dominated areas [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(10): 24286-. |
| [7] | Meizhe Liao, Zongwen Zhang, Keyu Bai. Situation and prospects of biodiversity of agricultural ecosystem conservation and utilization in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(7): 23017-. |
| [8] | Qingdong Dong, Chaonan Chen, Yanhong Li, Tixia Zhao, Zixin Sun, Zhe Zhang, Lianqi Zhu. Assessing the protection effectiveness and spillover/leakage effects of the national nature reserve group of Funiu Mountain area in Henan Province based on the NPP and human disturbance index [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(5): 22503-. |
| [9] | Lisong Wang, Qingqing Zhan, Jingping Liao, Hongwen Huang. Vascular plant diversity of National Key Protected Wild Plants, threatened species, and endemic species ex situ conserved in botanic gardens of China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(2): 22495-. |
| [10] | Chunpeng Guo, Maojun Zhong, Xiaoyi Wang, Shengnan Yang, Ke Tang, Lele Jia, Chunlan Zhang, Junhua Hu. An updated species checklist of amphibians and reptiles in Fujian Province, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(8): 22090-. |
| [11] | Shijia Peng, Yuan Luo, Hongyu Cai, Xiaoling Zhang, Zhiheng Wang. A new list of threatened woody species in China under future global change scenarios [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(5): 21459-. |
| [12] | Guangfu Zhang, Tianshi Xiong, Ting Sun, Kaidi Li, Liyuan Shao. Diversity, distribution, and conservation of rare and endangered plant species in Jiangsu Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(2): 21335-. |
| [13] | Yan Xie. Progress and application of IUCN Red List of Threatened Species [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(10): 22445-. |
| [14] | Zuchang Xu, Yahuang Luo, Shengyuan Qin, Guangfu Zhu, Dezhu Li. Current status of herbarium specimens and geographical distribution of bamboos (Gramineae: Bambsusoideae) in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(7): 897-909. |
| [15] | Run Zhou, Xiuqin Ci, Jianhua Xiao, Guanlong Cao, Jie Li. Effects and conservation assessment of climate change on the dominant group—The genusCinnamomum of subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forests [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(6): 697-711. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()