



Biodiv Sci ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (7): 897-909. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020373 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2020373
• Original Papers: Plant Diversity • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zuchang Xu1,2, Yahuang Luo3, Shengyuan Qin1,2, Guangfu Zhu1,2, Dezhu Li1,2,*( )
)
Received:2020-09-21
Accepted:2021-03-05
Online:2021-07-20
Published:2021-04-22
Contact:
Dezhu Li
Zuchang Xu, Yahuang Luo, Shengyuan Qin, Guangfu Zhu, Dezhu Li. Current status of herbarium specimens and geographical distribution of bamboos (Gramineae: Bambsusoideae) in China[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(7): 897-909.
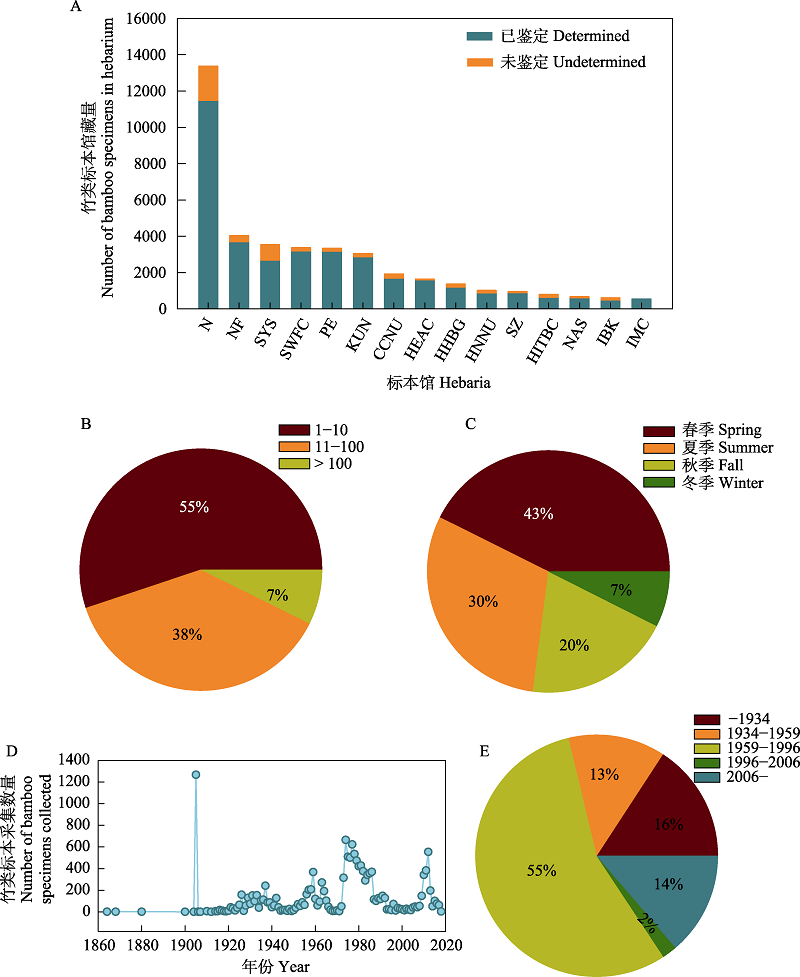
Fig. 1 Statistical depiction of bamboo specimen data collected in China. A, Herbarium statistics of top 15 herbaria with bamboo specimens collected in China (The code of the herbarium is shown in Appendix 2); B, Status of bamboo specimens in China at the species level; C, Season of collection of bamboo specimens in China; D, Year of collection of bamboo specimens in China; E, Relative proportions of bamboo specimens collected at various periods in China.
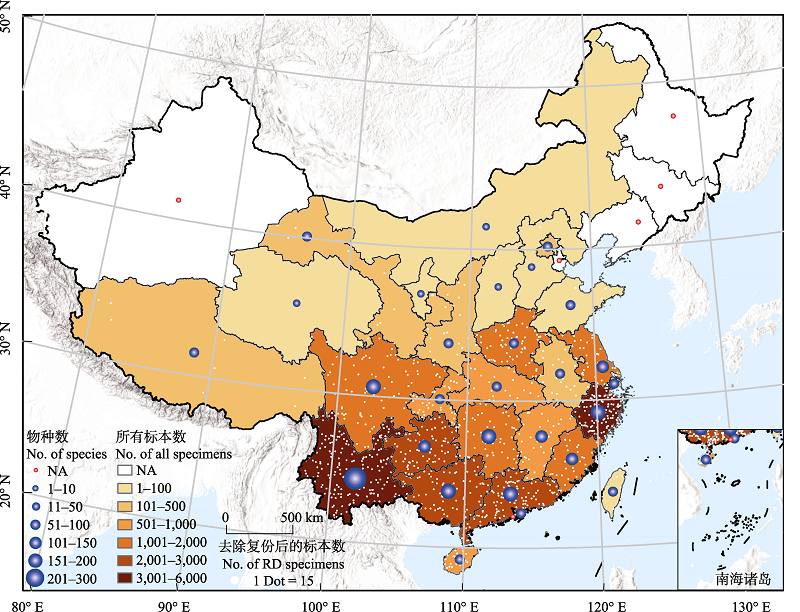
Fig. 2 Distribution of bamboo specimens and species in different provinces of China. The white dots indicate the number of specimens that removing duplicate (RD) specimens. Each white dot represents 15 specimens.
| 属 Genus | 文献记录物种数 Number of species based on literature | 标本记录物种数 Number of species based on specimens | 标本数 Specimens | 每个物种平均标本数 Mean specimens per species | Chao 1 | 比值 Ratio | 斜率 Slope |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 酸竹属 Acidosasa | 10 | 6 | 32 | 5.3 | 7 | -0.143 | 0.003 |
| 悬竹属 Ampelocalamus | 14 | 9 | 98 | 10.9 | - | - | 0.007 |
| 箣竹属 Bambusa | 90 | 62 | 2,188 | 35.3 | 65 | -0.046 | 0.003 |
| 巴山竹属 Bashania | 6 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| 单枝竹属 Bonia | 4 | 3 | 35 | 11.7 | 3 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 空竹属 Cephalostachyum | 7 | 5 | 91 | 18.2 | - | - | 0.000 |
| 方竹属 Chimonobambusa | 38 | 21 | 926 | 44.1 | 21 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 香竹属 Chimonocalamus | 10 | 11 | 263 | 23.9 | - | - | 0.000 |
| 牡竹属 Dendrocalamus | 37 | 31 | 1,146 | 37.0 | 33 | -0.061 | 0.002 |
| 镰序竹属 Drepanostachyum | 4 | 1 | 2 | 2.0 | - | - | 0.000 |
| 箭竹属 Fargesia | 87 | 56 | 831 | 14.8 | 59 | -0.051 | 0.003 |
| 铁竹属 Ferrocalamus | 2 | 1 | 22 | 22.0 | - | - | 0.000 |
| 贡山竹属 Gaoligongshania | 1 | 1 | 5 | 5.0 | - | - | 0.000 |
| 井冈寒竹属 Gelidocalamus | 12 | 8 | 76 | 9.5 | 8 | 0.000 | 0.003 |
| 巨竹属 Gigantochloa | 15 | 9 | 55 | 6.1 | 9 | 0.000 | 0.003 |
| 须弥筱竹属 Himalayacalamus | 2 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| 多枝竹属 Holttumochloa | 1 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| 纪如竹属 Hsuehochloa | 1 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| 箬竹属 Indocalamus | 32 | 20 | 1,317 | 65.9 | 22 | -0.091 | 0.002 |
| 大节竹属 Indosasa | 16 | 15 | 378 | 25.2 | - | - | 0.000 |
| 梨藤竹属 Melocalamus | 6 | 3 | 72 | 24.0 | - | - | 0.006 |
| 梨竹属 Melocanna | 1 | 1 | 8 | 8.0 | - | - | 0.000 |
| 新小竹属 Neomicrocalamus | 1 | 1 | 8 | 8.0 | - | - | 0.000 |
| 少穗竹属 Oligostachyum | 18 | 8 | 61 | 7.6 | - | - | 0.005 |
| 刚竹属 Phyllostachys | 61 | 52 | 5,868 | 112.8 | 53 | -0.019 | 0.001 |
| 苦竹属 Pleioblastus | 18 | 15 | 778 | 51.9 | - | - | 0.006 |
| 茶秆竹属 Pseudosasa | 17 | 14 | 577 | 41.2 | 22 | -0.364 | 0.006 |
| 泡竹属 Pseudostachyum | 1 | 1 | 65 | 65.0 | - | - | 0.000 |
| 冷箭竹属 Sarocalamus | 3 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| 赤竹属 Sasa | 9 | 10 | 83 | 8.3 | 28 | -0.643 | 0.013 |
| 华箬竹属 Sasamorpha | 3 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| ??簩竹属 Schizostachyum | 13 | 9 | 368 | 40.9 | 9 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 业平竹属 Semiarundinaria | 5 | 3 | 12 | 4.0 | - | - | 0.021 |
| 倭竹属 Shibataea | 7 | 7 | 110 | 15.7 | - | - | 0.003 |
| 唐竹属 Sinobambusa | 10 | 8 | 146 | 18.3 | - | - | 0.002 |
| 筱竹属 Thamnocalamus | 2 | 1 | 7 | 7.0 | 1 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 泰竹属 Thyrsostachys | 2 | 2 | 23 | 11.5 | - | - | 0.010 |
| 玉山竹属 Yushania | 70 | 51 | 609 | 11.9 | 53 | -0.038 | 0.003 |
| 总计 Total | 636 | 445 | 16,334 | 36.7 | 476 | -0.065 | 0.003 |
Table 1 Statistical analysis on herbarium specimens of bamboos in China at the genus level
| 属 Genus | 文献记录物种数 Number of species based on literature | 标本记录物种数 Number of species based on specimens | 标本数 Specimens | 每个物种平均标本数 Mean specimens per species | Chao 1 | 比值 Ratio | 斜率 Slope |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 酸竹属 Acidosasa | 10 | 6 | 32 | 5.3 | 7 | -0.143 | 0.003 |
| 悬竹属 Ampelocalamus | 14 | 9 | 98 | 10.9 | - | - | 0.007 |
| 箣竹属 Bambusa | 90 | 62 | 2,188 | 35.3 | 65 | -0.046 | 0.003 |
| 巴山竹属 Bashania | 6 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| 单枝竹属 Bonia | 4 | 3 | 35 | 11.7 | 3 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 空竹属 Cephalostachyum | 7 | 5 | 91 | 18.2 | - | - | 0.000 |
| 方竹属 Chimonobambusa | 38 | 21 | 926 | 44.1 | 21 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 香竹属 Chimonocalamus | 10 | 11 | 263 | 23.9 | - | - | 0.000 |
| 牡竹属 Dendrocalamus | 37 | 31 | 1,146 | 37.0 | 33 | -0.061 | 0.002 |
| 镰序竹属 Drepanostachyum | 4 | 1 | 2 | 2.0 | - | - | 0.000 |
| 箭竹属 Fargesia | 87 | 56 | 831 | 14.8 | 59 | -0.051 | 0.003 |
| 铁竹属 Ferrocalamus | 2 | 1 | 22 | 22.0 | - | - | 0.000 |
| 贡山竹属 Gaoligongshania | 1 | 1 | 5 | 5.0 | - | - | 0.000 |
| 井冈寒竹属 Gelidocalamus | 12 | 8 | 76 | 9.5 | 8 | 0.000 | 0.003 |
| 巨竹属 Gigantochloa | 15 | 9 | 55 | 6.1 | 9 | 0.000 | 0.003 |
| 须弥筱竹属 Himalayacalamus | 2 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| 多枝竹属 Holttumochloa | 1 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| 纪如竹属 Hsuehochloa | 1 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| 箬竹属 Indocalamus | 32 | 20 | 1,317 | 65.9 | 22 | -0.091 | 0.002 |
| 大节竹属 Indosasa | 16 | 15 | 378 | 25.2 | - | - | 0.000 |
| 梨藤竹属 Melocalamus | 6 | 3 | 72 | 24.0 | - | - | 0.006 |
| 梨竹属 Melocanna | 1 | 1 | 8 | 8.0 | - | - | 0.000 |
| 新小竹属 Neomicrocalamus | 1 | 1 | 8 | 8.0 | - | - | 0.000 |
| 少穗竹属 Oligostachyum | 18 | 8 | 61 | 7.6 | - | - | 0.005 |
| 刚竹属 Phyllostachys | 61 | 52 | 5,868 | 112.8 | 53 | -0.019 | 0.001 |
| 苦竹属 Pleioblastus | 18 | 15 | 778 | 51.9 | - | - | 0.006 |
| 茶秆竹属 Pseudosasa | 17 | 14 | 577 | 41.2 | 22 | -0.364 | 0.006 |
| 泡竹属 Pseudostachyum | 1 | 1 | 65 | 65.0 | - | - | 0.000 |
| 冷箭竹属 Sarocalamus | 3 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| 赤竹属 Sasa | 9 | 10 | 83 | 8.3 | 28 | -0.643 | 0.013 |
| 华箬竹属 Sasamorpha | 3 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| ??簩竹属 Schizostachyum | 13 | 9 | 368 | 40.9 | 9 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 业平竹属 Semiarundinaria | 5 | 3 | 12 | 4.0 | - | - | 0.021 |
| 倭竹属 Shibataea | 7 | 7 | 110 | 15.7 | - | - | 0.003 |
| 唐竹属 Sinobambusa | 10 | 8 | 146 | 18.3 | - | - | 0.002 |
| 筱竹属 Thamnocalamus | 2 | 1 | 7 | 7.0 | 1 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 泰竹属 Thyrsostachys | 2 | 2 | 23 | 11.5 | - | - | 0.010 |
| 玉山竹属 Yushania | 70 | 51 | 609 | 11.9 | 53 | -0.038 | 0.003 |
| 总计 Total | 636 | 445 | 16,334 | 36.7 | 476 | -0.065 | 0.003 |
| 省份 Province | 物种数 Species | Chao 1 | 比值 Ratio | 斜率 Slope | 省份 Province | 物种数 Species | Chao 1 | 比值 Ratio | 斜率 Slope |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 安徽 Anhui | 46 | 118 | -0.610 | 0.005 | 内蒙古 Inner Mongolia | 3 | - | - | 0.067 |
| 北京 Beijing | 14 | 32 | -0.563 | 0.005 | 宁夏 Ningxia | 2 | - | - | 0.000 |
| 重庆 Chongqing | 45 | 48 | -0.063 | 0.002 | 青海 Qinghai | 1 | - | - | 0.200 |
| 福建 Fujian | 91 | 134 | -0.321 | 0.004 | 陕西 Shaanxi | 37 | 48 | -0.229 | 0.004 |
| 甘肃 Gansu | 25 | 42 | -0.405 | 0.004 | 山东 Shandong | 12 | 14 | -0.143 | 0.004 |
| 广东 Guangdong | 124 | 179 | -0.307 | 0.003 | 上海 Shanghai | 22 | 30 | -0.267 | 0.006 |
| 广西 Guangxi | 132 | 170 | -0.224 | 0.003 | 山西 Shanxi | 6 | 11 | -0.455 | 0.008 |
| 贵州 Guizhou | 99 | 133 | -0.256 | 0.003 | 四川 Sichuan | 112 | 189 | -0.407 | 0.004 |
| 海南 Hainan | 48 | 89 | -0.461 | 0.005 | 台湾 Taiwan | 25 | 63 | -0.603 | 0.006 |
| 河北 Heibei | 9 | 13 | -0.308 | 0.008 | 香港 Hong Kong | 25 | 25 | 0.000 | 0.001 |
| 河南 Henan | 46 | 56 | -0.179 | 0.002 | 西藏 Xizang | 31 | 55 | -0.436 | 0.005 |
| 湖北 Hubei | 48 | 64 | -0.250 | 0.003 | 云南 Yunnan | 255 | 280 | -0.089 | 0.002 |
| 湖南 Hunan | 101 | 135 | -0.252 | 0.004 | 浙江 Zhejiang | 125 | 157 | -0.204 | 0.003 |
| 江苏 Jiangsu | 59 | 77 | -0.234 | 0.003 | 总计 Total | 446 | 478 | -0.067 | 0.001 |
| 江西 Jiangxi | 60 | 76 | -0.211 | 0.004 |
Table 2 Statistical analysis of herbarium specimens of bamboos in different provinces of China
| 省份 Province | 物种数 Species | Chao 1 | 比值 Ratio | 斜率 Slope | 省份 Province | 物种数 Species | Chao 1 | 比值 Ratio | 斜率 Slope |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 安徽 Anhui | 46 | 118 | -0.610 | 0.005 | 内蒙古 Inner Mongolia | 3 | - | - | 0.067 |
| 北京 Beijing | 14 | 32 | -0.563 | 0.005 | 宁夏 Ningxia | 2 | - | - | 0.000 |
| 重庆 Chongqing | 45 | 48 | -0.063 | 0.002 | 青海 Qinghai | 1 | - | - | 0.200 |
| 福建 Fujian | 91 | 134 | -0.321 | 0.004 | 陕西 Shaanxi | 37 | 48 | -0.229 | 0.004 |
| 甘肃 Gansu | 25 | 42 | -0.405 | 0.004 | 山东 Shandong | 12 | 14 | -0.143 | 0.004 |
| 广东 Guangdong | 124 | 179 | -0.307 | 0.003 | 上海 Shanghai | 22 | 30 | -0.267 | 0.006 |
| 广西 Guangxi | 132 | 170 | -0.224 | 0.003 | 山西 Shanxi | 6 | 11 | -0.455 | 0.008 |
| 贵州 Guizhou | 99 | 133 | -0.256 | 0.003 | 四川 Sichuan | 112 | 189 | -0.407 | 0.004 |
| 海南 Hainan | 48 | 89 | -0.461 | 0.005 | 台湾 Taiwan | 25 | 63 | -0.603 | 0.006 |
| 河北 Heibei | 9 | 13 | -0.308 | 0.008 | 香港 Hong Kong | 25 | 25 | 0.000 | 0.001 |
| 河南 Henan | 46 | 56 | -0.179 | 0.002 | 西藏 Xizang | 31 | 55 | -0.436 | 0.005 |
| 湖北 Hubei | 48 | 64 | -0.250 | 0.003 | 云南 Yunnan | 255 | 280 | -0.089 | 0.002 |
| 湖南 Hunan | 101 | 135 | -0.252 | 0.004 | 浙江 Zhejiang | 125 | 157 | -0.204 | 0.003 |
| 江苏 Jiangsu | 59 | 77 | -0.234 | 0.003 | 总计 Total | 446 | 478 | -0.067 | 0.001 |
| 江西 Jiangxi | 60 | 76 | -0.211 | 0.004 |
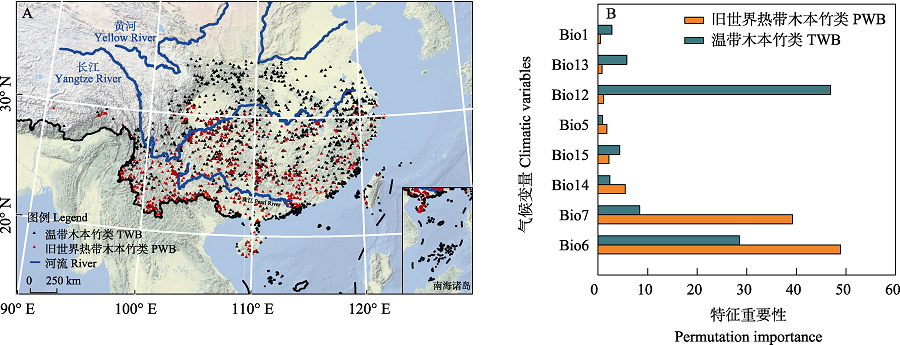
Fig. 3 Distribution map of bamboos in China (A) and permutation importance of the climatic variables (B). PWB, Paleotropical woody bamboos; TWB, Temperate woody bamboos; Bio1, Annual mean temperature; Bio5, Max temperature of warmest month; Bio6, Min temperature of the coldest month; Bio7, Temperature annual range; Bio12, Annual precipitation; Bio13, Precipitation of wettest month; Bio14, Precipitation of driest month; Bio15, Coefficient of variation of precipitation seasonality.
| [1] |
Boyle B, Hopkins N, Lu ZY, Raygoza Garay JA, Mozzherin D, Rees T, Matasci N, Narro ML, Piel WH, McKay SJ, Lowry S, Freeland C, Peet RK, Enquist BJ (2013) The taxonomic name resolution service: An online tool for automated stan-dardization of plant names. BMC Bioinformatics, 14, 16.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | Bridson D, Forman L (translated by Yao YJ, Xia NH, Li DZ, Li Y) (1998) The Herbarium Handbook, 3rd edn), pp. 184-242. Royal Botanic Gardens Kew. (in Chinese) |
| [ 姚一建, 夏念和, 李德铢, 李玉 (译) (1998) 标本馆手册(第3版), pp. 184-242. 英国邱园皇家植物园.] | |
| [3] | Chao A (1984) Nonparametric estimation of the number of classes in a population. Scandinavian Journal of Statistics, 11, 265-270. |
| [4] |
Chu C, Smith W, Solow A (2014) A hidden species-area curve. Environmental and Ecological Statistics, 21, 113-124.
DOI URL |
| [5] | Clark LG, Oliveira RP (2018) Diversity and evolution of the new world bamboos (Poaceae: Bambusoideae: Bambuseae, Olyreae). Keynote lecture in the 11th World Bamboo Congress, 14-18th August 2018. Xalapa, Mexico. |
| [6] |
Cui XY, Wang WJ, Yang XQ, Li S, Qin SY, Rong J (2016) Potential distribution of wild Camellia oleifera based on ecological niche modeling. Biodiversity Science, 24, 1117-1128. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 崔相艳, 王文娟, 杨小强, 李述, 秦声远, 戎俊 (2016) 基于生态位模型预测野生油茶的潜在分布. 生物多样性, 24, 1117-1128.] | |
| [7] |
GPWG (Grass Phylogeny Working Group) (2001) Phylogeny and subfamilial classification of the grasses (Poaceae). Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden, 88, 373-457.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
GPWG II (Grass Phylogeny Working Group II) (2012) New grass phylogeny resolves deep evolutionary relationships and discovers C4 origins. New Phytologist, 193, 304-312.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Guo ZH, Ma PF, Yang GQ, Hu JY, Liu YL, Xia EH, Zhong MC, Zhao L, Sun GL, Xu YX, Zhao YJ, Zhang YC, Zhang YX, Zhang XM, Zhou MY, Guo Y, Guo C, Liu JX, Ye XY, Chen YM, Yang Y, Han B, Lin CS, Lu Y, Li DZ (2019) Genome sequences provide insights into the reticulate origin and unique traits of woody bamboos. Molecular Plant, 12, 1353-1365.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
He X, Burgess KS, Gao LM, Li DZ (2019) Distributional responses to climate change for alpine species of Cyananthus and Primula endemic to the Himalaya-Hengduan Mountains. Plant Diversity, 41, 26-32.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Hijmans RJ, Cameron SE, Parra JL, Jones PG, Jarvis A (2005) Very high resolution interpolated climate surfaces for global land areas. International Journal of Climatology, 25, 1965-1978.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Janzen DH (1976) Why bamboos wait so long to flower? Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 7, 347-391.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Kelchner SA, Bamboo Phylogeny Group (BPG) (2013) Higher level phylogenetic relationships within the bamboos (Poaceae: Bambusoideae) based on five plastid markers. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 67, 404-413.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | Keng PC (1983) A revision of the genera of bamboos from the world (III). Journal of Bamboo Research, 2(1), 11-27. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 耿伯介 (1983) 世界竹亚科各属的考订(之三). 竹子研究汇刊, 2(1), 11-27.] | |
| [15] | Keng PC (1984) A revision of the genera of bamboos from the world (V). Journal of Bamboo Research, 3(1), 22-42. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 耿伯介 (1983) 世界竹亚科各属的考订(之五). 竹子研究汇刊, 3(1), 22-42.] | |
| [16] | Li DZ, Wang ZP, Zhu ZD, Xia NH, Jia LZ, Guo ZH, Yang GY, Stapleton CMA (2006) Bambuseae (Poaceae). In: Flora of China, Vol. 22 (eds Wu ZY, Raven PH, Hong DY), pp. 7-180. Science Press, Beijing & Missouri Botanical Garden Press, St. Louis. |
| [17] |
Liu CR, Berry PM, Dawson TP, Pearson RG (2005) Selecting thresholds of occurrence in the prediction of species distributions. Ecography, 28, 385-393.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Menard SW (2001) Applied Logistic Regression Analysis. Series: Quantitative Applications in the Social Sciences (Book 106), pp. 111. SAGE Publications, 2nd edition. |
| [19] |
McClure FA (1966) The bamboos: A fresh perspective. BioScience, 18, 129-130.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Nakai T (1931) Hokkaido Teikoku Daigaku Nogakubu Kiyo. Journal of the Faculty of Agriculture, 26, 180. |
| [21] |
Phillips SJ, Anderson RP, Schapire RE (2006) Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distributions. Ecological Modelling, 190, 231-259.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Saarela JM, Burke SV, Wysocki WP, Barrett MD, Clark LG, Craine JM, Peterson PM, Soreng RJ, Vorontsova MS, Duvall MR (2018) A 250 plastome phylogeny of the grass family (Poaceae): Topological support under different data partitions. PeerJ, 6, e4299.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Soderstrom TR, Young SM (1983) A guide to collecting bamboos. Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden, 70, 128-136.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Soreng RJ, Peterson PM, Romaschenko K, Davidse G, Teisher JK, Clark LG, Barberá P, Gillespie LJ, Zuloaga FO (2017) A worldwide phylogenetic classification of the Poaceae (Gramineae) II: An update and a comparison of two 2015 classifications. Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 55, 259-290.
DOI URL |
| [25] | Stapleton CMA (2004) Sarocalamus, a new Sino-Himalayan bamboo genus (Poaceae-Bambusoideae). Novon, 14, 346-347. |
| [26] |
Tittensor DP, Mora C, Jetz W, Lotze HK, Ricard D, Berghe EV, Worm B (2010) Global patterns and predictors of marine biodiversity across taxa. Nature, 466, 1098-1101.
DOI URL |
| [27] | Turland N, Wiersema J, Barrie F, Greuter W, Hawksworth D, Herendeen P, Knapp S, Kusber WH, Li DZ, Marhold K, May T, McNeill J, Monro A, Prado J, Price M, Smith G (2018) International Code of Nomenclature for Algae, Fungi, and Plants (Shenzhen Code). https://www.iapt-taxon.org/nomen/main.php. (accessed on 2019-01-27) |
| [28] | Vorontsova MS, Clark LG, Dransfield J, Govaerts R, Baker WJ (2016) World Checklist of Bamboos and Rattans, p. 102. Science Press, Beijing. |
| [29] | Wang KL, Chen JX, Fan X (2018) Analysis of geographical deviation of record collection of Rosaceae plant specimens in national specimen resource sharing platform. e-Science Technology & Application, 9(5), 54-63. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王凯莉, 陈佳欣, 范雪 (2018) 国家标本资源共享平台蔷薇科植物标本记录采集地理偏差分析. 科研信息化技术与应用, 9(5), 54-63.] | |
| [30] | Wang RZ, Li SJ, Zhang DX (2012) Statistical analyses of vascular plant specimen data from the herbarium of South China Botanical Garden, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IBSC). Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 20, 634-641. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王仁赞, 李世晋, 张奠湘 (2012) 中国科学院华南植物园标本馆维管植物标本数据统计分析. 热带亚热带植物学报, 20, 634-641.] | |
| [31] |
Wang YS, Xie BY, Wan FH, Xiao QM, Dai LY (2007) Application of ROC curve analysis in evaluating the performance of alien species’ potential distribution models. Biodiversity Science, 15, 365-372. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 王运生, 谢丙炎, 万方浩, 肖启明, 戴良英 (2007) ROC曲线分析在评价入侵物种分布模型中的应用. 生物多样性, 15, 365-372.] | |
| [32] |
Wong KM (1993) Four new genera of bamboos (Gramineae: Bambusoideae) from Malesia. Kew Bulletin, 48, 517-532.
DOI URL |
| [33] | Wu ZY (1980) Vegetation of China, pp. 411-416. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 吴征镒 (1980) 中国植被, 411-416页. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [34] | Yang WJ (2013) Geographical Sampling Bias in the Collections of Chinese Plants and Its Impacts on the Analysis of Biodiversity Patterns. PhD dissertation, Insititute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 阳文静 (2013) 中国植物采集的地理偏差及其对生物多样性格局分析的影响. 博士学位论文, 中国科学院植物研究所, 北京.] | |
| [35] |
Yang Y (2012) Holdings of type specimens of plants in herbaria of China. Biodiversity Science, 20, 512-516. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 杨永 (2012) 我国植物模式标本的馆藏量. 生物多样性, 20, 512-516.] | |
| [36] |
Zeng CX, Hollingsworth PM, Yang J, He ZS, Zhang ZR, Li DZ, Yang JB (2018) Genome skimming herbarium specimens for DNA barcoding and phylogenomics. Plant Methods, 14, 1-14.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Zhang YX, Ma PF, Li DZ (2018) A new genus of temperate woody bamboos (Poaceae, Bambusoideae, Arundinarieae) from a limestone montane area of China. PhytoKeys, 109, 67-76.
DOI URL |
| [38] | Zhang YX, Ren M, Xiao C (2018) The analysis of geographical bias of the collection of Chinese Rhododendraceae plants based on the data of National Specimen Information Infratructure. E-Science Technology & Application, 9(5), 72-83. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张玉雪, 任敏, 肖翠 (2018) 基于国家标本资源共享平台数据的中国杜鹃花科植物标本采集地理偏差分析. 科研信息化技术与应用, 9(5), 72-83.] |
| [1] | Jia Xu, Xiaojuan Cui, Yifei Zhang, Chang Wu, Yuandong Sun. Fish diversity and distribution in the Nanling region [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [2] | Shengxian Yang, Qing Yang, Xiaodong Li, Xin Chao, Huiqiu Liu, Lanruoxue Wei, Sang Ba. Deterministic processes dominate the geographic distribution pattern and community assembly of phytoplankton in typical plateau rivers [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(7): 23092-. |
| [3] | Yinger Mao, Xiumei Zhou, Nan Wang, Xiuxiu Li, Yuke You, Shangbin Bai. Impact of Phyllostachys edulis expansion to Chinese fir forest on the soil bacterial community [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2023, 31(6): 22659-. |
| [4] | Weinuo Liang, Liang Hu. Geographical distribution of freshwater and estuarial fish archaeological remains since the Neolithic Age in China and its biogeographical implications [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(8): 21471-. |
| [5] | Runming Yang, Akihiro Nakamura. Cavity-dwelling ants tend to colonize close to artificial light [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(8): 22067-. |
| [6] | Zhiwei Gao, Tianyu Qian, Jianping Jiang, Dejia Hou, Xuejian Deng, Daode Yang. Species diversity and distribution of amphibians and reptiles in Hunan Province, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(2): 21290-. |
| [7] | Jun Wang, Chao Zhao. Taxonomy, species diversity and distribution patterns of fungus-feeding Phlaeothripidae in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2022, 30(12): 22128-. |
| [8] | Junjie Li, Huanhuan Liu, Yangxue Wu, Lingda Zeng, Xiaolei Huang. A dataset on the diversity and geographical distributions of hemipteran insects in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(9): 1154-1158. |
| [9] | Renwu Wu, Xinge Nan, Hai Yan, Fan Yang, Yan Shi, Zhiyi Bao. On the history of the bamboo specimen collection in China by American plant collectors (1840-2010) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(7): 960-970. |
| [10] | Renwu Wu, Xinge Nan, Hai Yan, Fan Yang, Yan Shi, Zhiyi Bao. The history and influence of bamboo collection and introduction from China by Floyd Alonzo McClure [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(11): 1565-1575. |
| [11] | Gu Hanjiao, Zhang Cancan, Wang Jinsong, Shi Xuewen, Xia Ruixue, Liu Bin, Chen Fusheng, Bu Wensheng. Variation in basic morphological and functional traits of Chinese bamboo [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2019, 27(6): 585-594. |
| [12] | Yu Gao, Guanghui Lin. Algal diversity and their importance in ecological processes in typical mangrove ecosystems [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2018, 26(11): 1223-1235. |
| [13] | Ming Ouyang, Qingpei Yang, Xin Chen, Guangyao Yang, Jianmin Shi, Xiangmin Fang. Effects of the expansion of Phyllostachys edulis on species composition, structure and diversity of the secondary evergreen broad-leaved forests [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2016, 24(6): 649-657. |
| [14] | Yinbo Zhang, Jingxuan Fu, Yingli Liu, Fan Bai, Weiguo Sang. Delimiting protection redline of rare and endangered plants in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2015, 23(6): 733-739. |
| [15] | Guanghua Zhao,Yu Tian,Zhiyao Tang,Junsheng Li,Hui Zeng. Distribution of terrestrial national nature reserves in relation to human activities and natural environments in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2013, 21(6): 658-665. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn