



生物多样性 ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (11): 24181. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024181 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024181
李昕峪( ), 张雅璇(
), 张雅璇( ), 闫美辰(
), 闫美辰( ), 杨蕊含(
), 杨蕊含( ), 张小庆*(
), 张小庆*( )(
)( ), 姚志远*(
), 姚志远*( )(
)( )
)
收稿日期:2024-05-14
接受日期:2024-07-03
出版日期:2024-11-20
发布日期:2024-07-11
通讯作者:
E-mail: 基金资助:
Xinyu Li( ), Yaxuan Zhang(
), Yaxuan Zhang( ), Meichen Yan(
), Meichen Yan( ), Ruihan Yang(
), Ruihan Yang( ), Xiaoqing Zhang*(
), Xiaoqing Zhang*( )(
)( ), Zhiyuan Yao*(
), Zhiyuan Yao*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2024-05-14
Accepted:2024-07-03
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2024-07-11
Contact:
E-mail: Supported by:摘要:
本文总结了2023年全世界发表的现生蜘蛛目新分类单元。344位学者发表了75个国家和地区的1,311个新分类单元, 包括1新科70新属1,240新种, 隶属71科。这些新分类单元发表在63种刊物的315篇文章中, 其中科和属水平的修订、地区志或专著类的文章共有52篇, 占文章总数的16.5%; 运用DNA分子数据分析方法的论文共计53篇, 占文章总数的16.8%; 740个新种是基于雌雄两性标本发表, 占新种总数的59.7%, 500个新种仅基于雄或雌性标本发表, 占新种总数的40.3%。中国是2023年发现蜘蛛目新种最多的国家, 共412种, 占世界蜘蛛目新种总数的33.2%; 中国学者李枢强是2023年命名蜘蛛目新分类单元数量最多的学者, 共命名171个, 占世界新分类单元总数的13.0%。此外, 无论是命名蜘蛛目新分类单元数量还是参与命名新分类单元的学者数量, 均是中国学者位于第一。中国共有94位学者参与命名, 占世界新分类单元命名学者总数的27.3%; 这94位学者命名了中国和越南等11个国家和地区33个新属507个新种, 合计540个新分类单元, 命名新分类单元数量占世界41.2%, 该贡献率高于2022年的37.0%、2021年的33.8%和2016-2020年的平均贡献率28.1%。
李昕峪, 张雅璇, 闫美辰, 杨蕊含, 张小庆, 姚志远 (2024) 2023年世界现生蜘蛛目新分类单元. 生物多样性, 32, 24181. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024181.
Xinyu Li, Yaxuan Zhang, Meichen Yan, Ruihan Yang, Xiaoqing Zhang, Zhiyuan Yao (2024) New taxa of extant spiders (Araneae) from the world in 2023. Biodiversity Science, 32, 24181. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024181.
| 序号No. | 科名 Family name | 新属 New genus | 新种 New species | 新分类单元总数 Total number of new taxa | 序号 No. | 科名 Family name | 新属New genus | 新种New species | 新分类单元总数 Total number of new taxa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 线足蛛科 Actinopodidae | 0 | 7 | 7 | 37 | 狼蛛科 Lycosidae | 6 | 39 | 45 |
| 2 | 漏斗蛛科 Agelenidae | 5 | 29 | 34 | 38 | 拟态蛛科 Mimetidae | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | 暗蛛科 Amaurobiidae | 0 | 3 | 3 | 39 | 米图蛛科 Miturgidae | 5 | 52 | 57 |
| 4 | 阿南蛛科 Anamidae | 0 | 32 | 32 | 40 | 密蛛科 Mysmenidae | 1 | 23 | 24 |
| 5 | 近管蛛科 Anyphaenidae | 0 | 27 | 27 | 41 | 线蛛科 Nemesiidae | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| 6 | 园蛛科 Araneidae | 4 | 22 | 26 | 42 | 类球蛛科 Nesticidae | 0 | 18 | 18 |
| 7 | 螯耙蛛科 Barychelidae | 0 | 6 | 6 | 43 | 花洞蛛科 Ochyroceratidae | 0 | 4 | 4 |
| 8 | 本梅蛛科 Bemmeridae | 0 | 3 | 3 | 44 | 拟壁钱科 Oecobiidae | 0 | 6 | 6 |
| 9 | 开普蛛科 Caponiidae | 1 | 3 | 4 | 45 | 卵形蛛科 Oonopidae | 0 | 52 | 52 |
| 10 | 红螯蛛科 Cheiracanthiidae | 0 | 6 | 6 | 46 | 激蛛科 Orsolobidae | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 11 | 洞叶蛛科 Cicurinidae | 0 | 1 | 1 | 47 | 猫蛛科 Oxyopidae | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 12 | 管巢蛛科 Clubionidae | 0 | 7 | 7 | 48 | 二纺蛛科 Palpimanidae | 0 | 5 | 5 |
| 13 | 圆颚蛛科 Corinnidae | 2 | 21 | 23 | 49 | 鳞毛蛛科 Paratropididae | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| 14 | 栉足蛛科 Ctenidae | 0 | 10 | 10 | 50 | 逍遥蛛科 Philodromidae | 0 | 5 | 5 |
| 15 | 并齿蛛科 Cybaeidae | 3 | 7 | 10 | 51 | 幽灵蛛科 Pholcidae | 0 | 50 | 50 |
| 16 | 弓蛛科 Cyrtaucheniidae | 0 | 15 | 15 | 52 | 刺足蛛科 Phrurolithidae | 4 | 54 | 58 |
| 17 | 妖面蛛科 Deinopidae | 0 | 1 | 1 | 53 | 派模蛛科 Pimoidae | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 18 | 潮蛛科 Desidae | 0 | 12 | 12 | 54 | 盗蛛科 Pisauridae | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| 19 | 卷叶蛛科 Dictynidae | 0 | 7 | 7 | 55 | 距蛛科 Plectreuridae | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 20 | 长尾蛛科 Dipluridae | 0 | 45 | 45 | 56 | 褛网蛛科 Psechridae | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 21 | 丛蛛科 Drymusidae | 0 | 2 | 2 | 57 | 厚疣蛛科 Pycnothelidae | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 22 | 石蛛科 Dysderidae | 0 | 46 | 46 | 58 | 跳蛛科 Salticidae | 10 | 173 | 183 |
| 23 | 内迹蛛科 Entypesidae | 1 | 1 | 2 | 59 | 花皮蛛科 Scytodidae | 0 | 13 | 13 |
| 24 | 隆头蛛科 Eresidae | 0 | 1 | 1 | 60 | 拟扁蛛科 Selenopidae | 0 | 20 | 20 |
| 25 | 管网蛛科 Filistatidae | 0 | 2 | 2 | 61 | 巨蟹蛛科 Sparassidae | 2 | 128 | 130 |
| 26 | 丰特蛛科 Fonteferreidae* | 1 | 1 | 3 | 62 | 斯塔蛛科 Stasimopidae | 0 | 9 | 9 |
| 27 | 平腹蛛科 Gnaphosidae | 5 | 29 | 34 | 63 | 泰莱蛛科 Telemidae | 0 | 3 | 3 |
| 28 | 栅蛛科 Hahniidae | 0 | 13 | 13 | 64 | 肖蛸蛛科 Tetragnathidae | 0 | 5 | 5 |
| 29 | 盘腹蛛科 Halonoproctidae | 0 | 3 | 3 | 65 | 捕鸟蛛科 Theraphosidae | 8 | 58 | 66 |
| 30 | 七纺器蛛科 Heptathelidae | 0 | 6 | 6 | 66 | 球蛛科 Theridiidae | 0 | 10 | 10 |
| 31 | 小合蛛科 Hexurellidae | 0 | 4 | 4 | 67 | 球体蛛科 Theridiosomatidae | 2 | 8 | 10 |
| 32 | 异蛛科 Idiopidae | 0 | 1 | 1 | 68 | 蟹蛛科 Thomisidae | 0 | 16 | 16 |
| 33 | 弱蛛科 Leptonetidae | 0 | 7 | 7 | 69 | 管蛛科 Trachelidae | 0 | 5 | 5 |
| 34 | 皿蛛科 Linyphiidae | 5 | 49 | 54 | 70 | 妩蛛科 Uloboridae | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 35 | 光盔蛛科 Liocranidae | 1 | 7 | 8 | 71 | 拟平腹蛛科 Zodariidae | 0 | 24 | 24 |
| 36 | 节板蛛科 Liphistiidae | 0 | 3 | 3 | 合计 Total | 70 | 1,240 | 1,311 |
表1 2023年世界现生蜘蛛目新分类单元数
Table 1 Number of global new taxa of extant Araneae in 2023
| 序号No. | 科名 Family name | 新属 New genus | 新种 New species | 新分类单元总数 Total number of new taxa | 序号 No. | 科名 Family name | 新属New genus | 新种New species | 新分类单元总数 Total number of new taxa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 线足蛛科 Actinopodidae | 0 | 7 | 7 | 37 | 狼蛛科 Lycosidae | 6 | 39 | 45 |
| 2 | 漏斗蛛科 Agelenidae | 5 | 29 | 34 | 38 | 拟态蛛科 Mimetidae | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | 暗蛛科 Amaurobiidae | 0 | 3 | 3 | 39 | 米图蛛科 Miturgidae | 5 | 52 | 57 |
| 4 | 阿南蛛科 Anamidae | 0 | 32 | 32 | 40 | 密蛛科 Mysmenidae | 1 | 23 | 24 |
| 5 | 近管蛛科 Anyphaenidae | 0 | 27 | 27 | 41 | 线蛛科 Nemesiidae | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| 6 | 园蛛科 Araneidae | 4 | 22 | 26 | 42 | 类球蛛科 Nesticidae | 0 | 18 | 18 |
| 7 | 螯耙蛛科 Barychelidae | 0 | 6 | 6 | 43 | 花洞蛛科 Ochyroceratidae | 0 | 4 | 4 |
| 8 | 本梅蛛科 Bemmeridae | 0 | 3 | 3 | 44 | 拟壁钱科 Oecobiidae | 0 | 6 | 6 |
| 9 | 开普蛛科 Caponiidae | 1 | 3 | 4 | 45 | 卵形蛛科 Oonopidae | 0 | 52 | 52 |
| 10 | 红螯蛛科 Cheiracanthiidae | 0 | 6 | 6 | 46 | 激蛛科 Orsolobidae | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 11 | 洞叶蛛科 Cicurinidae | 0 | 1 | 1 | 47 | 猫蛛科 Oxyopidae | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 12 | 管巢蛛科 Clubionidae | 0 | 7 | 7 | 48 | 二纺蛛科 Palpimanidae | 0 | 5 | 5 |
| 13 | 圆颚蛛科 Corinnidae | 2 | 21 | 23 | 49 | 鳞毛蛛科 Paratropididae | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| 14 | 栉足蛛科 Ctenidae | 0 | 10 | 10 | 50 | 逍遥蛛科 Philodromidae | 0 | 5 | 5 |
| 15 | 并齿蛛科 Cybaeidae | 3 | 7 | 10 | 51 | 幽灵蛛科 Pholcidae | 0 | 50 | 50 |
| 16 | 弓蛛科 Cyrtaucheniidae | 0 | 15 | 15 | 52 | 刺足蛛科 Phrurolithidae | 4 | 54 | 58 |
| 17 | 妖面蛛科 Deinopidae | 0 | 1 | 1 | 53 | 派模蛛科 Pimoidae | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 18 | 潮蛛科 Desidae | 0 | 12 | 12 | 54 | 盗蛛科 Pisauridae | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| 19 | 卷叶蛛科 Dictynidae | 0 | 7 | 7 | 55 | 距蛛科 Plectreuridae | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 20 | 长尾蛛科 Dipluridae | 0 | 45 | 45 | 56 | 褛网蛛科 Psechridae | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 21 | 丛蛛科 Drymusidae | 0 | 2 | 2 | 57 | 厚疣蛛科 Pycnothelidae | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 22 | 石蛛科 Dysderidae | 0 | 46 | 46 | 58 | 跳蛛科 Salticidae | 10 | 173 | 183 |
| 23 | 内迹蛛科 Entypesidae | 1 | 1 | 2 | 59 | 花皮蛛科 Scytodidae | 0 | 13 | 13 |
| 24 | 隆头蛛科 Eresidae | 0 | 1 | 1 | 60 | 拟扁蛛科 Selenopidae | 0 | 20 | 20 |
| 25 | 管网蛛科 Filistatidae | 0 | 2 | 2 | 61 | 巨蟹蛛科 Sparassidae | 2 | 128 | 130 |
| 26 | 丰特蛛科 Fonteferreidae* | 1 | 1 | 3 | 62 | 斯塔蛛科 Stasimopidae | 0 | 9 | 9 |
| 27 | 平腹蛛科 Gnaphosidae | 5 | 29 | 34 | 63 | 泰莱蛛科 Telemidae | 0 | 3 | 3 |
| 28 | 栅蛛科 Hahniidae | 0 | 13 | 13 | 64 | 肖蛸蛛科 Tetragnathidae | 0 | 5 | 5 |
| 29 | 盘腹蛛科 Halonoproctidae | 0 | 3 | 3 | 65 | 捕鸟蛛科 Theraphosidae | 8 | 58 | 66 |
| 30 | 七纺器蛛科 Heptathelidae | 0 | 6 | 6 | 66 | 球蛛科 Theridiidae | 0 | 10 | 10 |
| 31 | 小合蛛科 Hexurellidae | 0 | 4 | 4 | 67 | 球体蛛科 Theridiosomatidae | 2 | 8 | 10 |
| 32 | 异蛛科 Idiopidae | 0 | 1 | 1 | 68 | 蟹蛛科 Thomisidae | 0 | 16 | 16 |
| 33 | 弱蛛科 Leptonetidae | 0 | 7 | 7 | 69 | 管蛛科 Trachelidae | 0 | 5 | 5 |
| 34 | 皿蛛科 Linyphiidae | 5 | 49 | 54 | 70 | 妩蛛科 Uloboridae | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 35 | 光盔蛛科 Liocranidae | 1 | 7 | 8 | 71 | 拟平腹蛛科 Zodariidae | 0 | 24 | 24 |
| 36 | 节板蛛科 Liphistiidae | 0 | 3 | 3 | 合计 Total | 70 | 1,240 | 1,311 |
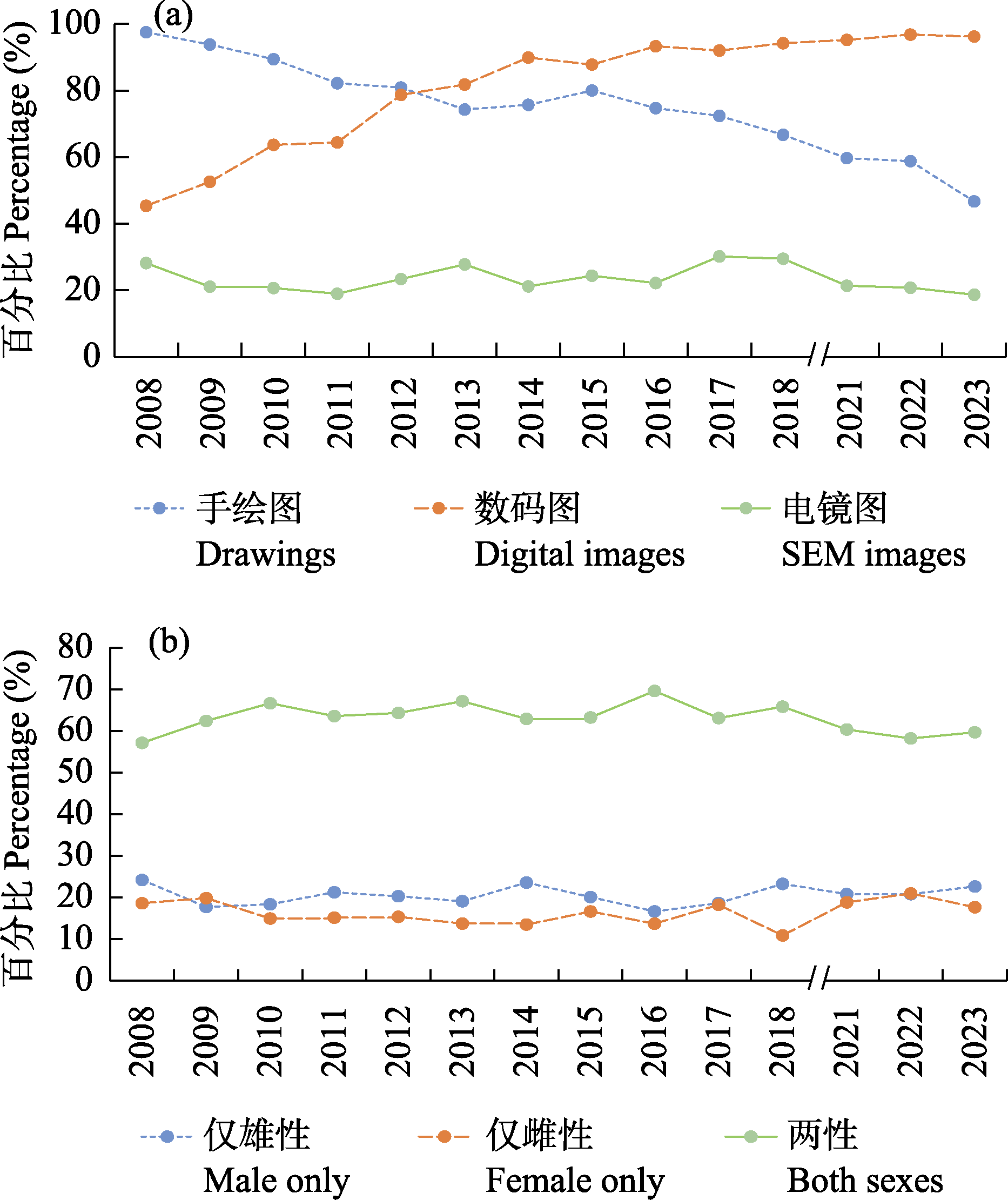
图2 2008-2018年和2021-2023年世界现生蜘蛛目特征图类型和物种性别。a: 手绘图、数码图和电镜图类型论文数量的百分比; b: 单性和两性新种数量的百分比。2008-2018年、2021年和2022年论文中的特征图类型和物种性别数据分别来自Bond等(2022)、张露丹等(2022)和杨蕊含等(2023)。
Fig. 2 Illustration techniques and sexes featured in the descriptions of extant Araneae in 2008-2018 and 2021-2023. a, Percentage of publications based on illustration techniques; b, Percentage of new species described based on sex. Data on illustration techniques and species sexes in 2008-2018, 2021, and 2022 papers are from Bond et al (2022), Zhang et al (2022) and Yang et al (2023), respectively.
| 排名 Ranking | 命名人 Author | 姓名 Name | 新属 New genus | 新种 New species | 总数 Total | 排名 Ranking | 命名人 Author | 姓名 Name | 新属 New genus | 新种 New species | 总数 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Li/S.Q. Li/S. Li | 李枢强 Shuqiang Li | 20 | 151 | 171 | 39 | Řezáč | Milan Řezáč | 1 | 19 | 20 |
| 2 | Jäger | Peter Jäger | 0 | 102 | 102 | 40 | Yang | 杨素芳 Sufang Yang | 0 | 19 | 19 |
| 3 | Liu | 刘杰 Jie Liu | 0 | 99 | 99 | 41 | Pham | Dinh Pham | 1 | 17 | 18 |
| 3 | Zhang | 张贺 He Zhang | 0 | 99 | 99 | 41 | Q. Zhang | 张秋秋 Qiuqiu Zhang | 0 | 18 | 18 |
| 5 | Lin | 林业杰 Yejie Lin | 9 | 64 | 73 | 41 | Yao | 姚志远 Zhiyuan Yao | 0 | 18 | 18 |
| 6 | Dupérré | Nadine Dupérré | 0 | 65 | 65 | 44 | Peñaherrera-R | Pedro Peñaherrera-R | 1 | 16 | 17 |
| 7 | Raven | Robert Raven | 5 | 55 | 60 | 45 | Li/B. Li | 李冰 Bing Li | 2 | 14 | 16 |
| 7 | Wang/C. Wang | 王成 Cheng Wang | 4 | 56 | 60 | 45 | Szűts | Tamás Szűts | 0 | 16 | 16 |
| 9 | Zhang/F. Zhang | 张锋 Feng Zhang | 3 | 55 | 58 | 47 | Rheims | Cristina Rheims | 2 | 13 | 15 |
| 10 | Bonaldo | Alexandre Bonaldo | 1 | 50 | 51 | 47 | Maddison | Wayne Maddison | 1 | 14 | 15 |
| 10 | Peng | 彭贤锦 Xianjin Peng | 1 | 50 | 51 | 47 | Rubio | Gonzalo Rubio | 0 | 15 | 15 |
| 10 | Tapia | Elicio Tapia | 0 | 51 | 51 | 50 | Lu | 卢影 Ying Lu | 2 | 12 | 14 |
| 13 | Zhang/Z.S. Zhang | 张志升 Zhisheng Zhang | 6 | 43 | 49 | 50 | Wang | 王苇杭 Weihang Wang | 1 | 13 | 14 |
| 14 | Zhang | 张俊霞 Junxia Zhang | 3 | 45 | 48 | 50 | Hedin | Marshal Hedin | 0 | 14 | 14 |
| 15 | Wang | 王露雨 Luyu Wang | 5 | 39 | 44 | 53 | Kaderka | Radan Kaderka | 1 | 12 | 13 |
| 16 | Marusik | Yuri Marusik | 2 | 37 | 39 | 53 | Fomichev | Alexander Fomichev | 0 | 13 | 13 |
| 17 | Mi | 米小其 Xiaoqi Mi | 0 | 38 | 38 | 53 | Tong | 佟艳丰 Yanfeng Tong | 0 | 13 | 13 |
| 18 | Yu | 余锟 Kun Yu | 3 | 33 | 36 | 56 | Guadanucci | José Guadanucci | 3 | 9 | 12 |
| 18 | Ott | Ricardo Ott | 0 | 36 | 36 | 56 | Hüsser | Martin Hüsser | 1 | 11 | 12 |
| 20 | Feitosa | Níthomas Feitosa | 0 | 35 | 35 | 56 | León-E | Roberto León-E | 1 | 11 | 12 |
| 21 | Brescovit | Antonio Brescovit | 2 | 31 | 33 | 56 | Liu/K.K. Liu | 刘科科 Keke Liu | 1 | 11 | 12 |
| 22 | Harvey | Mark Harvey | 0 | 32 | 32 | 56 | Lüddecke | Tim Lüddecke | 1 | 11 | 12 |
| 22 | Huber | Bernhard Huber | 0 | 32 | 32 | 56 | Řezáčová | Veronika Řezáčová | 1 | 11 | 12 |
| 22 | Rix | Michael Rix | 0 | 32 | 32 | 56 | Yu | 喻浩 Hao Yu | 1 | 11 | 12 |
| 22 | Wilson | Jeremy Wilson | 0 | 32 | 32 | 56 | Bertani | Rogério Bertani | 0 | 12 | 12 |
| 26 | Sherwood | Danniella Sherwood | 5 | 26 | 31 | 64 | Casas | Cristian Casas | 1 | 10 | 11 |
| 27 | Irfan | Muhammad Irfan | 4 | 26 | 30 | 64 | Tanasevitch | Andrei Tanasevitch | 1 | 10 | 11 |
| 27 | Lin | 林玉成 Yucheng Lin | 2 | 28 | 30 | 64 | Caleb | John Caleb | 0 | 11 | 11 |
| 27 | Zamani | Alireza Zamani | 1 | 29 | 30 | 64 | Esposito | Lauren Esposito | 0 | 11 | 11 |
| 27 | Crews | Sarah Crews | 0 | 30 | 30 | 64 | Griswold | Charles Griswold | 0 | 11 | 11 |
| 31 | Framenau | Volker Framenau | 4 | 25 | 29 | 64 | Morrill | Elizabeth Morrill | 0 | 11 | 11 |
| 31 | Mu | 母炎楠 Yannan Mu | 2 | 27 | 29 | 64 | Ramírez | Martín Ramírez | 0 | 11 | 11 |
| 33 | Yoo | Jung Sun Yoo | 1 | 25 | 26 | 71 | Lyle | Robin Lyle | 1 | 9 | 10 |
| 34 | Castanheira | Pedro Castanheira | 4 | 21 | 25 | 71 | Jang | Chang Moon Jang | 0 | 10 | 10 |
| 35 | Logunov | Dmitri Logunov | 3 | 20 | 23 | 71 | Kim | Seung Tae Kim | 0 | 10 | 10 |
| 35 | Wunderlich | Joerg Wunderlich | 2 | 21 | 23 | 71 | Kunt | Kadir Kunt | 0 | 10 | 10 |
| 37 | Álvarez-Padilla | Fernando Álvarez- Padilla | 0 | 21 | 21 | 71 | Milne | Marc Milne | 0 | 10 | 10 |
| 37 | Rivera-Quiroz | Francisco Rivera- Quiroz | 0 | 21 | 21 |
表2 2023年全世界命名蜘蛛目新分类单元10个及以上的学者
Table 2 Arachnologists who published 10 and more new taxa of Araneae in 2023
| 排名 Ranking | 命名人 Author | 姓名 Name | 新属 New genus | 新种 New species | 总数 Total | 排名 Ranking | 命名人 Author | 姓名 Name | 新属 New genus | 新种 New species | 总数 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Li/S.Q. Li/S. Li | 李枢强 Shuqiang Li | 20 | 151 | 171 | 39 | Řezáč | Milan Řezáč | 1 | 19 | 20 |
| 2 | Jäger | Peter Jäger | 0 | 102 | 102 | 40 | Yang | 杨素芳 Sufang Yang | 0 | 19 | 19 |
| 3 | Liu | 刘杰 Jie Liu | 0 | 99 | 99 | 41 | Pham | Dinh Pham | 1 | 17 | 18 |
| 3 | Zhang | 张贺 He Zhang | 0 | 99 | 99 | 41 | Q. Zhang | 张秋秋 Qiuqiu Zhang | 0 | 18 | 18 |
| 5 | Lin | 林业杰 Yejie Lin | 9 | 64 | 73 | 41 | Yao | 姚志远 Zhiyuan Yao | 0 | 18 | 18 |
| 6 | Dupérré | Nadine Dupérré | 0 | 65 | 65 | 44 | Peñaherrera-R | Pedro Peñaherrera-R | 1 | 16 | 17 |
| 7 | Raven | Robert Raven | 5 | 55 | 60 | 45 | Li/B. Li | 李冰 Bing Li | 2 | 14 | 16 |
| 7 | Wang/C. Wang | 王成 Cheng Wang | 4 | 56 | 60 | 45 | Szűts | Tamás Szűts | 0 | 16 | 16 |
| 9 | Zhang/F. Zhang | 张锋 Feng Zhang | 3 | 55 | 58 | 47 | Rheims | Cristina Rheims | 2 | 13 | 15 |
| 10 | Bonaldo | Alexandre Bonaldo | 1 | 50 | 51 | 47 | Maddison | Wayne Maddison | 1 | 14 | 15 |
| 10 | Peng | 彭贤锦 Xianjin Peng | 1 | 50 | 51 | 47 | Rubio | Gonzalo Rubio | 0 | 15 | 15 |
| 10 | Tapia | Elicio Tapia | 0 | 51 | 51 | 50 | Lu | 卢影 Ying Lu | 2 | 12 | 14 |
| 13 | Zhang/Z.S. Zhang | 张志升 Zhisheng Zhang | 6 | 43 | 49 | 50 | Wang | 王苇杭 Weihang Wang | 1 | 13 | 14 |
| 14 | Zhang | 张俊霞 Junxia Zhang | 3 | 45 | 48 | 50 | Hedin | Marshal Hedin | 0 | 14 | 14 |
| 15 | Wang | 王露雨 Luyu Wang | 5 | 39 | 44 | 53 | Kaderka | Radan Kaderka | 1 | 12 | 13 |
| 16 | Marusik | Yuri Marusik | 2 | 37 | 39 | 53 | Fomichev | Alexander Fomichev | 0 | 13 | 13 |
| 17 | Mi | 米小其 Xiaoqi Mi | 0 | 38 | 38 | 53 | Tong | 佟艳丰 Yanfeng Tong | 0 | 13 | 13 |
| 18 | Yu | 余锟 Kun Yu | 3 | 33 | 36 | 56 | Guadanucci | José Guadanucci | 3 | 9 | 12 |
| 18 | Ott | Ricardo Ott | 0 | 36 | 36 | 56 | Hüsser | Martin Hüsser | 1 | 11 | 12 |
| 20 | Feitosa | Níthomas Feitosa | 0 | 35 | 35 | 56 | León-E | Roberto León-E | 1 | 11 | 12 |
| 21 | Brescovit | Antonio Brescovit | 2 | 31 | 33 | 56 | Liu/K.K. Liu | 刘科科 Keke Liu | 1 | 11 | 12 |
| 22 | Harvey | Mark Harvey | 0 | 32 | 32 | 56 | Lüddecke | Tim Lüddecke | 1 | 11 | 12 |
| 22 | Huber | Bernhard Huber | 0 | 32 | 32 | 56 | Řezáčová | Veronika Řezáčová | 1 | 11 | 12 |
| 22 | Rix | Michael Rix | 0 | 32 | 32 | 56 | Yu | 喻浩 Hao Yu | 1 | 11 | 12 |
| 22 | Wilson | Jeremy Wilson | 0 | 32 | 32 | 56 | Bertani | Rogério Bertani | 0 | 12 | 12 |
| 26 | Sherwood | Danniella Sherwood | 5 | 26 | 31 | 64 | Casas | Cristian Casas | 1 | 10 | 11 |
| 27 | Irfan | Muhammad Irfan | 4 | 26 | 30 | 64 | Tanasevitch | Andrei Tanasevitch | 1 | 10 | 11 |
| 27 | Lin | 林玉成 Yucheng Lin | 2 | 28 | 30 | 64 | Caleb | John Caleb | 0 | 11 | 11 |
| 27 | Zamani | Alireza Zamani | 1 | 29 | 30 | 64 | Esposito | Lauren Esposito | 0 | 11 | 11 |
| 27 | Crews | Sarah Crews | 0 | 30 | 30 | 64 | Griswold | Charles Griswold | 0 | 11 | 11 |
| 31 | Framenau | Volker Framenau | 4 | 25 | 29 | 64 | Morrill | Elizabeth Morrill | 0 | 11 | 11 |
| 31 | Mu | 母炎楠 Yannan Mu | 2 | 27 | 29 | 64 | Ramírez | Martín Ramírez | 0 | 11 | 11 |
| 33 | Yoo | Jung Sun Yoo | 1 | 25 | 26 | 71 | Lyle | Robin Lyle | 1 | 9 | 10 |
| 34 | Castanheira | Pedro Castanheira | 4 | 21 | 25 | 71 | Jang | Chang Moon Jang | 0 | 10 | 10 |
| 35 | Logunov | Dmitri Logunov | 3 | 20 | 23 | 71 | Kim | Seung Tae Kim | 0 | 10 | 10 |
| 35 | Wunderlich | Joerg Wunderlich | 2 | 21 | 23 | 71 | Kunt | Kadir Kunt | 0 | 10 | 10 |
| 37 | Álvarez-Padilla | Fernando Álvarez- Padilla | 0 | 21 | 21 | 71 | Milne | Marc Milne | 0 | 10 | 10 |
| 37 | Rivera-Quiroz | Francisco Rivera- Quiroz | 0 | 21 | 21 |
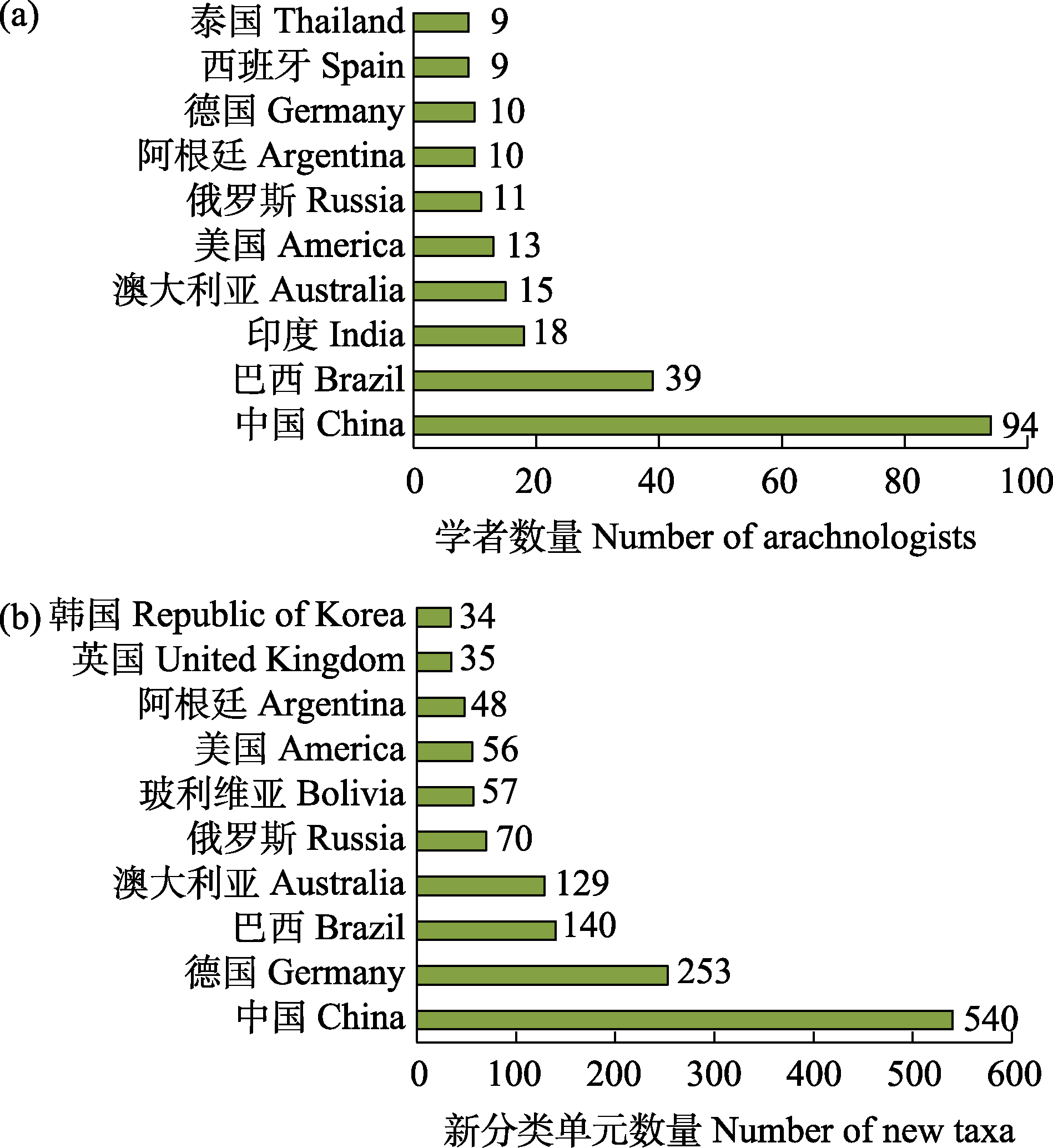

图3 2023年参与蜘蛛目新分类单元命名的学者情况。a: 2023年参与蜘蛛目新分类单元命名的学者数量位于前10位的国家; b: 2023年各国学者命名蜘蛛目新分类单元数量位于前10位的国家。
Fig. 3 Arachnologists describing new taxa in 2023. a, Top 10 countries with the largest number of arachnologists describing new taxa in 2023; b, Top 10 countries of origin of the most prolific arachnologists describing new taxa in 2023.
| [1] | Ballarin F, Eguchi K (2023) Integrative taxonomic revision of the genera Nesticella and Howaia in Japan with the description of five new species (Araneae, Nesticidae, Nesticellini). ZooKeys, 1174, 219-272. |
| [2] |
Bertani R (2023) Taxonomic revision and cladistic analysis of Lasiodora CL Koch, 1850 (Araneae, Theraphosidae) with notes on related genera. Zootaxa, 5390, 1-116.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | Bond JE, Godwin RL, Colby JD, Newton LG, Zahnle XJ, Agnarsson I, Hamilton CA, Kuntner M (2022) Improving taxonomic practices and enhancing its extensibility—An example from araneology. Diversity, 14, 5. |
| [4] | Crews SC (2023) But wait, there’s more! Descriptions of new species and undescribed sexes of flattie spiders (Araneae, Selenopidae, Karaops) from Australia. ZooKeys, 1150, 1-189. |
| [5] | Dupérré N, Tapia E, Bond JE (2023) Review of the spider genus Linothele (Mygalomorphae, Dipluridae) from Ecuador-An exceptional case of speciation in the Andes. Arthropoda, 1, 68-341. |
| [6] | García F, Bonaldo AB (2023) Taxonomic revision of the soldier spider genus Falconina Brignoli, 1985 (Araneae: Corinnidae: Corinninae). Zootaxa, 5343, 201-242. |
| [7] | Huber BA, Meng GL, Dupérré N, Herrera M, Inclán DJ, Wipfler B (2023) Humpback spiders from Ecuador: relationships, prosoma ‘inflation’, and genital asymmetry (Araneae: Pholcidae: Mecolaesthus). Invertebrate Systematics, 37, 117-151. |
| [8] | Jäger P (2023) Revision of the huntsman spider genus Micrommata Latreille, 1804 (Sparassidae: Sparassinae). Zootaxa, 5352, 1-45. |
| [9] |
Jiang JP, Du C, Liu B, Wang K, Cai L, Li Q, Huang XL (2022) Bio-inventory in China: Progress and perspectives. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22531. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [江建平, 杜诚, 刘冰, 王科, 蔡磊, 李强, 黄晓磊 (2022) 中国生物物种编目进展与展望. 生物多样性, 10, 22531.] | |
| [10] |
Ma KP (2015) Species catalogue of China: A remarkable achievement in the field of biodiversity science in China. Biodiversity Science, 23, 137-138. (in Chinese)
DOI |
| [马克平 (2015) 中国生物多样性编目取得重要进展. 生物多样性, 23, 137-138.] | |
| [11] | Mu YN, Zhang F (2023) Further additions to the guardstone spider fauna from China (Araneae: Phrurolithidae). Zootaxa, 5338, 1-104, Erratum, 5346, 599-600. |
| [12] | Rivera-Quiroz FA, Álvarez-Padilla F (2023) Integration or minimalism: Twenty-one new species of ghost spiders (Anyphaenidae: Anyphaena) from Mexico. European Journal of Taxonomy, 865, 1-94. |
| [13] | Wang C, Mi XQ, Wang WH, Gan JH, Irfan M, Zhong Y, Peng XJ (2023) Notes on twenty-nine species of jumping spiders from South China (Araneae: Salticidae). European Journal of Taxonomy, 902, 1-91. |
| [14] | WSC (2024) World Spider Catalog, Version 25.0. Natural History Museum Bern. http://wsc.nmbe.ch. (accessed on 2024-05-12) |
| [15] |
Yang RH, Yan MC, Zhang LD, Liu HX, Koh JKH, He QQ, Yao ZY (2023) New taxa of spiders (Araneae) from the world in 2022. Biodiversity Science, 31, 23175. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[杨蕊含, 闫美辰, 张露丹, 刘宏鑫, 许国丰, 何巧巧, 姚志远 (2023) 2022年世界蜘蛛目新分类单元. 生物多样性, 31, 23175.]
DOI |
|
| [16] | Yao ZY, Li SQ (2021) Annual report of Chinese spider taxonomy in 2020. Biodiversity Science, 29, 1058-1063. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [姚志远, 李枢强 (2021) 2020年中国蜘蛛分类年报. 生物多样性, 29, 1058-1063.] | |
| [17] | Yu K, Hoang QD, Maddison WP, Zhang JX (2023) Review of Chalcovietnamicus Marusik, 1991, with description of four new species (Araneae, Salticidae, Euophryini). Zootaxa, 5336, 451-480. |
| [18] |
Zhang LD, Lu Y, Chu C, He QQ, Yao ZY (2022) New spider taxa of the world in 2021. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22163. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[张露丹, 卢影, 褚畅, 何巧巧, 姚志远 (2022) 2021年世界蜘蛛新分类单元. 生物多样性, 30, 22163.]
DOI |
|
| [19] | Zhang QQ, Li Y, Lin YC, Li SQ, Yao ZY, Zhang XQ (2023) Regression of East Tethys resulted in a center of biodiversity: A study of Mysmenidae spiders from the Gaoligong Mountains, China. Zoological Research, 44, 737-738. |
| [20] | Zhao FY, Yang L, Zou QX, Ali A, Li SQ, Yao ZY (2023) Diversity of Pholcus spiders (Araneae: Pholcidae) in China’s Lüliang Mountains: An integrated morphological and molecular approach. Insects, 14, 364. |
| [1] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | 周璇, 张生芳, 刘宁, 鲁玉杰, 郑斯竹, 杨晓军, 路园园, 刘梅柯, 白明. 储藏物甲虫系统地位厘清及拉英汉名录更新[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24238-. |
| [10] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [11] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [12] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [13] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [14] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [15] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()