



生物多样性 ›› 2024, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (6): 24044. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024044 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2024044
连佳丽, 陈婧, 杨雪琴, 赵莹, 罗叙, 韩翠, 赵雅欣, 李建平*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-01-31
接受日期:2024-05-15
出版日期:2024-06-20
发布日期:2024-05-30
通讯作者:
* E-mail: lijianpingsas@163.com基金资助:
Jiali Lian, Jing Chen, Xueqin Yang, Ying Zhao, Xu Luo, Cui Han, Yaxin Zhao, Jianping Li*( )
)
Received:2024-01-31
Accepted:2024-05-15
Online:2024-06-20
Published:2024-05-30
Contact:
* E-mail: lijianpingsas@163.com摘要:
降水和生物多样性是维持干旱区荒漠草原生态系统平衡和稳定的关键因素, 研究降水变化背景下荒漠草原植物多样性、微生物多样性以及二者相互关系具有重要的理论和实践意义。本文以宁夏盐池荒漠草原为研究对象, 采用遮雨棚和滴灌技术模拟了5个降水梯度, 分别为正常降雨量的33%、66%、100% (CK)、133%和166% (记为R33, R66, RCK, R133, R166), 全面分析了降水变化对荒漠草原植物多样性和微生物多样性的影响。结果表明: (1)降水减少(R66)会显著降低植物群落的多样性和均匀度, 降水增加(R133)会使植物群落丰富度显著增加(P < 0.05); (2)细菌群落的Shannon-Wiener指数、Simpson指数、Ace指数以及真菌群落的Ace指数随降雨量的增加显著增加, 降水变化对真菌群落的Shannon-Wiener指数和Simpson指数影响显著(P < 0.05); (3)增水处理对土壤微生物群落β多样性有显著影响; (4)细菌与土壤碳氮比、碳磷比之间存在显著正相关关系(P < 0.05), 真菌与土壤碳氮比、碳磷比及氮磷比之间均存在极显著正相关关系(P < 0.01); (5)植物群落多样性与细菌Shannon-Wiener指数显著正相关, 与细菌Simpson指数、Ace指数及真菌Ace指数显著负相关(P < 0.05)。因此, 降水变化对荒漠草原植物多样性和微生物多样性产生了显著影响, 且二者之间存在紧密关联, 这不仅为模拟和预测荒漠草原生态系统对气候变化的响应和反馈提供借鉴, 也为该地区的生态保护和恢复提供了科学依据。
中图分类号:
连佳丽, 陈婧, 杨雪琴, 赵莹, 罗叙, 韩翠, 赵雅欣, 李建平 (2024) 荒漠草原植物多样性和微生物多样性对降水变化的响应. 生物多样性, 32, 24044. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024044.
Jiali Lian, Jing Chen, Xueqin Yang, Ying Zhao, Xu Luo, Cui Han, Yaxin Zhao, Jianping Li (2024) Responses of desert steppe plant diversity and microbial diversity to precipitation change. Biodiversity Science, 32, 24044. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2024044.
| 年份Year | 处理 Treat ment | 土壤含水量 Soil moisture (%) | 土壤有机碳含量 Soil organic carbon (g/kg) | 土壤全氮含量 Soil total nitrogen (g/kg) | 土壤全磷含量 Soil total phosphorus (g/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | R33 | 5.55 | 2.91 | 0.38 | 0.36 |
| R66 | 5.78 | 2.37 | 0.36 | 0.38 | |
| RCK | 8.40 | 3.13 | 0.40 | 0.38 | |
| R133 | 5.48 | 2.53 | 0.36 | 0.36 | |
| R166 | 8.88 | 2.78 | 0.38 | 0.37 | |
| 2020 | R33 | 4.75 | 2.13 | 0.35 | 0.40 |
| R66 | 4.84 | 3.01 | 0.43 | 0.41 | |
| RCK | 8.18 | 3.73 | 0.45 | 0.43 | |
| R133 | 4.78 | 2.56 | 0.31 | 0.38 | |
| R166 | 7.63 | 3.18 | 0.51 | 0.47 | |
| 2021 | R33 | 6.04 | 2.56 | 0.39 | 0.33 |
| R66 | 5.41 | 2.71 | 0.43 | 0.35 | |
| RCK | 7.78 | 3.07 | 0.50 | 0.35 | |
| R133 | 4.86 | 2.08 | 0.38 | 0.34 | |
| R166 | 7.01 | 3.14 | 0.48 | 0.35 | |
| 2022 | R33 | 1.30 | 2.96 | 0.35 | 0.35 |
| R66 | 2.01 | 3.39 | 0.41 | 0.36 | |
| RCK | 2.34 | 3.45 | 0.46 | 0.33 | |
| R133 | 2.55 | 3.33 | 0.27 | 0.30 | |
| R166 | 2.90 | 2.88 | 0.37 | 0.31 |
表1 研究区不同降水处理下土壤理化性质。R33: 正常降雨量的33%; R66: 正常降雨量的66%; RCK: 正常降雨量; R133: 正常降雨量的133%; R166: 正常降雨量的166%。
Table 1 Soil physical and chemical properties under different precipitation treatments in the study area. R33, 33% of normal rainfall; R66, 66% of normal rainfall; RCK, Normal rainfall; R133, 133% of normal rainfall; R166, 166% of normal rainfall.
| 年份Year | 处理 Treat ment | 土壤含水量 Soil moisture (%) | 土壤有机碳含量 Soil organic carbon (g/kg) | 土壤全氮含量 Soil total nitrogen (g/kg) | 土壤全磷含量 Soil total phosphorus (g/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | R33 | 5.55 | 2.91 | 0.38 | 0.36 |
| R66 | 5.78 | 2.37 | 0.36 | 0.38 | |
| RCK | 8.40 | 3.13 | 0.40 | 0.38 | |
| R133 | 5.48 | 2.53 | 0.36 | 0.36 | |
| R166 | 8.88 | 2.78 | 0.38 | 0.37 | |
| 2020 | R33 | 4.75 | 2.13 | 0.35 | 0.40 |
| R66 | 4.84 | 3.01 | 0.43 | 0.41 | |
| RCK | 8.18 | 3.73 | 0.45 | 0.43 | |
| R133 | 4.78 | 2.56 | 0.31 | 0.38 | |
| R166 | 7.63 | 3.18 | 0.51 | 0.47 | |
| 2021 | R33 | 6.04 | 2.56 | 0.39 | 0.33 |
| R66 | 5.41 | 2.71 | 0.43 | 0.35 | |
| RCK | 7.78 | 3.07 | 0.50 | 0.35 | |
| R133 | 4.86 | 2.08 | 0.38 | 0.34 | |
| R166 | 7.01 | 3.14 | 0.48 | 0.35 | |
| 2022 | R33 | 1.30 | 2.96 | 0.35 | 0.35 |
| R66 | 2.01 | 3.39 | 0.41 | 0.36 | |
| RCK | 2.34 | 3.45 | 0.46 | 0.33 | |
| R133 | 2.55 | 3.33 | 0.27 | 0.30 | |
| R166 | 2.90 | 2.88 | 0.37 | 0.31 |
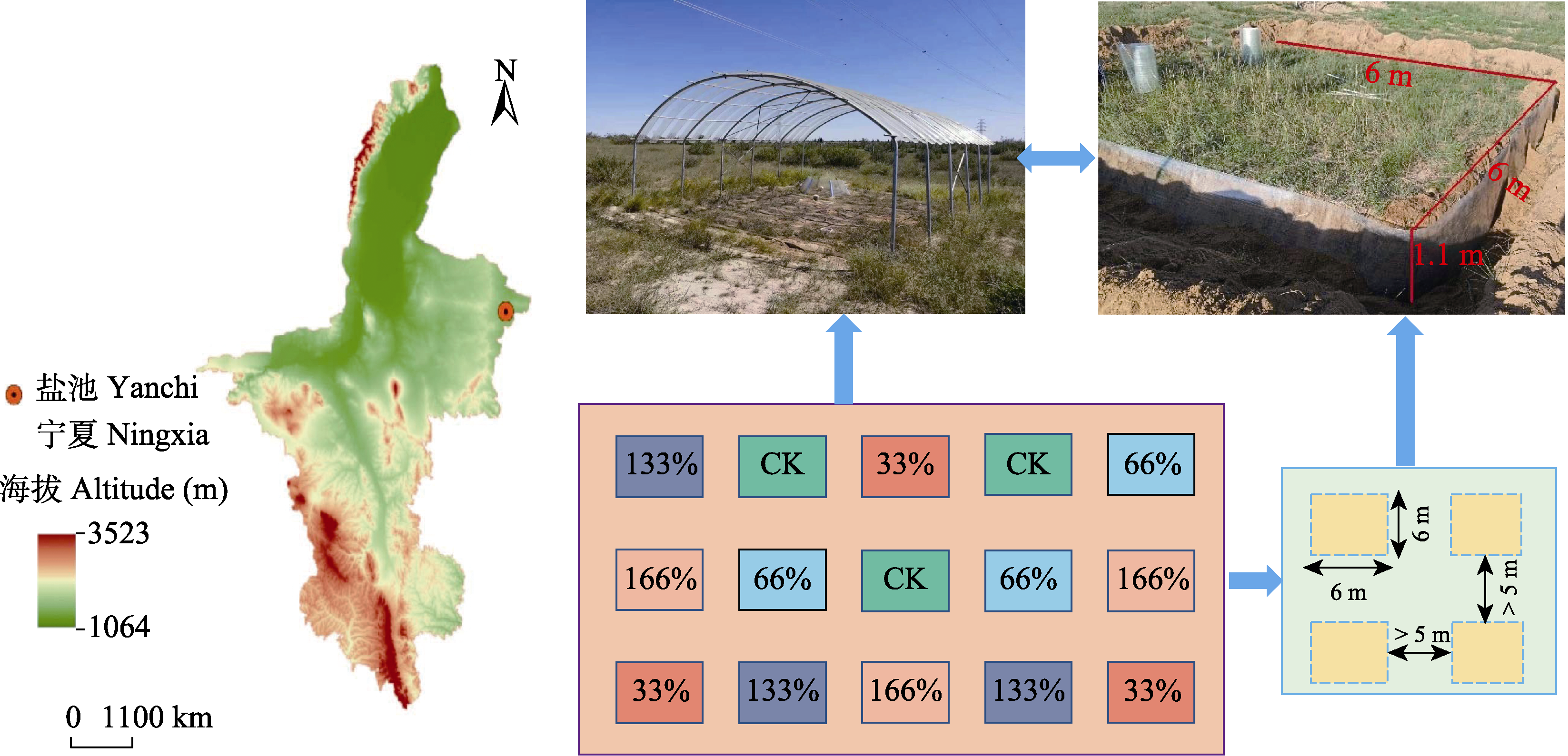
图1 荒漠草原野外试验区设计及降水调控装置。R33: 正常降雨量的33%; R66: 正常降雨量的66%; RCK: 正常降雨量; R133: 正常降雨量的133%; R166: 正常降雨量的166%。
Fig. 1 Desert steppe field test area design and precipitation control device. R33, 33% of normal rainfall; R66, 66% of normal rainfall; RCK, Normal rainfall; R133, 133% of normal rainfall; R166, 166% of normal rainfall.
| 年份 Year | 33% | 66% | 100% (CK) | 133% | 166% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 106.6 | 213.2 | 323.1 | 429.7 | 536.3 |
| 2020 | 66.5 | 133.0 | 201.5 | 268.0 | 334.5 |
| 2021 | 75.1 | 150.2 | 227.6 | 302.7 | 377.8 |
| 2022 | 103.1 | 206.2 | 312.5 | 415.6 | 518.7 |
表2 研究区野外试验期间不同降水处理下的降雨量
Table 2 Rainfall during field experiments and under different precipitation treatments during the growing season
| 年份 Year | 33% | 66% | 100% (CK) | 133% | 166% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 106.6 | 213.2 | 323.1 | 429.7 | 536.3 |
| 2020 | 66.5 | 133.0 | 201.5 | 268.0 | 334.5 |
| 2021 | 75.1 | 150.2 | 227.6 | 302.7 | 377.8 |
| 2022 | 103.1 | 206.2 | 312.5 | 415.6 | 518.7 |
| 物种 Species | R33 | R66 | RCK | R133 | R166 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 猪毛蒿 Artemisia scoparia | 0.27 | 0.24 | 0.14 | 0.36 | 0.32 |
| 牛枝子 Lespeseza potaninii | 0.32 | 0.30 | 0.32 | 0.17 | 0.23 |
| 远志 Polygala tenuifolia | 0.14 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.07 |
| 蒺藜草 Cenchrus echinatus | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.07 |
| 狗尾草 Setaria viridis | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.06 |
| 地锦 Euphorbia humifusa | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 0.03 |
| 小蒺藜 Tribulus terrester | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.07 |
| 米口袋 Gueldenstaedtia verna | 0.03 | 0.02 | - | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| 小画眉草 Eragrostis minor | 0.10 | 0.05 | - | 0.06 | 0.04 |
| 条叶车前 Plantago minuta | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | - | 0.01 |
| 蒙古冰草 Agropyron mongolicum | - | 0.12 | 0.16 | 0.24 | 0.20 |
| 猪毛菜 Salsola collina | - | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.05 |
| 乳浆大戟 Euphorbia esula | 0.06 | 0.04 | - | - | 0.06 |
| 骆驼蓬 Peganum harmala | 0.04 | - | - | 0.05 | - |
| 地肤 Kochia scoparia | - | 0.04 | 0.03 | - | - |
| 角蒿 Incarvillea sinensis | - | 0.01 | - | - | 0.01 |
| 拐轴鸦葱 Scorzonera divaricata | - | - | 0.05 | 0.04 | - |
| 砂珍棘豆 Oxytropis racemosa | - | - | 0.04 | 0.03 | - |
| 华北白前 Cynanchum mongolicum | - | 0.20 | - | - | - |
| 糙叶黄耆 Astragalus scaberrimus | - | 0.08 | - | - | - |
| 阿尔泰狗娃花 Aster altaicus | - | - | 0.04 | - | - |
| 飞廉 Carduus nutans | - | - | 0.04 | - | - |
| 沙葱 Allium mongolicum | - | - | - | 0.11 | - |
| 灰绿藜 Oxybasis glauca | - | - | - | - | 0.03 |
表3 不同降水处理下的物种重要值
Table 3 Importance values of species under different precipitation treatments
| 物种 Species | R33 | R66 | RCK | R133 | R166 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 猪毛蒿 Artemisia scoparia | 0.27 | 0.24 | 0.14 | 0.36 | 0.32 |
| 牛枝子 Lespeseza potaninii | 0.32 | 0.30 | 0.32 | 0.17 | 0.23 |
| 远志 Polygala tenuifolia | 0.14 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.07 |
| 蒺藜草 Cenchrus echinatus | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.07 |
| 狗尾草 Setaria viridis | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.06 |
| 地锦 Euphorbia humifusa | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 0.03 |
| 小蒺藜 Tribulus terrester | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.07 |
| 米口袋 Gueldenstaedtia verna | 0.03 | 0.02 | - | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| 小画眉草 Eragrostis minor | 0.10 | 0.05 | - | 0.06 | 0.04 |
| 条叶车前 Plantago minuta | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | - | 0.01 |
| 蒙古冰草 Agropyron mongolicum | - | 0.12 | 0.16 | 0.24 | 0.20 |
| 猪毛菜 Salsola collina | - | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.05 |
| 乳浆大戟 Euphorbia esula | 0.06 | 0.04 | - | - | 0.06 |
| 骆驼蓬 Peganum harmala | 0.04 | - | - | 0.05 | - |
| 地肤 Kochia scoparia | - | 0.04 | 0.03 | - | - |
| 角蒿 Incarvillea sinensis | - | 0.01 | - | - | 0.01 |
| 拐轴鸦葱 Scorzonera divaricata | - | - | 0.05 | 0.04 | - |
| 砂珍棘豆 Oxytropis racemosa | - | - | 0.04 | 0.03 | - |
| 华北白前 Cynanchum mongolicum | - | 0.20 | - | - | - |
| 糙叶黄耆 Astragalus scaberrimus | - | 0.08 | - | - | - |
| 阿尔泰狗娃花 Aster altaicus | - | - | 0.04 | - | - |
| 飞廉 Carduus nutans | - | - | 0.04 | - | - |
| 沙葱 Allium mongolicum | - | - | - | 0.11 | - |
| 灰绿藜 Oxybasis glauca | - | - | - | - | 0.03 |
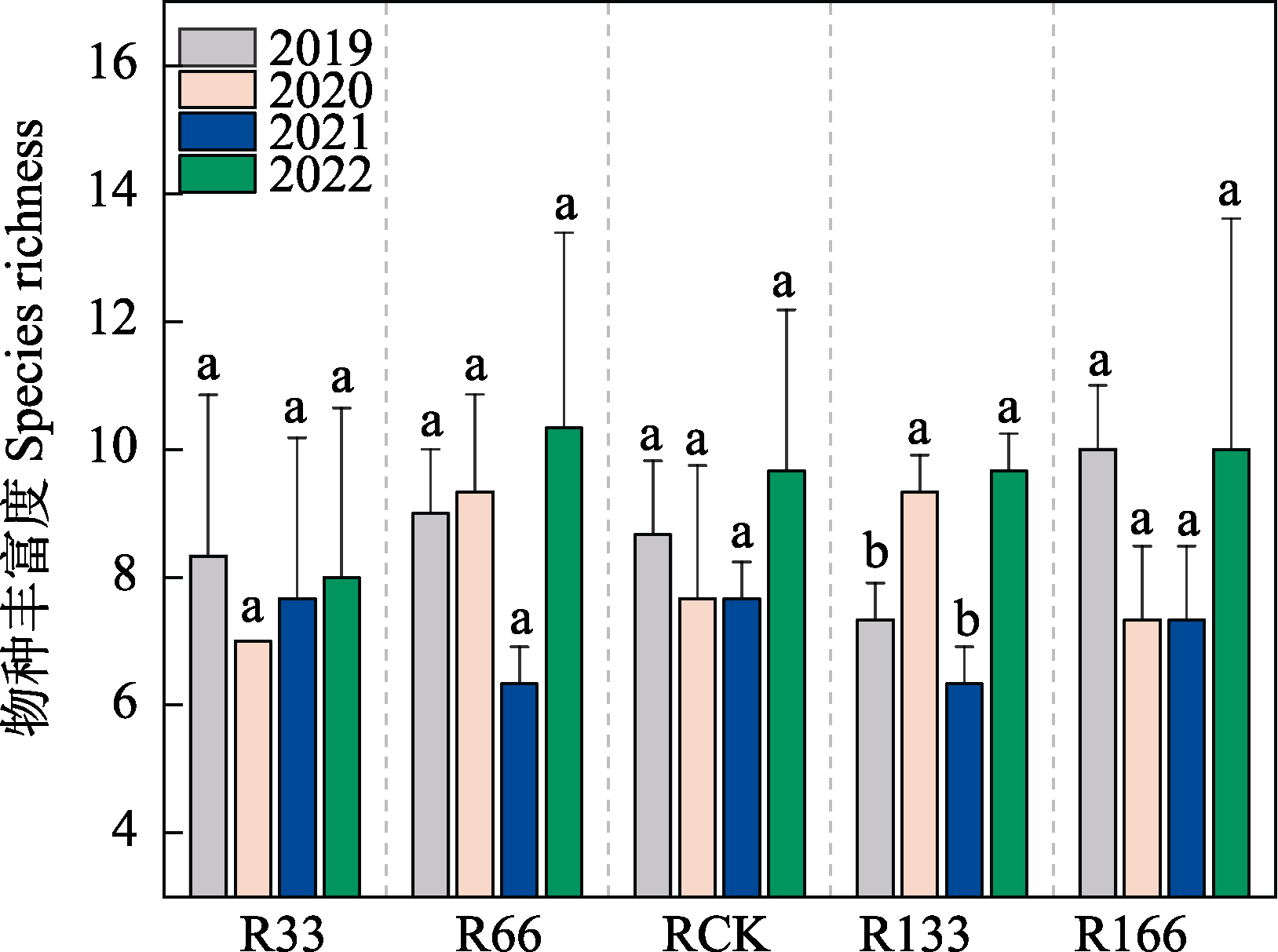
图3 2019-2022年降水变化下植物群落丰富度。不同小写字母表示同一处理不同年份间差异显著。R33: 正常降雨量的33%; R66: 正常降雨量的66%; RCK: 正常降雨量; R133: 正常降雨量的133%; R166: 正常降雨量的166%。
Fig. 3 The species richness of plant community under precipitation change from 2019 to 2022. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different years in the same treatment. R33, 33% of normal rainfall; R66, 66% of normal rainfall; RCK, Normal rainfall; R133, 133% of normal rainfall; R166, 166% of normal rainfall.
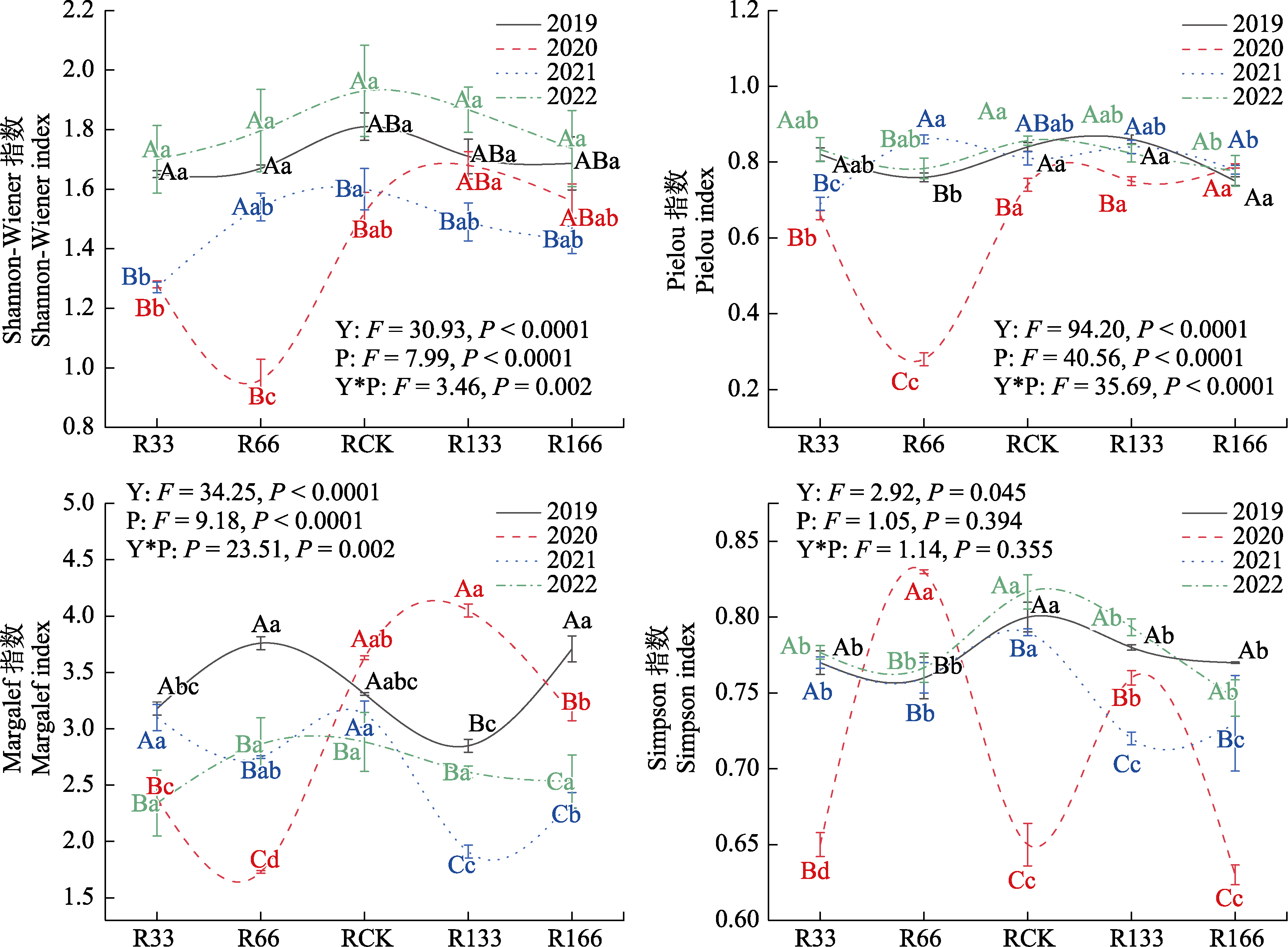
图4 2019-2022年降水变化下植物群落α多样性指数。Y: 年份; P: 降水处理。不同小写字母代表同年不同降水处理下差异显著(P < 0.05); 不同大写字母代表同一降水处理下不同年份差异显著(P < 0.05)。R33: 正常降雨量的33%; R66: 正常降雨量的66%; RCK: 正常降雨量; R133: 正常降雨量的133%; R166: 正常降雨量的166%。
Fig. 4 The α diversity index of plant community under precipitation change from 2019 to 2022. Y, Year; P, Precipitation treatment. Different lowercase letters represent significant differences under different precipitation treatments in the same year (P < 0.05); Different capital letters represent significant differences in different years under the same precipitation treatment (P < 0.05). R33, 33% of normal rainfall; R66, 66% of normal rainfall; RCK, Normal rainfall; R133, 133% of normal rainfall; R166, 166% of normal rainfall.
| 多样性指数 Diversity index | 处理 Treatment | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | P | 3.118 | 0.029 |
| Y | 92.387 | < 0.0001 | |
| P × Y | 1.420 | 0.229 | |
| Simpson指数 Simpson index | P | 2.257 | 0.086 |
| Y | 76.579 | < 0.0001 | |
| P × Y | 0.823 | 0.589 | |
| Ace指数 Ace index | P | 3.763 | 0.013 |
| Y | 153.875 | < 0.0001 | |
| P × Y | 2.965 | 0.014 |
表4 降水(P)、年份(Y)对细菌群落α多样性的交互影响
Table 4 Interactive effects of precipitation (P) and year (Y) on α diversity of bacterial community
| 多样性指数 Diversity index | 处理 Treatment | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | P | 3.118 | 0.029 |
| Y | 92.387 | < 0.0001 | |
| P × Y | 1.420 | 0.229 | |
| Simpson指数 Simpson index | P | 2.257 | 0.086 |
| Y | 76.579 | < 0.0001 | |
| P × Y | 0.823 | 0.589 | |
| Ace指数 Ace index | P | 3.763 | 0.013 |
| Y | 153.875 | < 0.0001 | |
| P × Y | 2.965 | 0.014 |
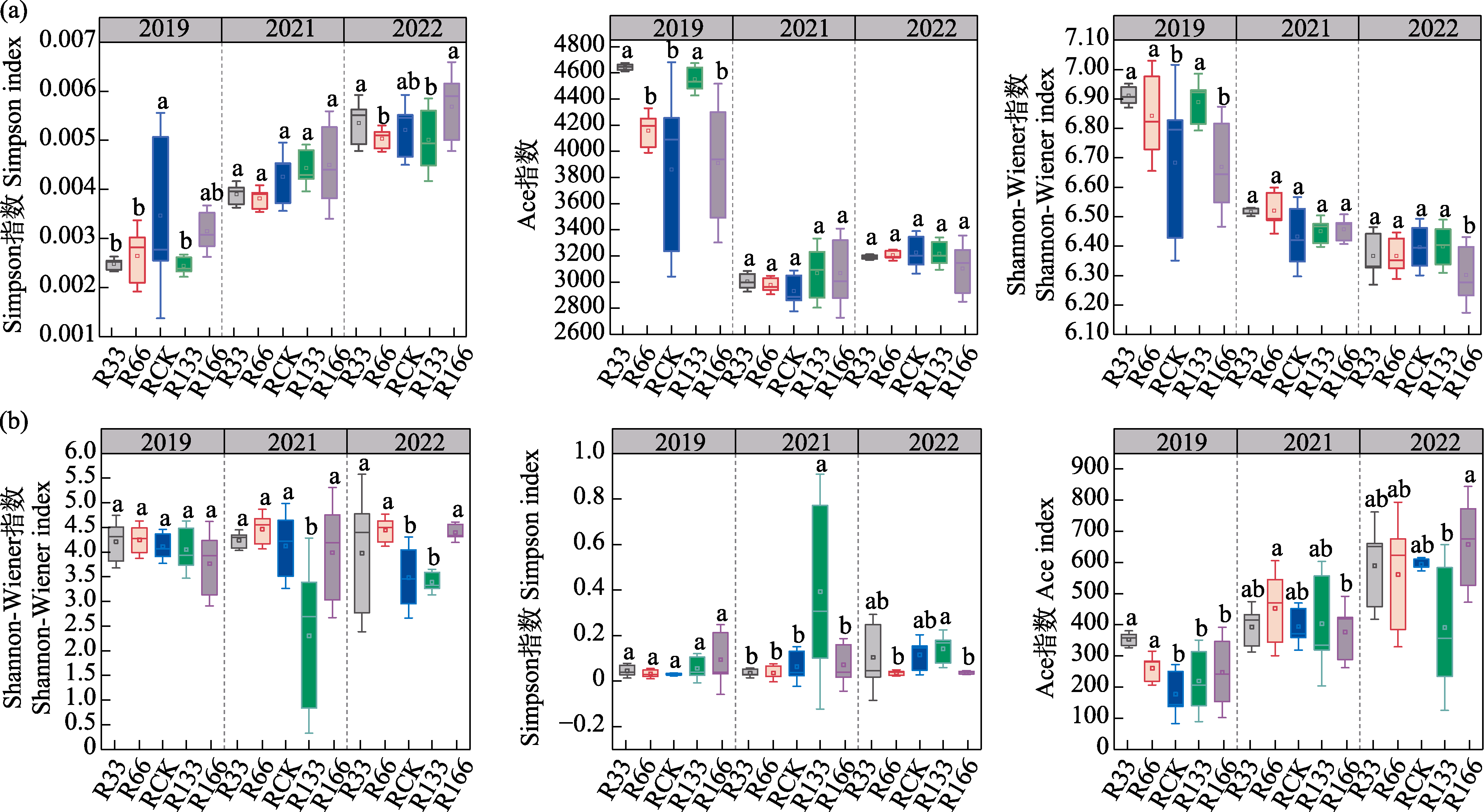
图5 基于OTU水平的2019、2021和2022年土壤细菌群落与真菌群落α多样性。(a)细菌; (b)真菌。R33: 正常降雨量的33%; R66: 正常降雨量的66%; RCK: 正常降雨量; R133: 正常降雨量的133%; R166: 正常降雨量的166%。不同小写字母代表同年不同降水处理下差异显著(P < 0.05)。
Fig. 5 The α diversity of soil bacterial community and fungal community in 2019, 2021 and 2022 based on OTU level. (a) Bacteria; (b) Fungi. R33, 33% of normal rainfall; R66, 66% of normal rainfall; RCK, Normal rainfall; R133, 133% of normal rainfall; R166, 166% of normal rainfall. Different lowercase letters represent significant differences under different precipitation treatments in the same year (P < 0.05).
| 多样性指数 Diversity index | 处理 Treatment | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | P | 4.771 | 0.004 |
| Y | 0.696 | 0.507 | |
| P × Y | 2.106 | 0.067 | |
| Simpson指数 Simpson index | P | 3.325 | 0.023 |
| Y | 1.609 | 0.217 | |
| P × Y | 1.980 | 0.084 | |
| Ace指数 Ace index | P | 1.685 | 0.179 |
| Y | 36.366 | < 0.0001 | |
| P × Y | 1.491 | 0.202 |
表5 降水(P)、年份(Y)对真菌群落α多样性的交互影响
Table 5 Interactive effects of precipitation (P) and year (Y) on α diversity of fungal community
| 多样性指数 Diversity index | 处理 Treatment | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | P | 4.771 | 0.004 |
| Y | 0.696 | 0.507 | |
| P × Y | 2.106 | 0.067 | |
| Simpson指数 Simpson index | P | 3.325 | 0.023 |
| Y | 1.609 | 0.217 | |
| P × Y | 1.980 | 0.084 | |
| Ace指数 Ace index | P | 1.685 | 0.179 |
| Y | 36.366 | < 0.0001 | |
| P × Y | 1.491 | 0.202 |
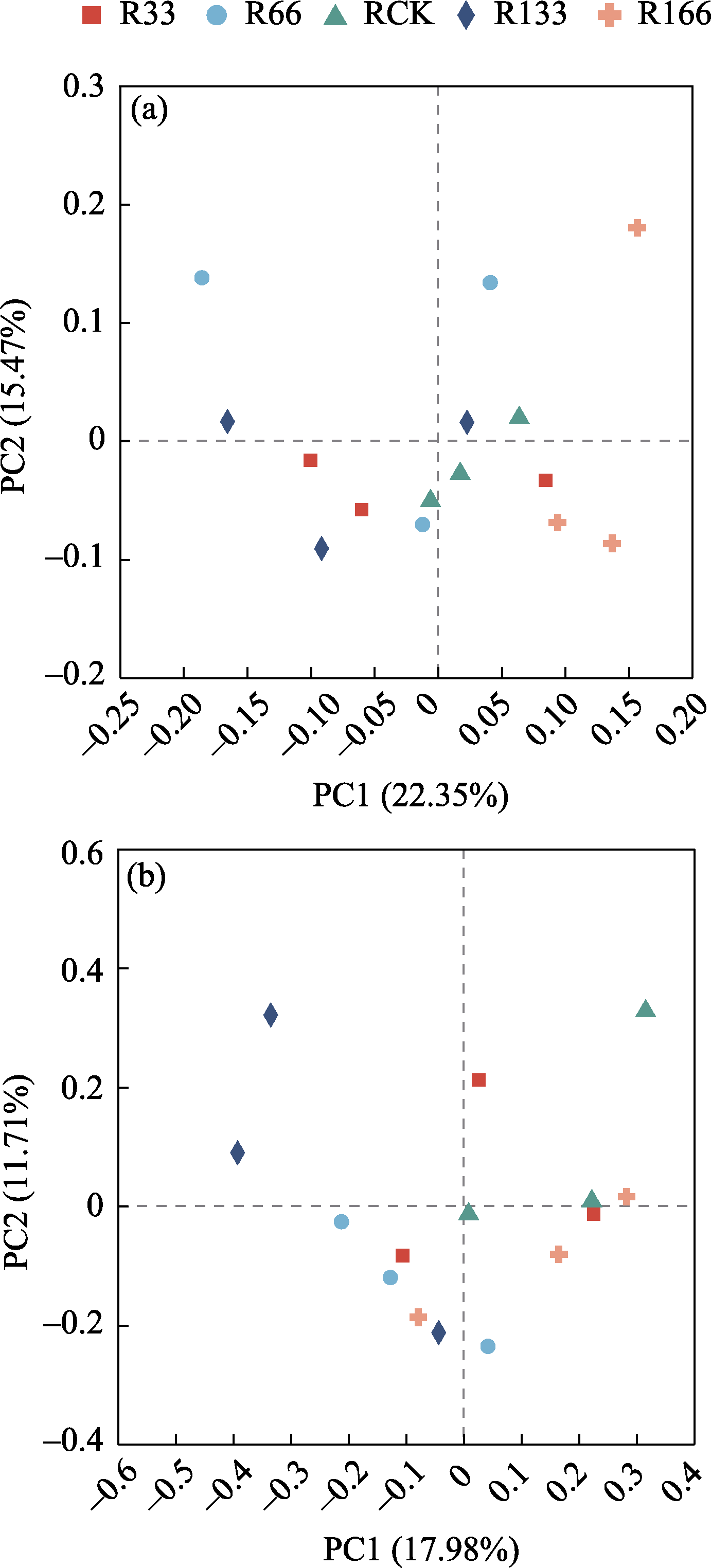
图6 降水变化下土壤细菌与真菌群落结构变化的主坐标分析。(a)细菌; (b)真菌。R33: 正常降雨量的33%; R66: 正常降雨量的66%; RCK: 正常降雨量; R133: 正常降雨量的133%; R166: 正常降雨量的166%。
Fig. 6 The principal co-ordinates analysis (PCoA) results of bacterial and fungal community structure. (a) Bacteria; (b) Fungi. R33, 33% of normal rainfall; R66, 66% of normal rainfall; RCK, Normal rainfall; R133, 133% of normal rainfall; R166, 166% of normal rainfall.
| 指标 Indices | 土壤全氮 TN | 土壤有机碳 SOC | 土壤全磷 TP | 碳氮比 C/N | 碳磷比 C/P | 氮磷比 N/P | 细菌 Bacteria | 真菌 Fungi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤全氮 TN | 1 | 0.72** | 0.49** | 0.16 | 0.21 | 0.57** | 0.18 | 0.24 |
| 土壤有机碳 SOC | 1 | 0.30 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.68** | 0.18 | 0.17 | |
| 土壤全磷 TP | 1 | -0.14 | -0.14 | 0.25 | -0.39* | -0.29 | ||
| 碳氮比 C/N | 1 | 0.92** | 0.53** | 0.37* | 0.77** | |||
| 碳磷比 C/P | 1 | 0.46** | 0.35* | 0.73** | ||||
| 氮磷比 N/P | 1 | 0.23 | 0.45** | |||||
| 细菌 Bacteria | 1 | 0.81** | ||||||
| 真菌 Fungi | 1 |
表6 不同降水处理土壤化学计量与土壤微生物的相关性分析
Table 6 Correlation analysis between soil stoichiometry and soil microorganisms under different precipitation treatments
| 指标 Indices | 土壤全氮 TN | 土壤有机碳 SOC | 土壤全磷 TP | 碳氮比 C/N | 碳磷比 C/P | 氮磷比 N/P | 细菌 Bacteria | 真菌 Fungi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤全氮 TN | 1 | 0.72** | 0.49** | 0.16 | 0.21 | 0.57** | 0.18 | 0.24 |
| 土壤有机碳 SOC | 1 | 0.30 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.68** | 0.18 | 0.17 | |
| 土壤全磷 TP | 1 | -0.14 | -0.14 | 0.25 | -0.39* | -0.29 | ||
| 碳氮比 C/N | 1 | 0.92** | 0.53** | 0.37* | 0.77** | |||
| 碳磷比 C/P | 1 | 0.46** | 0.35* | 0.73** | ||||
| 氮磷比 N/P | 1 | 0.23 | 0.45** | |||||
| 细菌 Bacteria | 1 | 0.81** | ||||||
| 真菌 Fungi | 1 |
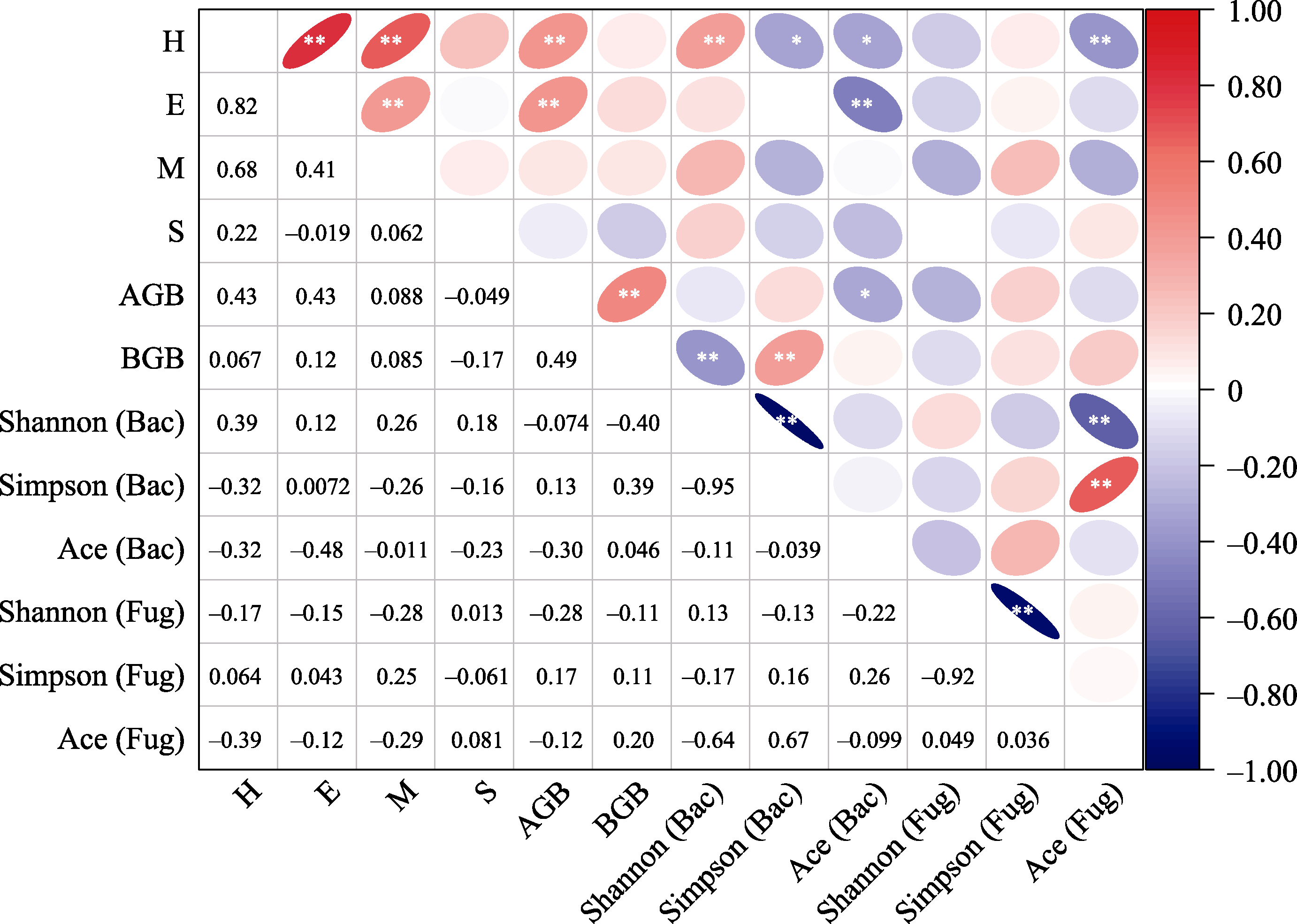
图7 植物群落α多样性指数与微生物群落多样性指数间相关性分析。H: 植物Shannon-Wiener指数; E: 植物Pielou指数; M: 植物Margalef指数; S: 植物Simpson指数; AGB: 植物地上生物量; BGB: 植物地下生物量; Shannon (Bac): 细菌Shannon-Wiener指数; Simpson (Bac): 细菌Simpson指数; Ace (Bac): 细菌Ace指数; Shannon (Fug): 真菌Shannon-Wiener指数; Simpson (Fug): 真菌Simpson指数; Ace (Fug): 真菌Ace指数。* P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01。
Fig. 7 Correlation analysis between plant community diversity index and microbial community diversity index. H, Plant Shannon-Wiener index; E, Plant Pielou index; M, Plant Margalef index; S, Plant Simpson index; AGB, Plant above-ground biomass; BGB, Plant below-ground biomass; Shannon (Bac), Bacterial Shannon-Wiener index; Simpson (Bac), Bacterial Simpson index; Ace (Bac), Bacterial Ace index; Shannon (Fug), Fungal Shannon-Wiener index; Simpson (Fug), Fungal Simpson index; Ace (Fug), Fungal Ace index.
| [1] | Bai CL, Alata, Chen HJ, Shan YM, Eerdunhua, Wang MJ (2013) Effects of addition of nitrogen and water on plant community characteristics of Stipa breviflora desert steppe. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 35(2), 69-75. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [白春利, 阿拉塔, 陈海军, 单玉梅, 额尔敦花, 王明玖 (2013) 氮素和水分添加对短花针茅荒漠草原植物群落特征的影响. 中国草地学报, 35(2), 69-75.] | |
| [2] | Bai YF, Zhao YJ, Wang Y, Zhou KL (2020) Assessment of ecosystem services and ecological regionalization of grasslands support establishment of ecological security barriers in Northern China. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 35, 675-689. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [白永飞, 赵玉金, 王扬, 周楷玲 (2020) 中国北方草地生态系统服务评估和功能区划助力生态安全屏障建设. 中国科学院院刊, 35, 675-689.] | |
| [3] | Bao SD (2000) Soil Agricultural Chemistry Analysis. China Agriculture Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [鲍士旦 (2000) 土壤农化分析. 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [4] | Barnett T, Zwiers F, Hengerl G, Allen M, Crowly T, Gillett N, Hasselmann K, Jones P, Santer B, Schnur R, Scott P, Taylor K, Tett S (2005) Detecting and attributing external influences on the climate system: A review of recent advances. Journal of Climate, 18, 1291-1314. |
| [5] | Bond-Lamberty B, Thomson A (2010) Temperature-associated increases in the global soil respiration record. Nature, 464, 579-582. |
| [6] |
Chen HX, Ma LN, Xin XP, Liu JY, Wang RZ (2018) Plant community responses to increased precipitation and belowground litter addition: Evidence from a 5-year semiarid grassland experiment. Ecology and Evolution, 8, 4587-4597.
DOI PMID |
| [7] | Chen LT, Jiang L, Jing X, Wang JL, Shi Y, Chu HY, He JS (2021) Above- and belowground biodiversity jointly drive ecosystem stability in natural alpine grasslands on the Tibetan Plateau. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 30, 1418-1429. |
| [8] | Chen QL, Cui HL, Su JQ, Penuelas J, Zhu YG (2019) Antibiotic resistomes in plant microbiomes. Trends in Plant Science, 24, 530-541. |
| [9] | Cheng Z, Cui Z, Shi JJ, Liu Y, La Pierre KJ, Wu GL (2021) Plant functional types drive differential responses of grassland ecosystem functions along a precipitation gradient. Ecological Indicators, 133, 108433. |
| [10] | Contosta AR, Frey SD, Cooper AB (2015) Soil microbial communities vary as much over time as with chronic warming and nitrogen additions. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 88, 19-24. |
| [11] | Cruz-Martínez K, Suttle KB, Brodie EL, Power ME, Andersen GL, Banfield JF (2009) Despite strong seasonal responses, soil microbial consortia are more resilient to long-term changes in rainfall than overlying grassland. The ISME Journal, 3, 738-744. |
| [12] |
Gang CC, Wang ZQ, Yang Y, Chen YZ, Zhang YZ, Li JL, Cheng JM (2016) The NPP spatiotemporal variation of global grassland ecosystems in response to climate change over the past 100 years. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 25(11), 1-14. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[刚成诚, 王钊齐, 杨悦, 陈奕兆, 张艳珍, 李建龙, 程积民 (2016) 近百年全球草地生态系统净初级生产力时空动态对气候变化的响应. 草业学报, 25(11), 1-14.]
DOI |
|
| [13] | Gao CY, Qi ZY, Zheng H, Chen XY, Qin JM, Hao J, Zhang NL, Wang CH, Dong KH (2022) Response of soil available nutrients and microbial characteristics to short-term grazing intensities. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 30, 1641-1650. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[高昌宇, 齐志远, 郑慧, 陈玺洋, 秦加敏, 郝杰, 张乃莉, 王常慧, 董宽虎 (2022) 土壤有效养分和微生物特征对短期不同放牧强度的响应. 草地学报, 30, 1641-1650.]
DOI |
|
| [14] |
García-Palacios P, Vandegehuchte ML, Shaw EA, Dam M, Post KH, Ramirez KS, Sylvain ZA, de Tomasel CM, Wall DH (2015) Are there links between responses of soil microbes and ecosystem functioning to elevated CO2, N deposition and warming? A global perspective. Global Change Biology, 21, 1590-1600.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | Guo YQ (2021) The Mechanism of Precipitation Regimes Affecting Soil Microbial Communities and Ecosystem Multifunctionality in Guanzhong Area of Shaanxi Province, China. PhD dissertation, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, Shaanxi. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郭彦青 (2021) 陕西关中地区降雨模式对土壤微生物群落和生态多功能性的影响机制. 博士学位论文, 西北农林科技大学, 陕西杨凌.] | |
| [16] |
Hagedorn F, Gavazov K, Alexander JM (2019) Above- and belowground linkages shape responses of mountain vegetation to climate change. Science, 365, 1119-1123.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
Hibbing ME, Fuqua C, Parsek MR, Peterson SB (2010) Bacterial competition: Surviving and thriving in the microbial jungle. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 8, 15-25
DOI PMID |
| [18] | Horz HP, Barbrook A, Field CB, Bohannan BJM (2004) Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria respond to multifactorial global change. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 101, 15136-15141. |
| [19] | Hu AG, Guan QY (2009) China Tackles Global Climate Change. Tsinghua University Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [胡鞍钢, 管清友 (2009) 中国应对全球气候变化. 清华大学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [20] | Huang JY, Yu HL, Liu JL, Ma F, Han L (2018) Effects of precipitation levels on the C:N:P stoichiometry in plants, microbes, and soils in a desert steppe in China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 5362-5373. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [黄菊莹, 余海龙, 刘吉利, 马飞, 韩磊 (2018) 控雨对荒漠草原植物、微生物和土壤C、N、P化学计量特征的影响. 生态学报, 38, 5362-5373.] | |
| [21] |
Le Provost G, Thiele J, Westphal C, Penone C, Allan E, Neyret M, van der Plas F, Ayasse M, Bardgett RD, Birkhofer K, Boch S, Bonkowski M, Buscot F, Feldhaar H, Gaulton R, Goldmann K, Gossner MM, Klaus VH, Kleinebecker T, Krauss J, Renner S, Scherreiks P, Sikorski J, Baulechner D, Blüthgen N, Bolliger R, Börschig C, Busch V, Chisté M, Fiore-Donno AM, Fischer M, Arndt H, Hoelzel N, John K, Jung K, Lange M, Marzini C, Overmann J, Paŝalić E, Perović DJ, Prati D, Schäfer D, Schöning I, Schrumpf M, Sonnemann I, Steffan-Dewenter I, Tschapka M, Türke M, Vogt J, Wehner K, Weiner C, Weisser W, Wells K, Werner M, Wolters V, Wubet T, Wurst S, Zaitsev AS, Manning P (2021) Contrasting responses of above- and belowground diversity to multiple components of land-use intensity. Nature Communications, 12, 3918.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | Li JW, He BY, Zhang XX, Hui HY, Li C, Han GD (2023) Effects on plant species composition and diversity of community under different stocking rates by abnormal precipitations in the desert steppe. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 43, 6433-6442. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李江文, 何邦印, 张晓曦, 回虹燕, 李彩, 韩国栋 (2023) 荒漠草原异常降水对不同载畜率植物群落物种组成及多样性的影响. 生态学报, 43, 6433-6442.] | |
| [23] |
Li YP, Xu H, Li YD, Luo TS, Chen DX, Zhou Z, Lin MX, Yang H (2016) Scale-dependent spatial patterns of species diversity in the tropical montane rain forest in Jianfengling, Hainan Island, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 40, 861-870. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[李艳朋, 许涵, 李意德, 骆土寿, 陈德祥, 周璋, 林明献, 杨怀 (2016) 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林物种多样性空间分布格局的尺度效应. 植物生态学报, 40, 861-870.]
DOI |
|
| [24] | Lin XC (2013) Global warming will aggravate the imbalance of precipitation distribution. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture and Life Sciences), 39(4), 412. (in Chinese) |
| [林小春 (2013) 全球变暖将加剧降水分布失衡. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 39(4), 412.] | |
| [25] | Liu K, Liu ZC, Li X, Shi XR, Lock TR, Kallenbach RL, Yuan ZY (2022) Precipitation-mediated responses of plant biomass production and allocation to changing soil pH in semiarid grasslands. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 339, 108123. |
| [26] | Liu MR, Liu ST, Ma CY, Li H, Chang SH, Hou FJ, Liu YJ (2023) Research progress of the responses of grassland plants and soil to the variation of temperature and precipitation. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 1-12. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘明蕊, 刘世婷, 马春燕, 李桧, 常生华, 侯扶江, 刘永杰 (2023) 草地植物和土壤对温度和降水变化的响应研究进展. 生态学杂志, 1-12.] https://link.cnki.net/urlid/21.1148.Q.20231026.1119.002. | |
| [27] | Luo X, Li JP, Zhang Y, Jing L, Wang YT, Zhang J (2021) Response of spatial and temporal variation of soil moisture to precipitation change in desert steppe. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 28(4), 142-150, 158. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [罗叙, 李建平, 张翼, 井乐, 王誉陶, 张娟 (2021) 荒漠草原土壤水分时空变化对降水变化的响应. 水土保持研究, 28(4), 142-150, 158.] | |
| [28] | Luo X, Wang YT, Zhang J, Li JP (2022) Responses of dominant species and rhizosphere soil stoichiometry to rainfall in typical steppe of the Loess Plateau. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42, 1002-1014. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [罗叙, 王誉陶, 张娟, 李建平 (2022) 黄土高原典型草原优势种植物及其根际土壤化学计量对降雨变化的响应. 生态学报, 42, 1002-1014.] | |
| [29] | Ma B, Cai YJ, Bork EW, Chang SX (2018) Defoliation intensity and elevated precipitation effects on microbiome and interactome depend on site type in northern mixed-grass prairie. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 122, 163-172. |
| [30] | Ma KP, Liu YM (1994) Measurement of biotic community diversity I α diversity (Part 2). Chinese Biodiversity, 2, 231-239. |
| [马克平, 刘玉明 (1994) 生物群落多样性的测度方法 I α多样性的测度方法(下). 生物多样性, 2, 231-239.] | |
| [31] | Ma L, Jiang XL, Liu GH, Yao LG, Liu WZ, Pan YT, Zuo YX (2020) Environmental factors and microbial diversity and abundance jointly regulate soil nitrogen and carbon biogeochemical processes in Tibetan wetlands. Environmental Science & Technology, 54, 3267-3277. |
| [32] | Miao BL, Liang CZ, Shi YB, Liang MW, Liu ZL (2019) Temporal changes in precipitation altered aboveground biomass in a typical steppe in Nei Mongol, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 43, 557-565. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[苗百岭, 梁存柱, 史亚博, 梁茂伟, 刘钟龄 (2019) 降水变化对内蒙古典型草原地上生物量的影响. 植物生态学报, 43, 557-565.]
DOI |
|
| [33] | Mishra AK, Sudalaimuthuasari N, Hazzouri KM, Saeed EE, Shah I, Amiri KMA (2022) Tapping into plant-microbiome interactions through the lens of multi-omics techniques. Cells, 11, 3254. |
| [34] | Mou HX, Liu BR, Li ZH, Li GQ, Ma DM (2022) Effects of mine water on soil microbial community structure and diversity in desert steppe. Arid Zone Research, 39, 1618-1630. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [牟红霞, 刘秉儒, 李子豪, 李国旗, 麻冬梅 (2022) 矿井水对荒漠草原土壤微生物群落结构及多样性的影响. 干旱区研究, 39, 1618-1630.] | |
| [35] | Nilsson RH, Larsson KH, Taylor AFS, Bengtsson-Palme J, Jeppesen TS, Schigel D, Kennedy P, Picard K, Glöckner FO, Tedersoo L, Saar I, Kõljalg U, Abarenkov K (2019) The UNITE database for molecular identification of fungi: Handling dark taxa and parallel taxonomic classifications. Nucleic Acids Research, 47, D259-D264. |
| [36] |
Porazinska DL, Farrer EC, Spasojevic MJ, Bueno de Mesquita CP, Sartwell SA, Smith JG, White CT, King AJ, Suding KN, Schmidt SK (2018) Plant diversity and density predict belowground diversity and function in an early successional alpine ecosystem. Ecology, 99, 1942-1952.
DOI PMID |
| [37] | Shen HH, Zhu YK, Zhao X, Geng XQ, Gao SQ, Fang JY (2016) Analysis of current grassland resources in China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 61, 139-154. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [沈海花, 朱言坤, 赵霞, 耿晓庆, 高树琴, 方精云 (2016) 中国草地资源的现状分析. 科学通报, 61, 139-154.] | |
| [38] | Tian HQ, Chen GS, Zhang C, Melillo JM, Hall CAS (2010) Pattern and variation of C:N:P ratios in China’s soils: A synthesis of observational data. Biogeochemistry, 98, 139-151. |
| [39] | Wan HX, Cai JJ, Guo YZ, Ma F, Xu H, Han XS, Wang YL, Dong LG (2020) Characteristics of root distributions of typical herbs in Loess Hilly Region of southern Ningxia. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 27(4), 149-156, 163. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [万海霞, 蔡进军, 郭永忠, 马璠, 许浩, 韩新生, 王月玲, 董立国 (2020) 宁夏南部黄土丘陵区典型草本根系分布特征. 水土保持研究, 27(4), 149-156, 163.] | |
| [40] | Wang HM, Liu H, Sang J, Li XY, Su M (2020) Spatial-temporal characteristics of vegetation cover and the correlation with climate in Hulunbeir. Journal of Inner Mongolia University (Natural Science Edition), 51, 539-547. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王海梅, 刘昊, 桑婧, 李鑫杨, 苏明 (2020) 呼伦贝尔植被覆盖时空变化特征及其与气候的相关性分析. 内蒙古大学学报(自然科学版), 51, 539-547.] | |
| [41] | Wohl DL, Arora S, Gladstone JR (2004) Functional redundancy supports biodiversity and ecosystem function in a closed and constant environment. Ecology, 85, 1534-1540. |
| [42] |
Wu LK, Lin XM, Lin WX (2014) Advances and perspective in research on plant-soil-microbe interactions mediated by root exudates. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 38, 298-310. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[吴林坤, 林向民, 林文雄 (2014) 根系分泌物介导下植物-土壤-微生物互作关系研究进展与展望. 植物生态学报, 38, 298-310.]
DOI |
|
| [43] | Xia WJ, Liu KL, Zhang LF, Liu J, Ye HC, Deng GQ, Chen J (2021) Effect of long-term fertilization on soil microbial biomass and enzyme activities in reddish paddy soil. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 58, 628-637. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [夏文建, 柳开楼, 张丽芳, 刘佳, 叶会财, 邓国强, 陈金 (2021) 长期施肥对红壤稻田土壤微生物生物量和酶活性的影响. 土壤学报, 58, 628-637.] | |
| [44] | Zak DR, Holmes WE, White DC, Peacock AD, Tilman D (2003) Plant diversity, soil microbial communities, and ecosystem function: Are there any links? Ecology, 84, 2042-2050. |
| [45] | Zhang Q, Xu CY, Zhang Z, Chen YD, Liu CL (2009) Spatial and temporal variability of precipitation over China, 1951-2005. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 95, 53-68. |
| [46] | Zhang Y (2022) The Response of Ningxia Desert Grassland Vegetation-Soil-Microbial to Precipitation Change and Warming. PhD dissertation, Ningxia University, Yinchuan. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张翼 (2022) 宁夏荒漠草原植被-土壤-微生物系统对降水变化和增温的响应. 博士学位论文, 宁夏大学, 银川.] | |
| [47] |
Zhou XY, Wang YT, Li JP (2023) Response of plant community composition to precipitation changes in typical grasslands in the Loess Plateau. Biodiversity Science, 31, 22118. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[周欣扬, 王誉陶, 李建平 (2023) 黄土高原典型草原植物群落组成对降水变化的响应. 生物多样性, 31, 22118.]
DOI |
| [1] | 张浩斌, 肖路, 刘艳杰. 夜间灯光对外来入侵植物和本地植物群落多样性和生长的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24553-. |
| [2] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [3] | 尹星元, 安慧, 邢彬彬, 苏诗玉, 文志林, 郭建超, 刘小平, 王波. 养分添加和降水变化对荒漠草原地上和地下生物量稳定性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 24073-. |
| [4] | 万凤鸣, 万华伟, 张志如, 高吉喜, 孙晨曦, 王永财. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的应用潜力[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23381-. |
| [5] | 张乃鹏, 梁洪儒, 张焱, 孙超, 陈勇, 王路路, 夏江宝, 高芳磊. 土壤类型和地下水埋深对黄河三角洲典型盐沼植物群落空间分异的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23370-. |
| [6] | 蒋陈焜, 郁文彬, 饶广远, 黎怀成, Julien B. Bachelier, Hartmut H. Hilger, Theodor C. H. Cole. 植物系统发生海报——以演化视角介绍植物多样性的科教资料项目[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24210-. |
| [7] | 韩赟, 迟晓峰, 余静雅, 丁旭洁, 陈世龙, 张发起. 青海野生维管植物名录[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23280-. |
| [8] | 陈又生, 宋柱秋, 卫然, 罗艳, 陈文俐, 杨福生, 高连明, 徐源, 张卓欣, 付鹏程, 向春雷, 王焕冲, 郝加琛, 孟世勇, 吴磊, 李波, 于胜祥, 张树仁, 何理, 郭信强, 王文广, 童毅华, 高乞, 费文群, 曾佑派, 白琳, 金梓超, 钟星杰, 张步云, 杜思怡. 西藏维管植物多样性编目和分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23188-. |
| [9] | 宋柱秋, 叶文, 董仕勇, 金梓超, 钟星杰, 王震, 张步云, 徐晔春, 陈文俐, 李世晋, 姚纲, 徐洲锋, 廖帅, 童毅华, 曾佑派, 曾云保, 陈又生. 广东省高等植物多样性编目和分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23177-. |
| [10] | 罗正明, 刘晋仙, 张变华, 周妍英, 郝爱华, 杨凯, 柴宝峰. 不同退化阶段亚高山草甸土壤原生生物群落多样性特征及驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23136-. |
| [11] | 梁彩群, 陈玉凯, 杨小波, 张凯, 李东海, 江悦馨, 李婧涵, 王重阳, 张顺卫, 朱子丞. 海南省野生维管植物编目和分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 23067-. |
| [12] | 李仕裕, 张奕奇, 邹璞, 宁祖林, 廖景平. 广东省植物园植物多样性迁地保护现状及发展建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22647-. |
| [13] | 朱晓华, 高程, 王聪, 赵鹏. 尿素对土壤细菌与真菌多样性影响的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22636-. |
| [14] | 吴浩, 余玉蓉, 王佳钰, 赵媛博, 高娅菲, 李小玲, 卜贵军, 薛丹, 吴林. 低水位增加灌木多样性和生物量但降低土壤有机碳含量: 以鄂西南贫营养泥炭地为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22600-. |
| [15] | 周欣扬, 王誉陶, 李建平. 黄土高原典型草原植物群落组成对降水变化的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22118-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()