



生物多样性 ›› 2008, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (6): 593-600. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2008.08121 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2008.08121
所属专题: 土壤生物与土壤健康
收稿日期:2008-05-27
接受日期:2008-10-27
出版日期:2008-11-20
发布日期:2008-11-20
通讯作者:
何琳燕
基金资助:
Fei Zhao, Xiafang Sheng, Zhi Huang, Linyan He( )
)
Received:2008-05-27
Accepted:2008-10-27
Online:2008-11-20
Published:2008-11-20
Contact:
Linyan He
About author:* E-mail: helyan0794@njau.edu.cn摘要:
不同土壤类型钾矿物分解细菌资源调查和高效稳定释钾、促生细菌的筛选鉴定有助于丰富微生物资源库,发掘和利用钾矿物分解细菌以及探究矿物生物风化机理等。作者采用以钾长石为唯一钾源的选择性细菌培养基, 从山东地区不同土壤和不同植物根际土壤中分离纯化了23株生长势良好的钾矿物分解细菌, 通过测定细菌代谢产物IAA和铁载体,研究其产生促生物质的能力, 通过摇瓶试验筛选高效释钾菌株, 采用16S rDNA限制性酶切多态性分析(amplified rDNA restriction analysis, ARDRA)方法研究了钾矿物分解细菌的遗传多样性, 根据16S rDNA同源性对高效释钾菌株进行了鉴定。结果表明, 供试菌株均产吲哚乙酸或其衍生物, 43.5%的分离菌株产极高量铁载体。ARDRA结果表明供试菌株在60%相似性水平上可分为11个基因型, 同一类型土壤上不同作物根际或不同类型土壤上同一作物根际的钾矿物分解细菌存在明显的遗传差异。摇瓶试验结果表明供试菌株中具有较显著释钾能力的菌株占17%, 39%的供试菌株无释钾能力。筛选到2株高效释钾菌株AFM2、AC2, 分别使溶液中钾含量增加了29.8%和25.4%。16S rDNA同源性分析表明菌株AC2、AHZ1与Bacillus mucilaginosus聚为一群, 该群与包含菌株AZH4的Paenibacillussp.中的种聚为一大发育分支, 该分支在细菌分类地位上隶属于Firmicutes; 菌株AFM2与Rhizobium sp. 和Agrobacterium tumefaciens聚为另一大发育分支, 该分支在细菌分类地位上隶属于Alphaproteobacteria。
赵飞, 盛下放, 黄智, 何琳燕 (2008) 山东地区钾矿物分解细菌的分离及生物学特性. 生物多样性, 16, 593-600. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2008.08121.
Fei Zhao, Xiafang Sheng, Zhi Huang, Linyan He (2008) Isolation of mineral potassium-solubilizing bacterial strains from agricultural soils in Shandong Province. Biodiversity Science, 16, 593-600. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2008.08121.
| 菌株 Strains | 采样地点 Sampling sites | 土壤类型 Soil type | 植物种类 Plants | 代谢产物 Metabolism products | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 吲哚乙酸 IAA | 铁载体 Sidersphore | ||||
| AC2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 无 Bulk | + + | + + |
| ACY2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 玉米 Maize | + + | + + |
| ACM2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 棉花 Cotton | + | + |
| ACG2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 高粱 Sorghum | + + | – |
| ACD2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 大豆 Soybean | + | + + |
| ACZ2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 杂草 Weeds | + + | + + |
| ACY3 | 曹县 Caoxian County | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 玉米 Maize | + + | – |
| ACZ3 | 曹县 Caoxian County | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 杂草 Weeds | + | – |
| AZZ4 | 临沭 Linshu County | 棕壤 Brown earth | 杂草 Weeds | + + | + + |
| AZH4 | 临沭 Linshu County | 棕壤 Brown earth | 红薯 Sweet potato | + | + |
| AZZ5 | 威海 Weihai City | 棕壤 Brown earth | 杂草 Weeds | + + | + + |
| AHY1 | 广饶 Guangrao County | 褐土 Cinnamon soil | 玉米 Maize | + + | – |
| AHZ1 | 广饶 Guangrao County | 褐土 Cinnamon soil | 杂草 Weeds | + | + + |
| ASY1 | 广饶 Guangrao County | 砂姜黑土 Lime concretion black soil | 玉米 Maize | + | + + |
| ASG1 | 广饶 Guangrao County | 砂姜黑土 Lime concretion black soil | 高粱 Sorghum | + | + + |
| ASZ1 | 广饶 Guangrao County | 砂姜黑土 Lime concretion black soil | 杂草 Weeds | + + | – |
| AZY2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 草甸盐土 Meadow solonchak | 玉米 Maize | ++ | + |
| AZZ2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 草甸盐土 Meadow solonchak | 杂草 Weeds | + | + |
| AF2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 风沙土 Aeolian soil | 无 Bulk | + | – |
| AFM2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 风沙土 Aeolian soil | 棉花 Cotton | + + | – |
| AFY2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 风沙土 Aeolian soil | 玉米 Maize | + | + |
| AY3 | 曹县 Caoxian County | 碱土 Solontz | 无 Bulk | + | + + |
| AYM3 | 曹县 Caoxian County | 碱土 Solontz | 棉花 Cotton | + | + |
表1 菌株的来源及代谢产物吲哚乙酸(IAA)和铁载体的分泌特征
Table 1 Indoleacetic acid (IAA) and sidersphore production of isolates obtained from the rhizosphere of various plants in different soils types, Shandong Province
| 菌株 Strains | 采样地点 Sampling sites | 土壤类型 Soil type | 植物种类 Plants | 代谢产物 Metabolism products | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 吲哚乙酸 IAA | 铁载体 Sidersphore | ||||
| AC2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 无 Bulk | + + | + + |
| ACY2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 玉米 Maize | + + | + + |
| ACM2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 棉花 Cotton | + | + |
| ACG2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 高粱 Sorghum | + + | – |
| ACD2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 大豆 Soybean | + | + + |
| ACZ2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 杂草 Weeds | + + | + + |
| ACY3 | 曹县 Caoxian County | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 玉米 Maize | + + | – |
| ACZ3 | 曹县 Caoxian County | 潮土 Fluvo-aquic soil | 杂草 Weeds | + | – |
| AZZ4 | 临沭 Linshu County | 棕壤 Brown earth | 杂草 Weeds | + + | + + |
| AZH4 | 临沭 Linshu County | 棕壤 Brown earth | 红薯 Sweet potato | + | + |
| AZZ5 | 威海 Weihai City | 棕壤 Brown earth | 杂草 Weeds | + + | + + |
| AHY1 | 广饶 Guangrao County | 褐土 Cinnamon soil | 玉米 Maize | + + | – |
| AHZ1 | 广饶 Guangrao County | 褐土 Cinnamon soil | 杂草 Weeds | + | + + |
| ASY1 | 广饶 Guangrao County | 砂姜黑土 Lime concretion black soil | 玉米 Maize | + | + + |
| ASG1 | 广饶 Guangrao County | 砂姜黑土 Lime concretion black soil | 高粱 Sorghum | + | + + |
| ASZ1 | 广饶 Guangrao County | 砂姜黑土 Lime concretion black soil | 杂草 Weeds | + + | – |
| AZY2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 草甸盐土 Meadow solonchak | 玉米 Maize | ++ | + |
| AZZ2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 草甸盐土 Meadow solonchak | 杂草 Weeds | + | + |
| AF2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 风沙土 Aeolian soil | 无 Bulk | + | – |
| AFM2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 风沙土 Aeolian soil | 棉花 Cotton | + + | – |
| AFY2 | 德州 Dezhou City | 风沙土 Aeolian soil | 玉米 Maize | + | + |
| AY3 | 曹县 Caoxian County | 碱土 Solontz | 无 Bulk | + | + + |
| AYM3 | 曹县 Caoxian County | 碱土 Solontz | 棉花 Cotton | + | + |
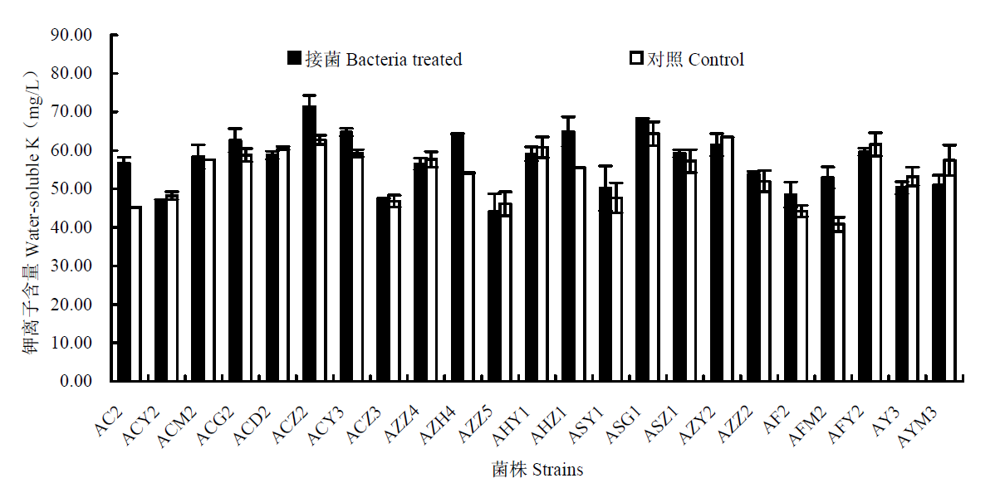
图1 液体培养条件下不同菌株分解钾长石释钾效能比较,接灭活菌为对照。
Fig. 1 Amount of potassium (K) released by bacterial strains after four days inoculation in liquid cultures. Controls were inoculated by autoclaved inocula.
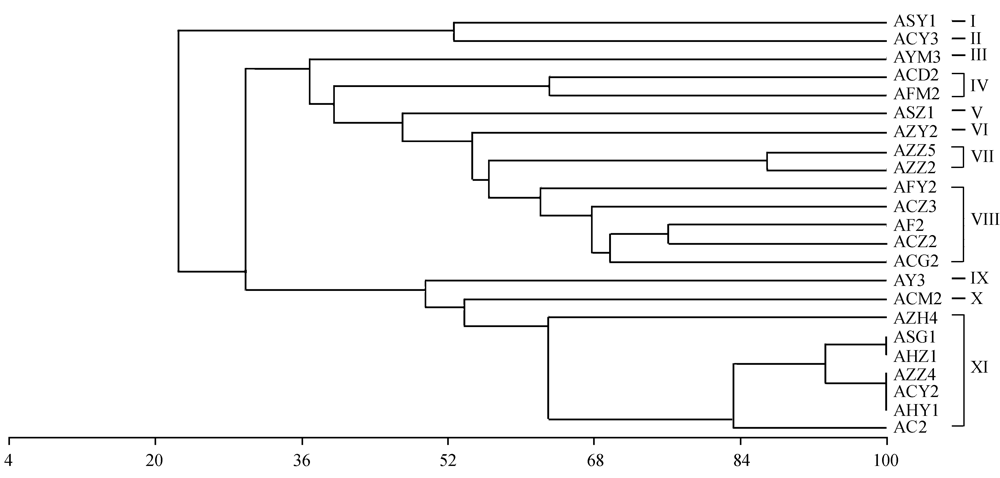
图2 根据16S rDNA限制性酶切片段分析得到的供试菌株聚类树状图
Fig. 2 A UPGMA dendrogram of 23 potassium-releasing bacterial strains based on amplified rDNA restriction analysis (ARDRA) patterns from Hae Ⅲ and MspⅠdigestion.
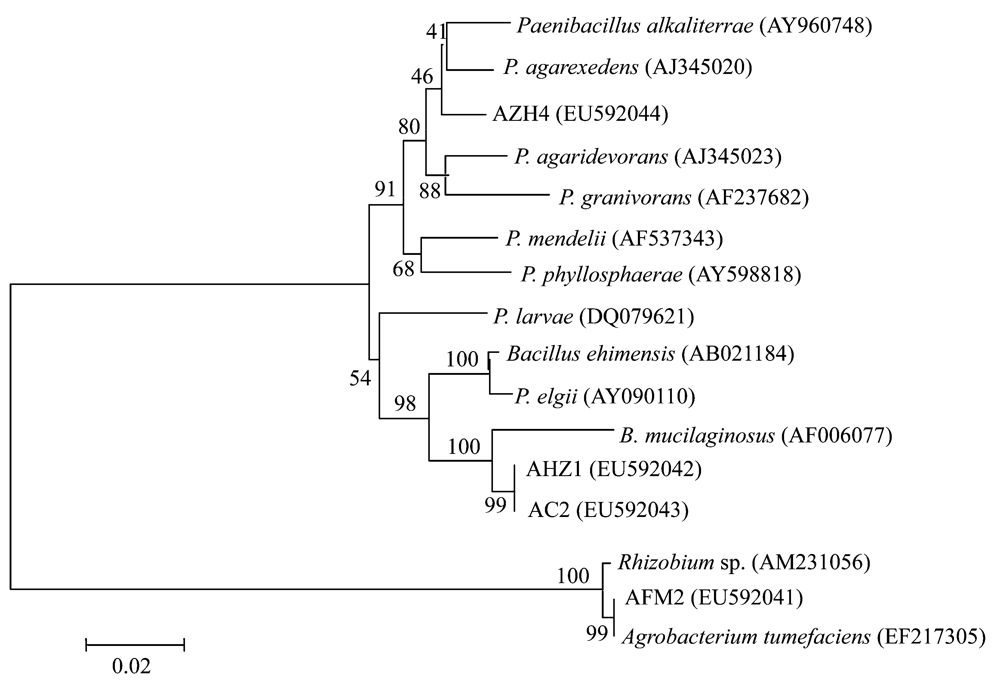
图3 基于2个高效释钾菌株AC2、AFM2和2个中等释钾效能菌株AHZ1、AZH4以及亲缘关系相近的菌株(分别属于Bacillus, Paebacillus, Rhizobium和Agrobacterium属)的16S rDNA序列构建的系统发育树,标尺代表进化距离。
Fig. 3 The phylogenetic tree based on the 16S rDNA sequences of four potassium-bearing mineral-dissolved bacteria strains and those of related species in the genusBacillus, Paebacillus, Rhizobium, and Agrobacterium. Scale bar indicates evolutionary distance.
| [1] | Banfield JF, Barker WW, Welch SA, Taunton A (1999) Biological impact on mineral dissolution: application of the lichen model to understanding mineral weathering in the rhizosphere. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 96,3404-3411. |
| [2] | Barker WW, Welch SA, Chu S, Banfield JF (1998) Experimental observations of the effects of bacteria on aluminosilicate weathering. American Mineralogist, 83,1551-1563. |
| [3] | Buss HL, Lüttge A, Brantley SL (2007) Etch pit formation on iron silicate surfaces during siderophore-promoted dissolution. Chemical Geology, 240,326-342. |
| [4] | Calvaruso C, Turpault MP, Frey-Klett P (2006) Root-associated bacteria contribute to mineral weathering and to mineral nutrition in trees: a budgeting analysis. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72,1258-1266. |
| [5] |
Compant S, Duffy B, Nowak J, Clément C, Barka E (2005) Use of plant growth-promoting bacteria for biocontrol of plant diseases: principles, mechanisms of action, and future prospects. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71,4951-4959.
DOI URL PMID |
| [6] |
Dell’Amico E, Cavalca L, Andreoni V (2005) Analysis of rhizobacterial communities in perennial Graminaceae from polluted water meadow soil, and screening of metal-resistant, potentially plant growth-promoting bacteria. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 52,153-162.
DOI URL PMID |
| [7] | Glick BR (1995) The enhancement of plant growth by free living bacteria. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 41,109-114. |
| [8] | Guan Y (管莹), Li DY (李登煜), Chen Q (陈强), Zhou JC (周俊初), Zhang WT (张伟涛), Jing GJ (荆光军) (2007) Genetic diversity of silicate bacteria isolated from saline-alkali soils in northern China by RAPD and BOXAIR PCR analysis. Journal of Agro-Environment Science (农业环境科学学报), 26,2043-2047. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [9] |
Hameeda B, Harini G, Rupela OP, Wani SP, Reddy G (2008) Growth promotion of maize by phosphate-solubilizing bacteria isolated from composts and macrofauna. Microbiological Research, 163,234-242.
DOI URL PMID |
| [10] | He JQ (贺积强), Li DY (李登煜), Zhang XP (张小平), Chen Q (陈强), Liang RY (梁如玉) (2003) Phenotypic aspects and phosphorus-releasing and potassium-releasing ability of silicate bacteria isolated from purple soils. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology (应用与环境生物学报), 9,71-77. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [11] | He LY (何琳燕), Sheng XF (盛下放), Lu GX (陆光祥), Huang WY (黄为一) (2004) Physiological and biochemical characteristics of silicate-dissolving bacteria in different soils and their capacities of releasing potassium. Soils (土壤), 36,434-437. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [12] |
Hiebert FK, Bennett PC (1992) Microbial control of silicate weathering in organic-rich ground water. Science, 258,278-281.
DOI URL PMID |
| [13] | Hu H (胡桦), Chen Q (陈强), Li DY (李登煜), Wu SS (吴思思), Xie ZL (谢卓霖), He JQ (贺积强), Zhou JC (周俊初) (2007) Genetic diversity of silicate bacteria isolated from purple soils. Acta Pedologica Sinica (土壤学报), 44,379-383. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [14] | Kalinowski BE, Liermann LJ, Brantley SL, Barnes A, Pantano CG (2000) X-ray photoelectron evidence for bacteria-enhanced dissolution of hornblende. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 64,1331-1343. |
| [15] |
Laguerre G, Allard M, Revoy F (1994) Rapid identification of rhizobia by restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of PCR-amplified 16S rRNA genes. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 60,56-63.
DOI URL PMID |
| [16] | Li DX (李定旭) (2003) Study on the effects of silicate bacteria on the growth and fruit quality of apples. Journal of Fruit Science (果树学报), 20,64-66. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [17] | Li J (李俊), Jiang X (姜昕), Li L (李力), Shen DL (沈德龙) (2006) Development of microbial fertilizer and maintaining of soil biological fertility. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China (中国土壤与肥料), (4),1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [18] | Li S (李莎), Li FC (李福春), Cheng LJ (程良娟) (2006) Recent development in bio -weathering research. Mineral Resources and Geology (矿产与地质), 20,577-582. |
| [19] | Li Y (李扬), Li DY (李登煜), Huang MY (黄明勇), Chen Q (陈强), Zhang XP (张小平), Liu X (刘旭) (2006) Study on biological characteristics of several silicate bacteria isolated from saline soil. Chinese Journal of Soil Science (土壤通报), 37,206-208. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [20] | Lian B (连宾), Fu PQ (傅平秋), Mo DM (莫德明), Liu CQ (刘丛强) (2002) A comprehensive review of the mechanism of potassium releasing by silicate bacteria. Acta Mineralogic Sinica (矿物学报), 22,179-183. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [21] | Rogers JR, Bennett PC (2004) Mineral stimulation of subsurface microorganisms: release of limiting nutrients from silicates. Chemical Geology, 203,91-108. |
| [22] | Sambrook J, Maniatis T, Fritsch EF (1989) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York. |
| [23] | Sheng XF (2005) Growth promotion and increased potassium uptake of cotton and rape by a potassium releasing strain of Bacillus edaphicus. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 37,1918-1922. |
| [24] |
Sheng XF, He LY (2006) Solubilization of potassium-bearing minerals by a wild-type strain of Bacillus edaphicus and its mutants and increased potassium uptake by wheat. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 52,66-72.
URL PMID |
| [25] | Sheng XF (盛下放) (2004) Distribution of silicate-dissolving bacteria in soils of China. Soils (土壤), 36,81-84. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [26] | Sheng XF (盛下放), Huang WY(黄为一) (2001) Physiological characteristics of strain NBT of silicate bacterium. Acta Pedologica Sinica (土壤学报), 38,569-574. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [27] | Sheng XF (盛下放), Huang WY (黄为一) (2002) Mechanism of potassium release from feldspar affected by the strain NBT of silicate bacterium. Acta Pedologica Sinica (土壤学报), 39,863-871. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [28] | Sheng XF, He LY, Huang WY (2002) The conditions of releasing potassium by a silicate-dissolving bacterial strain NBT. Agricultural Sciences in China, 1,662-666. |
| [29] |
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 24,1596-1599.
URL PMID |
| [30] | Wang P (王平), Dong B (董飙), Li FD (李阜棣), Hu ZJ (胡正嘉) (1994) Detection and determination of the siderophores produced by wheat rhizobacteria. Microbiology (微生物学通报), 21,323-326. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [31] | Zhang SM (张漱茗), Yan H (闫华), Liu GD (刘光栋), Liu ZH (刘兆辉) (1999) Soil potassium supplying capacity and release of non-exchangeable potassium in Shandong soils. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science (植物营养与肥料学报), 5(1),26-31. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [32] | Zhu CX (朱昌雄), Li J (李俊), Shen DL (沈德龙), Jiang X (姜昕) (2005) Research progress of bio-fertilizer standardization in China and some suggestions. Phosphate and Compound Fertilizer (磷肥与复肥), 20(4),5-7, 22. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 王嘉陈, 徐汤俊, 许唯, 张高季, 尤艺瑾, 阮宏华, 刘宏毅. 城市景观格局对大蚰蜒种群遗传结构的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24251-. |
| [2] | 冯晨, 张洁, 黄宏文. 统筹植物就地保护与迁地保护的解决方案: 植物并地保护(parallel situ conservation)[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23184-. |
| [3] | 李庆多, 栗冬梅. 全球蝙蝠巴尔通体流行状况分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23166-. |
| [4] | 齐海玲, 樊鹏振, 王跃华, 刘杰. 中国北方六省区胡桃的遗传多样性和群体结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23120-. |
| [5] | 熊飞, 刘红艳, 翟东东, 段辛斌, 田辉伍, 陈大庆. 基于基因组重测序的长江上游瓦氏黄颡鱼群体遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22391-. |
| [6] | 蒲佳佳, 杨平俊, 戴洋, 陶可欣, 高磊, 杜予州, 曹俊, 俞晓平, 杨倩倩. 长江下游外来生物福寿螺的种类及其种群遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22346-. |
| [7] | 何艺玥, 刘玉莹, 张富斌, 秦强, 曾燏, 吕振宇, 杨坤. 梯级水利工程背景下的嘉陵江干流蛇鮈群体遗传多样性和遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23160-. |
| [8] | 孙维悦, 舒江平, 顾钰峰, 莫日根高娃, 杜夏瑾, 刘保东, 严岳鸿. 基于保护基因组学揭示荷叶铁线蕨的濒危机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21508-. |
| [9] | 陶克涛, 白东义, 图格琴, 赵若阳, 安塔娜, 铁木齐尔·阿尔腾齐米克, 宝音德力格尔, 哈斯, 芒来, 韩海格. 基于基因组SNPs对东亚家马不同群体遗传多样性的评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21031-. |
| [10] | 崔静, 徐明芳, 章群, 李瑶, 曾晓舒, 李莎. 基于3种线粒体标记探讨中日沿海角木叶鲽遗传多样性差异[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21485-. |
| [11] | 孙军, 宋煜尧, 施义锋, 翟键, 燕文卓. 近十年中国海洋生物多样性研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22526-. |
| [12] | 栗冬梅, 杨卫红, 李庆多, 韩茜, 宋秀平, 潘虹, 冯云. 巴尔通体在滇西南蝙蝠中高度流行并具有丰富的遗传变异特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(9): 1245-1255. |
| [13] | 姚志, 郭军, 金晨钟, 刘勇波. 中国纳入一级保护的极小种群野生植物濒危机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(3): 394-408. |
| [14] | 叶俊伟, 田斌. 中国西南地区重要木本油料植物扁核木的遗传结构及成因[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(12): 1629-1637. |
| [15] | 向登高, 李跃飞, 李新辉, 陈蔚涛, 马秀慧. 多基因联合揭示海南鲌的遗传结构与遗传多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(11): 1505-1512. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn