



生物多样性 ›› 2015, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (1): 68-78. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2014148 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2014148
所属专题: 土壤生物与土壤健康
关大伟1,2, 李力1,2, 姜昕1,2, 马鸣超1,2, 曹凤明1,2, 周宝库3, 李俊1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2014-07-10
接受日期:2014-12-30
出版日期:2015-01-20
发布日期:2015-05-04
通讯作者:
李俊
作者简介:E-mail: jli@caas.ac.cn基金资助:
Dawei Guan1,2, Li Li1,2, Xin Jiang1,2, Mingchao Ma1,2, Fengming Cao1,2, Baoku Zhou3, Jun Li1,2,*( )
)
Received:2014-07-10
Accepted:2014-12-30
Online:2015-01-20
Published:2015-05-04
Contact:
Jun Li
摘要:
为揭示长期施肥对黑土大豆根瘤菌群体结构和多样性的影响, 采用BOX-PCR、IGS-PCR-RFLP和16S rDNA基因序列分析法, 对分离自黑龙江省7种长期不同施肥处理的254株大豆根瘤菌进行了遗传多样性和系统发育分析, 结合土壤理化性质分析了大豆根瘤菌群体结构和多样性与土壤因子间的关系。7种处理分别为不施肥(CK)、有机肥(OM)、单施氮肥(N1)、单施2倍氮肥(N2)、氮肥+有机肥(N1+OM)、氮肥磷肥混施(N1P1)和2倍氮肥磷肥混施(N2P2)。系统发育分析结果表明, 所有供试菌株均为慢生根瘤菌属(Bradyrhizobium), 其中大部分菌株与日本慢生大豆根瘤菌(Bradyrhizobium japonicum)相似性最高, 少部分菌株与辽宁慢生大豆根瘤菌(Bradyrhizobium liaoningense)相似性最高。BOX-PCR聚类分析结果表明, 供试菌株在70%相似性水平上分为15个群, 在与施肥处理相关性分析中分为3个群体, 分别对应于不施化肥处理(CK和OM)、化学氮肥处理(N1、N2、N1+OM)、氮肥磷肥处理(N1P1和N2P2)。典范对应分析结果表明, 土壤pH、速效氮和速效磷与根瘤菌群体结构相关性极显著(P=0.002, 0.004, 0.002)。不同施肥措施下大豆根瘤菌的多样性有明显差异: N2P2处理的丰富度指数和Shannon-Wiener指数显著高于其他处理; OM处理的Simpson指数最高; N1和N2处理的3种多样性指数都显著低于其他处理。通径分析结果表明, pH、速效磷对多样性指数有较高的直接正效应; 速效氮通过pH的间接负效应影响多样性指数。本研究表明, 长期施用化肥改变了根瘤菌群体结构, 单施氮肥减少大豆根瘤菌多样性, 而氮肥磷肥混施则有助于提高大豆根瘤菌多样性。
关大伟, 李力, 姜昕, 马鸣超, 曹凤明, 周宝库, 李俊 (2015) 长期施肥对黑土大豆根瘤菌群体结构和多样性的影响. 生物多样性, 23, 68-78. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2014148.
Dawei Guan, Li Li, Xin Jiang, Mingchao Ma, Fengming Cao, Baoku Zhou, Jun Li (2015) Influence of long-term fertilization on the community structure and diversity of soybean rhizobia in black soil. Biodiversity Science, 23, 68-78. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2014148.
| 处理 Treatment | 施肥种类 Fertilizer type | 施用量 Dose of fertilization (kg/ha) | 菌株数量 Number of strains |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 不施肥 No fertilizer | 0 | 32 |
| OM | 马粪 Horse manure | 18,600 | 32 |
| N1+OM | 尿素+马粪 Urea + Horse manure | 75+18,600 | 45 |
| N1 | 尿素 Urea | 75 | 48 |
| N2 | 尿素 Urea | 150 | 41 |
| N1P1 | 尿素+过磷酸钙 Urea & Calcium superphosphate | 75+150 | 28 |
| N2P2 | 尿素+过磷酸钙 Urea & Calcium superphosphate | 150 +300 | 28 |
表1 各处理施肥种类、施用量及分离菌株数量
Table 1 The dose of different fertilization and number of isolated rhizobium strains
| 处理 Treatment | 施肥种类 Fertilizer type | 施用量 Dose of fertilization (kg/ha) | 菌株数量 Number of strains |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 不施肥 No fertilizer | 0 | 32 |
| OM | 马粪 Horse manure | 18,600 | 32 |
| N1+OM | 尿素+马粪 Urea + Horse manure | 75+18,600 | 45 |
| N1 | 尿素 Urea | 75 | 48 |
| N2 | 尿素 Urea | 150 | 41 |
| N1P1 | 尿素+过磷酸钙 Urea & Calcium superphosphate | 75+150 | 28 |
| N2P2 | 尿素+过磷酸钙 Urea & Calcium superphosphate | 150 +300 | 28 |
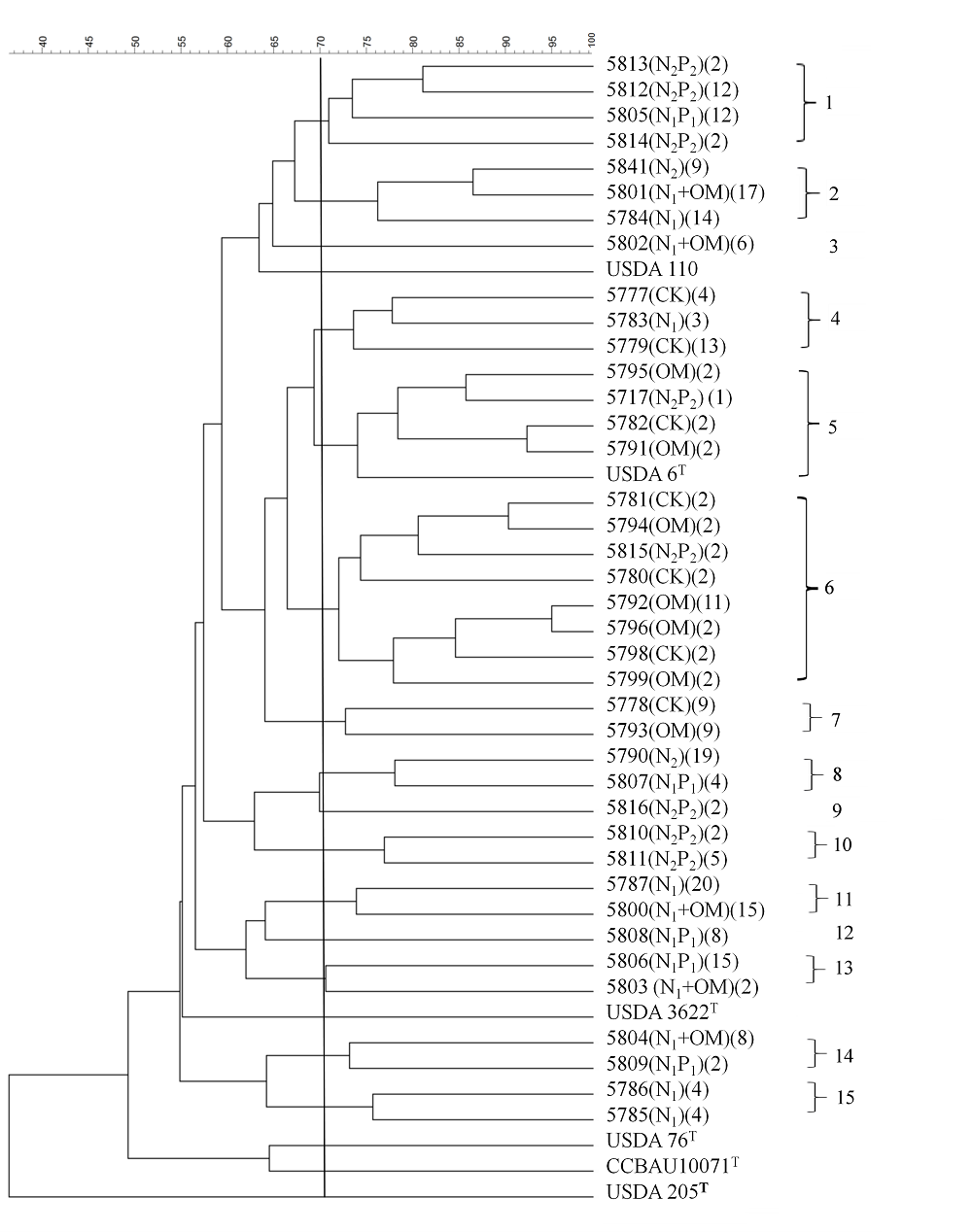
图1 BOX-PCR图谱聚类分析树状图。括号内的处理编号代表菌株分离地点, 括号内的数字代表具有相同BOX-PCR图谱的菌株数量。
Fig. 1 The dendrogram of BOX-PCR cluster analysis. The codes of the treatments in parenthesis refer to sampling sites, and the numbers in parenthesis refer to the strain numbers with same BOX-PCR type.
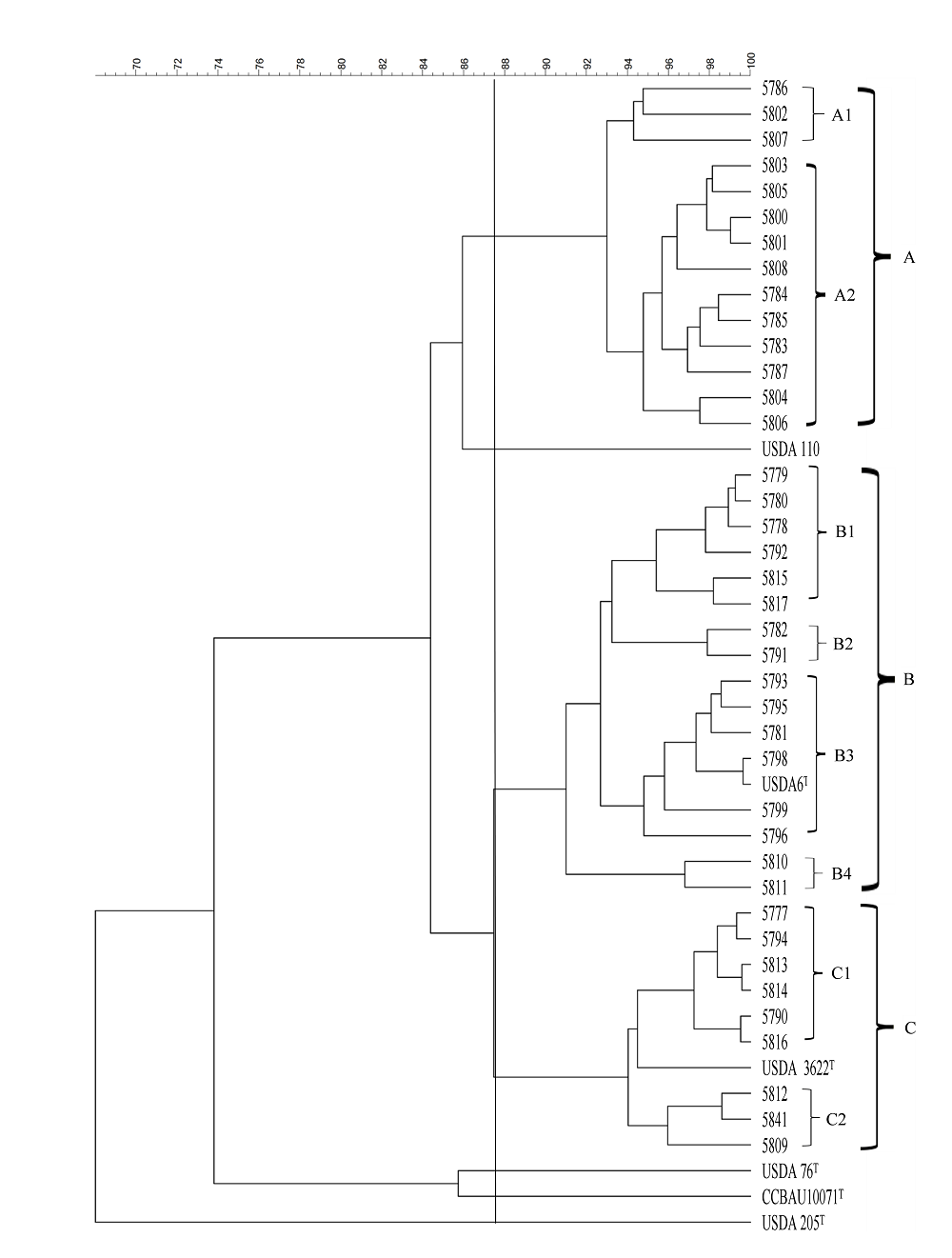
图2 IGS PCR-RFLP指纹图谱聚类分析树状图。A1和A2为群A的亚群, B1、B2、B3和B4为群B的亚群, C1和C2为群C的亚群。
Fig. 2 The dendrogram of IGS PCR-RFLP cluster analysis. A1 and A2 are subgroups of A group, B1, B2, B3and B4 are subgroups of B group, and C1 and C2 are subgroups of C group.
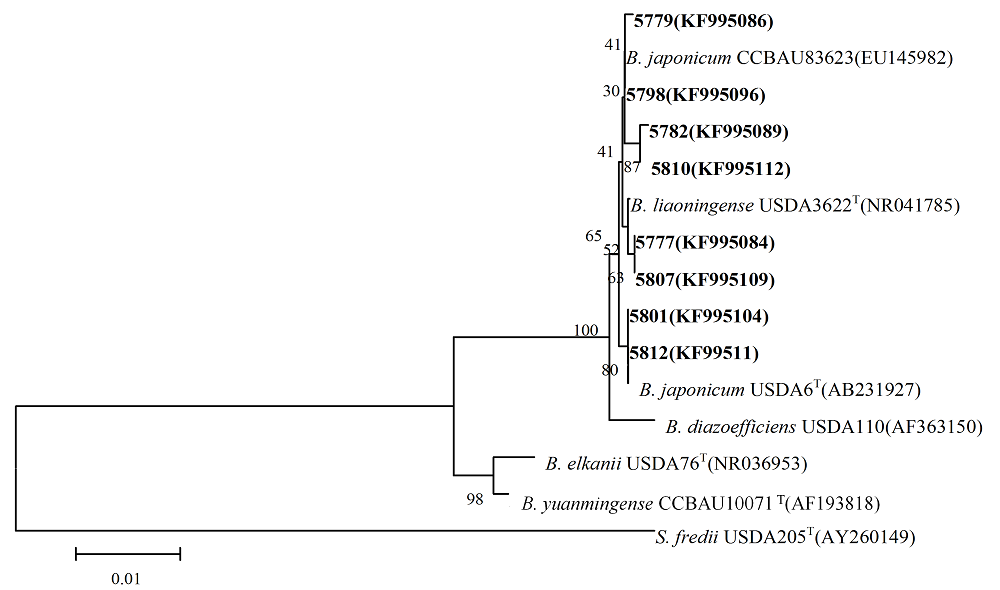
图3 代表菌株与参比菌株16S rDNA序列的Neighbor-joining聚类图。图中分支上的数字表示可信度, 括号内为GenBank登录号, 0.01表示遗传距离。
Fig. 3 Neighbor-joining clustering phylogenetic tree of 16S rDNA sequence between representatives of isolated rhizobia and the reference strains. The values on branch stand for reliabilities and the numbers in the parenthesis are GenBank accession numbers. 0.01 denoted genetic distances.
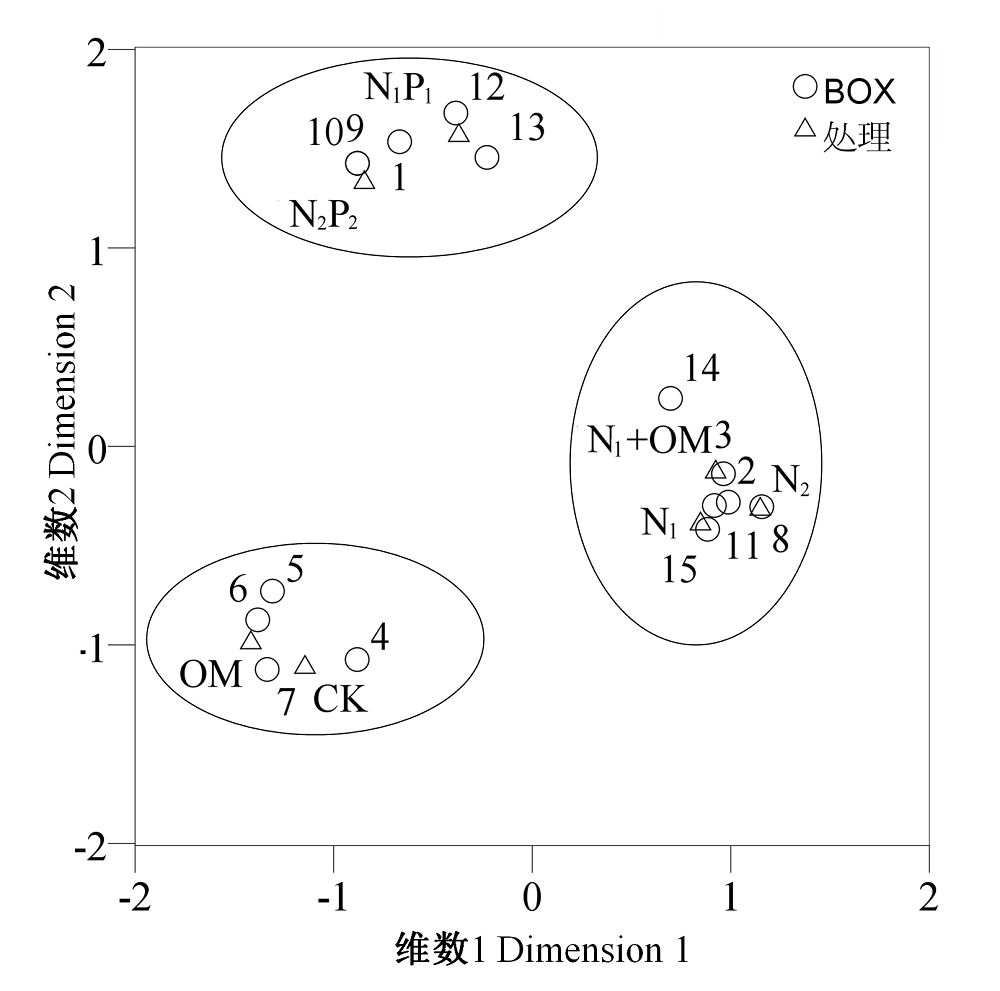
图4 大豆根瘤菌的BOX-PCR群与施肥处理进行相关性分析。图中?代表处理; ρ代表BOX-PCR群。
Fig. 4 Correlation analysis between fertilization treatments and BOX-PCR genomic groups of soybean rhizobia. ? Treatments; ρ Groups of BOX-PCR in the figure.
| 施肥处理 Treatments | pH | 有机质含量 Organic manure (g/kg) | 速效氮含量 Available N (mg/kg) | 速效磷含量 Available P (mg/kg) | 速效钾含量 Available K (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 6.91b | 22.3d | 54.10e | 2.32f | 175.27b |
| OM | 7.01a | 25.0b | 76.96c | 13.02d | 201.85a |
| N1 | 5.94d | 22.9cd | 75.85c | 2.92f | 158.40d |
| N2 | 5.00e | 23.0c | 95.39a | 5.48e | 143.78e |
| N1P1 | 5.94d | 24.5b | 69.12d | 58.10b | 167.00c |
| N2P2 | 4.94e | 23.6c | 95.65a | 124.93a | 154.12d |
| N1+OM | 6.32c | 28.0a | 85.72b | 14.35c | 199.58a |
表2 不同施肥处理土壤的理化性质
Table 2 Soil properties in different fertilization treatments
| 施肥处理 Treatments | pH | 有机质含量 Organic manure (g/kg) | 速效氮含量 Available N (mg/kg) | 速效磷含量 Available P (mg/kg) | 速效钾含量 Available K (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 6.91b | 22.3d | 54.10e | 2.32f | 175.27b |
| OM | 7.01a | 25.0b | 76.96c | 13.02d | 201.85a |
| N1 | 5.94d | 22.9cd | 75.85c | 2.92f | 158.40d |
| N2 | 5.00e | 23.0c | 95.39a | 5.48e | 143.78e |
| N1P1 | 5.94d | 24.5b | 69.12d | 58.10b | 167.00c |
| N2P2 | 4.94e | 23.6c | 95.65a | 124.93a | 154.12d |
| N1+OM | 6.32c | 28.0a | 85.72b | 14.35c | 199.58a |
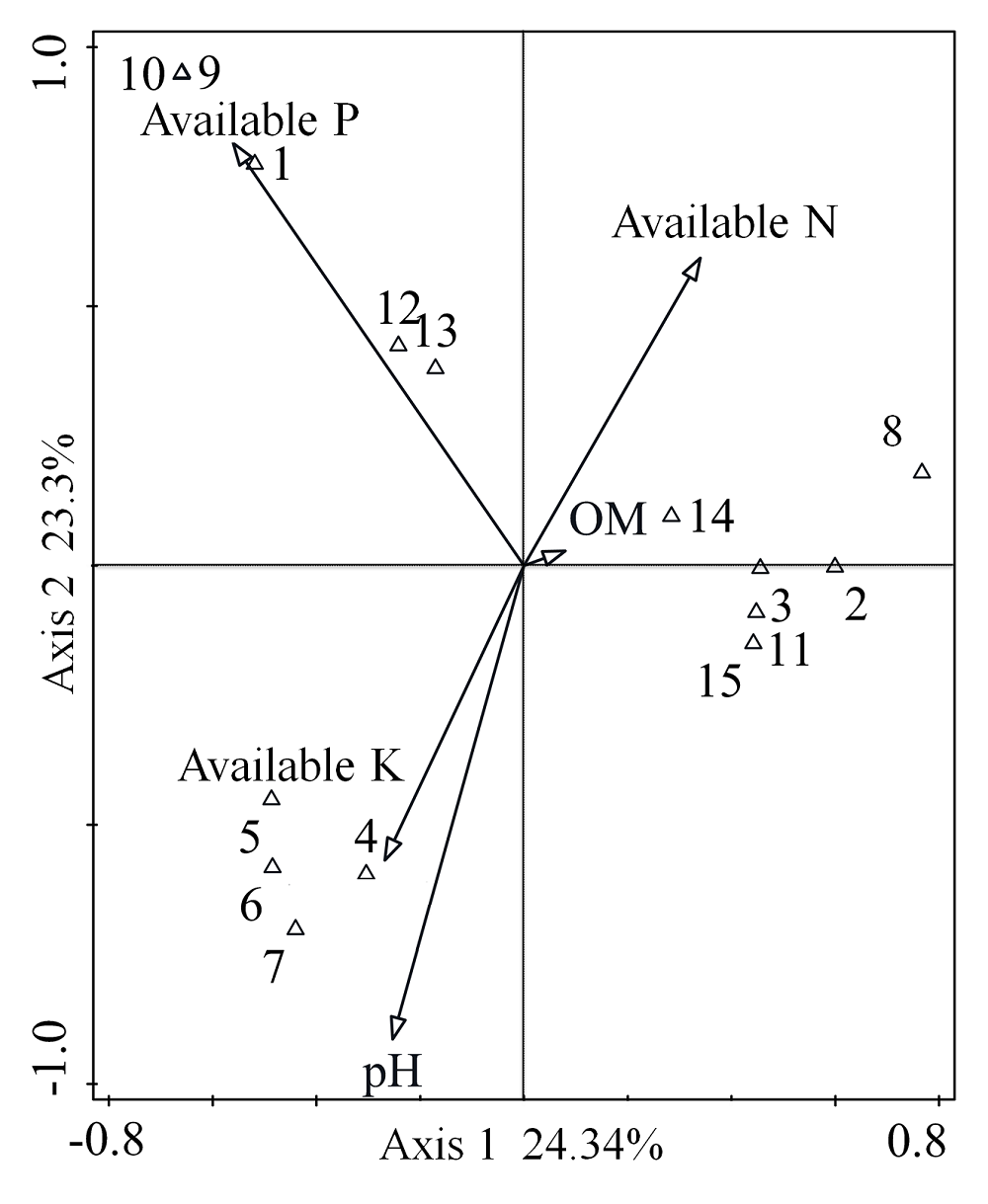
图5 大豆根瘤菌的BOX-PCR群与土壤理化性质典范对应分析。图中ρ代表BOX-PCR群。
Fig. 5 Canonical correspondence analysis between soil properties and BOX-PCR genomic groups of soybean rhizobia. ρ Groups of BOX-PCR in the figure.
| 多样性指数 Diversity index | 施肥处理 Treatments | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | OM | N1 | N2 | N1P1 | N2P2 | N1+OM | |
| 丰富度指数 Richness index | 1.485b* | 1.553b | 1.101d | 0.281e | 1.294c | 2.175a | 1.108d |
| Simpson指数 Simpson index | 0.767a | 0.815a | 0.562c | 0.431c | 0.682b | 0.707b | 0.706b |
| Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | 1.416b | 1.249c | 0.993d | 0.622e | 1.444b | 1.572a | 1.404b |
表3 不同施肥处理大豆根瘤菌多样性指数
Table 3 The diversity indexes of rhizobia in different fertilization treatments
| 多样性指数 Diversity index | 施肥处理 Treatments | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | OM | N1 | N2 | N1P1 | N2P2 | N1+OM | |
| 丰富度指数 Richness index | 1.485b* | 1.553b | 1.101d | 0.281e | 1.294c | 2.175a | 1.108d |
| Simpson指数 Simpson index | 0.767a | 0.815a | 0.562c | 0.431c | 0.682b | 0.707b | 0.706b |
| Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | 1.416b | 1.249c | 0.993d | 0.622e | 1.444b | 1.572a | 1.404b |
| 多样性指数 Diversity index | 土壤养分 Soil properties | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | 相关系数 Correlation coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丰富度指数 Richness index | X1 | 0.462 | 0.117 | -0.077 | -0.836 | -0.334 |
| X2 | 0.118 | 1.166 | 0.002 | -0.604 | 0.682 | |
| X3 | 0.074 | 0.009 | -0.309 | 0.253 | 0.027 | |
| X4 | -0.226 | -0.640 | -0.071 | 1.100 | 0.163 | |
| Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | X1 | -0.521 | 0.386 | 0.092 | -0.274 | -0.317 |
| X2 | -0.206 | 0.976 | -0.003 | -0.198 | 0.569 | |
| X3 | 0.130 | -0.008 | 0.370 | 0.083 | 0.575 | |
| X4 | 0.396 | -0.536 | 0.085 | 0.360 | 0.305 | |
| Simpson指数 Simpson index | X1 | -0.039 | 0.317 | -0.002 | -0.870 | -0.594 |
| X2 | -0.015 | 0.801 | 0.000 | -0.628 | 0.158 | |
| X3 | -0.010 | -0.006 | -0.010 | 0.263 | 0.237 | |
| X4 | 0.030 | -0.440 | 0.000 | 1.144 | 0.734 |
表4 土壤理化性质对大豆根瘤菌多样性的通径分析
Table 4 Analysis of path coefficients between diversity index of rhizobia and soil properties
| 多样性指数 Diversity index | 土壤养分 Soil properties | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | 相关系数 Correlation coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丰富度指数 Richness index | X1 | 0.462 | 0.117 | -0.077 | -0.836 | -0.334 |
| X2 | 0.118 | 1.166 | 0.002 | -0.604 | 0.682 | |
| X3 | 0.074 | 0.009 | -0.309 | 0.253 | 0.027 | |
| X4 | -0.226 | -0.640 | -0.071 | 1.100 | 0.163 | |
| Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | X1 | -0.521 | 0.386 | 0.092 | -0.274 | -0.317 |
| X2 | -0.206 | 0.976 | -0.003 | -0.198 | 0.569 | |
| X3 | 0.130 | -0.008 | 0.370 | 0.083 | 0.575 | |
| X4 | 0.396 | -0.536 | 0.085 | 0.360 | 0.305 | |
| Simpson指数 Simpson index | X1 | -0.039 | 0.317 | -0.002 | -0.870 | -0.594 |
| X2 | -0.015 | 0.801 | 0.000 | -0.628 | 0.158 | |
| X3 | -0.010 | -0.006 | -0.010 | 0.263 | 0.237 | |
| X4 | 0.030 | -0.440 | 0.000 | 1.144 | 0.734 |
| 1 |
Andrade DS, Murphy PJ, Giller KE ( 2002) The diversity of Phaseolus-nodulating rhizobial populations is altered by liming of acid soils planted with Phaseolus vulgaris L. in Brazil. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 68, 4025-4034.
DOI URL PMID |
| 2 |
Brockwell J, Pilka A, Holliday RA ( 1991) Soil pH is a major determinant of the numbers of naturally occurring Rhizobium meliloti in non-cultivated soils of New South Wales. Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture, 31, 211-219.
DOI URL |
| 3 |
Buckley DH, Schmidt TM ( 2003) Diversity and dynamics of microbial communities in soils from agro-ecosystems. Environmental Microbiology, 5, 441-452.
DOI URL PMID |
| 4 | Chen WX ( 陈文新), Wang ET ( 汪恩涛), Chen WF ( 陈文峰 ) ( 2004) The relationship between the symbiotic promiscuity of rhizobia and legumes and their geographical environments. Scientia Agricultura Sinica (中国农业科学), 37, 81-86. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 5 |
Escuredo PR, Minchin FR, Gogorcena Y, Iturbe-Ormaetxe I, Klucas RV, Becana M ( 1996) Involvement of activated oxygen in nitrate induced senescent of pea root nodules. Plant Physiology, 110, 1187-1195.
DOI URL PMID |
| 6 |
Grossman JM, Schipanski ME, Sooksanguan T, Seehaver S, Drinkwate LE ( 2011) Diversity of rhizobia in soybean [Glycine max(Vinton)] nodules varies under organic and conventional management. Applied Soil Ecology, 50, 14-20.
DOI URL |
| 7 |
Guan DW, Ma MC, Ma ZY, Jiang X, Li L, Cao FM, Shen DL, Chen HJ, Li J ( 2012) Analysis of two Bradyrhizobium japonicum strains with different symbiotic matching for nodulation by primary proteomic. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 11, 1377-1383.
DOI URL |
| 8 |
Guo JH, Liu XJ, Zhang Y, Shen JL, Han WX, Zhang WF, Christie P, Gouldin KWT ( 2010) Significant acidification in major Chinese croplands. Science, 327, 1008-1010.
DOI URL PMID |
| 9 | Hellsten A, Huss-Danell K ( 2001) Interaction effects of nitrogen and phosphorus on nodulation in red clover (Trifolium pratense L.). Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica, Section B: Soil and Plant Science, 50, 135-142. |
| 10 |
Herrmann L, Chotte JL, Thuita M, Lesueur D ( 2014) Effects of cropping systems, maize residues application and N fertilization on promiscuous soybean yields and diversity of native rhizobia in Central Kenya. Pedobiologia, 57, 75-85.
DOI URL |
| 11 |
Jorquera MA, Martínez OA, Marileo LG, Acuña JJ, Saggar S, Mora ML ( 2013) Effect of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization on the composition of rhizobacterial communities of two Chilean Andisol pastures. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 30, 99-107.
DOI URL PMID |
| 12 |
Kaschuk G, Hungria M, Andrade DS, Campo RJ ( 2006) Genetic diversity of rhizobia associated with common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) grown under no-tillage and conventional systems in Southern Brazil. Applied Soil Ecology, 32, 210-220.
DOI URL |
| 13 |
Lei X, Wang ET, Chen WF, Sui XH, Chen WX ( 2008) Diverse bacteria isolated from root nodules of wild Vicia species grown in temperate region of China. Archives of Microbiology, 190, 657-671.
DOI URL PMID |
| 14 | Li J ( 李俊), Shen DL ( 沈德龙), Lin XG ( 林先贵 ) ( 2011) Agricultural Microbial Research and Industrialization Progress (农业微生物研究与产业化进展). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 15 |
Li J, Xiao WL, Ma MC, Guan DW, Jiang X, Cao FM, Shen DL, Chen HJ, Li L ( 2011) Proteomic study on two Bradyrhizobium japonicum strains with different competitiveness for nodulation. Agricultural Sciences in China (中国农业科学英文版), 10, 1072-1079.
DOI URL |
| 16 |
Li M, Li Y, Chen WF, Sui XH, Li Y, Li Y Jr, Wang ET, Chen WX ( 2012) Genetic diversity, community structure and distribution of rhizobia in the root nodules of Caragana spp. from arid and semi-arid alkaline deserts, in the north of China. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 35, 239-245.
DOI URL PMID |
| 17 | Liu PF ( 刘朴方), Wang HY ( 王宏燕 ) ( 2012) Effects of organic and chemical fertilizer applications on the diversity of soybean rhizobia. Chinese Journal of Ecology (生态学杂志), 31, 1468-1472. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 18 | Lu RK ( 鲁如坤 ) ( 2000) Analysis Methods of Soil and Agricultural Chemistry (土壤农化分析). China Agricultural Science and Technology Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 19 |
Lu YL, Chen WF, Wang ET, Guan SH, Yan XR, Chen WX ( 2009) Genetic diversity and biogeography of rhizobia associated with Caragana species in three ecological regions of China. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 32, 351-361.
DOI URL PMID |
| 20 | Qian YQ( 钱迎倩) , Ma KP ( 马克平 ) ( 1994) The measurement of community diversity. In: Principles and Methodologies of Biodiversity Studies (生物多样性研究的原理与方法). China Science and Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 21 |
Malhi SS, Nyborg M, Harapiak JT ( 1998) Effects of long-term N fertilizer-induced acidification and liming on micronutrients in soil and in brome grass hay. Soil and Tillage Research, 48, 91-101.
DOI URL |
| 22 |
Man CX, Wang H, Chen WF, Sui XH, Wang ET, Chen WC ( 2008) Diverse rhizobia associated with soybean grown in the subtropical and tropical regions of China. Plant and Soil, 310, 77-87.
DOI URL |
| 23 |
Michie KA, Löwe J ( 2006) Dynamic filaments of the bacterial cytoskeleton. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 75, 467-492.
DOI URL PMID |
| 24 |
Mothapo NV, Grossman JM, Maul JE, Shi W, Isleib T ( 2013) Genetic diversity of resident soil rhizobia isolated from nodules of distinct hairy vetch (Vicia villosa Roth) genotypes. Applied Soil Ecology, 64, 201-213.
DOI URL |
| 25 |
Nassira R, Gilles B, Abdelhamid D, Karine H, Philippe LL, Gisèle L ( 2014) Genotypic and symbiotic diversity of rhizobium populations associated with cultivated lentil and pea in sub-humid and semi-arid regions of Eastern Algeria. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 37, 368-375.
DOI URL PMID |
| 26 |
Riccillo PM, Muglia CI, Bruijn FJ, Roe AJ, Booth IR, Aguilar OM ( 2000) Glutathione is involved in environmental stress responses in Rhizobium tropici, including acid tolerance. Journal of Bacteriology, 182, 1748-1753.
DOI URL PMID |
| 27 |
Smit E, Leeflang P, Gommans S, Broek J, Mil S, Wernars K ( 2001) Diversity and seasonal fluctuations of the dominant members of the bacterial soil community in a wheat field as determined by cultivation and molecular methods. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67, 2284-2291.
DOI URL PMID |
| 28 | Song YB ( 宋英博 ) ( 2010) Effect of different nitrogen application on protein and fat content in soybean. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences (黑龙江农业科学), 7, 52-53. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 29 | Sun JL ( 孙景玲), Wei D ( 魏丹), Ma XZ ( 马星竹), Liu DZ ( 刘德志), Guo WY ( 郭文义), Liu XL ( 刘晓莉), Lu WC ( 鹿文成 ) ( 2013) Establishing fertilization recommendation index of soybean in black soil region of Heilongjiang Province. Soybean Science (大豆科学), 32, 512-516. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 30 | Sun ZN ( 孙振宁), Duan XW ( 段兴武), Xie Y ( 谢云), Liu G ( 刘刚 ) ( 2012) Nutrient supplying capacity of typical black soil and fertilizer use efficiency of soybean in Heilongjiang Province. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin (中国农学通报), 28(15), 46-51. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 31 |
Terefework Z, Kaijalainen S, Lindström K ( 2001) AFLP fingerprinting as a tool to study the genetic diversity of Rhizobium galegae isolated from Galega orientalis and Galega officinalis. Journal of Biotechnology, 91, 169-180.
DOI URL PMID |
| 32 |
Tian CF, Wang ET, Han TX, Sui XH, Chen WX ( 2007) Genetic diversity of rhizobia associated with Vicia faba in three ecological regions of China. Archives of Microbiology, 188, 273-282.
DOI URL PMID |
| 33 | Vicent JM ( 1970) A Manual for the Practical Study of Root Nodule Bacteria. International Biological Programme Handbook No. 15. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford. |
| 34 |
Wang H, Man CX, Wang ET, Chen WX ( 2009) Diversity of rhizobia and interactions among the host legumes and rhizobial genotypes in an agricultural-forestry ecosystem. Plant and Soil, 314, 169-182.
DOI URL |
| 35 | Wang SQ ( 王树起), Han XZ ( 韩晓增), Qiao YF ( 乔云发), Yan J ( 严君), Li XH ( 李晓慧 ) ( 2009) Nodule growth, nodulation and nitrogen fixation in soybean (Glycine max L.) as affected by nitrogen application. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica (华北农学报), 24, 176-179. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 36 | Wang WW ( 王卫卫), Guan DW ( 关大伟), Ma MC ( 马鸣超), Li L ( 李力), Cao FM ( 曹凤明), Li J ( 李俊 ) ( 2013) Genetic diversity and phylogeny of soybean rhizobia isolated from northeast China. Soybean Science (大豆科学), 32, 433-437. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 37 | Wang Y ( 王英), Xie Y ( 谢云), Liu G ( 刘刚) , Duan XW ( 段兴武), Sun ZN ( 孙振宁 ) ( 2011) Experimental study on the impact of soil moisture on soybean growth in the North eastern black soil area of China. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas (干旱农业研究), 29(3), 53-57. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 38 |
Youseif SH, Abd El-Megeed FH, Ageez A, Mohamed ZK, Shamseldin A, Saleh SA ( 2014) Phenotypic characteristics and genetic diversity of rhizobia nodulating soybean in Egyptian soils. European Journal of Soil Biology, 60, 34-43.
DOI URL |
| 39 |
Zhang HX ( 张红侠), Feng RH ( 冯瑞华), Li J ( 李俊) , Guan DW ( 关大伟), Cao FM ( 曹凤明 ) ( 2010) Genetic diversity and phylogeny of soybean rhizobia isolated from the regions of Loess Plateau in China. Acta Microbiologica Sinica (微生物学报), 50, 1466-1473. (in Chinese with English abstract)
URL PMID |
| 40 | Zhang ML ( 张美玲), Zhu B ( 朱博), Li X ( 李旭), Ju WT ( 鞠文庭), Wei GH ( 韦革宏 ) ( 2008) Genetic diversity and co-evolution of Vicia rhizobia in different geographical environments. Journal of Northwest A & F University (西北农林科技大学学报) , 36, 192-198. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 41 |
Zhang WT ( 张伟涛), Yang KJ ( 杨江科), Yuan TY ( 袁天英), Zhou JC ( 周俊初 ) ( 2006) Genetic diversity and phylogeny of soybean bradyrhizobia isolated from south and north region of China. Acta Microbiologica Sinica (微生物学报), 46, 127-131. (in Chinese with English abstract)
URL PMID |
| [1] | 贾贞妮, 张意岑, 杜彦君, 任海保. 干扰对中亚热带森林群落物种多样性演替动态的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24078-. |
| [2] | 徐伟强, 苏强. 分形模型与一般性物种多度分布关系的检验解析:以贝类和昆虫群落为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23410-. |
| [3] | 陈蕾, 许志勇, 苏菩坤, 赖小甜, 赵兆. 依频声学多样性指数用于人类活动区域的适用能力[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(10): 24286-. |
| [4] | 卜向丽, 王静, 吴佳忆, 孙太福, 向荣伟, 鲁庆斌, 郝映红, 崔绍朋, 盛岩, 孟秀祥. 太行山东北部哺乳动物区系及多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(3): 331-339. |
| [5] | 尚素琴, 吴兴波, 王召龙, 彭鹤年, 周惠丽, 张红勇, 白映禄. 兴隆山国家级自然保护区不同生境的蝴蝶群落结构与种-多度分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(8): 983-992. |
| [6] | 李共国, 李平, 徐杭英, 于海燕, 俞建. 浙江水源地河流浮游动物多样性与环境因子的通径分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(2): 166-175. |
| [7] | 张全建, 杨彪, 付强, 王磊, 龚旭, 张远彬. 邛崃山系水鹿的冬季食性[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(10): 1192-1201. |
| [8] | 王国萍, 薛达元, 闻苡, 成功, 闵庆文. 土族生物资源利用相关的传统知识多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(7): 735-742. |
| [9] | 马燕婕, 何浩鹏, 沈文静, 刘标, 薛堃. 转基因玉米对田间节肢动物群落多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(4): 419-432. |
| [10] | 叶又茵, 项鹏, 王雨, 林茂. 福建6个港湾浮游植物多样性及其与水系的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(3): 285-293. |
| [11] | 周伟, 李明会, 李有兰. 滇西南四个自然保护区鱼类多样性及评价指标探究[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(3): 313-320. |
| [12] | 黄备, 魏娜, 孟伟杰, 张明霞. 基于压力-状态-响应模型的辽宁省长海海域海洋生物多样性评价[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(1): 48-54. |
| [13] | 刘哲, 李奇, 陈懂懂, 翟文婷, 赵亮, 徐世晓, 赵新全. 青藏高原高寒草甸物种多样性的海拔梯度分布格局及对地上生物量的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(4): 451-462. |
| [14] | 张敬怀. 珠江口及邻近海域大型底栖动物多样性随盐度、水深的变化趋势[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(3): 302-310. |
| [15] | 杨静, 贺学礼, 赵丽莉. 内蒙古荒漠沙柳AM真菌物种多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2011, 19(3): 377-385. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()