



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (4): 21425. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021425 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021425
所属专题: 青藏高原生物多样性与生态安全; 有机农业
潘雯1, 刘云慧1, 武泽浩1, 刘增力2, 韩文轩1,*( ), 宇振荣1
), 宇振荣1
收稿日期:2021-10-25
接受日期:2022-01-20
出版日期:2022-04-20
发布日期:2022-03-16
通讯作者:
韩文轩
作者简介:*E-mail: hanwenxuan@cau.edu.cn基金资助:
Wen Pan1, Yunhui Liu1, Zehao Wu1, Zengli Liu2, Wenxuan Han1,*( ), Zhenrong Yu1
), Zhenrong Yu1
Received:2021-10-25
Accepted:2022-01-20
Online:2022-04-20
Published:2022-03-16
Contact:
Wenxuan Han
摘要:
人类活动导致土地利用格局的剧烈变迁是全球生物多样性丧失的重要原因之一。为满足青海省生物多样性保护和社会经济发展对土地利用的需求, 本研究依据土地利用类型/干扰强度与生物多样性的关系, 制定了基线、美丽青海、智慧青海、和谐青海4种情景的设计方案, 并基于GeoSOS-FLUS模型和FLUS-Biodiversity模型分别模拟至2030年、2050年时, 4种情景下青海省土地利用布局及其原生群落平均物种多度(Mean Species Abundance, MSA)的空间格局演变。结果表明, 青海省大部分土地利用类型在现有格局的基础上均发生较大变化。其中, 基线情景(按原有发展趋势)中湿地、森林、草地的面积均有所下降, 导致生物多样性恢复速度缓慢。基于自然保护和经济发展的不同权衡, 美丽青海、智慧青海、和谐青海3种情景则对未来土地利用布局的优化效果较好, 大量中、高强度利用的草地恢复为湿地、原生林及低强度利用的草地, 部分常规农田转换为优质农田, 建设用地面积减少, 生物多样性因而得以较大提高。未来各情景下的青海省MSA值都能实现目标值, 生物多样性完整性相对于2020年都有所增加。
潘雯, 刘云慧, 武泽浩, 刘增力, 韩文轩, 宇振荣 (2022) 不同发展情景下青海省土地利用布局及生物多样性变化模拟. 生物多样性, 30, 21425. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021425.
Wen Pan, Yunhui Liu, Zehao Wu, Zengli Liu, Wenxuan Han, Zhenrong Yu (2022) Simulation of changes in land use distribution and biodiversity under different development scenarios in Qinghai Province. Biodiversity Science, 30, 21425. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021425.
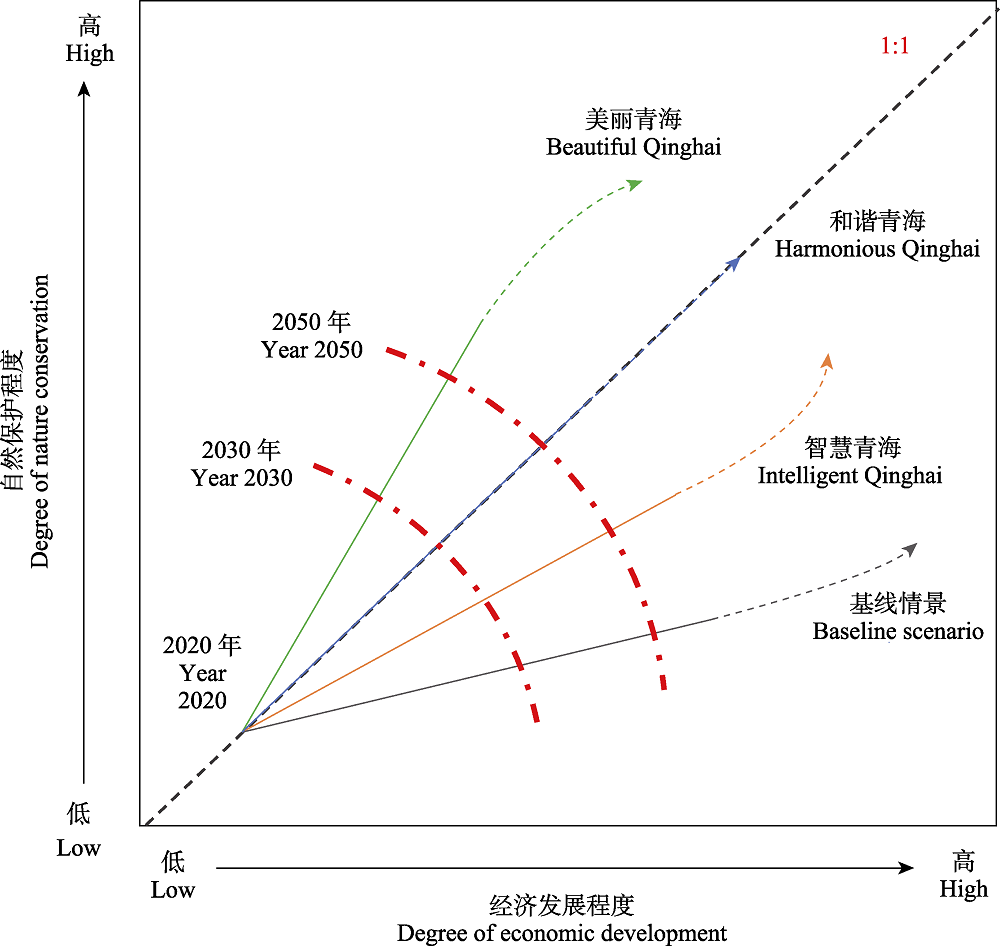
图1 本研究基于自然保护与经济发展权衡的情景设计的概念。“1:1”虚线表示自然保护程度与经济发展程度相等即二者始终处于均衡状态的特殊情景。曲线实线部分表示2030年和2050年4种情景下自然保护程度和经济发展程度的可能变化轨迹, 带箭头的密虚线部分表示2050年后其可能的变化趋势。情景目标的发展程度是有限制的, 在某一目标的发展程度达到或接近峰值时, 倾向于发展另一目标。红色点划线表示所有可能的情景在2030或2050年时的状态点(经济发展, 自然保护)构成的等值线。灰、棕、蓝和绿色线分别代表基线情景以及智慧青海、和谐青海和美丽青海3个理想情景的可能发展路径。
Fig. 1 Conception of scenario design in this study based on trade-offs between nature conservation and economic development. The “1:1” dashed line denotes the specific scenario under which nature conservation and economy development are kept in a strictly balanced way (i.e., the degrees of both parameters remain exactly identical). The solid parts of the four curves represent the possible change trajectories of natural conservation and economic development of the respective scenarios by 2030 and 2050, respectively; and the densely dashed lines with arrows represent their potential trends after 2050. The evolutional degree of certain scenario goal is limited; when the development of one goal is at or near its peak, it tends to develop another goal. The two dash-dotted red lines represent the isolines formed by the state points of (economic development, nature conservation) of all possible scenarios in 2030 or 2050. Gray, brown, blue and green lines stand for the possible pathways of the four scenarios: Baseline scenario, Intelligent Qinghai, Harmonious Qinghai and Beautiful Qinghai.
| Box 1 四个发展情景的设计思路和相关描述 (1)基线情景 基本描述: 该情景反映青海省社会、经济和环境等的自然变化情况, 主要目标为对现有的土地利用方式不做任何改进, 维持已有的自然保护地面积不变, 并按照现有趋势(2015-2020年)发展下去。 实现途径: 根据2015-2020年的土地利用类型数据, 运用马尔科夫链算法, 递推模拟出2030年、2050年土地利用类型的像元数量; 土地利用转换矩阵、邻域权重设置与2015-2020年一致。 愿景: 人口持续增加, 经济快速发展, 由于不限制进一步的土地开发, 生物多样性的恢复速度缓慢。 (2)美丽青海 基本描述: 该情景主要目标是最大限度地恢复自然生态系统, 扩大自然保护地的面积, 强调生物多样性的保护和恢复, 故命名为美丽青海。 实现途径: 限制低、中干扰湿地向高干扰湿地转换, 增大其邻域权重, 从而逐步扩大天然湿地面积, 恢复湿地的生物多样性; 限制森林向其他类型转换, 增大其邻域权重, 加强森林保护, 扩大森林面积; 减小常规农田邻域权重, 逐步缩减常规农田面积, 将农田转换成为草地、林地、湿地等土地利用类型, 增大优质农田的邻域权重, 适度发展基于自然生态的特色有机种植业; 降低草地的利用强度, 减少高强度草地的邻域权重, 育林、育草与禁牧、休牧、轮牧相结合; 限制其他土地利用类型向建设用地转换, 部分建设用地可转换为草地、人工湿地、优质农田, 城市规模逐渐变小。 愿景: 自然环境、人居环境质量提升, 生物多样性显著提高, 建设成生态文明高度发达的美丽青海。 (3)智慧青海 基本描述: 该情景主要目标是充分利用最新科技成果, 高效和可持续地开发利用自然生态系统对人类的各项服务功能, 最大限度地提高资源利用效率和产业效益, 从而满足社会经济的飞速发展, 故命名为智慧青海。 实现途径: 与美丽青海情景相比, 限制优质农田向湿地、森林、草地的转换, 扩大优质农田面积, 发展集约农业, 大面积应用与推广集约化和智能化的粮食生产系统; 限制建设的转换, 城市布局以重点城市群为中心, 城区更加紧凑、城乡间的连通性趋于更高, 城市规模较其他情景略有扩大; 高干扰湿地的邻域权重增加, 这是由于科技创新、科技成果转化模式逐渐成熟, 城市湿地(高强度湿地)的建设加大, 从而净化城市污水、去除污染物。 愿景: 区域城市化加大, 发挥青海气候冷凉干燥、清洁能源丰富等优势, 集约式高科技农业、畜牧业获大面积推广。 (4)和谐青海 基本描述: 该情景主要目标是促进人与自然和谐发展, 实现各类资源的环境友好型优化利用, 故命名为和谐青海, 是折衷了美丽青海和智慧青海情景设计策略的一种规划方案。 实现途径: 与美丽青海情景相比, 限制优质农田向其他土地利用类型的转换, 限制建设用地向常规农田转换, 适度发展农业和城市经济; 与智慧青海相比, 允许部分建设用地向林地、草地转换, 减少零散建设用地的面积, 城市趋于紧凑, 建设用地面积少于和谐青海情景, 多于美丽青海情景; 不提倡农业集约化发展, 而是提倡基于民间传统农艺和地方知识来指导农牧业和渔业的土地利用和管理, 依托日照、气候、种质等优势, 发展高质量草原牧场和农田。 愿景: 生态系统可持续发展, 生态系统服务功能增强, 实现自然生态单元和人类社会管理单元、自然生态承载力和人类发展生产力的“两个协同”。 |
| Box 1 四个发展情景的设计思路和相关描述 (1)基线情景 基本描述: 该情景反映青海省社会、经济和环境等的自然变化情况, 主要目标为对现有的土地利用方式不做任何改进, 维持已有的自然保护地面积不变, 并按照现有趋势(2015-2020年)发展下去。 实现途径: 根据2015-2020年的土地利用类型数据, 运用马尔科夫链算法, 递推模拟出2030年、2050年土地利用类型的像元数量; 土地利用转换矩阵、邻域权重设置与2015-2020年一致。 愿景: 人口持续增加, 经济快速发展, 由于不限制进一步的土地开发, 生物多样性的恢复速度缓慢。 (2)美丽青海 基本描述: 该情景主要目标是最大限度地恢复自然生态系统, 扩大自然保护地的面积, 强调生物多样性的保护和恢复, 故命名为美丽青海。 实现途径: 限制低、中干扰湿地向高干扰湿地转换, 增大其邻域权重, 从而逐步扩大天然湿地面积, 恢复湿地的生物多样性; 限制森林向其他类型转换, 增大其邻域权重, 加强森林保护, 扩大森林面积; 减小常规农田邻域权重, 逐步缩减常规农田面积, 将农田转换成为草地、林地、湿地等土地利用类型, 增大优质农田的邻域权重, 适度发展基于自然生态的特色有机种植业; 降低草地的利用强度, 减少高强度草地的邻域权重, 育林、育草与禁牧、休牧、轮牧相结合; 限制其他土地利用类型向建设用地转换, 部分建设用地可转换为草地、人工湿地、优质农田, 城市规模逐渐变小。 愿景: 自然环境、人居环境质量提升, 生物多样性显著提高, 建设成生态文明高度发达的美丽青海。 (3)智慧青海 基本描述: 该情景主要目标是充分利用最新科技成果, 高效和可持续地开发利用自然生态系统对人类的各项服务功能, 最大限度地提高资源利用效率和产业效益, 从而满足社会经济的飞速发展, 故命名为智慧青海。 实现途径: 与美丽青海情景相比, 限制优质农田向湿地、森林、草地的转换, 扩大优质农田面积, 发展集约农业, 大面积应用与推广集约化和智能化的粮食生产系统; 限制建设的转换, 城市布局以重点城市群为中心, 城区更加紧凑、城乡间的连通性趋于更高, 城市规模较其他情景略有扩大; 高干扰湿地的邻域权重增加, 这是由于科技创新、科技成果转化模式逐渐成熟, 城市湿地(高强度湿地)的建设加大, 从而净化城市污水、去除污染物。 愿景: 区域城市化加大, 发挥青海气候冷凉干燥、清洁能源丰富等优势, 集约式高科技农业、畜牧业获大面积推广。 (4)和谐青海 基本描述: 该情景主要目标是促进人与自然和谐发展, 实现各类资源的环境友好型优化利用, 故命名为和谐青海, 是折衷了美丽青海和智慧青海情景设计策略的一种规划方案。 实现途径: 与美丽青海情景相比, 限制优质农田向其他土地利用类型的转换, 限制建设用地向常规农田转换, 适度发展农业和城市经济; 与智慧青海相比, 允许部分建设用地向林地、草地转换, 减少零散建设用地的面积, 城市趋于紧凑, 建设用地面积少于和谐青海情景, 多于美丽青海情景; 不提倡农业集约化发展, 而是提倡基于民间传统农艺和地方知识来指导农牧业和渔业的土地利用和管理, 依托日照、气候、种质等优势, 发展高质量草原牧场和农田。 愿景: 生态系统可持续发展, 生态系统服务功能增强, 实现自然生态单元和人类社会管理单元、自然生态承载力和人类发展生产力的“两个协同”。 |
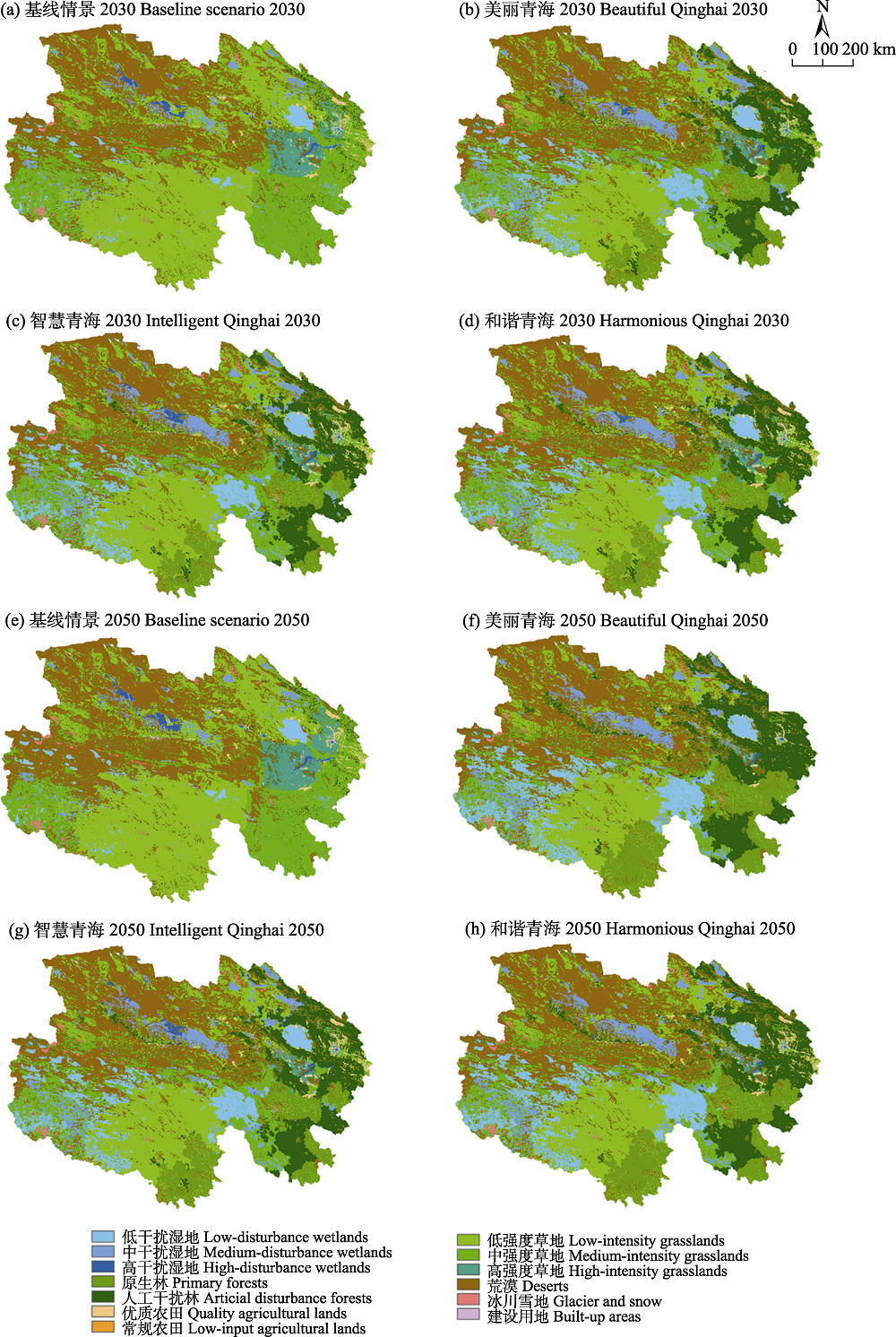
图3 青海省不同情景下2030年(a-d)和2050年(e-h)的土地利用空间分布模拟结果。各土地利用类型/干扰强度的描述参见附录2。
Fig. 3 Changes of spatial distribution of land use under different scenarios in Qinghai Province in 2030 (a-d) and 2050 (e-h). See Appendix 2 for the description of each land use type/disturbance intensity.
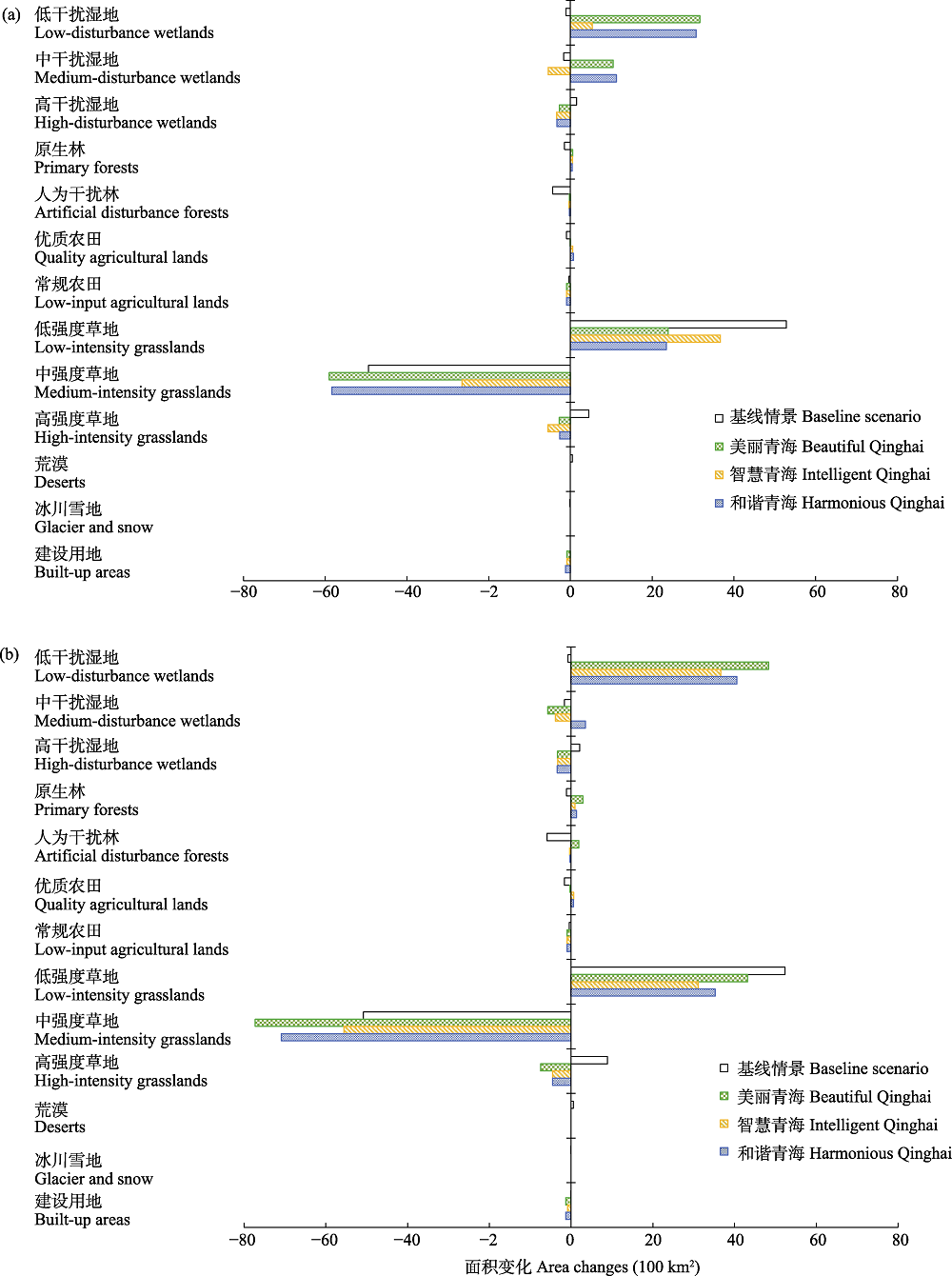
图4 不同情景下青海省2020-2030年(a)和2020-2050年(b)的土地利用类型/干扰强度的面积变化。各土地利用类型/干扰强度的描述参见附录2。
Fig. 4 Changes of land use types/disturbance intensities from 2020-2030 (a) and 2020-2050 (b) in Qinghai Province under different scenarios. See Appendix 2 for the description of each land use type/disturbance intensity.
| 情景 Scenarios | 年份 Year | MSA值 MSA value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 目标阈值 Target value | 模拟结果 Simulation result | ||
| 现状 Status quo | 2020 | - | 0.863 |
| 基线情景 Baseline scenario | 2030 | - | 0.881 |
| 2050 | - | 0.878 | |
| 美丽青海 Beautiful Qinghai | 2030 | 0.89 | 0.890 |
| 2050 | 0.91 | 0.910 | |
| 智慧青海 Intelligent Qinghai | 2030 | 0.89 | 0.886 |
| 2050 | 0.89 | 0.896 | |
| 和谐青海 Harmonious Qinghai | 2030 | 0.89 | 0.889 |
| 2050 | 0.89 | 0.900 | |
表1 青海省不同情景下的省域MSA值。MSA指平均物种多度, 省域MSA值定义参见公式2。
Table 1 Provincial MSA values of different scenarios in Qinghai Province. MSA means mean species abundance. See Equation 2 for the definition of regional MSA.
| 情景 Scenarios | 年份 Year | MSA值 MSA value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 目标阈值 Target value | 模拟结果 Simulation result | ||
| 现状 Status quo | 2020 | - | 0.863 |
| 基线情景 Baseline scenario | 2030 | - | 0.881 |
| 2050 | - | 0.878 | |
| 美丽青海 Beautiful Qinghai | 2030 | 0.89 | 0.890 |
| 2050 | 0.91 | 0.910 | |
| 智慧青海 Intelligent Qinghai | 2030 | 0.89 | 0.886 |
| 2050 | 0.89 | 0.896 | |
| 和谐青海 Harmonious Qinghai | 2030 | 0.89 | 0.889 |
| 2050 | 0.89 | 0.900 | |
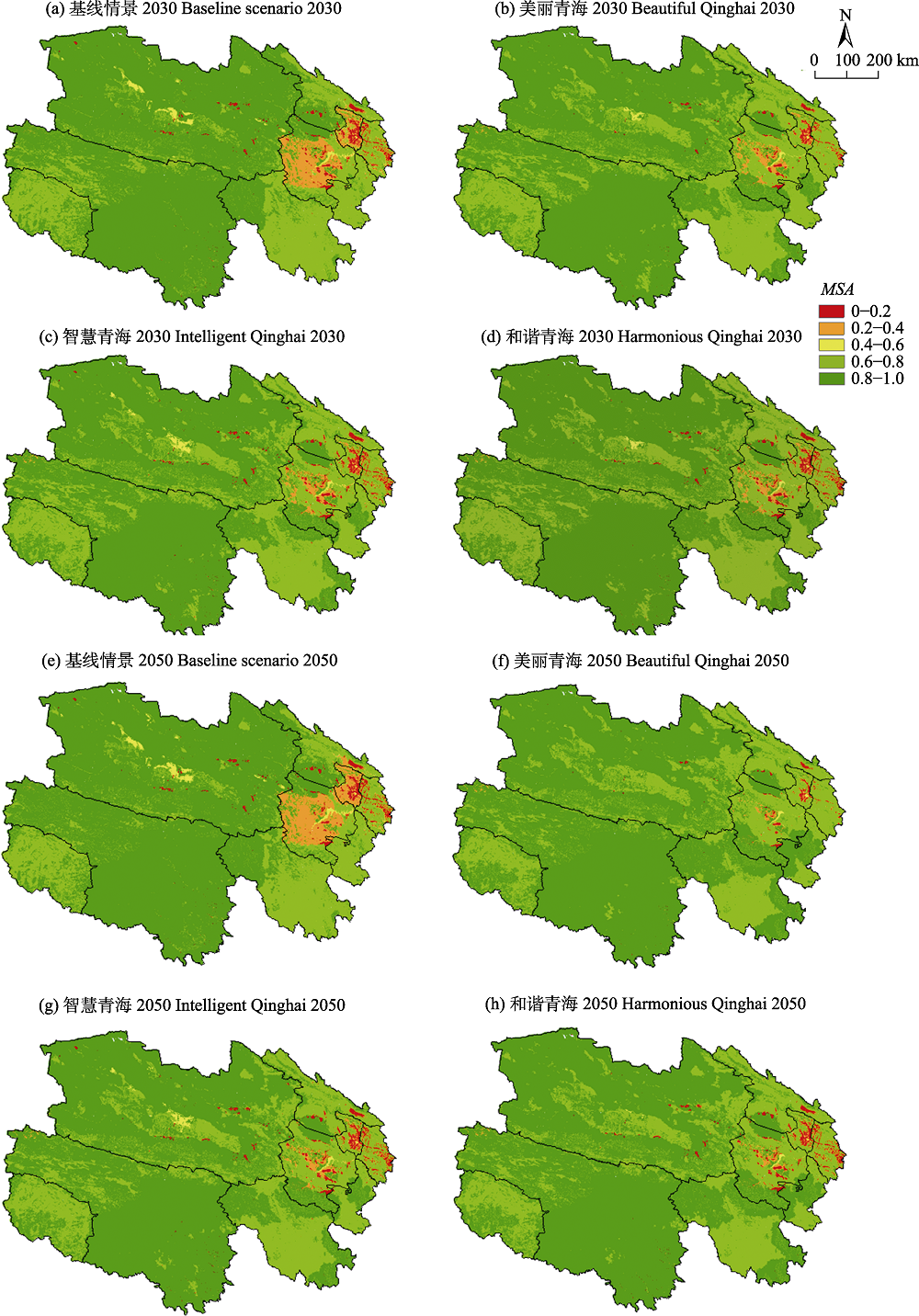
图5 不同情景下青海省2030年(a-d)和2050年(e-h)的MSA分布。MSA指平均物种多度, 区域MSA值定义参见公式2。
Fig. 5 Patterns of MSA under different scenarios in Qinghai Province in 2030 (a-d) and 2050 (e-h). MSA means mean species abundance. See Equation 2 for the definition of regional MSA.
| [1] |
Alkemade R, Oorschot M, Miles L, Nellemann C, Bakkenes M, ten Brink B (2009) GLOBIO3: A framework to investigate options for reducing global terrestrial biodiversity loss. Ecosystems, 12, 374-390.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Dalkey N, Helmer O (1963) An experimental application of the DELPHI method to the use of experts. Management Science, 9, 458-467.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Dong X (2009) Evaluation of forest resources in Qinghai Province. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 37, 5727-5728, 5751. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 董旭 (2009) 青海省森林资源评价. 安徽农业科学, 37, 5727-5728, 5751.] | |
| [4] | Fang JY, Zhu JL, Shi Y (2018) The responses of ecosystems to global warming. Chinese Science Bulletin, 63, 136-140. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 方精云, 朱江玲, 石岳 (2018) 生态系统对全球变暖的响应. 科学通报, 63, 136-140.] | |
| [5] | Fu BJ, Zhang LW (2014) Land-use change and ecosystem services: Concepts, methods and progress. Progress in Geography, 33, 441-446. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[ 傅伯杰, 张立伟 (2014) 土地利用变化与生态系统服务: 概念、方法与进展. 地理科学进展, 33, 441-446.]
DOI |
|
| [6] | Gitay H, Suarez A, Dokken DJ, Watson RT (2002) Climate Change and Biodiversity. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), Geneva, Switzerland. |
| [7] | IPBES (Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services) (2016) The methodological assessment report on scenarios and models of biodiversity and ecosystem services. https://digitallibrary.un.org/record/3793989. (accessed on 2022-03-11) |
| [8] | IPBES (Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services) 2021) Stakeholder days and 8th session of the IPBES plenary. https://enb.iisd.org/biodiversity/IPBES8. (accessed on 2021-12-20) |
| [9] |
Li X, Chen YM, Liu XP, Li D, He JQ (2011a) Concepts, methodologies, and tools of an integrated geographical simulation and optimization system. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 25, 633-655.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Li X, Liu XP (2006) An extended cellular automaton using case-based reasoning for simulating urban development in a large complex region. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 20, 1109-1136.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Li X, Shi X, He JQ, Liu X (2011b) Coupling simulation and optimization to solve planning problems in a fast-developing area. Annals of the Association of American Geographers, 101, 1032-1048.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Liu XP, Liang X, Li X, Xu XC, Ou JP, Chen YM, Li SY, Wang SJ, Pei FS (2017) A future land use simulation model (FLUS) for simulating multiple land use scenarios by coupling human and natural effects. Landscape and Urban Planning, 168, 94-116.
DOI URL |
| [13] | Liu XP, Zhao LF, Zeng L (2020) Flus-Biodiversity Software Manual. Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [ 刘小平, 赵林峰, 曾莉 (2020) FLUS-Biodiversity软件用户手册. 中山大学, 广州.] | |
| [14] | Lü AF, Zhou L, Zhu WB (2014) The remote sensing based dynamic monitoring of land desertification in Qinghai Province. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 29, 803-811. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吕爱锋, 周磊, 朱文彬 (2014) 青海省土地荒漠化遥感动态监测. 遥感技术与应用, 29, 803-811.] | |
| [15] |
Majer JD, Beeston G (1996) The biodiversity integrity index: An illustration using ants in western Australia. Conservation Biology, 10, 65-73.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Pereira HM, Leadley PW, Proença V, Alkemade R, Scharlemann JPW, Fernandez-Manjarrés JF, Araújo MB, Balvanera P, Biggs R, Cheung WWL, Chini L, Cooper HD, Gilman EL, Guénette S, Hurtt GC, Huntington HP, Mace GM, Oberdorff T, Revenga C, Rodrigues P, Scholes RJ, Sumaila UR, Walpole M (2010) Scenarios for global biodiversity in the 21st century. Science, 330, 1496-1501.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Pereira LM, Davies KK, den Belder E, Ferrier S, Karlsson-Vinkhuyzen S, Kim H, Kuiper JJ, Okayasu S, Palomo MG, Pereira HM, Peterson G, Sathyapalan J, Schoolenberg M, Alkemade R, Carvalho Ribeiro S, Greenaway A, Hauck J, King N, Lazarova T, Ravera F, Chettri N, Cheung WWL, Hendriks RJJ, Kolomytsev G, Leadley P, Metzger JP, Ninan KN, Pichs R, Popp A, Rondinini C, Rosa I, van Vuuren D, Lundquist CJ (2020) Developing multiscale and integrative nature-people scenarios using the Nature Futures Framework. People and Nature, 2, 1172-1195.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Polasky S, Nelson E, Pennington D, Johnson KA (2011) The impact of land-use change on ecosystem services, biodiversity and returns to landowners: A case study in the state of Minnesota. Environmental and Resource Economics, 48, 219-242.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Powers RP, Jetz W (2019) Global habitat loss and extinction risk of terrestrial vertebrates under future land-use-change scenarios. Nature Climate Change, 9, 323-329.
DOI |
| [20] |
Rosa IMD, Pereira HM, Ferrier S, Alkemade R, Acosta LA, Akcakaya HR, Belder E, Fazel AM, Fujimori S, Harfoot M, Harhash KA, Harrison PA, Hauck J, Hendriks RJJ, Hernández G, Jetz W, Karlsson VSI, Kim H, King N, Kok MTJ, Kolomytsev GO, Lazarova T, Leadley P, Lundquist CJ, Márquez JG, Meyer C, Navarro LM, Nesshöver C, Ngo HT, Ninan KN, Palomo MG, Pereira LM, Peterson GD, Pichs R, Popp A, Purvis A, Ravera F, Rondinini C, Sathyapalan J, Schipper AM, Seppelt R, Settele J, Sitas N, Vuuren D (2017) Multiscale scenarios for nature futures. Nature Ecology and Evolution, 1, 1416-1419.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Saito O, Kamiyama C, Hashimoto S, Matsui T, Shoyama K, Kabaya K, Uetake T, Taki H, Ishikawa Y, Matsushita K, Yamane F, Hori J, Ariga T, Takeuchi K (2019) Co-design of national-scale future scenarios in Japan to predict and assess natural capital and ecosystem services. Sustainability Science, 14, 5-21.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Sala OE, Chapin FS, Armesto JJ, Berlow E, Bloomfield J, Dirzo R, Huber-Sanwald E, Huenneke LF, Jackson RB, Kinzig A, Leemans R, Lodge DM, Mooney HA, Oesterheld M, Poff NL, Sykes MT, Walker BH, Walker M, Wall DH (2000)Global biodiversity scenarios for the year 2100. Science (New York), 287, 1770-1774. |
| [23] |
Scholes RJ, Biggs R (2005) A biodiversity intactness index. Nature, 434, 45-49.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Xin YJ, Du TY, Xin YC, Wu AD, Lu FG (2011) The evaluation of carrying capacity of grassland in Qinghai. Qinghai Prataculture, 20, 13-22. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 辛有俊, 杜铁瑛, 辛玉春, 吴阿迪, 陆福根 (2011) 青海草地载畜量计算方法与载畜压力评价. 青海草业, 20, 13-22.] | |
| [25] | Xu HG, Cao Y, Yu DD, Cao MC, He YX, Gill M, Pereira HM (2021) Ensuring effective implementation of the post-2020 global biodiversity targets. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 5, 411-418. |
| [26] | Yu DD, Tong WJ, Liu W, Yi JF, Chen MM, Cao MC, Xu HG (2021) A preliminary study on scenarios for biodiversity targets in China based on the “Nature Futures Framework”. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 37, 1234-1241. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 于丹丹, 童文君, 刘威, 伊剑锋, 陈萌萌, 曹铭昌, 徐海根 (2021) 基于“自然未来框架”的中国生物多样性保护目标情景研究初探. 生态与农村环境学报, 37, 1234-1241.] | |
| [27] | Zeng YN, Jin WP, He LL, Wu KJ, Yu FF, Xu YY (2012) Land use mapping using remote sensing for eastern part of Qinghai Plateau. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 28, 225-231. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 曾永年, 靳文凭, 何丽丽, 吴孔江, 于菲菲, 徐艳艳 (2012) 青海高原东部农业区土地利用遥感分类制图. 农业工程学报, 28, 225-231.] | |
| [28] | Zhang MX, Wang DX (2018) Quantitative investigation of the coupling relationship between urbanization and eco-environment in Qinghai Province. Qinghai Social Sciences, (3), 59-65. (in Chinese) |
| [ 张明霞, 王得祥 (2018) 青海城市化与生态环境耦合关系测度. 青海社会科学, (3), 59-65.] |
| [1] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [2] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [3] | 张雨琦, 文君, 张引, 李晟之. 大熊猫国家公园全民公益性评价研究: 基于利益相关者感知视角[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24240-. |
| [4] | 鄢德奎. 中国生物多样性保护政策的共同要素、不足和优化建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23293-. |
| [5] | 李雪萌, 蒋际宝, 张曾鲁, 刘晓静, 王亚利, 吴宜钊, 李银生, 邱江平, 赵琦. 宝天曼国家级自然保护区蚯蚓物种多样性及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23352-. |
| [6] | 王启蕃, 刘小慧, 朱紫薇, 刘磊, 王鑫雪, 汲旭阳, 周绍春, 张子栋, 董红雨, 张明海. 黑龙江北极村国家级自然保护区鸟类与兽类多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 24024-. |
| [7] | 所翟, 俞渃茜, 李媛辉, 徐基良. 基于实证分析中国自然保护区地方立法问题检视和优化路径[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23287-. |
| [8] | 刘啸林, 吴友贵, 张敏华, 陈小荣, 朱志成, 陈定云, 董舒, 李步杭, 丁炳扬, 刘宇. 浙江百山祖25 ha亚热带森林动态监测样地群落组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23294-. |
| [9] | 黄小龙, 蒙秉顺, 李海波, 冉伟, 杨伟, 王丞, 谢波, 张旭, 冉景丞, 张明明. 基于红外相机的黔金丝猴及其同域分布物种种间关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23402-. |
| [10] | 杨向林, 赵彩云, 李俊生, 种方方, 李文金. 植物入侵导致群落谱系结构更加聚集: 以广西国家级自然保护区草本植物为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24175-. |
| [11] | 毛锐锐, 沈拓, 李慧, 田琳楚, 谭海蓉, 卢李荣, 吴小刚, 范宗骥, 伍国仪, 李杰, 吴勇, 朱弼成, 肖治术. 广东车八岭国家级自然保护区无尾两栖类动物鸣声特征数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(10): 24356-. |
| [12] | 崔国发. 关于自然保护地整合优化工作中几个关键问题的讨论与建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 22447-. |
| [13] | 邢超, 林依, 周智强, 赵联军, 蒋仕伟, 林蓁蓁, 徐基良, 詹祥江. 基于DNA条形码技术构建王朗国家级自然保护区陆生脊椎动物遗传资源数据库及物种鉴定[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 22661-. |
| [14] | 陈本平, 陈建武, 凌征文, 杨旭, 陈鑫, 李生强, 杨彪. 四川老君山国家级自然保护区林下鸟兽多样性及动态变化数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22566-. |
| [15] | 姚雪, 陈星, 戴尊, 宋坤, 邢诗晨, 曹宏彧, 邹璐, 王健. 采集策略对叶附生苔类植物发现概率及物种多样性的重要性[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22685-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()