



生物多样性 ›› 2008, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (6): 562-569. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2008.08201 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2008.08201
郑健1,2, 郑勇奇1,*( ), 张川红1, 宗亦臣1, 李伯菁1, 吴超3
), 张川红1, 宗亦臣1, 李伯菁1, 吴超3
收稿日期:2008-08-19
接受日期:2008-10-29
出版日期:2008-11-20
发布日期:2008-11-20
通讯作者:
郑勇奇
基金资助:
Jian Zheng1,2, Yongqi Zheng1,*( ), Chuanhong Zhang1, Yichen Zong1, Bojing Li1, Chao Wu3
), Chuanhong Zhang1, Yichen Zong1, Bojing Li1, Chao Wu3
Received:2008-08-19
Accepted:2008-10-29
Online:2008-11-20
Published:2008-11-20
Contact:
Yongqi Zheng
About author:* E-mail: zhengyq@caf.ac.cn摘要:
花楸树(Sorbus pohuashanensis)是我国北方一种观赏兼经济用途的树种。本研究采用水平淀粉凝胶同工酶电泳技术, 对采自山东、山西、河北、辽宁4个省的8个花楸树天然群体的种子样本进行了分析, 旨在了解花楸树天然群体的遗传多样性和遗传结构, 为该树种的保护与利用提供科学依据。4个酶系统10个位点的检测结果表明, 花楸树群体水平上的遗传多样性较高, 每位点平均等位基因数(Na)为2.2000, 多态位点百分率(P)为100%, 期望杂合度(He)为0.4240。花楸树8个群体间的有效等位基因数(Ne)、He和Shannon信息指数差异较小,3个指标从高到低依次为: 河北驼梁山>河北雾灵山>山西庞泉沟>河北白石山>山东崂山>河北塞罕坝>山东泰山>辽宁老秃顶子。群体间遗传分化系数(Fst)为0.0758, 群体间总的基因流较高(Nm = 3.0472), 群体间遗传一致度较高(I为0.8585- 0.9872), 表明群体间遗传分化程度小。在单个群体中, 通过χ2检验, 花楸树群体有73.62%的位点组合显著偏离Hardy-Weinberg平衡(P<0.05), 总群体水平近交系数(Fit)和单个群体水平近交系数(Fis)分别为-0.3105和-0.4180, 表明无论在总体水平还是群体内个体间, 花楸树群体表现为杂合体过量的现象。UPGMA聚类结果显示, 8个群体的遗传距离与地理距离相关性不显著。
郑健, 郑勇奇, 张川红, 宗亦臣, 李伯菁, 吴超 (2008) 花楸树天然群体的遗传多样性研究. 生物多样性, 16, 562-569. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2008.08201.
Jian Zheng, Yongqi Zheng, Chuanhong Zhang, Yichen Zong, Bojing Li, Chao Wu (2008) Genetic diversity in natural populations of Sorbus pohuashanensis. Biodiversity Science, 16, 562-569. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2008.08201.
| 群体代号 Population code | 采样地 Seed collection site | 经纬度 Geographic location | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 家系数量 No. of families | 每家系种子数 No. of seeds per family | 样本大小 Sample size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDL | 山东崂山 Laoshan, Shandong | 120°37.5′E 36°11′N | 493-991 | 12 | 30 | 360 |
| SDT | 山东泰山 Taishan, Shandong | 117°06.1′E 36°15.8′N | 1,002-1,451 | 30 | 10 | 300 |
| SXP | 山西庞泉沟 Pangquangou, Shanxi | 111°25.7′E 37°53.6′N | 1,834-2,179 | 12 | 30 | 360 |
| HBB | 河北白石山 Baishishan, Hebei | 114°41.0′E 39°13.2′N | 1,654-1,931 | 12 | 30 | 360 |
| HBT | 河北驼梁山 Tuoliangshan, Hebei | 113°49.5′E 38°45.1′N | 1,564-1,971 | 30 | 8 | 240 |
| HBW | 河北雾灵山 Wulingshan, Hebei | 117°35.0′E 40°38.0′N | 809-1,847 | 30 | 8 | 240 |
| HBS | 河北塞罕坝 Saihanba, Hebei | 117°39.0′E 42°36.0′N | 1,287-1,674 | 30 | 8 | 240 |
| LNL | 辽宁老秃顶子 Laotudingzi, Liaoning | 124°53.9′E 41°19.2′N | 890-1,245 | 12 | 30 | 360 |
表1 花楸树采样群体的地理位置和样本量
Table 1 Geographic locations and sample size of Sorbus pohuashanensis populations
| 群体代号 Population code | 采样地 Seed collection site | 经纬度 Geographic location | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 家系数量 No. of families | 每家系种子数 No. of seeds per family | 样本大小 Sample size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDL | 山东崂山 Laoshan, Shandong | 120°37.5′E 36°11′N | 493-991 | 12 | 30 | 360 |
| SDT | 山东泰山 Taishan, Shandong | 117°06.1′E 36°15.8′N | 1,002-1,451 | 30 | 10 | 300 |
| SXP | 山西庞泉沟 Pangquangou, Shanxi | 111°25.7′E 37°53.6′N | 1,834-2,179 | 12 | 30 | 360 |
| HBB | 河北白石山 Baishishan, Hebei | 114°41.0′E 39°13.2′N | 1,654-1,931 | 12 | 30 | 360 |
| HBT | 河北驼梁山 Tuoliangshan, Hebei | 113°49.5′E 38°45.1′N | 1,564-1,971 | 30 | 8 | 240 |
| HBW | 河北雾灵山 Wulingshan, Hebei | 117°35.0′E 40°38.0′N | 809-1,847 | 30 | 8 | 240 |
| HBS | 河北塞罕坝 Saihanba, Hebei | 117°39.0′E 42°36.0′N | 1,287-1,674 | 30 | 8 | 240 |
| LNL | 辽宁老秃顶子 Laotudingzi, Liaoning | 124°53.9′E 41°19.2′N | 890-1,245 | 12 | 30 | 360 |
| 位点 Locus | 等位基因 Allele | 等位基因频率 Allele frequencies | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBW | HBS | HBT | HBB | SDL | SDT | SXP | LNL | ||||||||||||||
| Pgm-1 | a | 0.3229 | 0.3500 | 0.2497 | 0.1958 | 0.2458 | 0.2467 | 0.2917 | 0.4889 | ||||||||||||
| b | 0.4521 | 0.3667 | 0.4979 | 0.4181 | 0.4222 | 0.3433 | 0.4486 | 0.2278 | |||||||||||||
| c | 0.2550 | 0.2833 | 0.2542 | 0.3861 | 0.3319 | 0.4100 | 0.2597 | 0.2833 | |||||||||||||
| Pgm-2 | a | 0.6917 | 0.9417 | 0.4250 | 0.8194 | 0.1736 | 0.2233 | 0.7181 | 0.7514 | ||||||||||||
| b | 0.3083 | 0.0583 | 0.5750 | 0.1806 | 0.8264 | 0.7767 | 0.2819 | 0.2486 | |||||||||||||
| Pgm-3 | a | 0.6917 | 0.7396 | 0.5021 | 0.8986 | 0.3764 | 0.6167 | 0.9361 | 0.9333 | ||||||||||||
| b | 0.3083 | 0.2604 | 0.4979 | 0.1014 | 0.6236 | 0.3833 | 0.0639 | 0.0667 | |||||||||||||
| Pgi-1 | a | 0.0167 | 0.0125 | 0.0854 | 0.0181 | 0.0556 | 0.0000 | 0.0361 | 0.0153 | ||||||||||||
| b | 0.1437 | 0.2167 | 0.1187 | 0.1889 | 0.3889 | 0.2500 | 0.2153 | 0.2708 | |||||||||||||
| c | 0.8396 | 0.7708 | 0.7958 | 0.7931 | 0.5556 | 0.7500 | 0.7486 | 0.7139 | |||||||||||||
| Pgi-2 | a | 0.6854 | 0.9500 | 0.5583 | 0.6611 | 0.8333 | 0.9450 | 0.6264 | 0.7194 | ||||||||||||
| b | 0.3146 | 0.0500 | 0.4417 | 0.3389 | 0.1667 | 0.0550 | 0.3736 | 0.2806 | |||||||||||||
| Pgd-1 | a | 0.7562 | 0.6771 | 0.8729 | 0.9069 | 0.9347 | 0.9867 | 0.6917 | 0.9653 | ||||||||||||
| b | 0.2437 | 0.3229 | 0.1271 | 0.0931 | 0.0653 | 0.0133 | 0.3083 | 0.0347 | |||||||||||||
| Pgd-2 | a | 0.0375 | 0.1562 | 0.0042 | 0.1861 | 0.0000 | 0.2050 | 0.0278 | 0.1181 | ||||||||||||
| b | 0.9625 | 0.8438 | 0.9958 | 0.8139 | 1.0000 | 0.7950 | 0.9722 | 0.8819 | |||||||||||||
| Pgd-3 | a | 0.5104 | 0.5250 | 0.5104 | 0.5194 | 0.5056 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5014 | ||||||||||||
| b | 0.4896 | 0.4750 | 0.4896 | 0.4806 | 0.4944 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.4986 | |||||||||||||
| Mdh-1 | a | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | ||||||||||||
| b | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | |||||||||||||
| Mdh-2 | a | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | ||||||||||||
| b | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | |||||||||||||
表2 8个花楸树群体等位基因频率分布(群体代号同表1)
Table 2 Allele frequencies in eight natural populations of Sorbus pohuashanensis. Population codes are the same as in Table 1.
| 位点 Locus | 等位基因 Allele | 等位基因频率 Allele frequencies | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBW | HBS | HBT | HBB | SDL | SDT | SXP | LNL | ||||||||||||||
| Pgm-1 | a | 0.3229 | 0.3500 | 0.2497 | 0.1958 | 0.2458 | 0.2467 | 0.2917 | 0.4889 | ||||||||||||
| b | 0.4521 | 0.3667 | 0.4979 | 0.4181 | 0.4222 | 0.3433 | 0.4486 | 0.2278 | |||||||||||||
| c | 0.2550 | 0.2833 | 0.2542 | 0.3861 | 0.3319 | 0.4100 | 0.2597 | 0.2833 | |||||||||||||
| Pgm-2 | a | 0.6917 | 0.9417 | 0.4250 | 0.8194 | 0.1736 | 0.2233 | 0.7181 | 0.7514 | ||||||||||||
| b | 0.3083 | 0.0583 | 0.5750 | 0.1806 | 0.8264 | 0.7767 | 0.2819 | 0.2486 | |||||||||||||
| Pgm-3 | a | 0.6917 | 0.7396 | 0.5021 | 0.8986 | 0.3764 | 0.6167 | 0.9361 | 0.9333 | ||||||||||||
| b | 0.3083 | 0.2604 | 0.4979 | 0.1014 | 0.6236 | 0.3833 | 0.0639 | 0.0667 | |||||||||||||
| Pgi-1 | a | 0.0167 | 0.0125 | 0.0854 | 0.0181 | 0.0556 | 0.0000 | 0.0361 | 0.0153 | ||||||||||||
| b | 0.1437 | 0.2167 | 0.1187 | 0.1889 | 0.3889 | 0.2500 | 0.2153 | 0.2708 | |||||||||||||
| c | 0.8396 | 0.7708 | 0.7958 | 0.7931 | 0.5556 | 0.7500 | 0.7486 | 0.7139 | |||||||||||||
| Pgi-2 | a | 0.6854 | 0.9500 | 0.5583 | 0.6611 | 0.8333 | 0.9450 | 0.6264 | 0.7194 | ||||||||||||
| b | 0.3146 | 0.0500 | 0.4417 | 0.3389 | 0.1667 | 0.0550 | 0.3736 | 0.2806 | |||||||||||||
| Pgd-1 | a | 0.7562 | 0.6771 | 0.8729 | 0.9069 | 0.9347 | 0.9867 | 0.6917 | 0.9653 | ||||||||||||
| b | 0.2437 | 0.3229 | 0.1271 | 0.0931 | 0.0653 | 0.0133 | 0.3083 | 0.0347 | |||||||||||||
| Pgd-2 | a | 0.0375 | 0.1562 | 0.0042 | 0.1861 | 0.0000 | 0.2050 | 0.0278 | 0.1181 | ||||||||||||
| b | 0.9625 | 0.8438 | 0.9958 | 0.8139 | 1.0000 | 0.7950 | 0.9722 | 0.8819 | |||||||||||||
| Pgd-3 | a | 0.5104 | 0.5250 | 0.5104 | 0.5194 | 0.5056 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5014 | ||||||||||||
| b | 0.4896 | 0.4750 | 0.4896 | 0.4806 | 0.4944 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.4986 | |||||||||||||
| Mdh-1 | a | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | ||||||||||||
| b | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | |||||||||||||
| Mdh-2 | a | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | ||||||||||||
| b | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | |||||||||||||
| 群体 Population | 样本数量 Sample size | Na | Ne | P (%) | Ho | He | Is |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 河北雾灵山 HBW | 240 | 2.2000 | 1.8068 | 100.00 | 0.5717 | 0.4148 | 0.6206 |
| 河北塞罕坝 HBS | 240 | 2.2000 | 1.7510 | 100.00 | 0.5500 | 0.3819 | 0.5814 |
| 河北驼梁山 HBT | 240 | 2.2000 | 1.8423 | 100.00 | 0.5771 | 0.4192 | 0.6234 |
| 河北白石山 HBB | 360 | 2.2000 | 1.7854 | 100.00 | 0.5436 | 0.3875 | 0.5932 |
| 山东崂山 SDL | 360 | 2.1000 | 1.7837 | 90.00 | 0.5342 | 0.3850 | 0.5824 |
| 山东泰山 SDT | 300 | 2.1000 | 1.7538 | 100.00 | 0.5403 | 0.3810 | 0.5707 |
| 山西庞泉沟 SXP | 360 | 2.2000 | 1.7968 | 100.00 | 0.5900 | 0.4017 | 0.6054 |
| 辽宁老秃顶子 LNL | 360 | 2.2000 | 1.7159 | 100.00 | 0.5367 | 0.3728 | 0.5695 |
| 平均 Mean | 308 | 2.1750 | 1.7732 | 98.75 | 0.5555 | 0.3930 | 0.5933 |
表3 8个花楸树天然群体的遗传多样性(群体代号同表1)
Table 3 Genetic diversity in eight natural populations of Sorbus pohuashanensis. Population codes are the same as in Table 1.
| 群体 Population | 样本数量 Sample size | Na | Ne | P (%) | Ho | He | Is |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 河北雾灵山 HBW | 240 | 2.2000 | 1.8068 | 100.00 | 0.5717 | 0.4148 | 0.6206 |
| 河北塞罕坝 HBS | 240 | 2.2000 | 1.7510 | 100.00 | 0.5500 | 0.3819 | 0.5814 |
| 河北驼梁山 HBT | 240 | 2.2000 | 1.8423 | 100.00 | 0.5771 | 0.4192 | 0.6234 |
| 河北白石山 HBB | 360 | 2.2000 | 1.7854 | 100.00 | 0.5436 | 0.3875 | 0.5932 |
| 山东崂山 SDL | 360 | 2.1000 | 1.7837 | 90.00 | 0.5342 | 0.3850 | 0.5824 |
| 山东泰山 SDT | 300 | 2.1000 | 1.7538 | 100.00 | 0.5403 | 0.3810 | 0.5707 |
| 山西庞泉沟 SXP | 360 | 2.2000 | 1.7968 | 100.00 | 0.5900 | 0.4017 | 0.6054 |
| 辽宁老秃顶子 LNL | 360 | 2.2000 | 1.7159 | 100.00 | 0.5367 | 0.3728 | 0.5695 |
| 平均 Mean | 308 | 2.1750 | 1.7732 | 98.75 | 0.5555 | 0.3930 | 0.5933 |
| 位点 Locus | Fis | Fit | Fst | Nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pgm-1 | -0.1943 | -0.1631 | 0.0261 | 9.3373 |
| Pgm-2 | 0.3419 | 0.5342 | 0.2921 | 0.6057 |
| Pgm-3 | 0.3813 | 0.4948 | 0.1834 | 1.1130 |
| Pgi-1 | -0.2672 | -0.2245 | 0.0337 | 7.1665 |
| Pgi-2 | -0.4712 | -0.3251 | 0.0993 | 2.2685 |
| Pgd-1 | 0.0148 | 0.1172 | 0.1040 | 2.1546 |
| Pgd-2 | -0.1133 | -0.0304 | 0.0745 | 3.1065 |
| Pgd-3 | -0.9505 | -0.9499 | 0.0003 | **** |
| Mdh-1 | -1.0000 | -1.0000 | 0.0000 | **** |
| Mdh-2 | -1.0000 | -1.0000 | 0.0000 | **** |
| 平均 Mean | -0.4180 | -0.3105 | 0.0758 | 3.0472 |
表4 花楸树群体F-统计量及基因流
Table 4 Estimated F-statistics and gene flow in natural populations ofSorbus pohuashanensis
| 位点 Locus | Fis | Fit | Fst | Nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pgm-1 | -0.1943 | -0.1631 | 0.0261 | 9.3373 |
| Pgm-2 | 0.3419 | 0.5342 | 0.2921 | 0.6057 |
| Pgm-3 | 0.3813 | 0.4948 | 0.1834 | 1.1130 |
| Pgi-1 | -0.2672 | -0.2245 | 0.0337 | 7.1665 |
| Pgi-2 | -0.4712 | -0.3251 | 0.0993 | 2.2685 |
| Pgd-1 | 0.0148 | 0.1172 | 0.1040 | 2.1546 |
| Pgd-2 | -0.1133 | -0.0304 | 0.0745 | 3.1065 |
| Pgd-3 | -0.9505 | -0.9499 | 0.0003 | **** |
| Mdh-1 | -1.0000 | -1.0000 | 0.0000 | **** |
| Mdh-2 | -1.0000 | -1.0000 | 0.0000 | **** |
| 平均 Mean | -0.4180 | -0.3105 | 0.0758 | 3.0472 |
| HBW | HBS | HBT | HBB | SDL | SDT | SXP | LNL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBW | **** | 0.9728 | 0.9750 | 0.9788 | 0.9165 | 0.9325 | 0.9872 | 0.9726 |
| HBS | 0.0276 | **** | 0.9071 | 0.9681 | 0.8585 | 0.8959 | 0.9646 | 0.9624 |
| HBT | 0.0253 | 0.0975 | **** | 0.9374 | 0.9619 | 0.9515 | 0.9456 | 0.9307 |
| HBB | 0.0214 | 0.0324 | 0.0646 | **** | 0.8687 | 0.9140 | 0.9837 | 0.9855 |
| SDL | 0.0872 | 0.1526 | 0.0388 | 0.1408 | **** | 0.9751 | 0.8765 | 0.8807 |
| SDT | 0.0699 | 0.1099 | 0.0497 | 0.0899 | 0.0252 | **** | 0.9040 | 0.9226 |
| SXP | 0.0129 | 0.0361 | 0.0559 | 0.0164 | 0.1318 | 0.1010 | **** | 0.9776 |
| LNL | 0.0278 | 0.0383 | 0.0719 | 0.0146 | 0.1270 | 0.0806 | 0.0227 | **** |
表5 花楸树群体间遗传距离(D)(对角线下方)及遗传一致度(I)(对角线上方) (群体代号同表1)
Table 5 Genetic distance (below diagonal) and genetic identities (above diagonal) among Sorbus pohuashanensis.Population codes are the same as in Table 1.
| HBW | HBS | HBT | HBB | SDL | SDT | SXP | LNL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBW | **** | 0.9728 | 0.9750 | 0.9788 | 0.9165 | 0.9325 | 0.9872 | 0.9726 |
| HBS | 0.0276 | **** | 0.9071 | 0.9681 | 0.8585 | 0.8959 | 0.9646 | 0.9624 |
| HBT | 0.0253 | 0.0975 | **** | 0.9374 | 0.9619 | 0.9515 | 0.9456 | 0.9307 |
| HBB | 0.0214 | 0.0324 | 0.0646 | **** | 0.8687 | 0.9140 | 0.9837 | 0.9855 |
| SDL | 0.0872 | 0.1526 | 0.0388 | 0.1408 | **** | 0.9751 | 0.8765 | 0.8807 |
| SDT | 0.0699 | 0.1099 | 0.0497 | 0.0899 | 0.0252 | **** | 0.9040 | 0.9226 |
| SXP | 0.0129 | 0.0361 | 0.0559 | 0.0164 | 0.1318 | 0.1010 | **** | 0.9776 |
| LNL | 0.0278 | 0.0383 | 0.0719 | 0.0146 | 0.1270 | 0.0806 | 0.0227 | **** |
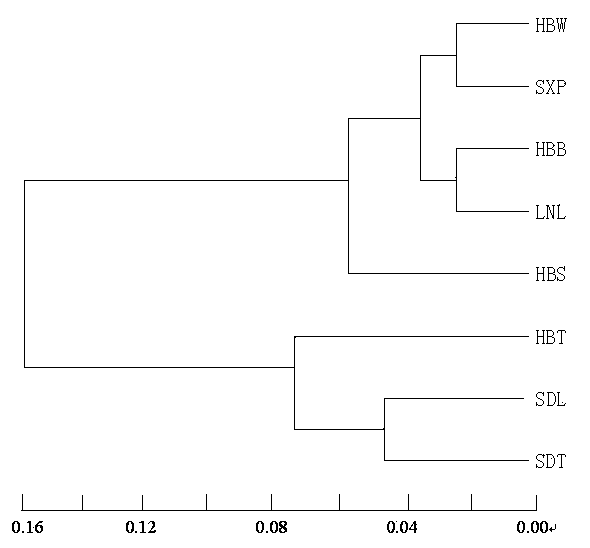
图2 花楸树群体遗传距离UPGMA聚类图(群体代号同表1)
Fig. 2 A UPGMA dendrogram of Sorbus pohuashanensis populations based on Nei’s genetic distance. Population codes are the same as inTable 1.
| [1] | Chen RW (陈荣伟), Xu XW (徐熙伟), Zhao BP (赵波平), Li J (李健), Wang CH (王春红) (2004) Seedling technology of Sorbus pohuashanensis (Hance) Hedl. Shandong Forestry Science and Technology (山东林业科技), (3),43. (in Chinese) |
| [2] | Cheng WC (郑万钧) (1985) Sylva Sinica (中国树木志), Vol 2. pp. 1009. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [3] | Cleliak WM, Pitel JA (1984) Techniques for Starch Gel Electrophoresis of Enzymes from Forest Tree Species. Information Report PI-X-42. Petawawa National Forestry Institute. Canadian Forestry Service. Chalk River, Ontario. |
| [4] | Demesure B, Guerroué BL, Lucchi G, Prat D, Petit R-J (2000) Genetic variability of a scattered temperate forest tree: Sorbus torminalis L. (Crantz). Annals of Forest Science, 57,63-71. |
| [5] | Ge S (葛颂) (1994) Electrophoretic data and studies of plant systematics and evolution. Journal of Wuhan Botanical Research (武汉植物学研究), 12,71-84. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [6] | Hamrick JL (1990) Isozymes and the analysis of genetic structure in plant populations. In: Isozymes in Plant Biology (eds Soltis DE, Soltis PS), pp. 87-105. Chapman and Hall, London. |
| [7] | Hamrick JL, Godt MJW (1989) Allozyme diversity in plant species. In: Plant Population Genetics, Breeding and Genetic Resources (eds Brown AHD, Clegg MT, Kahler AL, Weir BS), pp.43-63, Sinauer, Sunderland, MA. |
| [8] | Hamrick JL, Godt MJW, Sherman-Broyles SL (1992) Factors influencing genetic diversity in woody plant species. New Forests, 6,95-124. |
| [9] | He CZ (何承忠) (2005) Study on Genetic Diversity and Origin of Populus tomentosa (毛白杨遗传多样性及起源研究). PhD dissertation, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [10] | Jiang Y (姜雁), Li JY (李近雨) (1998) Preliminary study on seedling and introduction to Sorbus pohuashanensis. Journal of Hebei Forestry Science and Technology (河北林业科技), (4),1-4. (in Chinese) |
| [11] | Micales JA, Bonde MR (1995) Isozymes:methods and applications. In: Molecular Methods in Plant Pathology (eds Rudra PS, Uma SS), pp.115-130. CRC Press, London. |
| [12] | Nei M (1972) Genetic distance between populations. The American Naturalist, 6,283-293. |
| [13] |
Nei M (1978) Estimation of average heterozygosity and genetic distance from a small number of individuals. Genetics, 89,583-590.
URL PMID |
| [14] | Nelson-Jones EB, Briggs D, Smith AG (2002) The origin of intermediate species of the genus Sorbus. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 105,953-963. |
| [15] | Pías B, Guitián P (2006) Breeding system and pollen limitation in the masting tree Sorbus aucuparia L. (Rosaceae) in the NW Iberian Peninsula. Acta Oecologica, 29,97-103. |
| [16] | Raspé O, Jacquemart A-L (1998) Allozyme diversity and genetic structure of European populations of Sorbus aucuparia L. Heredity, 81,537-545. |
| [17] |
Sato T, Isagi Y, Sakio H, Osumi K, Goto S (2006) Effect of gene flow on spatial genetic structure in the riparian canopy tree Cercidiphyllum japonicum revealed by microsatellite analysis. Heredity, 96,79-84.
DOI URL PMID |
| [18] | Shen HL (沈海龙), Yang L (杨玲), Zhang JY (张建瑛), Feng DD (冯丹丹), Fan SH (范少辉) (2006) Influencing factors to seed dormancy and germination characteristics of Sorbus pohuashanensis. Scientia Silvae Sinicae (林业科学), 42(10),133-138. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [19] | Soltis DE, Haufler CH, Darow DC, Gastony GJ (1983) Starch gel electrophoresis of ferns: a compilation of grinding buffers, gel and electrode buffers, and staining schedule, American Fern Journal, 73,9-27. |
| [20] | Su XT (苏喜廷), Wang GY (王国义), Zhang SH (张淑华), Hua FJ (滑福建), Meng FL (孟凡力) (2005) Cutting effect of green wood of main broad-leaved tree species in Heilongjiang Province. Journal of Northeast Forestry University (东北林业大学学报), 33(5),13-14, 18. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [21] |
Sun M, Wong KC, Joe SYL (1998) Reproductive biology and population genetic structure of Kandelia candel (Rhizophoraceae), a viviparous mangrove species. American Journal of Botany, 85,1631-1637.
URL PMID |
| [22] | Sun XD (孙秀殿) (1999) Utilization and cultivation of Sorbus pohuashanensis (Hance) Hedl. Special Economic Animal and Plant (特种经济动植物), (4),32. (in Chinese) |
| [23] | Wang ZR (王中仁) (1996) Plant Allozyme Analysis (植物等位酶分析). Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [24] | Wang AZ (王爱芝), Shen HL (沈海龙), H J (黄剑), Li CH (李长海), Fan SH (范少辉) (2005) Callus induction from tender leaf and stem segment explants of Sorbus pohuashanens. Journal of Northeast Forestry University (东北林业大学学报), 33(2),12-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [25] | Wright S (1965) The interpretation of population structure by F-statistics with special regard to systems of mating. Evolution, 19,395-420. |
| [26] | Wright S (1978) Evolution and the genetics of populations, Vol. 4. Variability Within and Among Natural Populations. University of Chicago Press, Chicago. |
| [27] |
Yagihashi T, Hayashida M, Miyamota T (1998) Effects of bird ingestion on seed germination of Sorbus commixta. Oecologia, 114,209-212.
DOI URL PMID |
| [28] | Yeh FC, Yang RC, Boyle T (1997) POPGENE, The User Friendly Shareware for Population Genetic Analysis. Molecular Biology and Biotechnology Centre, University of Alberta, Edomonton, Canada. |
| [29] | Zheng J (郑健), Zheng YQ (郑勇奇), Wu C (吴超), Zhang CH (张川红), Zong YC (宗亦臣), Li BJ (李伯菁), Zhu YP (祝业平) (2007) Geographical distribution and patterns of natural regeneration of Sorbus pohuashanensis. Scientia Silvae Sinicae (林业科学), 43(12),86-93. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [1] | 王嘉陈, 徐汤俊, 许唯, 张高季, 尤艺瑾, 阮宏华, 刘宏毅. 城市景观格局对大蚰蜒种群遗传结构的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24251-. |
| [2] | 邓洪, 钟占友, 寇春妮, 朱书礼, 李跃飞, 夏雨果, 武智, 李捷, 陈蔚涛. 基于线粒体全基因组揭示斑鳠的种群遗传结构与演化历史[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24241-. |
| [3] | 李庆多, 栗冬梅. 全球蝙蝠巴尔通体流行状况分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23166-. |
| [4] | 冯晨, 张洁, 黄宏文. 统筹植物就地保护与迁地保护的解决方案: 植物并地保护(parallel situ conservation)[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23184-. |
| [5] | 齐海玲, 樊鹏振, 王跃华, 刘杰. 中国北方六省区胡桃的遗传多样性和群体结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23120-. |
| [6] | 熊飞, 刘红艳, 翟东东, 段辛斌, 田辉伍, 陈大庆. 基于基因组重测序的长江上游瓦氏黄颡鱼群体遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22391-. |
| [7] | 蒲佳佳, 杨平俊, 戴洋, 陶可欣, 高磊, 杜予州, 曹俊, 俞晓平, 杨倩倩. 长江下游外来生物福寿螺的种类及其种群遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22346-. |
| [8] | 何艺玥, 刘玉莹, 张富斌, 秦强, 曾燏, 吕振宇, 杨坤. 梯级水利工程背景下的嘉陵江干流蛇鮈群体遗传多样性和遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23160-. |
| [9] | 孙维悦, 舒江平, 顾钰峰, 莫日根高娃, 杜夏瑾, 刘保东, 严岳鸿. 基于保护基因组学揭示荷叶铁线蕨的濒危机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21508-. |
| [10] | 陶克涛, 白东义, 图格琴, 赵若阳, 安塔娜, 铁木齐尔·阿尔腾齐米克, 宝音德力格尔, 哈斯, 芒来, 韩海格. 基于基因组SNPs对东亚家马不同群体遗传多样性的评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21031-. |
| [11] | 崔静, 徐明芳, 章群, 李瑶, 曾晓舒, 李莎. 基于3种线粒体标记探讨中日沿海角木叶鲽遗传多样性差异[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21485-. |
| [12] | 孙军, 宋煜尧, 施义锋, 翟键, 燕文卓. 近十年中国海洋生物多样性研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22526-. |
| [13] | 栗冬梅, 杨卫红, 李庆多, 韩茜, 宋秀平, 潘虹, 冯云. 巴尔通体在滇西南蝙蝠中高度流行并具有丰富的遗传变异特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(9): 1245-1255. |
| [14] | 姚志, 郭军, 金晨钟, 刘勇波. 中国纳入一级保护的极小种群野生植物濒危机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(3): 394-408. |
| [15] | 叶俊伟, 田斌. 中国西南地区重要木本油料植物扁核木的遗传结构及成因[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(12): 1629-1637. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn