



生物多样性 ›› 2010, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (5): 523-527. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2010.523 cstr: 32101.14.SP.J.1003.2010.523
• 研究简报 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2010-03-02
接受日期:2010-08-22
出版日期:2010-09-20
发布日期:2010-09-20
通讯作者:
周江
作者简介:* E-mail: prattiip2006@vip.sohu.com基金资助:
Zhigang Li1, Fuwen Wei2, Jiang Zhou1,2,*( )
)
Received:2010-03-02
Accepted:2010-08-22
Online:2010-09-20
Published:2010-09-20
Contact:
Jiang Zhou
摘要:
海南长臂猿(Nomascus hainanus)是世界上最濒危的灵长类动物之一, 但目前有关海南长臂猿的种群遗传学方面的信息以及种群复壮所面临的困难未见报道。为更好地保护该极危物种, 作者以粪便为研究材料, 首次在分子生物学水平上测定了海南长臂猿1个群体(B群)共6个个体的线粒体D-loop区基因序列。结果显示: 202 bp的D-loop区基因共检测到5个变异位点, 4个单倍型, 单倍型多样性(h)为0.6000, 核苷酸多样性(π)为0.00829, 表明海南长臂猿B群的遗传多样性较低; 与此同时, 海南长臂猿还面临着种群数量过小, 性比失衡, 以及栖息地质量低下等严峻的问题。
李志刚, 魏辅文, 周江 (2010) 海南长臂猿线粒体D-loop区序列分析及种群复壮. 生物多样性, 18, 523-527. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2010.523.
Zhigang Li, Fuwen Wei, Jiang Zhou (2010) Mitochondrial DNA D-loop sequence analysis and population rejuvena- tion of Hainan gibbons (Nomascus hainanus). Biodiversity Science, 18, 523-527. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2010.523.
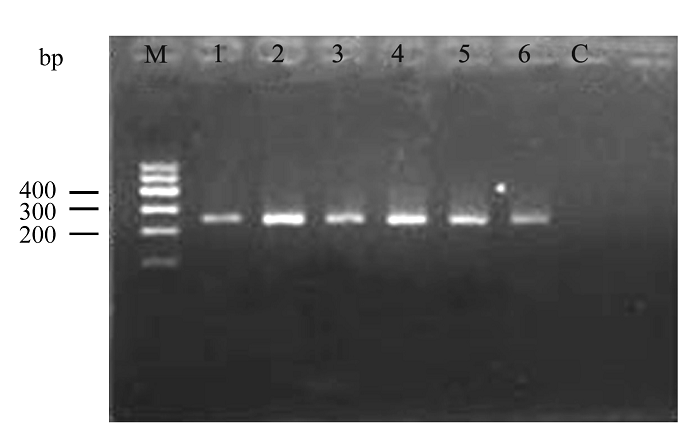
图1 海南长臂猿B群6个个体的mtDNA控制区部分扩增结果。M: DNA分子标准; C: 空白对照样品; 1-6为样品编号。
Fig. 1 The amplification result of partial mtDNA control region of six Hainan gibbon individuals in Group B. M indicates the Marker; C indicates control; 1-6 are the sample codes.
| Indiv- idual codes | 变异位点 Variable sites | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-10 | 11-20 | 21-30 | 31-40 | 41-50 | 51-60 | 61-70 | 71-80 | 81-90 | |
| 1 | TAGAACATCC | CCTCCCCATT | TCAACATTCC | AAACCTACCC | AACATGCGTA | TCAACCAACC | AAGATAGTCC | ATCTCGGACA | TGGCACATTA |
| 2 | - - - G - - - - - - | - - - TT - - - - - | - - - - - - - C - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - |
| 3 | - - - G - - - - - - | - - - TT - - - - - | - - - - - - - C - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - A- - - - - - - |
| 4 | - - - G - - - - - - | - - - TT - .- - - | - - - - - - - C - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - |
| 5 | - - - G - - - - - - | - - - TT - - - - - | - - - - - - - C - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - |
| 6 | - - - G - - - - - - | - - - TT - - - - - | - - - - - - - C - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - |
表1 海南长臂猿6个个体线粒体DNA控制区变异位点分布
Table 1 Variable sites of mitochondrial DNA control region among six individuals
| Indiv- idual codes | 变异位点 Variable sites | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-10 | 11-20 | 21-30 | 31-40 | 41-50 | 51-60 | 61-70 | 71-80 | 81-90 | |
| 1 | TAGAACATCC | CCTCCCCATT | TCAACATTCC | AAACCTACCC | AACATGCGTA | TCAACCAACC | AAGATAGTCC | ATCTCGGACA | TGGCACATTA |
| 2 | - - - G - - - - - - | - - - TT - - - - - | - - - - - - - C - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - |
| 3 | - - - G - - - - - - | - - - TT - - - - - | - - - - - - - C - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - A- - - - - - - |
| 4 | - - - G - - - - - - | - - - TT - .- - - | - - - - - - - C - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - |
| 5 | - - - G - - - - - - | - - - TT - - - - - | - - - - - - - C - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - |
| 6 | - - - G - - - - - - | - - - TT - - - - - | - - - - - - - C - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - |
| [1] | Chivers DJ (1974) The siamang in Malaysia: a field study of a primate in a tropical rain forest. Contributions to Primatology, 4, 1-335. |
| [2] | Cowlishaw G, Dunbar R (2000) Primate Conservation Biology. The University of Chicago Press, Chicago. |
| [3] | Frankham R (1998) Inbreeding and extinction: island populations. Conservation Biology, 12, 665-675. |
| [4] | Frankham R, Ballou JD, Briscoe DA (2002) Introduction to Conservation Genetics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| [5] | He L (何丽), Zhang YG (张于光), Li DQ (李迪强), Li DQ (李大全) (2010) Analysis on mitochondrial DNA D-loop sequences genetic polymorphism of Rhinopithecus roxellana. Chinese Journal of Zoology (动物学杂志), 45(1), 70-76. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [6] | Hayaishi SH, Kawamoto YH (2006) Low genetic diversity and biased distribution of mitochondrial DNA haplotypes in the Japanese macaque (Macaca fuscata yakui) on Yakushima Island. Primates, 47, 158-164. |
| [7] | Irwin DW, Kcher TD, Wilson AC (1991) Evolution of cytochrome b gene of mammals. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 32, 128-144. |
| [8] |
Jeanmougin F, Thompson JD, Gouy M, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1998) Multiple sequence alignment with Clustal X. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 23, 403-405.
URL PMID |
| [9] | Kressirer P (1993) Eine Molekulare Phylogenie der Gibbons (Hylobatidae). Diplomarbeit der Fakultat fur Biologie der Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitat, Munchen. |
| [10] |
Kumar S, Tamura K, Jakobusen IB, Nei M (2001) MEGA2: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis software. Bioinformatics, 17, 1244-1245.
DOI URL PMID |
| [11] |
Liu ZJ, Ren BP, Wei FW, Long YC, Hao YL, Li M (2007) Phylogeography and population structure of the Yunnan snub-nosed monkey (Rhinopithecus bieti) inferred from mitochondrial control region DNA sequence analysis. Molecular Ecology, 16, 3334-3349.
DOI URL PMID |
| [12] |
Liu ZH, Jiang HS (1989) Population structure of Hylobates concolor in Bawangling Nature Reserve, Hainan, China. American Journal of Primatology, 19, 247-254.
DOI URL PMID |
| [13] | Monda K, Simmons RE, Kressirer P, Su B, Woodruff DS (2007) Mitochondrial DNA hypervariable region-1 sequence variation and phylogeny of the concolor gibbons, Nomascus. American Journal of Primatology, 69, 1285-1306. |
| [14] |
Rozas J, Rozas R (1999) DnaSP version 3: an integrated program for molecular population genetics and molecular evolution analysis. Bioinformatics, 15, 174-175.
URL PMID |
| [15] | Soulé ME, Orians GH, Boersma PD (2001) Conservation Biology: Research Priorities for the Next Decade. Society for Conservation Biology, Island Press, Washington. |
| [16] | Young AG, Clarke GM (2000) Genetics Demography and Variability of Fragment Population. Cambridge University Press, London. |
| [17] | Zhou J, Wei FW, Li M, Zhang JF, Wang DL, Pan RL (2005) Hainan black-crested gibbon is headed for extinction. International Journal of Primatology, 26, 453-465. |
| [18] | Zhang BW, Li M, Ma LC, Wei FW (2006) A widely applicable protocol for DNA isolation from fecal samples. Biochemical Genetics, 44, 503-512. |
| [19] | Zhou J, Wei FW, Li M, Pui Lok CB, Wang DL (2008) Reproductive characters and mating behaviour of wild Nomascus hainanus. International Journal of Primatology, 29, 1037-1046. |
| [1] | 王嘉陈, 徐汤俊, 许唯, 张高季, 尤艺瑾, 阮宏华, 刘宏毅. 城市景观格局对大蚰蜒种群遗传结构的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24251-. |
| [2] | 冯晨, 张洁, 黄宏文. 统筹植物就地保护与迁地保护的解决方案: 植物并地保护(parallel situ conservation)[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23184-. |
| [3] | 李庆多, 栗冬梅. 全球蝙蝠巴尔通体流行状况分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23166-. |
| [4] | 齐海玲, 樊鹏振, 王跃华, 刘杰. 中国北方六省区胡桃的遗传多样性和群体结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23120-. |
| [5] | 熊飞, 刘红艳, 翟东东, 段辛斌, 田辉伍, 陈大庆. 基于基因组重测序的长江上游瓦氏黄颡鱼群体遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(4): 22391-. |
| [6] | 蒲佳佳, 杨平俊, 戴洋, 陶可欣, 高磊, 杜予州, 曹俊, 俞晓平, 杨倩倩. 长江下游外来生物福寿螺的种类及其种群遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22346-. |
| [7] | 何艺玥, 刘玉莹, 张富斌, 秦强, 曾燏, 吕振宇, 杨坤. 梯级水利工程背景下的嘉陵江干流蛇鮈群体遗传多样性和遗传结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23160-. |
| [8] | 孙维悦, 舒江平, 顾钰峰, 莫日根高娃, 杜夏瑾, 刘保东, 严岳鸿. 基于保护基因组学揭示荷叶铁线蕨的濒危机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21508-. |
| [9] | 陶克涛, 白东义, 图格琴, 赵若阳, 安塔娜, 铁木齐尔·阿尔腾齐米克, 宝音德力格尔, 哈斯, 芒来, 韩海格. 基于基因组SNPs对东亚家马不同群体遗传多样性的评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21031-. |
| [10] | 崔静, 徐明芳, 章群, 李瑶, 曾晓舒, 李莎. 基于3种线粒体标记探讨中日沿海角木叶鲽遗传多样性差异[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21485-. |
| [11] | 孙军, 宋煜尧, 施义锋, 翟键, 燕文卓. 近十年中国海洋生物多样性研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22526-. |
| [12] | 栗冬梅, 杨卫红, 李庆多, 韩茜, 宋秀平, 潘虹, 冯云. 巴尔通体在滇西南蝙蝠中高度流行并具有丰富的遗传变异特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(9): 1245-1255. |
| [13] | 姚志, 郭军, 金晨钟, 刘勇波. 中国纳入一级保护的极小种群野生植物濒危机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(3): 394-408. |
| [14] | 叶俊伟, 田斌. 中国西南地区重要木本油料植物扁核木的遗传结构及成因[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(12): 1629-1637. |
| [15] | 向登高, 李跃飞, 李新辉, 陈蔚涛, 马秀慧. 多基因联合揭示海南鲌的遗传结构与遗传多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(11): 1505-1512. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()