



生物多样性 ›› 2020, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (8): 1026-1035. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019352 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019352
冯斌1,2, 李迪强1,2,*( ), 张于光1,2, 薛亚东1,2
), 张于光1,2, 薛亚东1,2
收稿日期:2019-11-06
接受日期:2020-03-11
出版日期:2020-08-20
发布日期:2020-08-28
通讯作者:
李迪强
作者简介:. E-mail: lidq@caf.ac.cn基金资助:
Bin Feng1,2, Diqiang Li1,2,*( ), Yuguang Zhang1,2, Yadong Xue1,2
), Yuguang Zhang1,2, Yadong Xue1,2
Received:2019-11-06
Accepted:2020-03-11
Online:2020-08-20
Published:2020-08-28
Contact:
Diqiang Li
摘要:
建立自然保护区是生物多样性保护的根本措施, 而且自然保护区对减缓和适应气候变化具有重要的作用。生物多样性保护的压力在气候变化的胁迫下不断加剧, 因此, 有效的自然保护区管理必须考虑气候变化的影响。发展应对气候变化威胁的适应性管理技术以提高自然保护区管理有效性是自然保护区管理的迫切需求。但目前全球范围内还没有针对减缓和适应气候变化的自然保护区管理有效性评估工具。近半个世纪来广西气温持续升高且极端气候事件频次增加, 对广西各类生物生境产生了重要的影响。本文基于世界自然保护联盟(IUCN)的自然保护区减缓和适应气候变化管理框架和管理有效性评估框架, 在管理有效性跟踪工具(mangement effectiveness tracking tool, METT)基础上提出了自然保护区减缓和适应气候变化管理有效性评估工具(management effectiveness assessment tool of mitigation and adaptation on climate change, MEATMACC), 并使用该工具和METT对广西12个典型自然保护区进行了调查分析。结果表明: 国家级自然保护区的METT得分、MEATMACC得分分别比非国家级自然保护区高28.98%和43.91%; 国家级与非国家级自然保护区的METT得分无显著差异, 但MEATMACC得分差异极显著; 两个管理有效性评估工具得分率呈线性相关但差异不显著; 两个评估工具中背景、规划与影响3个要素得分率存在极显著差异。研究结果表明, 对于自然保护区减缓和适应气候变化的政策和技术支持仍需加强。
冯斌, 李迪强, 张于光, 薛亚东 (2020) 自然保护区减缓和适应气候变化的管理有效性评估: 以广西12个典型自然保护区为例. 生物多样性, 28, 1026-1035. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019352.
Bin Feng, Diqiang Li, Yuguang Zhang, Yadong Xue (2020) Evaluation on nature reserve management effectiveness of mitigation and adaptation on climate change: A case study of 12 typical nature reserves in Guangxi. Biodiversity Science, 28, 1026-1035. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019352.
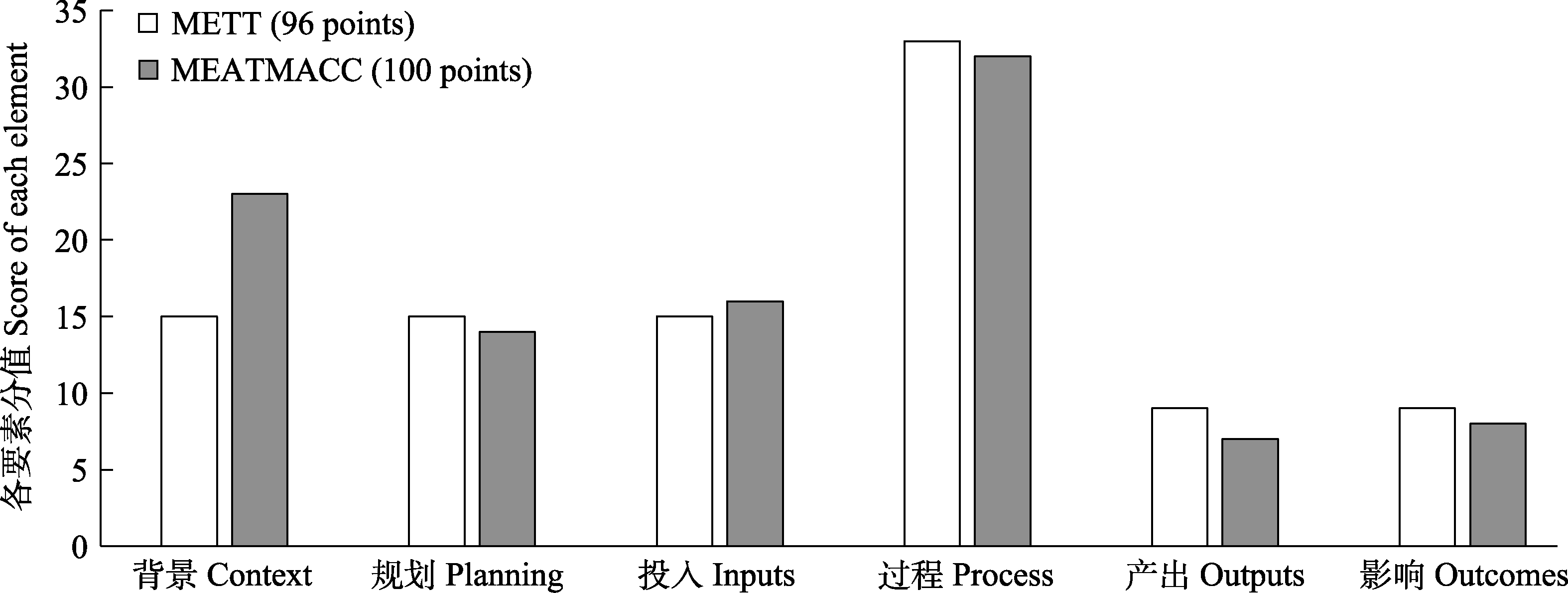
图1 管理有效性跟踪工具(METT)与减缓和适应气候变化管理有效性评估工具(MEATMACC)分值结构对比
Fig. 1 Score structure comparison of management effective tracking tool (METT) and management effectiveness assessment tool of mitigation and adaption on climate change (MEATMACC)
| 编号 No. | 评价内容 Evaluation content | 分数 Score |
|---|---|---|
| 一 | 背景 Context | 23 |
| 1 | 法律地位 Legal status | 3 |
| 2 | 规章条例 Nature reserve regulations | 3 |
| 附加项Additional point | 自然保护区出台了极端气候事件的应急方案 Nature reserves developed emergency plans for extreme weather events | 1 |
| 3 | 脆弱性 Vulnerability | 3 |
| 附加项 Additional point | 开展了脆弱性评估 A vulnerability assessment was carried out in the nature reserve | 1 |
| 4 | 不利影响 Negative influence | 3 |
| 5 | 管理执行 Law enforcement | 3 |
| 6 | 资源清单 Resource inventory | 3 |
| 7 | 合作伙伴 Partner | 3 |
| 二 | 规划 Planning | 14 |
| 8 | 管理目标 Management objectives | 3 |
| 9 | 规划设计 Planning and design | 3 |
| 附加项 Additional point | 自然保护区存在天然或人为的基因交流隔断 There is natural or artificial gene communication barriers in nature reserve | 1 |
| 规划设计已充分考虑应对气候变化影响的因素 Impact of climate change has considered when the nature reserve was planning | 1 | |
| 10 | 管理计划 Management plan | 3 |
| 附加项 Additional point | 应对气候变化工作已纳入管理计划 Climate change response has been incorporated into the management plan | 1 |
| 建立了制度和程序, 定期审查和更新管理计划 Established systems and procedures to review and update management plans on a regular basis | 1 | |
| 监测评价和研究结果能充分反映在管理计划中 The results of monitoring, research and evaluation can be fully reflected in the management plan | 1 | |
| 三 | 投入 Inputs | 16 |
| 11 | 科学研究 Scientific research | 3 |
| 12 | 员工数量 Number of employees | 3 |
| 13 | 资金预算 Funding budget | 3 |
| 14 | 固定预算 Fixed budget | 3 |
| 15 | 设施设备 Equipment and facilities | 3 |
| 附加项 Additional point | 具有应对极端气候事件的设备设施 The nature reserve has facilities to deal with extreme weather events | 1 |
| 四 | 过程 Process | 32 |
| 16 | 监测评估 Monitoring and evaluation | 3 |
| 附加项 Additional point | 选择了针对气候变化的监测指标并实施了监测 The monitoring indicators was confirmed and monitoring is conducted | 1 |
| 气候变化监测评估的结果应用于管理决策依据 The results of climate change monitoring is contributed to decision making | 1 | |
| 17 | 资源管理 Resource management | 3 |
| 18 | 人事管理 Human management | 3 |
表1 自然保护区减缓和适应气候变化管理有效性评估工具简表
Table 1 Summary of management effectiveness assessment tool of mitigation and adaption on climate change of nature reserve
| 编号 No. | 评价内容 Evaluation content | 分数 Score |
|---|---|---|
| 一 | 背景 Context | 23 |
| 1 | 法律地位 Legal status | 3 |
| 2 | 规章条例 Nature reserve regulations | 3 |
| 附加项Additional point | 自然保护区出台了极端气候事件的应急方案 Nature reserves developed emergency plans for extreme weather events | 1 |
| 3 | 脆弱性 Vulnerability | 3 |
| 附加项 Additional point | 开展了脆弱性评估 A vulnerability assessment was carried out in the nature reserve | 1 |
| 4 | 不利影响 Negative influence | 3 |
| 5 | 管理执行 Law enforcement | 3 |
| 6 | 资源清单 Resource inventory | 3 |
| 7 | 合作伙伴 Partner | 3 |
| 二 | 规划 Planning | 14 |
| 8 | 管理目标 Management objectives | 3 |
| 9 | 规划设计 Planning and design | 3 |
| 附加项 Additional point | 自然保护区存在天然或人为的基因交流隔断 There is natural or artificial gene communication barriers in nature reserve | 1 |
| 规划设计已充分考虑应对气候变化影响的因素 Impact of climate change has considered when the nature reserve was planning | 1 | |
| 10 | 管理计划 Management plan | 3 |
| 附加项 Additional point | 应对气候变化工作已纳入管理计划 Climate change response has been incorporated into the management plan | 1 |
| 建立了制度和程序, 定期审查和更新管理计划 Established systems and procedures to review and update management plans on a regular basis | 1 | |
| 监测评价和研究结果能充分反映在管理计划中 The results of monitoring, research and evaluation can be fully reflected in the management plan | 1 | |
| 三 | 投入 Inputs | 16 |
| 11 | 科学研究 Scientific research | 3 |
| 12 | 员工数量 Number of employees | 3 |
| 13 | 资金预算 Funding budget | 3 |
| 14 | 固定预算 Fixed budget | 3 |
| 15 | 设施设备 Equipment and facilities | 3 |
| 附加项 Additional point | 具有应对极端气候事件的设备设施 The nature reserve has facilities to deal with extreme weather events | 1 |
| 四 | 过程 Process | 32 |
| 16 | 监测评估 Monitoring and evaluation | 3 |
| 附加项 Additional point | 选择了针对气候变化的监测指标并实施了监测 The monitoring indicators was confirmed and monitoring is conducted | 1 |
| 气候变化监测评估的结果应用于管理决策依据 The results of climate change monitoring is contributed to decision making | 1 | |
| 17 | 资源管理 Resource management | 3 |
| 18 | 人事管理 Human management | 3 |
| 编号 No. | 评价内容 Evalution content | 分数 Score |
|---|---|---|
| 附加项 Additional point | 管理人员有应对气候变化资源管理的能力或技术 Managers have the capacity or skills to manage resources to deal with climate change | 1 |
| 19 | 能力建设 Capacity building | 3 |
| 附加项 Additional point | 管理人员接受应对气候变化的管理培训 Managers are trained in climate change management | 1 |
| 20 | 预算管理 Budget management | 3 |
| 21 | 设备设施维护 Equipment and facility maintenance | 3 |
| 22 | 宣传教育 Publicity and education | 3 |
| 附加项 Additional point | 宣传教育涉及气候变化对保护区影响内容 The publicity and education involves the impacts of climate change and mitigation and adaptation of nature reserves | 1 |
| 23 | 利益相关者 Stakeholders | 3 |
| 24 | 公众参与 Public participation | 3 |
| 五 | 产出 Outputs | 7 |
| 25 | 公众设施 Public facilities | 3 |
| 26 | 管理成效 Management efficiency | 3 |
| 附加项 Additional point | 积极规划恢复退化地区的保护区和/或保护区缓冲区 Active planning for conservation and/or conservation buffer zones in degraded areas | 1 |
| 六 | 影响 Outcomes | 8 |
| 27 | 经济效益 Economic benefit | 3 |
| 附加项 Additional point | 安排有改善社区居民经济和生活条件的项目 In the process of resource management, conservation areas arrange projects to improve the economic and living conditions of community residents | 1 |
| 争取了国内外减缓和适应气候变化的资金 Nature reserve has secured domestic and international funding for climate change mitigation and adaptation, such as REDD and CCBA | 1 | |
| 28 | 可持续发展 Sustainable development | 3 |
表1 (续)
Table 1 (continued)
| 编号 No. | 评价内容 Evalution content | 分数 Score |
|---|---|---|
| 附加项 Additional point | 管理人员有应对气候变化资源管理的能力或技术 Managers have the capacity or skills to manage resources to deal with climate change | 1 |
| 19 | 能力建设 Capacity building | 3 |
| 附加项 Additional point | 管理人员接受应对气候变化的管理培训 Managers are trained in climate change management | 1 |
| 20 | 预算管理 Budget management | 3 |
| 21 | 设备设施维护 Equipment and facility maintenance | 3 |
| 22 | 宣传教育 Publicity and education | 3 |
| 附加项 Additional point | 宣传教育涉及气候变化对保护区影响内容 The publicity and education involves the impacts of climate change and mitigation and adaptation of nature reserves | 1 |
| 23 | 利益相关者 Stakeholders | 3 |
| 24 | 公众参与 Public participation | 3 |
| 五 | 产出 Outputs | 7 |
| 25 | 公众设施 Public facilities | 3 |
| 26 | 管理成效 Management efficiency | 3 |
| 附加项 Additional point | 积极规划恢复退化地区的保护区和/或保护区缓冲区 Active planning for conservation and/or conservation buffer zones in degraded areas | 1 |
| 六 | 影响 Outcomes | 8 |
| 27 | 经济效益 Economic benefit | 3 |
| 附加项 Additional point | 安排有改善社区居民经济和生活条件的项目 In the process of resource management, conservation areas arrange projects to improve the economic and living conditions of community residents | 1 |
| 争取了国内外减缓和适应气候变化的资金 Nature reserve has secured domestic and international funding for climate change mitigation and adaptation, such as REDD and CCBA | 1 | |
| 28 | 可持续发展 Sustainable development | 3 |
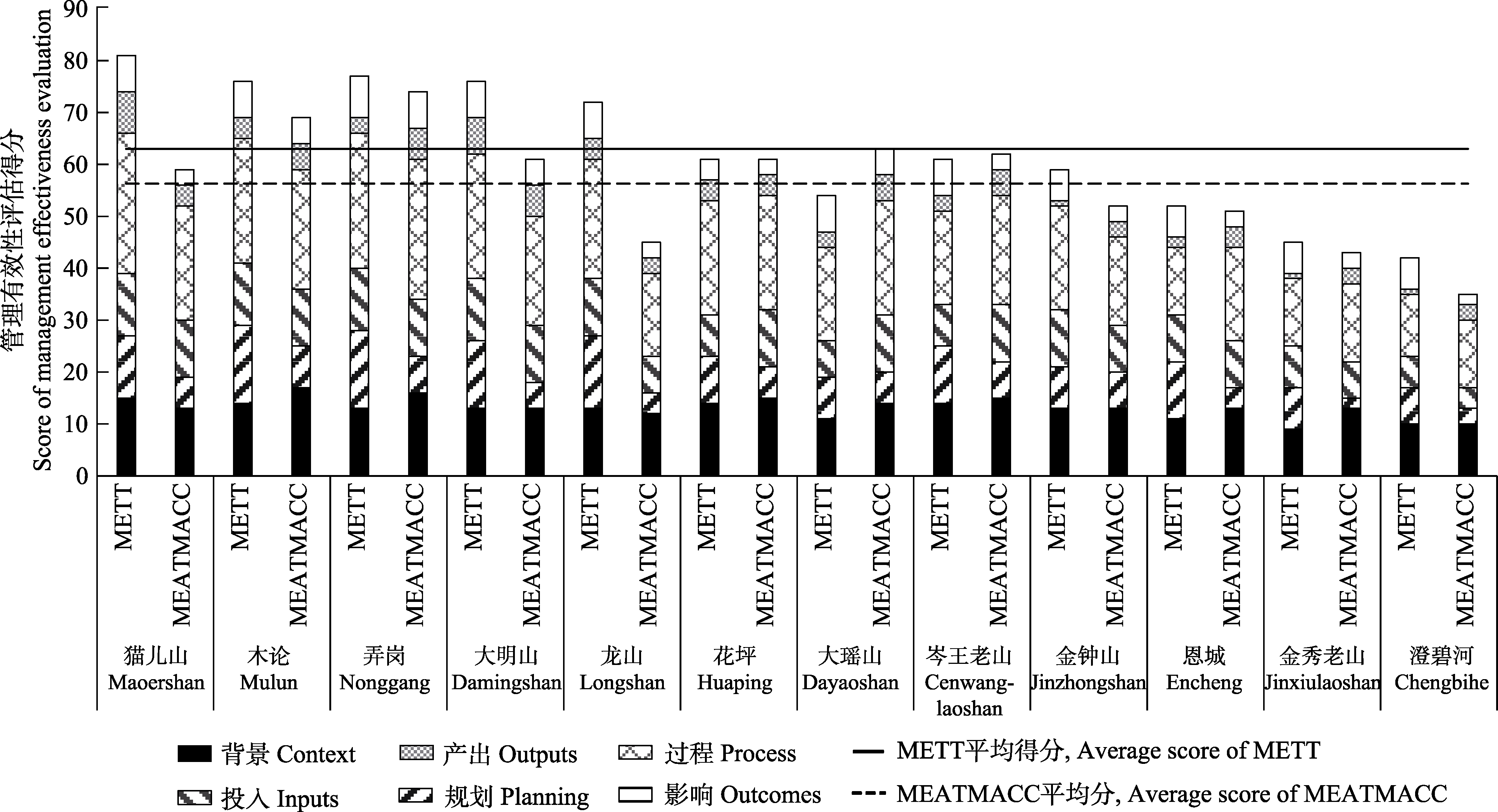
图2 广西12个自然保护区管理有效性跟踪工具(METT)与减缓和适应气候变化管理有效性评估工具(MEATMACC)得分
Fig. 2 Score of management effective tracking tool (METT), management effectiveness assessment tool of mitigation and adaption on climate change (MEATMACC) of 12 nature reserves in Guangxi
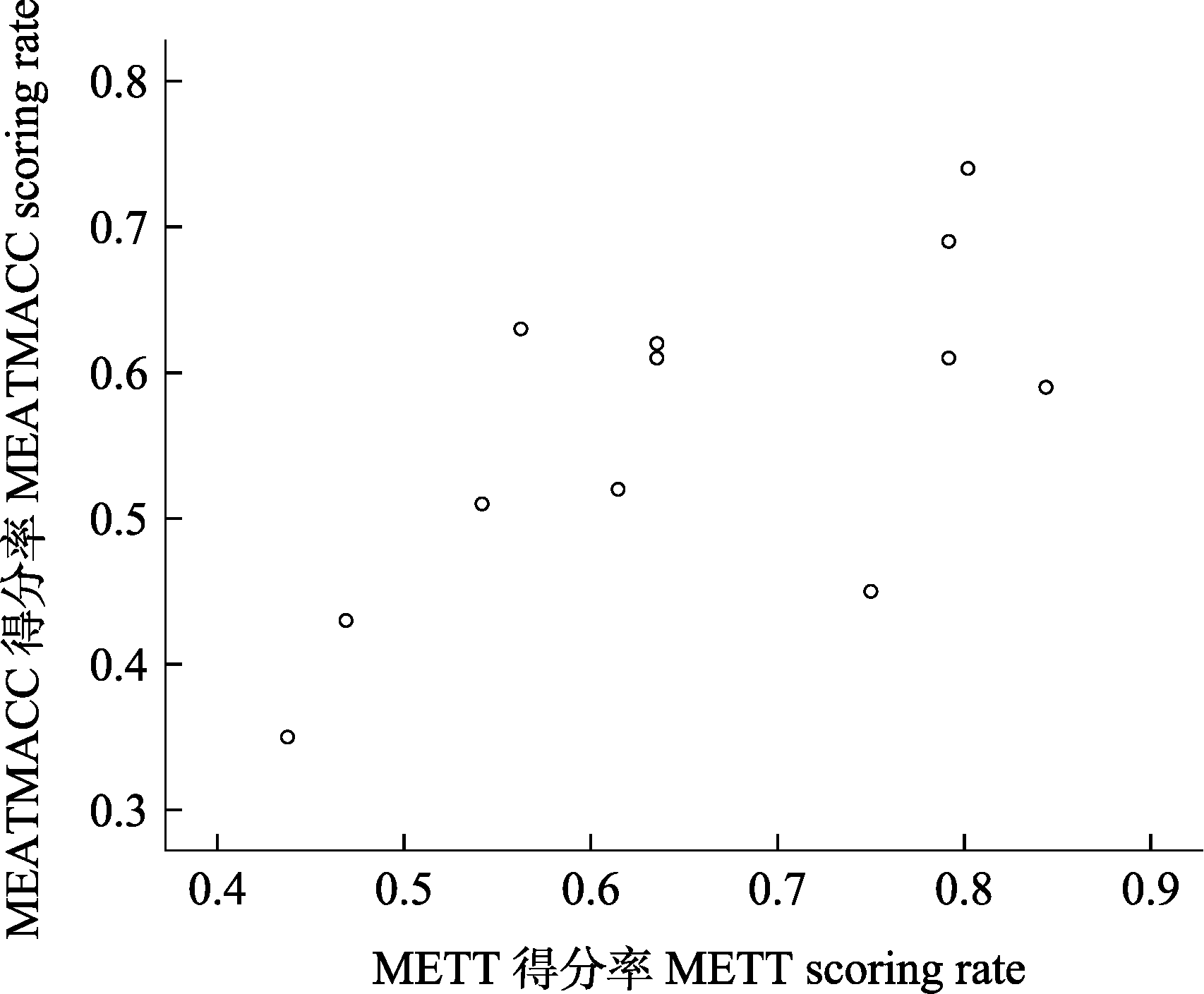
图3 管理有效性跟踪工具(METT)与减缓和适应气候变化管理有效性评估工具(MEATMACC)得分率相关性图
Fig. 3 Correlation figure of scoring rate on management effective tracking tool (METT), management effectiveness assessment tool of mitigation and adaption on climate change (MEATMACC)
| [1] | Abrahms B, Dipietro D, Graffis A, Hollander A (2017) Managing biodiversity under climate change: Challenges, frameworks, and tools for adaptation. Biodiversity and Conservation, 17, 1-17. |
| [2] | Belle EM, Stolton S, Dudley N (2012) Protected Area Management Effectiveness: A Regional Framework and Additional METT Module for Monitoring the Effects of Climate Change. UNEP-WCMC, Cambridge. |
| [3] | CBD Secretariat (2010) Decision Adopted by the Conference of the Parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity at Its Tenth Meeting. CBD, Nagoya. |
| [4] | Dudley N, Stolton S, Belokurov A, Krueger L, Lopoukhine N, MacKinnon K, Sandwith T, Sekhran N (2010) Natural Solutions: Protected Areas Helping People Cope with Climate Change. IUCN-WCPA, TNC, UNDP, WCS, The World Bank, WWF, Gland, Washington, DC, New York. |
| [5] | Fan JS, Li JS, Xia R, Hu LL, Li G (2014) Assessing the impact of climate change on the habitat distribution of the giant panda in the Qinling Mountains of China. Ecological Modeling, 274, 12-20. |
| [6] |
Forest II, Dylan C, John C (2015) Biodiversity increases the resistance of ecosystem productivity to climate extremes. Nature, 526, 574-577.
DOI URL PMID |
| [7] | Gross JE, Woodley S, Welling LA, Watson JE (2016) Adapting to climate change: Guidance for protected area managers and planners. In: Best Practice Protected Area Guidelines Series. IUCN, Gland. |
| [8] | Hannah L, Midgley G, Andelman S, Araújo M, Hughes G, Martinez-Meyer E, Pearson R, Williams P (2007) Protected area needs in a changing climate. Frontiers in Ecology and Environment, 5, 131-138. |
| [9] | He JL, Xie M, Huang Z, Li YL, Huang XS, Zhou ML (2016) Climate change in Guangxi. Journal of Meteorological Research and Application, 37(3), 11-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 何洁琳, 谢敏, 黄卓, 李艳兰, 黄雪松, 周美丽 (2016) 广西气候变化事实. 气象研究与应用, 373, 11-15.] | |
| [10] | Heller NE, Zavaleta ES (2009) Biodiversity management in the face of climate change: A review of 22 years of recommendations. Biological Conservation, 142, 1-32. |
| [11] | Hockings M, Stolton S, Dudley N (2010) Data credibility: What are the ‘right’ data for evaluating management effectiveness of protected areas? New Directions for Evaluation, 122, 53-63. |
| [12] | Hockings M, Stolton S, Leverington F, Dudley N, Courrau J (2006) Evaluating Effectiveness: A Framework for Assessing Management Effectiveness of Protected Areas, 2nd edn. IUCN, Gland. |
| [13] | IPCC(2007) Climate Change 2007: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| [14] | IPCC(2014) Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (Summary for policymakers). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| [15] | IUCN, UNEP-WCMC (2019) Protected Planet: The Global Database on Protected Areas Management Effectiveness (GD-PAME). UNEP-WCMC, IUCN, Cambridge. |
| [16] |
Kathy MK, Nigel D, Trevor S (2011) Natural solutions: Protected areas helping people to cope with climate change. Oryx, 45, 461-462.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Lemieux CJ, Thompson JL, Dawson J, Schuster RM (2012) Natural resource manager perceptions of agency performance on climate change. Journal of Environmental Management, 114, 178-189.
DOI URL PMID |
| [18] | Li HD, Shen WS, Liu HY, Zhang T (2015) State, problems and countermeasures of climate change risk management at nature reserve in China. World Forestry Research, 28(5), 69-73. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李海东, 沈渭寿, 刘海月, 张涛 (2015) 我国自然保护区应对气候变化风险现状、问题与对策. 世界林业研究, 285, 69-73.] | |
| [19] | Masumbuko B, Somda J (2014) Analysis of the Links Between Climate Change, Protected Areas and Communities in West Africa. UNEP-WCMC, Cambridge. |
| [20] |
Rannow S, Macgregor NA, Albrecht J, Crick HQ, Forster M, Heiland S, Janauer G, Morecroft MD, Neubert M, Sarbu A (2014) Managing protected areas under climate change: Challenges and priorities. Environmental Management, 54, 732-743.
DOI URL PMID |
| [21] | Scheffers BR, De ML, Bridge TC, Hoffmann AA, Pandolfi JM, Corlett RT, Butchart SM, Pearce-Kelly P, Kovacs KM, Dudgeon D (2016) The broad footprint of climate change from genes to biomes to people. Science, 354, aaf7671-aaf7679. |
| [22] | Tanner-Mcallister LS, Rhodes J, Hockings M (2014) Community and park manager’s perceptions of protected area management: A Southeast Queensland study. Australasian Journal of Environmental Management, 21, 320-336. |
| [23] |
Tanner-Mcallister LS, Rhodes J, Hockings M (2017) Managing for climate change on protected areas: An adaptive management decision making framework. Journal of Environmental Management, 204, 510-518.
DOI URL PMID |
| [24] | Tanner-Mcallister LS, Rhodes J, Hockings M (2018) A comparison of climate change impacts on park values on four Queensland World Heritage National Parks in Australia. Australasian Journal of Environmental Management, 25, 1-18. |
| [25] | TNC (2009) Conservation Action Planning Guidelines for Developing Strategies in the Face of Climate Change. The Nature Conservacy, Salt Lake City. |
| [26] | UNEP-WCMC, IUCN (2016) Protected Planet Report 2016: How Protected Areas Contribute to Achieving Global Targets for Biodiversity. UNEP-WCMC, Cambridge & IUCN, Gland. |
| [27] | UNEP-WCMC, IUCN, NGS (2018) Protected Planet Report 2018. UNEP-WCMC, Cambridge; IUCN, Gland & NGS, Washington, DC. |
| [28] | Wu JG, Wang L, Yang YW, Dai SF, Liu JQ, Zhu G (2011) Nature reserves need to face the challenge of climate change. Environment Protection, 12(4), 30-32. (in Chinese) |
| [ 吴建国, 王亮, 杨永伟, 代拴发, 刘建泉, 朱高 (2011) 自然保护区还需面对气候变化挑战. 环境保护, 124, 30-32.] | |
| [29] | Xue DY, Wu JY, Zhao FH (2012) Actions, progress and prospects in implementation of the Convention on Biological Diversity during the past 20 years in China. Biodiversity Science, 20, 623-632. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 薛达元, 武建勇, 赵富伟 (2012) 中国履行《生物多样性公约》二十年: 行动、进展与展望. 生物多样性, 20, 623-632.] |
| [1] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [2] | 顾婧婧, 刘宜卓, 苏杨. 基层地方政府在完成《昆蒙框架》中的作用和难点: 基于《联合国气候变化框架公约》任务的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24585-. |
| [3] | 李雪萌, 蒋际宝, 张曾鲁, 刘晓静, 王亚利, 吴宜钊, 李银生, 邱江平, 赵琦. 宝天曼国家级自然保护区蚯蚓物种多样性及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23352-. |
| [4] | 王启蕃, 刘小慧, 朱紫薇, 刘磊, 王鑫雪, 汲旭阳, 周绍春, 张子栋, 董红雨, 张明海. 黑龙江北极村国家级自然保护区鸟类与兽类多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 24024-. |
| [5] | 吴琪, 张晓青, 杨雨婷, 周艺博, 马毅, 许大明, 斯幸峰, 王健. 浙江钱江源-百山祖国家公园庆元片区叶附生苔多样性及其时空变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 24010-. |
| [6] | 曹可欣, 王敬雯, 郑国, 武鹏峰, 李英滨, 崔淑艳. 降水格局改变及氮沉降对北方典型草原土壤线虫多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23491-. |
| [7] | 所翟, 俞渃茜, 李媛辉, 徐基良. 基于实证分析中国自然保护区地方立法问题检视和优化路径[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23287-. |
| [8] | 刘啸林, 吴友贵, 张敏华, 陈小荣, 朱志成, 陈定云, 董舒, 李步杭, 丁炳扬, 刘宇. 浙江百山祖25 ha亚热带森林动态监测样地群落组成与结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23294-. |
| [9] | 黄小龙, 蒙秉顺, 李海波, 冉伟, 杨伟, 王丞, 谢波, 张旭, 冉景丞, 张明明. 基于红外相机的黔金丝猴及其同域分布物种种间关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23402-. |
| [10] | 杨向林, 赵彩云, 李俊生, 种方方, 李文金. 植物入侵导致群落谱系结构更加聚集: 以广西国家级自然保护区草本植物为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24175-. |
| [11] | 毛锐锐, 沈拓, 李慧, 田琳楚, 谭海蓉, 卢李荣, 吴小刚, 范宗骥, 伍国仪, 李杰, 吴勇, 朱弼成, 肖治术. 广东车八岭国家级自然保护区无尾两栖类动物鸣声特征数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(10): 24356-. |
| [12] | 崔国发. 关于自然保护地整合优化工作中几个关键问题的讨论与建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 22447-. |
| [13] | 邢超, 林依, 周智强, 赵联军, 蒋仕伟, 林蓁蓁, 徐基良, 詹祥江. 基于DNA条形码技术构建王朗国家级自然保护区陆生脊椎动物遗传资源数据库及物种鉴定[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 22661-. |
| [14] | 冯莉. 国际法视野下生物多样性和气候变化的协同治理[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 23110-. |
| [15] | 韦毅刚, 温放, 辛子兵, 符龙飞. 广西野生维管植物名录[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 23078-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()