



生物多样性 ›› 2020, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (8): 1036-1044. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019269 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019269
• 研究报告 • 上一篇
毕兴1,2, 杨朝辉1,3, 王丞1,3, 粟海军1,3, 张明明1,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2019-08-29
接受日期:2020-04-07
出版日期:2020-08-20
发布日期:2020-09-30
通讯作者:
张明明
作者简介:. E-mail: mmzhang@gzu.edu.cn基金资助:
Xing Bi1,2, Zhaohui Yang1,3, Cheng Wang1,3, Haijun Su1,3, Mingming Zhang1,3,*( )
)
Received:2019-08-29
Accepted:2020-04-07
Online:2020-08-20
Published:2020-09-30
Contact:
Mingming Zhang
摘要:
本文以具有典型喀斯特环境特点的贵州兴义坡岗自然保护区为例开展实地调查和文献研究。通过层次分析法和人与自然耦合系统模型构建, 从文化景观视角探讨了喀斯特地区自然与文化系统的历史演化过程中, 国家生态政策制度与乡规民约等乡土保护体系对生物文化多样性的驱动作用。研究结果表明: 坡岗保护区经历了管护主体和保护利用态度的转变, 保存了典型的喀斯特自然生态系统, 当地世居的少数民族群体在长期生存与适应过程中创造了极具特色的传统民族文化。坡岗自然保护区丰富的生物多样性与文化多样性形成一个地理重合、协同进化且相互作用的维持系统。生物文化多样性耦合体系主要存在国家政策制度类与乡规民约等乡土文化类两种驱动因素。应加强西南喀斯特地区的生物文化多样性的保护, 推动该地区生物多样性与文化多样性的协同发展; 除了政策与制度类驱动因子的直接作用, 还需要注重村规民约以及生态传统知识等乡土文化的驱动作用, 以避免保护区自然与文化保护体系的割离。
毕兴, 杨朝辉, 王丞, 粟海军, 张明明 (2020) 西南喀斯特地区生物文化多样性的演化与耦合: 以贵州兴义坡岗自然保护区为例. 生物多样性, 28, 1036-1044. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019269.
Xing Bi, Zhaohui Yang, Cheng Wang, Haijun Su, Mingming Zhang (2020) Coupling and co-evolution of biological and cultural diversity in the karst area of southwest China: A case study of Pogang Nature Reserve in Guizhou. Biodiversity Science, 28, 1036-1044. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019269.
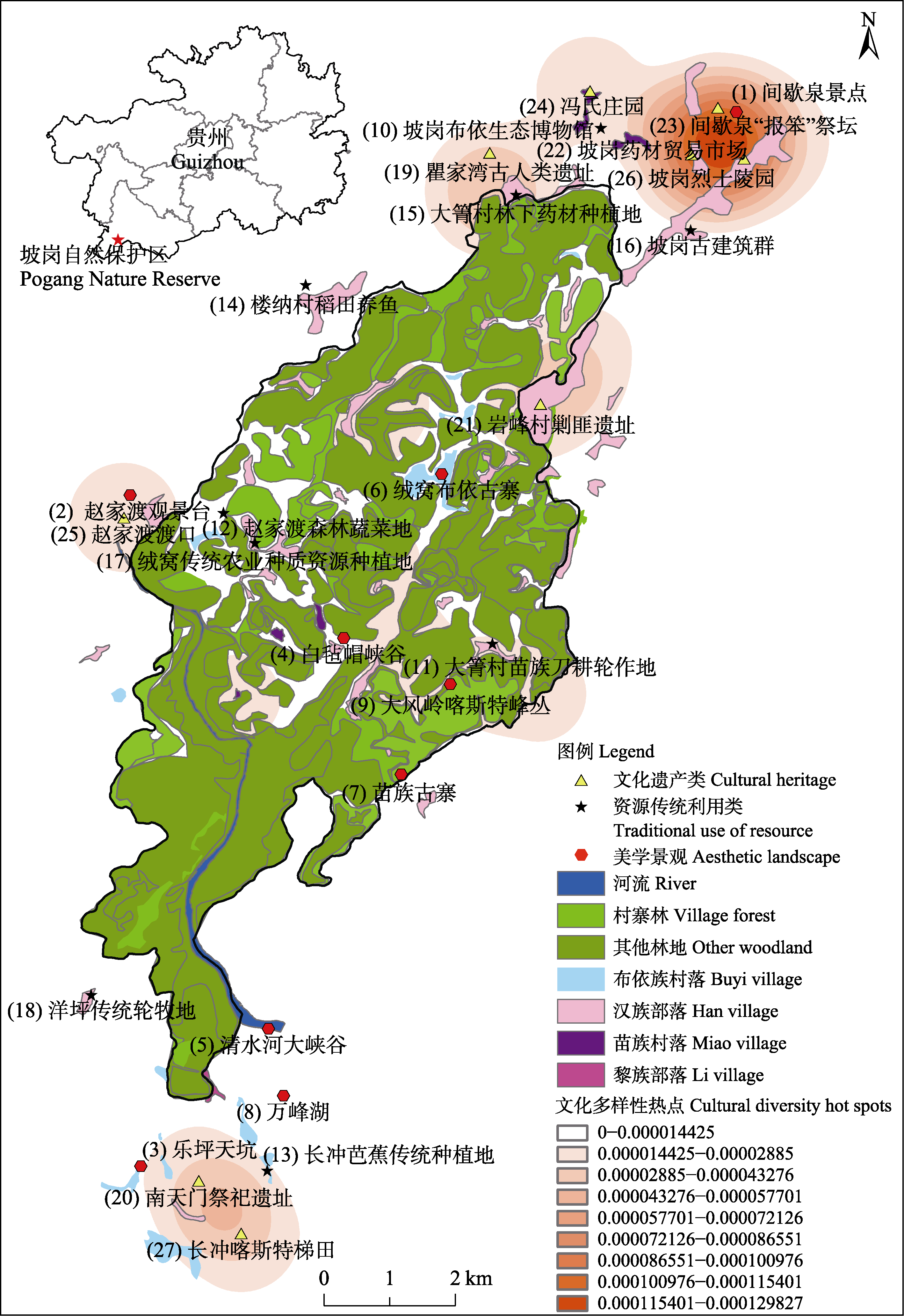
图1 坡岗保护区主要传统文化景观及其文化多样性热点分布图
Fig. 1 Distribution map of main traditional cultural landscape and cultural diversity hotspots in the Pogang Nature Reserve. (1) Jianxiequan scenic spot; (2) Zhaojiadu’s observation deck; (3) Leping sinkhole; (4) Baizhanmao canyon; (5) Qingshuihe canyon; (6) Ancient Buyi Village of Rongwo; (7) Ancient Miao Village; (8) Wanfeng Lake; (9) Dafengling karst peak clusters; (10) Buyi Eco-museum of Pogang; (11) Crop rotation area in Daqing Village; (12) Forest vegetable patch in Zhaojiadu; (13) The traditional plantation of banana in Changchong; (14) Rice-fish agricultural system in Louna Village; (15) The underwood medicinal planting in Daqing; (16) Pogang ancient building group; (17) Traditional planting of agricultural germplasm resources in Rongwo; (18) Traditional rotational grazing land in Yangping; (19) Ancient human sites in Qujiawan; (20) Sacrifice sites in Nantianmen; (21) Suppressing bandits site in Yanfeng Village; (22) Chinese medicinal trade market in Pogang; (23) “Baoben” altar in Jianxiequan; (24) The Fengs Manor; (25) Zhaojiadu ferry; (26) Pogang Martyrs’ Cemetery; (27) Karst terraces in Changchong.
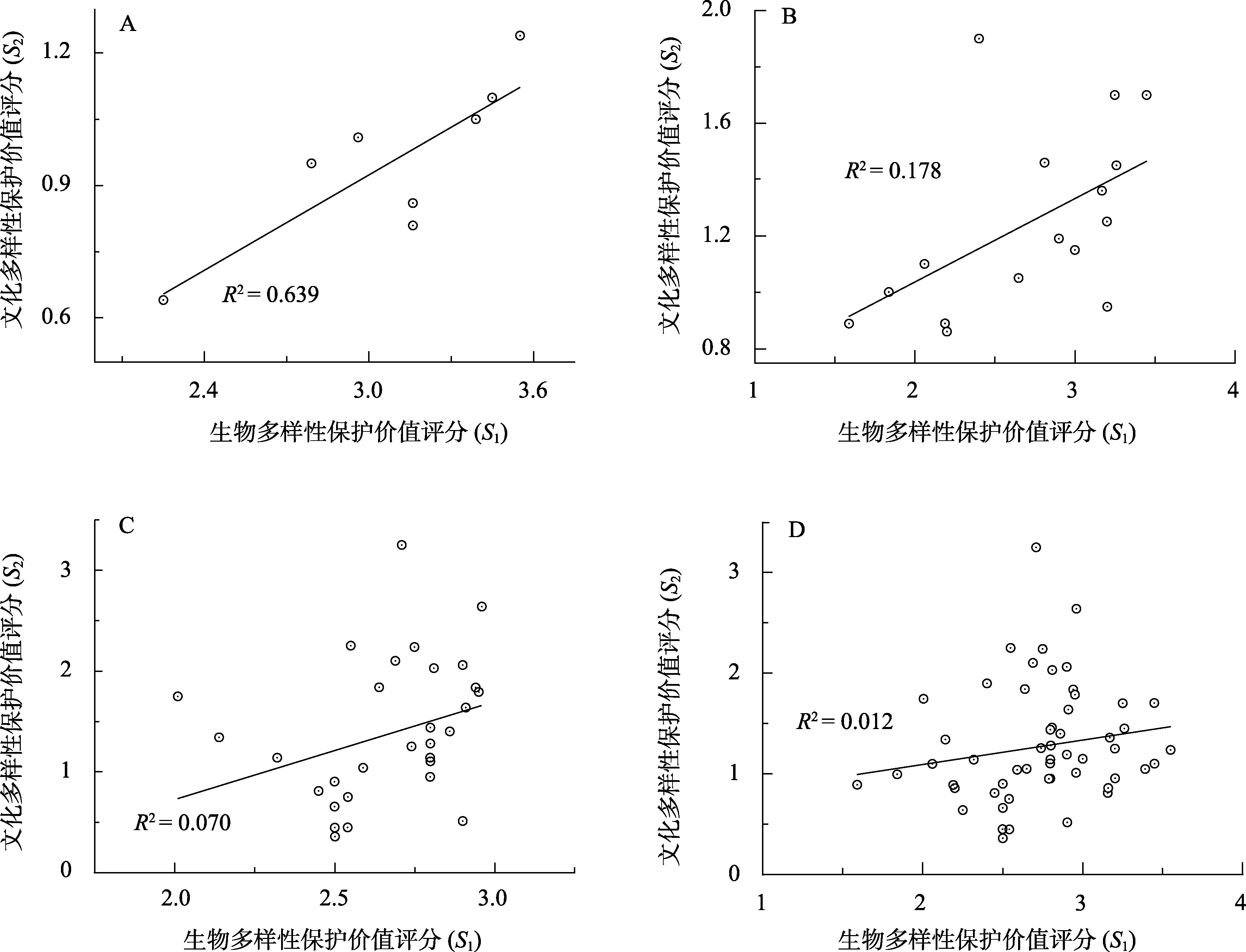
图2 基于Origin软件对坡岗自然保护区文化景观生物多样性保护价值指标(S1)与文化多样性保护价值指标(S2)的线性关系拟合结果。 (A)资源传统利用类; (B)美学景观类; (C)文化遗产类; (D)所有文化景观类。
Fig. 2 Based on the Origin, the linear regression correlation the biodiversity index (S1) and cultural diversity index (S2) of the Pogang Nature Reserve. (A) Traditional utilization of resources; (B) Aesthetic landscape; (C) Cultural heritage; (D) All types.
| [1] | Agnoletti M, Emanueli F (2016) Biocultural Diversity in Europe. Springer International Publishing, Cham, Switzerland. |
| [2] | Agnoletti M, Rotherham ID (2015) Landscape and biocultural diversity. Biodiversity and Conservation, 24, 3155-3165. |
| [3] | Arnaiz-Schmitz C, Herrero-Jáuregui C, Schmitz MF (2018) Losing a heritage hedgerow landscape. Biocultural diversity conservation in a changing social-ecological Mediterranean system. Science of the Total Environment, 637/638, 374-384. |
| [4] | Cao B, He LT, Zhang P (2015) A study of human fossils discovered at the Maomao Cave, Xingyi County, Guizhou Province. Acta Anthropologica, Sinica, 34, 451-460. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 曹波, 贺乐天, 张璞 (2015) 贵州兴义猫猫洞出土的人类化石. 人类学学报, 34, 451-460.] | |
| [5] | Hong SK (2013) Biocultural diversity conservation for island and islanders: Necessity, goal and activity. Journal of Marine and Island Cultures, 2, 102-106. |
| [6] | Inouye DW (2016) IPBES: Global collaboration on biodiversity and ecosystem services. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 12, 371. |
| [7] | Jiao YM, Cheng GD, Xiao DN (2002) A study on the cultural landscape of Hani’s terrace and its protection. Geographical Research, 21, 733-741. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 角媛梅, 程国栋, 肖笃宁 (2002) 哈尼梯田文化景观及其保护研究. 地理研究, 21, 733-741.] | |
| [8] | Kale J (2014) Florence Declaration on Cultural and Biological Diversity. Sociologija I Prostor, 52, 231-236. |
| [9] | Lan AJ, Zhang BP, Xiong KN, An YL (2003) Spatial pattern of the fragile karst environment in southwest Guizhou Province. Geographical Research, 22, 733-741. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 兰安军, 张百平, 熊康宁, 安裕论 (2003) 黔西南脆弱喀斯特生态环境空间格局分析. 地理研究, 22, 733-741.] | |
| [10] | Li CR, Chen ZP, Li M, Deng LX (2012) Study on woody ornamental plant resources of Pogang Nature Reserve in Xingyi City. Seed, 31, 62-65. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李从瑞, 陈志萍, 李茂, 邓伦秀 (2012) 兴义坡岗自然保护区木本观赏植物资源研究. 种子, 31, 62-65.] | |
| [11] |
Liu JG, Dietz T, Carpenter SR, Alberti M, Folke C, Moran E, Pell AN, Deadman P, Kratz T, Lubchenco J, Ostrom E, Ouyang Z, Provencher W, Redman CL, Schneider SH, Taylor WW (2007) Complexity of coupled human and natural systems. Science, 317, 1513-1516.
DOI URL PMID |
| [12] |
Maffi L, Woodley E (2010) Biocultural diversity conservation: A global sourcebook. Ecological Restoration, 3, 61-62.
DOI URL |
| [13] | Mao SX, Shen Y, Deng HB (2017) Progress in biocultural diversity research. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 8179-8186. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 毛舒欣, 沈园, 邓红兵 (2017) 生物文化多样性研究进展. 生态学报, 37, 8179-8186.] | |
| [14] | Pei SJ (2008) Biodiversity and cultural diversity. Kexue, 60(4), 33-36. (in Chinese) |
| [ 裴盛基 (2008) 生物多样性与文化多样性. 科学, 604, 33-36.] | |
| [15] | Pei SJ (2011) National culture and biodiversity conservation. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 26, 190-196. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 裴盛基 (2011) 民族文化与生物多样性保护. 中国科学院院刊, 26, 190-196.] | |
| [16] | Pretty B, Adams F, Berkes FS, Athayde N, Dudley E, Hunn L, Maffi K, Milton D, Rapport P, Robbins E, Sterling S, Stolton A, Tsing E, Vintinner SP (2009) The intersection of biological diversity and cultural diversity: Towards integration. Conservation and Society, 7, 100-112. |
| [17] | Qiu J (2010) The viewpoint of ecological philosophy about offering sacrifices to gods or ancestors in Pogang. Journal of Xingyi Normal University for Nationalities, ( 1), 1-3. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 邱靖 (2010) 坡岗祭祀活动的哲学生态观. 兴义民族师范学院学报, ( 1), 1-3.] | |
| [18] | Redford KH (1991) The ecologically noble savage. Cultural Survival Quarterly, 15, 46-48. |
| [19] | Saaty TL (1989) Group Decision Making and the AHP. In: Golden BL, Wasil EA, Harker PT (eds) The Analytic Hierarchy Process. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. |
| [20] | Shen Y, Li T, Tang MF, Deng HB (2019) Spatial patterns of biocultural diversity in Southwest China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39, 2454-2461. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 沈园, 李涛, 唐明方, 邓红兵 (2019) 西南地区生物文化多样性空间格局定量研究. 生态学报, 39, 2454-2461.] | |
| [21] | Taylor K, Lennon J (2011) Cultural landscapes: A bridge between culture and nature? International Journal of Heritage Studies, 17, 537-554. |
| [22] | Vlami V, Kokkoris IP, Zogaris S, Stamatis Z, Cartalis C, Kehayias G, Dimopoulos P (2017) Cultural landscapes and attributes of “culturalness” in protected areas: An exploratory assessment in Greece. Science of the Total Environment, 595, 229-243. |
| [23] | Wandersee SM, Li A, López-carr D, Yang YQ (2012) Perception and decisions in modeling coupled human and natural systems: A case study from Fanjingshan National Nature Reserve, China. Ecological Modelling, 229, 37-49. |
| [24] | Wang B, Huang Y, Li JT (2018) Amphibian species richness patterns in karst regions in southwest China and its environmental associations. Biodiversity Science, 26, 941-950. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王波, 黄勇, 李家堂 (2018) 西南喀斯特地貌区两栖动物丰富度分布格局与环境因子的关系. 生物多样性, 26, 941-950.] | |
| [25] | Xu ZF (2015) Conservation of biodiversity and cultural diversity are two sides of a coin: Xishuangbanna Dai’s ecological culture as an example. Biodiversity Science, 23, 126-130. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 许再富 (2015) 生物多样性保护与文化多样性保护是一枚硬币的两面: 以西双版纳傣族生态文化为例. 生物多样性, 23, 126-130.] | |
| [26] | Xue DY, Guo L (2009) On concepts and protection of traditional knowledge. Biodiversity Science, 17, 135-142. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 薛达元, 郭泺 (2009) 论传统知识的概念与保护. 生物多样性, 17, 135-142.] | |
| [27] | Yang LX, Pei SJ, Zhang Y (2019) Action research on Tibetan sacred nature sites (SNS) conservation in Tibetan community in NW Yunnan. Biodiversity Science, 27, 749-757. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨立新, 裴盛基, 张宇 (2019) 滇西北藏区自然圣境与传统文化驱动下的生物多样性保护. 生物多样性, 27, 749-757.] | |
| [28] | Zhang HH (2010) Study on geographical distribution of wild Orchidaceae in Guizhou. Guizhou Science, 28, 47-56. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张华海 (2010) 贵州野生兰科植物地理分布研究. 贵州科学, 28, 47-56.] | |
| [29] | Zhang HH, Long QD, Liao DP (2006) Comprehensive Scientific Investigation of Xingyi Pogang Nature Reserve. Guizhou Science and Technology Press, Guiyang. (in Chinese) |
| [ 张华海, 龙启德, 廖德平 (2006) 兴义坡岗自然保护区综合科学考察集 贵州科技出版社, 贵阳.] | |
| [30] | Zhang JY, Zhang YJ (2019) The evolution and identification of cultural landscape value in protected areas: A case of Mount Tai. Journal of Natural Resources, 34, 1833-1849. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张婧雅, 张玉钧 (2019) 自然保护地的文化景观价值演变与识别——以泰山为例. 自然资源学报, 34, 1833-1849.] |
| [1] | 赵勇强, 阎玺羽, 谢加琪, 侯梦婷, 陈丹梅, 臧丽鹏, 刘庆福, 隋明浈, 张广奇. 退化喀斯特森林自然恢复中不同生活史阶段木本植物物种多样性与群落构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23462-. |
| [2] | 熊松, 淦江, 谢彦军, 邓晰朝, 覃国乐, 彭晚霞, 曾馥平, 占志立, 谭卫宁, 黄国勤, 杜虎. 喀斯特常绿落叶阔叶林凋落物产量动态及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24248-. |
| [3] | 王斌, 钟艺倩, 杨美雪, 吴淼锐, 王艳萍, 陆芳, 陶旺兰, 李健星, 赵弘明, 刘晟源, 向悟生, 李先琨. 喀斯特季节性雨林优势树种叶片非结构性碳水化合物空间变异及生态驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24325-. |
| [4] | 程卓, 林晨, 龙春林. 独龙族传统生计及其生物多样性管理[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23019-. |
| [5] | 向文倩, 王文娟, 任明迅. 木棉文化的生物多样性传统知识及其传承与利用[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22524-. |
| [6] | 李佳奇, 郭屹立, 李冬兴, 王斌, 向悟生, 黄甫昭, 陆芳, 文淑均, 李健星, 陆树华, 李先琨. 桂西南北热带喀斯特季节性雨林土壤钾、钙、镁空间分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22352-. |
| [7] | 马瑞霞, 郭屹立, 李冬兴, 王斌, 向悟生, 黄甫昭, 陆芳, 文淑均, 李健星, 陆树华, 李先琨. 桂西南喀斯特季节性雨林幼树更新的空间分布格局及机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22251-. |
| [8] | 程卓, 张晴, 龙春林. 民族植物学研究现状(2017-2022)[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 22372-. |
| [9] | 鲁梦珍, 曾馥平, 宋同清, 彭晚霞, 张浩, 苏樑, 刘坤平, 谭卫宁, 杜虎. 喀斯特常绿落叶阔叶林死亡个体空间分布格局及生境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(4): 21340-. |
| [10] | 吴墨栩, 安明态, 田力, 刘锋. 茂兰喀斯特森林木本植物性系统数量特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(11): 22025-. |
| [11] | 楚雅南, 林晨, 毛文慧, 龙春林. 生物文化多样性研究新进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22463-. |
| [12] | 陈思淇, 张玉钧. 乡村景观生物多样性研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(10): 1411-1424. |
| [13] | 王存璐,陈浒,肖华,张红梅,李林芝,郭城,陈静,魏强. 黔西北石漠化地区两栖动物多样性及其生境选择[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(4): 485-495. |
| [14] | 贾梦可,郭屹立,李冬兴,王斌,向悟生,王爱龙,刘晟源,丁涛,黄甫昭,文淑均,陆树华,李先琨. 桂西南喀斯特季节性雨林叶凋落量的时空动态[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(4): 455-462. |
| [15] | 陈惠君, 杜虎, 宋同清, 彭晚霞, 张浩, 苏樑, 曾馥平. 木论喀斯特常绿落叶阔叶混交林群丛数量分类及稳定性[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(10): 1056-1068. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()