



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (7): 22240. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022240 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022240
沈梅1, 郭宁宁1, 罗遵兰1, 郭晓晨2, 孙光1, 肖能文1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-04-30
接受日期:2022-05-26
出版日期:2022-07-20
发布日期:2022-06-24
通讯作者:
肖能文
作者简介:*E-mail: xiaonw@163.com基金资助:
Mei Shen1, Ningning Guo1, Zunlan Luo1, Xiaochen Guo2, Guang Sun1, Nengwen Xiao1,*( )
)
Received:2022-04-30
Accepted:2022-05-26
Online:2022-07-20
Published:2022-06-24
Contact:
Nengwen Xiao
摘要:
使用eDNA宏条形码(eDNA metabarcoding)和地笼法检测了北京市3条水系在夏季和秋季两个季节的鱼类多样性, 旨在研究北京市鱼类群落的空间格局特征, 探索适用于北京鱼类生物多样性监测及保护的新方法。结果表明: 在北京市的34个采样点中, 利用eDNA metabarcoding共检测出鱼类55种, 显著高于传统方法所捕获的鱼类种数(35种), 鱼类组成以鲤形目和鲈形目为主。山区河流清水鱼的多样性要显著高于城区河流, 城区河流(北运河水系)群落结构较为单一, 以鲫(Carassius auratus)、麦穗鱼(Pseudorasbora parva)、泥鳅(Misgurnus anguillicaudatus)等耐污种为优势种; 山区河流(潮白河水系及大清河水系)以宽鳍鱲(Zacco platypus)、拉氏鱥(Rhynchocypris lagowskii)、马口鱼(Opsariichthys uncirostris)等为优势种。不同季节影响清水鱼群落结构的环境因子不同, 夏季主要是总溶解固体和电导率, 秋季主要是海拔和温度。清水鱼丰富度与环境因子及人类活动的相关性表明, 清水鱼的丰富度随着总溶解固体及灯光指数增加而显著降低, 且均与海拔、温度等存在显著相关性。本研究证明了eDNA metabarcoding方法用于监测北京市鱼类多样性及其时空分布的可行性。
沈梅, 郭宁宁, 罗遵兰, 郭晓晨, 孙光, 肖能文 (2022) 基于eDNA metabarcoding探究北京市主要河流鱼类分布及影响因素. 生物多样性, 30, 22240. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022240.
Mei Shen, Ningning Guo, Zunlan Luo, Xiaochen Guo, Guang Sun, Nengwen Xiao (2022) Explore the distribution and influencing factors of fish in major rivers in Beijing with eDNA metabarcoding technology. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22240. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022240.
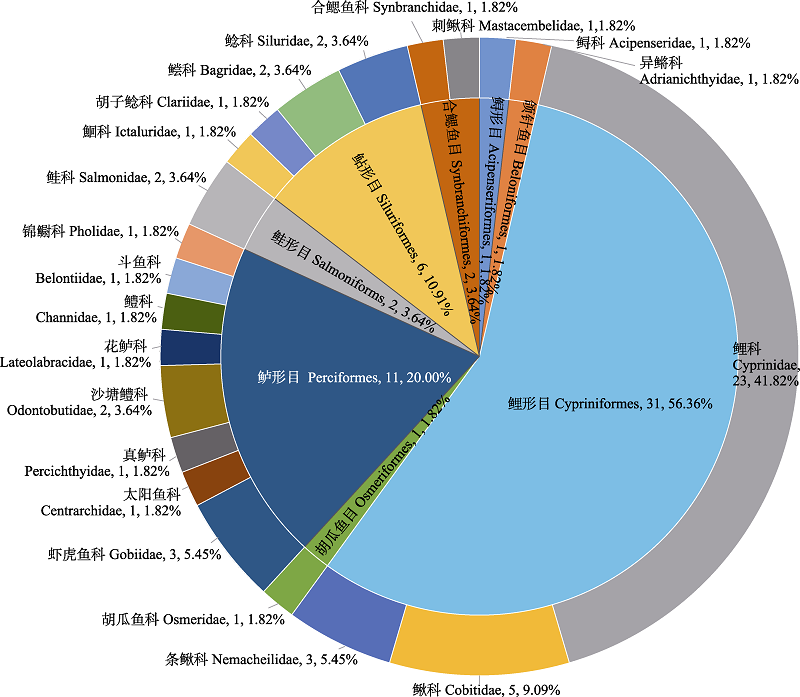
图2 eDNA metabarcoding识别鱼类物种在目和科分类学水平上的数量及所占比例
Fig. 2 Number and proportion of fish species identified by eDNA metabarcoding at the taxonomic level of order and family
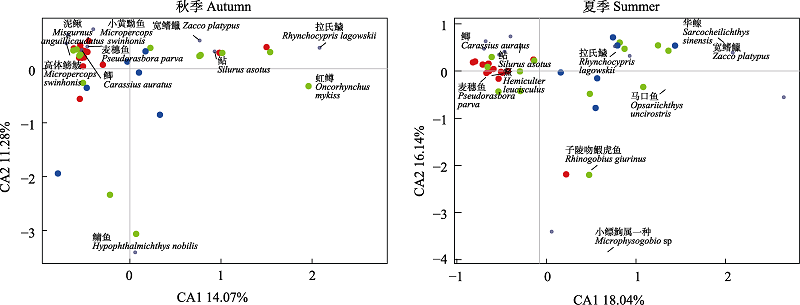
图3 3条水系在秋、夏季节鱼类群落组成分布。红色圆点表示北运河水系; 绿色圆点表示潮白河水系; 蓝色圆点表示大清河水系。
Fig. 3 Distribution of fish communities in the three river systems during the autumn and summer. Red dots represent Beiyun River System; Green dots represent Chaobai River System; Blue dots represent Daqing River System.
| 北运河水系 Beiyun River System | 潮白河水系 Chaobai River System | 大清河水系 Daqing River System | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 物种 Species | 优势度指数 Dominance index (Y) | 物种 Species | 优势度指数 Dominance index (Y) | 物种 Species | 优势度指数 Dominance index (Y) |
| 鲫 Carassius auratus | 0.5175 | 鲫 Carassius auratus | 0.2556 | 宽鳍鱲 Zacco platypus | 0.1517 |
| 麦穗鱼 Pseudorasbora parva | 0.0888 | 拉氏鱥 Rhynchocypris lagowskii | 0.1031 | 鲫 Carassius auratus | 0.1475 |
| 小黄黝鱼 Micropercops swinhonis | 0.0453 | 宽鳍鱲 Zacco platypus | 0.0807 | 拉氏鱥 Rhynchocypris lagowskii | 0.0968 |
| 泥鳅 Misgurnus anguillicaudatus | 0.0448 | 鲇 Silurus asotus | 0.0474 | 小黄黝鱼 Micropercops swinhonis | 0.0540 |
| 高体鳑鲏 Rhodeus ocellatus | 0.0345 | 子陵吻鰕虎鱼 Rhinogobius giurinus | 0.0350 | 马口鱼 Opsariichthys uncirostris | 0.0408 |
| ? Hemiculter leucisculus | 0.0205 | 麦穗鱼 Pseudorasbora parva | 0.0242 | 华鳈 Sarcocheilichthys sinensis | 0.0406 |
| - | - | - | - | 褐吻鰕虎鱼 Rhinogobius brunneus | 0.0400 |
| - | - | - | - | 子陵吻鰕虎鱼 Rhinogobius giurinus | 0.0376 |
| - | - | - | - | 鲇 Silurus asotus | 0.0340 |
| - | - | - | - | 北鳅 Lefua costata | 0.0241 |
| - | - | - | - | 鲤 Cyprinus carpio | 0.0233 |
表1 3条水系鱼类群落优势种的优势度指数
Table 1 Dominance index of dominant species in three river systems
| 北运河水系 Beiyun River System | 潮白河水系 Chaobai River System | 大清河水系 Daqing River System | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 物种 Species | 优势度指数 Dominance index (Y) | 物种 Species | 优势度指数 Dominance index (Y) | 物种 Species | 优势度指数 Dominance index (Y) |
| 鲫 Carassius auratus | 0.5175 | 鲫 Carassius auratus | 0.2556 | 宽鳍鱲 Zacco platypus | 0.1517 |
| 麦穗鱼 Pseudorasbora parva | 0.0888 | 拉氏鱥 Rhynchocypris lagowskii | 0.1031 | 鲫 Carassius auratus | 0.1475 |
| 小黄黝鱼 Micropercops swinhonis | 0.0453 | 宽鳍鱲 Zacco platypus | 0.0807 | 拉氏鱥 Rhynchocypris lagowskii | 0.0968 |
| 泥鳅 Misgurnus anguillicaudatus | 0.0448 | 鲇 Silurus asotus | 0.0474 | 小黄黝鱼 Micropercops swinhonis | 0.0540 |
| 高体鳑鲏 Rhodeus ocellatus | 0.0345 | 子陵吻鰕虎鱼 Rhinogobius giurinus | 0.0350 | 马口鱼 Opsariichthys uncirostris | 0.0408 |
| ? Hemiculter leucisculus | 0.0205 | 麦穗鱼 Pseudorasbora parva | 0.0242 | 华鳈 Sarcocheilichthys sinensis | 0.0406 |
| - | - | - | - | 褐吻鰕虎鱼 Rhinogobius brunneus | 0.0400 |
| - | - | - | - | 子陵吻鰕虎鱼 Rhinogobius giurinus | 0.0376 |
| - | - | - | - | 鲇 Silurus asotus | 0.0340 |
| - | - | - | - | 北鳅 Lefua costata | 0.0241 |
| - | - | - | - | 鲤 Cyprinus carpio | 0.0233 |
| 物种 Species | 样点数 Number of detected site | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 北运河水系 Beiyun River System | 潮白河水系 Chaobai River System | 大清河水系 Daqing River System | 总计 Total | |
| 北方须鳅 Barbatula nuda | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| 华鰁 Sarcocheilichthys sinensis | 4 | 5 | 4 | 13 |
| 黄尾鲴 Xenocypris davidi | 6 | 11 | 4 | 21 |
| 宽鳍鱲 Zacco platypus | 7 | 9 | 6 | 22 |
| 拉氏鱥 Rhynchocypris lagowskii | 9 | 9 | 6 | 24 |
| 马口鱼 Opsariichthys uncirostris | 10 | 9 | 5 | 24 |
| 北鳅 Lefua costata | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| 达里湖高原鳅 Triplophysa dalaica | 0 | 3 | 2 | 5 |
| 鳜 Siniperca chuatsi | 6 | 5 | 4 | 15 |
| 细鳞鲑 Brachymystax lenok | 1 | 3 | 0 | 4 |
表2 清水鱼在3条水系的检测的样点数情况
Table 2 Number of detected site of clearwater fish in each river system
| 物种 Species | 样点数 Number of detected site | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 北运河水系 Beiyun River System | 潮白河水系 Chaobai River System | 大清河水系 Daqing River System | 总计 Total | |
| 北方须鳅 Barbatula nuda | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| 华鰁 Sarcocheilichthys sinensis | 4 | 5 | 4 | 13 |
| 黄尾鲴 Xenocypris davidi | 6 | 11 | 4 | 21 |
| 宽鳍鱲 Zacco platypus | 7 | 9 | 6 | 22 |
| 拉氏鱥 Rhynchocypris lagowskii | 9 | 9 | 6 | 24 |
| 马口鱼 Opsariichthys uncirostris | 10 | 9 | 5 | 24 |
| 北鳅 Lefua costata | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| 达里湖高原鳅 Triplophysa dalaica | 0 | 3 | 2 | 5 |
| 鳜 Siniperca chuatsi | 6 | 5 | 4 | 15 |
| 细鳞鲑 Brachymystax lenok | 1 | 3 | 0 | 4 |
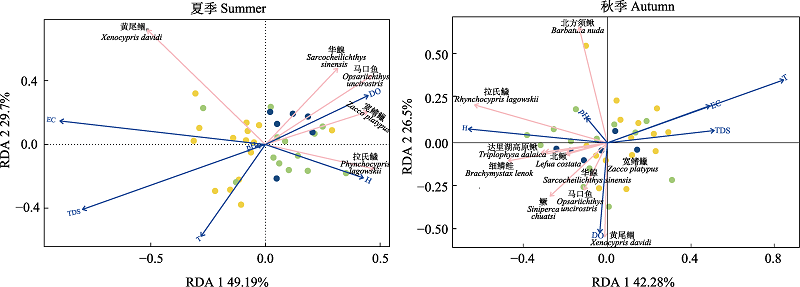
图6 冗余分析(RDA)探究清水鱼群落结构与测量环境变量之间的关系。DO: 溶解氧; TDS: 总溶解固体; T: 温度; H: 海拔; EC: 电导率。黄色圆点表示北运河水系; 绿色圆点表示潮白河水系; 蓝色圆点表示大清河水系。
Fig. 6 RDA exploring the relationship between community structure and measured environmental variables. DO, Dissolved oxygen; TDS, Total dissolved solids; T, Temperature; H, Height; EC, Electrical conductivity。Yellow dots represent Beiyun River System; Green dots represent Chaobai River System; Blue dots represent Daqing River System.
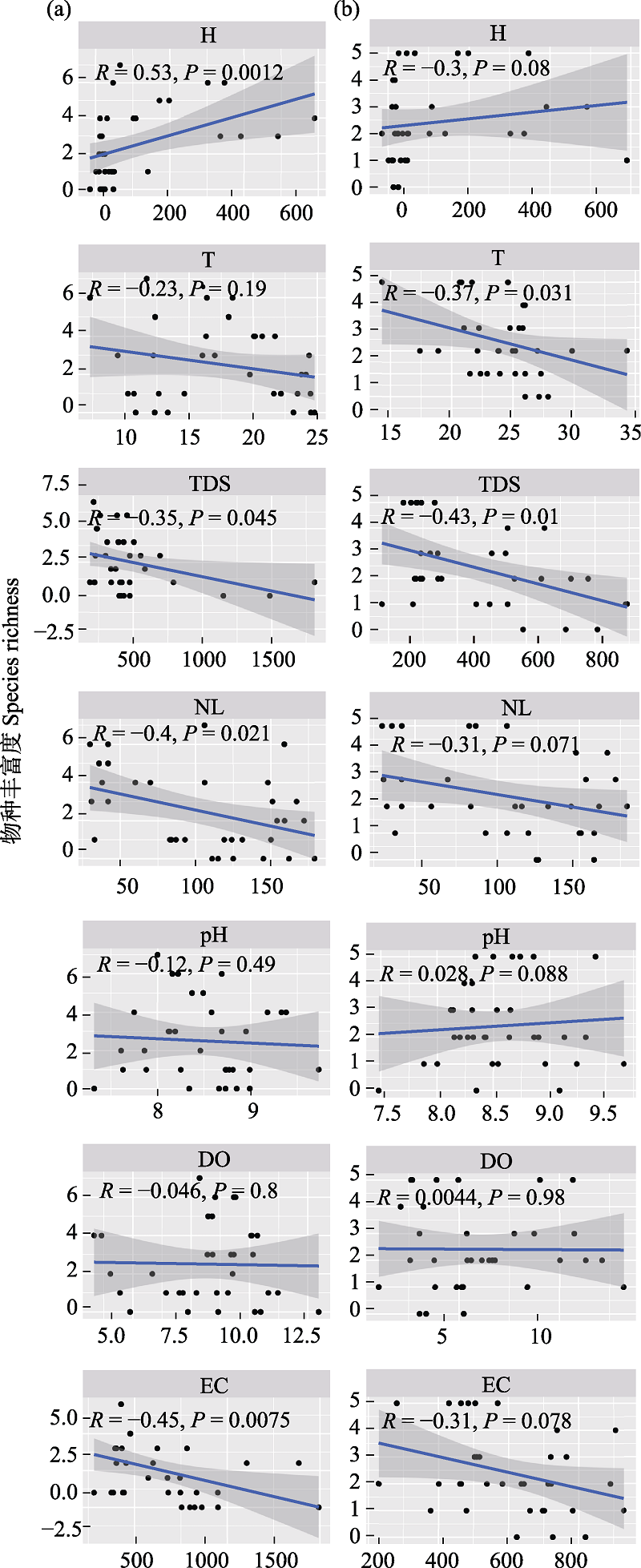
图7 清水鱼丰富度与环境因子及灯光指数的相关性。H: 海拔; pH: 酸碱度; T: 温度;DO: 溶解氧; TDS: 总溶解固体; EC: 电导率; NL: 夜间灯光; a: 秋季; b: 夏季。
Fig. 7 Correlation of clearwater fish abundance with environmental factors and lighting indices. H, Height; pH, Potential of hydrogen; T, Temperature; DO, Dissolved oxygen; TDS, Total dissolved solids; EC, Electrical conductivity; NL, Night light; a, Autumn; b, Summer.
| [1] | Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI- BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Research, 25, 3389-3402. |
| [2] |
Brown LR (2000) Fish communities and their associations with environmental variables, Lower San Joaquin River Drainage, California. Environmental Biology of Fishe, 57, 251- 269.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Chen SF, Zhou YQ, Chen YR, Gu J (2018) Fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics, 34, 884-890.
DOI URL |
| [4] | Chen W, Hu D, Fu BQ (2007) Research on Biodiversity of Beijing Wetland. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese) |
| [ 陈卫, 胡东, 付必谦 (2007) 北京湿地生物多样性研究. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [5] |
Civade R, Dejean T, Valentini A, Roset N, Raymond JC, Bonin A, Taberlet P, Pont D (2016) Spatial representativeness of environmental DNA metabarcoding signal for fish biodiversity assessment in a natural freshwater system. PLoS ONE, 11, e0157366.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Deiner K, Walser JC, Mächler E, Altermatt F (2015) Choice of capture and extraction methods affect detection of freshwater biodiversity from environmental DNA. Biological Conservation, 183, 53-63.
DOI URL |
| [7] | Du LF, Xu JX, Li YB, Qu XD, Liu M, Zhang M, Yu Y (2019) Fish community characteristics and spatial pattern in major rivers of Beijing city. Research of Environmental Sciences, 32, 447-457. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杜龙飞, 徐建新, 李彦彬, 渠晓东, 刘猛, 张敏, 余杨 (2019) 北京市主要河流鱼类群落的空间格局特征. 环境科学研究, 32, 447-457.] | |
| [8] |
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics, 26, 2460-2461.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Farriols MT, Ordines F, Somerfield PJ, Pasqual C, Hidalgo M, Guijarro B, Massuti E (2017) Bottom trawl impacts on Mediterranean demersal fish diversity: Not so obvious or are we too late? Continental Shelf Research, 137, 84-102.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Ji FF, Han DY, Yan L, Yan SH, Zha JM, Shen JZ (2022) Assessment of benthic invertebrate diversity and river ecological status along an urbanized gradient using environmental DNA metabarcoding and a traditional survey method. Science of the Total Environment, 806, 150587.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Kadye WT, Magadza CHD, Moyo NAG, Kativu S (2008) Stream fish assemblages in relation to environmental factors on a montane plateau (Nyika Plateau, Malawi). Environmental Biology of Fishes, 83, 417-428.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Li J, Li XH, Jia XP, Tan XC, Wang C, Li YF, Shao XF (2012) Relationship between fish community diversity and environmental factors in the Lianjiang River, Guangdong, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32, 5795-5805. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [ 李捷, 李新辉, 贾晓平, 谭细畅, 王超, 李跃飞, 邵晓风 (2012) 连江鱼类群落多样性及其与环境因子的关系. 生态学报, 32, 5795-5805.] | |
| [13] | Liu YQ, Fang JF (2003) The methods of clearwater fish aquaculture in the mountains. Fishery Modernization, 3, 15-16. (in Chinese) |
| [ 刘奕秋, 方杰锋 (2003) 山区清水鱼养殖方法. 渔业现代化, 3, 15-16.] | |
| [14] | Miya M, Sato Y, Fukunaga T, Sado T, Poulsen JY, Sato K, Minamoto T, Yamamoto S, Yamanaka H, Araki H, Kondoh M, Iwasaki W (2015) MiFish, a set of universal PCR primers for metabarcoding environmental DNA from fishes: Detection of more than 230 subtropical marine species. Royal Society Open Science, 2, 150088. |
| [15] |
Ruppert KM, Kline RJ, Rahman MS (2019) Past, present, and future perspectives of environmental DNA (eDNA) metabarcoding: A systematic review in methods, monitoring, and applications of global eDNA. Global Ecology and Conservation, 17, e00547.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Schenekar T, Schletterer M, Lecaudey LA, Weiss SJ (2020) Reference databases, primer choice, and assay sensitivity for environmental metabarcoding: Lessons learnt from a re-evaluation of an eDNA fish assessment in the Volga headwaters. River Research and Applications, 36, 1004-1013.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Shaw JLA, Clarke LJ, Wedderburn SD, Barnes TC, Weyrich LS, Cooper A (2016) Comparison of environmental DNA metabarcoding and conventional fish survey methods in a River System. Biological Conservation, 197, 131-138.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Shen M, Xiao NW, Lu L, Luo ZL, Shi NN, Sun G (2022) Methods and application of environmental dna detection of fish. Journal of Hydroecology, 42, 133-141. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 沈梅, 肖能文, 卢林, 罗遵兰, 史娜娜, 孙光 (2022) 环境DNA检测鱼类的方法及应用. 水生态学杂志, 42, 133-141.] | |
| [19] | Shu L, Lin JY, Xu Y, Cao T, Feng JM, Peng ZG (2020) Investigating the fish diversity in Erhai Lake based on enviromental DNA metabarcoding. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 44, 1080-1086. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 舒璐, 林佳艳, 徐源, 曹特, 封吉猛, 彭作刚 (2020) 基于环境DNA宏条形码的洱海鱼类多样性研究. 水生生物学报, 44, 1080-1086.] | |
| [20] |
Smith TA, Kraft CE (2005) Stream fish assemblages in relation to landscape position and local habitat variables. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society, 134, 430-440.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Thomsen PF, Willerslev E (2015) Environmental DNA-An emerging tool in conservation for monitoring past and present biodiversity. Biological Conservation, 183, 4-18.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Wang C, Tao M, Li AM, Shi P, Yang JH, Wang ZH, Zhang XW (2022) Research on the biodiversity of Qinhuai River based on environmental DNA metabarcoding. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 42, 611-624. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王晨, 陶孟, 李爱民, 施鹏, 杨江华, 王志浩, 张效伟 (2022) 基于环境DNA宏条形码技术的秦淮河生物多样性探究. 生态学报, 42, 611-624.] | |
| [23] | Wang FZ (1936) The Fishes of Peiping and Its Vicinity. Science Reports of the National University of Peking, 1(2), 1-28. |
| [24] | Wang HY (1994) Fauna of Beijing Fish and Amphibians and Reptiles. Beijing Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 王鸿媛 (1994) 北京鱼类和两栖、爬行动物志. 北京出版社, 北京.] | |
| [25] | Wang M, Jin XW, Lin XL, Du LN, Cui YD, Wu XP, Sun HY, Xie ZC, Wang XH, Wang BX (2021) Advances in the macrozoobenthos biodiversity monitoring and ecosystem assessment using environmental DNA metabarcoding. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 41, 7440-7453. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王萌, 金小伟, 林晓龙, 杜丽娜, 崔永德, 吴小平, 孙红英, 谢志才, 王新华, 王备新 (2021) 基于环境DNA宏条形码技术的底栖动物监测及水质评价研究进展. 生态学报, 41, 7440-7453.] | |
| [26] |
Wu JT, Mao RC, Li MY, Xia J, Song J, Cheng DD, Sun HT (2020) Assessment of aquatic ecological health based on determination of biological community variability of fish and macroinvertebrates in the Weihe River Basin, China. Journal of Environmental Management, 267, 110651.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Xie RL, Zhao GF, Yang JH, Wang ZH, Xu YP, Zhang XW, Wang ZJ (2021) eDNA metabarcoding revealed differential structures of aquatic communities in a dynamic freshwater ecosystem shaped by habitat heterogeneity. Environmental Research, 201, 111602.
DOI URL |
| [28] | Xu N, Xiong MH, Shao K, Que YF, Li JY (2020) Preliminary study on environmental DNA metabarcoding for detecting biodiversity in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Research of Environmental Sciences, 33, 1187-1196. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 徐念, 熊美华, 邵科, 阙延福, 李键庸 (2020) 长江中下游环境DNA宏条形码生物多样性检测技术初步研究. 环境科学研究, 33, 1187-1196.] | |
| [29] |
Yamamoto S, Masuda R, Sato Y, Sado T, Araki H, Kondoh M, Minamoto T, Miya M (2017) Environmental DNA metabarcoding reveals local fish communities in a species-rich coastal sea. Scientific Reports, 7, 40368.
DOI PMID |
| [30] | Zhang CG, Zhao YH (2013) Fishes in Beijing and Adjacent Areas, China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 张春光, 赵亚辉 (2013) 北京及其邻近地区的鱼类. 科学出版社, 北京] | |
| [31] |
Zhang CG, Zhao YH, Xing YC, Guo RL, Zhang Q, Feng Y, Fan EY (2011) Fish species diversity and conservation in Beijing and adjacent areas. Biodiversity Science, 19, 597-604. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 张春光, 赵亚辉, 邢迎春, 郭瑞禄, 张清, 冯云, 樊恩源 (2011) 北京及其邻近地区野生鱼类物种多样性及其资源保育. 生物多样性, 19, 597-604.]
DOI |
|
| [32] | Zhang CL (1933) Cyprinid Fishes in China. Fan Memorial Institute of Biology, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 张春霖 (1933) 中国鲤类志. 北平静生生物调查所, 北京.] | |
| [33] |
Zhang JJ, Kobert K, Flouri T, Stamatakis A (2014) PEAR: A fast and accurate Illumina Paired-End reAd mergeR. Bioinformatics, 30, 614-620.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Zhang S, Zhao JD, Yao M, Gilbert M (2020) A comprehensive and comparative evaluation of primers for metabarcoding eDNA from fish. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 11, 1609-1625.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Zou K, Chen J, Ruan H, Li Z, Guo W, Li M, Liu L (2020) eDNA metabarcoding as a promising conservation tool for monitoring fish diversity in a coastal wetland of the Pearl River Estuary compared to bottom trawling. Science of the Total Environment, 702, 134704.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [12] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [14] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [15] | 赵维洋, 王伟, 马冰然. 其他有效的区域保护措施(OECMs)研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()