



生物多样性 ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (12): 1309-1319. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019184 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019184
所属专题: 昆虫多样性与生态功能
收稿日期:2019-06-05
接受日期:2019-09-17
出版日期:2019-12-20
发布日期:2020-01-14
通讯作者:
杨贵军
基金资助:
Guijun Yang1,*( ),Min Wang1,Yichun Yang1,Xinyun Li1,Xinpu Wang2
),Min Wang1,Yichun Yang1,Xinyun Li1,Xinpu Wang2
Received:2019-06-05
Accepted:2019-09-17
Online:2019-12-20
Published:2020-01-14
Contact:
Yang Guijun
摘要:
理解山地物种丰富度分布格局及其成因对于山地生物多样性保护具有重要意义。本文基于贺兰山地区甲虫31科252属469种的分布信息, 结合相关气候与生境异质性数据, 系统地探讨了贺兰山地区甲虫及6个优势科物种丰富度地理格局及其影响因素。结果表明, 甲虫物种丰富度及科属区系分化强度以贺兰山中段最高, 南段比北段高, 西坡比东坡高。基于183个栅格内物种分布的二元数据聚类分析, 贺兰山甲虫分布可分为北段强旱生景观甲虫地理群、中西段半湿生景观甲虫地理群、中东段及南段半旱生景观甲虫地理群3个地理群。冗余分析(RDA)表明年均温和年均降水量是影响最显著的因子。方差分解结果显示, 水分与能量因子共同解释了全部甲虫物种丰富度57.1%的空间变异, 单独解释率分别为5.9%和7.1%。生境异质性解释了全部甲虫物种丰富度35.2%的变异, 单独解释率仅为1.8%。气候因素与生境异质性对不同优势科物种丰富度的相对影响并不一致。在贺兰山的南段和北段, 生境异质性和水分因子对甲虫物种丰富度影响作用明显。水分和能量因子是贺兰山地区甲虫物种丰富度空间分布格局的主导因子, 生境异质性有助于提高甲虫物种丰富度。从未解释的比例来分析, 地形和土壤因素可能对贺兰山甲虫物种丰富度存在重要影响。
杨贵军, 王敏, 杨益春, 李欣芸, 王新谱 (2019) 贺兰山甲虫物种丰富度分布格局及其环境解释. 生物多样性, 27, 1309-1319. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019184.
Guijun Yang, Min Wang, Yichun Yang, Xinyun Li, Xinpu Wang (2019) Distribution patterns and environmental interpretation of beetle species richness in Helan Mountain of northern China. Biodiversity Science, 27, 1309-1319. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019184.
| 科数 No. of family | 属数 No. of genus | 种数 No. of species | G指数 (DG) | F指数 (DF) | G-F指数 (DG-F) | 属区系分化强度 Genus fauna differentiation intensity (Dg) | 科区系分化强度 Family fauna differentiation intensity (Df) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 北段强旱生景观甲虫地理群 Xerophilic landscape beetle groups in the northern section (I) | 26 | 145 | 250 | 4.71 | 26.80 | 0.824 | 1.57 | 3.19 |
| 中西段半湿生景观甲虫地理群 Semi-hygric landscape beetle groups in the middle-western section (II) | 29 | 218 | 419 | 5.03 | 35.35 | 0.858 | 1.73 | 4.29 |
| 中东段及南段半旱生景观甲虫地理群Semi-xerophytic landscape beetle groups in the middle-east and south section (III) | 30 | 222 | 378 | 5.14 | 37.49 | 0.863 | 1.53 | 3.79 |
表1 贺兰山不同地理单元甲虫群落多样性比较
Table 1 Comparison of beetle diversity in different geographical units in Helan Mountain
| 科数 No. of family | 属数 No. of genus | 种数 No. of species | G指数 (DG) | F指数 (DF) | G-F指数 (DG-F) | 属区系分化强度 Genus fauna differentiation intensity (Dg) | 科区系分化强度 Family fauna differentiation intensity (Df) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 北段强旱生景观甲虫地理群 Xerophilic landscape beetle groups in the northern section (I) | 26 | 145 | 250 | 4.71 | 26.80 | 0.824 | 1.57 | 3.19 |
| 中西段半湿生景观甲虫地理群 Semi-hygric landscape beetle groups in the middle-western section (II) | 29 | 218 | 419 | 5.03 | 35.35 | 0.858 | 1.73 | 4.29 |
| 中东段及南段半旱生景观甲虫地理群Semi-xerophytic landscape beetle groups in the middle-east and south section (III) | 30 | 222 | 378 | 5.14 | 37.49 | 0.863 | 1.53 | 3.79 |
| 环境因子 Environmental factor | 物种丰富度 Species richness (Nsp) | 属区系分化强度 Genus fauna differentiation intensity (Dg) | 科区系分化强度 Family fauna differentiation intensity (Df) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔高差 Altitude difference (AD) | 0.54* | 0.27* | 0.46* |
| 植被类型数 Vegetation diversity (VD) | 0.55* | 0.49* | 0.27* |
| 植被归一化指数 Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) | 0.56* | 0.41* | 0.60* |
| 年均降水量 Mean annual precipitation (MAP) | 0.61* | 0.34* | 0.62* |
| 年均潜在蒸散量 Mean annual potential evapotranspiration (PET) | 0.31* | 0.50* | 0.25* |
| 年均实际蒸散量 Mean annual actual evapotranspiration (AET) | 0.49* | 0.39* | 0.36* |
| 年均温 Mean annual temperature (MAT) | -0.34* | -0.58* | -0.44* |
| 最冷月均温 Mean temperature of coldest month (MTCM) | -0.26* | -0.51* | -0.19* |
| 最热月均温 Mean temperature of warmest month (MTWM) | -0.41* | -0.58* | -0.34* |
| 年均太阳辐射 Mean annual solar radiation (MASR) | -0.56* | -0.32* | -0.57* |
表2 贺兰山甲虫物种丰富度和区系分化强度与环境因子的一元回归相关系数
Table 2 The correlation coefficients between beetle species richness, fauna differentiation intensity and environmental factors in Helan Mountain
| 环境因子 Environmental factor | 物种丰富度 Species richness (Nsp) | 属区系分化强度 Genus fauna differentiation intensity (Dg) | 科区系分化强度 Family fauna differentiation intensity (Df) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔高差 Altitude difference (AD) | 0.54* | 0.27* | 0.46* |
| 植被类型数 Vegetation diversity (VD) | 0.55* | 0.49* | 0.27* |
| 植被归一化指数 Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) | 0.56* | 0.41* | 0.60* |
| 年均降水量 Mean annual precipitation (MAP) | 0.61* | 0.34* | 0.62* |
| 年均潜在蒸散量 Mean annual potential evapotranspiration (PET) | 0.31* | 0.50* | 0.25* |
| 年均实际蒸散量 Mean annual actual evapotranspiration (AET) | 0.49* | 0.39* | 0.36* |
| 年均温 Mean annual temperature (MAT) | -0.34* | -0.58* | -0.44* |
| 最冷月均温 Mean temperature of coldest month (MTCM) | -0.26* | -0.51* | -0.19* |
| 最热月均温 Mean temperature of warmest month (MTWM) | -0.41* | -0.58* | -0.34* |
| 年均太阳辐射 Mean annual solar radiation (MASR) | -0.56* | -0.32* | -0.57* |
| 环境因子 Environmental factor | 解释率 Percentage of variance explained (%) | 贡献率 Contribution (%) | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年均温 Mean annual temperature (MAT) | 34.8 | 57.0 | 96.6 | 0.002 |
| 年均降水量 Mean annual precipitation (MAP) | 9.9 | 16.2 | 32.1 | 0.002 |
| 最冷月均温 Mean temperature of coldest month (MTCM) | 3.8 | 6.1 | 13 | 0.002 |
| 年均潜在蒸散量 Mean annual potential evapotranspiration (PET) | 3.6 | 5.9 | 13.3 | 0.002 |
| 海拔高差 Altitude difference (AD) | 3.0 | 4.9 | 11.7 | 0.002 |
| 最热月均温 Mean temperature of warmest month (MTWM) | 2.8 | 4.5 | 11.6 | 0.002 |
| 年均实际蒸散量 Mean annual actual evapotranspiration (AET) | 1.5 | 2.5 | 6.5 | 0.002 |
| 年均太阳辐射 Mean annual solar radiation (MASR) | 1.0 | 1.6 | 4.2 | 0.002 |
| 植被归一化指数 Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) | 0.6 | 0.9 | 2.5 | 0.002 |
| 植被类型数 Vegetation diversity (VD) | 0.3 | 0.5 | 1.4 | 0.048 |
表3 环境因子对甲虫物种丰富度分布的相对贡献
Table 3 The relative contribution of environmental factors for distribution of beetle species richness
| 环境因子 Environmental factor | 解释率 Percentage of variance explained (%) | 贡献率 Contribution (%) | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年均温 Mean annual temperature (MAT) | 34.8 | 57.0 | 96.6 | 0.002 |
| 年均降水量 Mean annual precipitation (MAP) | 9.9 | 16.2 | 32.1 | 0.002 |
| 最冷月均温 Mean temperature of coldest month (MTCM) | 3.8 | 6.1 | 13 | 0.002 |
| 年均潜在蒸散量 Mean annual potential evapotranspiration (PET) | 3.6 | 5.9 | 13.3 | 0.002 |
| 海拔高差 Altitude difference (AD) | 3.0 | 4.9 | 11.7 | 0.002 |
| 最热月均温 Mean temperature of warmest month (MTWM) | 2.8 | 4.5 | 11.6 | 0.002 |
| 年均实际蒸散量 Mean annual actual evapotranspiration (AET) | 1.5 | 2.5 | 6.5 | 0.002 |
| 年均太阳辐射 Mean annual solar radiation (MASR) | 1.0 | 1.6 | 4.2 | 0.002 |
| 植被归一化指数 Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) | 0.6 | 0.9 | 2.5 | 0.002 |
| 植被类型数 Vegetation diversity (VD) | 0.3 | 0.5 | 1.4 | 0.048 |
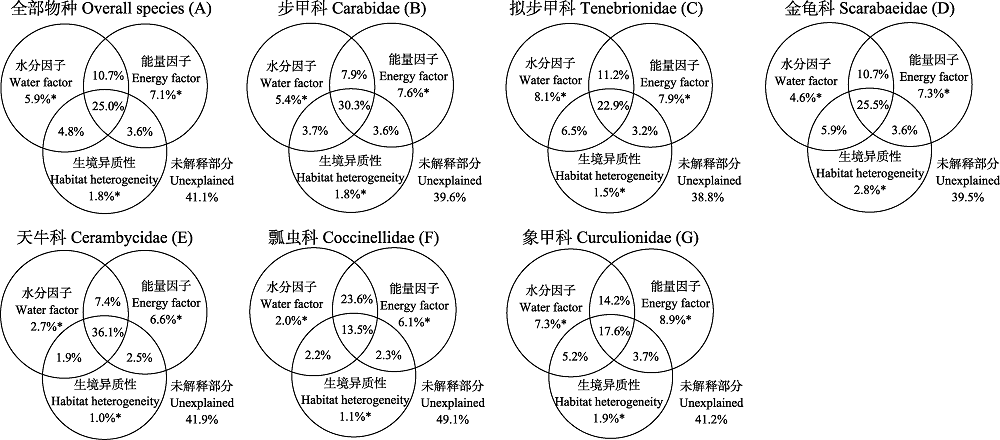
图6 水分、能量与生境异质性因子对甲虫全部物种和优势科丰富度分布的影响(A-G)。*P < 0.001。
Fig. 6 Relative influence of water, energy and habitat heterogeneity on distribution of beetle species richness of overall and dominant family. *P < 0.001.
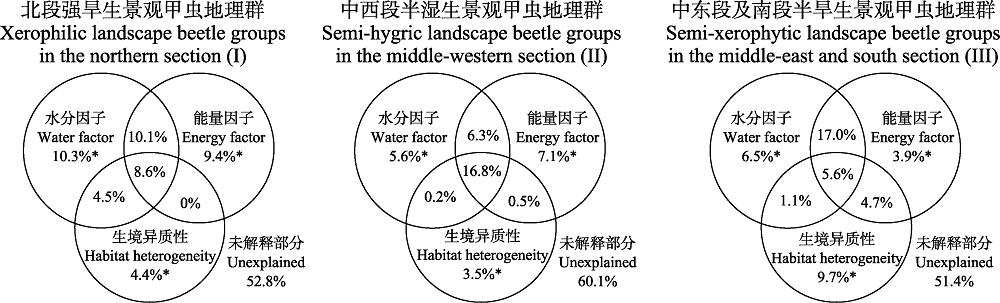
图7 水分、能量与生境异质性因子对不同地理单元甲虫丰富度分布格局的解释。*P < 0.001。
Fig. 7 Relative influence of water, energy and habitat heterogeneity on distribution of beetle species richness in different geographical units. *P < 0.001.
| [1] | Bai XS, Cai WZ, Nonnaizab ( 2013) Insects in Helan Mountain of Inner Mongolia. Inner Mongolia People’s Publishing House, Hohhot. (in Chinese) |
| [ 白晓拴, 彩万志, 能乃扎布 ( 2013) 内蒙古贺兰山地区昆虫. 内蒙古人民出版社, 呼和浩特.] | |
| [2] | Bai Y, Xu SQ, Deng SF ( 2006) Cluster analysis on the distribution patterns of grasshopper in Shaanxi. Acta Zootaxonomica Sinica, 31, 18-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 白义, 许升全, 邓素芳 ( 2006) 陕西蝗虫地理分布格局的聚类分析. 动物分类学报, 31, 18-24.] | |
| [3] | Cantón Y, Del Barrio G, Solé-Benet A, Lázaro R ( 2004) Topographic controls on the spatial distribution of ground cover in the Tabernas badlands of SE Spain. Catena, 55, 341-365. |
| [4] | Chen SB, Jiang GM, Ouyang ZY, Xu WH, Xiao Y ( 2011) Relative importance of water, energy, and heterogeneity in determining regional pteridophyte and seed plant richness in China. Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 49, 95-107. |
| [5] | Cox CB, Moore PD, Ladle R ( 2016) Biogeography: An Ecological and Evolutionary Approach. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester. |
| [6] | Diniz-Filho JAF, Marco PD, Hawkins BA ( 2010) Defying the curse of ignorance: Perspectives in insect macroecology and conservation biogeography. Insect Conservation and Diversity, 3, 172-179. |
| [7] | Dong J, Kergoat GJ, Vicente N, Rahmadi C, Xu S, Robillard T ( 2018) Biogeographic patterns and diversification dynamics of the genus Cardiodactylus Saussure (Orthoptera, Grylloidea, Eneopterinae) in Southeast Asia. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 129, 1-14. |
| [8] | Feng JM, Zhu YY ( 2010) Geographical patterns of diversity of Gymnosperms in northwest Yunnan and their correlation with flora differentiation. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 19, 830-835. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 冯建孟, 朱有勇 ( 2010) 滇西北地区裸子植物多样性的地理分布格局及其与区系分化之间的关系. 生态环境学报, 19, 830-835.] | |
| [9] | Gaston KJ ( 2000) Global patterns in biodiversity. Nature, 405, 220-227. |
| [10] | Gotelli NJ, Arnett AE ( 2000) Biogeographic effects of red fire ant invasion. Ecology Letters, 3, 257-261. |
| [11] | Green J, Bohannan BJM ( 2006) Spatial scaling of microbial biodiversity. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 21, 501-507. |
| [12] | Guo HB, Li BP, Qiang S, Yang DX, Song L ( 2009) Insect community structure in relation to environmental factors on bermudagrass lawn. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 32, 63-70. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郭海滨, 李保平, 强胜, 杨德鑫, 宋琳 ( 2009) 狗牙根草坪昆虫群落组成与环境因子相关性研究. 南京农业大学学报, 32, 63-70.] | |
| [13] | Guo K, Qiao GX ( 2005) Study on geographical distributional pattern of the subfamily Hormaphidinae (Homoptera, Ormaphididae). Acta Zootaxonomica Sinica, 30, 252-256. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 郭昆, 乔格侠 ( 2005) 扁蚜亚科(同翅目, 扁蚜科)蚜虫地理分布格局初探. 动物分类学报, 30, 252-256.] | |
| [14] | Hawkins BA ( 2001) Ecology’s oldest pattern? Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 16, 470. |
| [15] | Jaccard P ( 1912) The distribution of the flora in the alpine zone. New Phytologist, 11, 37-50. |
| [16] | Jia L ( 2014) Fauna and Distribution of Tenebrionid Beetles in Alxa Plateau (Coleoptera: Tenebrionoidea). PhD dissertation, Hebei University, Baoding. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 贾龙 ( 2014) 阿拉善高原拟步甲区系与地理分布(鞘翅目: 拟步甲总科). 博士学位论文, 河北大学, 保定.] | |
| [17] | Jiang ZG, Ji LQ ( 1999) Avian-mammalian species diversity in nine representative sites in China. Chinese Biodiversity, 7, 220-225. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 蒋志刚, 纪力强 ( 1999) 鸟兽物种多样性测度的G-F指数方法. 生物多样性, 7, 220-225.] | |
| [18] | Li G, Shen ZH, Ying JS, Fang JY ( 2009) The spatial pattern of species richness and diversity centers of gymnosperm in China. Biodiversity Science, 17, 272-279. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李果, 沈泽昊, 应俊生, 方精云 ( 2009) 中国裸子植物物种丰富度空间格局与多样性中心. 生物多样性, 17, 272-279.] | |
| [19] | Li HR, Chen XS ( 2009) The fauna and biogeography of planhoppers (Hemiptera, Fulgoroidea, Delphacidae) in Guizhou. Journal of Mountain Agriculture and Biology, 28, 485-491. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李红荣, 陈祥盛 ( 2009) 贵州飞虱科昆虫物种多样性及地理分布格局(半翅目, 蜡蝉总科, 飞虱科). 山地农业生物学报, 28, 485-491.] | |
| [20] | Li YC, Zhang DZ, He DH ( 2014) Species diversity of ground- dwelling beetles and its relationship with environmental factors in the artificial Caragana brushland of fixed sandy lands in Ningxia. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 50, 109-117. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李岳诚, 张大治, 贺达汉 ( 2014) 荒漠景观固沙柠条林地地表甲虫多样性及其与环境因子的关系. 林业科学, 50, 109-117.] | |
| [21] | Liang CZ, Zhu ZY, Li ZG ( 2012) The Vegetation of Helan Mountain. Sunshine Publishing House, Yinchuan. (in Chinese) |
| [ 梁存柱, 朱宗元, 李志刚 ( 2012) 贺兰山植被. 阳光出版社, 银川.] | |
| [22] | Liu DF, Zhang ZX, Jiang GF, Zhang DY, Liu JW, Huo GM ( 2009) Molecular biogeography of some species of the Acrididae in China. Science Bulletin, 54, 756-764. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘殿锋, 张志轩, 蒋国芳, 张大羽, 刘建文, 霍光明 ( 2009) 中国蝗科部分昆虫的分子生物地理学分析. 科学通报, 54, 756-764.] | |
| [23] | Lou QZ, Xu YC, Ma JH, Lü ZZ ( 2011) Diversity of ground- dwelling beetles within the southern Gurbantunggut Desert and its relationship with environmental factors. Biodiversity Science, 19, 441-452. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 娄巧哲, 徐养诚, 马吉宏, 吕昭智 ( 2011) 古尔班通古特沙漠南缘地表甲虫物种多样性及其与环境的关系. 生物多样性, 19, 441-452.] | |
| [24] | O’Brien EM ( 2006) Biological relativity to water-energy dynamics. Journal of Biogeography, 33, 1868-1888. |
| [25] | Qiao GX, Xu XQ, Qu YH, Zhang GX, Lei FM ( 2003) Species diversity and geographical distribution patterns of Drepanosiphidae in China. Acta Zootaxonomica Sinica, 28, 416-427. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 乔格侠, 徐晓群, 屈延华, 张广学, 雷富民 ( 2003) 中国斑蚜科物种多样性及地理分布格局. 动物分类学报, 28, 416-427.] | |
| [26] | Sanders NJ, Lessard JP, Fitzpatrick MC, Dunn RR ( 2007) Temperature, but not productivity or geometry, predicts elevational diversity gradients in ants across spatial grains. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 16, 640-649. |
| [27] | Schuldt A, Baruffol M, Böhnke M, Bruelheide H, Hädtle W, Lang AC, Nadrowski K, von Oheimb G, Voigt W, Zhou HZ, Assmann T ( 2010) Tree diversity promotes insect herbivory in subtropical forests of south-east China. Journal of Ecology, 98, 917-926. |
| [28] | Shah DN, Tonkin JD, Haase P, Jähnig SC ( 2015) Latitudinal patterns and large-scale environmental determinants of stream insect richness across Europe. Limnologica, 55, 33-43. |
| [29] | Shen MW, Chen SB, Bi MJ, Chen WD, Zhou KX ( 2016) Relationships between geographic patterns of ant species richness and environmental factors in China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 36, 7732-7739. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 沈梦伟, 陈圣宾, 毕孟杰, 陈文德, 周可新 ( 2016) 中国蚂蚁丰富度地理分布格局及其与环境因子的关系. 生态学报, 36, 7732-7739.] | |
| [30] | Thomas CFG, Marshall EJP ( 1999) Arthropod abundance and diversity in differently vegetated margins of arable fields. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 72, 131-144. |
| [31] | Turner JR ( 2004) Explaining the global biodiversity gradient: Energy, area, history and natural selection. Basic and Applied Ecology, 5, 435-448. |
| [32] | Wang JM, Cui PJ, Zhong YM, Li JW, Chu JM ( 2019) Biogeographic patterns and environmental interpretation of plant regional species richness in Alxa Plateau of northern China. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 41(3), 14-23. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王健铭, 崔盼杰, 钟悦鸣, 李景文, 褚建民 ( 2019) 阿拉善高原植物区域物种丰富度格局及其环境解释. 北京林业大学学报, 41(3), 14-23.] | |
| [33] | Wang W, Pei H, Liang CZ, Zhu ZY, Wang YL, Zhang T ( 2004) The diversity and spatial distribution of plant communities in the Helan Mountains. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 28, 361-368. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王炜, 裴浩, 梁存柱, 朱宗元, 王永利, 张韬 ( 2004) 贺兰山植物群落类型多样性及其空间分异. 植物生态学报, 28, 361-368.] | |
| [34] | Wang XM ( 2011) Comprehensive Scientific Investigation Report on Helan Mountain National Nature Reserve in Ningxia. Sunshine Publishing House, Yinchuan. (in Chinese) |
| [ 王小明 ( 2011) 宁夏贺兰山国家级自然保护区综合科学考察报告. 阳光出版社, 银川.] | |
| [35] | Wang XP, Yang GJ ( 2010) Insects of Helan Mountain in Ningxia. Ningxia People’s Publishing House, Yinchuan. (in Chinese) |
| [ 王新谱, 杨贵军 ( 2010) 宁夏贺兰山昆虫. 宁夏人民出版社, 银川.] | |
| [36] | Wang ZH, Tang ZY, Fang JY ( 2009) The species-energy hypothesis as a mechanism for species richness patterns. Biodiversity Science, 17, 613-624. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王志恒, 唐志尧, 方精云 ( 2009) 物种多样性地理格局的能量假说. 生物多样性, 17, 613-624.] | |
| [37] | Xu SQ, Zheng ZM, Li HH ( 2004) Cluster analysis on the distribution patterns of grasshopper in Ningxia. Zoological Research, 25, 96-104. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 许升全, 郑哲民, 李后魂 ( 2004) 宁夏蝗虫地理分布格局的聚类分析. 动物学研究, 25, 96-104.] | |
| [38] | Yang GJ, Jia L, Zhang JY, Yu YZ ( 2016) Distribution of darkling beetles and its relationships with topography in Helan Mountain, Ningxia. Journal of Environmental Entomology, 38, 77-86. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨贵军, 贾龙, 张建英, 于有志 ( 2016) 宁夏贺兰山拟步甲科昆虫分布与地形的关系. 环境昆虫学报, 38, 77-86.] | |
| [39] | Yang YC, Yang GJ, Wang J ( 2017) Effects of topographic factors on the distribution pattern of carabid species diversity in the Helan Mountains, northwestern China. Acta Entomologica Sinica, 60, 1060-1073. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨益春, 杨贵军, 王杰 ( 2017) 地形对贺兰山步甲群落物种多样性分布格局的影响. 昆虫学报, 60, 1060-1073.] | |
| [40] | Zhang K, Lin SL, Ji YQ, Yang CX, Wang XY, Yang CY, Wang HS, Jiang HD, Harrison RD, Yu DW ( 2016) Plant diversity accurately predicts insect diversity in two tropical landscapes. Molecular Ecology, 25, 4407-4419. |
| [41] | Zhang RZ ( 2011) Zoogeography of China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 张荣祖 ( 2011) 中国动物地理. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [42] | Zhang Y, Feng G ( 2018) Distribution pattern and mechanism of insect species diversity in Inner Mongolia. Biodiversity Science, 26, 701-706. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张宇, 冯刚 ( 2018) 内蒙古昆虫物种多样性分布格局及其机制. 生物多样性, 26, 701-706.] | |
| [43] | Zhang ZG, Jiang X, Zhang MB, Xu ZC, Deng DM, You YF ( 2018) Geographical distribution pattern of Issidae (Hemiptera: Fulgromorpha) from China. Journal of Jinggangshan University (Natural Science), 39, 97-103. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张争光, 江西, 张梦博, 徐镇超, 邓德美, 尤云菲 ( 2018) 中国瓢蜡蝉科(半翅目: 蜡蝉总科)昆虫的地理分布格局. 井冈山大学学报(自然科学版), 39, 97-103.] | |
| [44] | Zhao HG, Liu CY, Wang F, Wang JQ, Li Q, Yao YM ( 2007) Uplift time and its evolution of Helan Mountain. Science China (D: Geoscience), 66, 185-192. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 赵红格, 刘池洋, 王锋, 王建强, 李琼, 姚亚明 ( 2007) 贺兰山隆升时限及其演化. 中国科学( D辑: 地球科学), 66, 185-192.] | |
| [45] | Zobel M ( 1997) The relative role of species pools in determining plant species richness: An alternative explanation of species coexistence? Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 12, 266-269. |
| [1] | 莫笑梅, 张琪, 杨嘉欣, 郑国, 胡中民, 张晓珂, 梁思维, 崔淑艳. 北方典型草地土壤线虫代谢速率及能量流动对氮沉降和降水模式改变的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24341-. |
| [2] | 贾贞妮, 张意岑, 杜彦君, 任海保. 干扰对中亚热带森林群落物种多样性演替动态的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24078-. |
| [3] | 李艳朋, 陈洁, 卢春洋, 许涵. 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林64 ha次生林动态监测样地群落结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [4] | 曹东, 李焕龙, 彭扬, 魏存争. 植物基因组大小与性状关系的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24192-. |
| [5] | 韩永金, 梁咏亮, 佟一杰, 丁强, 田哲豪, 李露露, 李晓娟, 申昊, 朱亚超, 刘宁, 王新谱, 白明. 基于三种被动式采集方法采集的宁夏贺兰山甲虫标本照片数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24054-. |
| [6] | 刘双祺, 华方圆, 夏舫, 闫亮亮, 于方, 叶红, 彭澎, 张东元, 关雪燕, 付建平, 梁烜, 侯笑如, 李晓阳, 赵欣如. 城市绿地作为迁徙陆鸟中途停歇地的栖息地质量及其受留野措施的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 24046-. |
| [7] | 王鹏, 隋佳容, 丁欣瑶, 王伟中, 曹雪倩, 赵海鹏, 王彦平. 郑州城市公园鸟类群落嵌套分布格局及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23359-. |
| [8] | 林迪, 陈双林, 杜榷, 宋文龙, 饶固, 闫淑珍. 大别山黏菌的物种多样性调查[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23242-. |
| [9] | 任嘉隆, 王永珍, 冯怡琳, 赵文智, 严祺涵, 秦畅, 方静, 辛未冬, 刘继亮. 基于陷阱法采集的河西走廊戈壁荒漠甲虫数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23375-. |
| [10] | 孟敬慈, 王国栋, 曹光兰, 胡楠林, 赵美玲, 赵延彤, 薛振山, 刘波, 朴文华, 姜明. 中国芦苇沼泽植物物种丰富度分布格局及其驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23194-. |
| [11] | 施国杉, 刘峰, 曹光宏, 陈典, 夏尚文, 邓云, 王彬, 杨效东, 林露湘. 西双版纳热带季节雨林木本植物的beta多样性: 空间、环境与林分结构的作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24285-. |
| [12] | 王丽媛, 胡慧建, 姜杰, 胡一鸣. 南岭哺乳类和鸟类物种丰富度空间分布格局及其影响因子[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23026-. |
| [13] | 杨舒涵, 王贺, 陈磊, 廖蓥飞, 严光, 伍一宁, 邹红菲. 松嫩平原异质生境对土壤线虫群落特征的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23295-. |
| [14] | 王明慧, 陈昭铨, 李帅锋, 黄小波, 郎学东, 胡子涵, 尚瑞广, 刘万德. 云南普洱季风常绿阔叶林不同种子扩散方式的优势种空间点格局分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23147-. |
| [15] | 刘志发, 王新财, 龚粤宁, 陈道剑, 张强. 基于红外相机监测的广东南岭国家级自然保护区鸟兽多样性及其垂直分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 22689-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()