



生物多样性 ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (3): 297-305. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018217 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2018217
收稿日期:2018-08-07
接受日期:2019-01-07
出版日期:2019-03-20
发布日期:2019-03-20
通讯作者:
许涵
基金资助:
Wang Yingcan1,Lin Jiayi1,Xu Han2,*( ),Lin Mingxian3,Li Yide2
),Lin Mingxian3,Li Yide2
Received:2018-08-07
Accepted:2019-01-07
Online:2019-03-20
Published:2019-03-20
Contact:
Xu Han
摘要:
热带山地雨林中植物不同性别系统的数量和空间分布特征如何? 是否受自然环境条件影响? 这些问题的回答有助于更深入理解群落物种多样性是如何形成的。本文以海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林60 ha大样地中胸径大于1 cm的木本植物为研究对象, 描述了样地内木本植物性别系统的数量特征, 分析了雌雄异株植物空间分布与地形因子的相关关系。结果表明: 大样地内289种木本种子植物中有两性花植物176种, 单性花植物113种; 在单性花植物中, 51种为雌雄同株, 62种为雌雄异株。单性花植物植株数占所有植株总数的36.2%; 雌雄异株植物植株数占所有植株总数的21.5%, 占单性花植物植株数的59.5%。在20 m × 20 m样方的空间尺度, 雌雄异株植物呈现聚集分布的物种共有31种。以20 m × 20 m样方为分析单元, 雌雄异株植物种类的性别比例与海拔、凹凸度和坡度呈弱正相关; 个体相对多度仅和海拔呈弱正相关, 与坡度和凹凸度无相关; 而3个性别系统多样性指数与海拔、凹凸度和坡度均无显著关联。可见雌雄异株植物在海南热带山地雨林中占据了较大的比例, 但大部分种类种群较小, 其数量分布特征与地形因素紧密相关, 雌雄异株植物的存在对群落物种多样性的形成有较大贡献。
王颖灿, 林家怡, 许涵, 林明献, 李意德 (2019) 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林60 ha大样地木本植物性别系统数量特征. 生物多样性, 27, 297-305. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018217.
Wang Yingcan, Lin Jiayi, Xu Han, Lin Mingxian, Li Yide (2019) Numerical characteristics of plant sexual system of the woody plants in the 60 ha plot in the tropical rain forest in Jianfengling, Hainan Island. Biodiversity Science, 27, 297-305. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018217.
| 性别系统 Sexual system | 种名 Species | 植株数量No. of individuals | 重要值Importance value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 雌雄同株Monoecy | 红柯 Lithocarpus fenzelianus | 1,752 | 2.0 |
| 变色山槟榔 Pinanga baviensis | 14,753 | 1.4 | |
| 杏叶柯 Lithocarpus amygdalifolius | 1,360 | 1.3 | |
| 托盘青冈 Cyclobalanopsis patelliformis | 1,207 | 1.1 | |
| 海南蕈树 Altingia obovata | 1,793 | 1.1 | |
| 雌雄异株Dioecy | 白颜树 Gironniera subaequalis | 10,035 | 3.0 |
| 海南韶子 Nephelium topengii | 11,878 | 2.1 | |
| 香果新木姜子 Neolitsea ellipsoidea | 15,747 | 1.9 | |
| 东方肖榄 Platea parvifolia | 6,423 | 1.3 | |
| 海岛冬青 Ilex goshiensis | 4,550 | 1.1 |
表1 60 ha大样地内重要值 ≥ 1.0的雌雄同株和雌雄异株植物
Table 1 Monoecious and dioecious species with importance value larger than 1.0 in the 60 ha plot
| 性别系统 Sexual system | 种名 Species | 植株数量No. of individuals | 重要值Importance value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 雌雄同株Monoecy | 红柯 Lithocarpus fenzelianus | 1,752 | 2.0 |
| 变色山槟榔 Pinanga baviensis | 14,753 | 1.4 | |
| 杏叶柯 Lithocarpus amygdalifolius | 1,360 | 1.3 | |
| 托盘青冈 Cyclobalanopsis patelliformis | 1,207 | 1.1 | |
| 海南蕈树 Altingia obovata | 1,793 | 1.1 | |
| 雌雄异株Dioecy | 白颜树 Gironniera subaequalis | 10,035 | 3.0 |
| 海南韶子 Nephelium topengii | 11,878 | 2.1 | |
| 香果新木姜子 Neolitsea ellipsoidea | 15,747 | 1.9 | |
| 东方肖榄 Platea parvifolia | 6,423 | 1.3 | |
| 海岛冬青 Ilex goshiensis | 4,550 | 1.1 |
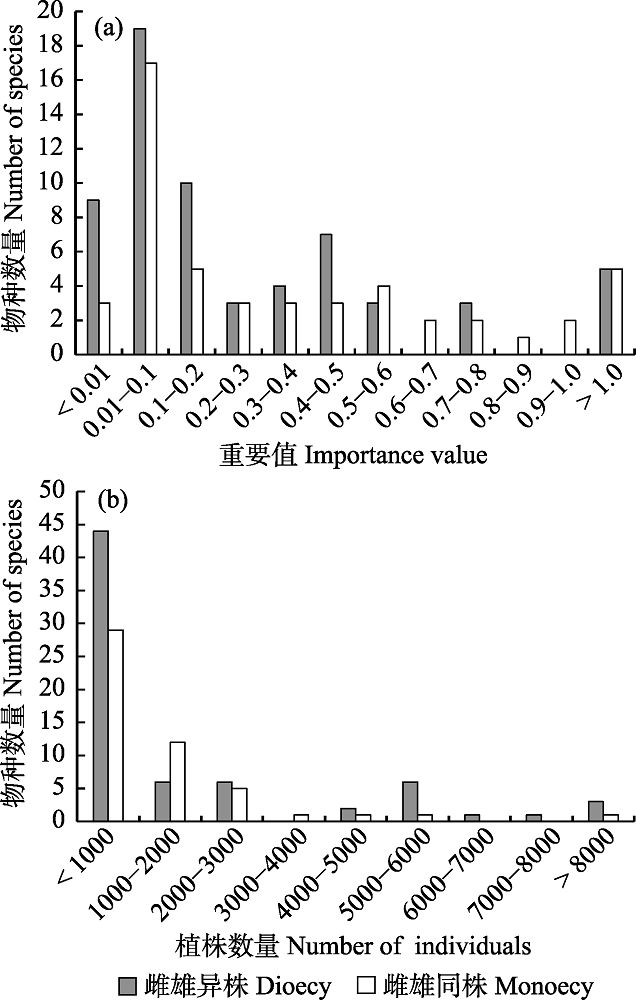
图1 60 ha大样地内不同重要值(a)和不同植株数量(b)的雌雄异株和雌雄同株植物的物种数量
Fig. 1 Number of dioecious and monoecious species with different importance value (a) and number of individuals (b) in the 60 ha plot
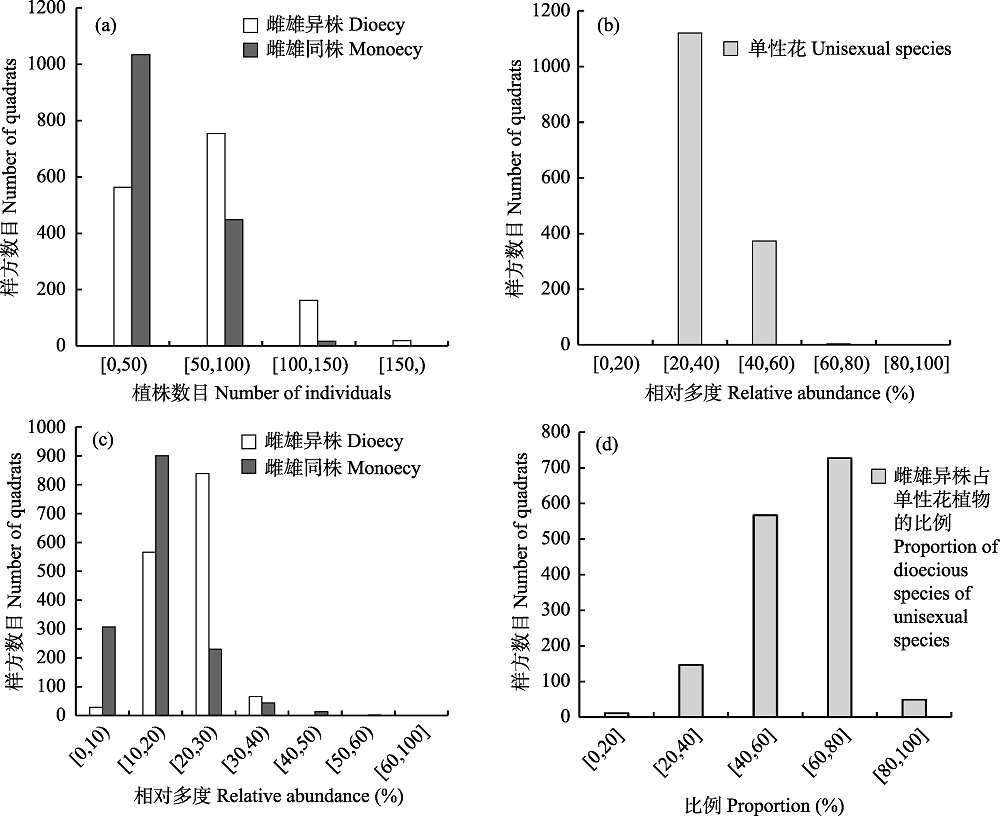
图2 60 ha大样地内20 m × 20 m样方水平各植物性别系统属性的样方数分布。(a)不同性别系统植株数量的样方数分布; (b)单性花植物相对多度的样方数分布; (c)不同性别系统相对多度的样方数分布; (d)雌雄异株植物占单性花比例的样方数分布。
Fig. 2 Characteristics of number of quadrats for different plant sexual systems at the 20 m × 20 m quadrat scale in the 60 ha plot. (a) Characteristics of number of quadrats and number of individuals for different sexual systems; (b) Characteristics of number of quadrats and relative abundance for unisexual species; (c) Characteristics of number of quadrats for and relative abundance for different sexual systems; (d) Characteristics of number of quadrats and proportion of dioecious species of unisexual species.
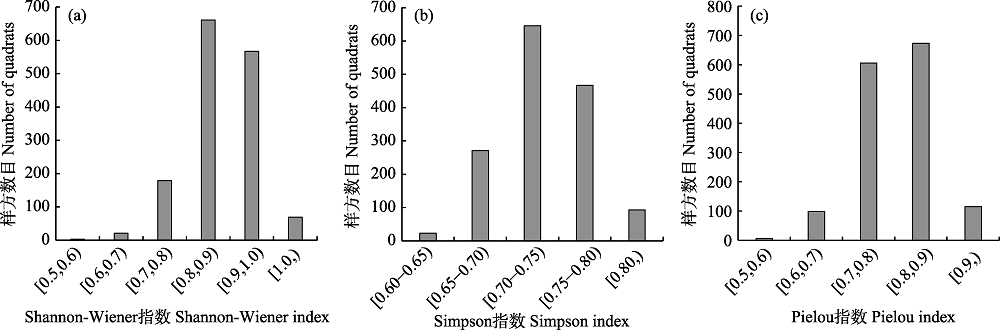
图3 60 ha大样地内20 m × 20 m样方水平的性别系统Shannon-Wiener指数、Simpson指数、Pielou均匀度指数的样方数分布
Fig. 3 Number of quadrats with different Shannon-Wiener index, Simpson index, Pielou index for sexual system diversity at the 20 m × 20 m quadrat scale in the 60 ha plot
| 地点及植物群落 Site and plant community | 物种数 No. of species | 不同性别系统占比 Proportion of different sexual systems of total number of species (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 两性花 Hermaphroditic species | 雌雄同株 Monoecy | 雌雄异株 Dioecy | ||
| 湖北大老岭落叶阔叶林, 中国 Deciduous broad-leaved forest in Hubei, China ( | 306 | 67.0 | 20.6 | 12.4 |
| 云南西双版纳热带雨林, 中国 Tropical rainforest in Xishuangbanna, Yunnan, China ( | 394 | 54.0 | 19.5 | 26.1 |
| 海南尖峰岭热带雨林, 中国 Tropical rainforest in Jianfengling, Hainan, China | 290 | 60.0 | 17.7 | 21.5 |
| 拉塞尔瓦热带雨林, 哥斯达黎加 Tropical rainforest in La Selva, Costa Rica ( | 333 | 65.0 | 11.4 | 23.1 |
| 砂拉越州热带雨林, 马来西亚 Tropical rainforest in Central Sarawak, Malaysia ( | 711 | 60.0 | 14.0 | 26.0 |
表2 海南尖峰岭热带雨林性别系统与国内外4个森林群落的比较
Table 2 Sexual system comparison among Jianfengling tropical rainforest and four forest communities in China and other countries
| 地点及植物群落 Site and plant community | 物种数 No. of species | 不同性别系统占比 Proportion of different sexual systems of total number of species (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 两性花 Hermaphroditic species | 雌雄同株 Monoecy | 雌雄异株 Dioecy | ||
| 湖北大老岭落叶阔叶林, 中国 Deciduous broad-leaved forest in Hubei, China ( | 306 | 67.0 | 20.6 | 12.4 |
| 云南西双版纳热带雨林, 中国 Tropical rainforest in Xishuangbanna, Yunnan, China ( | 394 | 54.0 | 19.5 | 26.1 |
| 海南尖峰岭热带雨林, 中国 Tropical rainforest in Jianfengling, Hainan, China | 290 | 60.0 | 17.7 | 21.5 |
| 拉塞尔瓦热带雨林, 哥斯达黎加 Tropical rainforest in La Selva, Costa Rica ( | 333 | 65.0 | 11.4 | 23.1 |
| 砂拉越州热带雨林, 马来西亚 Tropical rainforest in Central Sarawak, Malaysia ( | 711 | 60.0 | 14.0 | 26.0 |
| 指标 Indices | 海拔 Altitude | 坡度 Slope | 凹凸度 Convex |
|---|---|---|---|
| 性别比例 Proportion of dioecious species of all species in the 60 ha plot | 0.487 (+) | 0.344 (+) | 0.313 (+) |
| 相对多度 Relative abundance of dioecious species of all individuals | 0.408 (+) | 0.278 (n) | 0.275 (n) |
| Simpson指数 Simpson index | -0.019 (n) | -0.162 (n) | 0.192 (n) |
| Shannon-Wiener指数Shannon-Wiener index | -0.012 (n) | 0.163 (n) | -0.187 (n) |
| Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou index | -0.012 (n) | 0.163 (n) | -0.187 (n) |
表3 60 ha大样地地形因子与雌雄异株植物多样性的关联性分析
Table 3 Relationships among topographical factors and diversity indices of dioecious plants in the 60 ha plot
| 指标 Indices | 海拔 Altitude | 坡度 Slope | 凹凸度 Convex |
|---|---|---|---|
| 性别比例 Proportion of dioecious species of all species in the 60 ha plot | 0.487 (+) | 0.344 (+) | 0.313 (+) |
| 相对多度 Relative abundance of dioecious species of all individuals | 0.408 (+) | 0.278 (n) | 0.275 (n) |
| Simpson指数 Simpson index | -0.019 (n) | -0.162 (n) | 0.192 (n) |
| Shannon-Wiener指数Shannon-Wiener index | -0.012 (n) | 0.163 (n) | -0.187 (n) |
| Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou index | -0.012 (n) | 0.163 (n) | -0.187 (n) |
| 1 |
Chen J, Flemming TH, Zhang L, Wang H, Liu Y ( 2004) Patterns of fruit traits in a tropical rainforest in Xishuangbanna, SW China. Acta Oecologica, 26, 157-164.
DOI URL |
| 2 |
Chen J, Han QQ, Duan BL, Korpelainen H, Li CY ( 2017) Sex-specific competition differently regulates ecophysiological responses and phytoremediation of Populus cathayana under Pb stress. Plant and Soil, 421, 203-218.
DOI URL |
| 3 | Chen XS ( 2008) Community Level Plant Reproductive Traits of Tropical Rain Forest in Xishuangbanna, SW China. PhD dissertation, Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xishuangbanna, Mengla, Yunnan. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈心胜 ( 2008) 西双版纳热带雨林植物群落的繁殖生物学特性研究. 博士学位论文, 中国科学院西双版纳热带植物园, 云南勐腊.] | |
| 4 |
Chen XS, Li QJ ( 2008) Sexual systems and ecological correlates in an azonal tropical forests, SW China. Biotropica, 40, 160-167.
DOI URL |
| 5 | Darwin C ( 1877) The Different Forms of Flowers on Plants of the Same Species. John Murray, London. |
| 6 | Diggle PJ ( 1983) Statistical Analysis of Spatial Point Patterns. Academic Press, New York. |
| 7 | Du RQ ( 2009) Biostatistics. Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 杜荣骞 ( 2009) 生物统计学. 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| 8 |
Graff P, Rositano F, Aguiar MR ( 2013) Changes in sex ratios of a dioecious grass with grazing intensity: The interplay between gender traits, neighbour interactions and spatial patterns. Journal of Ecology, 101, 1146-1157.
DOI URL |
| 9 |
Heikrujam M, Sharma K, Prasad M, Agrawal V ( 2015) Review on different mechanisms of sex determination and sex- linked molecular markers in dioecious crops—A current update. Euphytica, 201, 161-194.
DOI URL |
| 10 |
Henry IM, Akagi T, Tao R, Comai L ( 2018) One hundred ways to invent the sexes: Theoretical and observed paths to dioecy in plants. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 69, 553-575.
DOI URL |
| 11 |
Huang SQ, Guo YH ( 2000) Progress in pollination biology. Chinese Science Bulletin, 45, 225-237. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 黄双全, 郭友好 ( 2000) 传粉生物学的研究进展. 科学通报, 45, 225-237.]
DOI URL |
|
| 12 |
Hultine KR, Grady KC, Wood TE, Shuster SM, Stella JC, Whitham TG ( 2016) Climate change perils for dioecious plant species. Nature Plants, 2, 16109.
DOI URL PMID |
| 13 | James DM ( 1991) Botany: An Introduction to Plant Biology. Saunders College Publishing, Austin. |
| 14 | Jiang YX, Lu JP ( 1991) Ecosystem of Tropical Forest of Jianfengling Mountain, Hainan Island, China. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 蒋有绪, 卢俊培 ( 1991) 中国海南岛尖峰岭热带林生态系统. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| 15 |
Jing SW, Coley PD ( 1990) Dioecy and herbivory: The effect of growth rate on plant defense in Acer negundo. Oikos, 58, 369-377.
DOI URL |
| 16 |
Juvany M, Munné-Bosch S ( 2015) Sex-related differences in stress tolerance in dioecious plants: A critical appraisal in a physiological context. Journal of Experimental Botany, 66, 6083-6092.
DOI URL |
| 17 |
Li TH, Jiang J, Chen JM, Fan SB ( 2004) The sexual polymorphism of seed plant. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 32, 48-52. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 李同华, 姜静, 陈建名, 范士波 ( 2004) 种子植物性别的多态性. 东北林业大学学报, 32, 48-52.]
DOI URL |
|
| 18 | Li YD, Chen BF, Zhou GY, Wu ZM, Zeng QB, Luo TS, Huang SN, Xie MD, Huang Q ( 2002) Research and Conservation of Tropical Forest and the Biodiversity: A Special Reference to Hainan Island, China. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 李意德, 陈步峰, 周光益, 吴仲民, 曾庆波, 骆土寿, 黄世能, 谢明东, 黄全 ( 2002) 中国海南岛热带森林及其生物多样性保护研究. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| 19 | Li YD, Xu H, Luo TS, Chen DX, Lin MX ( 2012) Bio-Checklist of Jianfengling Station. China Agricultural Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 李意德, 许涵, 骆土寿, 陈德祥, 林明献 ( 2012) 尖峰岭生态站生物物种数据集. 中国农业出版社, 北京.] | |
| 20 | Long R ( 2011) Study on Community Structure of Deciduous Broad-Leaf Forests and Their Plant Sexual System Diversity in Dalaoling, Hubei Province. PhD Dissertation, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 龙茹 ( 2011) 湖北大老岭落叶阔叶林群落结构和植物性系统多样性研究. 博士学位论文, 北京林业大学, 北京.] | |
| 21 | Long R, Shang C, Qu S, Zhang ZX ( 2011) Distribution pattern of plant sexual system diversity in Populus lasiocarpa Oliv. community. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 33, 34-41. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 龙茹, 尚策, 曲上, 张志翔 ( 2011) 大叶杨群落植物性系统多样性的分布格局. 北京林业大学学报, 33, 34-41.] | |
| 22 |
Machado LC, Vlopes A, Sazima M ( 2006) Plant sexual systems and review of the breeding system studies in the Caatinga, a Brazilian tropical dry forest. Annals of Botany, 97, 277-287.
DOI URL |
| 23 |
Maxime RM, Pierre-Olivier C ( 2015) High incidence of dioecy in young successional tropical forests. Journal of Ecology, 103, 725-732.
DOI URL |
| 24 |
McIntosh RP ( 1967) The continuum concept of vegetation. The Botanical Review, 33, 130-187.
DOI URL |
| 25 |
Pannell JR ( 2017) Plant sex determination. Current Biology, 27, 191-197.
DOI URL |
| 26 | Pielou EC ( 1975) Ecological Diversity. John Wiley & Sons, New York. |
| 27 |
Ramirez N ( 2005) Plant sexual systems, dichogamy, and herkogamy in the Venezuelan Central Plain. Flora Jena, 200, 30-48.
DOI URL |
| 28 |
Ramirez N, Brito Y ( 1990) Reproductive biology of a tropical palm swamp community in the Venezuelan LIanos. American Journal of Botany, 77, 1260-1271.
DOI URL |
| 29 |
Renner ( 2014) The relative and absolute frequencies of angiosperm sexual systems: Dioecy, monoecy, gynodioecy, and an updated online database. American Journal of Botany, 101, 1588-1596.
DOI URL |
| 30 | Robinson J ( 2008) The Evolution of Flower Size and Flowering Behaviour in Plants: The Role of Pollination and Pre-dispersal Seed Predation. Master dissertation, University of Southampton, UK. |
| 31 |
Shannon CE ( 1949) Communication theory of secrecy systems. The Bell System Technical Journal, 28, 656-715.
DOI URL PMID |
| 32 |
Simpson EH ( 1949) Measurement of diversity. Nature, 163, 688.
DOI |
| 33 |
Tao J, Zang RG, Li YD, Mao PL, Lin MX ( 2011) Characteristic of plant functional groups based on ecophysiological traits in a tropical montane rain forest of Hainan Island, South China. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 47(8), 14-18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 陶晶, 臧润国, 李意德, 毛培利, 林明献 ( 2011) 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林生理生态功能群特征. 林业科学, 47(8), 14-18.]
DOI URL |
|
| 34 |
Xu H, Li YD, Lin MX, Wu JH, Luo TS, Zhou Z, Chen DX, Yang H, Li GJ, Liu SR ( 2015 a) Community characteristics of a 60 ha dynamics plot in the tropical montane rain forest in Jianfengling, Hainan Island. Biodiversity Science, 23, 192-201. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 许涵, 李意德, 林明献, 吴建辉, 骆土寿, 周璋, 陈德祥, 杨怀, 李广建, 刘世荣 ( 2015 a) 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林60 ha动态监测样地群落结构特征. 生物多样性, 23, 192-201.]
DOI URL |
|
| 35 | Xu H, Li YD, Luo TS, Chen DX, Lin MX, Wu JH, Li YP, Yang H, Zhou Z ( 2015 b) Jianfengling Tropical Mountain Rain Forest Dynamic Plot: Community Characteristics, Tree Species and Their Distribution Patterns. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 许涵, 李意德, 骆土寿, 陈德祥, 林明献, 吴建辉, 李艳朋, 杨怀, 周璋 ( 2015 b) 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林——群落特征、树种及其分布格局. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| 36 |
Xu H, Li YD, Luo TS, Lin MX, Chen DX, Mo JH, Luo W, Huang H ( 2008) Influence of typhoon Damrey on the tropical montane rain forest community in Jianfengling, Hainan Island, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 32, 1323-1334. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 许涵, 李意德, 骆土寿, 林明献, 陈德祥, 莫锦华, 罗文, 黄豪 ( 2008) 达维台风对海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林群落的影响. 植物生态学报, 32, 1323-1334.]
DOI URL |
|
| 37 | Xu X, Yang F, Yin CY, Li CY ( 2007) Research advances in sex-specific responses of dioecious plants to environmental stresses. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 18, 2626-2631. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 胥晓, 杨帆, 尹春英, 李春阳 ( 2007) 雌雄异株植物对环境胁迫响应的性别差异研究进展. 应用生态学报, 18, 2626-2631.] | |
| 38 |
Yamakura T, Kanzaki M, Itoh A, Ohkubo T, Ogino K, Chai EOK, Lee HS, Ashton PS ( 1995) Topography of a large-scale research plot established within a tropical rain forest at Lambir, Sarawak. Tropics, 5, 41-56.
DOI URL |
| 39 |
Yan LH ( 2007) Sexual system and environmental adaptability of vines in Hupingshan Mountain, Hunan Province. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 35, 35-36, 39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 颜立红 ( 2007) 湖南壶瓶山藤本植物的有性系统及其环境适应性. 东北林业大学学报, 35, 35-36, 39.]
DOI URL |
|
| 40 |
Yin CY, Li CY ( 2007) Gender differences of dioecious plants related sex ratio: Recent advances and future prospects. Chinese Journal of Applied Environmental Biology, 13, 419-425. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 尹春英, 李春阳 ( 2007) 雌雄异株植物与性别比例有关的性别差异研究现状与展望. 应用与环境生物学报, 13, 419-425.]
DOI URL |
|
| 41 | Zeng QB, Li YD, Chen BF, Wu ZM, Zhou GY ( 1997) Research and Management of Tropical Forest Ecosystem. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 曾庆波, 李意德, 陈步峰, 吴仲民, 周光益 ( 1997) 热带森林生态系统研究与管理. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| 42 | Zhang DY ( 2004) Plant Life-History Evolution and Reproductive Ecology. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 张大勇 ( 2004) 植物生活史进化与繁殖生态学. 科学出版社, 北京.] |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [3] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [4] | 周昊, 王茗毅, 张楚格, 肖治术, 欧阳芳. 昆虫旅馆在独栖蜂多样性保护中的现状与挑战[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24472-. |
| [5] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [6] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [7] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [8] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [9] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [10] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [11] | 徐欢, 辛凤飞, 施宏亮, 袁琳, 薄顺奇, 赵欣怡, 邓帅涛, 潘婷婷, 余婧, 孙赛赛, 薛程. 生态修复技术集成应用对长江口北支生境与鸟类多样性提升效果评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24478-. |
| [12] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [13] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [14] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [15] | 张浩斌, 肖路, 刘艳杰. 夜间灯光对外来入侵植物和本地植物群落多样性和生长的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24553-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()