



生物多样性 ›› 2018, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (9): 962-971. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018033 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2018033
所属专题: 土壤生物与土壤健康
雷学明1, 沈芳芳1, 雷学臣1, 刘文飞1, 段洪浪1, 樊后保1, 吴建平2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2018-02-01
接受日期:2018-05-24
出版日期:2018-09-20
发布日期:2019-01-05
通讯作者:
吴建平
作者简介:# 共同第一作者
基金资助:
Xueming Lei1, Fangfang Shen1, Xuechen Lei1, Wenfei Liu1, Honglang Duan1, Houbao Fan1, Jianping Wu2,*( )
)
Received:2018-02-01
Accepted:2018-05-24
Online:2018-09-20
Published:2019-01-05
Contact:
Wu Jianping
About author:# Co-first authors
摘要:
土壤微生物是陆地生态系统重要的分解者和地上-地下相互作用的纽带。本文以亚热带杉木(Cunninghamia lanceolateata)人工林为对象, 通过模拟林冠层氮沉降和林下灌草去除, 设置4种处理, 包括: 对照(CK)、灌草去除(UR)、氮沉降(N)和氮沉降加灌草去除(N × UR)的野外控制实验, 研究土壤微生物群落结构的响应。本实验分别于2016年4月(春季)和10月(秋季)采集0-10 cm层土壤样品, 运用磷脂脂肪酸法(PLFAs)分析土壤微生物群落结构。结果表明: (1) 10月份土壤微生物总PLFAs量及其他类群土壤微生物PLFAs量显著高于4月份(P < 0.05), 真菌/细菌比值没有显著差异。土壤微生物PLFAs中细菌占优势, 其次为真菌, 放线菌的占比最小; (2)相比CK处理, UR处理下土壤微生物总PLFAs量、细菌PLFAs量、革兰氏阴性菌PLFAs量和放线菌PLFAs量有增加趋势, 但未达到显著差异水平(P > 0.05); (3)相对CK, UR、N和N × UR处理降低了4月份土壤微生物多样性(H°)和均匀度指数(J), 但提高了10月份土壤微生物多样性指数; (4)冗余分析表明, 土壤硝态氮和总磷含量与土壤微生物群落之间呈现显著相关。本研究表明土壤微生物PLFAs在各处理下都表现出明显的季节动态; 短期内林下灌草去除对土壤微生物PLFAs影响表现出一定的促进作用, 氮沉降对土壤微生物群落影响还不甚明显, 需要长期的监测研究来评估两者及其交互作用对土壤微生物群落及其功能的影响。
雷学明, 沈芳芳, 雷学臣, 刘文飞, 段洪浪, 樊后保, 吴建平 (2018) 模拟氮沉降和灌草去除对杉木人工林地土壤微生物群落结构的影响. 生物多样性, 26, 962-971. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018033.
Xueming Lei, Fangfang Shen, Xuechen Lei, Wenfei Liu, Honglang Duan, Houbao Fan, Jianping Wu (2018) Assessing influence of simulated canopy nitrogen deposition and understory removal on soil microbial community structure in a Cunninghamia lanceolata plantation. Biodiversity Science, 26, 962-971. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018033.
| 微生物类型 Microbial group | 特征磷脂脂肪酸 Phospholipids fatty acid characteristics | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|
| 细菌 Bacteria | i15:0, a15:0, 15:0, i16:0, 16:1 ω9c, 16:1 ω7c, 16:1 ω7t, i17:0, 17:0, a17:0, cy 17:0, 18:1 ω5c, 18:1 ω7c, i19:0, cy 19:0 | |
| 革兰氏阳性菌 Gram-positive bacteria | i14:0, i15:0, a15:0, i16:0, i17:0, a17:0 | |
| 革兰氏阴性菌 Gram-negative bacteria | 16:1 ω7c, cy 17:0, 18:1 ω7c, cy 19:0 | |
| 真菌 Fungi | 18:1 ω9c, 18:2 ω6c, 18:3 ω6c | |
| 放线菌 Actinomycetes | 10Me 16:0, 10Me 17:0, 10Me 18:0 |
表1 土壤微生物磷脂脂肪酸(PLFAs)分类
Table 1 Soil microbes as indicated by phospholipid fatty acids (PLFAs)
| 微生物类型 Microbial group | 特征磷脂脂肪酸 Phospholipids fatty acid characteristics | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|
| 细菌 Bacteria | i15:0, a15:0, 15:0, i16:0, 16:1 ω9c, 16:1 ω7c, 16:1 ω7t, i17:0, 17:0, a17:0, cy 17:0, 18:1 ω5c, 18:1 ω7c, i19:0, cy 19:0 | |
| 革兰氏阳性菌 Gram-positive bacteria | i14:0, i15:0, a15:0, i16:0, i17:0, a17:0 | |
| 革兰氏阴性菌 Gram-negative bacteria | 16:1 ω7c, cy 17:0, 18:1 ω7c, cy 19:0 | |
| 真菌 Fungi | 18:1 ω9c, 18:2 ω6c, 18:3 ω6c | |
| 放线菌 Actinomycetes | 10Me 16:0, 10Me 17:0, 10Me 18:0 |
| 处理 Treatment | 含水率 SWC (%) | pH | 有机碳 SOC (g/kg) | 全氮 TN (g/kg) | 全磷 TP (g/kg) | 硝态氮 NO3--N (mg/kg) | 铵态氮 NH4+-N (mg/kg) | 速效磷 AP (mg/kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春季 Spring | CK | 40.85 ± 2.14Aa | 4.45 ± 0.11Aa | 41.16 ± 3.55Aa | 2.29 ± 0.19Aa | 0.19 ± 0.01Bab | 0.06 ± 0.01Ab | 10.97 ± 1.21 Aa | 5.20 ± 0.60Aa |
| UR | 40.80 ± 4.38 Aa | 4.35 ± 0.01Aa | 36.08 ± 2.86Aa | 2.04 ± 0.16Aab | 0.21 ± 0.01Ba | 0.05 ± 0.01Ab | 10.74 ± 1.07Aa | 4.91 ± 0.99Aa | |
| N | 32.26 ± 2.41Aa | 4.34 ± 0.01Aa | 30.74 ± 4.77Aa | 1.70 ± 0.21Ab | 0.17 ± 0.01Bb | 0.09 ± 0.04Ab | 12.79 ± 2.47Aa | 3.37 ± 0.55Aa | |
| N × UR | 33.76 ± 2.16Aa | 4.40 ± 0.01Aa | 38.53 ± 2.82Aa | 2.20 ± 0.13Aab | 0.20 ± 0.01Bab | 0.21 ± 0.07Aa | 15.29 ± 1.65Aa | 4.04 ± 0.52Aa | |
| 秋季 Autumn | CK | 38.99 ± 3.26Aa | 4.70 ± 0.19Aa | 37.92 ± 5.78Aa | 1.75 ± 0.62Aa | 0.83 ± 0.09Aa | 0.20 ± 0.05Aa | 3.80 ± 0.35Ba | 1.38 ± 0.72Ba |
| UR | 34.81 ± 1.54Aa | 4.39 ± 0.06Aa | 37.73 ± 7.78Aa | 2.15 ± 0.53Aa | 0.57 ± 0.11Ab | 0.15 ± 0.02Aa | 4.46 ± 0.32Ba | 3.46 ± 1.07Aa | |
| N | 32.35 ± 2.12Aa | 4.37 ± 0.03Aa | 28.57 ± 3.95Aa | 2.03 ± 0.46Aa | 0.55 ± 0.07Ab | 0.22 ± 0.02Aa | 4.22 ± 0.40Ba | 0.98 ± 0.33Ba | |
| N × UR | 35.75 ± 2.73Aa | 4.35 ± 0.05Aa | 34.81 ± 1.76Aa | 2.20 ± 0.30Aa | 0.87 ± 0.10Aab | 0.33 ± 0.09Aa | 4.21 ± 0.36Ba | 2.52 ± 1.01Aa |
表2 不同处理下土壤理化性质
Table 2 Soil physical-chemical properties under different treatments
| 处理 Treatment | 含水率 SWC (%) | pH | 有机碳 SOC (g/kg) | 全氮 TN (g/kg) | 全磷 TP (g/kg) | 硝态氮 NO3--N (mg/kg) | 铵态氮 NH4+-N (mg/kg) | 速效磷 AP (mg/kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春季 Spring | CK | 40.85 ± 2.14Aa | 4.45 ± 0.11Aa | 41.16 ± 3.55Aa | 2.29 ± 0.19Aa | 0.19 ± 0.01Bab | 0.06 ± 0.01Ab | 10.97 ± 1.21 Aa | 5.20 ± 0.60Aa |
| UR | 40.80 ± 4.38 Aa | 4.35 ± 0.01Aa | 36.08 ± 2.86Aa | 2.04 ± 0.16Aab | 0.21 ± 0.01Ba | 0.05 ± 0.01Ab | 10.74 ± 1.07Aa | 4.91 ± 0.99Aa | |
| N | 32.26 ± 2.41Aa | 4.34 ± 0.01Aa | 30.74 ± 4.77Aa | 1.70 ± 0.21Ab | 0.17 ± 0.01Bb | 0.09 ± 0.04Ab | 12.79 ± 2.47Aa | 3.37 ± 0.55Aa | |
| N × UR | 33.76 ± 2.16Aa | 4.40 ± 0.01Aa | 38.53 ± 2.82Aa | 2.20 ± 0.13Aab | 0.20 ± 0.01Bab | 0.21 ± 0.07Aa | 15.29 ± 1.65Aa | 4.04 ± 0.52Aa | |
| 秋季 Autumn | CK | 38.99 ± 3.26Aa | 4.70 ± 0.19Aa | 37.92 ± 5.78Aa | 1.75 ± 0.62Aa | 0.83 ± 0.09Aa | 0.20 ± 0.05Aa | 3.80 ± 0.35Ba | 1.38 ± 0.72Ba |
| UR | 34.81 ± 1.54Aa | 4.39 ± 0.06Aa | 37.73 ± 7.78Aa | 2.15 ± 0.53Aa | 0.57 ± 0.11Ab | 0.15 ± 0.02Aa | 4.46 ± 0.32Ba | 3.46 ± 1.07Aa | |
| N | 32.35 ± 2.12Aa | 4.37 ± 0.03Aa | 28.57 ± 3.95Aa | 2.03 ± 0.46Aa | 0.55 ± 0.07Ab | 0.22 ± 0.02Aa | 4.22 ± 0.40Ba | 0.98 ± 0.33Ba | |
| N × UR | 35.75 ± 2.73Aa | 4.35 ± 0.05Aa | 34.81 ± 1.76Aa | 2.20 ± 0.30Aa | 0.87 ± 0.10Aab | 0.33 ± 0.09Aa | 4.21 ± 0.36Ba | 2.52 ± 1.01Aa |
| 处理 Treatment | 微生物总量 Total PLFAs | 细菌量 Bacterial PLFAs | 革兰氏阳性菌 量 G+ PLFAs | 革兰氏阴性菌 量 G- PLFAs | 真菌量 Fungal PLFAs | 放线菌量 Actinomycetes PLFAs | 真菌:细菌 F/B ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春季 Spring | CK | 75.01 ± 5.44Ba | 21.02 ± 1.47Aa | 10.21 ± 0.61Ba | 8.21 ± 0.61Aa | 8.07 ± 1.21Aa | 4.91 ± 0.29Aa | 0.38 ± 0.04Aa |
| UR | 78.63 ± 4.87Ba | 22.37 ± 2.15Aa | 11.87 ± 0.73Ba | 7.97 ± 0.94Aa | 7.80 ± 1.80Aa | 5.42 ± 0.31Aa | 0.34 ± 0.06Aa | |
| N | 71.09 ± 12.45Ba | 20.06 ± 4.30Aa | 9.89 ± 2.30Ba | 7.58 ± 1.52Aa | 7.80 ± 1.53Aa | 4.83 ± 1.14Aa | 0.40 ± 0.01Aa | |
| N × UR | 58.14 ± 7.12Ba | 16.44 ± 2.40Ba | 8.40 ± 1.41Ba | 5.92 ± 0.72Ba | 5.54 ± 0.54Ba | 3.63 ± 0.68Ba | 0.35 ± 0.02Aa | |
| 秋季 Autumn | CK | 132.03 ± 10.74Ab | 25.58 ± 1.59Aa | 22.38 ± 2.08Aa | 8.63 ± 0.78Aa | 8.56 ± 1.16Aa | 5.69 ± 0.26Aa | 0.34 ± 0.05Aa |
| UR | 166.28 ± 9.36Aa | 28.11 ± 2.60Aa | 24.90 ± 2.23Aa | 9.58 ± 1.21Aa | 10.62 ± 0.68Aa | 6.02 ± 0.39Aa | 0.38 ± 0.02Aa | |
| N | 134.77 ± 14.07Aab | 26.24 ± 2.39Aa | 22.96 ± 2.75Aa | 8.51 ± 0.87Aa | 9.66 ± 1.04Aa | 5.87 ± 0.87Aa | 0.37 ± 0.03Aa | |
| N × UR | 128.27 ± 10.60Ab | 26.97 ± 3.75Aa | 22.26 ± 1.88Aa | 9.07 ± 1.40Aa | 9.99 ± 1.14Aa | 6.04 ± 0.90Aa | 0.38 ± 0.04Aa |
表3 不同处理下土壤各类群微生物磷脂脂肪酸(PLFAs)量(单位: nmol/g)
Table 3 The amount of soil microbial phospholipid fatty acids (PLFAs) under different treatments (unit: nmol/g)
| 处理 Treatment | 微生物总量 Total PLFAs | 细菌量 Bacterial PLFAs | 革兰氏阳性菌 量 G+ PLFAs | 革兰氏阴性菌 量 G- PLFAs | 真菌量 Fungal PLFAs | 放线菌量 Actinomycetes PLFAs | 真菌:细菌 F/B ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 春季 Spring | CK | 75.01 ± 5.44Ba | 21.02 ± 1.47Aa | 10.21 ± 0.61Ba | 8.21 ± 0.61Aa | 8.07 ± 1.21Aa | 4.91 ± 0.29Aa | 0.38 ± 0.04Aa |
| UR | 78.63 ± 4.87Ba | 22.37 ± 2.15Aa | 11.87 ± 0.73Ba | 7.97 ± 0.94Aa | 7.80 ± 1.80Aa | 5.42 ± 0.31Aa | 0.34 ± 0.06Aa | |
| N | 71.09 ± 12.45Ba | 20.06 ± 4.30Aa | 9.89 ± 2.30Ba | 7.58 ± 1.52Aa | 7.80 ± 1.53Aa | 4.83 ± 1.14Aa | 0.40 ± 0.01Aa | |
| N × UR | 58.14 ± 7.12Ba | 16.44 ± 2.40Ba | 8.40 ± 1.41Ba | 5.92 ± 0.72Ba | 5.54 ± 0.54Ba | 3.63 ± 0.68Ba | 0.35 ± 0.02Aa | |
| 秋季 Autumn | CK | 132.03 ± 10.74Ab | 25.58 ± 1.59Aa | 22.38 ± 2.08Aa | 8.63 ± 0.78Aa | 8.56 ± 1.16Aa | 5.69 ± 0.26Aa | 0.34 ± 0.05Aa |
| UR | 166.28 ± 9.36Aa | 28.11 ± 2.60Aa | 24.90 ± 2.23Aa | 9.58 ± 1.21Aa | 10.62 ± 0.68Aa | 6.02 ± 0.39Aa | 0.38 ± 0.02Aa | |
| N | 134.77 ± 14.07Aab | 26.24 ± 2.39Aa | 22.96 ± 2.75Aa | 8.51 ± 0.87Aa | 9.66 ± 1.04Aa | 5.87 ± 0.87Aa | 0.37 ± 0.03Aa | |
| N × UR | 128.27 ± 10.60Ab | 26.97 ± 3.75Aa | 22.26 ± 1.88Aa | 9.07 ± 1.40Aa | 9.99 ± 1.14Aa | 6.04 ± 0.90Aa | 0.38 ± 0.04Aa |
| 变量 Variables | N | UR | N × UR | 季节 Season | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | |
| 微生物总量 Total PLFAs | 3.736 | 0.077 | 0.383 | 0.548 | 3.220 | 0.098 | 54.433 | < 0.001 |
| 细菌量 Bacterial PLFAs | 0.864 | 0.371 | 0.016 | 0.902 | 0.733 | 0.409 | 11.335 | 0.003 |
| 革兰氏阳性菌量 G+ PLFAs | 1.431 | 0.255 | 0.166 | 0.691 | 1.691 | 0.218 | 88.942 | < 0.001 |
| 革兰氏阴性菌量 G- PLFAs | 1.365 | 0.265 | 0.020 | 0.891 | 0.412 | 0.533 | 4.105 | 0.055 |
| 真菌量 Fungal PLFAs | 0.510 | 0.489 | 0.002 | 0.965 | 1.628 | 0.226 | 8.117 | 0.009 |
| 放线菌量 Actinomycetes PLFAs | 0.772 | 0.397 | 0.010 | 0.922 | 0.968 | 0.345 | 5.481 | 0.029 |
| 真菌: 细菌 F/B ratio | 0.246 | 0.629 | 0.089 | 0.771 | 0.199 | 0.663 | 0.004 | 0.953 |
表4 三因素方差分析氮沉降、灌草去除及两者交互作用和季节对土壤微生物磷脂脂肪酸(PLFAs)的影响
Table 4 The effects of nitrogen deposition, understory removal, the interactions between nitrogen deposition and understory removal and seasons on soil microbial phospholipid fatty acids (PLFAs) analyzed by Three-Way ANOVA
| 变量 Variables | N | UR | N × UR | 季节 Season | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | P | F | P | F | P | F | P | |
| 微生物总量 Total PLFAs | 3.736 | 0.077 | 0.383 | 0.548 | 3.220 | 0.098 | 54.433 | < 0.001 |
| 细菌量 Bacterial PLFAs | 0.864 | 0.371 | 0.016 | 0.902 | 0.733 | 0.409 | 11.335 | 0.003 |
| 革兰氏阳性菌量 G+ PLFAs | 1.431 | 0.255 | 0.166 | 0.691 | 1.691 | 0.218 | 88.942 | < 0.001 |
| 革兰氏阴性菌量 G- PLFAs | 1.365 | 0.265 | 0.020 | 0.891 | 0.412 | 0.533 | 4.105 | 0.055 |
| 真菌量 Fungal PLFAs | 0.510 | 0.489 | 0.002 | 0.965 | 1.628 | 0.226 | 8.117 | 0.009 |
| 放线菌量 Actinomycetes PLFAs | 0.772 | 0.397 | 0.010 | 0.922 | 0.968 | 0.345 | 5.481 | 0.029 |
| 真菌: 细菌 F/B ratio | 0.246 | 0.629 | 0.089 | 0.771 | 0.199 | 0.663 | 0.004 | 0.953 |
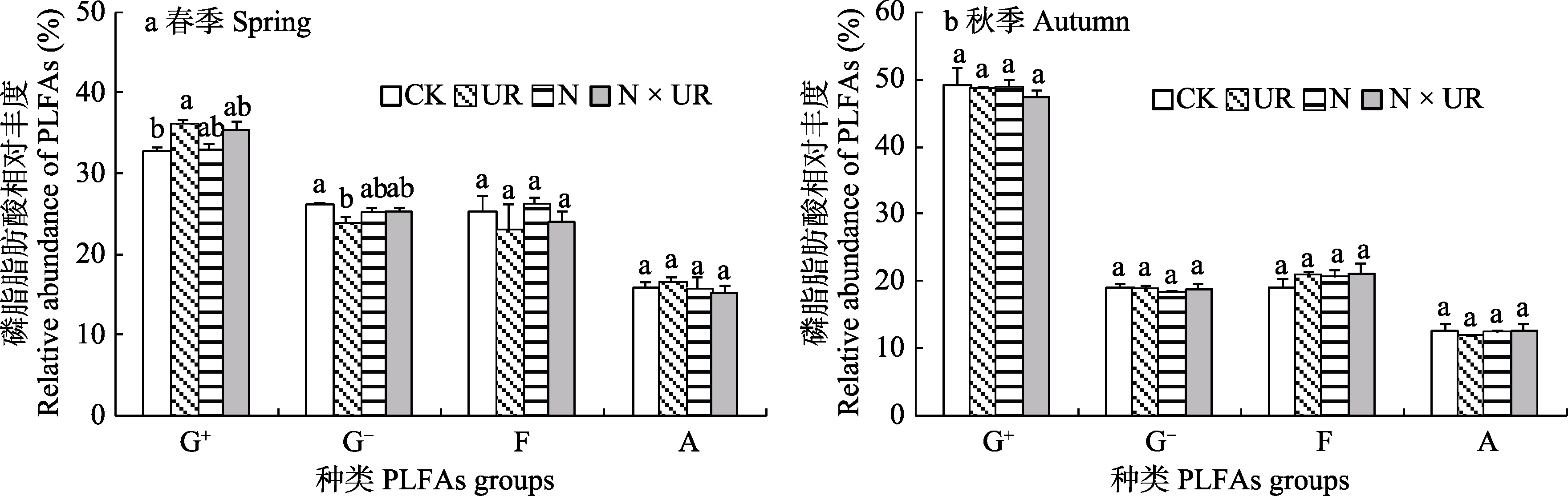
图1 不同处理下土壤微生物磷脂脂肪酸(PLFAs)相对丰度。(1) CK: 对照; UR: 灌草去除处理; N: 氮沉降处理; N × UR: 氮沉降和灌草去除交互处理; (2) G+: 革兰氏阳性菌; G-: 革兰氏阴性菌; F: 真菌; A: 放线菌。
Fig. 1 Relative abundance of the soil microbial PLFAs under different treatments. (1) CK, Control; UR, Understory removal; N, Nitrogen deposition; N × UR, Interactions between nitrogen deposition and understory removal; (2) G+, Gram-positive bacteria; G-, Gram-negative bacteria; F, Fungi; A, Actinomycetes.
| 处理 Treatment | 春季 Spring | 秋季 Autumn | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shannon- Wiener (H°) | Pielou (J) | Shannon- Wiener (H°) | Pielou index (J) | |
| CK | 1.53 ± 0.02Aa | 0.46 ± 0.01Aa | 1.40 ± 0.01Ba | 0.42 ± 0.01Aa |
| UR | 1.46 ± 0.05Aab | 0.45 ± 0.01Aa | 1.46 ± 0.02Aa | 0.41 ± 0.01Aa |
| N | 1.47 ± 0.05Aab | 0.44 ± 0.02Aa | 1.41 ± 0.02Aa | 0.42 ± 0.01Aa |
| N × UR | 1.36 ± 0.02Ab | 0.42 ± 0.01Ab | 1.43 ± 0.01Aa | 0.43 ± 0.01Aa |
表5 不同处理下土壤微生物磷脂脂肪酸(PLFAs)多样性指数
Table 5 Diversity indices of soil microbial phospholipid fatty acids (PLFAs) under different treatments
| 处理 Treatment | 春季 Spring | 秋季 Autumn | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shannon- Wiener (H°) | Pielou (J) | Shannon- Wiener (H°) | Pielou index (J) | |
| CK | 1.53 ± 0.02Aa | 0.46 ± 0.01Aa | 1.40 ± 0.01Ba | 0.42 ± 0.01Aa |
| UR | 1.46 ± 0.05Aab | 0.45 ± 0.01Aa | 1.46 ± 0.02Aa | 0.41 ± 0.01Aa |
| N | 1.47 ± 0.05Aab | 0.44 ± 0.02Aa | 1.41 ± 0.02Aa | 0.42 ± 0.01Aa |
| N × UR | 1.36 ± 0.02Ab | 0.42 ± 0.01Ab | 1.43 ± 0.01Aa | 0.43 ± 0.01Aa |
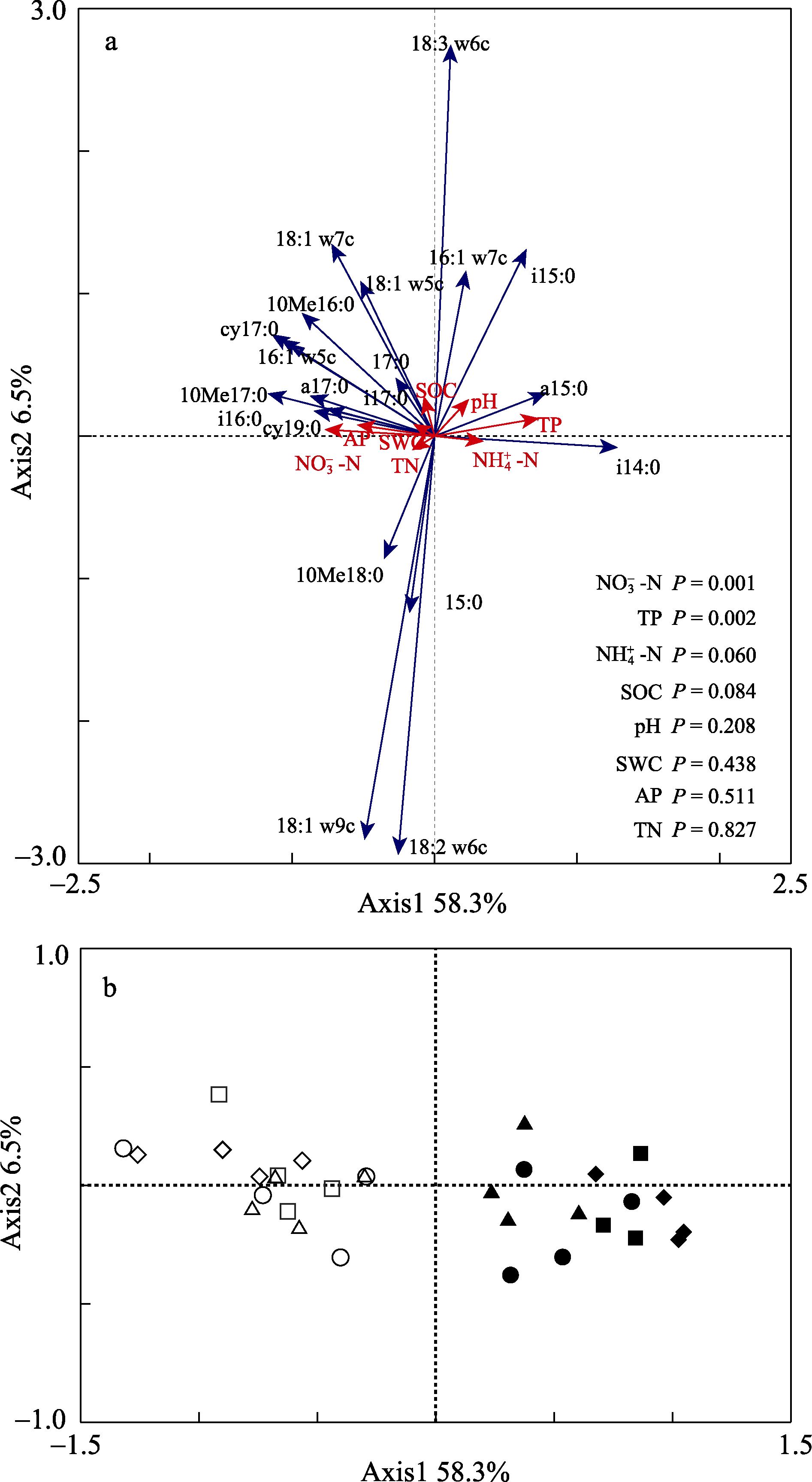
图2 土壤微生物群落结构与土壤环境因子之间的冗余分析。图a为环境因子与微生物PLFAs群落冗余分析;图b为冗余分析中各处理的排列。其中? CK对照; £ UR灌草去除处理; ¯ N氮沉降处理; r N × UR氮沉降和灌草去除交互处理。空心表示春季采样, 实心表示秋季采样。
Fig.2 Redundancy analysis (RDA) of soil microbial community structure and soil environmental factors. ? CK, Control, £ UR, Understory removal; ¯ N, Nitrogen deposition; r N × UR, Interactions between nitrogen deposition and understory removal, where hollow and solid were expressed as sampling in spring and autumn, respectively.
| [1] | Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Canadian Journal of Biochemistry and Physiology, 37, 911-917. |
| [2] | Chu HY, Wang YF, Shi Y, Lü XT, Zhu YG, Han XG (2017) Current status and development trend of soil microbial biogeography. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 32, 585-592. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [褚海燕, 王艳芬, 时玉, 吕晓涛, 朱永官, 韩兴国 (2017) 土壤微生物生物地理学研究现状与发展态势. 中国科学院院刊, 32, 585-592.] | |
| [3] | Frey SD, Knorr M, Parrent JL, Simpson RT (2004) Chronic nitrogen enrichment affects the structure and function of the soil microbial community in temperate hardwood and pine forests. Forest Ecology and Management, 196, 159-171. |
| [4] | Frostegård A, Bååth E (1996) The use of phospholipid fatty acid analysis to estimate bacterial and fungal biomass in soil. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 22, 59-65. |
| [5] | Fu X, Yang F, Wang J, Di Y, Dai X, Zhang X, Wang H (2015) Understory vegetation leads to changes in soil acidity and in microbial communities 27 years after reforestation. Science of the Total Environment, 502, 280-286. |
| [6] | Galloway JN, Townsend AR, Erisman JW, Bekunda M, Cai Z, Freney JR, Martineli LA, Seitzinqer SP, Sutton MA (2008) Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: Recent trends, questions, and potential solutions. Science, 320, 889-892. |
| [7] | Ge F (2002) Modern Ecology. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [戈峰 (2002) 现代生态学. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [8] | He TX, Li YP, Zhang FY, Wang QK (2015) Effects of understory removal on soil respiration and microbial community composition structure in a Chinese fir plantation. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 39, 797-806. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [贺同鑫, 李艳鹏, 张方月, 王清奎 (2015) 林下植被剔除对杉木林土壤呼吸和微生物群落结构的影响. 植物生态学报, 39, 797-806.] | |
| [9] | He YL, Fu MY (2002) Review of studies on understorey of plantations. Forest Research, 15, 727-733. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [何艺玲, 傅懋毅 (2002) 人工林林下植被的研究现状. 林业科学研究, 15, 727-733.] | |
| [10] | Hong PZ, Liu SR, Yu HL, Hao J (2016) Effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on soil microbial biomass and community structure in a young plantation of Castanopsis hystrix. Journal of Shandong University (Natural Science), 51, 18-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [洪丕征, 刘世荣, 于浩龙, 郝建 (2016) 模拟氮沉降对红椎人工幼龄林土壤微生物生物量和微生物群落结构的影响. 山东大学学报(理学版), 51, 18-28.] | |
| [11] | Houle D, Moore JD (2008) Soil solution, foliar concentrations and tree growth response to 3-year of ammonium-nitrate addition in two boreal forests of Québec, Canada. Forest Ecology and Management, 255, 2049-2060. |
| [12] | Huang XR, Guo PP, Wu WW, Hu BY, Yi ZG (2016) Influence of simulated nitrogen deposition enhancement on soil microbial community of different tree species. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 35, 1420-1426. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [黄幸然, 郭萍萍, 吴旺旺, 胡宝叶, 易志刚 (2016) 模拟氮沉降增加对不同树种土壤微生物群落结构的影响. 生态学杂志, 35, 1420-1426.] | |
| [13] | Huang YM, Yang WQ, Zhang J, Lu CT, Liu X, Wang W, Guo W, Zhang DJ (2014) Response of soil microorganism and soil enzyme activity to understory plant removal in the subalpine coniferous plantation of western Sichuan. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34, 4183-4192. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [黄玉梅, 杨万勤, 张健, 卢昌泰, 刘旭, 王伟, 郭伟, 张丹桔 (2014) 川西亚高山针叶林土壤微生物及酶对林下植物去除的响应. 生态学报, 34, 4183-4192.] | |
| [14] | Irenem U, Annc K, Rosemarie M (2009) Flooding effects on soil microbial communities. Applied Soil Ecology, 42, 1-8. |
| [15] | Lin GG, Zhao Q, Zhao L, Li HC, Zeng DH (2012) Effects of understory removal and nitrogen addition on the soil chemical and biological properties of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica plantation in Keerqin sandy land. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 23, 1188-1194. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [林贵刚, 赵琼, 赵蕾, 李慧超, 曾德慧 (2012) 林下植被去除与氮添加对樟子松人工林土壤化学和生物学性质的影响. 应用生态学报, 23, 1188-1194.] | |
| [16] | Liu CX, Jiao RZ, Dong YH, Sun QW, Zhou XW, Li FQ (2015) Effect of nitrogen deposition on soil microbial community structure determined with the PLFA metod. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 51(6), 155-162. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘彩霞, 焦如珍, 董玉红, 孙启武, 周新武, 李峰卿 (2015) 应用PLFA方法分析氮沉降对土壤微生物群落结构的影响. 林业科学, 51(6), 155-162.] | |
| [17] | Liu WF, Fan HB (2011) Impacts of nitrogen deposition on C, N, and P fluxes in the litterfall of Chinese fir plantation. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 47(3), 89-95. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘文飞, 樊后保 (2011) 杉木人工林凋落物C, N, P归还量对氮沉降的响应. 林业科学, 47(3), 89-95.] | |
| [18] | Liu WQ, Liu BY, Wang J, Lei CY (2010) Responses of soil microbial communities to moss cover and nitrogen addition. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30, 1691-1698. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘蔚秋, 刘滨扬, 王江, 雷纯义 (2010) 不同环境条件下土壤微生物对模拟大气氮沉降的响应. 生态学报, 30, 1691-1698.] | |
| [19] | Lu RK (1998) Soil Agrochemistry Analysis Protocoes. China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [鲁如坤 (1998) 土壤农业化学分析方法. 中国农业科技出版社, 北京.] | |
| [20] | Lu YH (2015) Recent development of soil microbiology and future perspectives. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 30, 257-265. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陆雅海 (2015) 土壤微生物学研究现状与展望. 中国科学院院刊, 30, 257-265.] | |
| [21] | Luo D, Shi ZM, Tang JC, Liu SR, Lu LH (2014) Soil microbial community structure of monoculture and mixed plantation stands of native tree species in south subtropical China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 25, 2543-2550. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [罗达, 史作民, 唐敬超, 刘世荣, 卢立华 (2014) 南亚热带乡土树种人工纯林及混交林土壤微生物群落结构. 应用生态学报, 25, 2543-2550.] | |
| [22] | Marhan S, Kandeler E, Scheu S (2007) Phospholipid fatty acid profiles and xylanase activity in particle size fractions of forest soil and casts of Lumbricus terrestris L. (Oligochaeta, Lumbricidae). Applied Soil Ecology, 35, 421-422. |
| [23] | Matsushima M, Chang SX (2007) Effects of understory removal, N fertilization, and litter layer removal on soil N cycling in a 13-year-old white spruce plantation infested with Canada bluejoint grass. Plant and Soil, 292, 243-258. |
| [24] | Michaels S, Johannes R (2010) Considering fungal: Bacterial dominance in soils—methods, controls, and ecosystem implications. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 42, 1385-1395. |
| [25] | Moore-Kucera J, Dick RP (2008) PLFA profiling of microbial community structure and seasonal shifts in soils of a Douglas fir chronosequence. Microbial Ecology, 55, 500-511. |
| [26] | Nilsson LO, Bååth E, Falkengrengrerup U, Wallander H (2007) Growth of ectomycorrhizal mycelia and composition of soil microbial communities in oak forest soils along a nitrogen deposition gradient. Oecologia, 153, 375-384. |
| [27] | Schadt C, Martin A, Lipson D, Schmidt S (2003) Seasonal dynamics of previously unknown fungal lineages in Tundra soil. Science, 301, 1359-1361. |
| [28] | Sun ZY, Huang YH, Yang L, Schaefer V, Chen YQ (2017) Plantation age, understory vegetation, and species-specific traits of target seedlings alter the competition and facilitation role of Eucalyptus in South China. Restoration Ecology, 31, 1-10. |
| [29] | Vitousek PM, Aber JD, Howarth RW, Likens GE, Matson PA, Schindler DW, Schlesinger WH, Tilman DG (1997) Human alteration of the global nitrogen cycle: Sources and consequences. Ecological Applications, 7, 737-750. |
| [30] | Wan SZ, Zhang CL, Chen YQ, Zhao J, Wang XL, Wu JP, Zhou LX, Lin YB, Liu ZF, Fu SL (2014) The understory fern Dicranopteris dichotoma facilitates the overstory Eucalyptus trees in subtropical plantations. Ecosphere, 5(5), 51. |
| [31] | Wang FM, Zou B, Li HF, Li ZA (2014) The effect of understory removal on microclimate and soil properties in two subtropical lumber plantations. Journal of Forest Research, 19, 238-243. |
| [32] | Wei XH, Blanco JA, Jiang H, Kimmins JPH (2012) Effects of nitrogen deposition on carbon sequestration in Chinese fir forest ecosystems. Science of the Total Environment, 416, 351-361. |
| [33] | Wu JP, Liu WF, Fan HB, Huang GM, Wan SZ, Yuan YH, Ji CF (2013a) Asynchronous responses of soil microbial community and understory plant community to simulated nitrogen deposition in a subtropical forest. Ecology and Evolution, 3, 3895-3905. |
| [34] | Wu JP, Liu ZF (2014) Effects of abiotic factors on forest net ecosystem production. Plant Science Journal, 32, 97-104. |
| [吴建平, 刘占锋 (2014) 环境因子对森林净生态系统生产力的影响. 植物科学学报, 32, 97-104.] | |
| [35] | Wu JP, Liu ZF, Huang GM, Chen DM, Zhang WX, Shao YH, Wan SZ, Fu SL (2014) Response of soil respiration and ecosystem carbon budget to vegetation removal in Eucalyptus plantations with contrasting ages. Scientific Reports, 4, 6262. |
| [36] | Wu JP, Liu ZF, Sun YX, Zhou LX, Lin YB, Fu SL (2013b) Introduced Eucalyptus urophylla plantations change the composition of the soil microbial community in subtropical China. Land Degradation and Development, 24, 400-406. |
| [37] | Wu JP, Liu ZF, Wang XL, Sun YX, Zhou LX, Lin YB, Fu SL (2011) Effects of understory removal and tree girdling on soil microbial community composition and litter decomposition in two Eucalyptus plantations in South China. Functional Ecology, 25, 921-931. |
| [38] | Yang W, Yan YE, Jiang F, Leng X, Chen XL, An SQ (2016) Response of the soil microbial community composition and biomass to a short-term Spartina alterniflora, invasion in a coastal wetland of eastern China. Plant and Soil, 408, 1-14. |
| [39] | Yin K, Zhang L, Chen D, Tian Y, Zhang F, Wen M, Yuan C (2016) Understory herb layer exerts strong controls on soil microbial communities in subtropical plantations. Scientific Reports, 6, 27066. |
| [40] | Yuan YH, Fan HB, Li HX, Liu WF, Shen FF, Guo HB (2012) Effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on soil microorganism in a Chinese fir plantation. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 48(9), 8-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [袁颖红, 樊后保, 李辉信, 刘文飞, 沈芳芳, 郭虎波 (2012) 模拟氮沉降对杉木人工林土壤微生物的影响. 林业科学, 48(9), 8-14.] | |
| [41] | Yuan YH, Fan HB, Liu WF, Huang RZ, Shen FF, Hu F, Li HX (2013) Effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on soil enzyme activities and microbial community functional diversities in a Chinese fir plantation. Soils, 45, 120-128. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [袁颖红, 樊后保, 刘文飞, 黄荣珍, 沈芳芳, 胡锋, 李辉信 (2013) 模拟氮沉降对杉木人工林(Cunninghamia lanceolata)土壤酶活性及微生物群落功能多样性的影响. 土壤, 45, 120-128.] | |
| [42] | Zak DR, Ringelberg DB, Pregizter KS, Randlett DL, White DC, Curtis P (1996) Soil microbial communities beneath Populus grandidentata crown under elevated atmospheric CO2. Ecological Applications, 6, 257-262. |
| [43] | Zeng J, Liu XJ, Song L, Lin XG, Zhang HZ, Shen CC, Chu HY (2016) Nitrogen fertilization directly affects soil bacterial diversity and indirectly affects bacterial community composition. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 92, 41-49. |
| [44] | Zeng QP, He BH (2016) Effect of nitrogen deposition on soil microbial community structure determined with the PLFA method under the Masson Pine forest from Mt. Jinyun, Chongqing. Environmental Science, 37, 3590-3597. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [曾清苹, 何丙辉 (2016) 应用PLFA法分析氮沉降对缙云山马尾松林土壤微生物群落结构的影响. 环境科学, 37, 3590-3597.] | |
| [45] | Zhang JJ, Li YG, Chang SX, Jiang PK, Zhou GM, Liu J, Wu JS, Shen ZM (2014) Understory vegetation management affected greenhouse gas emissions and labile organic carbon pools in an intensively managed Chinese chestnut plantation. Plant and Soil, 376, 363-375. |
| [46] | Zhao J, Wan SZ, Li ZA, Shao YH, Xu GL, Liu ZF, Zhou LX, Fu SL (2012) Dicranopteris-dominated understory as major driver of intensive forest ecosystem in humid subtropical and tropical region. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 49, 78-87. |
| [47] | Zhu YG, Shen RF, He JZ, Wang YF, Han XG, Jia ZJ (2017) China soil microbiome initiative: Progress and perspective. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 32, 554-565. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [朱永官, 沈仁芳, 贺纪正, 王艳芬, 韩兴国, 贾仲君 (2017) 中国土壤微生物组: 进展与展望. 中国科学院院刊, 32, 554-565.] | |
| [48] | Zogg GP, Zak DR, Ringelberg DB, MacDonald NW, Pregitzer KS, White DC (1997) Compositional and functional shifts in microbial communities due to soil warming. Soil Science Society of America, 61, 475-481. |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [3] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [4] | 周昊, 王茗毅, 张楚格, 肖治术, 欧阳芳. 昆虫旅馆在独栖蜂多样性保护中的现状与挑战[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24472-. |
| [5] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [6] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [7] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [8] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [9] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [10] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [11] | 徐欢, 辛凤飞, 施宏亮, 袁琳, 薄顺奇, 赵欣怡, 邓帅涛, 潘婷婷, 余婧, 孙赛赛, 薛程. 生态修复技术集成应用对长江口北支生境与鸟类多样性提升效果评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24478-. |
| [12] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [13] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [14] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [15] | 张浩斌, 肖路, 刘艳杰. 夜间灯光对外来入侵植物和本地植物群落多样性和生长的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24553-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()