



生物多样性 ›› 2025, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (7): 25010. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2025010 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2025010
收稿日期:2025-01-10
接受日期:2025-03-20
出版日期:2025-07-20
发布日期:2025-08-14
通讯作者:
*E-mail: shzh@urban.pku.edu.cn
基金资助:
Ling Hu1,2( ), Zehao Shen3,2,*(
), Zehao Shen3,2,*( )(
)( )
)
Received:2025-01-10
Accepted:2025-03-20
Online:2025-07-20
Published:2025-08-14
Contact:
*E-mail: shzh@urban.pku.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
随着地球科学与生命科学的融合发展, 由地质学、地貌学、古气候学、基因组学、系统发育学、种群遗传学和生物地理学等多学科关联形成的地理基因组学(geogenomics)将地表景观变化与生物演化联系起来, 成为检验地质假设、重建地球历史及其生物协同演化的一个有效途径, 并在全球生态保护方面展现出巨大潜力。本文通过Web of Science核心数据库的文献检索和计量分析, 探讨了地理基因组学研究主题和热点的演变, 并系统介绍了地理基因组学的基础概念和关键科学问题及其与相关研究领域的关系。作为一门正在兴起的多领域交叉学科, 地理基因组学深度整合了地质、气候和基因组数据, 反演了地质构造运动、生物类群分化历史和分布变迁的时空格局和相互影响, 对促进地质学和生物进化研究具有重要意义。本文重点关注5个研究内容: 检验地质假说、阐明区域或洲际尺度的地质过程、推断区域多样性演化历史、地质重建中的不确定性与尺度效应以及病原体的地理分布模式和扩散起源。目前, 尽管我国在这一领域的相关研究还非常有限, 但已针对若干重要科学问题展开, 如青藏高原的差异性隆升历史, 长江和黄河水系的演变等。未来还应进一步加强多学科方法的应用, 开发更好的工具, 并推动建立全球地理基因组学研究数据库。
虎灵, 沈泽昊 (2025) 地理基因组学: 研究方法与进展. 生物多样性, 33, 25010. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2025010.
Ling Hu, Zehao Shen (2025) Geogenomics: Research methods and advances. Biodiversity Science, 33, 25010. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2025010.
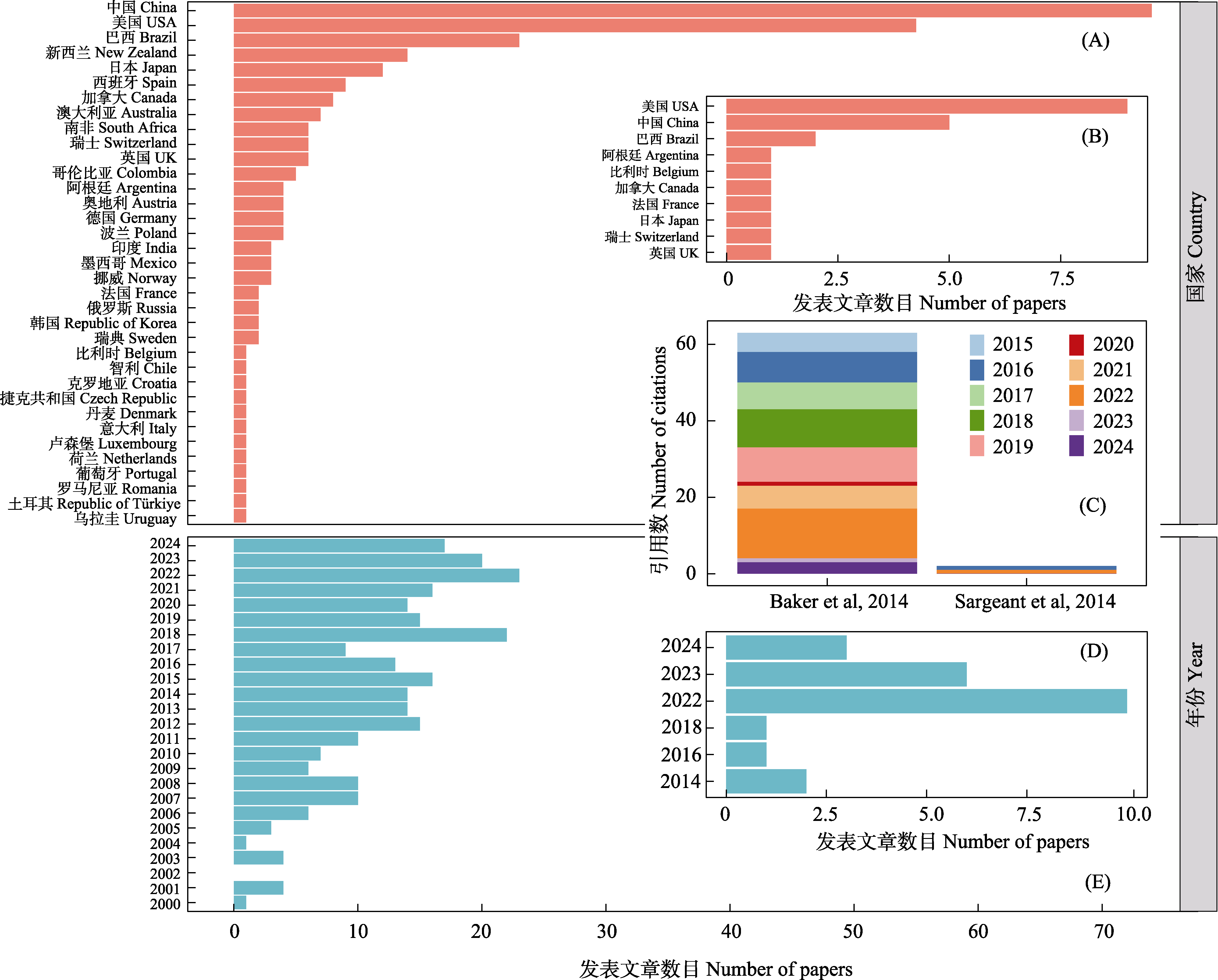
图1 结合地质地貌和基因组的不同国家(A)和不同年份(E)、以地理基因组学为主题词的不同国家(B)和不同年份(D)的相关研究的发文量以及Baker等(2014)和Sargeant等(2014)文章的引用情况(C)
Fig. 1 The national publications (A) and annual publications (E) in combined geology, geomorphology, and genomics research, and national publications (B) and annual publications (D) with geogenomics as the key word. Article citation by Baker et al (2014) and Sargeant et al (2014) (C).
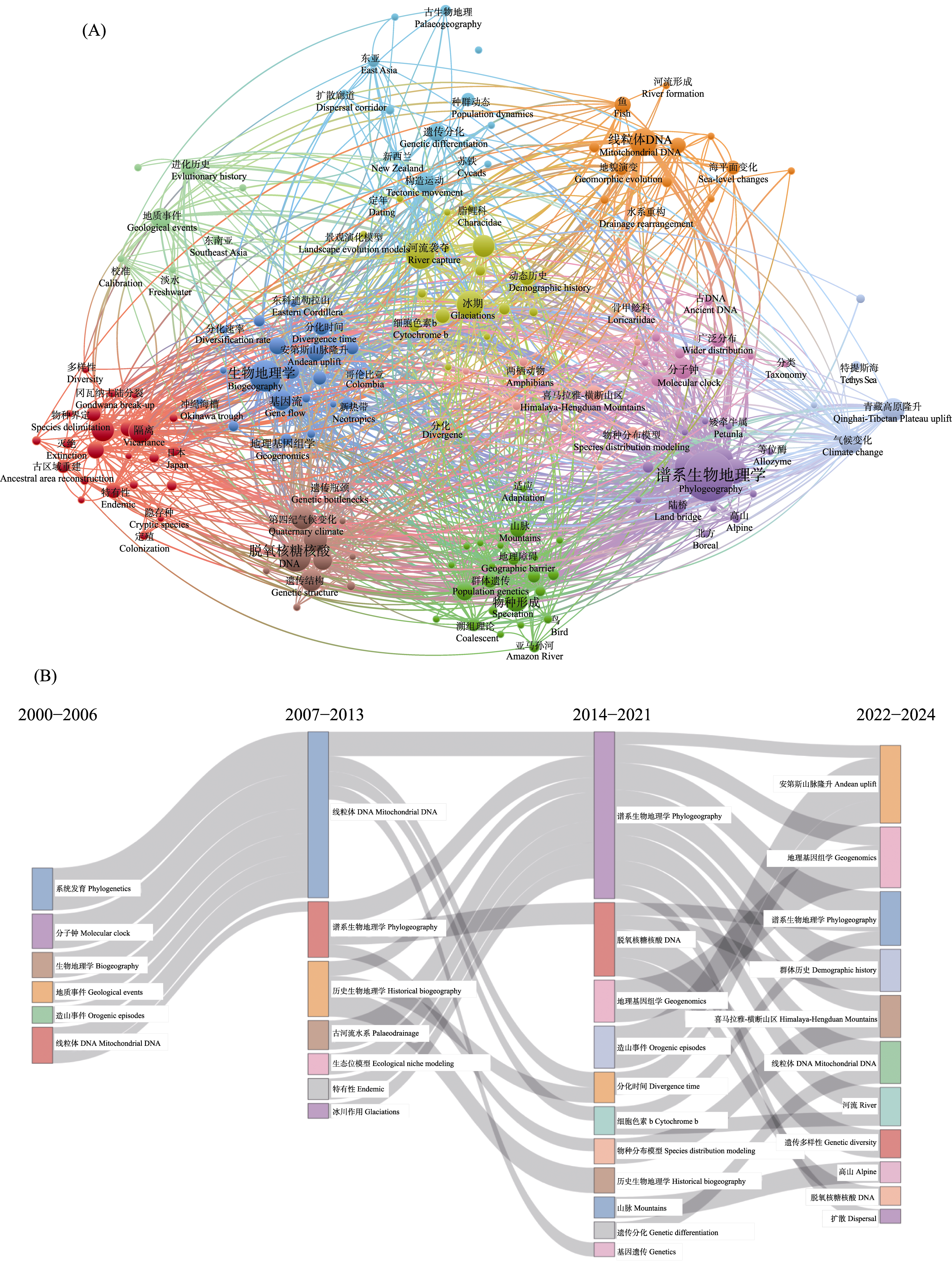
图2 结合地质地貌和基因组的相关研究的关键词共现情况(A) (颜色代表不同聚类, 圆圈大小代表关键词的出现频次, 连线代表关键词同时出现)和研究主题演化结果(B)
Fig. 2 Co-occurrence of keywords in related studies combining geology, geomorphology, and genomics (A) (the colors represent different clusters, the size of the circles represents the frequency of occurrence of the keywords, and the lines represent the co-occurrence of the keywords), and the result of thematic evolution (B)
| 聚类标签 Name | 连接权重 Weight link | 总连接强度权重 Weight total links strength | 排名前5的关键词 Top 5 keywords |
|---|---|---|---|
| 地理隔离 Vicariance | 403 | 529 | 地理隔离; 系统发育; 多样化; 扩散; 特有性 Vicariance; phylogenetics; diversification; dispersal; endemic |
| 物种形成 Speciation | 363 | 438 | 物种形成; 生态位模型; 山脉; 群体遗传学; 溯祖理论 Speciation; ecological niche modeling; mountains; population genetics; coalescent |
| 生物地理学 Biogeography | 473 | 633 | 生物地理学; 基因流; 安第斯山脉隆升; 分化时间; 河流 Biogeography; gene flow; Andean uplift; divergence time; river |
| 河流袭夺 River capture | 348 | 506 | 河流袭夺; 冰期; 基因组; 动态历史; 基因渐渗 River capture; glaciations; genome; demographic history; introgression |
| 谱系生物地理学 Phylogeography | 389 | 764 | 谱系生物地理学; 避难所; 遗传多样性; 更新世; 陆桥 Phylogeography; refugia; genetic diversity; Pleistocene; land bridge |
| 构造运动 Tectonic movement | 196 | 239 | 构造运动; 遗传分化; 种群动态; 东亚; 古地理 Tectonic movement; genetic differentiation; population dynamics; East Asia; palaeogeography |
| 线粒体DNA Mitochondrial DNA | 241 | 338 | 线粒体DNA; 鱼; 古水系; 地貌演化; 海平面变化 Mitochondrial DNA; fish; Palaeodrainage; geomorphic evolution; sea-level changes |
| 脱氧核糖核酸 DNA | 260 | 441 | 脱氧核糖核酸; 叶绿体DNA; 第四纪气候; 遗传结构; 冰期避难所 DNA; chloroplast DNA; quaternary climate; genetic structure; glacial refugia |
| 分子钟 Molecular clock | 179 | 226 | 分子钟; 广泛分布; 系统发育基因组学; 贝叶斯分析; 古DNA Molecular clock; wide distribution; phylogenomic; Bayesian analyses; ancient DNA |
| 喜马拉雅-横断山区 Himalaya-Hengduan Mountains | 87 | 112 | 喜马拉雅-横断山区; 物种分布模型; 两栖动物; 水系演化; 环境变化 Himalaya-Hengduan Mountains; species distribution modeling; amphibians; drainage evolution; environmental changes |
| 地质事件 Geological events | 126 | 165 | 地质事件; 进化历史; 东南亚; 校准; 淡水 Geological events; evolutionary history; Southeast Asia; calibration; freshwater |
| 气候变化 Climate change | 121 | 171 | 气候变化; 青藏高原隆升; 墨西拿盐度危机; 特提斯海; 茜草科 Climate change; Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau uplift; Messinian salinity crisis; Tethys Sea; Rubiaceae |
表1 地理基因组学相关领域关键词共现分析聚类结果频率排名前5的关键词
Table 1 The top 5 keywords with the frequency of co-occurrence analysis clustering results in the field of geogenomics
| 聚类标签 Name | 连接权重 Weight link | 总连接强度权重 Weight total links strength | 排名前5的关键词 Top 5 keywords |
|---|---|---|---|
| 地理隔离 Vicariance | 403 | 529 | 地理隔离; 系统发育; 多样化; 扩散; 特有性 Vicariance; phylogenetics; diversification; dispersal; endemic |
| 物种形成 Speciation | 363 | 438 | 物种形成; 生态位模型; 山脉; 群体遗传学; 溯祖理论 Speciation; ecological niche modeling; mountains; population genetics; coalescent |
| 生物地理学 Biogeography | 473 | 633 | 生物地理学; 基因流; 安第斯山脉隆升; 分化时间; 河流 Biogeography; gene flow; Andean uplift; divergence time; river |
| 河流袭夺 River capture | 348 | 506 | 河流袭夺; 冰期; 基因组; 动态历史; 基因渐渗 River capture; glaciations; genome; demographic history; introgression |
| 谱系生物地理学 Phylogeography | 389 | 764 | 谱系生物地理学; 避难所; 遗传多样性; 更新世; 陆桥 Phylogeography; refugia; genetic diversity; Pleistocene; land bridge |
| 构造运动 Tectonic movement | 196 | 239 | 构造运动; 遗传分化; 种群动态; 东亚; 古地理 Tectonic movement; genetic differentiation; population dynamics; East Asia; palaeogeography |
| 线粒体DNA Mitochondrial DNA | 241 | 338 | 线粒体DNA; 鱼; 古水系; 地貌演化; 海平面变化 Mitochondrial DNA; fish; Palaeodrainage; geomorphic evolution; sea-level changes |
| 脱氧核糖核酸 DNA | 260 | 441 | 脱氧核糖核酸; 叶绿体DNA; 第四纪气候; 遗传结构; 冰期避难所 DNA; chloroplast DNA; quaternary climate; genetic structure; glacial refugia |
| 分子钟 Molecular clock | 179 | 226 | 分子钟; 广泛分布; 系统发育基因组学; 贝叶斯分析; 古DNA Molecular clock; wide distribution; phylogenomic; Bayesian analyses; ancient DNA |
| 喜马拉雅-横断山区 Himalaya-Hengduan Mountains | 87 | 112 | 喜马拉雅-横断山区; 物种分布模型; 两栖动物; 水系演化; 环境变化 Himalaya-Hengduan Mountains; species distribution modeling; amphibians; drainage evolution; environmental changes |
| 地质事件 Geological events | 126 | 165 | 地质事件; 进化历史; 东南亚; 校准; 淡水 Geological events; evolutionary history; Southeast Asia; calibration; freshwater |
| 气候变化 Climate change | 121 | 171 | 气候变化; 青藏高原隆升; 墨西拿盐度危机; 特提斯海; 茜草科 Climate change; Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau uplift; Messinian salinity crisis; Tethys Sea; Rubiaceae |

图3 结合地质地貌和基因组的相关研究文献共被引分析结果(A) (每个节点代表一篇被引文献, 节点的大小与被引频次成正比, 红色年轮代表该文献在这一时间段存在突发性变化, 每个节点之间的连线代表被引文献的时间演化情况, 线条的粗细则代表了共被引的强度)以及被引用次数最多的25篇文献(B) (浅蓝色代表该文献还未出现, 深蓝色代表文献开始出现, 红线表示该文献的高引时间段)
Fig. 3 Visualization of clusters in terms of timeline view of the document co-citation analysis in combined geology, geomorphology, and genomics research (A) (each node represents a cited literature; the size of the node is proportional to the cited frequency, the red tree rings represents the burst, the line between each node represents the temporal evolution of the cited literature, and the line thickness represents the co-citation strength); and top 25 references with the strongest citation bursts (B) (the light blue line indicates that the document has not appeared, dark blue line indicates that the document has begun to appear, and red line indicates the highly cited period of the document)
| 学科 Disciplines | 方法和数据 Methods and data | 研究问题 Research question | 时间尺度 Temporal scale (yr)* | 空间尺度 Spatial scale | 应用 Applications | 参考文献 References | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 谱系生物地理学 Phylogeography | 方法: 系统发育重建; 谱系结构分析; 中性理论; 最大熵模型; 生态位模型; 谱系多样性; 区系相似性分析; 分子钟分析; 谱系扩散隔离分析等。 数据: 分子遗传数据; 气候变化, 环境; 化石; 物种地理分布; 系统发育; 土地利用; 人类活动等。 Methods: Phylogenetic reconstruction; genetic structure analysis; neutral theory; maximum entropy model; ecological niche modeling; phylogenetic diversity; floral similarity analysis; molecular clock analysis; dispersal-vicariance analysis, etc. Data: Genetic data; climate change; environmental; fossil; geographical distribution of species; phylogeny; land use; human activities, etc. | 谱系的地理分布和种群的进化历史等。 Geographic distribution of lineages; evolutionary history of populations | 103-106 | 局部-区域 Local- regional | 物种形成假说检验; 物种遗传多样性分析; 物种分化研究; 扩散和隔离分化研究等。 Speciation hypothesis testing; genetic diversity analysis of species; species differentiation; dispersal-vicariance -divergence, etc. | Emerson & Hewitt, | ||||||
| 景观遗传学 Landscape genetics | 方法: Mantel检验; 遗传多样性估计; 结构方程模型; 最小成本路径分析; Monmonier最大差异算法; 回归分析; 距离隔离检验等。 数据: 分子遗传; 环境变化; 土地利用; 人类活动等。 Methods: Mantel test; genetic diversity estimates; structural equation models; least cost paths analysis; Monmonier’s maximum difference algorithm; regression analysis; isolation-by-distance test, etc. Data: Genetic data; environmental change; land use; human activities, etc. | 景观结构的遗传效应; 景观对基因流动的影响; 基于物种的时空尺度耦合等。 Genetic effects of landscape structure; influence of landscape on gene flow; spatio-temporal scale coupling based on species | 10-102 | 局部-区域 Local- regional | 确定保护单元; 评估种群状况; 管理入侵物种; 种群恢复等。 Identification of conservation units; assessment of population status; management of invasive species; population recovery, etc. | Manel et al, | ||||||
| 保护遗传学 Conservation genetics | 方法: 遗传多样性分析; 贝叶斯聚类分析; 物种分布模拟等。 数据: 分子遗传数据; 物种分布数据等。 Methods: Genetic diversity analysis; Bayesian cluster analysis; species distribution modeling, etc. Data: Genetic data; geographical distribution of species, etc. | 濒危物种保护; 遗传多样性保护; 保持物种进化潜力等。 Conservation of endangered species; conservation of genetic diversity; preservation of species’ evolutionary potential, etc. | 10-102 | 局部- 区域 Local- regional | 评估种群结构; 确定物种保护单元; 保护管理对策制定等。 Population structure assessment; identification of species conservation units; formulation of conservation management strategies, etc. | Hedrick, | ||||||
| 保护生物地理学 Conservation biogeography | 方法: 物种丰富度和特有性分析; 遗传多样性估计; 空间多样性分析; GIS; 基因流分析; 敏感性分析; 网络分析; 物种分布模型; 生态位模型; 生物气候包络模型等。 数据: 分子遗传; 物种分布数据; 遥感; 土地利用; 人类活动等。 Methods: Species richness and endemic analysis; genetic diversity estimates; spatial diversity analysis; GIS; gene flow; sensitivity analysis; network analysis; species distribution modeling; ecological niche modeling; bioclimate envelope modeling, etc. Data: Genetic data; geographical distribution of species; remote sensing; land use; human activities, etc. | 生物多样性保护; 生态格局与过程的时空动态和保护决策等。 Biodiversity conservation; temporal and spatial dynamics of ecological patterns and processes and conservation decisions, etc. | 103-106 | 区域- 全球 Regional- global | 评估种群规模; 保护区规划; 物种分布模拟; 物种入侵模式和驱动因素分析; 自然保护区评估; 气候避难所的识别等。 Assessment of population size; protected area planning; species distribution modeling; species invasion patterns and driving factors analysis; assessment of nature reserve; identification of climate refuges, etc. | Whittaker et al, | ||||||
| 生物地理学 Biogeography | 方法: 空间自相关分析; 热点分析; Mantel检验; 贝叶斯分析; 遗传结构分析; 系统发育分析; 物种分布模型; 谱系地理格局分析; 物种扩散-灭绝模型; 生态位模型等。 数据: 分子遗传; 遥感; 气候变化; 环境; 物种分布; 古气候; 化石; 土地利用; 人类活动等。 Methods: Spatial autocorrelation analysis; hotspot analysis; Mantel test; Bayesian analysis; genetic structure analysis; phylogenetic analysis; species distribution modeling; phylogeographical pattern analysis; dispersal-extinction analysis; ecological niche modeling, etc. Data: Genetic data; remote sensing; climate change; environmental; geographical distribution of species; paleoclimate; fossil; land use; human activities, etc. | 现存物种的起源; 物种分布模式; 植物区系; 生物多样性保护等。 Origin of existing species; distribution patterns of species; flora; biodiversity conservation, etc. | 10-106 | 区域- 全球 Regional- global | 植物区系划分; 山地植被与地理环境的关系; 物种起源扩散研究等。 Division of flora; the relationship between mountain vegetation and geographic environment; species origin and diffusion, etc. | McDowall, | ||||||
| 地理基因组学 Geogenomics | 方法: 年代学分析; 岩相分析; 地球化学分析; 隔离屏障模拟分析; 系统发育分析; 遗传结构分析、基因流分析; 分化时间分析; 种群动态分析; 情景模拟分析; 一致性检验; 统计假设检验等。 数据: 分子遗传; 物种分布数据; 遥感; 地质与历史事件; 地质年代; 沉积学; 古气候等。 Methods: Chronological analysis; petrographic analysis; geochemical analysis; dispersal- vicariance simulation analysis; phylogenetic analysis; genetic structure analysis; gene flow analysis; differentiation time analysis; population dynamics analysis; scenario simulation analysis; concordance test; statistical hypothesis testing, etc. Data: Genetic data; geographical distribution of species; remote sensing; geological and historical events; geologic age; sedimentary evidence; paleoclimate, etc. | 检验地质假说; 阐明区域或洲际地质过程; 多样性历史分析; 地质重建中的不确定性与尺度效应; 病原体基因组的地理分布。 Test geological hypotheses; elucidate regional or intercontinental geological processes; history of diversity; addressing uncertainties in geological reconstruction and scale effects; geographic distribution of the genomes of pathogens. | 103-106 | 区域 Regional | 亚马孙河形成; 安第斯山脉隆升历史等。 Drainage basin reconfiguration of Amazon through time; Andean uplift history, etc. | Baker et al, | ||||||
表2 地理基因组学与相关学科的比较
Table 2 Comparison of geogenomics and related disciplines
| 学科 Disciplines | 方法和数据 Methods and data | 研究问题 Research question | 时间尺度 Temporal scale (yr)* | 空间尺度 Spatial scale | 应用 Applications | 参考文献 References | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 谱系生物地理学 Phylogeography | 方法: 系统发育重建; 谱系结构分析; 中性理论; 最大熵模型; 生态位模型; 谱系多样性; 区系相似性分析; 分子钟分析; 谱系扩散隔离分析等。 数据: 分子遗传数据; 气候变化, 环境; 化石; 物种地理分布; 系统发育; 土地利用; 人类活动等。 Methods: Phylogenetic reconstruction; genetic structure analysis; neutral theory; maximum entropy model; ecological niche modeling; phylogenetic diversity; floral similarity analysis; molecular clock analysis; dispersal-vicariance analysis, etc. Data: Genetic data; climate change; environmental; fossil; geographical distribution of species; phylogeny; land use; human activities, etc. | 谱系的地理分布和种群的进化历史等。 Geographic distribution of lineages; evolutionary history of populations | 103-106 | 局部-区域 Local- regional | 物种形成假说检验; 物种遗传多样性分析; 物种分化研究; 扩散和隔离分化研究等。 Speciation hypothesis testing; genetic diversity analysis of species; species differentiation; dispersal-vicariance -divergence, etc. | Emerson & Hewitt, | ||||||
| 景观遗传学 Landscape genetics | 方法: Mantel检验; 遗传多样性估计; 结构方程模型; 最小成本路径分析; Monmonier最大差异算法; 回归分析; 距离隔离检验等。 数据: 分子遗传; 环境变化; 土地利用; 人类活动等。 Methods: Mantel test; genetic diversity estimates; structural equation models; least cost paths analysis; Monmonier’s maximum difference algorithm; regression analysis; isolation-by-distance test, etc. Data: Genetic data; environmental change; land use; human activities, etc. | 景观结构的遗传效应; 景观对基因流动的影响; 基于物种的时空尺度耦合等。 Genetic effects of landscape structure; influence of landscape on gene flow; spatio-temporal scale coupling based on species | 10-102 | 局部-区域 Local- regional | 确定保护单元; 评估种群状况; 管理入侵物种; 种群恢复等。 Identification of conservation units; assessment of population status; management of invasive species; population recovery, etc. | Manel et al, | ||||||
| 保护遗传学 Conservation genetics | 方法: 遗传多样性分析; 贝叶斯聚类分析; 物种分布模拟等。 数据: 分子遗传数据; 物种分布数据等。 Methods: Genetic diversity analysis; Bayesian cluster analysis; species distribution modeling, etc. Data: Genetic data; geographical distribution of species, etc. | 濒危物种保护; 遗传多样性保护; 保持物种进化潜力等。 Conservation of endangered species; conservation of genetic diversity; preservation of species’ evolutionary potential, etc. | 10-102 | 局部- 区域 Local- regional | 评估种群结构; 确定物种保护单元; 保护管理对策制定等。 Population structure assessment; identification of species conservation units; formulation of conservation management strategies, etc. | Hedrick, | ||||||
| 保护生物地理学 Conservation biogeography | 方法: 物种丰富度和特有性分析; 遗传多样性估计; 空间多样性分析; GIS; 基因流分析; 敏感性分析; 网络分析; 物种分布模型; 生态位模型; 生物气候包络模型等。 数据: 分子遗传; 物种分布数据; 遥感; 土地利用; 人类活动等。 Methods: Species richness and endemic analysis; genetic diversity estimates; spatial diversity analysis; GIS; gene flow; sensitivity analysis; network analysis; species distribution modeling; ecological niche modeling; bioclimate envelope modeling, etc. Data: Genetic data; geographical distribution of species; remote sensing; land use; human activities, etc. | 生物多样性保护; 生态格局与过程的时空动态和保护决策等。 Biodiversity conservation; temporal and spatial dynamics of ecological patterns and processes and conservation decisions, etc. | 103-106 | 区域- 全球 Regional- global | 评估种群规模; 保护区规划; 物种分布模拟; 物种入侵模式和驱动因素分析; 自然保护区评估; 气候避难所的识别等。 Assessment of population size; protected area planning; species distribution modeling; species invasion patterns and driving factors analysis; assessment of nature reserve; identification of climate refuges, etc. | Whittaker et al, | ||||||
| 生物地理学 Biogeography | 方法: 空间自相关分析; 热点分析; Mantel检验; 贝叶斯分析; 遗传结构分析; 系统发育分析; 物种分布模型; 谱系地理格局分析; 物种扩散-灭绝模型; 生态位模型等。 数据: 分子遗传; 遥感; 气候变化; 环境; 物种分布; 古气候; 化石; 土地利用; 人类活动等。 Methods: Spatial autocorrelation analysis; hotspot analysis; Mantel test; Bayesian analysis; genetic structure analysis; phylogenetic analysis; species distribution modeling; phylogeographical pattern analysis; dispersal-extinction analysis; ecological niche modeling, etc. Data: Genetic data; remote sensing; climate change; environmental; geographical distribution of species; paleoclimate; fossil; land use; human activities, etc. | 现存物种的起源; 物种分布模式; 植物区系; 生物多样性保护等。 Origin of existing species; distribution patterns of species; flora; biodiversity conservation, etc. | 10-106 | 区域- 全球 Regional- global | 植物区系划分; 山地植被与地理环境的关系; 物种起源扩散研究等。 Division of flora; the relationship between mountain vegetation and geographic environment; species origin and diffusion, etc. | McDowall, | ||||||
| 地理基因组学 Geogenomics | 方法: 年代学分析; 岩相分析; 地球化学分析; 隔离屏障模拟分析; 系统发育分析; 遗传结构分析、基因流分析; 分化时间分析; 种群动态分析; 情景模拟分析; 一致性检验; 统计假设检验等。 数据: 分子遗传; 物种分布数据; 遥感; 地质与历史事件; 地质年代; 沉积学; 古气候等。 Methods: Chronological analysis; petrographic analysis; geochemical analysis; dispersal- vicariance simulation analysis; phylogenetic analysis; genetic structure analysis; gene flow analysis; differentiation time analysis; population dynamics analysis; scenario simulation analysis; concordance test; statistical hypothesis testing, etc. Data: Genetic data; geographical distribution of species; remote sensing; geological and historical events; geologic age; sedimentary evidence; paleoclimate, etc. | 检验地质假说; 阐明区域或洲际地质过程; 多样性历史分析; 地质重建中的不确定性与尺度效应; 病原体基因组的地理分布。 Test geological hypotheses; elucidate regional or intercontinental geological processes; history of diversity; addressing uncertainties in geological reconstruction and scale effects; geographic distribution of the genomes of pathogens. | 103-106 | 区域 Regional | 亚马孙河形成; 安第斯山脉隆升历史等。 Drainage basin reconfiguration of Amazon through time; Andean uplift history, etc. | Baker et al, | ||||||
| 研究区域 Areas | 研究类群 Taxa | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|
| 亚马孙河 Amazon River | 哺乳动物(灵长类动物); 鸟类; 植物(灌木、乔木); 爬行动物 Mammal (primates); bird; plants (shrubs; trees); reptiles | Pupim et al, |
| 安第斯山脉 Andean Mountains | 植物(乔木); 节肢动物(昆虫) Plants (trees); arthropods (insects) | Gianni et al, |
| 太平洋岛屿 Pacific Islands | 节肢动物(蜘蛛) Arthropods (spiders) | Elias et al, |
| 日本 Japan | 鱼类 Fish | Masuda et al, |
| 全球 Global | 二倍体真核生物(哺乳动物; 爬行动物; 鱼类; 鸟类; 无脊椎动物; 植物(非乔木; 乔木)) Diploid eukaryotes (mammal; reptiles; fish; bird; invertebrate; plants (non-tree; trees)) | Araya-Donoso et al, |
| 阿尔卑斯山 Alps | 哺乳动物(臆羚) Mammal (northern chamois) | Leugger et al, |
| 青藏高原 Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau | 植物(乔木; 灌木; 草本); 两栖动物; 爬行动物; 节肢动物(蜘蛛); 鱼类; 鸟类 Plants (trees; shrubs; herbs); amphibians; reptiles; arthropods (spiders); fish; birds | Song et al, |
| 全球 Global | 病原体 Pathogens | Sargeant et al, |
表3 迄今地理基因组学的主要研究区域和类群
Table 3 The taxa and study areas of geogenomics up to the present
| 研究区域 Areas | 研究类群 Taxa | 参考文献 References |
|---|---|---|
| 亚马孙河 Amazon River | 哺乳动物(灵长类动物); 鸟类; 植物(灌木、乔木); 爬行动物 Mammal (primates); bird; plants (shrubs; trees); reptiles | Pupim et al, |
| 安第斯山脉 Andean Mountains | 植物(乔木); 节肢动物(昆虫) Plants (trees); arthropods (insects) | Gianni et al, |
| 太平洋岛屿 Pacific Islands | 节肢动物(蜘蛛) Arthropods (spiders) | Elias et al, |
| 日本 Japan | 鱼类 Fish | Masuda et al, |
| 全球 Global | 二倍体真核生物(哺乳动物; 爬行动物; 鱼类; 鸟类; 无脊椎动物; 植物(非乔木; 乔木)) Diploid eukaryotes (mammal; reptiles; fish; bird; invertebrate; plants (non-tree; trees)) | Araya-Donoso et al, |
| 阿尔卑斯山 Alps | 哺乳动物(臆羚) Mammal (northern chamois) | Leugger et al, |
| 青藏高原 Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau | 植物(乔木; 灌木; 草本); 两栖动物; 爬行动物; 节肢动物(蜘蛛); 鱼类; 鸟类 Plants (trees; shrubs; herbs); amphibians; reptiles; arthropods (spiders); fish; birds | Song et al, |
| 全球 Global | 病原体 Pathogens | Sargeant et al, |
| [1] |
Alexander DH, Novembre J, Lange K (2009) Fast model-based estimation of ancestry in unrelated individuals. Genome Research, 19, 1655-1664.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | Antonelli A (2022) The rise and fall of Neotropical biodiversity. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 199, 8-24. |
| [3] | Antonelli A, Kissling WD, Flantua SGA, Bermúdez MA, Mulch A, Muellner-Riehl AN, Kreft H, Linder HP, Badgley C, Fjeldså J, Fritz SA, Rahbek C, Herman F, Hooghiemstra H, Hoorn C (2018a) Geological and climatic influences on mountain biodiversity. Nature Geoscience, 11, 718-725. |
| [4] | Antonelli A, Zizka A, Carvalho FA, Scharn R, Bacon CD, Silvestro D, Condamine FL (2018b) Amazonia is the primary source of Neotropical biodiversity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 115, 6034-6039. |
| [5] | Araya-Donoso R, Baty SM, Alonso-Alonso P, Sanín MJ, Wilder BT, Munguia-Vega A, Dolby GA (2022) Implications of barrier ephemerality in geogenomic research. Journal of Biogeography, 49, 2050-2063. |
| [6] | Aria M, Cuccurullo C (2017) bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. Journal of Informetrics, 11, 959-975. |
| [7] | Avise JC (2009) Phylogeography: Retrospect and prospect. Journal of Biogeography, 36, 3-15. |
| [8] | Avise JC, Arnold J, Ball RM, Bermingham E, Lamb T, Neigel JE, Reeb CA, Saunders NC (1987) Intraspecific phylogeography: The mitochondrial DNA bridge between population genetics and systematics. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 18, 489-522. |
| [9] | Bacon CD, Velásquez-Puentes FJ, Hoorn C, Antonelli A (2018) Iriarteeae palms tracked the uplift of Andean Cordilleras. Journal of Biogeography, 45, 1653-1663. |
| [10] | Baker PA, Fritz SC, Dick CW, Eckert AJ, Horton BK, Manzoni S, Ribas CC, Garzione CN, Battisti DS (2014) The emerging field of geogenomics: Constraining geological problems with genetic data. Earth-Science Reviews, 135, 38-47. |
| [11] | Bedoya AM (2024) Botany and geogenomics: Constraining geological hypotheses in the neotropics with large-scale genetic data derived from plants. American Journal of Botany, 111, e16306. |
| [12] |
Bedoya AM, Leaché AD, Olmstead RG (2021) Andean uplift, drainage basin formation, and the evolution of plants living in fast-flowing aquatic ecosystems in northern South America. New Phytologist, 232, 2175-2190.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Beheregaray LB (2008) Twenty years of phylogeography: The state of the field and the challenges for the Southern Hemisphere. Molecular Ecology, 17, 3754-3774.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | Boubli JP, Ribas C, Lynch Alfaro JW, Alfaro ME, da Silva MNF, Pinho GM, Farias IP (2015) Spatial and temporal patterns of diversification on the Amazon: A test of the riverine hypothesis for all diurnal primates of Rio Negro and Rio Branco in Brazil. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 82, 400-412. |
| [15] | Bouckaert R, Vaughan TG, Barido-Sottani J, Duchêne S, Fourment M, Gavryushkina A, Heled J, Jones G, Kühnert D, De Maio N, Matschiner M, Mendes FK, Müller NF, Ogilvie HA, du Plessis L, Popinga A, Rambaut A, Rasmussen D, Siveroni I, Suchard MA, Wu CH, Xie D, Zhang C, Stadler T, Drummond AJ (2019) BEAST 2.5: An advanced software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Computational Biology, 15, e1006650. |
| [16] |
Chan LM, Brown JL, Yoder AD (2011) Integrating statistical genetic and geospatial methods brings new power to phylogeography. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 59, 523-537.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
Chen C (2017) Science mapping: A systematic review of the literature. Journal of Data and Information Science, 2, 1-40.
DOI |
| [18] | Chen F, Xue G, Wang YK, Zhang HC, Clift PD, Xing YW, He J, Albert JS, Chen J, Xie P (2023) Evolution of the Yangtze River and its biodiversity. The Innovation, 4, 100417. |
| [19] | Clark MK, Schoenbohm LM, Royden LH, Whipple KX, Burchfiel BC, Zhang X, Tang W, Wang E, Chen L (2004) Surface uplift, tectonics, and erosion of eastern Tibet from large-scale drainage patterns. Tectonics, 23, TC1006. |
| [20] | Cornuet JM, Pudlo P, Veyssier J, Dehne-Garcia A, Gautier M, Leblois R, Marin JM, Estoup A (2014) DIYABC v2.0: A software to make approximate Bayesian computation inferences about population history using single nucleotide polymorphism, DNA sequence and microsatellite data. Bioinformatics, 30, 1187-1189. |
| [21] | Cun YZ, Wang XQ (2010) Plant recolonization in the Himalaya from the southeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: Geographical isolation contributed to high population differentiation. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 56, 972-982. |
| [22] | Dal Vechio F, Prates I, Grazziotin FG, Zaher H, Graboski R, Rodrigues MT (2020) Rain forest shifts through time and riverine barriers shaped the diversification of South American terrestrial pit vipers (Bothrops jararacussu species group). Journal of Biogeography, 47, 516-526. |
| [23] | Darwin CR (translated by Li GY, Kong Q, Li JX, Zhou CL) (2014) The Voyage of the Beagle. China Youth Publishing Group, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [李光玉, 孔雀, 李嘉兴, 周辰亮 (译) (2014) “小猎犬”号科学考察记. 中国青年出版社, 北京.] | |
| [24] | Dawson MN, Ribas CC, Dolby GA, Fritz SC (2022) Geogenomics: Toward synthesis. Journal of Biogeography, 49, 1657-1661. |
| [25] | Deng T, Ding L (2015) Paleoaltimetry reconstructions of the Tibetan Plateau: Progress and contradictions. National Science Review, 2, 417-437. |
| [26] | Ding L, Kapp P, Cai FL, Garzione CN, Xiong ZY, Wang HQ, Wang C (2022) Timing and mechanisms of Tibetan Plateau uplift. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 3, 652-667. |
| [27] | Dolby GA, Bennett SEK, Dorsey RJ, Stokes MF, Riddle BR, Lira-Noriega A, Munguia-Vega A, Wilder BT (2022) Integrating Earth-life systems: A geogenomic approach. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 37, 371-384. |
| [28] | Drummond AJ, Ho SYW, Phillips MJ, Rambaut A (2006) Relaxed phylogenetics and dating with confidence. PLoS Biology, 4, e88. |
| [29] |
Drummond AJ, Rambaut A (2007) BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 7, 214.
PMID |
| [30] | Elias NU, Responte MA, Wu CY, Chiu YF, Peng P, Liao H, Brown RM, Su YC (2024) A shift in the host web occupancy of dew-drop spiders associated with genetic divergence in the Southwest Pacific. Journal of Biogeography, 51, 1049-1063. |
| [31] | Emerson BC, Hewitt GM (2005) Phylogeography. Current Biology, 15, R367-R371. |
| [32] |
Ewers RM, Didham RK, Pearse WD, Lefebvre V, Rosa IMD, Carreiras JMB, Lucas RM, Reuman DC (2013) Using landscape history to predict biodiversity patterns in fragmented landscapes. Ecology Letters, 16, 1221-1233.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
Excoffier L, Marchi N, Marques DA, Matthey-Doret R, Gouy A, Sousa VC (2021) fastsimcoal2: Demographic inference under complex evolutionary scenarios. Bioinformatics, 37, 4882-4885.
DOI PMID |
| [34] | Fasanella M, Mathiasen P, Juri G, Díaz DG, Hasbún R, Premoli AC (2023) Ancient vicariance is reinforced by adaptive divergence in the southern beech: Contributions from geogenomics. Journal of Biogeography, 50, 564-575. |
| [35] | Finarelli JA, Badgley C (2010) Diversity dynamics of Miocene mammals in relation to the history of tectonism and climate. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 277, 2721-2726. |
| [36] | Fine PVA (2015) Ecological and evolutionary drivers of geographic variation in species diversity. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 46, 369-392. |
| [37] | Fordham G, Shanee S, Peck M (2020) Effect of river size on Amazonian primate community structure: A biogeographic analysis using updated taxonomic assessments. American Journal of Primatology, 82, e23136. |
| [38] | Fritz SA, Schnitzler J, Eronen JT, Hof C, Böhning-Gaese K, Graham CH (2013) Diversity in time and space: Wanted dead and alive. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 28, 509-516. |
| [39] | Futuyma DJ (translated by Ge S, Gu HY, Rao GY, Zhang DX, Yang J, Kong HZ, Wang YF) (2016) Evolution, 3rd edn. Higher Education Press. Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [葛颂, 顾红雅, 饶广远, 张德兴, 杨继, 孔宏智, 王宇飞 (译) (2016) 生物进化. 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| [40] |
Gianni GM, Navarrete C, Echaurren A, Díaz M, Butler KL, Horton BK, Encinas A, Folguera A (2020) Northward propagation of Andean genesis: Insights from Early Cretaceous synorogenic deposits in the Aysén-Río Mayo basin. Gondwana Research, 77, 238-259.
DOI |
| [41] | Gregory-Wodzicki KM (2000) Uplift history of the central and northern Andes: A review. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 112, 1091-1105. |
| [42] | He C, Braun J, Tang H, Yuan X, Acevedo-Trejos E, Ott RF, de Quay GS (2024) Drainage divide migration and implications for climate and biodiversity. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 5, 177-192. |
| [43] | Hedrick PW (2001) Conservation genetics: Where are we now? Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 16, 629-636. |
| [44] | Hewitt G (2000) The genetic legacy of the Quaternary ice ages. Nature, 405, 907-913. |
| [45] |
Hoorn C, Wesselingh FP, ter Steege H, Bermudez MA, Mora A, Sevink J, Sanmartín I, Sanchez-Meseguer A, Anderson CL, Figueiredo JP, Jaramillo C, Riff D, Negri FR, Hooghiemstra H, Lundberg J, Stadler T, Särkinen T, Antonelli A (2010) Amazonia through time: Andean uplift, climate change, landscape evolution, and biodiversity. Science, 330, 927-931.
DOI PMID |
| [46] | Horton BK (2018) Sedimentary record of Andean Mountain building. Earth-Science Reviews, 178, 279-309. |
| [47] | Hu A, Wang J, Sun H, Niu B, Si G, Wang J, Yeh CF, Zhu X, Lu X, Zhou J, Yang Y, Ren M, Dong H, Zhang G (2020) Mountain biodiversity and ecosystem functions: Interplay between geology and contemporary environments. The International Society for Microbial Ecology, 14, 931-944. |
| [48] |
Huang S, Meijers MJM, Eyres A, Mulch A, Fritz SA (2019) Unravelling the history of biodiversity in mountain ranges through integrating geology and biogeography. Journal of Biogeography, 46, 1777-1791.
DOI |
| [49] |
Hubisz MJ, Falush D, Stephens M, Pritchard JK (2009) Inferring weak population structure with the assistance of sample group information. Molecular Ecology Resources, 9, 1322-1332.
DOI PMID |
| [50] | Jiang Y, Tang J, Liu XJ, Daroch M (2023) Polyphasic characterization of a novel hot-spring cyanobacterium Thermocoleostomius sinensis gen et sp. nov. and genomic insights into its carbon concentration mechanism. Frontiers in Microbiology, 14, 1176500. |
| [51] |
Jin DM, Yuan Q, Dai XL, Kozlowski G, Song YG (2024) Enhanced precipitation has driven the evolution of subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forests in Eastern China since the early Miocene: Evidence from ring-cupped oaks. Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 62, 677-686.
DOI |
| [52] | Leugger F, Broquet T, Karger DN, Rioux D, Buzan E, Corlatti L, Crestanello B, Curt-Grand-Gaudin N, Hauffe HC, Rolečková B, Šprem N, Tissot N, Tissot S, Valterová R, Yannic G, Pellissier L (2022) Dispersal and habitat dynamics shape the genetic structure of the Northern chamois in the Alps. Journal of Biogeography, 49, 1848-1861. |
| [53] | Lexer C, Mangili S, Bossolini E, Forest F, Stölting KN, Pearman PB, Zimmermann NE, Salamin N (2013) ‘Next generation’ biogeography: Towards understanding the drivers of species diversification and persistence. Journal of Biogeography, 40, 1013-1022. |
| [54] | Li XX, Qian JS, Huang JH, Zhu R, Lin PC, He DK (2023) Genetic memory of fishes on river development in Himalayas. Quaternary Sciences, 43, 819-837. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李茜茜, 钱建硕, 黄俊豪, 朱仁, 林鹏程, 何德奎 (2023) 鱼类遗传对喜马拉雅河流演化的记忆. 第四纪研究, 43, 819-837.] | |
| [55] |
Li Y, Zhang XX, Mao RL, Yang J, Miao CY, Li Z, Qiu YX (2017) Ten Years of landscape genomics: Challenges and opportunities. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8, 2136.
DOI PMID |
| [56] | Liow LH, Uyeda J, Hunt G (2023) Cross-disciplinary information for understanding macroevolution. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 38, 250-260. |
| [57] | Liu F, Chai J, Huang G, Liu J, Chen ZY (2015) Modulation of decadal ENSO-like variation by effective solar radiation. Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans, 72, 52-61. |
| [58] | Liu ZX, Zhao YQ (2023) Methods to detect and characterize introgression. Hereditas (Beijing), 45, 128-143. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘泽璇, 赵毅强 (2023) 基因渗入的检测和表征方法. 遗传, 45, 128-143.] | |
| [59] | Luna LW, Naka LN, Thom G, Knowles LL, Sawakuchi AO, Aleixo A, Ribas CC (2023) Late Pleistocene landscape changes and habitat specialization as promoters of population genomic divergence in Amazonian floodplain birds. Molecular Ecology, 32, 214-228. |
| [60] |
Luo YF, Li SQ (2022) The stepwise Indian-Eurasian collision and uplift of the Himalayan-Tibetan Plateau drove the diversification of high-elevation Scytodes spiders. Cladistics, 38, 582-594.
DOI PMID |
| [61] | Manel S, Schwartz MK, Luikart G, Taberlet P (2003) Landscape genetics: Combining landscape ecology and population genetics. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 18, 189-197. |
| [62] | Manish K, Pandit MK (2018) Geophysical upheavals and evolutionary diversification of plant species in the Himalaya. PeerJ, 6, e5919. |
| [63] | Mao KS, Wang Y, Liu JQ (2021) Evolutionary origin of species diversity on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 59, 1142-1158. |
| [64] | Masuda T, Shimono Y, Kishi D, Koizumi I (2023) Systematic headwater sampling of white-spotted charr reveals stream capture events across dynamic topography. Journal of Biogeography, 50, 453-466. |
| [65] | McDowall RM (2004) What biogeography is: A place for process. Journal of Biogeography, 31, 345-351. |
| [66] | Meng Q, Xie Z, Xu H, Guo J, Tang Y, Ma T, Peng Q, Wang B, Mao Y, Yan S, Yang J, Dong D, Duan Y, Zhang F, Gao T (2022) Out of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: Origin, evolution and historical biogeography of Morchella (both Elata and Esculenta clades). Frontiers in Microbiology, 13, 1078663. |
| [67] | Milanovsky EE (1987) Rifting evolution in geological history. Tectonophysics, 143, 103-118. |
| [68] | Mourthé Í, Hilário RR, Carvalho WD, Boubli JP (2022) Filtering effect of large rivers on primate distribution in the Brazilian Amazonia. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 10, 857920. |
| [69] | Murienne J, Barragán Á, Manzi S, Samaniego P, Moret P (2022) How tectonic, volcanic and climatic processes in Andean ‘sky islands’ shaped the diversification of endemic ground beetles. Journal of Biogeography, 49, 2077-2090. |
| [70] | Musher LJ, Del-Rio G, Marcondes RS, Brumfield RT, Bravo GA, Thom G (2024) Geogenomic predictors of genetree heterogeneity explain phylogeographic and introgression history: A case study in an Amazonian bird (Thamnophilus aethiops). Systematic Biology, 73, 36-52. |
| [71] |
Patterson N, Moorjani P, Luo Y, Mallick S, Rohland N, Zhan YP, Genschoreck T, Webster T, Reich D (2012) Ancient admixture in human history. Genetics, 192, 1065-1093.
DOI PMID |
| [72] |
Pérez-Escobar OA, Zizka A, Bermúdez MA, Meseguer AS, Condamine FL, Hoorn C, Hooghiemstra H, Pu YS, Bogarín D, Boschman LM, Pennington RT, Antonelli A, Chomicki G (2022) The Andes through time: Evolution and distribution of Andean floras. Trends in Plant Science, 27, 364-378.
DOI PMID |
| [73] |
Pickrell JK, Patterson N, Barbieri C, Berthold F, Gerlach L, Güldemann T, Kure B, Mpoloka SW, Nakagawa H, Naumann C, Lipson M, Loh PR, Lachance J, Mountain J, Bustamante CD, Berger B, Tishkoff SA, Henn BM, Stoneking M, Reich D, Pakendorf B (2012) The genetic prehistory of southern Africa. Nature Communications, 3, 1143.
DOI PMID |
| [74] | Pingel H, Strecker MR, Mulch A, Alonso RN, Cottle J, Rohrmann A (2020) Late Cenozoic topographic evolution of the Eastern Cordillera and Puna Plateau margin in the southern Central Andes (NW Argentina). Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 535, 116112. |
| [75] | Posadas P, Crisci JV, Katinas L (2006) Historical biogeography: A review of its basic concepts and critical issues. Journal of Arid Environments, 66, 389-403. |
| [76] | Prevedello JA, Gotelli NJ, Metzger JP (2016) A stochastic model for landscape patterns of biodiversity. Ecological Monographs, 86, 462-479. |
| [77] |
Pupim FN, Sawakuchi AO, Almeida RP, Ribas CC, Kern AK, Hartmann GA, Chiessi CM, Tamura LN, Mineli TD, Savian JF, Grohmann CH, Bertassoli DJ, Stern AG, Cruz FW, Cracraft J (2019) Chronology of Terra Firme formation in Amazonian Lowlands reveals a dynamic Quaternary landscape. Quaternary Science Reviews, 210, 154-163.
DOI |
| [78] | Qi DL, Guo SC, Chao Y, Kong QH, Li CZ, Xia MZ, Xie BS, Zhao K (2015) The biogeography and phylogeny of schizothoracine fishes (Schizopygopsis) in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Zoologica Scripta, 44, 523-533. |
| [79] | Qin SY, Zuo ZY, Guo C, Du XY, Liu SY, Yu XQ, Xiang XG, Rong J, Liu B, Liu ZF, Ma PF, Li DZ (2023) Phylogenomic insights into the origin and evolutionary history of evergreen broadleaved forests in East Asia under Cenozoic climate change. Molecular Ecology, 32, 2850-2868. |
| [80] |
Rahbek C, Borregaard MK, Antonelli A, Colwell RK, Holt BG, Nogues-Bravo D, Richardson K, Rosing MT, Whittaker RJ, Fjeldså J (2019) Building mountain biodiversity: Geological and evolutionary processes. Science, 365, 1114-1119.
DOI PMID |
| [81] |
Raj A, Stephens M, Pritchard JK (2014) fastSTRUCTURE: Variational inference of population structure in large SNP data sets. Genetics, 197, 573-589.
DOI PMID |
| [82] | Regmi B, Douglas MR, Wangchuk K, Zbinden ZD, Edds DR, Tshering S, Douglas ME (2023) The Himalayan uplift and evolution of aquatic biodiversity across Asia: Snowtrout (Cyprininae: Schizothorax) as a test case. PLoS ONE, 18, e0289736. |
| [83] | Ribas CC, Fritz SC, Baker PA (2022) The challenges and potential of geogenomics for biogeography and conservation in Amazonia. Journal of Biogeography, 49, 1839-1847. |
| [84] | Richardson DM, Whittaker RJ (2010) Conservation biogeography—Foundations, concepts and challenges. Diversity and Distributions, 16, 313-320. |
| [85] | Ruokolainen K, Moulatlet GM, Zuquim G, Hoorn C, Tuomisto H (2019) Geologically recent rearrangements in central Amazonian river network and their importance for the riverine barrier hypothesis. Frontiers of Biogeography, 11, e45046. |
| [86] |
Sanderson MJ (2002) Estimating absolute rates of molecular evolution and divergence times: A penalized likelihood approach. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 19, 101-109.
DOI PMID |
| [87] | Sanín MJ, Mejía-Franco FG, Paris M, Valencia-Montoya WA, Salamin N, Kessler M, Olivares I, Jaramillo JS, Cardona A (2022) Geogenomics of montane palms points to Miocene-Pliocene Andean segmentation related to strike-slip tectonics. Journal of Biogeography, 49, 1711-1725. |
| [88] |
Santorelli S Jr, Magnusson WE, Deus CP (2018) Most species are not limited by an Amazonian river postulated to be a border between endemism areas. Scientific Reports, 8, 2294.
DOI PMID |
| [89] | Sargeant DP, Hedden MW, Deverasetty S, Strong CL, Alaniz IJ, Bartlett AN, Brandon NR, Brooks SB, Brown FA, Bufi F, Chakarova M, David RP, Dobritch KM, Guerra HP, Levit KS, Mathew KR, Matti R, Maza DQ, Mistry S, Novakovic N, Pomerantz A, Rafalski TF, Rathnayake V, Rezapour N, Ross CA, Schooler SG, Songao S, Tuggle SL, Wing HJ, Yousif S, Schiller MR (2014) The Geogenomic Mutational Atlas of Pathogens (GoMAP) Web System. PLoS ONE, 9, e92877. |
| [90] | Sax DF, Gaines SD (2003) Species diversity: From global decreases to local increases. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 18, 561-566. |
| [91] | Schoene B, Condon DJ, Morgan L, McLean N (2013) Precision and accuracy in geochronology. Elements, 9, 19-24. |
| [92] | Segelbacher G, Cushman SA, Epperson BK, Fortin MJ, Francois O, Hardy OJ, Holderegger R, Taberlet P, Waits LP, Manel S (2010) Applications of landscape genetics in conservation biology: Concepts and challenges. Conservation Genetics, 11, 375-385. |
| [93] | Shen ZH, Ji CJ (2010) Landscape genetics: Principles and its applications for the genetic effects of habitat fragmentation. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30, 5066-5076. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [沈泽昊, 吉成均 (2010) 景观遗传学原理及其在生境片断化遗传效应研究中的应用. 生态学报, 30, 5066-5076.] | |
| [94] | Silva FE, Luna LW, Batista R, Röhe F, Gubili C, Farias IP, Hrbek T, Valsecchi J, Ribas CC, McDevitt AD, Dellicour S, Flot JF, Boubli JP (2024) Impact of Quaternary Amazonian river dynamics on the diversification of uakari monkeys (genus Cacajao). Journal of Biogeography, 51, 1505-1517. |
| [95] |
Smith SA, O’Meara BC (2012) treePL: Divergence time estimation using penalized likelihood for large phylogenies. Bioinformatics, 28, 2689-2690.
DOI PMID |
| [96] | Song K, Gao B, Halvarsson P, Fang Y, Klaus S, Jiang YX, Swenson JE, Sun YH, Höglund J (2021) Demographic history and divergence of sibling grouse species inferred from whole genome sequencing reveal past effects of climate change. BMC Ecology and Evolution, 21, 194. |
| [97] | Spicer RA, Su T, Valdes PJ, Farnsworth A, Wu FX, Shi GL, Spicer TEV, Zhou ZK (2021) Why ‘the uplift of the Tibetan Plateau’ is a myth. National Science Review, 8, nwaa091. |
| [98] | Struth L, Babault J, Teixell A (2015) Drainage reorganization during mountain building in the river system of the Eastern Cordillera of the Colombian Andes. Geomorphology, 250, 370-383. |
| [99] | Sun H, Li ZM, Landis JB, Qian LS, Zhang TC, Deng T (2022) Effects of drainage reorganization on phytogeographic pattern in Sino-Himalaya. Alpine Botany, 132, 141-151. |
| [100] | Tan XX, Li M (2018) From conservation genetics to conservation genomics. Journal of Anhui University (Natural Science Edition), 42(6), 22-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [谭鑫鑫, 李明 (2018) 从保护遗传学到保护基因组学. 安徽大学学报(自然科学版), 42(6), 22-28.] | |
| [101] | Tang J, Du LM, Li MJ, Yao D, Jiang Y, Waleron M, Waleron K, Daroch M (2022a) Characterization of a novel hot-spring Cyanobacterium Leptodesmis sichuanensis sp. nov. and genomic insights of molecular adaptations into its habitat. Frontiers in Microbiology, 12, 739625. |
| [102] | Tang J, Shah MR, Yao D, Jiang Y, Du LM, Zhao KL, Li LH, Li MJ, Waleron MM, Waleron M, Waleron K, Daroch M (2022b) Polyphasic identification and genomic insights of Leptothermofonsia sichuanensis gen. sp. nov., a novel thermophilic cyanobacteria within Leptolyngbyaceae. Frontiers in Microbiology, 13, 765105. |
| [103] | Tang J, Zhou HZ, Jiang Y, Yao D, Waleron KF, Du LM, Daroch M (2023) Characterization of a novel thermophilic cyanobacterium within Trichocoleusaceae, Trichothermofontia sichuanensis gen. et sp. nov., and its CO2-concentrating mechanism. Frontiers in Microbiology, 14, 1111809. |
| [104] | Tarr GAM, Shringi S, Phipps AI, Besser TE, Mayer J, Oltean HN, Wakefield J, Tarr PI, Rabinowitz P (2018) Geogenomic segregation and temporal trends of human pathogenic Escherichia coli O157:H7, Washington, USA, 2005-2014. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 24, 32-39. |
| [105] | Thomas ER, Allen CS, Etourneau J, King ACF, Severi M, Winton VHL, Mueller J, Crosta X, Peck VL (2019) Antarctic sea ice proxies from marine and ice core archives suitable for reconstructing sea ice over the past 2000 years. Geosciences, 9, 506. |
| [106] | van der Meer FD, van der Werff HMA, Hecker CA, Bakker WH, Noomen MF, van der Meijde M, Carranza EJM, de Smeth JB, Woldai T (2012) Multi- and hyperspectral geologic remote sensing: A review. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 14, 112-128. |
| [107] |
van Eck NJ, Waltman L (2010) Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics, 84, 523-538.
PMID |
| [108] | von Humboldt A, Bonpland A translated by Romanowski S (2009) Essay on the Geography of Plants. University of Chicago Press, Chicago. |
| [109] | Wallace AR (translated by Peng Z, Yuan WL, et al) (2004) The Malay Archipelago. China People’s University Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [彭珍, 袁伟亮等 (译) (2004) 马来群岛自然科学考察记. 中国人民大学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [110] | Wang KL, Zhou XH, Liu DT, Li YZ, Yao Z, He WM, Liu YB (2022) The uplift of the Hengduan Mountains contributed to the speciation of three Rhododendron species. Global Ecology and Conservation, 35, e02085. |
| [111] | Wang P, Zheng HB, Liu SF (2013) Geomorphic constraints on middle Yangtze River reversal in eastern Sichuan Basin, China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 69, 70-85. |
| [112] |
Waters JM, Craw D, Youngson JH, Wallis GP (2001) Genes meet geology: Fish phylogeographic pattern reflects ancient, rather than modern, drainage connections. Evolution, 55, 1844-1851.
PMID |
| [113] | Wen J, Zhang JQ, Nie ZL, Zhong Y, Sun H (2014) Evolutionary diversifications of plants on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Frontiers in Genetics, 5, 4. |
| [114] | Westphal D, Mancini AN, Baden AL (2021) Primate landscape genetics: A review and practical guide. Evolutionary Anthropology: Issues, News, and Reviews, 30, 171-184. |
| [115] | Whittaker RJ, Araújo MB, Jepson P, Ladle RJ, Watson JEM, Willis KJ (2005) Conservation Biogeography: Assessment and prospect. Diversity and Distributions, 11, 3-23. |
| [116] | Wiens JJ, Donoghue MJ (2004) Historical biogeography, ecology and species richness. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 19, 639-644. |
| [117] | Xiang KL, Erst AS, Yang J, Peng HW, Ortiz RdC, Jabbour F, Erst TV, Wang W (2021) Biogeographic diversification of Eranthis (Ranunculaceae) reflects the geological history of the three great Asian plateaus. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 288, 20210281. |
| [118] | Xu W, Dong WJ, Fu TT, Gao W, Lu CQ, Yan F, Wu YH, Jiang K, Jin JQ, Chen HM, Zhang YP, Hillis DM, Che J (2021) Herpetological phylogeographic analyses support a Miocene focal point of Himalayan uplift and biological diversification. National Science Review, 8, nwaa263. |
| [119] | Yan F, Zhou WW, Zhao HT, Yuan ZY, Wang YY, Jiang K, Jin JQ, Murphy RW, Che J, Zhang YP (2013) Geological events play a larger role than Pleistocene climatic fluctuations in driving the genetic structure of Quasipaa boulengeri (Anura: Dicroglossidae). Molecular Ecology, 22, 1120-1133. |
| [120] | Yang L, Yuan WM, Wang K (2018) Research advances of thermochronology in Mineral Deposits. Earth Science, 43, 1887-1902. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杨莉, 袁万明, 王珂 (2018) 热年代学方法、技术手段及其在矿床地质中的研究进展. 地球科学, 43, 1887-1902.] | |
| [121] | Yang WJ, Feng LD, Jiao PF, Xiang L, Yang LB, Olonova MV, Chepinoga VV, Al-Shehbaz IA, Liu JQ, Hu QJ (2023) Out of the Qinghai-Tibet plateau: Genomic biogeography of the alpine monospecific genus Megadenia (Biscutelleae, Brassicaceae). Molecular Ecology, 32, 492-503. |
| [122] |
Yang ZH (2007) PAML 4: Phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 24, 1586-1591.
DOI PMID |
| [123] | Yao TD, Wu FY, Ding L, Sun JM, Zhu LP, Piao SL, Deng T, Ni XJ, Zheng HB, Ouyang H (2015) Multispherical interactions and their effects on the Tibetan Plateau’s earth system: A review of the recent researches. National Science Review, 2, 468-488. |
| [124] | Yousefi M, Mahmoudi A, Vaissi S, Kafash A (2023) Diversity, diversification and distribution of Iranian vertebrates: The legacy of mountains uplifting, past climatic oscillations, sea level fluctuations and geographical barriers. Biodiversity and Conservation, 32, 7-36. |
| [125] | Yue LL, Chen G, Sun WB, Sun H (2012) Phylogeography of Buddleja crispa (Buddlejaceae) and its correlation with drainage system evolution in southwestern China. American Journal of Botany, 99, 1726-1735. |
| [126] | Zapata S, Calderon-Diaz L, Jaramillo C, Oboh-Ikuenobe F, Piedrahita JC, Rodríguez-Cuevas M, Cardona A, Sobel ER, Parra M, Valencia V, Patiño A, Jaramillo-Rios JS, Flores M, Glodny J (2023) Drainage and sedimentary response of the Northern Andes and the Pebas system to Miocene strike-slip tectonics: A source to sink study of the Magdalena Basin. Basin Research, 35, 1674-1717. |
| [127] |
Zhang Q, Yang YC, Liu B, Lu LM, Sauquet H, Li DZ, Chen ZD (2024) Meta-analysis provides insights into the origin and evolution of East Asian evergreen broad-leaved forests. New Phytologist, 242, 2369-2379.
DOI PMID |
| [128] | Zhang ZJ, Daly JS, Li CA, Tyrrell S, Sun XL, Yan Y (2017) Sedimentary provenance constraints on drainage evolution models for SE Tibet: Evidence from detrital K-feldspar. Geophysical Research Letters, 44, 4064-4073. |
| [129] | Zheng HY, Guo XL, Price M, He XJ, Zhou SD (2021) Effects of mountain uplift and climatic oscillations on phylogeography and species divergence of Chamaesium (Apiaceae). Frontiers in Plant Science, 12, 673200. |
| [130] | Zuckerberg B, Strong C, LaMontagne JM, St George S, Betancourt JL, Koenig WD (2020) Climate dipoles as continental drivers of plant and animal populations. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 35, 440-453. |
| [1] | 陈楠, 张全国. 实验进化研究途径[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24171-. |
| [2] | 罗正明, 刘晋仙, 张变华, 周妍英, 郝爱华, 杨凯, 柴宝峰. 不同退化阶段亚高山草甸土壤原生生物群落多样性特征及驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23136-. |
| [3] | 毛莹儿, 周秀梅, 王楠, 李秀秀, 尤育克, 白尚斌. 毛竹扩张对杉木林土壤细菌群落的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22659-. |
| [4] | 赵雯, 王丹丹, 热依拉·木民, 黄开钏, 刘顺, 崔宝凯. 阿尔山地区兴安落叶松林土壤微生物群落结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22258-. |
| [5] | 夏凡, 杨婧, 李建, 史洋, 盖立新, 黄文华, 张经纬, 杨南, 高福利, 韩莹莹, 鲍伟东. 北京地区四个豹猫亚种群肠道菌群的组成[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(9): 22103-. |
| [6] | 孙翌昕, 李英滨, 李玉辉, 李冰, 杜晓芳, 李琪. 高通量测序技术在线虫多样性研究中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22266-. |
| [7] | 高程, 郭良栋. 微生物物种多样性、群落构建与功能性状研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22429-. |
| [8] | 夏呈强, 李毅, 党延茹, 察倩倩, 贺晓艳, 秦启龙. 中印度洋与南海西部表层海水细菌多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(1): 21407-. |
| [9] | 郭英荣, 兰文军, 邹思成, 袁荣斌, 董晓雨, 曹吉锐, 杨清培, 宋庆妮. 江西武夷山国家级自然保护区林下鸟类和兽类资源的红外相机监测[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(6): 811-818. |
| [10] | 陆奇丰, 黄至欢, 骆文华. 极小种群濒危植物广西火桐、丹霞梧桐的叶绿体基因组特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(5): 586-595. |
| [11] | 戴冬, 邢华, 杨佳绒, 刘雅静, 蔡焕满, 刘宇. 植物群落稀有种维持机制与土壤反馈的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(12): 1687-1699. |
| [12] | 王楠, 黄菁华, 霍娜, 杨盼盼, 张欣玥, 赵世伟. 宁南山区不同植被恢复方式下土壤线虫群落特征:形态学鉴定与高通量测序法比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(11): 1513-1529. |
| [13] | 杨锡福, 张洪茂, 张知彬. 植物大年结实及其与动物贮食行为之间的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(7): 821-832. |
| [14] | 靳新影, 张肖冲, 金多, 陈韵, 李靖宇. 腾格里沙漠东南缘不同生物土壤结皮细菌多样性及其季节动态特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(6): 718-726. |
| [15] | 韩本凤, 周欣, 张雪. 基因组学技术在病毒鉴定与宿主溯源中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(5): 587-595. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn