



生物多样性 ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (6): 811-818. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020307 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2020307
所属专题: 数据论文
郭英荣1, 兰文军2, 邹思成2, 袁荣斌2, 董晓雨3, 曹吉锐3, 杨清培3, 宋庆妮3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-07-31
接受日期:2020-11-22
出版日期:2021-06-20
发布日期:2021-05-30
通讯作者:
宋庆妮
作者简介:* E-mail: songqingni@126.com基金资助:
Yingrong Guo1, Wenjun Lan2, Sicheng Zou2, Rongbin Yuan2, Xiaoyu Dong3, Jirui Cao3, Qingpei Yang3, Qingni Song3,*( )
)
Received:2020-07-31
Accepted:2020-11-22
Online:2021-06-20
Published:2021-05-30
Contact:
Qingni Song
摘要:
红外相机技术已成为野生动物监测的一种有效手段, 在自然保护区物种资源的清查中具有重要的应用价值。为了进一步完善江西武夷山国家级自然保护区鸟兽的编目信息, 2016年11月至2018年8月, 我们按样线法布设了52台红外相机进行连续监测。本次调查累计18,417个相机工作日, 拍摄到独立有效照片8,908张, 记录到野生兽类与鸟类共62种, 其中兽类20种, 隶属5目13科, 鸟类42种, 隶属5目14科。国家I级重点保护野生动物有2种, 即黑麂(Muntiacus crinifrons)和黄腹角雉(Tragopan caboti), 国家II级重点保护野生动物有亚洲黑熊(Ursus thibetanus)、毛冠鹿(Elaphodus cephalophus)和中华鬣羚(Capricornis milneedwardsii)等10种。被IUCN红色名录评估为易危的有4种, 近危的5种。兽类相对多度指数居于前三位的依次为小麂(Muntiacus reevesi)、藏酋猴(Macaca thibetana)和野猪(Sus scrofa); 鸟类相对多度指数位于前三位的是白鹇(Lophura nycthemera)、紫啸鸫(Myophonus caeruleus)和黑领噪鹛(Garrulax pectoralis)。物种相对多度指数沿海拔梯度呈现中部高、两侧低的单峰模式, 以800-1,200 m的区域最高。本文结果可为保护区的野生动物资源清查提供基础数据, 也为后续保护区管理政策的制定提供参考。
郭英荣, 兰文军, 邹思成, 袁荣斌, 董晓雨, 曹吉锐, 杨清培, 宋庆妮 (2021) 江西武夷山国家级自然保护区林下鸟类和兽类资源的红外相机监测. 生物多样性, 29, 811-818. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020307.
Yingrong Guo, Wenjun Lan, Sicheng Zou, Rongbin Yuan, Xiaoyu Dong, Jirui Cao, Qingpei Yang, Qingni Song (2021) Camera-trapping survey of wild mammals and ground-dwelling birds in the Jiangxi Wuyishan National Nature Reserve, China. Biodiversity Science, 29, 811-818. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020307.
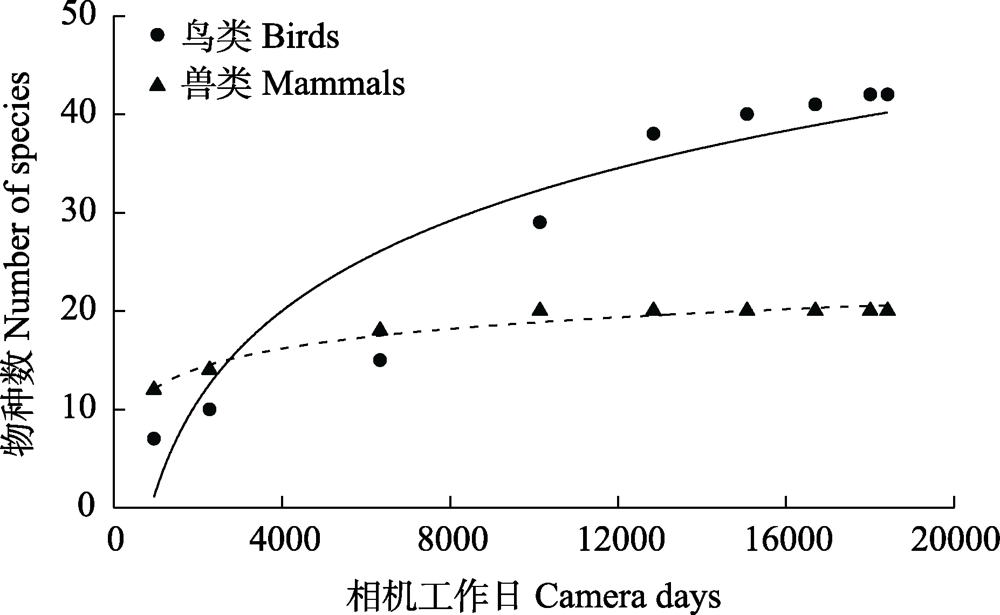
图2 江西武夷山国家级自然保护区内兽类与林下鸟类物种数量与相机工作日拟合的稀疏化曲线
Fig. 2 Rarefaction curves for estimating species number of mammals and ground-dwelling birds with increased camera days in the Jiangxi Wuyishan National Nature Reserve
| 环境变量 Environmental variables | 相机位点数 No. of camera sites | 相机工作日Camera days | 独立照片数 No. of independent photographs | 物种数 No. of species | 相对多度指数 Relative abundance index (RAI) | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index (H') |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔 Elevation | ||||||
| <800 m | 4 | 1,257 | 573 | 21 | 455.8 | 1.949 |
| 800-1,000 m | 8 | 3,425 | 1,980 | 41 | 578.1 | 2.155 |
| 1,000-1,200 m | 12 | 4,427 | 2,476 | 46 | 559.0 | 1.785 |
| 1,200-1,400 m | 9 | 2,967 | 1,295 | 27 | 436.4 | 1.602 |
| 1,400-1,600 m | 7 | 2,776 | 1,174 | 36 | 422.9 | 2.031 |
| 1,600-1,800 m | 7 | 2,288 | 735 | 30 | 321.2 | 1.808 |
| >1,800 m | 5 | 1,277 | 675 | 19 | 528.6 | 1.520 |
| 功能区划 Functional zone | ||||||
| 核心区 Core zone | 30 | 9,915 | 4,528 | 47 | 456.8 | 1.910 |
| 缓冲区 Buffer zone | 11 | 4,153 | 2,205 | 38 | 531.4 | 1.863 |
| 实验区 Experimental zone | 11 | 4,349 | 2,164 | 44 | 499.4 | 2.324 |
表1 江西武夷山国家级自然保护区兽类和林下鸟类在不同海拔与功能区的分布规律
Table 1 Species diversity of mammals and ground-dwelling birds by camera-trapping in different elevation gradients and different functional zones in the Jiangxi Wuyishan National Nature Reserve
| 环境变量 Environmental variables | 相机位点数 No. of camera sites | 相机工作日Camera days | 独立照片数 No. of independent photographs | 物种数 No. of species | 相对多度指数 Relative abundance index (RAI) | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index (H') |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔 Elevation | ||||||
| <800 m | 4 | 1,257 | 573 | 21 | 455.8 | 1.949 |
| 800-1,000 m | 8 | 3,425 | 1,980 | 41 | 578.1 | 2.155 |
| 1,000-1,200 m | 12 | 4,427 | 2,476 | 46 | 559.0 | 1.785 |
| 1,200-1,400 m | 9 | 2,967 | 1,295 | 27 | 436.4 | 1.602 |
| 1,400-1,600 m | 7 | 2,776 | 1,174 | 36 | 422.9 | 2.031 |
| 1,600-1,800 m | 7 | 2,288 | 735 | 30 | 321.2 | 1.808 |
| >1,800 m | 5 | 1,277 | 675 | 19 | 528.6 | 1.520 |
| 功能区划 Functional zone | ||||||
| 核心区 Core zone | 30 | 9,915 | 4,528 | 47 | 456.8 | 1.910 |
| 缓冲区 Buffer zone | 11 | 4,153 | 2,205 | 38 | 531.4 | 1.863 |
| 实验区 Experimental zone | 11 | 4,349 | 2,164 | 44 | 499.4 | 2.324 |
| [1] | Chen SW, Yu JP, Chen XN, Shen XL, Li S, Ma KP (2016) Camera-trapping survey on the diversity of mammal and pheasant species in Gutianshan National Nature Reserve, Zhejiang Province. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 36,292-301. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 陈声文, 余建平, 陈小南, 申小莉, 李晟, 马克平 (2016) 利用红外相机网络调查古田山自然保护区的兽类及雉类多样性. 兽类学报, 36,292-301.] | |
| [2] | Cheng SL, Fang Y, Cheng L, Zhong ZY, Zheng YQ, Wang XM, Cheng YJ (2009) Pheasants and their conservation status in Wuyishan National Nature Reserve in Jiangxi Province. Journal of Hainan Normal University (Natural Science), 22,83-85. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 程松林, 方毅, 程林, 钟志宇, 郑元庆, 王小民, 程义杰 (2009) 江西武夷山自然保护区的雉类资源及其保护. 海南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 22,83-85.] | |
| [3] | Cheng SL, Mao YX, Hu EY, Lei P, Yuan RB, Zou SC (2017) Population biology and altitudinal distribution of Tragopan caboti in Jiangxi Wuyishan Nature Reserve . Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 53(10),160-167. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 程松林, 毛夷仙, 胡尔夷, 雷平, 袁荣斌, 邹思成 (2017) 江西武夷山自然保护区黄腹角雉种群生物学及海拔分布特征. 林业科学, 53(10),160-167.] | |
| [4] | Cheng SL, Wu SY, Zhong ZY, Mao YX (2013a) Supplement of animals list in Jiangxi Wuyishan National Nature Reserve. Jiangxi Forestry Science and Technology, (2),40-43, 52. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 程松林, 吴淑玉, 钟志宇, 毛夷仙 (2013a) 江西武夷山国家级自然保护区动物名录增补. 江西林业科技, (2),40-43, 52.] | |
| [5] | Cheng SL, Yuan RB, Zou SC (2013b) Black muntjac ( Muntiacus crinifrons) found at Jiangxi Wuyishan . Acta Theriologica Sinica, 33,94, 93. (in Chinese) |
| 程松林, 袁荣斌, 邹思成 (2013b) 江西武夷山发现黑麂. 兽类学报, 33,94, 93.] | |
| [6] |
Colwell RK, Lees DC (2000) The mid-domain effect: Geometric constraints on the geography of species richness. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 15,70-76.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Frey S, Fisher JT, Burton AC, Volpe JP (2017) Investigating animal activity patterns and temporal niche partitioning using camera-trap data: Challenges and opportunities. Remote Sensing in Ecology and Conservation, 3,123-132.
DOI URL |
| [8] | He BS, Sun RQ, Chen P, Dong W, Wang J, Wang DJ, Li S (2016) Baseline survey of mammal and bird diversity using camera-trapping in the Changqing National Nature Reserve of Shaanxi Province. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 36,348-356. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 何百锁, 孙瑞谦, 陈鹏, 董伟, 王军, 王大军, 李晟 (2016) 基于红外相机技术调查长青国家级自然保护区兽类和鸟类多样性. 兽类学报, 36,348-356.] | |
| [9] | Jiang ZG, Ma Y, Wu Y, Wang YX (2015) China's Mammal Diversity and Geographic Distribution. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 蒋志刚, 马勇, 吴毅, 王应祥 (2015) 中国哺乳动物多样性及地理分布. 科学出版社. 北京.] | |
| [10] | Li GL, Li DQ, Xue YD, Wang XL, Yang JY, Yu HL (2014) Distribution of wildlife surveyed with infra-red cameras in the Shennongjia National Nature Reserve. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 50(9),97-104. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 李广良, 李迪强, 薛亚东, 王秀磊, 杨敬元, 余辉亮 (2014) 利用红外相机研究神农架自然保护区野生动物分布规律. 林业科学, 50(9),97-104.] | |
| [11] |
Li S, Wang DJ, Xiao ZS, Li XH, Wang TM, Feng LM, Wang Y (2014) Camera-trapping in wildlife research and conservation in China: Review and outlook. Biodiversity Science, 22,685-695. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
李晟, 王大军, 肖治术, 李欣海, 王天明, 冯利民, 王云 (2014) 红外相机技术在我国野生动物研究与保护中的应用与前景. 生物多样性, 22,685-695.]
DOI |
|
| [12] |
Liu F, Li DQ, Wu JG (2012) Using infra-red cameras to survey wildlife in Beijing Songshan National Nature Reserve. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32,730-739. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| 刘芳, 李迪强, 吴记贵 (2012) 利用红外相机调查北京松山国家级自然保护区的野生动物物种. 生态学报, 32,730-739.] | |
| [13] | Liu XZ (2003) Scientific Survey of the Wuyishan Nature Reserve in Jiangxi. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 刘信中 (2003) 江西武夷山自然保护区科学考察集. 科学出版社. 北京.] | |
| [14] | Ma KP (2015) Species Catalogue of China: A remarkable achievement in the field of biodiversity science in China. Biodiversity Science, 23,137-138. (in Chinese) |
| 马克平 (2015) 中国生物多样性编目取得重要进展. 生物多样性, 23,137-138.] | |
| [15] |
Seki SI (2010) Camera-trapping at artificial bathing sites provides a snapshot of a forest bird community. Journal of Forest Research, 15,307-315.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Wang C, Zhou DQ, Liang S, Su HJ, Hu CS, Zhang MM (2019) Camera-trapping survey on mammals and birds in Guizhou Chishui Alsophila National Nature Reserve . Biodiversity Science, 27,1147-1152. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
王丞, 周大庆, 梁盛, 粟海军, 胡灿实, 张明明 (2019) 贵州赤水桫椤国家级自然保护区鸟兽多样性红外相机初步监测. 生物多样性, 27,1147-1152.]
DOI |
|
| [17] | Wang GH, Li SQ, Shi ZP, Wang SN, Ye JP, Zhou QH (2016) Preliminary survey of mammal and bird diversity of Guangxi Maoershan National Nature Reserve—Based on infrared camera monitoring. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 36,338-347. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 汪国海, 李生强, 施泽攀, 王绍能, 叶建平, 周岐海 (2016) 广西猫儿山自然保护区的兽类和鸟类多样性初步调查——基于红外相机监测数据. 兽类学报, 36,338-347.] | |
| [18] |
Wang XP, Fang JY, Tang ZY (2009) The mid-domain effect hypothesis: Models, evidence and limitations. Biodiversity Science, 17,568-578. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
王襄平, 方精云, 唐志尧 (2009) 中域效应假说: 模型、证据和局限性. 生物多样性, 17,568-578.]
DOI |
|
| [19] | Xiao ZS (2016) Wildlife resource inventory using camera trapping in natural reserves in China. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 36,270-271. (in Chinese) |
| 肖治术 (2016) 红外相机技术促进我国自然保护区野生动物资源编目调查. 兽类学报, 36,270-271.] | |
| [20] |
Xiao ZS, Li XH, Wang XZ, Zhou QH, Quan RC, Shen XL, Li S (2014) Developing camera-trapping protocols for wildlife monitoring in Chinese forests. Biodiversity Science, 22,704-711. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
肖治术, 李欣海, 王学志, 周岐海, 权锐昌, 申小莉, 李晟 (2014) 探讨我国森林野生动物红外相机监测规范. 生物多样性, 22,704-711.]
DOI |
|
| [21] | Zhang ZW, Ding CQ, Ding P, Zheng GM (2003) The current status and a conservation strategy for species of Galliformes in China. Biodiversity Science, 11,414-421. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
张正旺, 丁长青, 丁平, 郑光美 (2003) 中国鸡形目鸟类的现状与保护对策. 生物多样性, 11,414-421.]
DOI |
|
| [22] | Zheng GM (2017) Checklist on the Classification and Distribution of the Birds of China, 3rd edn, Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 郑光美 (2017) 中国鸟类分类与分布名录(第三版), 科学出版社. 北京.] |
| [1] | 吴晓晴 张美惠 葛苏婷 李漫淑 宋坤 沈国春 达良俊 张健. 上海近自然林重建过程中木本植物物种多样性与地上生物量的时空动态——以闵行区生态岛为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | 王太, 宋福俊, 张永胜, 娄忠玉, 张艳萍, 杜岩岩. 河西走廊内陆河水系鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [3] | 张晶晶, 黄文彬, 陈奕廷, 杨泽鹏, 柯伟业, 彭昭杰, 魏世超, 张志伟, 胡怡思, 余文华, 周文良. 广东南澎列岛海洋生态国家级自然保护区造礁石珊瑚多样性及分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [4] | 尚华丹, 张楚晴, 王梅, 裴文娅, 李国宏, 王鸿斌. 中国杨树害虫物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [5] | 吴昱萱, 王平, 胡晓生, 丁一, 彭甜恬, 植秋滢, 巴德木其其格, 李文杰, 关潇, 李俊生. 呼伦贝尔草地退化现状评估与植被特征变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [6] | 王大伟, 程帅, 冯佳伟, 王天明. 东北地区张广才岭2015-2020年野生动物红外相机监测数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24384-. |
| [7] | 陈自宏, 张翼飞, 陈凯, 陈见影, 徐玲. 高黎贡山南段昆虫病原真菌物种多样性及影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [8] | 谭珂, 宁瑶, 王仁芬, 王晴, 梁丹萍, 辛子兵, 温放. 中国苦苣苔科植物名录与地理分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [9] | 韩佳楠, 苏杨, 李霏, 刘君妍, 赵依林, 李琳, 赵建成, 梁红柱, 李敏. 河北省苔藓植物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [10] | 李东红, 郝媛媛, 甘辉林, 张航, 刘耀猛, 他富源, 胡桂馨. 祁连山北麓中段不同类型草地蝗虫种类及分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24119-. |
| [11] | 牛红玉, 陈璐, 赵恒月, 古丽扎尔·阿不都克力木, 张洪茂. 城市化对动物的影响: 从群落到个体[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [12] | 白雪, 李正飞, 刘洋, 张君倩, 张多鹏, 罗鑫, 杨佳莉, 杜丽娜, 蒋玄空, 武瑞文, 谢志才. 西江流域大型底栖无脊椎动物物种多样性及维持机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| [13] | 许佳, 崔小娟, 张翼飞, 吴昌, 孙远东. 南岭地区鱼类多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [14] | 鲁彬悦, 李坤, 王晨溪, 李晟. 基于传感器标记的野生动物追踪技术在中国的应用现状与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23497-. |
| [15] | 邝起宇, 胡亮. 广东东海岛与硇洲岛海域底栖贝类物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 24065-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()