



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (1): 21407. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021407 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021407
夏呈强1,#, 李毅2,3,#,*( ), 党延茹3, 察倩倩3, 贺晓艳3, 秦启龙3
), 党延茹3, 察倩倩3, 贺晓艳3, 秦启龙3
收稿日期:2021-10-11
接受日期:2021-10-20
出版日期:2022-01-20
发布日期:2022-01-29
通讯作者:
李毅
作者简介:* E-mail: liyi@sxau.edu.cn# 共同第一作者
基金资助:
Chengqiang Xia1,#, Yi Li2,3,#,*( ), Yanru Dang3, Qianqian Cha3, Xiaoyan He3, Qilong Qin3
), Yanru Dang3, Qianqian Cha3, Xiaoyan He3, Qilong Qin3
Received:2021-10-11
Accepted:2021-10-20
Online:2022-01-20
Published:2022-01-29
Contact:
Yi Li
About author:First author contact:# Co-first authors
摘要:
细菌在海洋生物地球化学循环中发挥着重要作用。为更好地了解海洋细菌的特征及其在海洋环境中的潜在作用, 本文利用纯培养与16S rRNA基因高通量测序技术对中印度洋与南海西部海域表层海水细菌多样性进行研究。纯培养结果表明, 自中印度洋与南海西部表层海水中共分离275株可培养海洋细菌, 隶属于4门49属75种。变形菌门是绝对优势类群(占总株数的68.7%), 其次是放线菌门(21.5%)、拟杆菌门(9.1%)和厚壁菌门(0.7%)。在属水平, 微杆菌属(Microbacterium)与弧菌属(Vibrio)是主要的优势属, 共占总株数的30.0%。在3种分离培养基中, 自1/10 × 2216E培养基中分离细菌的数目与种类最多(89株, 30属); 分离菌株中的细菌菌株有7、9与3个属分别仅在2216E、1/10 × 2216E及葡萄糖甘露糖(glucose-mannose, GM)培养基中生长。此外, 共分离培养出50株细菌(26种)可能代表潜在新分类单元。高通量测序结果显示, 中印度洋和南海西部表层海水中共有23个门531个属。优势门类为变形菌门(72.2%)和拟杆菌门(15.3%), 优势属为嗜冷杆菌属(Psychrobacter, 24.4%)、盐单胞菌属(Halomonas, 16.3%)和亚硫酸杆菌属(Sulfitobacter, 13.9%)。此外, 中印度洋表层海水细菌Shannon-Wiener指数与Pielou均匀度指数显著高于南海西部(P < 0.05), 且细菌群落结构显著不同(P < 0.05)。综合纯培养与原位细菌数据得出, 中印度洋与南海西部海洋细菌具有丰富的多样性, 具有进一步开发研究的价值。
夏呈强, 李毅, 党延茹, 察倩倩, 贺晓艳, 秦启龙 (2022) 中印度洋与南海西部表层海水细菌多样性. 生物多样性, 30, 21407. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021407.
Chengqiang Xia, Yi Li, Yanru Dang, Qianqian Cha, Xiaoyan He, Qilong Qin (2022) Diversity of culturable and in situ bacteria in surface seawater from the central Indian Ocean and the western South China Sea. Biodiversity Science, 30, 21407. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021407.
| 站位 Station | 经度 Longitude | 纬度 Latitude | 温度 Temperature (℃) | OTU | Margalef丰富度指数 Margalef’s richness index | Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou’s evenness index | Faith系统发育多样性指数 Faith’s PD index | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IO_1 | 51.30°E | 36.93°S | 19.8 | 519 | 45.15 | 0.75 | 32.00 | 6.77 |
| IO_14 | 85.36°E | 19.52°S | 25.4 | 354 | 30.77 | 0.59 | 29.17 | 4.99 |
| IO_20 | 96.62°E | 11.29°S | 29.2 | 349 | 30.33 | 0.62 | 26.18 | 5.24 |
| SCS_4 | 111.47°E | 9.25°N | 30.5 | 470 | 40.88 | 0.55 | 35.39 | 4.88 |
| SCS_6 | 112.52°E | 12.78°N | 30.0 | 380 | 33.03 | 0.49 | 31.09 | 4.22 |
| SCS_7 | 113.25°E | 15.17°N | 29.6 | 379 | 32.95 | 0.54 | 30.76 | 4.63 |
| SCS_8 | 114.20°E | 17.17°N | 30.0 | 424 | 36.87 | 0.53 | 35.08 | 4.66 |
| SCS_9 | 115.45°E | 19.19°N | 30.9 | 323 | 28.07 | 0.52 | 27.58 | 4.32 |
表1 中印度洋与南海西部采样位点信息及非培养细菌群落生物多样性指数
Table 1 The information of sampling stations of the central Indian Ocean and the western South China Sea and biodiversity indices of uncultured bacterial communities
| 站位 Station | 经度 Longitude | 纬度 Latitude | 温度 Temperature (℃) | OTU | Margalef丰富度指数 Margalef’s richness index | Pielou均匀度指数 Pielou’s evenness index | Faith系统发育多样性指数 Faith’s PD index | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IO_1 | 51.30°E | 36.93°S | 19.8 | 519 | 45.15 | 0.75 | 32.00 | 6.77 |
| IO_14 | 85.36°E | 19.52°S | 25.4 | 354 | 30.77 | 0.59 | 29.17 | 4.99 |
| IO_20 | 96.62°E | 11.29°S | 29.2 | 349 | 30.33 | 0.62 | 26.18 | 5.24 |
| SCS_4 | 111.47°E | 9.25°N | 30.5 | 470 | 40.88 | 0.55 | 35.39 | 4.88 |
| SCS_6 | 112.52°E | 12.78°N | 30.0 | 380 | 33.03 | 0.49 | 31.09 | 4.22 |
| SCS_7 | 113.25°E | 15.17°N | 29.6 | 379 | 32.95 | 0.54 | 30.76 | 4.63 |
| SCS_8 | 114.20°E | 17.17°N | 30.0 | 424 | 36.87 | 0.53 | 35.08 | 4.66 |
| SCS_9 | 115.45°E | 19.19°N | 30.9 | 323 | 28.07 | 0.52 | 27.58 | 4.32 |

图3 三种不同培养基分离培养的(A)细菌多样性及(B)不同属的维恩分析。2216E, 2216E培养基; 1/10 × 2216E, 稀释10倍的2216E培养基; GM, 葡萄糖甘露糖培养基。
Fig. 3 Bacterial diversity and Venn analysis of differential genera isolated in three different media. 2216E, 2216E culture medium; 1/10 × 2216E, Diluted 10 times of 2216E culture medium; GM, Glucose-mannose culture medium.
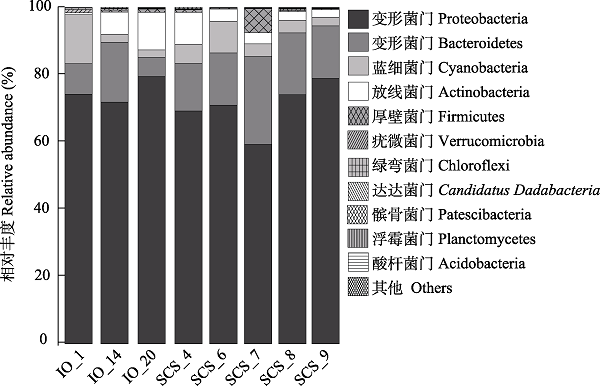
图4 中印度洋与南海西部表层海水中原位细菌在门水平上的组成分布
Fig. 4 In situ bacterial composition distributions at phylum level across the surface seawaters of the central Indian Ocean (IO) and the western South China Sea (SCS)

图5 中印度洋与南海西部表层海水中原位细菌在属水平上的分布
Fig. 5 In situ bacterial composition distributions at genus level across the surface seawaters of the central Indian Ocean (IO) and the western South China Sea (SCS)
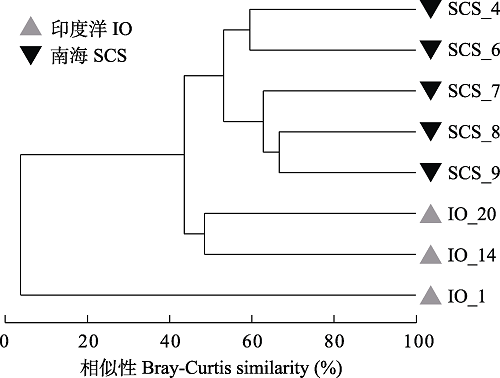
图6 基于Bray-Curtis相似性的中印度洋及南海西部表层海水中ASV聚类分析
Fig. 6 The cluster dendrogram analysis based on Bray-Curtis similarity of ASVs in the surface seawaters of the central Indian Ocean (IO) and the western South China Sea (SCS)
| [1] |
Brakstad OG, Lødeng AGG (2005) Microbial diversity during biodegradation of crude oil in seawater from the North Sea. Microbial Ecology, 49, 94-103.
PMID |
| [2] |
Bryant JA, Aylward FO, Eppley JM, Karl DM, Church MJ, DeLong EF (2016) Wind and sunlight shape microbial diversity in surface waters of the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre. The ISME Journal, 10, 1308-1322.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Bull AT, Stach JEM, Ward AC, Goodfellow M (2005) Marine actinobacteria: Perspectives, challenges, future directions. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 87, 65-79.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley R, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nature Methods, 7, 335-336.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | Clarke KR (1993) Non-parametric multivariate analysis of changes in community structure. Australian Journal of Ecology, 18, 117-143. |
| [6] |
Curson ARJ, Todd JD, Sullivan MJ, Johnston AWB (2011) Catabolism of dimethylsulphoniopropionate: Microorganisms, enzymes and genes. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 9, 849-859.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Dang YR, Sun YY, Sun LL, Yuan XX, Li Y, Qin QL, Chen XL, Zhang YZ, Shi M, Zhang XY (2019) Muricauda nanhaiensis sp. nov., isolated from seawater of the South China Sea. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 69, 2089-2094.
DOI URL |
| [8] | Du R, Yu M, Cheng JG, Zhang JJ, Tian XR, Zhang XH (2019) Diversity and sulfur oxidation characteristics of cultivable sulfur oxidizing bacteria in hydrothermal fields of Okinawa Trough. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 59, 1036-1049. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杜瑞, 于敏, 程景广, 张静静, 田晓荣, 张晓华 (2019) 冲绳海槽热液区可培养硫氧化细菌多样性及其硫氧化特性. 微生物学报, 59, 1036-1049.] | |
| [9] |
Frankena J, van Verseveld HW, Stouthamer AH (1988) Substrate and energy costs of the production of exocellular enzymes by Bacillus licheniformis. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 32, 803-812.
PMID |
| [10] | Gauch HG, Scruggs WM (1980) Variants of Bray-Curtis polar ordination. Vegetatio, 40, 147-153. |
| [11] |
Glöckner FO, Fuchs BM, Amann R (1999) Bacterioplankton compositions of lakes and oceans: A first comparison based on fluorescence in situ hybridization. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 65, 3721-3726.
PMID |
| [12] |
Goodfellow M, Fiedler HP (2010) A guide to successful bioprospecting: Informed by actinobacterial systematics. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 98, 119-142.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Hanson CA, Fuhrman JA, Horner-Devine MC, Martiny JBH (2012) Beyond biogeographic patterns: Processes shaping the microbial landscape. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 10, 497-506.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
Ivanova EP, Gorshkova NM, Sawabe T, Zhukova NV, Hayashi K, Kurilenko VV, Alexeeva Y, Buljan V, Nicolau DV, Mikhailov VV, Christen R (2004) Sulfitobacter delicatus sp. nov. and Sulfitobacter dubius sp. nov., respectively from a starfish (Stellaster equestris) and sea grass (Zostera marina). International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 54, 475-480.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
Keylock CJ (2005) Simpson diversity and the Shannon-Wiener index as special cases of a generalized entropy. Oikos, 109, 203-207.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Koblížek M, Béjà O, Bidigare RR, Christensen S, Benitez-Nelson B, Vetriani C, Kolber MK, Falkowski PG, Kolber ZS (2003) Isolation and characterization of Erythrobacter sp. strains from the upper ocean. Archives of Microbiology, 180, 327-338.
DOI URL |
| [17] | Li HY, Chen MX, Jiao NZ (2012) The community composition of bacterioplankton at typical station in the Changjiang Estuary. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 34, 183-188. (in Chinese) |
| [ 李和阳, 陈明霞, 焦念志 (2012) 长江口典型站位浮游细菌类群的组成特征研究. 海洋学报(中文版), 34, 183-188.] | |
| [18] |
Li Y, Sun LL, Sun ML, Su HN, Zhang XY, Xie BB, Chen XL, Zhang YZ, Qin QL (2018) Vertical and horizontal biogeographic patterns and major factors affecting bacterial communities in the open South China Sea. Scientific Reports, 8, 8800.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Li Y, Wang ZB, Zhang XY, Dang YR, Sun LL, Zhang WP, Fu HH, Yang GP, Wang M, McMinn A, Chen XL, Chen Y, Wang S, Zhang YZ, Qin QL (2021) Experimental evidence for long-term coexistence of copiotrophic and oligotrophic bacteria in pelagic surface seawater. Environmental Microbiology, 23, 1162-1173.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Lin Y, Liu RH, Zhou S, Zhu XY, Wang JY, Zhang XH (2021) Diversity of culturable heterotrophic bacteria from sediments of the Mariana Trench and their ability to degrade dimethylsulfoniopropionate (DMSP). Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 61, 828-844. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 林钰, 刘荣华, 周顺, 朱晓雨, 王金燕, 张晓华 (2021) 马里亚纳海沟沉积物可培养异养细菌的多样性及其DMSP降解能力. 微生物学报, 61, 828-844.] | |
| [21] |
Liu JW, Yang HM, Zhao MX, Zhang XH (2014a) Spatial distribution patterns of benthic microbial communities along the Pearl Estuary, China. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 37, 578-589.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Liu YJ, Tian XP, Huang XF, Long LJ, Zhang S (2014b) Diversity of cultivable bacteria isolated from marine sediment environments in South China Sea. Microbiology China, 41, 661-673. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 刘玉娟, 田新朋, 黄小芳, 龙丽娟, 张偲 (2014) 中国南海沉积环境可培养细菌多样性研究. 微生物学通报, 41, 661-673.] | |
| [23] |
Louca S, Parfrey LW, Doebeli M (2016) Decoupling function and taxonomy in the global ocean microbiome. Science, 353, 1272-1277.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Qin QL, Zhang XY, Wang XM, Liu GM, Chen XL, Xie BB, Dang HY, Zhou BC, Yu J, Zhang YZ (2010) The complete genome of Zunongwangia profunda SM-A 87 reveals its adaptation to the deep-sea environment and ecological role in sedimentary organic nitrogen degradation. BMC Genomics, 11, 247. |
| [25] | Qu TD, Girton JB, Whitehead JA (2006) Deepwater overflow through Luzon Strait. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 111, C01002. |
| [26] | R Core Team (2016) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. |
| [27] |
Rappé MS, Giovannoni SJ (2003) The uncultured microbial majority. Annual Review of Microbiology, 57, 369-394.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Salazar G, Cornejo-Castillo FM, Benítez-Barrios V, Fraile- Nuez E, Álvarez-Salgado XA, Duarte CM, Gasol JM, Acinas SG (2016) Global diversity and biogeography of deep-sea pelagic prokaryotes. The ISME Journal, 10, 596- 608.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Schut F, de Vries EJ, Gottschal JC, Robertson BR, Harder W, Prins RA, Button DK (1993) Isolation of typical marine bacteria by dilution culture: Growth, maintenance, and characteristics of isolates under laboratory conditions. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 59, 2150-2160.
DOI PMID |
| [30] | Su J, Ming HX, Chen QR, Zhang CX, Guan DM, Fan JF (2020) Analysis on bacterial diversity in Nansha deep-sea sediments. Journal of Biology, 37(1), 50-53. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 苏洁, 明红霞, 陈泉睿, 张春鑫, 关道明, 樊景凤 (2020) 南沙海区深海沉积物中细菌多样性分析. 生物学杂志, 37(1), 50-53.] | |
| [31] |
Sun LL, Dang YR, Li Y, Qin QL, Su HN, Li PY, Chen XL, Zhang YZ, Zhang XY (2019) Parvularcula marina sp. nov., isolated from surface water of the South China Sea, and emended description of the genus Parvularcula. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 69, 2571-2576.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Wang J, Kan JJ, Borecki L, Zhang XD, Wang DX, Sun J (2016) A snapshot on spatial and vertical distribution of bacterial communities in the eastern Indian Ocean. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 35, 85-93.
DOI |
| [33] |
Wang XW, Liu ZY, Peng SQ (2017) Impact of tidal mixing on water mass transformation and circulation in the South China Sea. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 47, 419-432.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Williams TJ, Wilkins D, Long E, Evans F, DeMaere MZ, Raftery MJ, Cavicchioli R (2013) The role of planktonic Flavobacteria in processing algal organic matter in coastal East Antarctica revealed using metagenomics and metaproteomics. Environmental Microbiology, 15, 1302- 1317.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
Yoon JH, Kang KH, Oh TK, Park YH (2004) Erythrobacter aquimaris sp. nov., isolated from sea water of a tidal flat of the Yellow Sea in Korea. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 54, 1981-1985.
DOI URL |
| [36] | Yu QW, Hu LQ, Li F, Yi XX, Gao CH (2015) Diversity and biotoxicity of cultivable marine bacteria isolated from deep-sea sediment of the South China Sea. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 46, 2203-2208. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 于清武, 胡丽琴, 李菲, 易湘茜, 高程海 (2015) 南海深海沉积物可培养细菌多样性及其生物毒性分析. 南方农业学报, 46, 2203-2208.] | |
| [37] | Yu SX, Wang YC, Li JL, Pang YL, Qin S (2019) Comparative analysis of bacteria communities from water and surface sediment in northern South China Sea. Advances in Marine Science, 37(1), 102-114. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 于淑贤, 王寅初, 李佳霖, 庞云龙, 秦松 (2019) 南海北部水层间及沉积表层细菌群落的比较分析. 海洋科学进展, 37(1), 102-114.] | |
| [38] |
Zhang Y, Li J, Cheng XH, Luo YF, Mai ZM, Zhang S (2018) Community differentiation of bacterioplankton in the epipelagic layer in the South China Sea. Ecology and Evolution, 8, 4932-4948.
DOI URL |
| [39] | Zhuang K, Hu XJ, Cao YC, Xu YN, Zhang JS, Wen GL (2020) Bacterial community structure and its utilization characteristics of carbon sources in water of South China Sea under different low-nutrient culture conditions. Microbiology China, 47, 2697-2710. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 庄康, 胡晓娟, 曹煜成, 许云娜, 张建设, 文国樑 (2020) 不同寡营养培养条件下南海水体细菌群落结构及其对碳源的利用特征. 微生物学通报, 47, 2697-2710.] |
| [1] | 罗正明, 刘晋仙, 张变华, 周妍英, 郝爱华, 杨凯, 柴宝峰. 不同退化阶段亚高山草甸土壤原生生物群落多样性特征及驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 23136-. |
| [2] | 毛莹儿, 周秀梅, 王楠, 李秀秀, 尤育克, 白尚斌. 毛竹扩张对杉木林土壤细菌群落的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22659-. |
| [3] | 赵雯, 王丹丹, 热依拉·木民, 黄开钏, 刘顺, 崔宝凯. 阿尔山地区兴安落叶松林土壤微生物群落结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22258-. |
| [4] | 夏凡, 杨婧, 李建, 史洋, 盖立新, 黄文华, 张经纬, 杨南, 高福利, 韩莹莹, 鲍伟东. 北京地区四个豹猫亚种群肠道菌群的组成[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(9): 22103-. |
| [5] | 孙翌昕, 李英滨, 李玉辉, 李冰, 杜晓芳, 李琪. 高通量测序技术在线虫多样性研究中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22266-. |
| [6] | 高程, 郭良栋. 微生物物种多样性、群落构建与功能性状研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(10): 22429-. |
| [7] | 陆奇丰, 黄至欢, 骆文华. 极小种群濒危植物广西火桐、丹霞梧桐的叶绿体基因组特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(5): 586-595. |
| [8] | 王楠, 黄菁华, 霍娜, 杨盼盼, 张欣玥, 赵世伟. 宁南山区不同植被恢复方式下土壤线虫群落特征:形态学鉴定与高通量测序法比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(11): 1513-1529. |
| [9] | 靳新影, 张肖冲, 金多, 陈韵, 李靖宇. 腾格里沙漠东南缘不同生物土壤结皮细菌多样性及其季节动态特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(6): 718-726. |
| [10] | 韩本凤, 周欣, 张雪. 基因组学技术在病毒鉴定与宿主溯源中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(5): 587-595. |
| [11] | 张全建, 杨彪, 付强, 王磊, 龚旭, 张远彬. 邛崃山系水鹿的冬季食性[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(10): 1192-1201. |
| [12] | 陆琪,胡强,施小刚,金森龙,李晟,姚蒙. 基于分子宏条形码分析四川卧龙国家级自然保护区雪豹的食性[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(9): 960-969. |
| [13] | 刘君, 王宁, 崔岱宗, 卢磊, 赵敏. 大小兴安岭可培养细菌的资源多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(8): 903-910. |
| [14] | 刘君, 王宁, 崔岱宗, 卢磊, 赵敏. 小兴安岭大亮子河国家森林公园不同生境下土壤细菌多样性和群落结构[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(8): 911-918. |
| [15] | 刘山林. DNA条形码参考数据集构建和序列分析相关的新兴技术[J]. 生物多样性, 2019, 27(5): 526-533. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()