



生物多样性 ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (5): 22345. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022345 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022345
• 研究报告: 植物多样性 • 下一篇
谢艳秋1, 黄晖1,2, 王春晓1, 何雅琴3, 江怡萱1, 刘子琳1, 邓传远1,*( ), 郑郁善1
), 郑郁善1
收稿日期:2022-06-24
接受日期:2023-04-10
出版日期:2023-05-20
发布日期:2023-05-19
通讯作者:
* E-mail: 基金资助:
Yanqiu Xie1, Hui Huang1,2, Chunxiao Wang1, Yaqin He3, Yixuan Jiang1, Zilin Liu1, Chuanyuan Deng1,*( ), Yushan Zheng1
), Yushan Zheng1
Received:2022-06-24
Accepted:2023-04-10
Online:2023-05-20
Published:2023-05-19
Contact:
* E-mail: 摘要:
福建海岛具有丰富的滨海特有植物资源, 研究其物种丰富度的分布格局及机制, 能够为滨海特有植物资源保护提供依据。本研究探讨了福建53个海岛滨海特有植物的种-面积关系, 以及景观、人为干扰和气候3个方面10个环境因子对滨海特有植物物种丰富度的影响。同时还探讨了不同生活型(乔木、灌木、草本)对海岛环境因子的响应。结果表明: 滨海特有植物和不同生活型植物的种-面积关系呈现物种丰富度随着面积增加而增加的趋势, 滨海特有植物、乔木、灌木和草本的种-面积关系的斜率(z)分别为0.16、0.15、0.15和0.14。景观环境因子中的面积、形状指数和周长面积比是解释福建海岛滨海特有植物及不同生活型植物物种丰富度的主要决定因素, 滨海特有植物及各生活型植物物种丰富度随着面积和形状指数的增加而增加, 而滨海特有植物、灌木和草本的物种丰富度随着周长面积比的增加而减少。此外, 不同生活型植物的物种丰富度对海岛环境因子的响应存在差异, 除景观方面的因子外, 气候对乔木的解释率最大, 达9.82%。综上所述, 相比于其他海岛生态系统, 福建海岛滨海特有植物及不同生活型植物的物种丰富度与面积密切相关, 其较低的斜率(z)表明滨海特有植物对海岛生境的敏感性较弱。景观方面的环境因子相比气候和人为干扰方面贡献了更多的解释率。以往研究发现岛屿环境因子与生境异质性显著相关, 如岛屿越大、形状越不规则、周长面积比越低, 则生境异质性越高。因此生境异质性的提升可能是解释滨海特有植物丰富度随景观环境因子变化的内在机制。
谢艳秋, 黄晖, 王春晓, 何雅琴, 江怡萱, 刘子琳, 邓传远, 郑郁善 (2023) 福建海岛滨海特有植物种-面积关系及物种丰富度决定因素. 生物多样性, 31, 22345. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022345.
Yanqiu Xie, Hui Huang, Chunxiao Wang, Yaqin He, Yixuan Jiang, Zilin Liu, Chuanyuan Deng, Yushan Zheng (2023) Determinants of species-area relationship and species richness of coastal endemic plants in the Fujian islands. Biodiversity Science, 31, 22345. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022345.
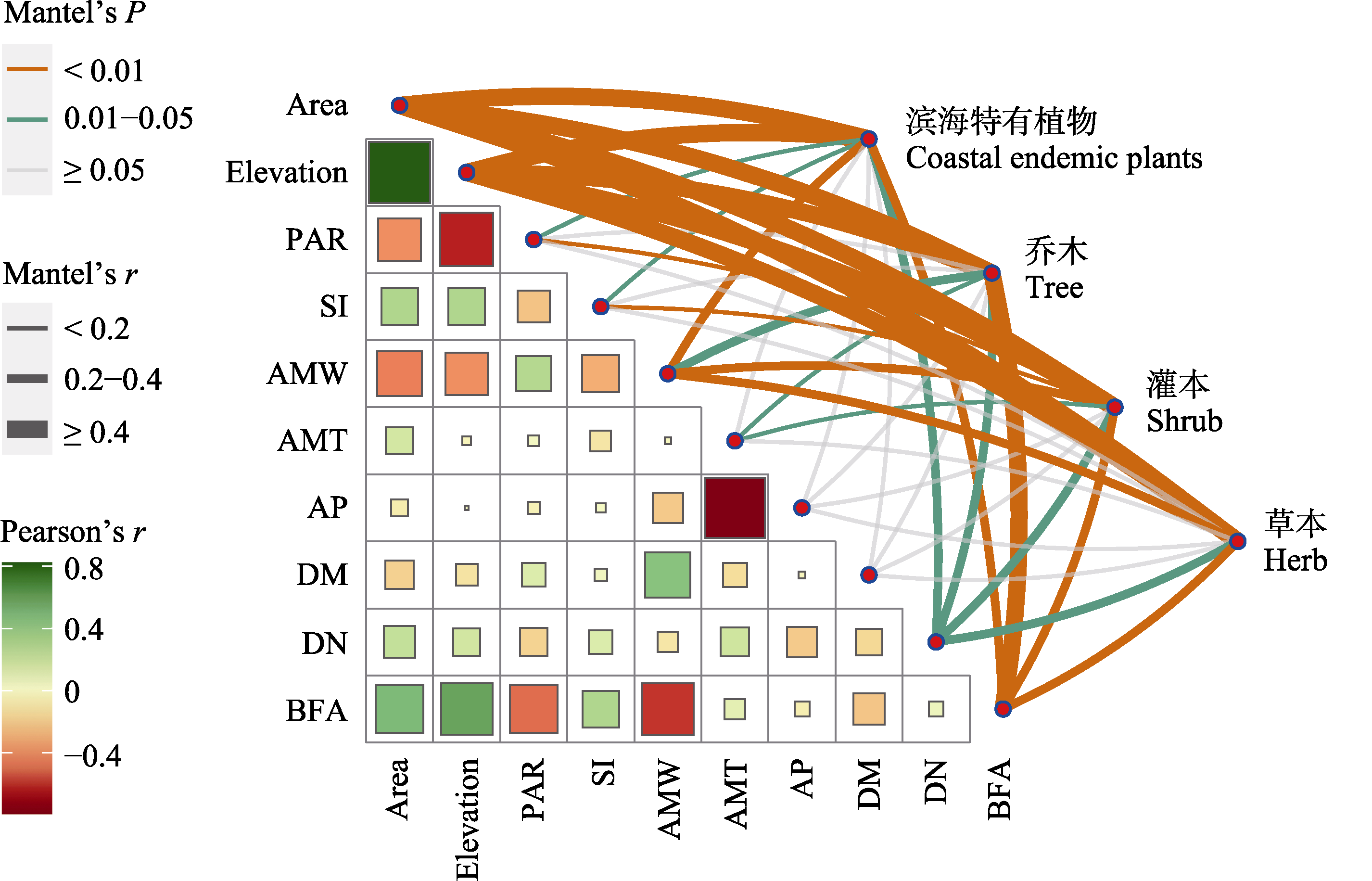
图4 环境因子之间的Pearson相关性分析和Mantel检验。Area: 面积; Elevation: 海拔; PAR: 周长面积比; SI: 形状指数; AMW: 年均风速; AMT: 年均温; AP: 年降水量; DM: 距大陆距离; DN: 距最近大岛距离; BFA: 建筑与农田面积占比。* P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001。
Fig. 4 Pearson correlation and Mantel test between environmental factors. Area, Area; Elevation, Elevation; PAR, Perimeter area ratio; SI, Shape index; AMW, Annual mean wind; AMT, Annual mean temperature; AP, Annual precipitation; DM, Distance to the mainland; DN, Distance to the nearest big island; BFA, Proportion of buildings to farmland area. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001.
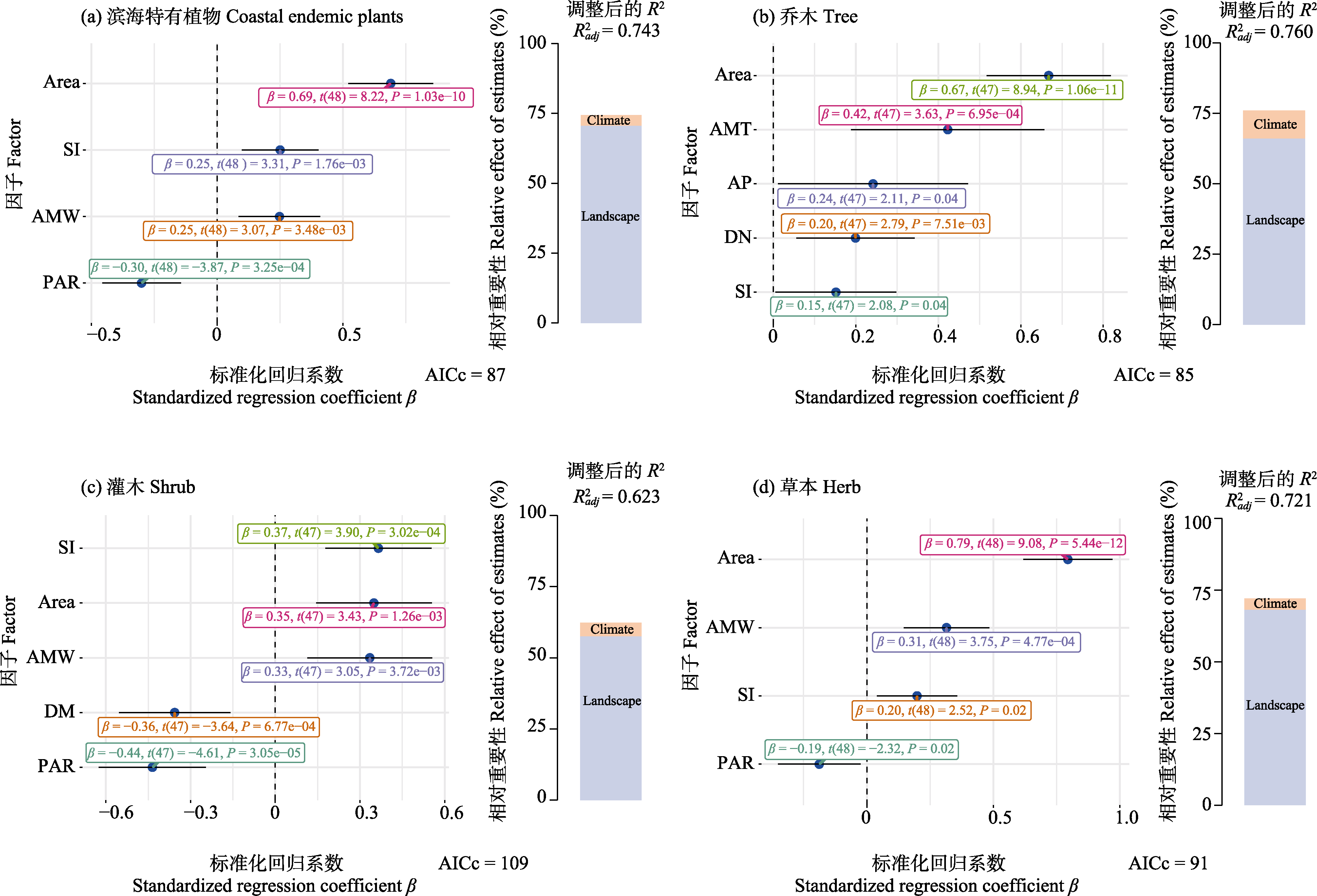
图5 滨海特有植物以及不同生活型物种丰富度的最佳模型选择和层次分割分析。图中森林图为使用全子集回归, 并根据最小AICc值筛选得出的最优模型, 森林图中虚线左侧为负相关, 右侧为正相关。柱形图为基于最优模型的层次分割分析。Area: 面积; Elevation: 海拔; PAR: 周长面积比; SI: 形状指数; AMW: 年均风速; AMT: 年均温; AP: 年降水量; DM: 距大陆距离; DN: 距最近大岛距离; BFA: 建筑与农田面积占比。
Fig. 5 The best model selection and hierarchical partitioning analysis of coastal endemic plants and different growth forms of species richness. The forest plot in the figure shows the optimal model obtained by using full subset regression and screening based on the minimum AICc value. The left side of the dashed line in the forest plot shows a negative correlation, while the right side shows a positive correlation. The column chart is a hierarchical segmentation analysis based on the optimal model. Area, Area; Elevation, Elevation; PAR, Perimeter area ratio; SI, Shape index; AMW, Annual mean wind; AMT, Annual mean temperature; AP, Annual precipitation; DM, Distance to the mainland; DN, Distance to the nearest big island; BFA, Proportion of buildings to farmland area.
| [1] |
Borges PAV, Hortal J (2009) Time, area and isolation: Factors driving the diversification of Azorean arthropods. Journal of Biogeography, 36, 178-191.
DOI URL |
| [2] | Cabral JS, Weigelt P, Kissling WD, Kreft H (2014) Biogeographic, climatic and spatial drivers differentially affect α-, β- and γ-diversities on oceanic archipelagos. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 281, 20133246. |
| [3] |
Cagnolo L, Valladares G, Salvo A, Cabido M, Zak M (2009) Habitat fragmentation and species loss across three interacting trophic levels: Effects of life-history and food-web traits. Conservation Biology, 23, 1167-1175.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
Chen C, Yang X, Tan X, Wang Y (2020) The role of habitat diversity in generating the small-island effect. Ecography, 43, 1241-1249.
DOI URL |
| [5] | Chen ZH, Tang ZL, Chiu PL (1995) A study on the flora of the islands of Zhejiang Province. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 17, 405-412. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈征海, 唐正良, 裘宝林 (1995) 浙江海岛植物区系的研究. 云南植物研究, 17, 405-412.] | |
| [6] |
Chiarucci A, Bacaro G, Triantis KA, Fernández-Palacios JM (2011) Biogeographical determinants of pteridophytes and spermatophytes on oceanic archipelagos. Systematics and Biodiversity, 9, 191-201.
DOI URL |
| [7] | Chisholm RA, Fung T, Chimalakonda D, O’Dwyer JP (2016) Maintenance of biodiversity on islands. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 283, 20160102. |
| [8] | Committee of Fujian Province Island Resources Comprehensive Investigation (1996) Comprehensive Survey and Research Report on Island Resources of Fujian Province. China Ocean Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [福建省海岛资源综合调查委员会 (1996) 福建省海岛资源综合调查研究报告. 海洋出版社, 北京.] | |
| [9] |
Ewers RM, Didham RK (2006) Confounding factors in the detection of species responses to habitat fragmentation. Biological Reviews, 81, 117-142.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
Fahrig L (2013) Rethinking patch size and isolation effects: The habitat amount hypothesis. Journal of Biogeography, 40, 1649-1663.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Fang JY, Wang XP, Shen ZH, Tang ZY, He JS, Yu D, Jiang Y, Wang ZH, Zheng CY, Zhu JL, Guo ZD (2009) Methods and protocols for plant community inventory. Biodiversity Science, 17, 533-548. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[方精云, 王襄平, 沈泽昊, 唐志尧, 贺金生, 于丹, 江源, 王志恒, 郑成洋, 朱江玲, 郭兆迪 (2009) 植物群落清查的主要内容、方法和技术规范. 生物多样性, 17, 533-548.]
DOI |
|
| [12] |
Francisco-Ortega J, Santos-Guerra A, Kim SC, Crawford D (2000) Plant genetic diversity in the Canary Islands: A conservation perspective. American Journal of Botany, 87, 909-919.
PMID |
| [13] |
Heatwole H (1991) Factors affecting the number of species of plants on islands of the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Journal of Biogeography, 18, 213-221.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Hoffmeister TS, Vet LEM, Biere A, Holsinger K, Filser J (2005) Ecological and evolutionary consequences of biological invasion and habitat fragmentation. Ecosystems, 8, 657-667.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Honnay O, Piessens K, Van Landuyt W, Hermy M, Gulinck H (2003) Satellite based land use and landscape complexity indices as predictors for regional plant species diversity. Landscape and Urban Planning, 63, 241-250.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Hu G, Feeley KJ, Wu JG, Xu GF, Yu MJ (2011) Determinants of plant species richness and patterns of nestedness in fragmented landscapes: Evidence from land-bridge islands. Landscape Ecology, 26, 1405-1417.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Irl SDH, Obermeier A, Beierkuhnlein C, Steinbauer MJ (2020) Climate controls plant life-form patterns on a high-elevation oceanic island. Journal of Biogeography, 47, 2261-2273.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Irl SDH, Schweiger AH, Steinbauer MJ, Ah-Peng C, Arévalo JR, Beierkuhnlein C, Chiarucci A, Daehler CC, Fernández- Palacios JM, Flores O, Kueffer C, Maděra P, Otto R, Schweiger JMI, Strasberg D, Jentsch A (2021) Human impact, climate and dispersal strategies determine plant invasion on islands. Journal of Biogeography, 48, 1889-1903.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Kalmar A, Currie DJ (2006) A global model of island biogeography. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 15, 72-81.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Kohn DD, Walsh DM (1994) Plant species richness—The effect of island size and habitat diversity. Journal of Ecology, 82, 367-377.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Kreft H, Jetz W, Mutke J, Kier G, Barthlott W (2008) Global diversity of island floras from a macroecological perspective. Ecology Letters, 11, 116-127.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
Kubota Y, Shiono T, Kusumoto B (2015) Role of climate and geohistorical factors in driving plant richness patterns and endemicity on the east Asian continental islands. Ecography, 38, 639-648.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Liu JL, Vellend M, Wang Z, Yu MJ (2018) High beta diversity among small islands is due to environmental heterogeneity rather than ecological drift. Journal of Biogeography, 45, 2252-2261.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Lomolino M (2000) A species-based theory of insular zoogeography. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 9, 39-58.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
MacArthur RH, Wilson EO (1963) An equilibrium theory of insular zoogeography. Evolution, 17, 373-387.
DOI URL |
| [26] | MacArthur RH, Wilson EO (1967) The Theory of Island Biogeography. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [27] |
Mologni F, Bellingham PJ, Tjørve E, Cameron EK, Wright AE, Burns KC, Munoz F (2021) Similar yet distinct distributional patterns characterize native and exotic plant species richness across northern New Zealand islands. Journal of Biogeography, 48, 1731-1745.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Murcia C (1995) Edge effects in fragmented forests: Implications for conservation. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 10, 58-62.
DOI URL |
| [29] | Neter J, Kutner MH, Nachtsheim CJ, Wasserman W (1996) Applied Linear Statistical Model: Regression, Analysis of Variance, and Experimental Design. Irwin Professional Publishing, Chicago. |
| [30] |
Neufeld C, Starko S, Burns K (2017) Disturbance and diversity in a continental archipelago: A mechanistic framework linking area, height, and exposure. Ecosphere, 8, e01957.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Panitsa M, Tzanoudakis D, Triantis KA, Sfenthourakis S (2006) Patterns of species richness on very small islands: The plants of the Aegean archipelago. Journal of Biogeography, 33, 1223-1234.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Parepa M, Fischer M, Bossdorf O (2013) Environmental variability promotes plant invasion. Nature Communications, 4, 1604.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
Pinheiro HT, Bernardi G, Simon T, Joyeux JC, Macieira RM, Gasparini JL, Rocha C, Rocha LA (2017) Island biogeography of marine organisms. Nature, 549, 82-85.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Ricklefs RE (1987) Community diversity: Relative roles of local and regional processes. Science, 235, 167-171.
PMID |
| [35] |
Rojas-Sandoval J, Ackerman JD, Tremblay RL (2020) Island biogeography of native and alien plant species: Contrasting drivers of diversity across the Lesser Antilles. Diversity and Distributions, 26, 1539-1550.
DOI URL |
| [36] | Rosenzweig ML (1995) Species Diversity in Space and Time. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
| [37] | Santos AMC, Whittaker RJ, Triantis KA, Borges PAV, Jones OR, Quicke DLJ, Hortal J (2010) Are species-area relationships from entire archipelagos congruent with those of their constituent islands? Global Ecology and Biogeography, 19, 527-540. |
| [38] |
Schrader J, König C, Triantis KA, Trigas P, Kreft H, Weigelt P (2020) Species-area relationships on small islands differ among plant growth forms. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 29, 814-829.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Sfenthourakis S, Triantis KA (2009) Habitat diversity, ecological requirements of species and the small island effect. Diversity and Distributions, 15, 131-140.
DOI URL |
| [40] | Shi DF, Guo L, Lü HF (1996) Flora of the Taizhou islands. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry College, 13, 48-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [施德法, 郭亮, 吕洪飞 (1996) 台州列岛植物区系的研究. 浙江林学院学报, 13, 48-52.] | |
| [41] |
Steinbauer MJ, Irl SDH, González-Mancebo JM, Breiner FT, Hernández-Hernández R, Hopfenmüller S, Kidane Y, Jentsch A, Beierkuhnlein C (2017) Plant invasion and speciation along elevational gradients on the oceanic island La Palma, Canary Islands. Ecology and Evolution, 7, 771-779.
DOI PMID |
| [42] |
Tamme R, Götzenberger L, Zobel M, Bullock JM, Hooftman DAP, Kaasik A, Pärtel M (2014) Predicting species’ maximum dispersal distances from simple plant traits. Ecology, 95, 505-513.
PMID |
| [43] |
Triantis KA, Mylonas M, Lika K, Vardinoyannis K (2003) A model for the species-area-habitat relationship. Journal of Biogeography, 30, 19-27.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Valli AT, Kougioumoutzis K, Iliadou E, Panitsa M, Trigas P (2019) Determinants of alpha and beta vascular plant diversity in Mediterranean island systems: The Ionian islands, Greece. Nordic Journal of Botany, 37, e02156.
DOI URL |
| [45] | Wang JW, Wei X, Chen QX, Li XW, Yang S (2017) Factors affecting species richness and beta diversity of vascular plants on small islands in the Wenzhou region of eastern China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 523-540. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王金旺, 魏馨, 陈秋夏, 李效文, 杨升 (2017) 温州沿海小型海岛植物丰富度和β多样性及其影响因子. 生态学报, 37, 523-540.] | |
| [46] |
Wang ZM, Ye W, Xing FW (2019) Bryophyte diversity on a tropical continental island (Hainan, China): Potential vulnerable species and environmental indicators. Journal of Bryology, 41, 350-360.
DOI URL |
| [47] | Whittaker RJ, Fernández-Palacios JM (2007) Island Biogeography: Ecology, Evolution, and Conservation. Oxford University Press, New York. |
| [48] |
Whittaker RJ, Triantis KA, Ladle RJ (2008) A general dynamic theory of oceanic island biogeography. Journal of Biogeography, 35, 977-994.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
Wu JG (2004) Effects of changing scale on landscape pattern analysis: Scaling relations. Landscape Ecology, 19, 125-138.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
Yu J, Shen L, Li DD, Guo SL (2019) Determinants of bryophyte species richness on the Zhoushan Archipelago, China. Basic and Applied Ecology, 37, 38-50.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
Yu MJ, Hu G, Feeley KJ, Wu JG, Ding P (2012) Richness and composition of plants and birds on land-bridge islands: Effects of island attributes and differential responses of species groups. Journal of Biogeography, 39, 1124-1133.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 贾贞妮, 张意岑, 杜彦君, 任海保. 干扰对中亚热带森林群落物种多样性演替动态的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24078-. |
| [2] | 郑博瀚, 陈鑫瑶, 倪健. 中国维管植物生长型和生活型数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23468-. |
| [3] | 孟敬慈, 王国栋, 曹光兰, 胡楠林, 赵美玲, 赵延彤, 薛振山, 刘波, 朴文华, 姜明. 中国芦苇沼泽植物物种丰富度分布格局及其驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23194-. |
| [4] | 施国杉, 刘峰, 曹光宏, 陈典, 夏尚文, 邓云, 王彬, 杨效东, 林露湘. 西双版纳热带季节雨林木本植物的beta多样性: 空间、环境与林分结构的作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24285-. |
| [5] | 王丽媛, 胡慧建, 姜杰, 胡一鸣. 南岭哺乳类和鸟类物种丰富度空间分布格局及其影响因子[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23026-. |
| [6] | 杨舒涵, 王贺, 陈磊, 廖蓥飞, 严光, 伍一宁, 邹红菲. 松嫩平原异质生境对土壤线虫群落特征的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23295-. |
| [7] | 王明慧, 陈昭铨, 李帅锋, 黄小波, 郎学东, 胡子涵, 尚瑞广, 刘万德. 云南普洱季风常绿阔叶林不同种子扩散方式的优势种空间点格局分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23147-. |
| [8] | 刘志发, 王新财, 龚粤宁, 陈道剑, 张强. 基于红外相机监测的广东南岭国家级自然保护区鸟兽多样性及其垂直分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 22689-. |
| [9] | 陈声文, 任海保, 童光蓉, 王宁宁, 蓝文超, 薛建华, 米湘成. 钱江源国家公园木本植物物种多样性空间分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 22587-. |
| [10] | 商晓凡, 张健, 高浩杰, 库伟鹏, 毕玉科, 李修鹏, 阎恩荣. 岛屿面积与气候共同影响舟山群岛种子植物丰富度格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(12): 23392-. |
| [11] | 王彦平, 张敏楚, 詹成修. 嵌套分布格局研究进展: 分析方法、影响机制及保护应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(12): 23314-. |
| [12] | 高德, 王彦平. 小岛屿效应检测方法研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(12): 23299-. |
| [13] | 杨科, 丁城志, 陈小勇, 丁刘勇, 黄敏睿, 陈晋南, 陶捐. 怒江流域鱼类多样性及空间分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21334-. |
| [14] | 田璐嘉, 杨小波, 李东海, 李龙, 陈琳, 梁彩群, 张培春, 李晨笛. 海口和三亚两城市破碎化林地中鸟类群落多样性与嵌套分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(6): 21424-. |
| [15] | 肖兰, 董标, 张琳婷, 邓传远, 李霞, 刘建辉, 吴端聪. 渤海区无居民海岛植物物种丰富度分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(4): 21231-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn