



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (4): 21231. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021231 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2021231
• 研究报告: 植物多样性 • 下一篇
肖兰1,2, 董标2, 张琳婷2, 邓传远4, 李霞2, 刘建辉3,*( ), 吴端聪4
), 吴端聪4
收稿日期:2021-06-03
接受日期:2021-12-14
出版日期:2022-04-20
发布日期:2022-04-20
通讯作者:
刘建辉
作者简介:*E-mail: liujianhuiirc@126.com基金资助:
Lan Xiao1,2, Biao Dong2, Linting Zhang2, Chuanyuan Deng4, Xia Li2, Jianhui Liu3,*( ), Duancong Wu4
), Duancong Wu4
Received:2021-06-03
Accepted:2021-12-14
Online:2022-04-20
Published:2022-04-20
Contact:
Jianhui Liu
摘要:
为了解渤海区小型无居民海岛植物物种丰富度的分布格局, 本研究以渤海区9个无居民海岛为研究对象, 基于种-面积关系和种-多度对数正态分布模型探究了无居民海岛植物的物种丰富度分布格局。结果表明: (1)位于温带地区的无居民海岛木本植物相对多度符合对数正态分布特征, 表明海岛木本植物群落中多度较大的物种数较少, 而多度较小的物种甚至是稀有种或罕见种较多; (2)渤海区多数无居民海岛物种数介于60-130之间, 表明总体丰富度较高; (3)通过分析海岛与周边保护区的空间关系发现, 物种丰富度高的海岛基本位于保护区内, 总体上渤海区海岛植物热点区得到了有效保护。综上所述, 种-多度分布模型和种-面积关系均是揭示海岛植物物种丰富度分布的重要手段, 同时可初步推断, 生态位理论对海岛植物物种多样性的维持显得更为重要。
肖兰, 董标, 张琳婷, 邓传远, 李霞, 刘建辉, 吴端聪 (2022) 渤海区无居民海岛植物物种丰富度分布格局. 生物多样性, 30, 21231. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021231.
Lan Xiao, Biao Dong, Linting Zhang, Chuanyuan Deng, Xia Li, Jianhui Liu, Duancong Wu (2022) Distribution pattern of plant species richness of uninhabited islands in the Bohai Sea area. Biodiversity Science, 30, 21231. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2021231.
| 岛屿名称 Island name | 所属省 Province | 物质组成 Properties | 面积 Area (ha) | 距大陆距离 Distance to the mainland (km) | 距大陆距离或距最近海岛距离 Distance to the mainland or nearest island (m) | 生活型组成 Life form | 植被覆盖率 Vegetation cover | 样方数量 No. of investigation plots | 丰富度 Richness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 情人岛 Qingrendao | 辽宁 Liaoning | 基岩岛 Bedrock island | 6.15 | 0.56 | 3,802 | 乔木、灌木、草本 Tree, shrub, and herb | 82.22% | 10 | 81 |
| 金州南坨子 Jinzhounantuozi | 辽宁 Liaoning | 基岩岛 Bedrock island | 11.55 | 0.66 | 2,155 | 灌木、草本 Shrub, and herb | 98.82% | 11 | 104 |
| 鹿鸣岛 Lumingdao | 辽宁 Liaoning | 基岩岛 Bedrock island | 75.6 | 0.89 | 596 | 乔木、灌木、草本 Tree, shrub, and herb | 95.54% | 7 | 108 |
| 双岛 Shuangdao | 辽宁 Liaoning | 基岩岛 Bedrock island | 14.66 | 0.65 | 6 | 乔木、灌木、草本 Tree, shrub, and herb | 97.47% | 10 | 106 |
| 羊砣子岛 Yangtuozidao | 山东 Shandong | 基岩岛 Bedrock island | 10.42 | 13.58 | 155 | 乔木、灌木、草本 Tree, shrub, and herb | 79.25% | 3 | 107 |
| 南砣子岛 Nantuozidao | 山东 Shandong | 基岩岛 Bedrock island | 14.67 | 15 | 455 | 乔木、灌木、草本 Tree, shrub, and herb | 75.64% | 3 | 107 |
| 鱼鳞岛 Yulindao | 山东 Shandong | 基岩岛 Bedrock island | 1.24 | 14.44 | 455 | 灌木、草本 Shrub, and herb | 39.52% | 3 | 67 |
| 广利岛Guanglidao | 山东 Shandong | 沙泥岛 Sandy island | 12.67 | 0.1 | 1,000 | 灌木、草本 Shrub, and herb | 68.85% | 1 | 32 |
| 东蚂蚁岛Dongmayidao | 辽宁 Liaoning | 基岩岛 Bedrock island | 87.2 | 7.53 | 22 | 乔木、灌木、草本 Tree, shrub, and herb | 91.38% | 16 | 127 |
表1 渤海区9个调查岛屿的基本信息
Table 1 Basic information of 9 investigated islands in the Bohai Sea area
| 岛屿名称 Island name | 所属省 Province | 物质组成 Properties | 面积 Area (ha) | 距大陆距离 Distance to the mainland (km) | 距大陆距离或距最近海岛距离 Distance to the mainland or nearest island (m) | 生活型组成 Life form | 植被覆盖率 Vegetation cover | 样方数量 No. of investigation plots | 丰富度 Richness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 情人岛 Qingrendao | 辽宁 Liaoning | 基岩岛 Bedrock island | 6.15 | 0.56 | 3,802 | 乔木、灌木、草本 Tree, shrub, and herb | 82.22% | 10 | 81 |
| 金州南坨子 Jinzhounantuozi | 辽宁 Liaoning | 基岩岛 Bedrock island | 11.55 | 0.66 | 2,155 | 灌木、草本 Shrub, and herb | 98.82% | 11 | 104 |
| 鹿鸣岛 Lumingdao | 辽宁 Liaoning | 基岩岛 Bedrock island | 75.6 | 0.89 | 596 | 乔木、灌木、草本 Tree, shrub, and herb | 95.54% | 7 | 108 |
| 双岛 Shuangdao | 辽宁 Liaoning | 基岩岛 Bedrock island | 14.66 | 0.65 | 6 | 乔木、灌木、草本 Tree, shrub, and herb | 97.47% | 10 | 106 |
| 羊砣子岛 Yangtuozidao | 山东 Shandong | 基岩岛 Bedrock island | 10.42 | 13.58 | 155 | 乔木、灌木、草本 Tree, shrub, and herb | 79.25% | 3 | 107 |
| 南砣子岛 Nantuozidao | 山东 Shandong | 基岩岛 Bedrock island | 14.67 | 15 | 455 | 乔木、灌木、草本 Tree, shrub, and herb | 75.64% | 3 | 107 |
| 鱼鳞岛 Yulindao | 山东 Shandong | 基岩岛 Bedrock island | 1.24 | 14.44 | 455 | 灌木、草本 Shrub, and herb | 39.52% | 3 | 67 |
| 广利岛Guanglidao | 山东 Shandong | 沙泥岛 Sandy island | 12.67 | 0.1 | 1,000 | 灌木、草本 Shrub, and herb | 68.85% | 1 | 32 |
| 东蚂蚁岛Dongmayidao | 辽宁 Liaoning | 基岩岛 Bedrock island | 87.2 | 7.53 | 22 | 乔木、灌木、草本 Tree, shrub, and herb | 91.38% | 16 | 127 |
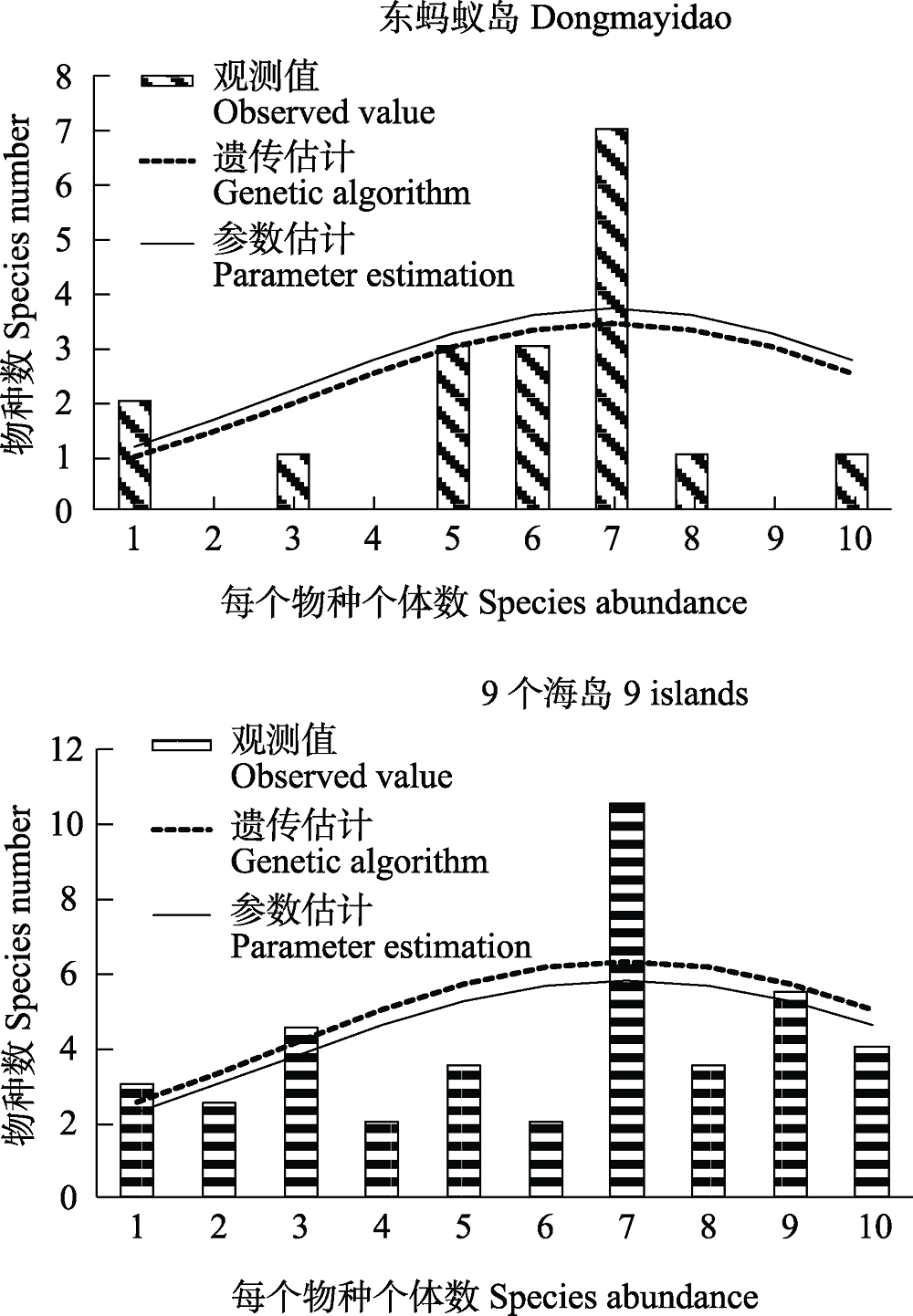
图2 运用对数正态分布模型预测渤海区单岛和9个海岛的木本植物物种数
Fig. 2 No. of woody plant species in Dongmayidao and 9 islands in the Bohai Sea area fitting by logarithmic normal distribution model
| 东蚂蚁岛木本植物 Woody plants in Dongmayidao | 9个海岛木本植物 Woody plants in 9 islands | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 倍频程 Class | 参数估计 Parameter estimation | 遗传估计 Genetic algorithm | 倍频程 Class | 参数估计 Parameter estimation | 遗传估计 Genetic algorithm | ||||||||
| a | 0.1800 | 0.1882 | a | 0.1600 | 0.1612 | ||||||||
| S0 | 3.7000 | 3.4367 | S0 | 6.3000 | 5.7879 | ||||||||
| R | 观测S(R) Observed | 期望S(R) Expected | χ2 | 期望S(R) Expected | χ2 | R | 观测S(R) Observed | 期望S(R) Expected | χ2 | 期望S(R) Expected | χ2 | ||
| 1 | -6 | 2 | 1.15 | 0.62 | 0.96 | 1.13 | 1 | -6 | 3 | 2.51 | 0.10 | 2.27 | 0.23 |
| 2 | -5 | 0 | 1.65 | 1.65 | 1.42 | 1.42 | 2 | -5 | 2.5 | 3.32 | 0.20 | 3.02 | 0.09 |
| 3 | -4 | 1 | 2.20 | 0.66 | 1.95 | 0.46 | 3 | -4 | 4.5 | 4.18 | 0.02 | 3.82 | 0.12 |
| 4 | -3 | 0 | 2.76 | 2.76 | 2.50 | 2.50 | 4 | -3 | 2 | 5.00 | 1.80 | 4.58 | 1.45 |
| 5 | -2 | 3 | 3.25 | 0.02 | 2.98 | 0.00 | 5 | -2 | 3.5 | 5.69 | 0.84 | 5.22 | 0.56 |
| 6 | -1 | 3 | 3.58 | 0.09 | 3.32 | 0.03 | 6 | -1 | 2 | 6.14 | 2.79 | 5.64 | 2.35 |
| 7 | 0 | 7 | 3.70 | 2.94 | 3.44 | 3.69 | 7 | 0 | 10.5 | 6.30 | 2.80 | 5.79 | 3.84 |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | 3.58 | 1.86 | 3.32 | 1.62 | 8 | 1 | 3.5 | 6.14 | 1.14 | 5.64 | 0.81 |
| 9 | 2 | 0 | 3.25 | 3.25 | 2.98 | 2.98 | 9 | 2 | 5.5 | 5.69 | 0.01 | 5.22 | 0.02 |
| 10 | 3 | 1 | 2.76 | 1.13 | 2.50 | 0.90 | 10 | 3 | 4 | 5.00 | 0.20 | 4.58 | 0.07 |
| ∑ | 18 | 14.98 | 14.73 | ∑ | 41 | 9.90 | 9.54 | ||||||
| 预测理论值 Expected value | 37 | / | 33 | / | 预测理论值 Expected value | 70 | / | 64 | / | ||||
表2 对数正态分布模型预测结果及多度分布检验表
Table 2 Predicted results of logarithmic normal distribution model and abundance distribution test table
| 东蚂蚁岛木本植物 Woody plants in Dongmayidao | 9个海岛木本植物 Woody plants in 9 islands | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 倍频程 Class | 参数估计 Parameter estimation | 遗传估计 Genetic algorithm | 倍频程 Class | 参数估计 Parameter estimation | 遗传估计 Genetic algorithm | ||||||||
| a | 0.1800 | 0.1882 | a | 0.1600 | 0.1612 | ||||||||
| S0 | 3.7000 | 3.4367 | S0 | 6.3000 | 5.7879 | ||||||||
| R | 观测S(R) Observed | 期望S(R) Expected | χ2 | 期望S(R) Expected | χ2 | R | 观测S(R) Observed | 期望S(R) Expected | χ2 | 期望S(R) Expected | χ2 | ||
| 1 | -6 | 2 | 1.15 | 0.62 | 0.96 | 1.13 | 1 | -6 | 3 | 2.51 | 0.10 | 2.27 | 0.23 |
| 2 | -5 | 0 | 1.65 | 1.65 | 1.42 | 1.42 | 2 | -5 | 2.5 | 3.32 | 0.20 | 3.02 | 0.09 |
| 3 | -4 | 1 | 2.20 | 0.66 | 1.95 | 0.46 | 3 | -4 | 4.5 | 4.18 | 0.02 | 3.82 | 0.12 |
| 4 | -3 | 0 | 2.76 | 2.76 | 2.50 | 2.50 | 4 | -3 | 2 | 5.00 | 1.80 | 4.58 | 1.45 |
| 5 | -2 | 3 | 3.25 | 0.02 | 2.98 | 0.00 | 5 | -2 | 3.5 | 5.69 | 0.84 | 5.22 | 0.56 |
| 6 | -1 | 3 | 3.58 | 0.09 | 3.32 | 0.03 | 6 | -1 | 2 | 6.14 | 2.79 | 5.64 | 2.35 |
| 7 | 0 | 7 | 3.70 | 2.94 | 3.44 | 3.69 | 7 | 0 | 10.5 | 6.30 | 2.80 | 5.79 | 3.84 |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | 3.58 | 1.86 | 3.32 | 1.62 | 8 | 1 | 3.5 | 6.14 | 1.14 | 5.64 | 0.81 |
| 9 | 2 | 0 | 3.25 | 3.25 | 2.98 | 2.98 | 9 | 2 | 5.5 | 5.69 | 0.01 | 5.22 | 0.02 |
| 10 | 3 | 1 | 2.76 | 1.13 | 2.50 | 0.90 | 10 | 3 | 4 | 5.00 | 0.20 | 4.58 | 0.07 |
| ∑ | 18 | 14.98 | 14.73 | ∑ | 41 | 9.90 | 9.54 | ||||||
| 预测理论值 Expected value | 37 | / | 33 | / | 预测理论值 Expected value | 70 | / | 64 | / | ||||
| 岛屿名称 Island name | 干扰类型及干扰程度 Interference type and degree | 开发强度 Exploitative intensity | 调查物种数 No. of species surveyed | 预测物种数 No. of species estimated | 误差 Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 情人岛 Qingrendao | 人类活动/弱 Human activities/Light | 6.0% | 81 | 86 | 6.17% |
| 金州南坨子 Jinzhounantuozi | 近无干扰 Near non-interfering | 0.6% | 104 | 105 | 0.96% |
| 鹿鸣岛 Lumingdao | 人类活动/中 Human activities/Moderate | 2.6% | 108 | 143 | 32.41% |
| 双岛 Shuangdao | 人类活动/弱 Human activities/Light | 1.4% | 106 | 108 | 1.89% |
| 羊砣子岛 Yangtuozidao | 近无干扰 Near non-interfering | 1.8% | 107 | 100 | -6.54% |
| 南砣子岛 Nantuozidao | 近无干扰 Near non-interfering | 4.6% | 107 | 105 | -1.87% |
| 鱼鳞岛 Yulindao | 放牧/弱 Graze/Light | 1.3% | 67 | 45 | -32.84% |
| 广利岛 Guanglidao | 人类活动/强 Human activities/Strong | 19.4% | 32 | 56 | 75.00% |
| 东蚂蚁岛 Dongmayidao | 人类活动/弱 Human activities/Light | 0.02% | 127 | 144 | 13.39% |
表3 种-面积关系的模型预测结果及海岛干扰因子
Table 3 Prediction results of species-area relationships model and island impact factor
| 岛屿名称 Island name | 干扰类型及干扰程度 Interference type and degree | 开发强度 Exploitative intensity | 调查物种数 No. of species surveyed | 预测物种数 No. of species estimated | 误差 Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 情人岛 Qingrendao | 人类活动/弱 Human activities/Light | 6.0% | 81 | 86 | 6.17% |
| 金州南坨子 Jinzhounantuozi | 近无干扰 Near non-interfering | 0.6% | 104 | 105 | 0.96% |
| 鹿鸣岛 Lumingdao | 人类活动/中 Human activities/Moderate | 2.6% | 108 | 143 | 32.41% |
| 双岛 Shuangdao | 人类活动/弱 Human activities/Light | 1.4% | 106 | 108 | 1.89% |
| 羊砣子岛 Yangtuozidao | 近无干扰 Near non-interfering | 1.8% | 107 | 100 | -6.54% |
| 南砣子岛 Nantuozidao | 近无干扰 Near non-interfering | 4.6% | 107 | 105 | -1.87% |
| 鱼鳞岛 Yulindao | 放牧/弱 Graze/Light | 1.3% | 67 | 45 | -32.84% |
| 广利岛 Guanglidao | 人类活动/强 Human activities/Strong | 19.4% | 32 | 56 | 75.00% |
| 东蚂蚁岛 Dongmayidao | 人类活动/弱 Human activities/Light | 0.02% | 127 | 144 | 13.39% |
| [1] |
Brown JH (1984) On the relationship between abundance and distribution of species. The American Naturalist, 124, 255- 279.
DOI URL |
| [2] | Chen GL, Tan LZ, Fan CY, Zhang XN, Zhang CY, Zhao XH (2017) Species-area relationships within sample plot in a broad-leaved Korean pine forest at Jiaohe, Jilin Province. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 4770-4777. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈桂莲, 谭凌照, 范春雨, 张新娜, 张春雨, 赵秀海 (2017) 吉林蛟河阔叶红松林样地种-面积关系. 生态学报, 37, 4770-4777.] | |
| [3] |
Costanzi JM, Steifetten Ø (2019) Island biogeography theory explains the genetic diversity of a fragmented rock ptarmigan (Lagopus muta) population. Ecology and Evolution, 9, 3837-3849.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Dengler J (2009) Which function describes the species-area relationship best? A review and empirical evaluation. Journal of Biogeography, 36, 728-744.
DOI URL |
| [5] | Ding D (1994) Geological survey of cross-sea channel in Bohai Strait. Marine Geology Letters, (3), 5-7. (in Chinese) |
| [ 丁东 (1994) 渤海海峡跨海通道的地质概况. 海洋地质动态, (3), 5-7.] | |
| [6] |
Fang JY, Wang XP, Shen ZH, Tang ZY, He JS, Yu D, Jiang Y, Wang ZH, Zheng CY, Zhu JL, Guo ZD (2009) Methods and protocols for plant community inventory. Biodiversity Science, 17, 533-548. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 方精云, 王襄平, 沈泽昊, 唐志尧, 贺金生, 于丹, 江源, 王志恒, 郑成洋, 朱江玲, 郭兆迪 (2009) 植物群落清查的主要内容、方法和技术规范. 生物多样性, 17, 533-548.]
DOI |
|
| [7] |
Hill JK, Hamer KC (1998) Using species abundance models as indicators of habitat disturbance in tropical forests. Journal of Applied Ecology, 35, 458-460.
DOI URL |
| [8] | Ke XD (2018) Woody Plant Community Diversity and the Scale Effects in a Subtropical Forest. PhD dissertation, South China Agricultural University, Guangzhou. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 柯娴氡 (2018) 亚热带木本植物群落多样性与尺度效应研究. 博士学位论文, 华南农业大学, 广州.] | |
| [9] | Krebs CJ (2001) Ecology: The Experimental Analysis of Distribution and Abundance, 5th edn. Benjamin/Cummings, California. |
| [10] |
Krishnamani R, Kumar A, Harte J (2004) Estimating species richness at large spatial scales using data from small discrete plots. Ecography, 27, 637-642.
DOI URL |
| [11] | Li XM, Wu CZ, Gu W, Ye R, Zhang HB, Qi P, Wang SQ, Zhou SY, Wei YJ, Cai YH (2017) The biogeographical distribution of tree species-abundance and its relation to climatic factors in mass islands. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 36, 87-90. |
| [12] | Li XM, Lü LL, Hu XS, Cao RQ, Wu CZ, Hou CY (2019) Prediction of woody plant species richness of Zhejiang island based on GIS. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University, 37, 511-516. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 李晓明, 吕林玲, 胡喜生, 曹荣青, 吴承祯, 侯纯扬 (2019) 基于GIS的浙江海岛木本植物物种丰富度预测. 四川农业大学学报, 37, 511-516.] | |
| [13] | Liu CR, Ma KP, Zhou WN (1995) Measurement of biotic community diversity. III. Statistical issue related to species-abundance distribution. Chinese Biodiversity, 3, 157-169. (in Chinese) |
| [ 刘灿然, 马克平, 周文能 (1995) 生物群落多样性的测度方法. III. 与物种-多度分布模型有关的统计问题. 生物多样性, 3, 157-169.] | |
| [14] |
Liu XY, Zhao CL, Xu MS, Liang QM, Zhu XT, Li L, Yan ER (2019) Beta diversity of vascular plants and its drivers in sea-islands of Eastern China. Biodiversity Science, 27, 380-387. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 刘翔宇, 赵慈良, 许洺山, 梁启明, 朱晓彤, 李亮, 阎恩荣 (2019) 中国东部海岛维管植物的beta多样性及其驱动因素. 生物多样性, 27, 380-387.]
DOI |
|
| [15] | Ma KM, Fu BJ, Zhou HF (1999) Studies on species and pattern diversities of the forest landscapes of Donglingshan Mountain region, Beijing, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 19, 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 马克明, 傅伯杰, 周华锋 (1999) 北京东灵山地区森林的物种多样性和景观格局多样性研究. 生态学报, 19, 1-7.] | |
| [16] | McCune B, Grace JB (2002) Analysis of Ecological Communities. MJM Software Design, Gleneden Beach, USA. |
| [17] |
Naves RP, Grøtan V, Prado PI, Vidal E, Batista JLF (2020) Tropical forest management altered abundances of individual tree species but not diversity. Forest Ecology and Management, 475, 118399.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Peng SL, Yin ZY, Ren H, Guo QF (2003) Advances in research on the species-abundance relationship models in multi-species collection. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 23, 1590-1605. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 彭少麟, 殷祚云, 任海, 郭勤峰 (2003) 多物种集合的种-多度关系模型研究进展. 生态学报, 23, 1590-1605.] | |
| [19] | Pielou EC (1975) Ecological Diversity, pp. 269-270. John Wiley & Sons, New York. |
| [20] |
Pigolotti S, Cencini M (2009) Speciation-rate dependence in species-area relationships. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 260, 83-89.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Pinheiro HT, Bernardi G, Simon T, Joyeux JC, Macieira RM, Gasparini JL, Rocha C, Rocha LA (2017) Island biogeography of marine organisms. Nature, 549, 82-85.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Preston FW (1948) The commonness, and rarity, of species. Ecology, 29, 254-283.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Sun Q, Lu JB, Wu JG, Zhang FF (2008) Effects of island area on plant species distribution and conservation implications in the Thousand Island Lake region. Biodiversity Science, 16, 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 孙雀, 卢剑波, 邬建国, 张凤凤 (2008) 千岛湖库区岛屿面积对植物分布的影响及植物物种多样性保护研究. 生物多样性, 16, 1-7.]
DOI |
|
| [24] | Sun Q, Lu JB, Zhang FF, Xu GF (2009) Plant species diversity in relation to island size. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 29, 2195-2202. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 孙雀, 卢剑波, 张凤凤, 徐高福 (2009) 植物物种多样性与岛屿面积的关系. 生态学报, 29, 2195-2202.] | |
| [25] |
Tang ZY, Qiao XJ, Fang JY (2009) Species-area relationship in biological communities. Biodiversity Science, 17, 549-559. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 唐志尧, 乔秀娟, 方精云 (2009) 生物群落的种-面积关系. 生物多样性, 17, 549-559.]
DOI |
|
| [26] |
Ugland KI, Gray JS, Ellingsen KE (2003) The species-accumulation curve and estimation of species richness. Journal of Animal Ecology, 72, 888-897.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Ulrich W, Soliveres S, Thomas AD, Dougill AJ, Maestre FT (2016) Environmental correlates of species rank- Abundance distributions in global drylands. Perspectives in Plant Ecology, Evolution and Systematics, 20, 56-64.
DOI URL |
| [28] | Wang JW, Wei X, Chen QX, Li XW, Yang S (2017) Factors affecting species richness and beta diversity of vascular plants on small islands in the Wenzhou region of Eastern China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 523-540. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王金旺, 魏馨, 陈秋夏, 李效文, 杨升 (2017) 温州沿海小型海岛植物丰富度和β多样性及其影响因子. 生态学报, 37, 523-540.] | |
| [29] |
Watt AD (1998) Measuring disturbance in tropical forests: A critique of the use of species-abundance models and indicator measures in general. Journal of Applied Ecology, 35, 467-469.
DOI URL |
| [30] | Wu CZ, Hong W, Wu JL, Zheng QR (2000) Studies on Kernel density estimation of species abundance distribution in two communities of rare and endangered plants. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 8, 301-307. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吴承祯, 洪伟, 吴继林, 郑群瑞 (2000) 两种珍稀植物群落物种多度分布的核方法研究. 热带亚热带植物学报, 8, 301-307.] | |
| [31] | Wu CZ, Hong W, He DJ (1998) A calculating method of the log-normal distribution model of species abundance. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 4, 409-413. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 吴承祯, 洪伟, 何东进 (1998) 物种多度对数正态分布模型的一种数值计算方法. 应用与环境生物学报, 4, 409-413.] | |
| [32] | Wu ZY (1995) Vegetation of China, 3rd edn. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 吴征镒 (1995) 中国植被(第三版). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [33] |
Xiao L, Zhang LT, Yang SC, Zheng ZH, Jiang DG (2018) Flora and species composition similarity of the uninhabited islands in the nearshore Xiamen. Biodiversity Science, 26, 1212-1222. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[ 肖兰, 张琳婷, 杨盛昌, 郑志翰, 姜德刚 (2018) 厦门近岸海域无居民海岛植物区系和物种组成相似性. 生物多样性, 26, 1212-1222.]
DOI |
|
| [34] | Xie JY, Chen LZ, Ghirelli L, Chiesura LF (1995) Biodiversity studies on Quercus ilex woods in Veneto, Italy. Acta Botanica Sinica, 37, 386-393. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 谢晋阳, 陈灵芝, Ghirelli L, Chiesura LF (1995) 意大利威尼托大区刺叶栎林的生物多样性研究. 植物学报, 37, 386-393.] | |
| [35] | Yin ZY, Liao WB (1999) Studies on log normal distribution patterns of species abundance of south subtropical forest community, China. Guihaia, 19, 221-224. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 殷祚云, 廖文波 (1999) 南亚热带森林群落种-多度的对数正态分布模型研究. 广西植物, 19, 221-224.] | |
| [36] | Zhao ZM, Guo YQ (1990) Principles and Methods of Community Ecology. Chongqing Science and Technology Literature Publishing House, Chongqing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 赵志模, 郭依泉 (1990) 群落生态原理与方法. 重庆科学技术文献出版社, 重庆.] |
| [1] | 贾贞妮, 张意岑, 杜彦君, 任海保. 干扰对中亚热带森林群落物种多样性演替动态的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24078-. |
| [2] | 顾燚芸, 薛嘉祈, 高金会, 谢心仪, 韦铭, 雷进宇, 闻丞. 一种基于公众科学数据的区域性鸟类多样性评价方法[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 24080-. |
| [3] | 孟敬慈, 王国栋, 曹光兰, 胡楠林, 赵美玲, 赵延彤, 薛振山, 刘波, 朴文华, 姜明. 中国芦苇沼泽植物物种丰富度分布格局及其驱动因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23194-. |
| [4] | 施国杉, 刘峰, 曹光宏, 陈典, 夏尚文, 邓云, 王彬, 杨效东, 林露湘. 西双版纳热带季节雨林木本植物的beta多样性: 空间、环境与林分结构的作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24285-. |
| [5] | 王丽媛, 胡慧建, 姜杰, 胡一鸣. 南岭哺乳类和鸟类物种丰富度空间分布格局及其影响因子[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(1): 23026-. |
| [6] | 刘志发, 王新财, 龚粤宁, 陈道剑, 张强. 基于红外相机监测的广东南岭国家级自然保护区鸟兽多样性及其垂直分布特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(8): 22689-. |
| [7] | 陈声文, 任海保, 童光蓉, 王宁宁, 蓝文超, 薛建华, 米湘成. 钱江源国家公园木本植物物种多样性空间分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 22587-. |
| [8] | 谢艳秋, 黄晖, 王春晓, 何雅琴, 江怡萱, 刘子琳, 邓传远, 郑郁善. 福建海岛滨海特有植物种-面积关系及物种丰富度决定因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(5): 22345-. |
| [9] | 高德, 王彦平. 小岛屿效应检测方法研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(12): 23299-. |
| [10] | 杨科, 丁城志, 陈小勇, 丁刘勇, 黄敏睿, 陈晋南, 陶捐. 怒江流域鱼类多样性及空间分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21334-. |
| [11] | 刘高慧, 崔建国, 王玥, 王洪良, 香宝, 肖能文. 四川省康定市两栖动物多样性及其时空分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(6): 21494-. |
| [12] | 田璐嘉, 杨小波, 李东海, 李龙, 陈琳, 梁彩群, 张培春, 李晨笛. 海口和三亚两城市破碎化林地中鸟类群落多样性与嵌套分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(6): 21424-. |
| [13] | 王爱霞, 马婧婧, 龚会蝶, 范国安, 王茂, 赵红梅, 程军回. 北疆一年生早春短命植物物种丰富度分布格局及其影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(6): 735-745. |
| [14] | 郑进凤, 唐蓉, 贺霜, 陈月红, 伍素, 张凯, 徐雨, 邹晓. 贵州花溪大学城破碎化林地鸟类多样性与嵌套分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(5): 661-667. |
| [15] | 黄小波, 郎学东, 李帅锋, 刘万德, 苏建荣. 生态系统多功能性的指标选择与驱动因子: 研究现状与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(12): 1673-1686. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn