



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (9): 22349. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022349 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022349
马子驭1, 何再新2, 王一晴1,*( ), 宋大昭1, 夏凡1,3, 崔士明1, 苏红信4, 邓建林2, 李平4, 李晟3,*(
), 宋大昭1, 夏凡1,3, 崔士明1, 苏红信4, 邓建林2, 李平4, 李晟3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-06-25
接受日期:2022-09-23
出版日期:2022-09-20
发布日期:2022-09-26
通讯作者:
王一晴,李晟
作者简介:shengli@pku.edu.cn基金资助:
Ziyu Ma1, Zaixin He2, Yiqing Wang1,*( ), Dazhao Song1, Fan Xia1,3, Shiming Cui1, Hongxin Su4, Jianlin Deng2, Ping Li4, Sheng Li3,*(
), Dazhao Song1, Fan Xia1,3, Shiming Cui1, Hongxin Su4, Jianlin Deng2, Ping Li4, Sheng Li3,*( )
)
Received:2022-06-25
Accepted:2022-09-23
Online:2022-09-20
Published:2022-09-26
Contact:
Yiqing Wang,Sheng Li
About author:First author contact:# Co-first author
摘要:
云豹(Neofelis nebulosa)是中国大型猫科动物中对森林生态系统依赖性最高的物种。中国作为云豹的主要分布区, 由于长期以来缺乏深入研究和有效保护, 在盗猎、森林采伐、土地利用变化等威胁因素的共同作用下, 云豹在中国的分布范围和种群数量近数十年来均大幅缩减, 其分布现状亟需全面评估。本研究系统检索和查阅了国内1950年以来的云豹标本、野外调查记录、地方志、新闻报道等直接证据, 整理了中国各省级行政区内云豹记录存在的年代; 基于2010-2020年国内55个地区的红外相机监测数据, 结合同期研究文献中记录的中国云豹确认分布位点, 校准了已发表的云豹栖息地适合度模型, 并在此基础上叠加保护地和行政区划图层, 根据2010-2020年间森林覆盖率的减量评估云豹栖息地适合度的变化, 以识别我国的云豹关键栖息地和保护优先区。结果显示, 1950-2009年, 我国的云南、西藏、四川、陕西、甘肃、重庆、贵州、广西、广东、海南、湖北、湖南、安徽、江西、浙江、福建以及台湾共17个省级行政区有云豹分布, 但其中12个迄今已超过20年无确凿记录, 且目前仅在云南省和西藏自治区仍有云豹记录延续。当前我国大陆地区云豹潜在栖息地总面积64,093 km2, 分别位于9个连续的栖息地斑块中, 其中3个为跨境斑块。2010-2020年间, 我国境内共在5个自然保护区的10个样区记录到云豹, 全部位于西藏东南部以及云南西部和南部的2个跨境栖息地斑块(即“喜马拉雅-横断山脉西侧-若开山脉”和“无量山南麓-安南山脉”)的边缘。2010-2020年间, 这两个斑块在中国境内区域的年均森林覆盖率减量(0.84%)小于境外(1.57%)。从本研究的结果推断, 中国目前确认分布的云豹种群极有可能维持在跨境分布的生境中, 面临内部和跨境的双重挑战。相关保护地应有针对性地加强反盗猎执法, 并开展栖息地恢复工作以提升云豹栖息地质量与斑块连通性, 同时与周边分布区国家开展跨境保护合作, 为现有云豹种群的长期生存和发展提供必要基础。
马子驭, 何再新, 王一晴, 宋大昭, 夏凡, 崔士明, 苏红信, 邓建林, 李平, 李晟 (2022) 中国云豹种群分布现状与关键栖息地信息更新. 生物多样性, 30, 22349. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022349.
Ziyu Ma, Zaixin He, Yiqing Wang, Dazhao Song, Fan Xia, Shiming Cui, Hongxin Su, Jianlin Deng, Ping Li, Sheng Li (2022) An update on the current distribution and key habitats of the clouded leopard (Neofelis nebulosa) populations in China. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22349. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022349.
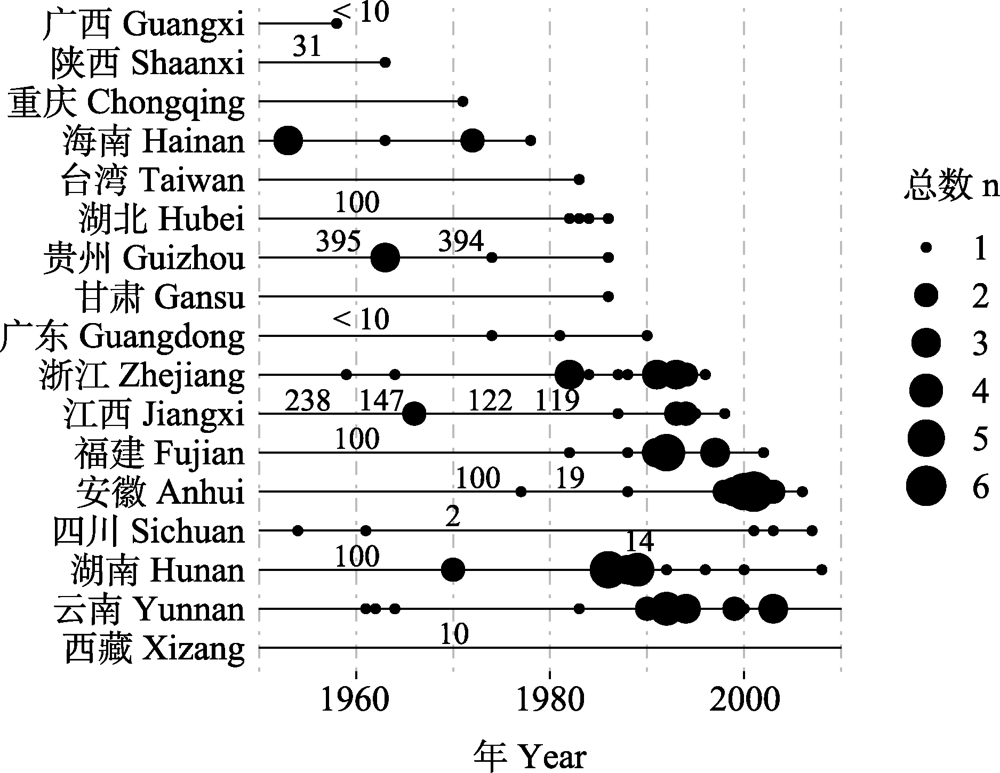
图1 1950-2010年云豹在标本、文献、地方志、报道和其他国内可查证的历史记录总结。横轴以10年为刻度, 各省、市、自治区名称后的黑色线段表示云豹分布证据延续的年代, 黑色圆点表示有确切采集时间、地点的标本以及可查证的活体或死体及其记录年份, 其大小表示当年记录总数(n); 黑线上的灰色数字表示该地区相应年代的年均云豹猎获量记载或估计。
Fig. 1 Overview of the historical records of Neofelis nebulosa collected from specimens, literature, local gazetteers, reports and other verifiable sources during 1950-2010 in China. With the decades marked on the horizontal axis, the black segment of lines following each administrative region’s name depict the time span of existing N. nebulosa evidence in the respective regions, while the black dots on them mark the well-curated specimens and valid reports of live or dead individuals and their year of collection, with the sizes of the dots showing tallies of the year’s individuals (n); and the grey numbers above the black lines present records or estimates of mean annual numbers of N. nebulosa hunted in relevant regions and time periods.
| 省区 Province | 年 Year | 地区 Region | 数据来源 Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| 西藏 Xizang | 现存 Extant | 墨脱县, 错那县 Medog and Cona | 本研究 This study; Li等, |
| 云南 Yunnan | 现存 Extant | 勐腊县、盈江县、陇川县、瑞丽市、贡山县 Mengla, Yingjiang, Longchuan, Ruili, and Gongshan | 本研究 This study; 刘炎林等, |
| 湖南 Hunan | 2008 | 八大公山国家级自然保护区 Badagongshan NNR | 八大公山自然博物馆标本 Specimen |
| 四川 Sichuan | 2007 | 长宁县 Changning | 李蔓等, |
| 安徽 Anhui | 2006 | 歙县 Shexian | 皖南国家野生动物救助中心记录 Rescue record |
| 福建 Fujian | 2002 | 梅花山国家级自然保护区 Meihuashan NNR | 龙岩市志 Gazetteer |
| 江西 Jiangxi | 1998 | 万载县 Wanzai | 万载县志 Gazetteer |
| 浙江 Zhejiang | 1996 | 临安区 Lin’an | 杭州电视台综合频道新闻报道 Media report |
| 广东 Guangdong | 1990 | 仁化县 Renhua | 韶关市林业志 Gazetteer |
| 甘肃 Gansu | 1986 | 白水江国家级自然保护区 Baishuijiang NNR | 马国瑶, |
| 贵州 Guizhou | 1986 | 梵净山国家级自然保护区 Fanjingshan NNR | 梵净山保护区标本馆标本 Specimen in Fanjingshan NNR |
| 湖北 Hubei | 1986 | 利川市 Lichuan | 恩施州林业志 Gazetteer |
| 台湾 Taiwan | 1983 | 不详 Unknown | Chiang等, |
| 海南 Hainan | 1978 | 东方市购入 Purchased from Dongfang | 华南濒危动物研究所标本 Specimen |
| 重庆 Chongqing | 1971 | 不详2 Unknown | 西华师范大学珍稀动植物研究所标本 Specimen |
| 陕西 Shaanxi | 1963 | 汉阴县 Hanyin | 闵芝兰等, |
| 广西 Guangxi | 1958 | 靖西市 Jingxi | 汪松等, |
表1 中国南方各省、直辖市和自治区云豹的最后确认分布记录(省区按年份排列)
Table 1 Last confirmed Neofelis nebulosa presence records in each provincial administrative division of southern China. Records are listed in the order of years. NNR: National Nature Reserve.
| 省区 Province | 年 Year | 地区 Region | 数据来源 Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| 西藏 Xizang | 现存 Extant | 墨脱县, 错那县 Medog and Cona | 本研究 This study; Li等, |
| 云南 Yunnan | 现存 Extant | 勐腊县、盈江县、陇川县、瑞丽市、贡山县 Mengla, Yingjiang, Longchuan, Ruili, and Gongshan | 本研究 This study; 刘炎林等, |
| 湖南 Hunan | 2008 | 八大公山国家级自然保护区 Badagongshan NNR | 八大公山自然博物馆标本 Specimen |
| 四川 Sichuan | 2007 | 长宁县 Changning | 李蔓等, |
| 安徽 Anhui | 2006 | 歙县 Shexian | 皖南国家野生动物救助中心记录 Rescue record |
| 福建 Fujian | 2002 | 梅花山国家级自然保护区 Meihuashan NNR | 龙岩市志 Gazetteer |
| 江西 Jiangxi | 1998 | 万载县 Wanzai | 万载县志 Gazetteer |
| 浙江 Zhejiang | 1996 | 临安区 Lin’an | 杭州电视台综合频道新闻报道 Media report |
| 广东 Guangdong | 1990 | 仁化县 Renhua | 韶关市林业志 Gazetteer |
| 甘肃 Gansu | 1986 | 白水江国家级自然保护区 Baishuijiang NNR | 马国瑶, |
| 贵州 Guizhou | 1986 | 梵净山国家级自然保护区 Fanjingshan NNR | 梵净山保护区标本馆标本 Specimen in Fanjingshan NNR |
| 湖北 Hubei | 1986 | 利川市 Lichuan | 恩施州林业志 Gazetteer |
| 台湾 Taiwan | 1983 | 不详 Unknown | Chiang等, |
| 海南 Hainan | 1978 | 东方市购入 Purchased from Dongfang | 华南濒危动物研究所标本 Specimen |
| 重庆 Chongqing | 1971 | 不详2 Unknown | 西华师范大学珍稀动植物研究所标本 Specimen |
| 陕西 Shaanxi | 1963 | 汉阴县 Hanyin | 闵芝兰等, |
| 广西 Guangxi | 1958 | 靖西市 Jingxi | 汪松等, |
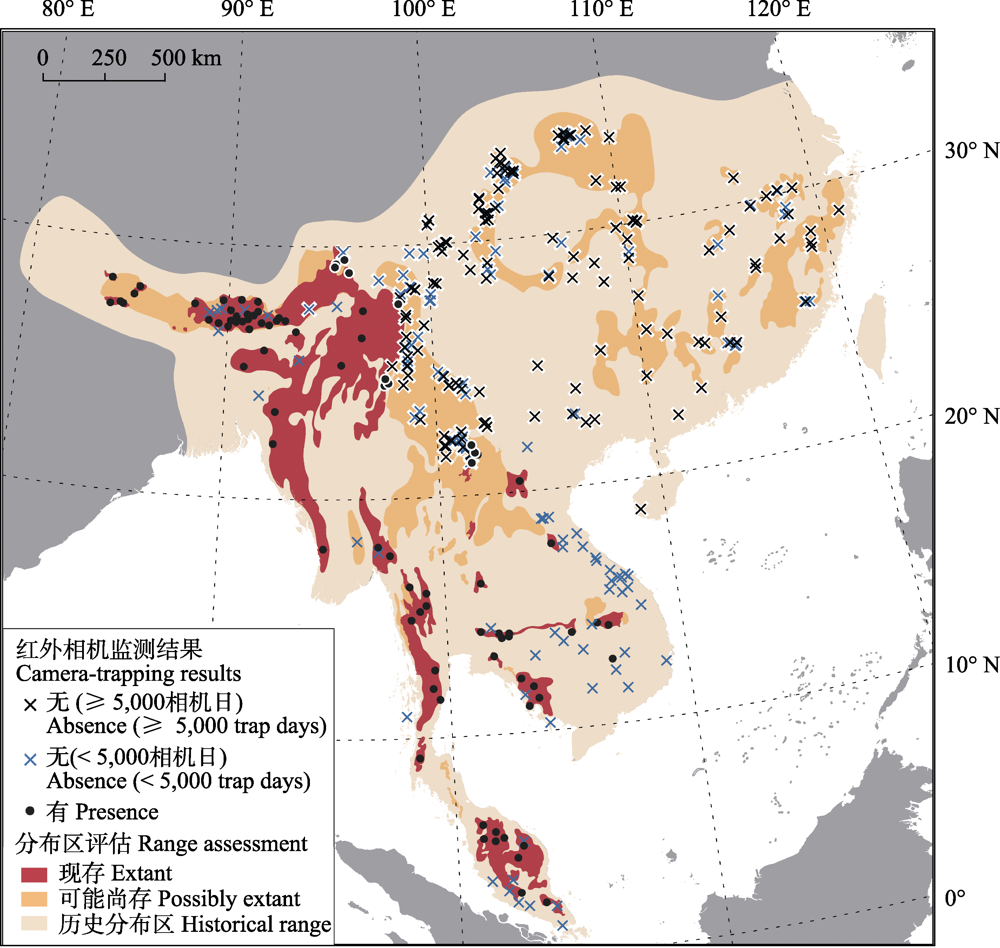
图2 2010-2020年云豹历史分布区域内红外相机监测结果分布及现有云豹分布区的评估。图中点位代表红外相机监测样区: 圆点为有云豹、叉号为无云豹; 无云豹的样区又根据监测力度区分为黑色高确定性和蓝色低确定性结果; 背景分布区示意图为IUCN红色名录2020年的最新评估结果, 最大历史分布区范围数据来自MacDonald等(2019)。
Fig. 2 Neofelis nebulosa presence and absence records in its historical range from 2010-2020 camera trapping results, overlaid with its current IUCN Red List range assessment. Markings on the map represent camera-trapping sites and their results: Dots mark N. nebulosa presences and crosses mark absences; Moreover, absence sites are colored with black (high certainty) or blue (low certainty) according to their surveying efforts; Extant N. nebulosa range in the background illustrates the latest assessment by the IUCN Red List in 2020, and its maximum historical range represent data from MacDonald et al (2019).
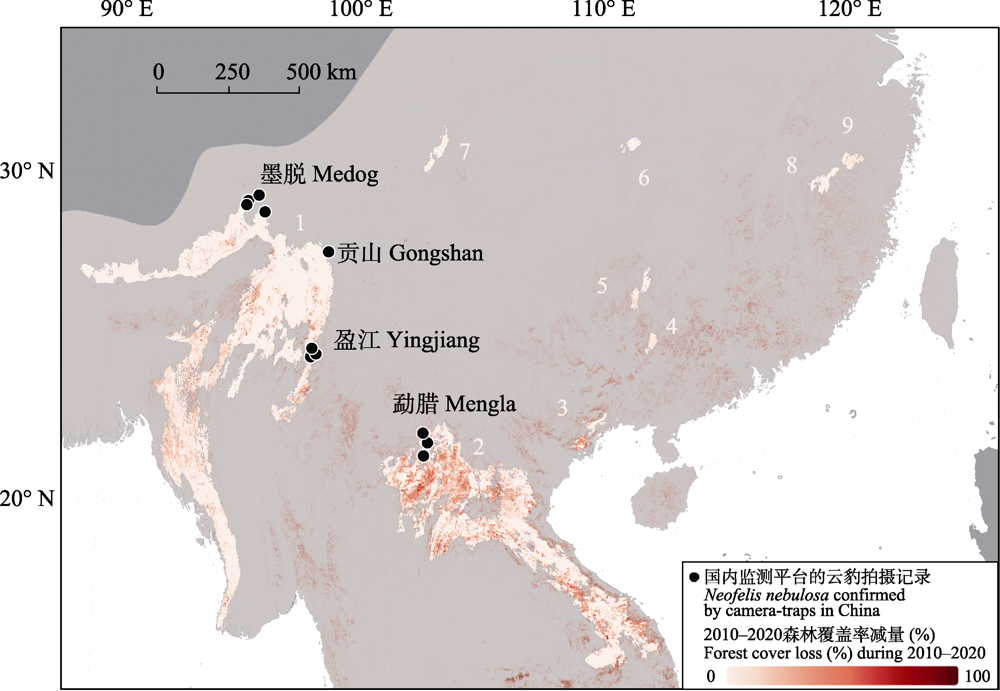
图3 本研究建议关注保护的云豹适宜栖息地斑块。背景为地区2010?2020年森林覆盖率减量。深灰色区域为云豹可能的最大历史分布区; 镂空斑块为本研究关注的云豹现有潜在栖息地(斑块编号与名称参看表2); 黑点表示目前国内确认有云豹的监测样区。
Fig. 3 Potential habitats of Neofelis nebulosa that demand conservation attention suggested by this study, and forest cover loss from 2010 to 2020 in the region. Dark grey area represents the maximum potential historical distribution of N. nebulosa; Unshaded patches within the area represent the current potential habitats focused in this study (see Table 2 for patch ID and name); Black dots show sites with current confirmed N. nebulosa presences.
| 编号 No. | 潜在栖息地 Potential habitats | 面积 Area (km2) | 高质量栖息地比例 High-quality habitat (%) | 保护地覆盖 Protected area (%) | 年均森林覆盖率减量Annual forest loss (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 喜马拉雅-横断山脉西侧-若开山脉Himalaya-Western Hengduan-Arakan Mountains | 274,408 | 83.18 | 13.92 | 0.412 ± 0.014 |
| 西藏自治区 Xizang | 38,594 | 75.76 | 3.36 | 0.198 ± 0.002 | |
| 云南省 Yunnan | 1,110 | 58.38 | 31.26 | 0.565 ± 0.021 | |
| 境外 Abroad | 234,704 | 84.52 | 15.57 | 0.447 ± 0.015 | |
| 2 | 无量山南麓-安南山脉 South Wuliangshan-Annamite | 195,476 | 87.20 | 28.81 | 1.118 ± 0.032 |
| 云南省 Yunnan | 1,669 | 68.30 | 68.36 | 0.081 ± 0.005 | |
| 境外 Abroad | 193,807 | 87.37 | 28.47 | 1.127 ± 0.032 | |
| 编号 No. | 潜在栖息地 Potential habitats | 面积 Area (km2) | 高质量栖息地比例 High-quality habitat (%) | 保护地覆盖 Protected area (%) | 年均森林覆盖率减量Annual forest loss (%) |
| 3 | 十万大山?越南北部高地 Shiwandashan-North Vietnam | 4,372 | 63.06 | 19.99 | 1.299 ± 0.232 |
| 广西壮族自治区 Guangxi | 2,135 | 57.19 | 29.41 | 0.565 ± 0.020 | |
| 境外 Abroad | 2,237 | 68.66 | 11.00 | 2.004 ± 0.252 | |
| 4 | 大瑶山 Dayaoshan | 1,790 | 56.31 | 13.07 | 0.579 ± 0.013 |
| 广西壮族自治区 Guangxi | 1,790 | 56.31 | 13.07 | 0.579 ± 0.013 | |
| 5 | 桂林西北 Northwest of Guilin | 4,393 | 43.32 | 32.55 | 0.404 ± 0.007 |
| 广西壮族自治区 Guangxi | 3,688 | 51.38 | 36.33 | 0.444 ± 0.008 | |
| 湖南省 Hunan | 705 | 1.13 | 12.77 | 0.196 ± 0.011 | |
| 6 | 武陵山 Wuling Mountains | 2,378 | 40.24 | 41.67 | 0.031 ± 0.002 |
| 湖南省 Hunan | 717 | 62.62 | 77.68 | 0.016 ± 0.002 | |
| 湖北省 Hubei | 1,661 | 30.58 | 26.13 | 0.038 ± 0.002 | |
| 7 | 邛崃山 Qionglai Mountains | 4,365 | 38.26 | 41.53 | 0.049 ± 0.002 |
| 四川省 Sichuan | 4,365 | 38.26 | 41.53 | 0.049 ± 0.002 | |
| 8 | 武夷山-马头山 Wuyishan-Matoushan | 4,387 | 61.59 | 18.05 | 0.168 ± 0.005 |
| 江西省 Jiangxi | 2,009 | 59.18 | 7.86 | 0.094 ± 0.005 | |
| 福建省 Fujian | 2,378 | 63.62 | 26.66 | 0.230 ± 0.009 | |
| 9 | 九龙山 Jiulongshan | 3,272 | 39.70 | 1.77 | 0.465 ± 0.008 |
| 浙江省 Zhejiang | 2,951 | 54.52 | 1.97 | 0.482 ± 0.009 | |
| 福建省 Fujian | 321 | 38.09 | 0.00 | 0.309 ± 0.020 |
表2 中国大陆地区云豹潜在栖息地统计。列举每个潜在栖息地斑块的面积、该斑块内部高质量栖息地比例、保护地覆盖率,以及2010-2020年间年均森林覆盖率的减量和标准误差。各黑体编号条目为该栖息地斑块总论, 其下条目为该斑块中按行政区划的各论。
Table 2 Statistics of Neofelis nebulosa potential habitats relevant to mainland China. Area, high-quality habitat percentage, protected area percentage, annual forest loss were listed for each potential habitat patch from 2010-2020. Every numbered row in bold presents the overall statistics for each patch, with statistics according to administrative division present below.
| 编号 No. | 潜在栖息地 Potential habitats | 面积 Area (km2) | 高质量栖息地比例 High-quality habitat (%) | 保护地覆盖 Protected area (%) | 年均森林覆盖率减量Annual forest loss (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 喜马拉雅-横断山脉西侧-若开山脉Himalaya-Western Hengduan-Arakan Mountains | 274,408 | 83.18 | 13.92 | 0.412 ± 0.014 |
| 西藏自治区 Xizang | 38,594 | 75.76 | 3.36 | 0.198 ± 0.002 | |
| 云南省 Yunnan | 1,110 | 58.38 | 31.26 | 0.565 ± 0.021 | |
| 境外 Abroad | 234,704 | 84.52 | 15.57 | 0.447 ± 0.015 | |
| 2 | 无量山南麓-安南山脉 South Wuliangshan-Annamite | 195,476 | 87.20 | 28.81 | 1.118 ± 0.032 |
| 云南省 Yunnan | 1,669 | 68.30 | 68.36 | 0.081 ± 0.005 | |
| 境外 Abroad | 193,807 | 87.37 | 28.47 | 1.127 ± 0.032 | |
| 编号 No. | 潜在栖息地 Potential habitats | 面积 Area (km2) | 高质量栖息地比例 High-quality habitat (%) | 保护地覆盖 Protected area (%) | 年均森林覆盖率减量Annual forest loss (%) |
| 3 | 十万大山?越南北部高地 Shiwandashan-North Vietnam | 4,372 | 63.06 | 19.99 | 1.299 ± 0.232 |
| 广西壮族自治区 Guangxi | 2,135 | 57.19 | 29.41 | 0.565 ± 0.020 | |
| 境外 Abroad | 2,237 | 68.66 | 11.00 | 2.004 ± 0.252 | |
| 4 | 大瑶山 Dayaoshan | 1,790 | 56.31 | 13.07 | 0.579 ± 0.013 |
| 广西壮族自治区 Guangxi | 1,790 | 56.31 | 13.07 | 0.579 ± 0.013 | |
| 5 | 桂林西北 Northwest of Guilin | 4,393 | 43.32 | 32.55 | 0.404 ± 0.007 |
| 广西壮族自治区 Guangxi | 3,688 | 51.38 | 36.33 | 0.444 ± 0.008 | |
| 湖南省 Hunan | 705 | 1.13 | 12.77 | 0.196 ± 0.011 | |
| 6 | 武陵山 Wuling Mountains | 2,378 | 40.24 | 41.67 | 0.031 ± 0.002 |
| 湖南省 Hunan | 717 | 62.62 | 77.68 | 0.016 ± 0.002 | |
| 湖北省 Hubei | 1,661 | 30.58 | 26.13 | 0.038 ± 0.002 | |
| 7 | 邛崃山 Qionglai Mountains | 4,365 | 38.26 | 41.53 | 0.049 ± 0.002 |
| 四川省 Sichuan | 4,365 | 38.26 | 41.53 | 0.049 ± 0.002 | |
| 8 | 武夷山-马头山 Wuyishan-Matoushan | 4,387 | 61.59 | 18.05 | 0.168 ± 0.005 |
| 江西省 Jiangxi | 2,009 | 59.18 | 7.86 | 0.094 ± 0.005 | |
| 福建省 Fujian | 2,378 | 63.62 | 26.66 | 0.230 ± 0.009 | |
| 9 | 九龙山 Jiulongshan | 3,272 | 39.70 | 1.77 | 0.465 ± 0.008 |
| 浙江省 Zhejiang | 2,951 | 54.52 | 1.97 | 0.482 ± 0.009 | |
| 福建省 Fujian | 321 | 38.09 | 0.00 | 0.309 ± 0.020 |
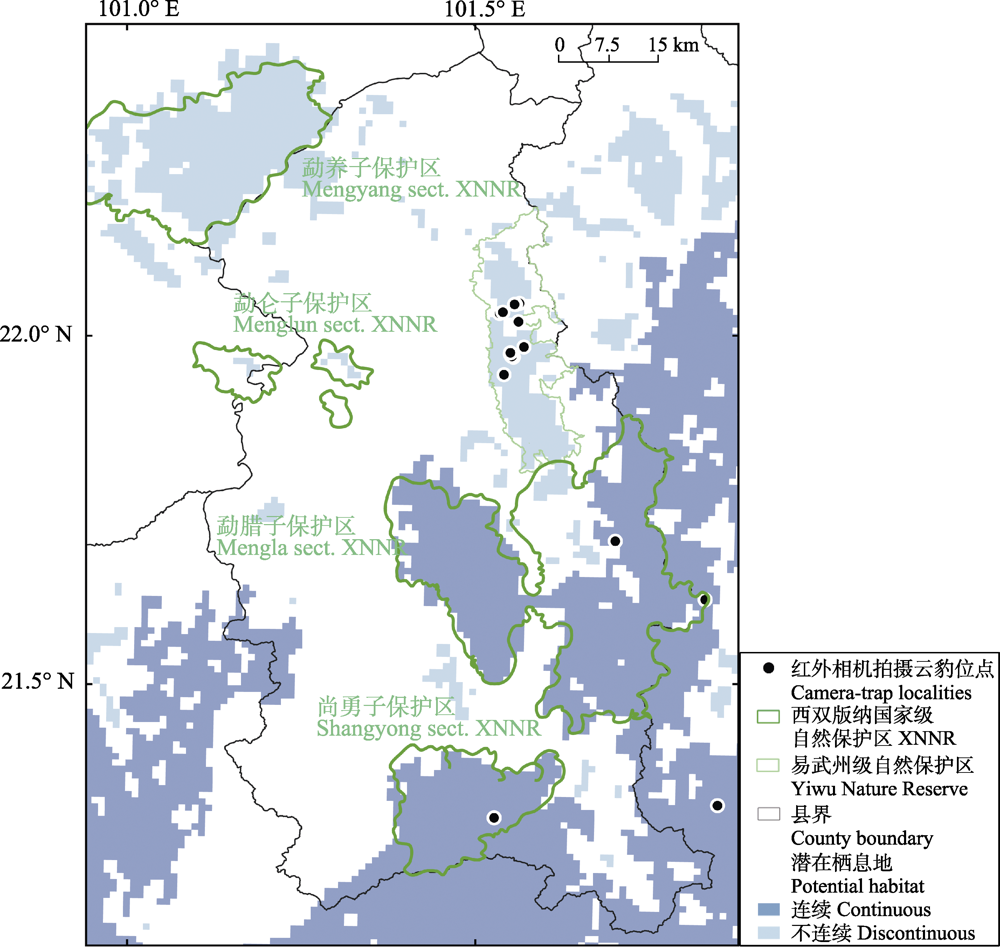
图4 云南省勐腊县云豹潜在栖息地分布和保护地覆盖情况。XNNR: 西双版纳国家级自然保护区。
Fig. 4 Neofelis nebulosa habitat distribution and protected area coverage in Mengla County, Yunnan Province. XNNR, Xishuangbanna National Nature Reserve.
| [1] | Austin SC, Tewes ME, Grassman LI Jr, Silvy NJ (2007) Ecology and conservation of the leopard cat Prionailurus bengalensis and clouded leopard Neofelis nebulosa in Khao Yai National Park, Thailand. Acta Zoologica Sinica, 53, 1-14. |
| [2] | Bivand R, Keitt T, Rowlingson R (2021) rgdal: Bindings for the 'Geospatial' Data Abstraction Library. R package version 1.5-23. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=rgdal. (accessed on 2021-07-28) |
| [3] | Borah J, Sharma T, Das D, Rabha N, Basumatary NKA, Ahmed MF, Vattakaven J (2013) Abundance and density estimates for common leopard Panthera pardus and clouded leopard Neofelis nebulosa in Manas National Park, Assam, India. Oryx, 49, 149-155 |
| [4] |
Buckley-Beason VA, Johnson WE, Nash WG, Stanyon R, Menninger JC, Driscoll CA, Howard J, Bush M, Page JE, Roelke ME, Stone G, Martelli PP, Wen C, Ling L, Duraisingam RK, Lam PV, O’Brien SJ (2006) Molecular evidence for species-level distinctions in clouded leopards. Current Biology, 16, 2371-2376.
PMID |
| [5] |
Carter NH, Levin SA, Grimm V (2019) Effects of human-induced prey depletion on large carnivores in protected areas: Lessons from modeling tiger populations in stylized spatial scenarios. Ecology and Evolution, 9, 11298-11313.
DOI |
| [6] | Chen WH (2003) Preliminary analysis on the reasons of the frequent occurrences of clouded leopards in Shitai, Anhui. Anhui Forestry Science & Technology, (4), 11-12. (in Chinese) |
| [陈文豪 (2003) 安徽石台云豹频繁出现的原因初探. 安徽林业科技, (4), 11-12.] | |
| [7] |
Chiang PJ, Pei KJC, Vaughan MR, Li CF, Chen MT, Liu JN, Lin CY, Lin LK, Lai YC (2015) Is the clouded leopard Neofelis nebulosa extinct in Taiwan, and could it be reintroduced? An assessment of prey and habitat. Oryx, 49, 261-269.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Christiansen P (2008) Species distinction and evolutionary differences in the clouded leopard (Neofelis nebulosa) and Diard’s clouded leopard (Neofelis diardi). Journal of Mammalogy, 89, 1435-1446.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Cole LES, Bhagwat SA, Willis KJ (2014) Recovery and resilience of tropical forests after disturbance. Nature Communications, 5, 3906.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
D’Cruze N, MacDonald DW (2015) Clouded in mystery: The global trade in clouded leopards. Biodiversity and Conservation, 24, 3505-3526.
DOI URL |
| [11] | Feng LM, Jutzeler E (2010) Clouded leopard. Cat News, 5, 34-36. |
| [12] |
Ghimirey Y, Acharya R (2018) The vulnerable clouded leopard Neofelis nebulosa in Nepal: An update. Oryx, 52, 166-170.
DOI URL |
| [13] | Grassman L, Lynam A, Mohamad S, Duckworth JW, Bora J, Wilcox D, Ghimirey Y, Reza A, Rahman H (2016) Neofelis nebulosa. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/14519/198843258. (acc- essed on 2021-07-28) |
| [14] | Gray T, Borah J, Coudrat CNZ, Ghimirey Y, Giordano A, Greenspan E, Petersen W, Rostro-García S, Shariff M, Wai-Ming W (2021) Neofelis nebulosa. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2021. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/14519/198843258. . (accessed on 2021-09-05) |
| [15] | Griffith E (1821) General and Particular Descriptions of the Vertebrated Animals: Arranged Conformably to the Modern Discoveries and Improvements in Zoology. Order Quadrumana, (vol. 1), pp. 36-37. Baldwin, Cradock, and Joy, London. |
| [16] |
Guo YR, Lan WJ, Zou SC, Yuan RB, Dong XY, Cao JR, Yang QP, Song QN (2021) Camera-trapping survey of wild mammals and ground-dwelling birds in the Jiangxi Wuyishan National Nature Reserve, China. Biodiversity Science, 29, 811-818. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [郭英荣, 兰文军, 邹思成, 袁荣斌, 董晓雨, 曹吉锐, 杨清培, 宋庆妮 (2021) 江西武夷山国家级自然保护区林下鸟类和兽类资源的红外相机监测. 生物多样性, 29, 811-818.] | |
| [17] |
Hansen MC, Potapov PV, Moore R, Hancher M, Turubanova SA, Tyukavina A, Thau D, Stehman SV, Goetz SJ, Loveland TR, Kommareddy A, Egorov A, Chini L, Justice CO, Townshend JRG (2013) High-resolution global maps of 21st-century forest cover change. Science, 342, 850-853.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
He RC, Wang L, Quan RC (2020) Introduction to Transboundary Animal Diversity Monitoring Platform of Southern Yunnan, China and Southeast Asia. Biodiversity Science, 28, 1097-1103. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [贺如川, 王林, 权锐昌 (2020) 中国滇南-东南亚跨境动物多样性监测平台概述. 生物多样性, 28, 1097-1103.] | |
| [19] | Hijmans JR (2021) raster: Geographic Data Analysis and Modeling. R package version 3.4-10. https://CRAN.R-proj ect.org/package=raster. (accessed on 2021-07-28) |
| [20] |
Hua FY, Bruijnzeel LA, Meli P, Martin PA, Zhang J, Nakagawa S, Miao XR, Wang WY, McEvoy C, Peña-Arancibia JL, Brancalion PHS, Smith P, Edwards DP, Balmford A (2022) The biodiversity and ecosystem service contributions and trade-offs of forest restoration approaches. Science, 376, 839-844.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Kaszta Ż, Cushman SA, Htun S, Naing H, Burnham D, MacDonald DW (2020) Simulating the impact of Belt and Road Initiative and other major developments in Myanmar on an ambassador felid, the clouded leopard, Neofelis nebulosa. Landscape Ecology, 35, 727-746.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Lau MWN, Fellowes JR, Chan BPL (2010) Carnivores (Mammalia: Carnivora) in South China: A status review with notes on the commercial trade. Mammal Review, 40, 247-292.
DOI URL |
| [23] | Li J, Wang XL, Yang MW, Chen DX, Wang XJ, Luo P, Liu F, Xue YD, Li GL, Zhang YG, Zhang Y, Li DQ (2020) Construction progress of camera-trapping database from the Nature Reserves Biological Specimen Resources Sharing Sub-platform. Biodiversity Science, 28, 1081-1089. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李佳, 王秀磊, 杨明伟, 陈大祥, 王晓菊, 罗平, 刘芳, 薛亚东, 李广良, 张于光, 张宇, 李迪强 (2020) 自然保护区生物标本资源共享子平台红外相机数据库建设进展. 生物多样性, 28, 1081-1089.] | |
| [24] | Li M, Fu YW, Liao T, Li DR, Ran JH, Du YP, Yang XY (2020) Distribution change and its causes of the clouded leopard (Neofelis nebulosa) in southeastern Sichuan. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40, 5940-5948. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李蔓, 付焱文, 廖婷, 李东睿, 冉江洪, 杜一平, 杨旭煜 (2020) 四川东南地区云豹(Neofelis nebulosa)分布区变化及其成因. 生态学报, 40, 5940-5948.] | |
| [25] |
Li S (2020) Development progress and outlook of the wildlife camera-trapping networks in China. Biodiversity Science, 28, 1045-1048. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
[李晟 (2020) 中国野生动物红外相机监测网络建设进展与展望. 生物多样性, 28, 1045-1048.]
DOI |
|
| [26] | Li S, McShea WJ, Wang DJ, Gu XD, Shen XL (2020) Retreat of large carnivores across the giant panda distribution range. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 4, 1327-1331. |
| [27] |
Li S, McShea WJ, Wang DJ, Shen XL, Bu HL, Guan TP, Wang F, Gu XD, Zhang XF, Liao HH (2020) Construction progress of the Camera-trapping Network for the Mountains of Southwest China. Biodiversity Science, 28, 1049-1058. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [李晟, McShea WJ, 王大军, 申小莉, 卜红亮, 官天培, 王放, 古晓东, 张晓峰, 廖灏泓 (2020) 西南山地红外相机监测网络建设进展. 生物多样性, 28, 1049-1058.] | |
| [28] |
Li S, Wang DJ, Xiao ZS, Li XH, Wang TM, Feng LM, Wang Y (2014) Camera-trapping in wildlife research and conservation in China: Review and outlook. Biodiversity Science, 22, 685-695. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[李晟, 王大军, 肖治术, 李欣海, 王天明, 冯利民, 王云 (2014) 红外相机技术在我国野生动物研究与保护中的应用与前景. 生物多样性, 22, 685-695.]
DOI |
|
| [29] |
Li XY, Bleisch WV, Liu XW, Jiang XL (2021) Camera-trap surveys reveal high diversity of mammals and pheasants in Medog, Tibet. Oryx, 55, 177-180.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Li XY, Hu WQ, Pu CZ, Li Q, Yu QP, Hu ZC, Bleisch WV, Jiang X (2020) Camera-trapping monitoring platform for mammals and pheasants in the Longitudinal Range and Gorge Region of Southwest China: Protocol, progress and future outlook. Biodiversity Science, 28, 1090-1096. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [李学友, 胡文强, 普昌哲, 李权, 于秋鹏, 胡哲畅, William V. Bleisch, 蒋学龙 (2020) 西南纵向岭谷区兽类及雉类红外相机监测平台: 方案、进展与前景. 生物多样性, 28, 1090-1096.] | |
| [31] | Liu JG, Li SX, Ouyang ZY, Tam C, Chen XD (2008) Ecological and socioeconomic effects of China’s policies for ecosystem services. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 105, 9477-9482. |
| [32] |
Liu K, He J, Zhang JH, Feng J, Yu Q, Gu CM, Wu HL (2017) Mammal resource status in the mountain forest ecosystems of southern Anhui Province based on camera trap data. Biodiversity Science, 25, 896-903. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[刘凯, 贺君, 张继辉, 冯俊, 宇强, 顾长明, 吴海龙 (2017) 基于红外相机技术的皖南山区森林生态系统兽类资源现状. 生物多样性, 25, 896-903.]
DOI |
|
| [33] | Liu SY, Wu Y, Li S (2020) Handbook of the Mammals of China, 2nd edn. The Straits Publishing & Distributing Group, Fuzhou. (in Chinese) |
| [刘少英, 吴毅, 李晟 (2020) 中国兽类图鉴(第二版). 海峡出版发行集团, 福州.] | |
| [34] |
Liu YL, Song DZ, Liu BB, Xia F, Chen YL, Wang YQ, Huang QW (2020) Overview of the Camera-trapping Platform for Felid Species in China: Data integration by a conservation NGO. Biodiversity Science, 28, 1067-1074. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [刘炎林, 宋大昭, 刘蓓蓓, 夏凡, 陈月龙, 王一晴, 黄巧雯 (2020) 中国猫科动物红外相机监测平台介绍: 民间环保机构的数据整合. 生物多样性, 28, 1067-1074.] | |
| [35] | Ma GY (1988) Preliminary report on the inventory of mammals in Baishuijiang Nature Reserve. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 23(5), 26-28. (in Chinese) |
| [马国瑶 (1988) 白水江自然保护区兽类调查初报. 动物学杂志, 23(5), 26-28.] | |
| [36] | MacArthur RH, Wilson EO (2001) The Theory of Island Biogeography. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [37] |
MacDonald DW, Bothwell HM, Kaszta Ż, Ash E, Bolongon G, Burnham D, Can ÖE, Campos-Arceiz A, Channa P, Clements GR, Hearn AJ, Hedges L, Htun S, Kamler JF, Kawanishi K, MacDonald EA, Mohamad SW, Moore J, Naing H, Onuma M, Penjor U, Rasphone A, Rayan DM, Ross J, Singh P, Tan CKW, Wadey J, Yadav BP, Cushman SA (2019) Multi-scale habitat modelling identifies spatial conservation priorities for mainland clouded leopards (Neofelis nebulosa). Diversity and Distributions, 25, 1639-1654.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
MacDonald EA, Hinks A, Weiss DJ, Dickman A, Burnham D, Sandom CJ, Malhi Y, MacDonald DW (2017) Identifying ambassador species for conservation marketing. Global Ecology and Conservation, 12, 204-214.
DOI URL |
| [39] | Min S, D’Cruze N, MacDonald DW (2018) A note on felid trade at local markets in Myanmar. Cat News, 67, 25-28. |
| [40] | Min ZL, Chen FG, Huang HF (1966) New records on the mammals of Shaanxi Province. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 2(3), 54-55. (in Chinese) |
| [闵芝兰, 陈服官, 黄洪富 (1966) 陕西省兽类新纪录. 动物学杂志, 2(3), 54-55.] | |
| [41] |
Mohamad SW, Rayan DM, Christopher WCT, Hamirul M, Mohamed A, Lau CF, Siwan ES (2015) The first description of population density and habitat use of the mainland clouded leopard Neofelis nebulosa within a logged-primary forest in South East Asia. Population Ecology, 57, 495-503.
DOI URL |
| [42] | Oswell AH (2010) The Big Cat Trade in Myanmar and Thailand. TRAFFIC Southeast Asia, Petaling Jaya, Selangor, Malaysia. |
| [43] |
Penjor U, MacDonald DW, Wangchuk S, Tandin T, Tan CKW (2018) Identifying important conservation areas for the clouded leopard Neofelis nebulosa in a mountainous landscape: Inference from spatial modeling techniques. Ecology and Evolution, 8, 4278-4291.
DOI PMID |
| [44] | Petersen WJ, Savini T, Ngoprasert D (2020) Strongholds under siege: Range-wide deforestation and poaching threaten mainland clouded leopards (Neofelis nebulosa). Global Ecology and Conservation, 24, e01354. |
| [45] |
Rao M, Myint T, Zaw T, Htun S (2005) Hunting patterns in tropical forests adjoining the Hkakaborazi National Park, north Myanmar. Oryx, 39, 292-300.
DOI URL |
| [46] | Ripple WJ, Estes JA, Beschta RL, Wilmers CC, Ritchie EG (2014) Status and ecological effects of the world’s largest carnivores. Science, 343, 1241484. |
| [47] | Sheng HL (1976) Diets of the tiger, leopard and clouded leopard. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 11(1), 41. (in Chinese) |
| [盛和林 (1976) 虎、豹和云豹的食物. 动物学杂志, 11(1), 41.] | |
| [48] | Sheng HL, Lu HJ (1982) Valuable mammals in Jiangxi Province. Chinese Journal of Wildlife, (4), 6-8. (in Chinese) |
| [盛和林, 陆厚基 (1982) 江西省的珍贵兽类. 野生动物, (4), 6-8.] | |
| [49] | Sheng HL, Lu HJ, Wang PC (1984) Problems in the exploitation of wild mammal resources in Jiangxi Province. Journal of East China Normal University (Natural Science), (2), 89-94. (in Chinese) |
| [盛和林, 陆厚基, 王培潮 (1984) 江西省哺乳动物资源的开发问题. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), (2), 89-94.] | |
| [50] | Shou ZH, Wang S, Lu CK, Zhang LG (1966) A survey of the mammals of Hainan Island, China. Acta Zootaxonomica Sinica, 3, 260-275. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [寿振黄, 汪松, 陆长坤, 张銮光 (1966) 海南岛的兽类调查. 动物分类学报, 3, 260-275.] | |
| [51] | Smith A, Xie Y (2009) A Guide to the Mammals of China. Hunan Education Publishing House, Changsha. (in Chinese) |
| [Smith A, 解焱 (2009) 中国兽类野外手册. 湖南教育出版社, 长沙.] | |
| [52] | State Forestry Administration (2009) Survey of Key Protected Terrestrial Animal in China. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [国家林业局 (2009) 中国重点陆生野生动物资源调查. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [53] |
Tan CKW, Rocha DG, Clements GR, Brenes-Mora E, Hedges L, Kawanishi K, Mohamad SW, Mark Rayan D, Bolongon G, Moore J, Wadey J, Campos-Arceiz A, MacDonald DW (2017) Habitat use and predicted range for the mainland clouded leopard Neofelis nebulosa in Peninsular Malaysia. Biological Conservation, 206, 65-74.
DOI URL |
| [54] | UNEP-WCMC, IUCN (2021) Protected Planet: The World Database on Protected Areas (WDPA) and World Database on Other Effective Area-based Conservation Measures (WD-OECM), August 2021, UNEP-WCMC and IUCN, Cambridge, UK. http://www.protectedplanet.net. (accessed on 2021-07-28) |
| [55] | Vitkalova A, Feng LM, Rybin A, Gerber B, Miquelle D, Wang TM, Yang HT, Shevtsova E, Aramile V, Ge JP (2018) Transboundary cooperation improves endangered species monitoring and conservation actions: A case study of the global population of Amur leopards. Conservation Letters, 11, e12574. |
| [56] |
Wan YQ, Li JQ, Yang XW, Li S, Xu HG (2020) Progress of the China mammal diversity observation network (China BON-Mammal) based on camera-trapping. Biodiversity Science, 28, 1115-1124. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [万雅琼, 李佳琦, 杨兴文, 李晟, 徐海根 (2020) 基于红外相机的中国哺乳动物多样性观测网络建设进展. 生物多样性, 28, 1115-1124.] | |
| [57] | Wang GH, Li SQ, Shi ZP, Wang SN, Ye JP, Zhou QH (2016) Preliminary survey of mammal and bird diversity of Guangxi Maoershan National Nature Reserve: Based on infrared camera monitoring. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 36, 338-347. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [汪国海, 李生强, 施泽攀, 王绍能, 叶建平, 周岐海 (2016) 广西猫儿山自然保护区的兽类和鸟类多样性初步调查——基于红外相机监测数据. 兽类学报, 36, 338-347.] | |
| [58] | Wang S, Lu CK, Gao YT, Lu TC (1962) Mammal research in southwest Guangxi. Acta Zoologica Sinica, 14, 555-570. (in Chinese) |
| [汪松, 陆长坤, 高耀亭, 卢汰春 (1962) 广西西南部兽类的研究. 动物学报, 14, 555-570.] | |
| [59] |
Wang TM, Royle JA, Smith JLD, Zou L, Lu XY, Li T, Yang HT, Li ZL, Feng RN, Bian YJ, Feng LM, Ge JP (2018) Living on the edge: Opportunities for Amur tiger recovery in China. Biological Conservation, 217, 269-279.
DOI URL |
| [60] | Wei FW, Yang QS, Wu Y, Jiang XL, Liu SY, Li BG, Yang G, Li M, Zhou J, Li S, Hu YB, Ge DY, Li S, Yu WH, Chen BY, Zhang ZJ, Zhou CQ, Wu SB, Zhang L, Chen ZZ, Chen SD, Deng HQ, Jiang TL, Zhang LB, Shi HY, Lu XL, Li Q, Liu Z, Cui YQ, Li YC (2021) Catalogue of mammals in China (2021). Acta Theriologica Sinica, 41, 487-501. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[魏辅文, 杨奇森, 吴毅, 蒋学龙, 刘少英, 李保国, 杨光, 李明, 周江, 李松, 胡义波, 葛德燕, 李晟, 余文华, 陈炳耀, 张泽均, 周材权, 吴诗宝, 张立, 陈中正, 陈顺德, 邓怀庆, 江廷磊, 张礼标, 石红艳, 卢学理, 李权, 刘铸, 崔雅倩, 李玉春 (2021) 中国兽类名录(2021). 兽类学报, 41, 487-501.]
DOI |
|
| [61] |
Wu JP, Luo H, Zhu XL, Li BZ, Liu WL, Ci P (2016) Monitoring mammals and birds with camera traps at different altitudes of Medog, Tibet. Biodiversity Science, 24, 351-354. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
[吴建普, 罗红, 朱雪林, 李炳章, 刘务林, 次平 (2016) 西藏墨脱不同海拔区鸟兽红外相机监测. 生物多样性, 24, 351-354.]
DOI |
|
| [62] |
Xie WH, Yang XF, Yu JJ, Li JN, Tao SL, Lu ZJ, Wang XZ, Xiao ZS (2014) A survey of mammals and birds using camera traps in Badagongshan Forest Dynamics Plot, Central China. Biodiversity Science, 22, 816-818. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
[谢文华, 杨锡福, 于家捷, 李俊年, 陶双伦, 卢志军, 王学志, 肖治术 (2014) 运用红外相机对八大公山森林动态样地鸟兽的初步调查. 生物多样性, 22, 816-818.]
DOI |
|
| [63] |
Xu WH, Zang ZH, Du A, Ouyang ZY (2021) The experiences of Northeast China Tiger and Leopard National Park pilot. Biodiversity Science, 29, 295-297. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
[徐卫华, 臧振华, 杜傲, 欧阳志云 (2021) 东北虎豹国家公园试点经验. 生物多样性, 29, 295-297.]
DOI |
|
| [64] |
Yu GQ, Kang ZJ, Liu MS, Chen ZF, Deng ZC (2018) Preliminary survey using infrared camera reveals fauna and avifauna diversity at Hupingshan National Nature Reserve, Hunan, China. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 38, 104-112. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [于桂清, 康祖杰, 刘美斯, 陈振法, 邓忠次 (2018) 利用红外相机对湖南壶瓶山国家级自然保护区兽类和鸟类多样性的初步调查. 兽类学报, 38, 104-112.] | |
| [65] |
Zeng ZZ, Estes L, Ziegler AD, Chen AP, Searchinger T, Hua FY, Guan KY, Jintrawet A, Wood EF (2018) Highland cropland expansion and forest loss in Southeast Asia in the twenty-first century. Nature Geoscience, 11, 556-562.
DOI URL |
| [66] | Zhang YZ (1997) Distribution of Mammalian Species in China. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [张荣祖 (1997) 中国哺乳动物分布. 中国林业出版社, 北京.] | |
| [67] | Zheng WC, Zhang SS, Pan CC, Liu JL, Ji GH (2014) Mammal and avian diversities detected by infrared camera in Jiulongshan National Nature Reserve. Journal of Zhejiang Forestry Science and Technology, 34(1), 17-22. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郑伟成, 章书声, 潘成椿, 刘菊莲, 季国华 (2014) 红外相机技术监测九龙山国家级自然保护区鸟兽多样性. 浙江林业科技, 34(1), 17-22.] |
| [1] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [2] | 张雨琦, 文君, 张引, 李晟之. 大熊猫国家公园全民公益性评价研究: 基于利益相关者感知视角[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24240-. |
| [3] | 韩思成, 陆道炜, 韩宇辰, 栗若寒, 杨晶, 孙戈, 杨陆, 钱俊伟, 方翔, 罗述金. 北京近郊浅山地区的野生豹猫分布及环境影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 24138-. |
| [4] | 姜熠辉, 刘岳, 曾旭, 林喆滢, 王楠, 彭吉豪, 曹玲, 曾聪. 东海六个国家级海洋保护区鱼类多样性和连通性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24128-. |
| [5] | 田瑜, 李俊生. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》“3030”目标的内涵及实现路径分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24086-. |
| [6] | 鄢德奎. 中国生物多样性保护政策的共同要素、不足和优化建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(5): 23293-. |
| [7] | 崔国发. 关于自然保护地整合优化工作中几个关键问题的讨论与建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 22447-. |
| [8] | 林木青, 张应明, 欧阳芳, 束祖飞, 朱朝东, 肖治术. 广东车八岭国家级自然保护区独栖性胡蜂多样性空间分布特征及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22310-. |
| [9] | 王一晴, 马子驭, 王刚, 刘炎林, 宋大昭, 刘蓓蓓, 李露, 范新国, 黄巧雯, 李晟. 太行山华北豹袭击家畜的时空特点与管理建议: 以山西省和顺县为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(9): 21510-. |
| [10] | 刘童祎, 姜立云, 乔格侠. 中国半翅目等29目昆虫新分类单元2021年年度报告[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(8): 22300-. |
| [11] | 孙维悦, 舒江平, 顾钰峰, 莫日根高娃, 杜夏瑾, 刘保东, 严岳鸿. 基于保护基因组学揭示荷叶铁线蕨的濒危机制[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21508-. |
| [12] | 张敏, 田春坡, 车先丽, 赵岩岩, 陈什旺, 周霞, 邹发生. 广东省鸟类新记录及其与自然和社会经济因素的关联性[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(5): 21396-. |
| [13] | 吴必虎, 谢冶凤, 李奕, 丛丽. 生态保护红线战略视域下自然保护地如何划界和分区管控?[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(4): 21372-. |
| [14] | 张书杰, 庄优波. 管控视角下生态空间与生态保护红线关系研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(4): 21441-. |
| [15] | 朱华, 杜凡. 设立云南金沙江干热河谷萨王纳植被自然保护地的建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(3): 21519-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()