



Biodiv Sci ›› 2021, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (6): 811-818. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020307 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2020307
Special Issue: 数据论文
• Bioinventories • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yingrong Guo1, Wenjun Lan2, Sicheng Zou2, Rongbin Yuan2, Xiaoyu Dong3, Jirui Cao3, Qingpei Yang3, Qingni Song3,*( )
)
Received:2020-07-31
Accepted:2020-11-22
Online:2021-06-20
Published:2021-05-30
Contact:
Qingni Song
Yingrong Guo, Wenjun Lan, Sicheng Zou, Rongbin Yuan, Xiaoyu Dong, Jirui Cao, Qingpei Yang, Qingni Song. Camera-trapping survey of wild mammals and ground-dwelling birds in the Jiangxi Wuyishan National Nature Reserve, China[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2021, 29(6): 811-818.
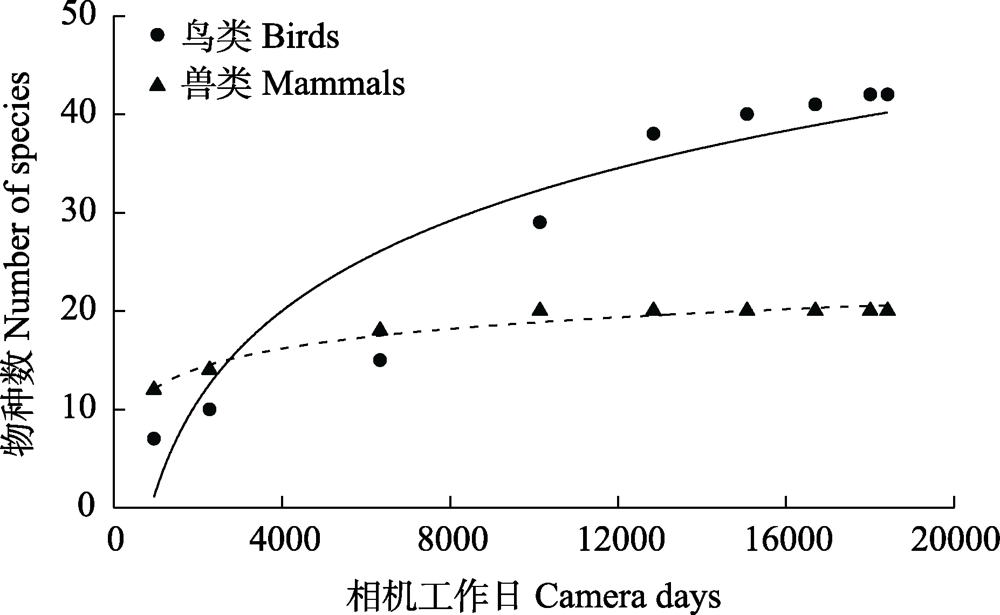
Fig. 2 Rarefaction curves for estimating species number of mammals and ground-dwelling birds with increased camera days in the Jiangxi Wuyishan National Nature Reserve
| 环境变量 Environmental variables | 相机位点数 No. of camera sites | 相机工作日Camera days | 独立照片数 No. of independent photographs | 物种数 No. of species | 相对多度指数 Relative abundance index (RAI) | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index (H') |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔 Elevation | ||||||
| <800 m | 4 | 1,257 | 573 | 21 | 455.8 | 1.949 |
| 800-1,000 m | 8 | 3,425 | 1,980 | 41 | 578.1 | 2.155 |
| 1,000-1,200 m | 12 | 4,427 | 2,476 | 46 | 559.0 | 1.785 |
| 1,200-1,400 m | 9 | 2,967 | 1,295 | 27 | 436.4 | 1.602 |
| 1,400-1,600 m | 7 | 2,776 | 1,174 | 36 | 422.9 | 2.031 |
| 1,600-1,800 m | 7 | 2,288 | 735 | 30 | 321.2 | 1.808 |
| >1,800 m | 5 | 1,277 | 675 | 19 | 528.6 | 1.520 |
| 功能区划 Functional zone | ||||||
| 核心区 Core zone | 30 | 9,915 | 4,528 | 47 | 456.8 | 1.910 |
| 缓冲区 Buffer zone | 11 | 4,153 | 2,205 | 38 | 531.4 | 1.863 |
| 实验区 Experimental zone | 11 | 4,349 | 2,164 | 44 | 499.4 | 2.324 |
Table 1 Species diversity of mammals and ground-dwelling birds by camera-trapping in different elevation gradients and different functional zones in the Jiangxi Wuyishan National Nature Reserve
| 环境变量 Environmental variables | 相机位点数 No. of camera sites | 相机工作日Camera days | 独立照片数 No. of independent photographs | 物种数 No. of species | 相对多度指数 Relative abundance index (RAI) | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index (H') |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海拔 Elevation | ||||||
| <800 m | 4 | 1,257 | 573 | 21 | 455.8 | 1.949 |
| 800-1,000 m | 8 | 3,425 | 1,980 | 41 | 578.1 | 2.155 |
| 1,000-1,200 m | 12 | 4,427 | 2,476 | 46 | 559.0 | 1.785 |
| 1,200-1,400 m | 9 | 2,967 | 1,295 | 27 | 436.4 | 1.602 |
| 1,400-1,600 m | 7 | 2,776 | 1,174 | 36 | 422.9 | 2.031 |
| 1,600-1,800 m | 7 | 2,288 | 735 | 30 | 321.2 | 1.808 |
| >1,800 m | 5 | 1,277 | 675 | 19 | 528.6 | 1.520 |
| 功能区划 Functional zone | ||||||
| 核心区 Core zone | 30 | 9,915 | 4,528 | 47 | 456.8 | 1.910 |
| 缓冲区 Buffer zone | 11 | 4,153 | 2,205 | 38 | 531.4 | 1.863 |
| 实验区 Experimental zone | 11 | 4,349 | 2,164 | 44 | 499.4 | 2.324 |
| [1] | Chen SW, Yu JP, Chen XN, Shen XL, Li S, Ma KP (2016) Camera-trapping survey on the diversity of mammal and pheasant species in Gutianshan National Nature Reserve, Zhejiang Province. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 36,292-301. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 陈声文, 余建平, 陈小南, 申小莉, 李晟, 马克平 (2016) 利用红外相机网络调查古田山自然保护区的兽类及雉类多样性. 兽类学报, 36,292-301.] | |
| [2] | Cheng SL, Fang Y, Cheng L, Zhong ZY, Zheng YQ, Wang XM, Cheng YJ (2009) Pheasants and their conservation status in Wuyishan National Nature Reserve in Jiangxi Province. Journal of Hainan Normal University (Natural Science), 22,83-85. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 程松林, 方毅, 程林, 钟志宇, 郑元庆, 王小民, 程义杰 (2009) 江西武夷山自然保护区的雉类资源及其保护. 海南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 22,83-85.] | |
| [3] | Cheng SL, Mao YX, Hu EY, Lei P, Yuan RB, Zou SC (2017) Population biology and altitudinal distribution of Tragopan caboti in Jiangxi Wuyishan Nature Reserve . Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 53(10),160-167. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 程松林, 毛夷仙, 胡尔夷, 雷平, 袁荣斌, 邹思成 (2017) 江西武夷山自然保护区黄腹角雉种群生物学及海拔分布特征. 林业科学, 53(10),160-167.] | |
| [4] | Cheng SL, Wu SY, Zhong ZY, Mao YX (2013a) Supplement of animals list in Jiangxi Wuyishan National Nature Reserve. Jiangxi Forestry Science and Technology, (2),40-43, 52. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 程松林, 吴淑玉, 钟志宇, 毛夷仙 (2013a) 江西武夷山国家级自然保护区动物名录增补. 江西林业科技, (2),40-43, 52.] | |
| [5] | Cheng SL, Yuan RB, Zou SC (2013b) Black muntjac ( Muntiacus crinifrons) found at Jiangxi Wuyishan . Acta Theriologica Sinica, 33,94, 93. (in Chinese) |
| 程松林, 袁荣斌, 邹思成 (2013b) 江西武夷山发现黑麂. 兽类学报, 33,94, 93.] | |
| [6] |
Colwell RK, Lees DC (2000) The mid-domain effect: Geometric constraints on the geography of species richness. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 15,70-76.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Frey S, Fisher JT, Burton AC, Volpe JP (2017) Investigating animal activity patterns and temporal niche partitioning using camera-trap data: Challenges and opportunities. Remote Sensing in Ecology and Conservation, 3,123-132.
DOI URL |
| [8] | He BS, Sun RQ, Chen P, Dong W, Wang J, Wang DJ, Li S (2016) Baseline survey of mammal and bird diversity using camera-trapping in the Changqing National Nature Reserve of Shaanxi Province. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 36,348-356. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 何百锁, 孙瑞谦, 陈鹏, 董伟, 王军, 王大军, 李晟 (2016) 基于红外相机技术调查长青国家级自然保护区兽类和鸟类多样性. 兽类学报, 36,348-356.] | |
| [9] | Jiang ZG, Ma Y, Wu Y, Wang YX (2015) China's Mammal Diversity and Geographic Distribution. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 蒋志刚, 马勇, 吴毅, 王应祥 (2015) 中国哺乳动物多样性及地理分布. 科学出版社. 北京.] | |
| [10] | Li GL, Li DQ, Xue YD, Wang XL, Yang JY, Yu HL (2014) Distribution of wildlife surveyed with infra-red cameras in the Shennongjia National Nature Reserve. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 50(9),97-104. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 李广良, 李迪强, 薛亚东, 王秀磊, 杨敬元, 余辉亮 (2014) 利用红外相机研究神农架自然保护区野生动物分布规律. 林业科学, 50(9),97-104.] | |
| [11] |
Li S, Wang DJ, Xiao ZS, Li XH, Wang TM, Feng LM, Wang Y (2014) Camera-trapping in wildlife research and conservation in China: Review and outlook. Biodiversity Science, 22,685-695. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
李晟, 王大军, 肖治术, 李欣海, 王天明, 冯利民, 王云 (2014) 红外相机技术在我国野生动物研究与保护中的应用与前景. 生物多样性, 22,685-695.]
DOI |
|
| [12] |
Liu F, Li DQ, Wu JG (2012) Using infra-red cameras to survey wildlife in Beijing Songshan National Nature Reserve. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32,730-739. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| 刘芳, 李迪强, 吴记贵 (2012) 利用红外相机调查北京松山国家级自然保护区的野生动物物种. 生态学报, 32,730-739.] | |
| [13] | Liu XZ (2003) Scientific Survey of the Wuyishan Nature Reserve in Jiangxi. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 刘信中 (2003) 江西武夷山自然保护区科学考察集. 科学出版社. 北京.] | |
| [14] | Ma KP (2015) Species Catalogue of China: A remarkable achievement in the field of biodiversity science in China. Biodiversity Science, 23,137-138. (in Chinese) |
| 马克平 (2015) 中国生物多样性编目取得重要进展. 生物多样性, 23,137-138.] | |
| [15] |
Seki SI (2010) Camera-trapping at artificial bathing sites provides a snapshot of a forest bird community. Journal of Forest Research, 15,307-315.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Wang C, Zhou DQ, Liang S, Su HJ, Hu CS, Zhang MM (2019) Camera-trapping survey on mammals and birds in Guizhou Chishui Alsophila National Nature Reserve . Biodiversity Science, 27,1147-1152. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
王丞, 周大庆, 梁盛, 粟海军, 胡灿实, 张明明 (2019) 贵州赤水桫椤国家级自然保护区鸟兽多样性红外相机初步监测. 生物多样性, 27,1147-1152.]
DOI |
|
| [17] | Wang GH, Li SQ, Shi ZP, Wang SN, Ye JP, Zhou QH (2016) Preliminary survey of mammal and bird diversity of Guangxi Maoershan National Nature Reserve—Based on infrared camera monitoring. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 36,338-347. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| 汪国海, 李生强, 施泽攀, 王绍能, 叶建平, 周岐海 (2016) 广西猫儿山自然保护区的兽类和鸟类多样性初步调查——基于红外相机监测数据. 兽类学报, 36,338-347.] | |
| [18] |
Wang XP, Fang JY, Tang ZY (2009) The mid-domain effect hypothesis: Models, evidence and limitations. Biodiversity Science, 17,568-578. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
王襄平, 方精云, 唐志尧 (2009) 中域效应假说: 模型、证据和局限性. 生物多样性, 17,568-578.]
DOI |
|
| [19] | Xiao ZS (2016) Wildlife resource inventory using camera trapping in natural reserves in China. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 36,270-271. (in Chinese) |
| 肖治术 (2016) 红外相机技术促进我国自然保护区野生动物资源编目调查. 兽类学报, 36,270-271.] | |
| [20] |
Xiao ZS, Li XH, Wang XZ, Zhou QH, Quan RC, Shen XL, Li S (2014) Developing camera-trapping protocols for wildlife monitoring in Chinese forests. Biodiversity Science, 22,704-711. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
肖治术, 李欣海, 王学志, 周岐海, 权锐昌, 申小莉, 李晟 (2014) 探讨我国森林野生动物红外相机监测规范. 生物多样性, 22,704-711.]
DOI |
|
| [21] | Zhang ZW, Ding CQ, Ding P, Zheng GM (2003) The current status and a conservation strategy for species of Galliformes in China. Biodiversity Science, 11,414-421. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
张正旺, 丁长青, 丁平, 郑光美 (2003) 中国鸡形目鸟类的现状与保护对策. 生物多样性, 11,414-421.]
DOI |
|
| [22] | Zheng GM (2017) Checklist on the Classification and Distribution of the Birds of China, 3rd edn, Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| 郑光美 (2017) 中国鸟类分类与分布名录(第三版), 科学出版社. 北京.] |
| [1] | Xiao-Qing Wu Meihui Zhang Suting Ge Manshu Li Kun Song Guochun Shen Jian Zhang. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Woody Plant Species Diversity and Aboveground Biomass during Near-Natural Forest Reconstruction in Shanghai: A Case Study from the Eco-Island in Minhang District [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(5): 24444-. |
| [2] | Tai Wang, Fujun Song, Yongsheng Zhang, Zhongyu Lou, Yanping Zhang, Yanyan Du. Fish diversity and resource status in interior drainage systems of Hexi Corridor [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24387-. |
| [3] | Jingjing Zhang, Wenbin Huang, Yiting Chen, Zepeng Yang, Weiye Ke, Zhaojie Peng, Shichao Wei, Zhiwei Zhang, Yisi Hu, Wenhua Yu, Wenliang Zhou. Reef-building coral diversity and distribution characteristics in the National Nature Reserve for Marine Ecology of Guangdong Nanpeng Islands [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(4): 24424-. |
| [4] | Shang Huadan, Zhang Chuqing, Wang Mei, Pei Wenya, Li Guohong, Wang Hongbin. Species diversity and geographic distribution of poplar pests in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [5] | Wu Yuxuan, Wang Ping, Hu Xiaosheng, Ding Yi, Peng Tiantian, Zhi Qiuying, Bademu Qiqige, Li Wenjie, Guan Xiao, Li Junsheng. Evaluation of grassland degradation status and vegetation characteristics changes in Hulunbuir [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [6] | Wang Dawei, Cheng Shuai, Feng Jiawei, Wang Tianming. The wildlife camera-trapping dataset of Zhangguangcai Mountains in Northeast China (2015-2020) [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(2): 24384-. |
| [7] | Zihong Chen, Yifei Zhang, Kai Chen, Jianying Chen, Ling Xu. Species diversity of entomopathogenic fungi and the influencing factors in the Southern Gaoligong Mountains [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 24228-. |
| [8] | Ke Tan, Yao Ning, Renfen Wang, Qing Wang, Danping Liang, Zibing Xin, Fang Wen. A dataset on the checklist and geographical distribution of Gesneriaceae in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2025, 33(1): 23275-. |
| [9] | Jianan Han, Yang Su, Fei Li, Junyan Liu, Yilin Zhao, Lin Li, Jiancheng Zhao, Hongzhu Liang, Min Li. Bryophytes diversity of Hebei Province, China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(9): 24096-. |
| [10] | Hongyu Niu, Lu Chen, Hengyue Zhao, Gulzar Abdukirim, Hongmao Zhang. Effects of urbanization on animals: From community to individual level [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(8): 23489-. |
| [11] | Xue Bai, Zhengfei Li, Yang Liu, Junqian Zhang, Duopeng Zhang, Xin Luo, Jiali Yang, Lina Du, Xuankong Jiang, Ruiwen Wu, Zhicai Xie. Species diversity and maintenance mechanisms of benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages in the Xijiang River [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23499-. |
| [12] | Jia Xu, Xiaojuan Cui, Yifei Zhang, Chang Wu, Yuandong Sun. Fish diversity and distribution in the Nanling region [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [13] | Binyue Lu, Kun Li, Chenxi Wang, Sheng Li. The application and outlook of wildlife tracking using sensor-based tags in China [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 23497-. |
| [14] | Qiyu Kuang, Liang Hu. Species diversity and geographical distribution of marine benthic shell-bearing mollusks around Donghai Island and Naozhou Island, Guangdong Province [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 24065-. |
| [15] | Yongqiang Zhao, Xiyu Yan, Jiaqi Xie, Mengting Hou, Danmei Chen, Lipeng Zang, Qingfu Liu, Mingzhen Sui, Guangqi Zhang. Species diversity and community assembly of woody plants at different life history stages during the natural restoration of degraded karst forests [J]. Biodiv Sci, 2024, 32(5): 23462-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2022 Biodiversity Science
Editorial Office of Biodiversity Science, 20 Nanxincun, Xiangshan, Beijing 100093, China
Tel: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn ![]()