



生物多样性 ›› 2022, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (8): 22207. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022207 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022207
收稿日期:2022-04-21
接受日期:2022-06-15
出版日期:2022-08-20
发布日期:2022-08-31
通讯作者:
杜诚
作者简介:*E-mail: caragana_tu@hotmail.com
Cheng Du1,*( ), Jun Liu2, Wen Ye3, Shuai Liao4
), Jun Liu2, Wen Ye3, Shuai Liao4
Received:2022-04-21
Accepted:2022-06-15
Online:2022-08-20
Published:2022-08-31
Contact:
Cheng Du
摘要:
2021年中国共发表高等植物新分类群342个, 其中新科1个, 新属11个, 新种289个, 新亚种3个, 新变种18个, 新变型20个。新发表的物种分别属于苔类植物门(5个新种)、藓类植物门(4个新种)、石松门(3个新种)、蕨类植物门(22个新种)、裸子植物门(2个新种)、被子植物门(253个新种)。其中111个新种同时提供了详细的分子证据, 76个在发表时就依据IUCN标准被评估处于受威胁的状态。云南、西藏、四川和广西等西南4省区发表的新种最多, 共占全国新种发表总数的63.3%; 新种发现密度最高的省级行政单位是台湾、海南、云南、浙江和广东等省区。2021年中国共发表植物新组合(等级) 134个, 新名称9个; 发表国家级新记录62个; 将92个名称处理为62个名称的异名; 对7个名称进行了应用订正; 重新承认了2个属和10个物种; 新指定后选(新)模式物种49个; 还新发现多年未曾发现的物种9个, 排除物种分布7个。2021年中国高等植物净新增364个分类群, 占全国植物总数的0.98%, 230个高等植物名称发生变动, 占全国植物总数的0.62%。
杜诚, 刘军, 叶文, 廖帅 (2022) 中国植物新分类群、新名称变化2021年年度报告. 生物多样性, 30, 22207. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022207.
Cheng Du, Jun Liu, Wen Ye, Shuai Liao (2022) 2021 annual report on new taxa and nomenclatural changes of Chinese plants. Biodiversity Science, 30, 22207. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022207.
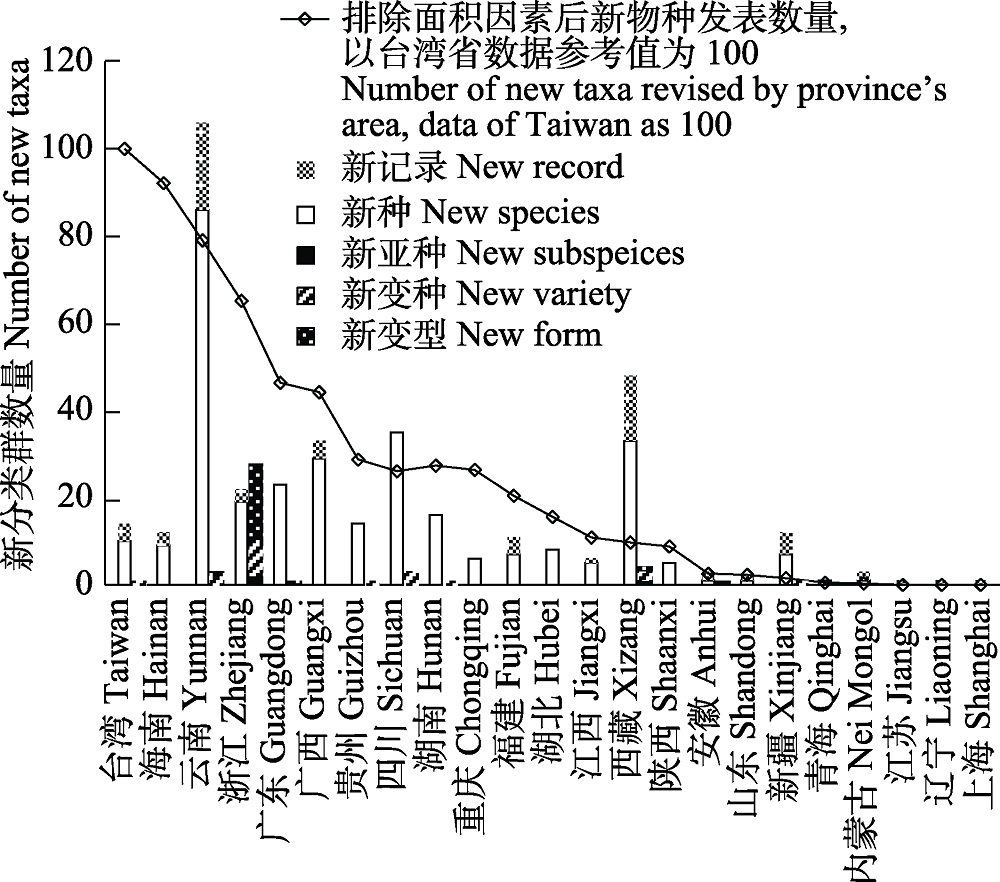
图1 2021年中国23个省区发表的新分类群和国家级新记录种数量(其他省份没有发现新分类群或新记录)
Fig. 1 The number of Chinese new taxa and newly recorded taxa published by 23 provinces in 2021. Provinces without new taxa or new record were not listed.
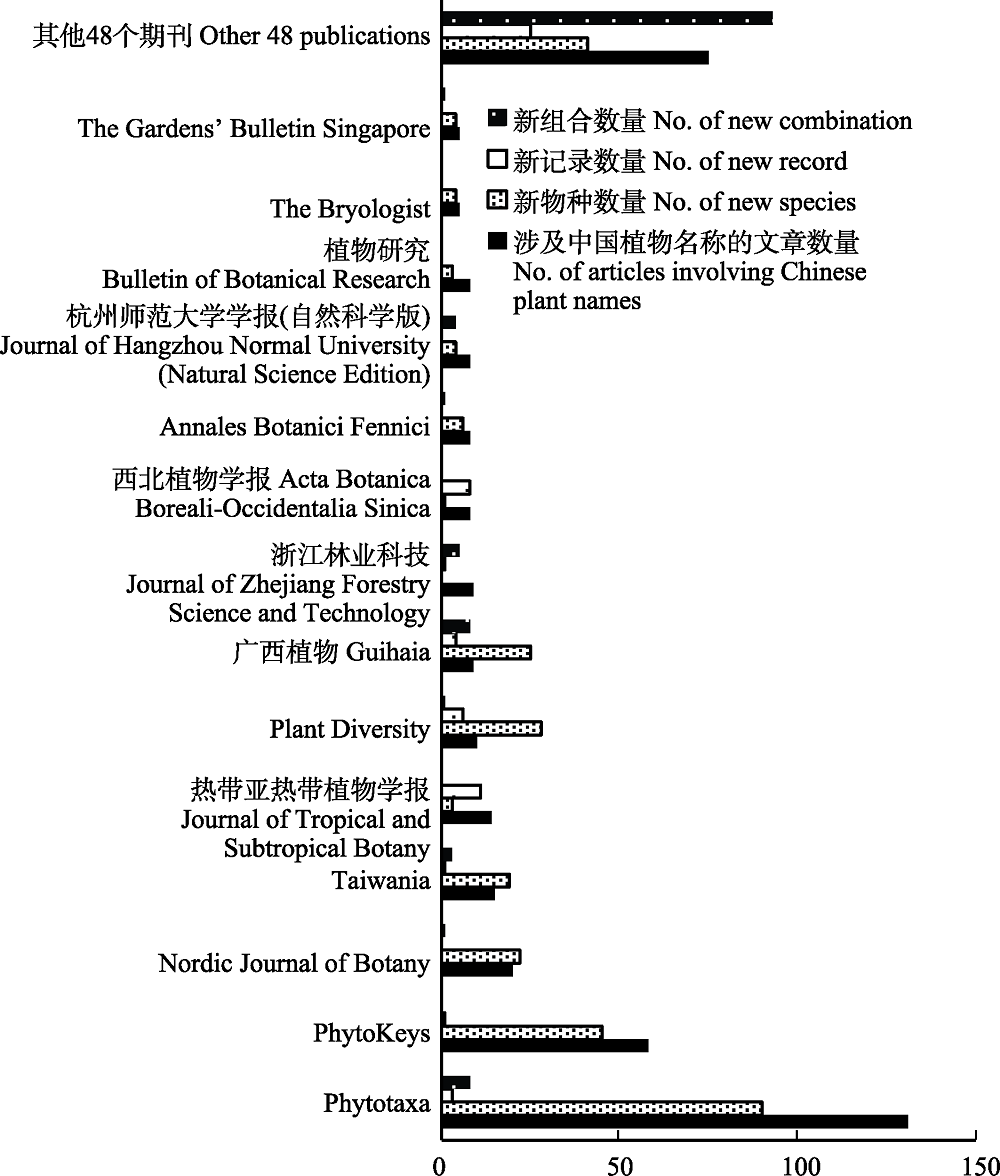
图2 2021发表中国植物名称相关论文最多的14期刊及其新种、新记录和新组合的发表数量
Fig. 2 Top 14 journals in which new names and name changes of Chinese plants were published, and the number of new species, record and combinations they published
| [1] |
Bakalin VA, Fedosov VE, Fedorova AV, Ma WZ (2021a) Obtusifoliaceae, a new family of leafy liverworts to accommodate Konstantinovia, newly described from the Hengduan Mts. (South China) and Obtusifolium (Cephaloziineae, Marchantiophyta). Plant Systematics and Evolution, 307, 62.
DOI URL |
| [2] | Bakalin VA, Fedosov VE, Long DG, Fedorova AV, Maltseva Y (2021b) Protoharpanthus gen. nov. (Harpanthaceae)—A relict relative of Harpanthus from the Sino-Himalaya. The Bryologist, 124, 218-229. |
| [3] |
Chen YS, Xu LS, Ke R, Harris A, Li HM (2021) Lihengia: A new genus of Asteraceae distinct from Dubyaea. Taxon, 70, 620-634.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Du C, Liao S, Boufford DE, Ma JS (2020) Twenty years of Chinese vascular plant novelties, 2000 through 2019. Plant Diversity, 42, 393-398.
DOI URL |
| [5] | Du C, Liu J, Ye W, Liao S, Ge BJ, Liu B, Ma JS (2021) Annual report of new taxa and new names for Chinese plants in 2020. Biodiversity Science, 29, 1011-1020. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [杜诚, 刘军, 叶文, 廖帅, 葛斌杰, 刘冰, 马金双 (2021) 中国植物新分类群、新名称2020年度报告. 生物多样性, 29, 1011-1020.] | |
| [6] | Du C, Ma JS (2022) Chinese Plant Taxonomists. Higher Education Press, Beijing. |
| [杜诚, 马金双 (2022) 中国植物分类学者. 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| [7] | Fawcett S, Smith AR (2021) A generic classification of the Thelypteridaceae. SIDA, Botanical Miscellany Series, 59, 1-112. |
| [8] |
Guo XL, Price M, Gou W, Zhou SD, Gao XF, He XJ (2021) Resurrection of the genus Similisinocarum (Apiaceae) based on evidence from morphology and ITS sequences. Phytotaxa, 497, 127-137.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Lee CK, Fuse S, Poopath M, Pooma R, Tamura MN (2021) Phylogenetics and infrafamilial classification of Commelinaceae (Commelinales). Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 198, 117-130.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Parmar G, Dang VC, Rabarijaona RN, Chen ZD, Jackes BR, Barrett RL, Zhang ZZ, Niu YT, Trias-Blasi A, Wen J, Lu LM (2021) Phylogeny, character evolution and taxonomic revision of Causonis, a segregate genus from Cayratia (Vitaceae). Taxon, 70, 1188-1218.
DOI URL |
| [11] | Qin WH, Meng WQ, Zhang D, Wang Y, Li ZL, Sun L, Liu K (2021) A new Amaryllidaceae genus, Shoubiaonia, from Yunnan Province, China. Nordic Journal of Botany, 39, 1-8. |
| [12] | Stapleton CMA (2021) We need to talk about Fargesia: New combinations and a new genus in the temperate Sino- Himalayan bamboos (Poaceae: Bambusoideae). Journal of the American Bamboo Society, 31, 1-16. |
| [13] | Turland NJ, Wiersema JH, Barrie FR, Greuter W, Hawksworth DL, Herendeen PS, Knapp S, Kusber WH, Li DZ, Marhold K, May TW, McNeill J, Monro AM, Prado J, Price MJ, Smith GF (2018) International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (Shenzhen Code) adopted by the Nineteenth International Botanical Congress Shenzhen, China, July 2017. Regnum Vegetabile 159. Koeltz Botanical Books, Glashütten. |
| [14] |
Wan X, Zhang LB (2021) Global new species of vascular plants published in 2020. Biodiversity Science, 29, 1003-1010. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| [万霞, 张丽兵 (2021) 2020年发表的全球维管植物新种. 生物多样性, 29, 1003-1010.] | |
| [15] | Wang GT, Shu JP, Jiang GB, Chen YQ, Wang RJ (2021) Morphology and molecules support the new monotypic genus Fenghwaia (Rhamnaceae) from South China. PhytoKeys, 171, 25-35. |
| [16] | Wang Y (2021) Capsulea Y. Wang, a new genus of Urticaceae from Shaanxi Province, China. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 41, 1-3. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王勇 (2021) 蒴果麻属, 陕西省荨麻科一新属. 植物研究, 41, 1-3.] | |
| [17] |
Xiang CL, Pan HL, Min DZ, Zhang DG, Zhao F, Liu B, Li B (2021) Rediscovery of Mazus lanceifolius reveals a new genus and a new species in Mazaceae. PhytoKeys, 171, 1-24.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Xin XW, Zhao H, Gao DM, Qu CY, Liu HY, Wang CC (2021) Schkuhria, a newly naturalized genus of Asteraceae in China. Plant Science Journal, 39, 1-4. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [辛晓伟, 赵宏, 高德民, 曲畅游, 刘红燕, 王聪聪 (2021) 中国菊科一新归化属——史库菊属. 植物科学学报, 39, 1-4.] | |
| [19] |
Xu YD, Yuan MD, Wang RJ (2021) Morphology and molecules support the new monotypic genus Parainvolucrella (Rubiaceae) from Asia. PhytoKeys, 180, 53-64.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Zhang RP, Huang YF, Zhu XY (2021) Ohashia, a new genus of Derris-like Millettioid legumes (Leguminosae, Papilionoideae) as revealed by molecular phylogenetic evidence. Taxon, 70, 1219-1228.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Zhou J, Wei J, Niu JM, Liu XL, Liu ZW (2021) Molecular phylogenetics of Pterocyclus (Apiaceae) based on nrDNA ITS sequences: Revised circumscription with a restored species. Phytotaxa, 498, 131-138.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 周志华, 金效华, 罗颖, 李迪强, 岳建兵, 刘芳, 何拓, 李希, 董晖, 罗鹏. 中国林草部门落实《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》的机制、成效分析及建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24487-. |
| [2] | 田志奇, 苏杨. 环境相关国际公约的中国履约模式和在《生物多样性公约》中的应用: 从完成《昆蒙框架》目标和发挥国家公园作用的角度[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24593-. |
| [3] | 弋维, 艾鷖, 吴萌, 田黎明, 泽让东科. 青藏高原高寒草甸土壤古菌群落对不同放牧强度的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24339-. |
| [4] | 宋阳, 柳军, 何少林, 徐薇, 程琛, 刘博, 余绩庆. 我国能源企业生物多样性保护主流化管理路径[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24345-. |
| [5] | 耿江天, 王菲, 赵华斌. 城市化对中国蝙蝠影响的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(8): 24109-. |
| [6] | 李邦泽, 张树仁. 中国莎草科最新物种名录和分类纲要[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 24106-. |
| [7] | 胡宗刚. 抗战胜利后中美曾筹划合编《中国植物志》[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24220-. |
| [8] | 池玉杰, 张心甜, 田志炫, 关成帅, 谷新治, 刘智会, 王占斌, 王金杰. 东北亚地区白粉菌的物种多样性与寄主物种多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(4): 23443-. |
| [9] | 江建平, 蔡波, 王斌, 陈蔚涛, 温知新, 张德志, 隋璐璐, 马舜, 王伟波. 中国脊椎动物2023年度新增物种报告[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24327-. |
| [10] | 曹焕喜, 周青松, 罗阿蓉, 唐璞, 李廷景, 李泽建, 陈华燕, 牛泽清, 朱朝东. 2023年现生膜翅目新分类单元[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24319-. |
| [11] | 杜诚, 刘军, 叶文, 廖帅. 中国植物新分类群、新名称变化2023年度报告[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24253-. |
| [12] | 万霞, 张丽兵. 世界维管植物新分类群2023年度报告[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24322-. |
| [13] | 徐思远, 连琦琦, 张瑞欣, 赵嘉腾, 周璇, 周露, 陈芹, 白明. 2023年全球鞘翅目现生类群新分类单元[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24307-. |
| [14] | 努日耶·木合太尔, 张秀英, 苏比奴尔·艾力, 李后魂. 中国鳞翅目新物种2023年度报告[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24428-. |
| [15] | 林晨, 杨棋程, 吴艳玲, 侯鹏, 张冰, 杨定. 2023年中国双翅目新分类单元[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24328-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()