



生物多样性 ›› 2020, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (5): 596-605. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020133 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2020133
收稿日期:2020-03-31
接受日期:2020-03-31
出版日期:2020-05-20
发布日期:2020-06-19
通讯作者:
李彬彬
Received:2020-03-31
Accepted:2020-03-31
Online:2020-05-20
Published:2020-06-19
Contact:
Binbin V Li
摘要:
随着新冠肺炎(COVID-19)的暴发, 野生动物、生物多样性和人类健康的关系再次引起广泛讨论。近20年来, 国际社会对于生物多样性与健康的研究日益增多, 并将它作为生物多样性保护与研究的重要方向之一。One Health作为一个新的理念框架, 通过交叉学科的研究和行动来推动包括人、所有其他动物及环境的健康。这个理念被不同国家、国际组织及协定所接纳及推广, 包括《生物多样性公约》等。本文通过总结近些年生物多样性对健康的影响方式、One Health的定义与发展历史、进入生物多样性议程的过程, 提出中国应用One Health改进相关野生动物管理以降低公共卫生危机的可能性的建议, 以及One Health框架内增强生物多样性保护所需的研究方向。One Health在中国的应用与发展应重视生物多样性研究和保护在其中的作用, 利用在景观生态学、群落内物种关系动态变化、气候变化影响、土地利用变化模式与趋势的研究, 与人类健康相结合, 提高One Health在应对公共健康和环境健康风险方面的准确性与及时性。同时, 需要加强我国在野生动物管理方面的投入和力度, 增强生物多样性保护与公共健康的联系, 将预警与干预措施前移, 减少疾病暴发带来的社会经济成本。
李彬彬 (2020) 推进生物多样性保护与人类健康的共同发展——One Health. 生物多样性, 28, 596-605. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020133.
Binbin V Li (2020) Creating synergy between biodiversity conservation and human health — One Health. Biodiversity Science, 28, 596-605. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2020133.
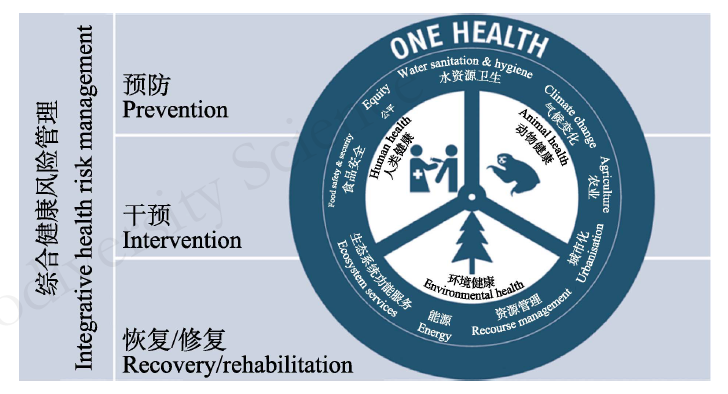
图1 One Health框架(改编自http://climvib.eu/? post_type= post&s=one+health)
Fig. 1 Framework for One Health (Adapted from http://climvib.eu/? post_type=post&s=one+health)
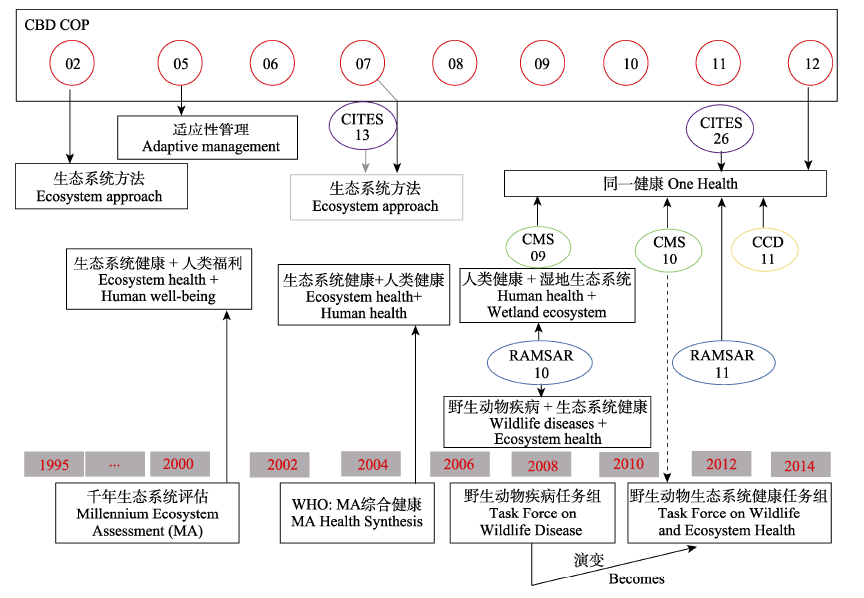
图2 生态系统方法和One Health进入生物多样性议程的过程(改编自Lajaunie & Mazzega, 2016)。CBD: 生物多样性公约; CCD: 防治荒漠化公约; COP: 缔约方大会; CITES: 濒危野生动植物种国际贸易公约; CMS: 野生动物迁徙物种保护公约; RAMSAR: 国际重要湿地公约。
Fig. 2 Process of the Ecosystem Approach and the One Health framework entering international biodiversity agenda (Adapted from Lajaunie & Mazzega, 2016). CBD, Convention on Biological Diversity; CCD, Convention to Combat Desertification; COP, Conference of the Parties; CITES, Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora; CMS, The Convention on Migratory Species; RAMSAR, Ramsar Convention.
| [1] | Barrett MA, Osofsky SA (2013) One Health: Interdependence of people, other species, and the planet. In: Jekel’s Epidemiology, Biostatistics, Preventive Medicine, and Public Health, 4th edn (eds Katz DL, Elmore JG, Wild DMG, Lucan SC), pp. 364-377. Elsevier/Saunders, Philadelphia. |
| [2] | Bertzky B, Corrigan C, Kemsey J, Kenney S, Ravilious C, Besançon C, Burgess N (2012) Protected Planet Report 2012: Tracking Progress Towards Global Targets for Protected Areas. United Nations Environment Programme’s World Conservation Monitoring Centre (UNEP-WCMC), Cambridge. |
| [3] | Bonds MH, Andrew PD, Donald CK (2012) Disease ecology, biodiversity, and the latitudinal gradient in income. PLoS Biology, 10, 12. |
| [4] | Bonilla-Aldana, DK, Dhama K, Rodriguez-Morales AJ (2020) Revisiting the One Health approach in the context of COVID-19: A look into the ecology of this emerging disease. Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences, 8, 234-237. |
| [5] | Butler CD (2014) Climate change and global health: A new conceptual framework—Mini review. CAB Reviews, 9, 027. |
| [6] |
Cardoso O, Porcher JM, Sanchez W (2014) Factory discharged pharmaceuticals could be a relevant source of aquatic environment contamination: Review of evidence and need for knowledge. Chemosphere, 115, 20-30.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Cincotta RP, Wisnewski J, Engelman R (2000) Human population in the biodiversity hotspots. Nature, 404, 990-992.
DOI URL PMID |
| [8] | Cleaveland S, Borner M, Gislason M (2014) Ecology and conservation: Contributions to One Health. Revue Scientifique et Technique (International Office of Epizootics), 33, 615-627. |
| [9] |
Cleaveland S, Laurenson MK, Taylor LH (2001) Diseases of humans and their domestic mammals: Pathogen characteristics, host range and the risk of emergence. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series B: Biological Sciences, 356, 991-999.
DOI URL PMID |
| [10] |
Dornelas M, Gotelli NJ, McGill B, Shimadzu H, Moyes F, Sievers C, Magurran AE (2014) Assemblage time series reveal biodiversity change but not systematic loss. Science, 344, 296-299.
DOI URL PMID |
| [11] | FAO, OIE, WHO, UN System Influenza Coordination, UNICEF, the World Bank (2008) Contributing to One World, One Health: A Strategic Framework for Reducing Risks of Infectious Diseases at the Animal-Human-Ecosystems Interface. Geneva. |
| [12] |
Gibbs EPJ (2005) Emerging zoonotic epidemics in the interconnected global community. Veterinary Record, 157, 673-679.
URL PMID |
| [13] |
Gibbs EPJ (2014) The evolution of One Health: A decade of progress and challenges for the future. Veterinary Record, 174, 85-91.
DOI URL PMID |
| [14] |
Gilbert M, Golding N, Zhou H, Wint GRW, Robinson TP, Tatem AJ, Lai S, Zhou S, Jiang H, Guo D, Huang Z, Messina JP, Xiao X, Linard C, Boeckel TP, Martin V, Bhatt S, Gething PW, Farrar JJ, Hay SI, Yu HJ (2014) Predicting the risk of avian influenza a H7N9 infection in live-poultry markets across Asia. Nature Communications, 5, 4116.
DOI URL PMID |
| [15] |
Hahn MB, Gangnon RE, Barcellos C, Asner GP, Patz JA (2014) Influence of deforestation, logging, and fire on Malaria in the Brazilian Amazon. PLoS ONE, 9, e85725.
DOI URL PMID |
| [16] |
Huxham M, Kumara MP, Jayatissa LP, Krauss KW, Kairo J, Langat J, Mencuccini M, Skov MW, Kirui B (2010) Intra- and interspecific facilitation in mangroves may increase resilience to climate change threats. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 365, 2127-2135.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Jones KE, Patel NG, Levy MA, Storeygard A, Balk D, Gittleman JL, Daszak P (2008) Global trends in emerging infectious diseases. Nature, 451, 990-993.
DOI URL PMID |
| [18] |
Karpinets TV, Vancheswaran G, Wargo J, Futreal AP, Christopher WS, Zhang J (2018) Linking associations of rare low-abundance species to their environments by association networks. Frontiers in Microbiology, 9, 297.
DOI URL PMID |
| [19] |
Keesing F, Belden LK, Daszak P, Dobson A, Harvell CD, Holt RD, Hudson P, Jolles A, Jones KE, Mitcell CE, Myers SS, Bogich T, Ostfeld RS (2010) Impacts of biodiversity on the emergence and transmission of infectious diseases. Nature, 468, 647-652.
DOI URL PMID |
| [20] | Lajaunie C, Mazzega P (2016) One Health and biodiversity conventions. The emergence of health issues in biodiversity conventions. IUCN Academy of Environmental Law eJournal, 7, 105-121. |
| [21] | Lajaunie C, Morand S (2015) A legal tool for participatory methods in land systems science: The Thai model of Health Impact Assessment and the consideration of zoonotic diseases concerns into policies. GLP Newsletter, 11, 30-33. |
| [22] |
Mace GM, Norris K, Fitter AH (2012) Biodiversity and ecosystem services: A multilayered relationship. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 27, 19-26.
DOI URL PMID |
| [23] |
Markevych I, Tiesler CM, Fuertes E, Romanos M, Dadvand P, Nieuwenhuijsen MJ, Berdel D, Koletzko S, Heinrich J (2014) Access to urban green spaces and behavioural problems in children: Results from the GINIplus and LISAplus studies. Environment International, 71, 29-35.
DOI URL |
| [24] | McIvor AL, Möller I, Spencer T, Spalding M (2013) Mangroves as a sustainable coastal defence. In: Proceeding of the 7th International Conference on Asian and Pacific Coasts, APAC 2013, pp. 956-963. Bali, Indonesia. |
| [25] |
McShane TO, Hirsch PD, Trung TC, Songorwa AN, Kinzig A, Monteferri B, Mutekanga D, Thang HV, Dammert JL, Pulgar-Vidal M, Welch-Devine M, Brosius JP, Coppolillo P, O’Connor S (2011) Hard choices: Making trade-offs between biodiversity conservation and human well-being. Biological Conservation, 144, 966-972.
DOI URL |
| [26] | Nie EQ, Xia Y, Wang T, Lu JH (2016) One Health—A new approach to control emerging infectious diseases. Journal of Microbes and Infection, 11, 3-7. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 聂恩琼, 夏尧, 汪涛, 陆家海 (2016) One Health——应对新发传染病的新理念. 微生物与感染, 11, 3-7.] | |
| [27] |
Olson SH, Reed P, Cameron, KN, Ssebide BJ, Johnson CK, Morse SS, Karesh WB, Mazet JAK, Joly DO (2012) Dead or alive: Animal sampling during Ebola hemorrhagic fever outbreaks in humans. Emerging Health Threats Journal, 5, 9134.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Orlando EF, Guillette JLJ (2007) Sexual dimorphic responses in wildlife exposed to endocrine disrupting chemicals. Environmental Research, 104, 163-173.
DOI URL PMID |
| [29] |
Ostfeld RS, Keesing F (2000) The function of biodiversity in the ecology of vector-borne zoonotic diseases. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 78, 2061-2078.
DOI URL |
| [30] | Pang SF, Yuan LP (2015) Version and practice of OIE “One Health”. China Animal Health Inspection, 32(10), 58-60. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 庞素芬, 袁丽萍 (2015) 世界动物卫生组织“同一健康”理念和实践. 中国动物检疫, 32(10), 58-60.] | |
| [31] | Patz J, Corvalan C, Horwitz P, Campbell-Lendrum D, Watts N, Maiero M, Olson S, Hales J, Miller C, Campbell K, Romanelli C, Cooper D (2012) Our Planet, Our Health, Our Future. Human health and the Rio conventions: Biological diversity, climate change and desertification. WHO. Geneva. |
| [32] |
Rohr JR, Civitello DJ, Halliday FW, Hudson PJ, Lafferty KD, Wood CL, Mordecai EA (2020) Towards common ground in the biodiversity-disease debate. Nature Ecology and Evolution, 4, 24-33.
DOI URL PMID |
| [33] | Romanelli C, Cooper D, Campbell-Lendrum D, Maiero M, Karesh WB, Hunter D, Golden CD (2015) Connecting Global Priorities: Biodiversity and Human Health: A State of Knowledge Review. World Health Organistion & Secretariat of the UN Convention on Biological Diversity. |
| [34] |
Romanelli C, Cooper HD, de Souza Diaz BF (2014) The integration of biodiversity into One Health. Revue Scientifique et Technique, 33, 487-496.
DOI URL PMID |
| [35] |
Sandifer PA, Sutton-Grier AE, Ward BP (2015) Exploring connections among nature, biodiversity, ecosystem services, and human health and well-being: Opportunities to enhance health and biodiversity conservation. Ecosystem Services, 12, 1-15.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Shwartz A, Turbe A, Simon L, Julliard R (2014) Enhancing urban biodiversity and its influence on city-dwellers: An experiment. Biological Conservation, 171, 82-90.
DOI URL |
| [37] | Von Hertzen L, Ilkka H, Tari H (2011) Natural immunity. EMBO Reports 12, 11, 1089-1093. |
| [38] | Wells NM (2014) The role of nature in children’s resilience: Cognitive and social processes. In: Greening in the Red Zone (eds Tidball KG, Krasny ME), pp. 95-109. Springer, Dordrecht. |
| [39] |
Wilcox BA, Gubler DJ (2005) Disease ecology and the global emergence of zoonotic pathogens. Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine, 10, 263-272.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Wood CL, Lafferty KD (2013) Biodiversity and disease: A synthesis of ecological perspectives on Lyme disease transmission. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 28, 239-247.
DOI URL PMID |
| [41] |
Wood CL, Lafferty KD, DeLeo G, Young HS, Hudson PJ, Kuris AM (2014) Does biodiversity protect humans against infectious disease? Ecology, 95, 817-832.
DOI URL |
| [42] | World Health Organization (WHO) (2013) Mental Health Action Plan 2013-2020. World Health Organization, Geneva. |
| [43] |
Wu J, Liu L, Wang G, Lu J (2016) One Health in China. Infection Ecology & Epidemiology, 6, 33843.
DOI URL PMID |
| [44] |
Zowalaty ME, Järhult JD (2020) From SARS to COVID-19: A previously unknown SARS-CoV-2 virus of pandemic potential infecting humans—Call for a One Health approach. One Health, 100124.
DOI URL PMID |
| [1] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [12] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [14] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [15] | 赵维洋, 王伟, 马冰然. 其他有效的区域保护措施(OECMs)研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
