



生物多样性 ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (3): 273-285. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018258 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2018258
李强1,王彬1,邓云2,林露湘2,达佤扎喜1,张志明1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2018-09-25
接受日期:2019-01-16
出版日期:2019-03-20
发布日期:2019-01-31
通讯作者:
张志明
基金资助:
Li Qiang1,Wang Bin1,Deng Yun2,Lin Luxiang2,Dawa Zhaxi1,Zhang Zhiming1,*( )
)
Received:2018-09-25
Accepted:2019-01-16
Online:2019-03-20
Published:2019-01-31
Contact:
Zhang Zhiming
摘要:
林窗作为森林群落中一种重要的干扰方式, 对林下物种构成有着重要的影响。开展林窗空间格局及其特征指数与林下植物多样性关系研究对于探讨林窗对林下生物多样性的影响有重要意义, 有助于进一步了解群落动态, 在物种多样性保护方面也具有指导作用。本研究在西双版纳热带雨林地区随机选取3块大小为1 ha的热带雨林为研究样地, 采用轻小型六旋翼无人机搭载Sony ILCE-A7r可见光传感器, 分别获取各个样地的高清数字影像, 结合数字表面高程模型以及各个样地的地形数据用以确定各样区的林窗分布格局, 并进一步提取出各林窗的景观格局指数。结合地面样方基础调查数据, 对各样地各林窗下植物多样性情况进行统计, 旨在分析热带雨林林窗空间分布格局以及林窗下植物多样性对各林窗空间格局特征的响应情况。研究表明, 西双版纳州热带雨林林窗呈大而分散的空间分布, 林窗空间格局特征指数如林窗形状复杂性指数、林窗面积都与林下植物多样性呈显著正相关关系。在面积小的林窗下, 较之林窗形状复杂性因子, 林窗面积大小对林下植物多样性影响更显著; 在面积达到一定程度后, 相对于面积因子, 林窗形状复杂性指数对林下植物多样性影响更显著, 各样地林窗皆趋于向各自所处样地顶极群落发展。
李强, 王彬, 邓云, 林露湘, 达佤扎喜, 张志明 (2019) 西双版纳热带雨林林窗空间分布格局及其特征数与林窗下植物多样性的相关性. 生物多样性, 27, 273-285. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018258.
Li Qiang, Wang Bin, Deng Yun, Lin Luxiang, Dawa Zhaxi, Zhang Zhiming (2019) Correlation between spatial distribution of forest canopy gaps and plant diversity indices in Xishuangbanna tropical forests. Biodiversity Science, 27, 273-285. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018258.
图1 研究区概况图。图中各颜色边框均为样地内1 ha范围, 且各颜色对应作图各采样点位置。
Fig. 1 Map of the four sample locations in this study. Each color border in the figure is within 1 hectare of the sample land, and each color corresponds to the position of sampling points in the drawing.
| 44 km样地 44 km plot | 茶厂后山样地 Tea factory backhill plot | 勐仑水库样地 Menglun Reservoir plot | 大平掌样地 Dapingzhang plot | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大林窗数 Large gap number | 13 | 9 | 12 | 21 |
| 小林窗数 Small gap number | 27 | 18 | 14 | 32 |
| 林窗数 Gap number | 40 | 27 | 26 | 53 |
| 最大林窗面积 Largest gap area (m2) | 294.26 | 121.78 | 266.42 | 160.53 |
| 最小林窗面积 Smallest gap area (m2) | 4.1 | 4.64 | 4.17 | 4.2 |
| 林窗总面积 Total area of gap (m2) | 1,208.72 | 600.00 | 1,286.91 | 1,640.25 |
| 林窗空隙率 Gap fraction | 12.10% | 6% | 12.85% | 16.40% |
表1 4个样地的林窗数据
Table 1 Data of the canopy gaps of four forest plots
| 44 km样地 44 km plot | 茶厂后山样地 Tea factory backhill plot | 勐仑水库样地 Menglun Reservoir plot | 大平掌样地 Dapingzhang plot | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 大林窗数 Large gap number | 13 | 9 | 12 | 21 |
| 小林窗数 Small gap number | 27 | 18 | 14 | 32 |
| 林窗数 Gap number | 40 | 27 | 26 | 53 |
| 最大林窗面积 Largest gap area (m2) | 294.26 | 121.78 | 266.42 | 160.53 |
| 最小林窗面积 Smallest gap area (m2) | 4.1 | 4.64 | 4.17 | 4.2 |
| 林窗总面积 Total area of gap (m2) | 1,208.72 | 600.00 | 1,286.91 | 1,640.25 |
| 林窗空隙率 Gap fraction | 12.10% | 6% | 12.85% | 16.40% |
| 44 km样地 44 km plot | 茶厂后山样地 Tea factory backhill plot | 勐仑水库样地 Menglun Reservoir plot | 大平掌样地 Dapingzhang plot | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数量比例 Quantity ratio | 小林窗 Small gap | 67.50% | 66.70% | 53.80% | 60.40% |
| 大林窗 Large gap | 32.50% | 33.30% | 46.20% | 39.60% | |
| 面积比例 Area ratio | 小林窗 Small gap | 24% | 30.10% | 14.10% | 23.30% |
| 大林窗 Large gap | 76% | 69.90% | 85.90% | 76.70% | |
| 空隙率 Gap fraction | 小林窗 Small gap | 2.90% | 1.80% | 1.81% | 3.80% |
| 大林窗 Large gap | 9.20% | 4.20% | 11.05% | 12.60% | |
| 平均最小邻近距离 Mean Euclidean near- neighbor distance (ENN) | 林窗 Gap | 10.80 | 10.02 | 11.11 | 8.49 |
| 小林窗 Small gap | 11.45 | 9.74 | 16.28 | 9.57 | |
| 大林窗 Large gap | 17.16 | 17.89 | 18.82 | 14.18 |
表2 4个样地的林窗空间特征指数
Table 2 Spatial characteristic index of the canopy gaps of four forests
| 44 km样地 44 km plot | 茶厂后山样地 Tea factory backhill plot | 勐仑水库样地 Menglun Reservoir plot | 大平掌样地 Dapingzhang plot | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数量比例 Quantity ratio | 小林窗 Small gap | 67.50% | 66.70% | 53.80% | 60.40% |
| 大林窗 Large gap | 32.50% | 33.30% | 46.20% | 39.60% | |
| 面积比例 Area ratio | 小林窗 Small gap | 24% | 30.10% | 14.10% | 23.30% |
| 大林窗 Large gap | 76% | 69.90% | 85.90% | 76.70% | |
| 空隙率 Gap fraction | 小林窗 Small gap | 2.90% | 1.80% | 1.81% | 3.80% |
| 大林窗 Large gap | 9.20% | 4.20% | 11.05% | 12.60% | |
| 平均最小邻近距离 Mean Euclidean near- neighbor distance (ENN) | 林窗 Gap | 10.80 | 10.02 | 11.11 | 8.49 |
| 小林窗 Small gap | 11.45 | 9.74 | 16.28 | 9.57 | |
| 大林窗 Large gap | 17.16 | 17.89 | 18.82 | 14.18 |
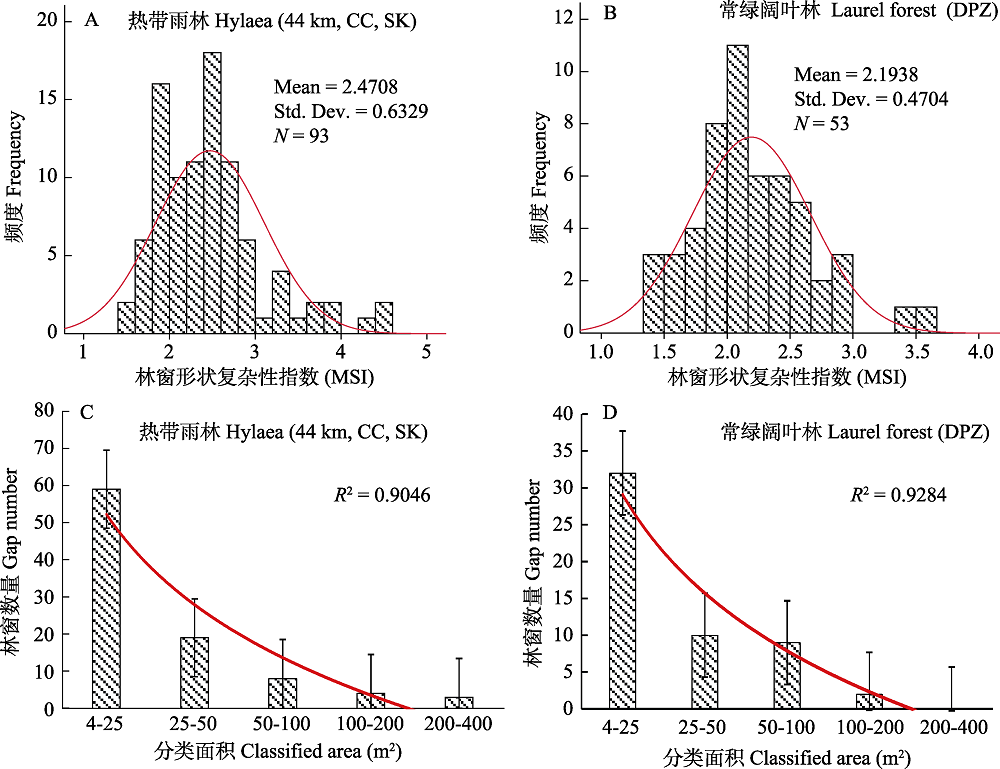
图3 4个样地的林窗形状指数和面积空间分布。44 km: 44 km样地; CC: 茶厂后山样地; DPZ: 大平掌样地; SK: 勐仑水库样地。
Fig. 3 Shape index and area spatial distribution of the four forest canopy gaps. 44 km, 44 km plot; CC, Tea factory backhill plot; SK, Menglun Reservoir plot; DPZ, Dapingzhang plot.
| 分类面积 Classified by area (m2) | 林窗数量 No. of gaps | 数量百分比 % | 面积 Area (m2) | 面积百分比 % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 热带雨林 Tropical forest | ||||
| 4-25 | 59 | 63.44 | 648.99 | 20.96 |
| 25-50 | 19 | 20.43 | 588.53 | 19.01 |
| 50-100 | 8 | 8.60 | 541.68 | 17.50 |
| 100-200 | 4 | 4.30 | 523.73 | 16.92 |
| 200-400 | 3 | 3.23 | 792.7 | 25.61 |
| 合计 Total | 93 | 100 | 3,095.63 | 100 |
| 常绿阔叶林 Evergreen broad-leaved forest | ||||
| 4-25 | 32 | 60.38 | 382.3 | 23.31 |
| 25-50 | 10 | 18.87 | 375.9 | 22.92 |
| 50-100 | 9 | 16.98 | 599.19 | 36.53 |
| 100-200 | 2 | 3.77 | 282.81 | 17.24 |
| 200-400 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 合计 Total | 53 | 100.00 | 1,640.2 | 100.00 |
表3 热带雨林和常绿阔叶林样地的林窗数量、面积及其比例
Table 3 The numbers and area of the canopy gaps of the tropical forest plots and the evergreen broad-leaved forest plot
| 分类面积 Classified by area (m2) | 林窗数量 No. of gaps | 数量百分比 % | 面积 Area (m2) | 面积百分比 % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 热带雨林 Tropical forest | ||||
| 4-25 | 59 | 63.44 | 648.99 | 20.96 |
| 25-50 | 19 | 20.43 | 588.53 | 19.01 |
| 50-100 | 8 | 8.60 | 541.68 | 17.50 |
| 100-200 | 4 | 4.30 | 523.73 | 16.92 |
| 200-400 | 3 | 3.23 | 792.7 | 25.61 |
| 合计 Total | 93 | 100 | 3,095.63 | 100 |
| 常绿阔叶林 Evergreen broad-leaved forest | ||||
| 4-25 | 32 | 60.38 | 382.3 | 23.31 |
| 25-50 | 10 | 18.87 | 375.9 | 22.92 |
| 50-100 | 9 | 16.98 | 599.19 | 36.53 |
| 100-200 | 2 | 3.77 | 282.81 | 17.24 |
| 200-400 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 合计 Total | 53 | 100.00 | 1,640.2 | 100.00 |
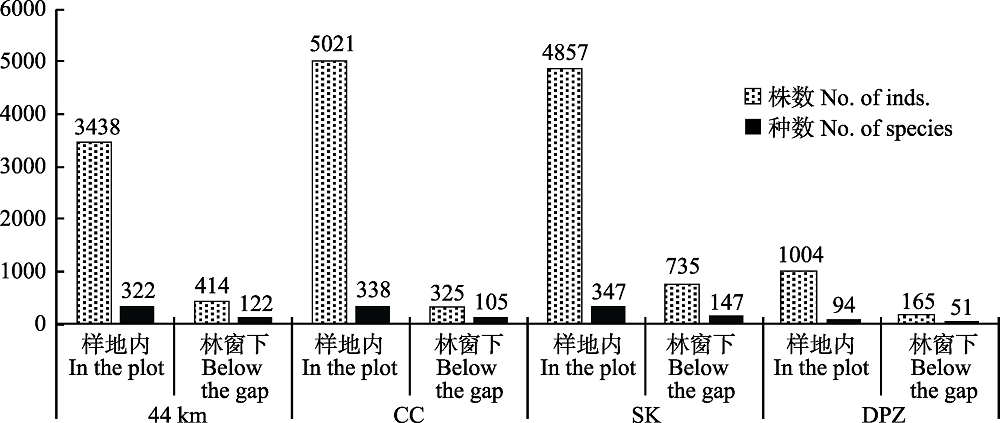
图4 4个样地林窗下与林下植物的个体数和种数(样地代号同图3)
Fig.4 Number of plant individuals and species under the canopy gaps and under the forests in the four plots. Plot codes are the same as Fig.3.
| 样地 Samples | 物种丰富度 Species richness | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | Simpson指数 Simpson index | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最大值 Max. | 均值 Mean | 最大值 Max. | 均值 Mean | 最大值 Max. | 均值 Mean | |
| 44 km | 145 | 10.35 | 3.3698 | 1.2404 | 0.959 | 0.5742 |
| 茶厂后山样地 CC | 67 | 10.8519 | 3.0483 | 1.7553 | 0.9417 | 0.7731 |
| 大平掌样地 DPZ | 34 | 3.1132 | 2.8178 | 0.5582 | 0.9291 | 0.2868 |
| 勐仑水库样地 SK | 164 | 28.2692 | 3.0656 | 1.8432 | 0.9452 | 0.7233 |
表4 4个样地林窗下植物的多样性指数
Table 4 Plant diversity indices under the canopy gaps of four forest plots. 44 km, 44 km plot; CC, Tea factory backhill plot; SK, Menglun Reservoir plot; DPZ, Dapingzhang plot.
| 样地 Samples | 物种丰富度 Species richness | Shannon-Wiener指数 Shannon-Wiener index | Simpson指数 Simpson index | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最大值 Max. | 均值 Mean | 最大值 Max. | 均值 Mean | 最大值 Max. | 均值 Mean | |
| 44 km | 145 | 10.35 | 3.3698 | 1.2404 | 0.959 | 0.5742 |
| 茶厂后山样地 CC | 67 | 10.8519 | 3.0483 | 1.7553 | 0.9417 | 0.7731 |
| 大平掌样地 DPZ | 34 | 3.1132 | 2.8178 | 0.5582 | 0.9291 | 0.2868 |
| 勐仑水库样地 SK | 164 | 28.2692 | 3.0656 | 1.8432 | 0.9452 | 0.7233 |
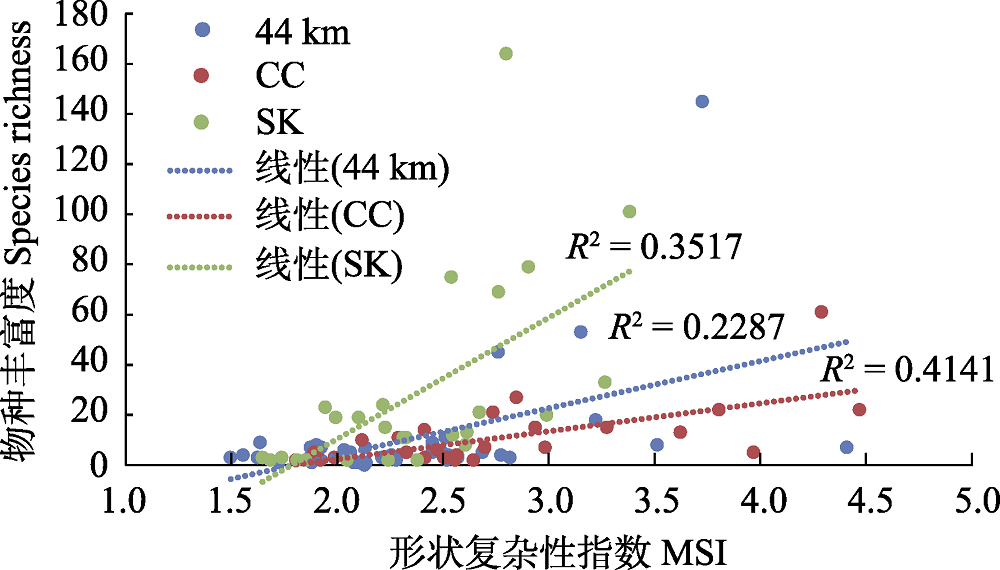
图7 热带雨林林窗下植物物种丰富度与林窗形状复杂性指数(MSI)的线性关系图(样地代号同图3)
Fig. 7 Linear relationship between species richness and shape index (MSI) of the rainforest canopy gaps. Plot codes are the same as Fig.3.
| 16 |
Guo QH, Wu FF, Hu TY, Chen LH, Liu J, Zhao XQ, Gao S, Pang SX ( 2016) Perspectives and prospects of unmanned aerial vehicle in remote sensing monitoring of biodiversity. Biodiversity Science, 24, 1267-1278. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 郭庆华, 吴芳芳, 胡天宇, 陈琳海, 刘瑾, 赵晓倩, 高上, 庞树鑫 ( 2016) 无人机在生物多样性遥感监测中的应用现状与展望. 生物多样性, 24, 1267-1278.]
DOI URL |
|
| 17 | Hao ZM ( 2017) A discussion on the characteristics of forest canopy gap and its effect on plant diversity. Shanxi Forestry Science and Technology, 46(4), 57-59. (in Chinese) |
| [ 郝再明 ( 2017) 浅议林窗的特征及其对植物多样性的影响. 山西林业科技, 46(4), 57-59.] | |
| 18 |
Herwitz SR, Sandler B, Slye RE ( 2000) Twenty-one years of crown area change in the Jasper Ridge Biological Preserve based on georeferenced multitemporal aerial photographs. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 21, 45-60.
DOI URL |
| 19 |
Hobi ML, Ginzler C, Commarmot B, Bugmann H ( 2016) Gap pattern of the largest primeval beech forest of Europe revealed by remote sensing. Ecosphere, 6(5), 1-15.
DOI URL |
| 20 | Hu JB, Zhang J ( 2018) Unmanned aerial vehicle remote sensing in ecology: Advances and prospects. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 25-35. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 胡健波, 张健 ( 2018) 无人机遥感在生态学中的应用进展. 生态学报, 38, 25-35.] | |
| 21 | Hu LL, Li JS, Wu XP, Yan BQ, Zhu JJ, Luo JW, Xiao NW ( 2010) Rewiews on methods of measuring geometric chracteristics of forest gaps involving gap size, gap shape, and the height of canopy trees surrounding the gap. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30, 1911-1919. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 胡理乐, 李俊生, 吴晓莆, 闫伯前, 朱教君, 罗建武, 肖能文 ( 2010) 林窗几何特征的测定方法. 生态学报, 30, 1911-1919.] | |
| 22 |
Huang LJ, Lin X, Liu XZ, Zhuang CW, Xiao RB ( 2017) The relation among biomass, at different stand ages biodiversity and LAI of trees in Guangdong Province. Journal of Southwest Forestry College, 37(6), 91-98. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 黄柳菁, 林欣, 刘兴诏, 庄长伟, 肖荣波 ( 2017) 广东不同林龄乔木生物量及物种多样性与叶面积指数的关系. 西南林业大学学报, 37(6), 91-98.]
DOI URL |
|
| 23 |
Hubbell SP, Foster RB, O'Brien ST, Harms KE, Condit R, Wechsler B, Wrignt SJ, de Lao SL ( 1999) Light-Gap disturbances, recruitment limitation, and tree diversity in a neotropical forest. Science, 283, 554-557.
DOI URL |
| 24 |
Karsten RJ, Jovanovic M, Meilby H, Perales E, Reynel C ( 2013) Regeneration in canopy gaps of tierra-firme forest in the Peruvian Amazon: Comparing reduced impact logging and natural, unmanaged forests. Forest Ecology and Management, 310, 663-671.
DOI URL |
| 1 |
Aizen MA, Feinsinger P ( 1994) Habitat fragmentation, native insect pollinators, and feral honey bees in Argentine “Chaco Serrano”. Ecological Applications, 4, 378-392.
DOI URL |
| 2 |
Bao WK, Liu ZG, Yuan YF, Liu RD, Liu CL ( 2001) Gap formation features of humid evergreen broad leaved forest in central subtropical Wawushan Mountain, Sichuan Province, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 12, 485-490. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| 25 |
Lachat T, Chumak M, Chumak V, Jakoby O, Müller J, Tanadini M, Wermelinger B, Wermelinger R, Didham R, Jonsell M ( 2016) Influence of canopy gaps on saproxylic beetles in primeval beech forests: A case study from the Uholka-Shyrokyi Luh forest, Ukraine. Insect Conservation and Diversity, 9, 559-573.
DOI URL |
| 26 |
Lawton RO, Putz FE ( 1988) Natural disturbance and gap-phase regeneration in a wind-exposed tropical cloud forest. Ecology, 69, 764-777.
DOI URL |
| 2 |
[ 包维楷, 刘照光, 袁亚夫, 刘仁东, 刘朝禄 ( 2001) 瓦屋山中亚热带湿性常绿阔叶林的林窗形成特征. 应用生态学报, 12, 485-490.]
DOI URL |
| 3 |
Cescatti A ( 2007) Indirect estimates of canopy gap fraction based on the linear conversion of hemispherical photographs: Methodology and comparison with standard thresholding techniques. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 143, 1-12.
DOI URL |
| 27 |
Liu Q, Wu HD, Tan YH, Zhang JL ( 2017) Liana diversity and its climbing situation on trees in Xishuangbanna tropical seasonal rainforest. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 53(8), 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 刘奇, 吴怀栋, 谭运洪, 张教林 ( 2017) 西双版纳热带季雨林木质藤本多样性及其攀援方式. 林业科学, 53(8), 1-8.]
DOI URL |
|
| 4 |
Chen L, Liu GH, Liu D, Shi SL ( 2017) Plant diversity and elevation dynamics in forest gaps of varying sizes in subalpine coniferous forest. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 37(10), 90-97. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 陈力, 刘国华, 刘丹, 石松林 ( 2017) 亚高山针叶林不同大小林窗植物多样性及其海拔动态. 中南林业科技大学学报, 37(10), 90-97.]
DOI URL |
|
| 5 | Chen WB, Xiao DN, Li XZ ( 2002) Classification, application, and creation of landscape indices. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 13, 121-125. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈文波, 肖笃宁, 李秀珍 ( 2002) 景观指数分类、应用及构建研究. 应用生态学报, 13, 121-125.] | |
| 28 | Lobo E ( 2013) Spatial Distribution of Canopy Gaps in a Tropical Forest Landscape and Its Influence on the Tree Community. PhD dissertation, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Champaign. |
| 29 |
Muscolo A, Bagnato S, Sidari M, Mercurio R ( 2014) A review of the roles of forest canopy gaps. Journal of Forestry Research, 25, 725-736.
DOI URL |
| 6 |
Coates KD, Burton PJ ( 1997) A gap-based approach for development of silvicultural systems to address ecosystem management objectives. Forest Ecology & Management, 99, 337-354.
DOI URL |
| 7 |
Cui JY, Zeng HC, Wang YQ, Zhang Y, Hu YH, Su ZY ( 2015) Canopy structure and radiation attenuation effects of broad- leaved forest in Yinpingshan National Nature Reserve. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 30(4), 45-49. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| 30 | Nonogaki S, Masumoto S, Nemoto T ( 2017) High-speed gridding system for geological surfaces using multi-threading technology. International Journal of Geoinformatics, 13, 1-10. |
| 31 |
Offde S, Brown VK ( 1994) Effects of habitat fragmentation on Amazonian termite communities. Journal of Tropical Ecology, 10, 197-206.
DOI URL |
| 7 |
[ 崔佳玉, 曾焕忱, 王永强, 张毅, 胡益珩, 苏志尧 ( 2015) 银瓶山自然保护区阔叶林冠层结构与辐射消减效应. 西北林学院学报, 30(4), 45-49.]
DOI URL |
| 8 | de Vries PG ( 1986) Sampling Theory for Forest Inventory. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. |
| 9 |
Devagiri GM, Khaple AK, Mohan S, Venkateshamurthy P, Tomar S, Arunkumar AN, Joshi G ( 2016) Species diversity, regeneration and dominance as influenced by canopy gaps and their characteristics in tropical evergreen forests of Western Ghats, India. Journal of Forestry Research, 27, 799-810.
DOI URL |
| 10 |
Dewalt SJ, Schnitzer SA, Denslow JS ( 2000) Density and diversity of lianas along a chronosequence in a central Panamanian lowland forest. Journal of Tropical Ecology, 16, 1-19.
DOI URL |
| 32 | Ou XK, Jin ZZ, Peng MC, Fang B, Fang JM ( 1997) Distribution of vegetations in Mengyang Nature Reserve of Xishuangbanna and their ecological characteristics. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 8(s1), 8-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 欧晓昆, 金振洲, 彭明春, 方波, 房俊民 ( 1997) 西双版纳勐养自然保护区植被的分布与生态特征. 应用生态学报, 8(s1), 8-19.] | |
| 11 | Fang YR, Pan L, Xue L ( 2018) Relationship between canopy structure and understory light and soil biochemical property in a Cunninghamia lanceolata stand suffering from ice-snow damage. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 27, 609-616. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 方怡然, 潘澜, 薛立 ( 2018) 冰雪灾害后的杉木人工林冠层结构与林下光照及土壤生化特性的关系. 生态环境学报, 27, 609-616.] | |
| 12 |
Feldmann E, DröΒler L, Hauck M, Kucbel S, Pichler V, Leuschner C ( 2018) Canopy gap dynamics and tree understory release in a virgin beech forest, Slovakian Carpathians. Forest Ecology and Management, 415, 38-46.
DOI URL |
| 13 |
Fox TJ, Knutson MG, Hines RK ( 2000) Mapping forest canopy gaps using air-photo interpretation and ground surveys. Wildlife Society Bulletin, 28, 882-889.
DOI URL |
| 33 |
Pedersen BS, Howard JL ( 2004) The influence of canopy gaps on overstory tree and forest growth rates in a mature mixed-age, mixed-species forest. Forest Ecology and Management, 196, 351-366.
DOI URL |
| 34 |
Peng SL, Liu Q ( 2002) The dynamics of forest litter and its responses to global warming. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 22, 1534-1544. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| 14 |
Getzin S, Wiegand K, Schöning I ( 2012) Assessing biodiversity in forests using very high-resolution images and unmanned aerial vehicles. Methods in Ecology & Evolution, 3, 397-404.
DOI URL |
| 15 |
Guan YY, Fei F, Guan QW, Chen B ( 2016) Advances in studies of forest gap ecology. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 52(4), 91-99. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| 34 |
[ 彭少麟, 刘强 ( 2002) 森林凋落物动态及其对全球变暖的响应. 生态学报, 22, 1534-1544.]
DOI URL |
| 35 |
Remondino F ( 2011) Heritage recording and 3D modeling with photogrammetry and 3D scanning. Remote Sensing, 3, 1104-1138.
DOI URL |
| 36 | Runkle JR ( 1992) Guidelines and Sample Protocol for Sampling Forest Gaps. U. S. Forest Service, Portland. |
| 37 |
Sakio H ( 1997) Effects of natural disturbance on the regeneration of riparian forests in a Chichibu Mountains, central Japan. Plant Ecology, 132, 181-195.
DOI URL |
| 38 |
Salvadorvan ED, Bogaert J, Pvan H, Impens I ( 1998) Influence of tree-fall orientation on canopy gap shape in an Ecuadorian rain forest. Journal of Tropical Ecology, 14, 865-869.
DOI URL |
| 39 |
Schliemann SA, Bockheim JG ( 2011) Methods for studying treefall gaps: A review. Forest Ecology and Management, 261, 1143-1151.
DOI URL |
| 40 |
Senécal JF, Doyon F, Messier C ( 2018) Management implications of varying gap detection height thresholds and other canopy dynamics processes in temperate deciduous forests. Forest Ecology and Management, 410, 84-94.
DOI URL |
| 41 |
Senécal JF, Doyon F, Messier C ( 2018) Tree death not resulting in gap creation: An investigation of canopy dynamics of northern temperate deciduous forests. Remote Sensing, 10, 121-138.
DOI URL |
| 42 |
Senécal JF, Doyon F, St-Onge B ( 2018) Discrimination of canopy gaps and non-regenerating openings in old-growth temperate deciduous forests using airborne LiDAR data. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 48, 774-782.
DOI URL |
| 43 |
Spies TA, Franklin JF, Thomas TB ( 1988) Coarse woody debris in douglas-fir forests of western Oregon and Washington. Ecology, 69, 1689-1702.
DOI URL |
| 44 |
Stohlgren TJ, Bachand RR, Onami Y, Binkley D ( 1998) Species-environment relationships and vegetation patterns: effects of spatial scale and tree life-stage. Plant Ecology, 135, 215-228.
DOI URL |
| 45 |
Sui DD, Wang Y, Lian JY, Zhang J, Hu JB, Ouyang XJ, Fang ZJ, Cao HL, Ye WH ( 2017) Gap distribution patterns in the south subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest of Dinghushan. Biodiversity Science, 25, 382-392. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 隋丹丹, 王悦, 练琚愉, 张健, 胡健波, 欧阳学军, 范宗骥, 曹洪麟, 叶万辉 ( 2017) 鼎湖山南亚热带常绿阔叶林林窗分布格局及其成因. 生物多样性, 25, 382-392.]
DOI URL |
|
| 46 | Tan H, Zhu JJ, Kang HZ ( 2007) A research review on forest gap disturbance. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 26, 587-594. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 谭辉, 朱教君, 康宏樟 ( 2007) 林窗干扰研究. 生态学杂志, 26, 587-594.] | |
| 47 | Wang B, Sun H, Xu Q, Tian J, Li Q, Chen YY, Yang RL, Zhang ZM ( 2018) Height measurement of a Cedar (Cedrus deodara) community based on unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) 3D photogrammetry technology. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38, 3524-3533. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 王彬, 孙虎, 徐倩, 田冀, 李强, 陈盈赟, 杨汝兰, 张志明 ( 2018) 基于无人机3D摄影技术的雪松(Cedrus deodara)群落高度测定. 生态学报, 38, 3524-3533.] | |
| 48 |
Wang JX, Zhang YP ( 2002) A review on within-gap micro-environmental heterogeneity and species’ response. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 26, 69-74. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 王进欣, 张一平 ( 2002) 林窗微环境异质性及物种的响应. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 26, 69-74.]
DOI URL |
|
| 49 | Xia B, Lan TH, Shan A, Deng F, Yao G ( 1996) Canopy gaps in subalpine spruce-fir forests of the hills around Bitahai Lake, Yunnan Province. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 5(4), 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 夏冰, 兰涛贺, 善安, 邓飞, 姚淦 ( 1996) 云南亚高山云冷杉林林窗的研究. 植物资源与环境学报, 5(4), 1-8.] | |
| 50 |
Yang DR, Zhao TZ, Wang RW, Zhang GM, Song QS ( 2001) Study on pollination ecology of fig wasp (Ceratosolen sp.) in the tropical rainforest of Xishuangbanna, China. Zoological Research, 22, 125-130. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
| 15 |
[ 管云云, 费菲, 关庆伟, 陈斌 ( 2016) 林窗生态学研究进展. 林业科学, 52(4), 91-99.]
DOI URL |
| 50 |
[ 杨大荣, 赵庭周, 王瑞武, 张光明, 宋启示 ( 2001) 西双版纳热带雨林聚果榕小蜂的传粉生态学. 动物学研究, 22, 125-130.]
DOI URL |
| 51 | Yang Q, Han L, Chen J, Bai ZL ( 2006) Strategy, protective status and value of tropical rain forest in Xishuangbanna. Genomics and Applied Biology, 25, 341-348. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 杨清, 韩蕾, 陈进, 白志林 ( 2006) 西双版纳热带雨林的价值、保护现状及其对策. 基因组学与应用生物学, 25, 341-348.] | |
| 52 |
Yang XD, Sha LQ ( 2001) Species composition and diversity of soil mesofauna in the ‘Holy Hills’ fragmentary tropical rain forest of Xishuangbanna, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 12, 261-265. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 杨效东, 沙丽清 ( 2001) 西双版纳“龙山”片断热带雨林中小型土壤动物群落组成与多样性研究. 应用生态学报, 12, 261-265.]
DOI URL |
|
| 53 |
Zang RG, Xu HC ( 1998) Advances in forest gap disturbance research. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 34(1), 90-98. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 臧润国, 徐化成 ( 1998) 林隙(GAP)干扰研究进展. 林业科学, 34(1), 90-98.]
DOI URL |
|
| 54 |
Zang RG, Xu HC ( 1999) Regeneration response of main tree species to gap size and gap development phase in the Korean pine broadleaved forest in Jiaohe, Northeast China. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 35(3), 2-9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 臧润国, 徐化成 ( 1999) 红松阔叶林主要树种对林隙大小及其发育阶段更新反应规律的研究. 林业科学, 35(3), 2-9.]
DOI URL |
|
| 55 |
Zhang CY, Gao LS, Zhao XH ( 2006) Microenvironment heterogeneity of canopy gap and response of species regeneration. Hebei Journal of Forestry and Orchard Research, 21, 162-166. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 张春雨, 高露双, 赵秀海 ( 2006) 林隙微环境异质性及物种更新响应研究进展. 河北林果研究, 21, 162-166.]
DOI URL |
|
| 56 |
Zhang J, Hu JB, Lian JB, Fan ZJ, Ouyang XJ, Ye WH ( 2016) Seeing the forest from drones, testing the potential of lightweight drones as a tool for long-term forest monitoring. Biological Conservation, 198, 60-69.
DOI URL |
| 57 | Zhang LN, Fan JX, Hou XD, Sun ZY, Chen Q ( 2016) Comparison of common spatial interpolation methods instratigraphic data analysis: A case study of the stratigraphic thickness of the Ordovician pagoda formation in the upper Yangtze region. Journal of Stratigraphy, 40, 420-428. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张琳娜, 樊隽轩, 侯旭东, 孙宗元, 陈清 ( 2016) 地层数据的常用空间插值方法介绍和比较分析——以上扬子区宝塔组厚度重建为例. 地层学杂志, 40, 420-428.] | |
| 58 |
Zhang Q, Dao JY, Guo H ( 2014) Xishuangbanna rainforest China’s largest realm of tropical fauna and flora. Cultural Geography, ( 11), 58-69. (in Chinese)
DOI URL |
|
[ 张秋, 刀俊云, 郭洪 ( 2014) 西双版纳热带雨林: 中国最大的热带动植物王国. 环球人文地理, ( 11), 58-69.]
DOI URL |
|
| 59 | Zhang YH, Wang ZX ( 1999) The influence of gaps to the herb. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 19(1), 94-99. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张艳华, 王志西 ( 1999) 林隙对草本植物的影响. 植物研究, 19(1), 94-99.] | |
| 60 | Zhang YP, Dou JX, Liu YH, Ma YX ( 2004) Radiation characteristics in a tropical seasonal rain canopy gap. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 15, 929-934. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 张一平, 窦军霞, 刘玉洪, 马友鑫 ( 2004) 热带季节雨林林窗辐射特征研究. 应用生态学报, 15, 929-934.] | |
| 61 |
Zhang ZM, Xu Q, Wang B, Sun H, Geng YP, Tian J ( 2017) Applications of unmanned aerial vehicles remote sensing technology in landscape ecology. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 4029-4036. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 张志明, 徐倩, 王彬, 孙虎, 耿宇鹏, 田冀 ( 2017) 无人机遥感技术在景观生态学中的应用. 生态学报, 37, 4029-4036.]
DOI URL |
|
| 62 |
Zhuang JJ, Liu XJ, Ye YZ, Zhu XL ( 2012) Study on the gap characteristics and the correlation between gap and gap edge wood of permanent plots in Baotianman Nature Reserve. Journal of Henan Agricultural University, 46, 542-548. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI URL |
|
[ 庄静静, 刘晓静, 叶永忠, 朱学灵 ( 2012) 宝天曼固定样地林窗特征及与林窗边缘木的相关性研究. 河南农业大学学报, 46, 542-548.]
DOI URL |
| [1] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [2] | 张浩斌, 肖路, 刘艳杰. 夜间灯光对外来入侵植物和本地植物群落多样性和生长的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24553-. |
| [3] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [4] | 袁敬毅, 张旭, 田镇朋, 王梓柘, 高永萍, 姚迪昭, 关宏灿, 李文楷, 刘婧, 张宏, 马勤. 结合无人机高分辨率可见光影像和激光雷达点云的城市植物群落树种组成和数量特征提取方法对比[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24237-. |
| [5] | 连佳丽, 陈婧, 杨雪琴, 赵莹, 罗叙, 韩翠, 赵雅欣, 李建平. 荒漠草原植物多样性和微生物多样性对降水变化的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24044-. |
| [6] | 万凤鸣, 万华伟, 张志如, 高吉喜, 孙晨曦, 王永财. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的应用潜力[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23381-. |
| [7] | 张乃鹏, 梁洪儒, 张焱, 孙超, 陈勇, 王路路, 夏江宝, 高芳磊. 土壤类型和地下水埋深对黄河三角洲典型盐沼植物群落空间分异的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23370-. |
| [8] | 蒋陈焜, 郁文彬, 饶广远, 黎怀成, Julien B. Bachelier, Hartmut H. Hilger, Theodor C. H. Cole. 植物系统发生海报——以演化视角介绍植物多样性的科教资料项目[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(11): 24210-. |
| [9] | 韩赟, 迟晓峰, 余静雅, 丁旭洁, 陈世龙, 张发起. 青海野生维管植物名录[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23280-. |
| [10] | 陈又生, 宋柱秋, 卫然, 罗艳, 陈文俐, 杨福生, 高连明, 徐源, 张卓欣, 付鹏程, 向春雷, 王焕冲, 郝加琛, 孟世勇, 吴磊, 李波, 于胜祥, 张树仁, 何理, 郭信强, 王文广, 童毅华, 高乞, 费文群, 曾佑派, 白琳, 金梓超, 钟星杰, 张步云, 杜思怡. 西藏维管植物多样性编目和分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23188-. |
| [11] | 宋柱秋, 叶文, 董仕勇, 金梓超, 钟星杰, 王震, 张步云, 徐晔春, 陈文俐, 李世晋, 姚纲, 徐洲锋, 廖帅, 童毅华, 曾佑派, 曾云保, 陈又生. 广东省高等植物多样性编目和分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(9): 23177-. |
| [12] | 梁彩群, 陈玉凯, 杨小波, 张凯, 李东海, 江悦馨, 李婧涵, 王重阳, 张顺卫, 朱子丞. 海南省野生维管植物编目和分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 23067-. |
| [13] | 李仕裕, 张奕奇, 邹璞, 宁祖林, 廖景平. 广东省植物园植物多样性迁地保护现状及发展建议[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22647-. |
| [14] | 吴浩, 余玉蓉, 王佳钰, 赵媛博, 高娅菲, 李小玲, 卜贵军, 薛丹, 吴林. 低水位增加灌木多样性和生物量但降低土壤有机碳含量: 以鄂西南贫营养泥炭地为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22600-. |
| [15] | 黄雨菲, 路春燕, 贾明明, 王自立, 苏越, 苏艳琳. 基于无人机影像与面向对象-深度学习的滨海湿地植物物种分类[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(3): 22411-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn