



生物多样性 ›› 2023, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (3): 22411. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022411 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2022411
黄雨菲1, 路春燕1,2,*( ), 贾明明3, 王自立1, 苏越1, 苏艳琳1
), 贾明明3, 王自立1, 苏越1, 苏艳琳1
收稿日期:2022-07-19
接受日期:2022-11-07
出版日期:2023-03-20
发布日期:2023-02-22
通讯作者:
路春燕
作者简介:* E-mail: luchunyan@fafu.edu.cn基金资助:
Yufei Huang1, Chunyan Lu1,2,*( ), Mingming Jia3, Zili Wang1, Yue Su1, Yanlin Su1
), Mingming Jia3, Zili Wang1, Yue Su1, Yanlin Su1
Received:2022-07-19
Accepted:2022-11-07
Online:2023-03-20
Published:2023-02-22
Contact:
Chunyan Lu
摘要:
明确滨海湿地植物物种类型及其分布状况是实现滨海湿地精细化生物多样性监测的基础, 对于滨海湿地的保护管理与生态可持续发展均具有重要意义。本研究以无人机可见光遥感影像为基础数据源, 在定量分析最优分割尺度与最优分类特征组合的基础上, 应用面向对象-U-net深度学习方法对闽江河口湿地植物物种类型进行分类, 并与K最近邻、决策树、随机森林和贝叶斯分类方法进行精度对比分析, 以期为滨海湿地植物物种遥感精细分类与生物多样性保护管理提供方法借鉴与科学参考。研究结果表明, 利用面向对象-U-net深度学习方法提取不同滨海湿地植物物种类型的分类精度可达95.67%, 总体精度较其他分类方法提高6.67%-13.67%, Kappa系数提高0.12-0.31, 且分类整体性好。此外, 实现植物物种光谱特征、形状特征、纹理特征与高度特征的最优特征选择对于有效提高湿地植物物种信息分类精度具有重要作用, 应用最优分割尺度实现影像分割可提高整体分类效率。
黄雨菲, 路春燕, 贾明明, 王自立, 苏越, 苏艳琳 (2023) 基于无人机影像与面向对象-深度学习的滨海湿地植物物种分类. 生物多样性, 31, 22411. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022411.
Yufei Huang, Chunyan Lu, Mingming Jia, Zili Wang, Yue Su, Yanlin Su (2023) Plant species classification of coastal wetlands based on UAV images and object- oriented deep learning. Biodiversity Science, 31, 22411. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2022411.
| 类型 Types | 特征指标 Feature factors | 公式/解释 Formula/Explanation | 筛选为最优特征组合 Be screened into the optimal feature combination | 参考文献 References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 光谱特征 Spectral features | Mean_R | 红波段光谱亮度均值 Mean of red spectral brightness | 蔡林菲等, | ||
| Mean_G | 绿波段光谱亮度均值 Mean of green spectral brightness | √ | 蔡林菲等, | ||
| Mean_B | 蓝波段光谱亮度均值 Mean of blue spectral brightness | √ | 蔡林菲等, | ||
| SD_R | 红波段光谱亮度标准差 Standard deviation of red spectral brightness | √ | 路春燕等, | ||
| SD_G | 绿波段光谱亮度标准差 Standard deviation of green spectral brightness | √ | 路春燕等, | ||
| SD_B | 蓝波段光谱亮度标准差 Standard deviation of blue spectral brightness | √ | 路春燕等, | ||
| GBDI | 绿蓝差异指数 Green-blue difference index, GBDI = (G - B)/(R + G + B) | √ | 周涛等, | ||
| ExG | 过绿指数 Excess green index, ExG = (2G - R - B)/(G + R + B) | √ | 井然等, | ||
| NGBDI | 归一化绿蓝差异指数 Normalized green-blue difference index, NGBDI = (G - B)/(G + B) | √ | 汪小钦等, | ||
| NGRDI | 归一化绿红差异指数 Normalized green-red difference index, NGRDI = (G - R)/(G + R) | √ | Hunt et al, | ||
| VDVI | 可见光波段差异植被指数 Visible-band difference vegetation index, VDVI = (2G - B - R)/(2G + B + R) | 汪小钦等, | |||
| ExG-ExR | 过绿减过红指数 Excess green minus excess red index, ExG-ExR = (3G - 2.4R - B)/(R + G + B) | √ | 丁雷龙等, | ||
| DEVI | 差异增强植被指数 Difference enhanced vegetation index, DEVI = G/3G + R/3G + B/3G | 周涛等, | |||
| 纹理特征 Texture features | GLCM_Mean | 均值 Mean, | √ | 蔡林菲等, | |
| GLCM_SD | 标准差 Standard deviation, | √ | 蔡林菲等, | ||
| GLCM_Homogeneity | 协同性 Homogeneity, | 路春燕等, | |||
| GLCM_Contrast | 对比度 Contrast, | 路春燕等, | |||
| GLCM_Dissimilarity | 相异性 Dissimilarity, | √ | 路春燕等, | ||
| GLCM_Entropy | 信息熵 Entropy, | √ | 路春燕等, | ||
| GLCM_Secondary moment | 二阶矩 Secondary moment, | 路春燕等, | |||
| GLCM_Correlation | 相关性 Correlation, | √ | 路春燕等, | ||
| 形状特征 Shape features | Shape index | 形状指数, 反映整个斑块形状特点的指数 Shape index, an index reflecting the shape characteristics of the entire patch | √ | 耿仁方等, | |
| Compactness | 紧凑性, 反映斑块在空间分布上的紧密程度 Compactness, reflecting the tightness of patch distribution in space | √ | 耿仁方等, | ||
| Density | 密度, 反映单位面积上的斑块数量 Density, reflecting the number of patches per unit area | √ | 耿仁方等, | ||
| Area | 面积, 反映斑块所占空间的大小 Area, reflecting the size of the space occupied by the patch | √ | 耿仁方等, | ||
| Rectangularity fit | 矩形度, 反映斑块对其外接矩形的充满程度 Rectangularity fit, reflecting the degree of patch filling its surrounding rectangle | √ | 耿仁方等, | ||
| 特征类型 Feature types | 特征指标 Feature factors | 公式/解释 Formula/Explanation | 筛选为最优特征组合 Be screened into the optimal feature combination | 参考文献 References | |
| 高度特征 Height features | Max_Height | 高度最大值 Maximum height | 徐逸等, | ||
| Min_Height | 高度最小值 Minimum height | 徐逸等, | |||
| Mean_Height | 高度均值 Average height | 徐逸等, | |||
| SD_Height | 高度标准差 Standard deviation of height | 徐逸等, | |||
表1 基于无人机可见光影像的特征空间信息
Table 1 Information of feature space based on the visible-light images of unmanned aerial vehicle
| 类型 Types | 特征指标 Feature factors | 公式/解释 Formula/Explanation | 筛选为最优特征组合 Be screened into the optimal feature combination | 参考文献 References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 光谱特征 Spectral features | Mean_R | 红波段光谱亮度均值 Mean of red spectral brightness | 蔡林菲等, | ||
| Mean_G | 绿波段光谱亮度均值 Mean of green spectral brightness | √ | 蔡林菲等, | ||
| Mean_B | 蓝波段光谱亮度均值 Mean of blue spectral brightness | √ | 蔡林菲等, | ||
| SD_R | 红波段光谱亮度标准差 Standard deviation of red spectral brightness | √ | 路春燕等, | ||
| SD_G | 绿波段光谱亮度标准差 Standard deviation of green spectral brightness | √ | 路春燕等, | ||
| SD_B | 蓝波段光谱亮度标准差 Standard deviation of blue spectral brightness | √ | 路春燕等, | ||
| GBDI | 绿蓝差异指数 Green-blue difference index, GBDI = (G - B)/(R + G + B) | √ | 周涛等, | ||
| ExG | 过绿指数 Excess green index, ExG = (2G - R - B)/(G + R + B) | √ | 井然等, | ||
| NGBDI | 归一化绿蓝差异指数 Normalized green-blue difference index, NGBDI = (G - B)/(G + B) | √ | 汪小钦等, | ||
| NGRDI | 归一化绿红差异指数 Normalized green-red difference index, NGRDI = (G - R)/(G + R) | √ | Hunt et al, | ||
| VDVI | 可见光波段差异植被指数 Visible-band difference vegetation index, VDVI = (2G - B - R)/(2G + B + R) | 汪小钦等, | |||
| ExG-ExR | 过绿减过红指数 Excess green minus excess red index, ExG-ExR = (3G - 2.4R - B)/(R + G + B) | √ | 丁雷龙等, | ||
| DEVI | 差异增强植被指数 Difference enhanced vegetation index, DEVI = G/3G + R/3G + B/3G | 周涛等, | |||
| 纹理特征 Texture features | GLCM_Mean | 均值 Mean, | √ | 蔡林菲等, | |
| GLCM_SD | 标准差 Standard deviation, | √ | 蔡林菲等, | ||
| GLCM_Homogeneity | 协同性 Homogeneity, | 路春燕等, | |||
| GLCM_Contrast | 对比度 Contrast, | 路春燕等, | |||
| GLCM_Dissimilarity | 相异性 Dissimilarity, | √ | 路春燕等, | ||
| GLCM_Entropy | 信息熵 Entropy, | √ | 路春燕等, | ||
| GLCM_Secondary moment | 二阶矩 Secondary moment, | 路春燕等, | |||
| GLCM_Correlation | 相关性 Correlation, | √ | 路春燕等, | ||
| 形状特征 Shape features | Shape index | 形状指数, 反映整个斑块形状特点的指数 Shape index, an index reflecting the shape characteristics of the entire patch | √ | 耿仁方等, | |
| Compactness | 紧凑性, 反映斑块在空间分布上的紧密程度 Compactness, reflecting the tightness of patch distribution in space | √ | 耿仁方等, | ||
| Density | 密度, 反映单位面积上的斑块数量 Density, reflecting the number of patches per unit area | √ | 耿仁方等, | ||
| Area | 面积, 反映斑块所占空间的大小 Area, reflecting the size of the space occupied by the patch | √ | 耿仁方等, | ||
| Rectangularity fit | 矩形度, 反映斑块对其外接矩形的充满程度 Rectangularity fit, reflecting the degree of patch filling its surrounding rectangle | √ | 耿仁方等, | ||
| 特征类型 Feature types | 特征指标 Feature factors | 公式/解释 Formula/Explanation | 筛选为最优特征组合 Be screened into the optimal feature combination | 参考文献 References | |
| 高度特征 Height features | Max_Height | 高度最大值 Maximum height | 徐逸等, | ||
| Min_Height | 高度最小值 Minimum height | 徐逸等, | |||
| Mean_Height | 高度均值 Average height | 徐逸等, | |||
| SD_Height | 高度标准差 Standard deviation of height | 徐逸等, | |||
| 分割尺度 Segmentation scale | 分割效果 Segmentation effect | 分割尺度 Segmentation scale | 分割效果 Segmentation effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| 33 |  | 49 |  |
| 35 |  | 51 |  |
| 37 |  | 54 |  |
| 39 |  | 56 |  |
| 43 |  | 58 |  |
| 46 |  | 62 |  |
表2 最优精细至最优粗略分割尺度分割效果对比
Table 2 Performance comparison of optimal fine to rough segmentation scales
| 分割尺度 Segmentation scale | 分割效果 Segmentation effect | 分割尺度 Segmentation scale | 分割效果 Segmentation effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| 33 |  | 49 |  |
| 35 |  | 51 |  |
| 37 |  | 54 |  |
| 39 |  | 56 |  |
| 43 |  | 58 |  |
| 46 |  | 62 |  |
| 湿地植被类型 Wetland vegetation type | K最近邻 K-nearest neighbor | 决策树 Decision tree | 随机森林 Random forest | 贝叶斯 Bayes | U-net深度学习 U-net deep learning | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 生产者精度 Producer accuracy (%) | 用户精度 User accuracy (%) | 生产者精度 Producer accuracy (%) | 用户精度 User accuracy (%) | 生产者精度 Producer accuracy (%) | 用户精度 User accuracy (%) | 生产者精度 Producer accuracy (%) | 用户精度 User accuracy (%) | 生产者精度 Producer accuracy (%) | 用户精度 User accuracy (%) | |
| 短叶茳芏 Cyperus malaccensis | 60.00 | 92.31 | 80.95 | 100.00 | 90.48 | 100.00 | 71.43 | 100.00 | 75.00 | 93.75 |
| 三棱藨草 Scirpus mariqueter | 58.06 | 58.06 | 80.00 | 66.67 | 86.67 | 61.90 | 96.67 | 72.50 | 90.32 | 82.35 |
| 厚藤 Ipomoea pescaprae | 75.00 | 100.00 | 75.00 | 54.55 | 81.25 | 65.00 | 100.00 | 72.73 | 87.50 | 100.00 |
| 芦苇 Phragmites australis | 93.30 | 84.78 | 87.08 | 92.39 | 83.73 | 96.15 | 88.04 | 97.87 | 98.56 | 97.17 |
| 秋茄 Kandelia candel | 37.50 | 64.29 | 79.17 | 67.86 | 95.83 | 62.16 | 95.83 | 65.71 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| 总体精度 Overall accuracy (%) | 82.00 | 84.67 | 85.33 | 89.00 | 95.67 | |||||
| Kappa系数 Kappa coefficient | 0.60 | 0.70 | 0.73 | 0.79 | 0.91 | |||||
表3 不同分类方法分类精度比较
Table 3 Comparison of classification accuracy of different methods
| 湿地植被类型 Wetland vegetation type | K最近邻 K-nearest neighbor | 决策树 Decision tree | 随机森林 Random forest | 贝叶斯 Bayes | U-net深度学习 U-net deep learning | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 生产者精度 Producer accuracy (%) | 用户精度 User accuracy (%) | 生产者精度 Producer accuracy (%) | 用户精度 User accuracy (%) | 生产者精度 Producer accuracy (%) | 用户精度 User accuracy (%) | 生产者精度 Producer accuracy (%) | 用户精度 User accuracy (%) | 生产者精度 Producer accuracy (%) | 用户精度 User accuracy (%) | |
| 短叶茳芏 Cyperus malaccensis | 60.00 | 92.31 | 80.95 | 100.00 | 90.48 | 100.00 | 71.43 | 100.00 | 75.00 | 93.75 |
| 三棱藨草 Scirpus mariqueter | 58.06 | 58.06 | 80.00 | 66.67 | 86.67 | 61.90 | 96.67 | 72.50 | 90.32 | 82.35 |
| 厚藤 Ipomoea pescaprae | 75.00 | 100.00 | 75.00 | 54.55 | 81.25 | 65.00 | 100.00 | 72.73 | 87.50 | 100.00 |
| 芦苇 Phragmites australis | 93.30 | 84.78 | 87.08 | 92.39 | 83.73 | 96.15 | 88.04 | 97.87 | 98.56 | 97.17 |
| 秋茄 Kandelia candel | 37.50 | 64.29 | 79.17 | 67.86 | 95.83 | 62.16 | 95.83 | 65.71 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| 总体精度 Overall accuracy (%) | 82.00 | 84.67 | 85.33 | 89.00 | 95.67 | |||||
| Kappa系数 Kappa coefficient | 0.60 | 0.70 | 0.73 | 0.79 | 0.91 | |||||
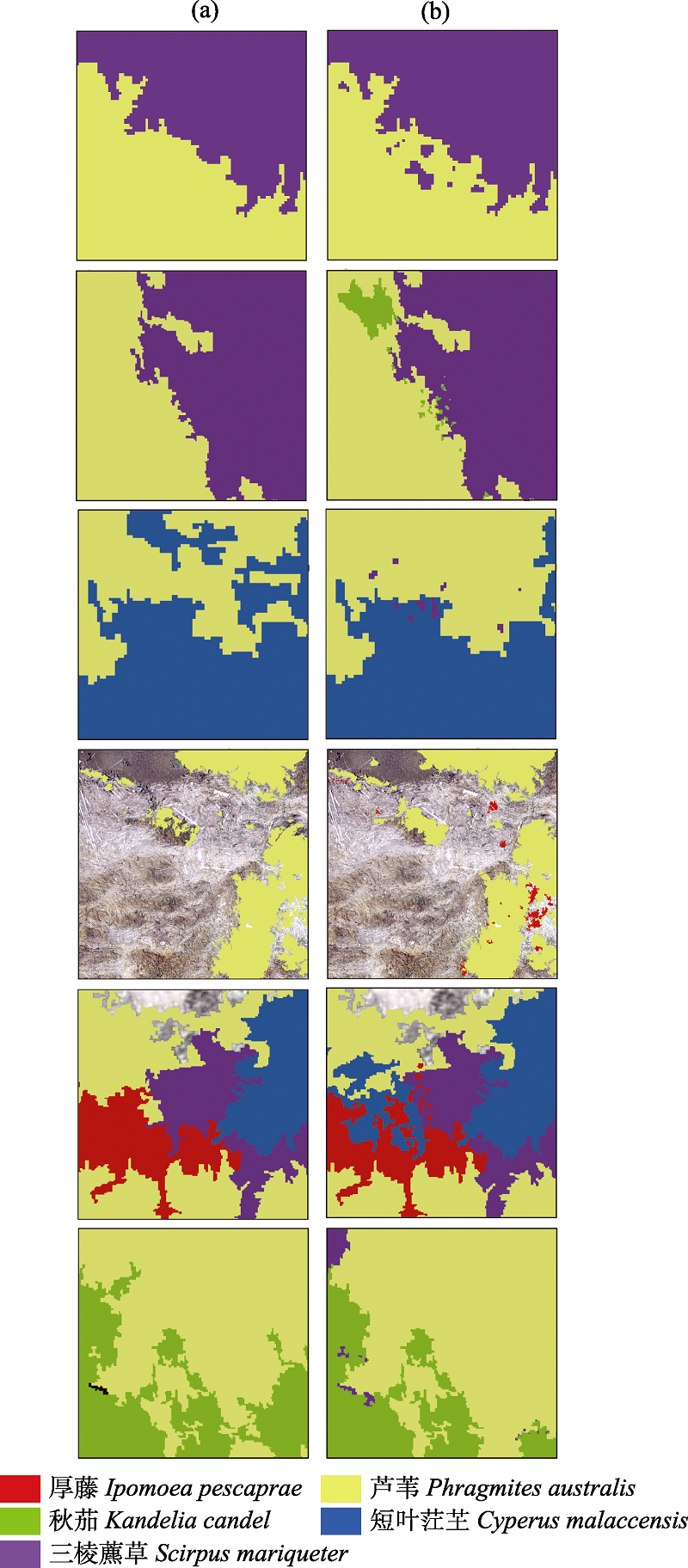
图6 面向对象-U-net深度学习(a)与U-net深度学习(b)方法分类结果局部细节对比。群落交界处各植物种类混生, 边界不清晰, 特征相似, 基于像素分类方法的结果“椒盐”现象明显, 易出现错分问题, 而面向对象分类方法可有效避免该问题, 能更为准确地区分不同植物种类。
Fig. 6 Local detail comparison of classification results between object-oriented U-net deep learning (a) and U-net deep learning (b). At the community boundary, plant species are often mixed with unclear outline and similar image characteristics. The results based on pixel classification method show obvious “pepper and salt” phenomenon, which is prone to misclassification. In contrast, object-oriented method could effectively avoid this problem and distinguish different plant species more accurately.
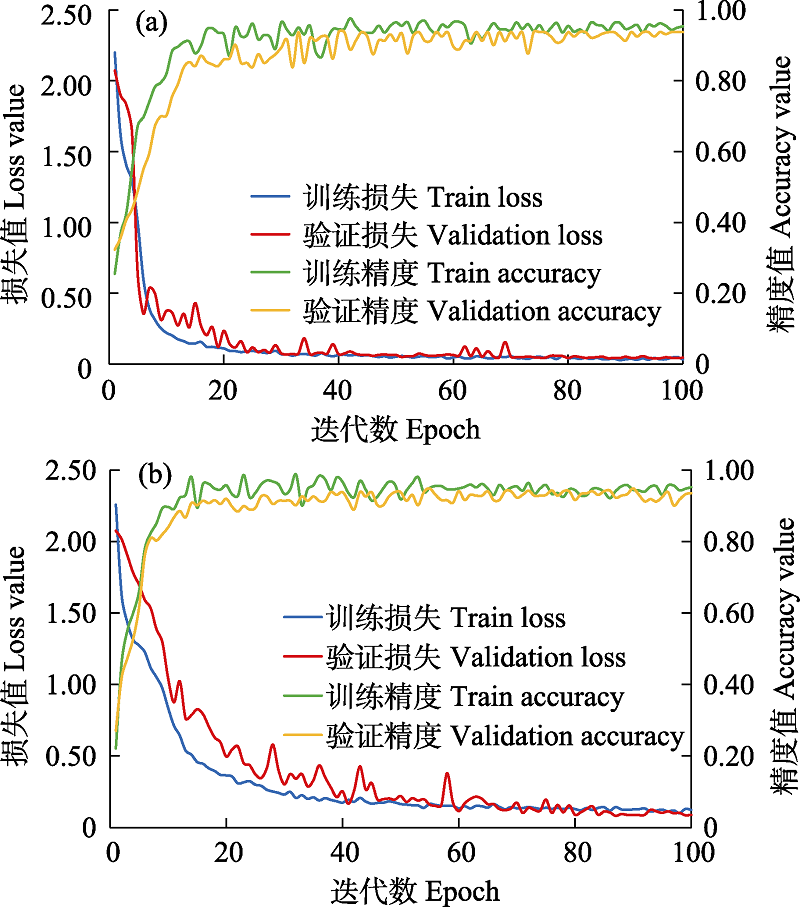
图7 面向对象-U-net深度学习(a)与U-net深度学习(b)分类方法的模型训练与验证损失值及精度对比
Fig. 7 Loss value and accuracy comparison of model training and validation between object-oriented U-net deep learning (a) and U-net deep learning (b)
| [1] | Barbier EB, Acreman M, Knowler D (1997) Economic Valuation of Wetlands: A Guide for Policy Makers and Planners. Ramsar Convention Bureau, Gland. |
| [2] |
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Machine Learning, 45, 5-32.
DOI URL |
| [3] | Breiman L, Friedman JH, Olshen RA, Stone CJ (1984) Classification and regression trees. Biometrics, 40, 874. |
| [4] | Cai LF, Wu DS, Fang LM, Zheng XY (2019) Tree species identification using XGBoost based on GF-2 images. Forest Resources Management, (5), 44-51. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [蔡林菲, 吴达胜, 方陆明, 郑辛煜 (2019) 基于XGBoost的高分二号影像树种识别. 林业资源管理, (5), 44-51.] | |
| [5] | Chen C, Ma Y, Hu YB, Zhang JY (2019) A convolution neural network model with adaptive learning rate and its application—A case study of remote sensing classification of coastal wetland. Marine Environmental Science, 38, 621-627. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [陈琛, 马毅, 胡亚斌, 张靖宇 (2019) 一种自适应学习率的卷积神经网络模型及应用——以滨海湿地遥感分类为例. 海洋环境科学, 38, 621-627.] | |
| [6] | Cheng DB, Zhang SC, Liu XY, Sun K, Zong M (2017) Feature selection by combining subspace learning with sparse representation. Multimedia Systems, 23, 285-291. |
| [7] |
Cover TM, Hart PE (1967) Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 13, 21-27.
DOI URL |
| [8] | Dai QL, Luo B, Zheng C, Wang LG (2020) Regional multiscale Markov random field for remote sensing image classification. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 24, 245-253. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [代沁伶, 罗斌, 郑晨, 王雷光 (2020) 区域多尺度马尔可夫随机场的遥感影像分类. 遥感学报, 24, 245-253.] | |
| [9] | Ding LL, Li QZ, Du X, Tian YC, Yuan C (2016) Vegetation extraction method based on color indices from UAV images. Remote Sensing for Natural Resources, 28(1), 78-86. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [丁雷龙, 李强子, 杜鑫, 田亦陈, 袁超 (2016) 基于无人机图像颜色指数的植被识别. 国土资源遥感, 28(1), 78-86.] | |
| [10] |
Drǎguţ L, Csillik O, Eisank C, Tiede D (2014) Automated parameterisation for multi-scale image segmentation on multiple layers. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 88, 119-127.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Drǎguţ L, Tiede D, Levick SR (2010) ESP: A tool to estimate scale parameter for multiresolution image segmentation of remotely sensed data. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 24, 859-871.
DOI URL |
| [12] | Fei XY, He XK, Xie HX, Wang HM, Chen S, Chen TY (2021) Classification of Linhong River estuary wetland based on GF-1 satellite image. Journal of Jiangsu Ocean University (Natural Science Edition), 30(2), 50-57. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [费鲜芸, 何鑫坤, 谢宏璇, 王灏旻, 陈实, 陈天羽 (2021) 基于GF-1卫星影像的临洪河口湿地遥感分类. 江苏海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 30(2), 50-57.] | |
| [13] | Gao H, Li JB, He T, Sun ZG, Fan AL, Zhu H, Ren P, Zhai SJ (2017) Silica distribution characteristics in plant-soil systems of typical vegetation communities and ecotones in Min River estuary wetland. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 31, 279-285. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [高会, 李家兵, 何涛, 孙志高, 范爱连, 祝贺, 任鹏, 翟水晶 (2017) 闽江河口典型植被群落带及交错带植物-土壤体系中硅素的分布特征. 水土保持学报, 31, 279-285.] | |
| [14] | Geng RF, Fu BL, Cai JT, Chen XY, Lan FW, Yu HM, Li QX (2019) Object-based karst wetland vegetation classification method using unmanned aerial vehicle images and random forest algorithm. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 21, 1295-1306. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[耿仁方, 付波霖, 蔡江涛, 陈晓雨, 蓝斐芜, 余杭洺, 李青逊 (2019) 基于无人机影像和面向对象随机森林算法的岩溶湿地植被识别方法研究. 地球信息科学学报, 21, 1295-1306.]
DOI |
|
| [15] |
Guo QH, Liu J (2018) Remote sensing has become an indispensable technology for biodiversity research protection and change monitoring. Biodiversity Science, 26, 785-788. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
[郭庆华, 刘瑾 (2018) 遥感已经成为生物多样性研究保护与变化监测不可或缺的技术手段. 生物多样性, 26, 785-788.]
DOI |
|
| [16] | Hu HJ, Zhang RT, Chen JR (2001) Plant ecology of the outer coast of the Minjiang River estuary in Fujian. Haiyang Xuebao, 23(5), 110-115. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [胡慧娟, 张娆挺, 陈剑榕 (2001) 福建闽江口外海岸植物生态. 海洋学报, 23(5), 110-115.] | |
| [17] | Hua L, Sui HG, Ding W, Fu HB (2019) Automatic geometric correction of complex sea condition remote sensing image based on decision tree classification. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 326, 012006. |
| [18] | Huang SD, Xu WH, Xiong Y, Wu C, Dai F, Xu HF, Wang LG, Kou WL (2021) Combining textures and spatial features to extract tea plantations based on object-oriented method by using multispectral image. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 41, 2565-2571. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [黄邵东, 徐伟恒, 熊源, 吴超, 代飞, 徐海峰, 王雷光, 寇卫利 (2021) 结合纹理和空间特征的多光谱影像面向对象茶园提取. 光谱学与光谱分析, 41, 2565-2571.] | |
| [19] |
Hunt ER Jr, Cavigelli M, Daughtry CST, Mcmurtrey JE, Walthall CL (2005) Evaluation of digital photography from model aircraft for remote sensing of crop biomass and nitrogen status. Precision Agriculture, 6, 359-378.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Jia QY, Zhou L, Xie YB, Zhou GS (2006) Study on biomass dynamics of Phragmites communis community in Panjin wetland. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 22(4), 25-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [贾庆宇, 周莉, 谢艳兵, 周广胜 (2006) 盘锦湿地芦苇群落生物量动态特征研究. 气象与环境学报, 22(4), 25-29.] | |
| [21] | Jing R, Deng L, Zhao WJ, Gong ZN (2016) Object-oriented aquatic vegetation extracting approach based on visible vegetation indices. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 27, 1427-1436. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
|
[井然, 邓磊, 赵文吉, 宫兆宁 (2016) 基于可见光植被指数的面向对象湿地水生植被提取方法. 应用生态学报, 27, 1427-1436.]
DOI |
|
| [22] |
Kong JX, Zhang ZC, Zhang J (2019) Classification and identification of plant species based on multi-source remote sensing data: Research progress and prospect. Biodiversity Science, 27, 796-812. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[孔嘉鑫, 张昭臣, 张健 (2019) 基于多源遥感数据的植物物种分类与识别: 研究进展与展望. 生物多样性, 27, 796-812.]
DOI |
|
| [23] |
Li QT, Wang CZ, Zhang B, Lu LL (2015) Object-based crop classification with landsat-MODIS enhanced time-series data. Remote Sensing, 7, 16091-16107.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Liu BF, Guo YM (2003) Waterfowl resources and protection in Minjiang River estuary wetland. Chinese Wildlife, 24(4), 6-7. (in Chinese) |
| [刘伯锋, 郭玉民 (2003) 闽江河口湿地水禽资源及其保护. 野生动物, 24(4), 6-7.] | |
| [25] |
Liu K, Gong H, Cao JJ, Zhu YH (2019) Comparison of mangrove remote sensing classification based on multi-type UAV data. Tropical Geography, 39, 492-501. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
| [刘凯, 龚辉, 曹晶晶, 朱远辉 (2019) 基于多类型无人机数据的红树林遥感分类对比. 热带地理, 39, 492-501.] | |
| [26] | Liu RH, Liang SC, Zhao HY, Qi GC, Li LX, Jiang Y, Niu ZG (2017) Progress of Chinese coastal wetland based on remote sensing. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 32, 998-1011. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘润红, 梁士楚, 赵红艳, 漆光超, 李丽香, 姜勇, 牛振国 (2017) 中国滨海湿地遥感研究进展. 遥感技术与应用, 32, 998-1011.] | |
| [27] |
Liu RQ, Li JL, Sun C, Sun WW, Cao LD, Tian P (2021) Classification of Yancheng coastal wetland vegetation based on vegetation phenological characteristics derived from Sentinel-2 time-series. Acta Geographica Sinica, 76, 1680-1692. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[刘瑞清, 李加林, 孙超, 孙伟伟, 曹罗丹, 田鹏 (2021) 基于Sentinel-2遥感时间序列植被物候特征的盐城滨海湿地植被分类. 地理学报, 76, 1680-1692.]
DOI |
|
| [28] | Lu CY, Lei YF, Su Y, Huang YF, Liu MY, Jia MM (2021) Remote sensing analysis of wetland dynamics based on object-oriented and deep learning in the low-elevation coastal zone of Southeast Fujian. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 36, 713-727. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [路春燕, 雷依凡, 苏颖, 黄雨菲, 刘明月, 贾明明 (2021) 基于面向对象-深度学习的闽东南低海拔海岸带地区湿地动态遥感分析. 遥感技术与应用, 36, 713-727.] | |
| [29] | Lu CY, Li L, Wang ZL, Su YL, Su Y, Huang YF, Jia MM, Mao DH (2022) The national nature reserves in China: Are they effective in conserving mangroves? Ecological Indicators, 142, 109265. |
| [30] | Lu CY, Lin P (1990) Afforesting techniques of Kandelia candel mangrove and their ecological principle. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 29, 694-698. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [卢昌义, 林鹏 (1990) 秋茄红树林的造林技术及其生态学原理. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 29, 694-698.] | |
| [31] |
Lu CY, Liu JF, Jia MM, Liu MY, Man WD, Fu WW, Zhong LX, Lin XQ, Su Y, Gao YB (2018) Dynamic analysis of mangrove forests based on an optimal segmentation scale model and multi-seasonal images in Quanzhou Bay, China. Remote Sensing, 10, 2020.
DOI URL |
| [32] | Luo YM (2016) Sustainability associated coastal eco- environmental problems and coastal science development in China. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 31, 1133-1142. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [骆永明 (2016) 中国海岸带可持续发展中的生态环境问题与海岸科学发展. 中国科学院院刊, 31, 1133-1142.] | |
| [33] | Mo LJ, Cao Y, Hu YM, Liu M, Xia D (2012) Object-oriented classification for satellite remote sensing of wetlands: A case study in southern Hangzhou Bay area. Wetland Science, 10, 206-213. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [莫利江, 曹宇, 胡远满, 刘淼, 夏栋 (2012) 面向对象的湿地景观遥感分类——以杭州湾南岸地区为例. 湿地科学, 10, 206-213.] | |
| [34] | Nie Q, Qi KK, Zhao YF (2021) Object-oriented classification of high-resolution image combining super-pixel segmentation. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, (6), 44-49. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [聂倩, 七珂珂, 赵艳福 (2021) 融入超像素分割的高分辨率影像面向对象分类. 测绘通报, (6), 44-49.] | |
| [35] | Niu X (2021) Research on residential buildings recognition by decision tree classification model. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 46(3), 163-168. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [牛宵 (2021) 决策树分类模型的住宅建筑物图斑识别. 测绘科学, 46(3), 163-168.] | |
| [36] | Ouyang PY, Liu N, Zhang WW, Wang J, Jian SG (2011) Biological and ecophysiological characteristics of a beach plant Ipomoea pescaprae. Journal of Hunan University of Science & Technology (Natural Science Edition), 26(4), 117-121. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [欧阳蒲月, 刘楠, 张伟伟, 王俊, 简曙光 (2011) 海滩植物厚藤(Ipomoea pescaprae)的生物学及生理生态特性. 湖南科技大学学报(自然科学版), 26(4), 117-121.] | |
| [37] | Pan WH, Chen JJ, Zhang CG, Lin J (2011) Dynamic monitoring analysis of expansion of Spartina alterniflora in Fujian. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 32(S1), 174-177. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [潘卫华, 陈家金, 张春桂, 林晶 (2011) 福建沿海水域互花米草蔓延的动态监测分析. 中国农业气象, 32(S1), 174-177.] | |
| [38] |
Pashaei M, Kamangir H, Starek MJ, Tissot P (2020) Review and evaluation of deep learning architectures for efficient land cover mapping with UAS hyper-spatial imagery: A case study over a wetland. Remote Sensing, 12, 959.
DOI URL |
| [39] | Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) -Net:Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015 (eds Navab N, Hornegger J, Wells W, Frangi A), pp. 234-241. Springer, Cham. |
| [40] | Shen YY, Huang XY, Huang SR, Shen YQ, Chen XY (2020) Identification and validation of sea-wave echoes collected by a Doppler weather radar based on a Bayes classifier. Marine Sciences, 44(6), 83-90. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [沈妍琰, 黄兴友, 黄书荣, 沈艳秋, 陈晓颖 (2020) 基于贝叶斯分类器的多普勒天气雷达海浪回波识别和效果检验. 海洋科学, 44(6), 83-90.] | |
| [41] | Shi PR, Chen YF, Liu H, Wu YH (2018) Parameters of multi-segmentation based on segmentation evaluation function. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 33, 628-637. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [施佩荣, 陈永富, 刘华, 吴云华 (2018) 基于分割评价函数的多尺度分割参数的选择. 遥感技术与应用, 33, 628-637.] | |
| [42] | Song HR, Su GH, Sun JH, Wei HL, Lin WR (2021) Landscape changes of the Yancheng wetland in the past 20 years: Evidence from random forest. Marine Geology Frontiers, 37(12), 75-82. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [宋怀荣, 苏国辉, 孙记红, 魏合龙, 林文荣 (2021) 基于随机森林的盐城湿地近20年景观格局变化. 海洋地质前沿, 37(12), 75-82.] | |
| [43] | Song J, Liu XL (2021) Improving the accuracy of forest identification in mountainous areas from multi-source remote sensing data—The Sunan County section of Qilian Mountains National Park as an example. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 30(10), 1-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [宋洁, 刘学录 (2021) 基于多源遥感数据提高山地森林识别精度——以祁连山国家公园肃南县段为例. 草业学报, 30(10), 1-14.] | |
| [44] | Sun WW, Yang G, Chen C, Chang MH, Huang K, Meng XZ, Liu LY (2020) Development status and literature analysis of China’s earth observation remote sensing satellites. Journal of Remote Sensing (Chinese), 24, 479-510. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孙伟伟, 杨刚, 陈超, 常明会, 黄可, 孟祥珍, 刘良云 (2020) 中国地球观测遥感卫星发展现状及文献分析. 遥感学报, 24, 479-510.] | |
| [45] | Tong C, Huang JF, Wang WQ, Liao J, Liu ZX, Zeng CS (2012) Methane dynamics of a brackish-water tidal Phragmites australis marsh in the Minjiang River estuary. Acta Geographica Sinica, 67, 1165-1180. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [仝川, 黄佳芳, 王维奇, 廖稷, 刘泽雄, 曾从盛 (2012) 闽江口半咸水芦苇潮汐沼泽湿地甲烷动态. 地理学报, 67, 1165-1180.] | |
| [46] |
Wan LM, Zhang HS, Lin GH, Lin H (2019) A small-patched convolutional neural network for mangrove mapping at species level using high-resolution remote-sensing image. Annals of GIS, 25, 45-55.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Wang L, Shi C, Tian JY, Song XN, Jia MM, Li XJ, Liu XM, Zhong RF, Yin DM, Yang SS, Guo XX (2018) Researches on mangrove forest monitoring methods based on multi-source remote sensing. Biodiversity Science, 26, 838-849. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[王乐, 时晨, 田金炎, 宋晓楠, 贾明明, 李小娟, 刘晓萌, 钟若飞, 殷大萌, 杨杉杉, 郭先仙 (2018) 基于多源遥感的红树林监测. 生物多样性, 26, 838-849.]
DOI |
|
| [48] | Wang XQ, Wang MM, Wang SQ, Wu YD (2015) Extraction of vegetation information from visible unmanned aerial vehicle images. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 31(5), 152-159. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [汪小钦, 王苗苗, 王绍强, 吴云东 (2015) 基于可见光波段无人机遥感的植被信息提取. 农业工程学报, 31(5), 152-159.] | |
| [49] | Wang ZQ, Zhou Y, Wang SX, Wang FT, Xu ZY (2021) House building extraction from high-resolution remote sensing images based on IEU-Net. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 25, 2245-2254. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王振庆, 周艺, 王世新, 王福涛, 徐知宇 (2021) IEU-Net高分辨率遥感影像房屋建筑物提取. 遥感学报, 25, 2245-2254.] | |
| [50] |
Wei SS, Zhang H, Wang C, Wang YY, Xu L (2019) Multi-temporal SAR data large-scale crop mapping based on U-net model. Remote Sensing, 11, 68.
DOI URL |
| [51] | Wen X, Jia MM, Li XY, Wang ZM, Zhong CR, Feng EH (2020) Identification of mangrove canopy species based on visible unmanned aerial vehicle images. Journal of Forest and Environment, 40, 486-496. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [闻馨, 贾明明, 李晓燕, 王宗明, 钟才荣, 冯尔辉 (2020) 基于无人机可见光影像的红树林冠层群落识别. 森林与环境学报, 40, 486-496.] | |
| [52] |
Xu Y, Zhang CL, Jiang RJ, Wang ZF, Zhu MC, Shen GC (2021) UAV-based hyperspectral images and monitoring of canopy tree diversity. Biodiversity Science, 29, 647-660. (in Chinese with English abstract)
DOI |
|
[徐岩, 张聪伶, 降瑞娇, 王子斐, 朱梦晨, 沈国春 (2021) 无人机高光谱影像与冠层树种多样性监测. 生物多样性, 29, 647-660.]
DOI |
|
| [53] | Xu Y, Zhen JN, Jiang XP, Wang JJ (2021) Mangrove species classification with UAV-based remote sensing data and XGBoost. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 25, 737-752. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [徐逸, 甄佳宁, 蒋侠朋, 王俊杰 (2021) 无人机遥感与XGBoost的红树林物种分类. 遥感学报, 25, 737-752.] | |
| [54] | Zhan X, Pan WB, Zheng P, Ke JY, Chen QL (2017) Landscape naturalness assessment of the Minjiang River Estuary Wetland Nature Reserve and surrounding areas. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37, 6895-6904. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [占昕, 潘文斌, 郑鹏, 柯锦燕, 陈奇亮 (2017) 闽江河口湿地自然保护区及其周边区域景观自然性评价. 生态学报, 37, 6895-6904.] | |
| [55] | Zhang CY, Chen SL, Li P, Liu QL (2022) Spatiotemporal dynamic remote sensing monitoring of typical wetland vegetation in the current Huanghe River Estuary Reserve. Haiyang Xuebao, 44(1), 125-136. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张晨宇, 陈沈良, 李鹏, 刘清兰 (2022) 现行黄河口保护区典型湿地植被时空动态遥感监测. 海洋学报, 44(1), 125-136.] | |
| [56] | Zhang LQ, Yong XK (1992) Studies on phenology and spatial distribution pattern of Scirpus mariqueter population. Acta Phytoecologica et Geobotanica Sinica, 16, 43-51. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张利权, 雍学葵 (1992) 海三棱藨草种群的物候与分布格局研究. 植物生态学与地植物学学报, 16, 43-51.] | |
| [57] | Zhang SC, Li XL, Zong M, Zhu XF, Cheng DB (2017) Learning k for kNN classification. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology, 8(3), 1-19. |
| [58] | Zhou T, Hu ZQ, Han JZ, Zhang H (2021) Green vegetation extraction based on visible light image of UAV. China Environmental Science, 41, 2380-2390. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [周涛, 胡振琪, 韩佳政, 张浩 (2021) 基于无人机可见光影像的绿色植被提取. 中国环境科学, 41, 2380-2390.] | |
| [59] | Zhou ZM, Chen BQ, Xu R, Fang W (2021) Identification of the mangrove species using UAV hyperspectral images: A case study of Zhangjiangkou Mangrove National Nature Reserve. Haiyang Xuebao, 43(9), 137-145. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [周在明, 陈本清, 徐冉, 方维 (2021) 基于无人机高光谱特征的红树林种群识别研究——以漳江口红树林国家级自然保护区为例. 海洋学报, 43(9), 137-145.] |
| [1] | 袁敬毅, 张旭, 田镇朋, 王梓柘, 高永萍, 姚迪昭, 关宏灿, 李文楷, 刘婧, 张宏, 马勤. 结合无人机高分辨率可见光影像和激光雷达点云的城市植物群落树种组成和数量特征提取方法对比[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24237-. |
| [2] | 宋远昊, 龚吕, 李贲, 胡阳, 李秀珍. 辽河口不同退塘还湿方式对大型底栖动物的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24316-. |
| [3] | 张乃鹏, 梁洪儒, 张焱, 孙超, 陈勇, 王路路, 夏江宝, 高芳磊. 土壤类型和地下水埋深对黄河三角洲典型盐沼植物群落空间分异的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(2): 23370-. |
| [4] | 申小虎, 朱翔宇, 史洪飞, 王传之. 基于机器学习鸟声识别算法研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(11): 23272-. |
| [5] | 张昭臣, 胡健波, 杨庆松, 练琚愉, 李步杭, 王希华, 叶万辉, 张健. 中国亚热带4个森林动态监测样地无人机可见光遥感影像数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(9): 1181-1185. |
| [6] | 徐岩, 张聪伶, 降瑞娇, 王子斐, 朱梦晨, 沈国春. 无人机高光谱影像与冠层树种多样性监测[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(5): 647-660. |
| [7] | 曲方圆, 李淑芸, 赵林林, 杨松颖, 万铭扬, 蔡吕彤, 张朝晖. 黄海生态区保护空缺分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(3): 385-393. |
| [8] | 李有志, 崔丽娟, 潘旭, 宁宇, 李伟, 康晓明, 李凯, 孙宝娣, 于菁菁. 辽河口湿地植物多样性及物种功能型空间分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(4): 471-478. |
| [9] | 黄雅琴, 李荣冠, 王建军, 郑成兴, 郑凤武, 林俊辉, 江锦祥, 李淑珠. 湄洲湾潮间带底栖生物多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2010, 18(2): 156-161. |
| [10] | 徐卫华, 欧阳志云, 蒋泽银, 郑华, 刘建国. 大相岭山系大熊猫生境评价与保护对策研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2006, 14(3): 223-231. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn