



生物多样性 ›› 2019, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (10): 1090-1100. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019195 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2019195
李雪晴1,2, 孙赫英1,2, 何德奎1,*( ), 陈毅峰1
), 陈毅峰1
收稿日期:2019-06-13
接受日期:2019-08-30
出版日期:2019-10-20
发布日期:2019-10-20
通讯作者:
何德奎
基金资助:
Xueqing Li1,2, Heying Sun1,2, Dekui He1,*( ), Yifeng Chen1
), Yifeng Chen1
Received:2019-06-13
Accepted:2019-08-30
Online:2019-10-20
Published:2019-10-20
Contact:
Dekui He
摘要:
澜沧江-湄公河是东南亚最大的河流, 也是世界上淡水生物多样性最高的三大河流之一。由于特殊的地理位置和国际河流属性, 澜沧江-湄公河淡水鱼类的多样性现状仍缺乏系统的认识。本文在近20年调查的基础上, 系统整理了澜沧江-湄公河中上游32个支流或亚流域的淡水鱼类物种名录, 在此基础上对其种类组成和分布进行了分析, 并利用分类学多样性指数对澜沧江-湄公河中上游流域的物种多样性进行了评估。结果表明, 澜沧江-湄公河中上游共记录了淡水鱼类745种, 分属于2纲17目63科229属, 其中鲤形目鱼类451种, 占物种数的60.5%。分类学多样性指数显示, 从源头到中游, 淡水鱼类在分类阶元上的分布越来越均匀, 亲缘关系越来越远, 分类多样性越来越高。聚类分析(cluster analysis, CA)和多维尺度分析(multi-dimensional scaling, MDS)表明, 当Jaccard相似性系数为8.69时, 澜沧江-湄公河中上游32个亚流域可以分为源区、上游和中游3组; 相似性分析(ANOSIM)结果显示, 各组之间淡水鱼类组成差异显著(R = 0.877, P = 0.001)。相似性百分比分析(similarity percentage analysis, SIMPER)结果表明, 导致3组差异性的鱼类主要是鲤形目和鲇形目鱼类, 且随着地势阶梯的升高出现了科级、属级类群的替代。近几十年来, 随着流域各国人口的增长和经济的快速发展, 澜沧江-湄公河鱼类多样性和渔业资源面临严重威胁, 未来需加强流域内国家间合作, 在流域尺度上制定科学保护计划。
李雪晴, 孙赫英, 何德奎, 陈毅峰 (2019) 澜沧江-湄公河中上游淡水鱼类多样性. 生物多样性, 27, 1090-1100. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019195.
Xueqing Li, Heying Sun, Dekui He, Yifeng Chen (2019) Freshwater fish diversity in the upper and middle reaches of the Lancang-Mekong River. Biodiversity Science, 27, 1090-1100. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2019195.
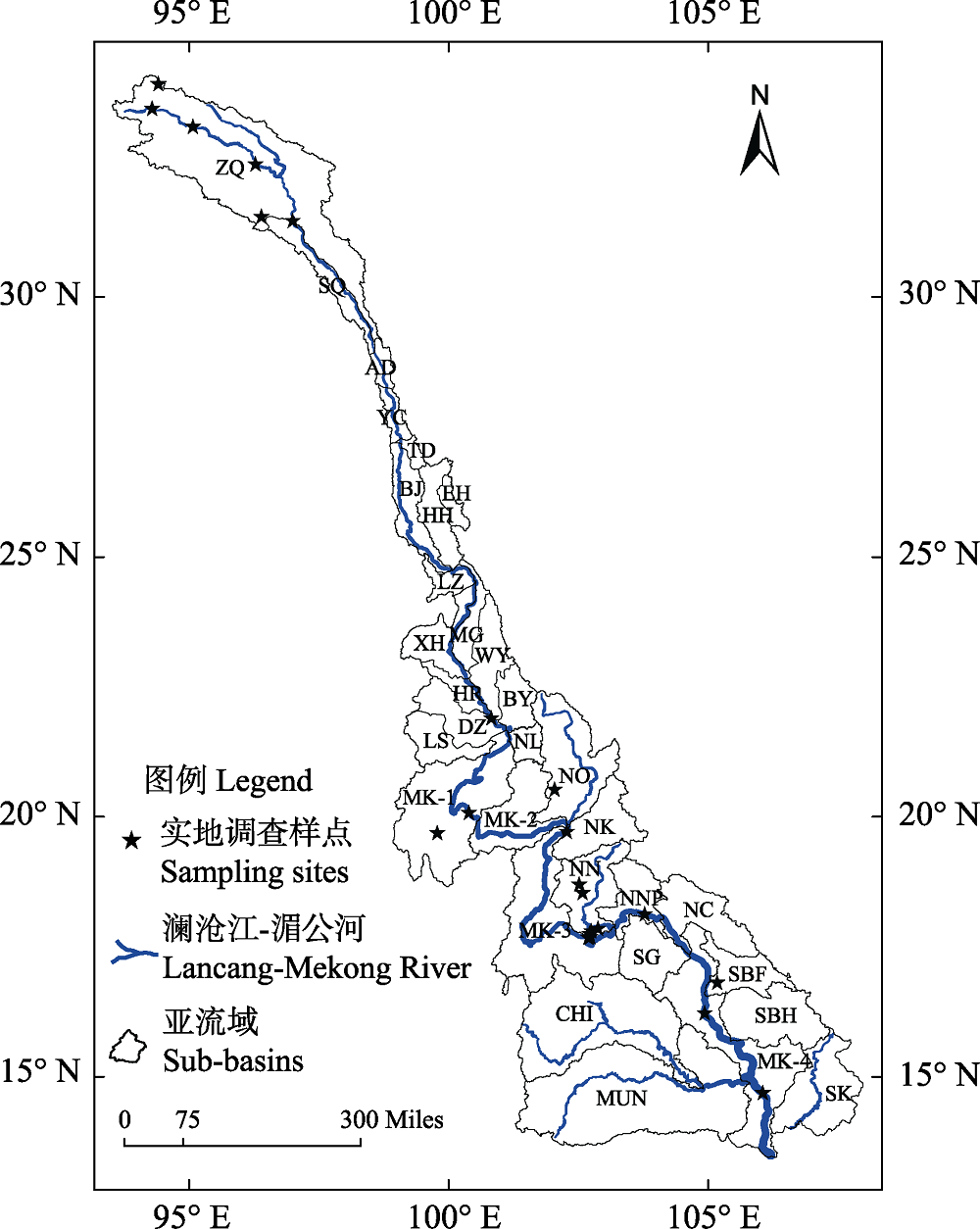
图1 澜沧江-湄公河中上游流域、地理单元(亚流域或支流)以及调查样点分布图。亚流域划分: ZQ: 扎曲; SQ: 色曲; AD: 阿东河; YC: 永春河; TD: 通甸河; EH: 洱海; BJ: 沘江; HH: 黑惠江; LZ: 罗闸河; MG: 勐嘎河; XH: 小黑河; WY: 威远江; HR: 黑河; BY: 补远江; LS: 流沙河; NL: 南腊河; DZ: 大中河; MK-1: 中老边界-博胶; MK-2: 博胶-琅勃拉邦南乌江口; NO: 南乌江; NK: 南康河; NN: 南俄河; MK-3: 琅勃拉邦南乌江口-万象南俄河口; NNP: 南涅河; NC: 南卡丁河; SG: 颂堪河; CHI: 锡河; MUN:蒙河; SBF: 色邦非河; SBH: 色邦亨河; SK: 塞公河; MK-4: 颂堪河口-老挝与柬埔寨边界。
Fig. 1 Map of the upper and middle reaches of the Lancang-Mekong River, the geographic regions (sub-basins or tributaries) and investigation spots in this study. Sub-basins Division: ZQ: Zaqu; SQ: Sequ; AD: Adong River; YC: Yongchun River; TD: Tongdian River; EH: Erhai; BJ: Bijiang; HH: Heihui River; LZ: Luoza River; MG: Mengga River; XH: Xiaohei River; WY: Weiyuan River; HR: Hei River; BY: Buyuan River; LS: Liusha River; NL: Nanla River; DZ: Dazhong River; MK-1: The Border between China and LAOs-Bokeo, LAOs; MK-2: Bokeo-Nam Ou River Estuary, Luang Prabang; NO: Nam Ou River; NK: Nam Khan River; NN: Nam Ngum River; MK-3: Nam Ou River Estuary, Luang Prabang-Nam Ngum Estuary, Vientiane; NNP: Nam Nhiep River; NC: Nam Cadinh River; SG: Songkhram River; CHI: Chi River; MUN: Mun; SBF: Se Bang Fai River; SBH: Se Bang Hieng River; SK: Se Kong River; MK-4: Songkhram Estuary-the border between LAOs and Cambodia.
| 亚流域 Sub-basin | 物种数 Species number | 平均分类差异指数 Average taxonomic distinctness (Δ+) | 分类差异变异指数 Variation in taxonomic distinctness (Λ+) | 亚流域 Sub-basin | 物种数 Species number | 平均分类差异指数 Average taxonomic distinctness (Δ+) | 分类差异变异指数 variation in taxonomic distinctness (Λ+) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZQ | 17 | 60.88 | 434.52 | NL | 116 | 65.78 | 221.76 |
| SQ | 24 | 61.45 | 348.62 | MK-1 | 240 | 68.52 | 233.13 |
| AD | 10 | 60.89 | 550.32 | MK-2 | 99 | 67.47 | 232.44 |
| YC | 21 | 63.05 | 379.28 | NO | 105 | 65.64 | 247.45 |
| TD | 26 | 62.95 | 370.35 | NK | 85 | 67.68 | 227.93 |
| BJ | 54 | 64.72 | 261.12 | MK-3 | 223 | 70.52 | 223.58 |
| HH | 39 | 66.37 | 256.32 | NN | 157 | 67.92 | 224.96 |
| EH | 23 | 56.92 | 396.82 | NNP | 123 | 69.65 | 220.26 |
| LZ | 49 | 65.92 | 218.71 | NC | 104 | 69.47 | 226.98 |
| XH | 62 | 65.67 | 221.7 | SG | 70 | 72.31 | 182.76 |
| MG | 10 | 66.22 | 210.17 | CHI | 170 | 71.55 | 185.59 |
| WY | 32 | 67.06 | 242.95 | MUN | 294 | 71.68 | 198.2 |
| HR | 23 | 64.19 | 331.85 | SBF | 72 | 68.46 | 237.22 |
| DZ | 11 | 60.73 | 406.74 | SBH | 157 | 69.83 | 216.84 |
| BY | 100 | 66.5 | 247.27 | SK | 94 | 65.67 | 244.18 |
| LS | 109 | 66.14 | 226.43 | MK-4 | 379 | 71.45 | 195.07 |
表1 澜沧江-湄公河中上游32个亚流域平均分类差异指数(Δ+)和分类差异变异指数(Λ+) (河流代号见图1)。
Table 1 Average taxonomic distinctness (Δ+) and variation in taxonomic distinctness (Λ+) of 32 sub-basins in the upper and middle Lancang-Mekong River. Sub-basin codes are shown in Fig. 1.
| 亚流域 Sub-basin | 物种数 Species number | 平均分类差异指数 Average taxonomic distinctness (Δ+) | 分类差异变异指数 Variation in taxonomic distinctness (Λ+) | 亚流域 Sub-basin | 物种数 Species number | 平均分类差异指数 Average taxonomic distinctness (Δ+) | 分类差异变异指数 variation in taxonomic distinctness (Λ+) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZQ | 17 | 60.88 | 434.52 | NL | 116 | 65.78 | 221.76 |
| SQ | 24 | 61.45 | 348.62 | MK-1 | 240 | 68.52 | 233.13 |
| AD | 10 | 60.89 | 550.32 | MK-2 | 99 | 67.47 | 232.44 |
| YC | 21 | 63.05 | 379.28 | NO | 105 | 65.64 | 247.45 |
| TD | 26 | 62.95 | 370.35 | NK | 85 | 67.68 | 227.93 |
| BJ | 54 | 64.72 | 261.12 | MK-3 | 223 | 70.52 | 223.58 |
| HH | 39 | 66.37 | 256.32 | NN | 157 | 67.92 | 224.96 |
| EH | 23 | 56.92 | 396.82 | NNP | 123 | 69.65 | 220.26 |
| LZ | 49 | 65.92 | 218.71 | NC | 104 | 69.47 | 226.98 |
| XH | 62 | 65.67 | 221.7 | SG | 70 | 72.31 | 182.76 |
| MG | 10 | 66.22 | 210.17 | CHI | 170 | 71.55 | 185.59 |
| WY | 32 | 67.06 | 242.95 | MUN | 294 | 71.68 | 198.2 |
| HR | 23 | 64.19 | 331.85 | SBF | 72 | 68.46 | 237.22 |
| DZ | 11 | 60.73 | 406.74 | SBH | 157 | 69.83 | 216.84 |
| BY | 100 | 66.5 | 247.27 | SK | 94 | 65.67 | 244.18 |
| LS | 109 | 66.14 | 226.43 | MK-4 | 379 | 71.45 | 195.07 |
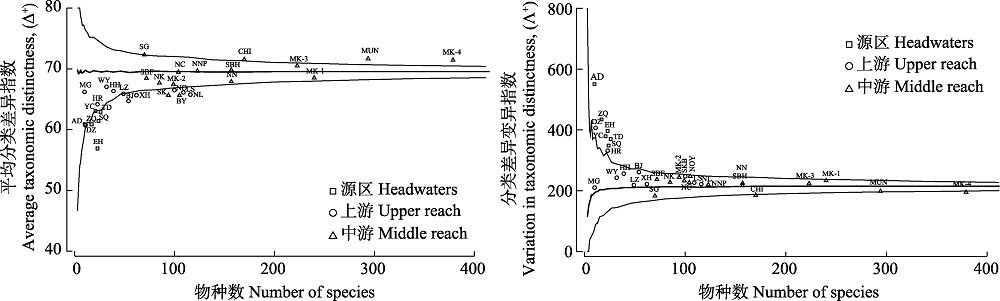
图2 澜沧江-湄公河中上游32个亚流域平均分类差异指数(Δ+)和分类差异变异指数(Λ+)的95%的置信区间漏斗图(河流代号同图1)。
Fig. 2 The 95% probability funnels of average taxonomic distinctness (Δ+) and variation in taxonomic distinctness (Λ+) for 32 sub-basins of the upper and middle reaches of Lancang-Mekong River. Sub-basin codes are shown in Fig. 1.
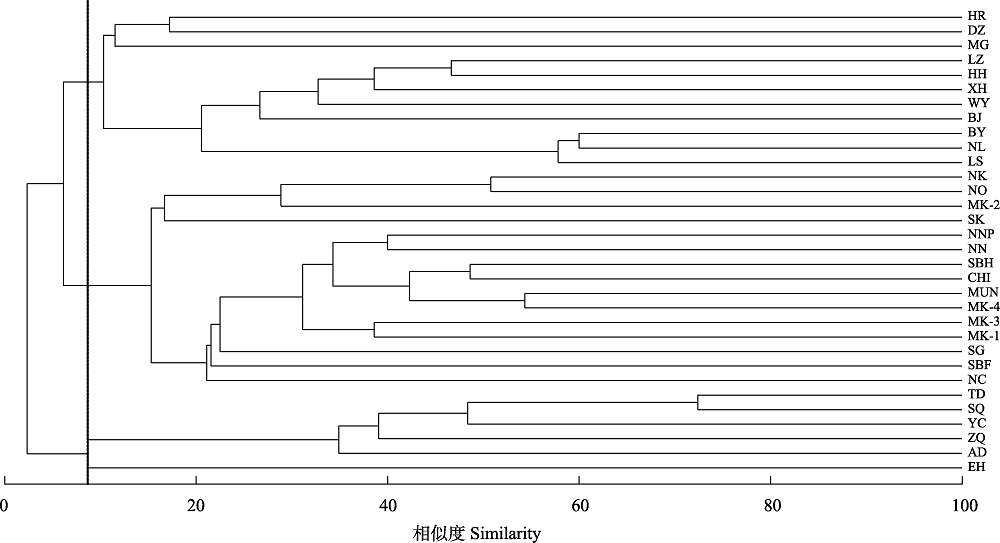
图3 基于Jaccard相似性矩阵和组平均聚类法构建的澜沧江-湄公河中上游32个亚流域淡水鱼类聚类树状图(河流代号见图1)
Fig. 3 Cluster analysis of 32 sub-basins freshwater fish data for the upper and middle reaches of the Lancang-Mekong River based on Jaccard similarity matrix and group average clustering method. Sub-basin codes are shown in Fig. 1.
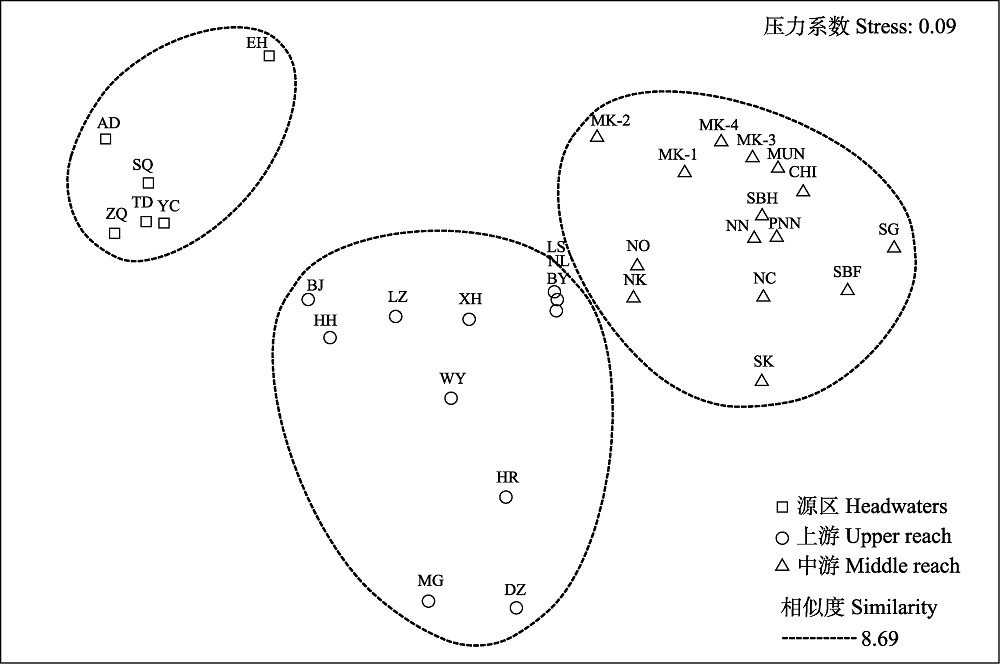
图4 基于Jaccard相似性矩阵的澜沧江-湄公河中上游32个亚流域淡水鱼类组成的多维尺度分析(MDS)排序图(河流代号见图1)
Fig. 4 Multi-dimensional scaling analysis of freshwater fish in 32 sub-basins in the upper and middle reaches of the Lancang-Mekong River based on Jaccard similarity matrix. Sub- basin codes are shown in Fig. 1.
| 关键属 Key genus | 源区和上游 Headwaters & upper reach | 上游和中游 Upper reach & middle reach | 源区和中游 Headwaters & middle reach |
|---|---|---|---|
| 高鲮属 Altigena | 2.47 | - | - |
| 纹胸鮡属 Glyptothorax | 7.62 | 2.37 | 2.15 |
| 半鲿属 Hemibagrus | - | 1.9 | - |
| 间吸鳅属 Hemimyzon | 2.4 | - | - |
| 长臀鲃属 Mystacoleucus | - | 1.97 | 2.15 |
| 鳠属 Mystus | - | 1.95 | 2.07 |
| 纹唇鱼属 Osteochilus | - | 1.83 | 1.97 |
| 无齿𩷶属 Pangasianodon | - | 1.8 | - |
| 单孔鲀属 Pao | - | 1.83 | 1.99 |
| 鮡属 Pareuchiloglanis | 3.11 | - | - |
| 吻孔鲃属 Poropuntius | 2.97 | 2.39 | 2.02 |
| 褶鮡属 Pseudecheneis | 3.23 | - | - |
| 波鱼属 Rasbora | - | 3.17 | 3.1 |
| 南鳅属 Schistura | 2.83 | 3.92 | 2.79 |
| 裂腹鱼属 Schizothorax | 6.25 | - | 2.61 |
| 结鱼属 Tor | 2.68 | - | - |
| 高原鳅属 Triplophysa | 6.18 | - | 2.27 |
表2 澜沧江-湄公河中上游3个生物地理区淡水鱼类组成相似的主要属及其贡献率
Table 2 The genera contributing to similarity of freshwater fish composition among three biogeographical regions in the upper and middle reaches of the Lancang-Mekong River.
| 关键属 Key genus | 源区和上游 Headwaters & upper reach | 上游和中游 Upper reach & middle reach | 源区和中游 Headwaters & middle reach |
|---|---|---|---|
| 高鲮属 Altigena | 2.47 | - | - |
| 纹胸鮡属 Glyptothorax | 7.62 | 2.37 | 2.15 |
| 半鲿属 Hemibagrus | - | 1.9 | - |
| 间吸鳅属 Hemimyzon | 2.4 | - | - |
| 长臀鲃属 Mystacoleucus | - | 1.97 | 2.15 |
| 鳠属 Mystus | - | 1.95 | 2.07 |
| 纹唇鱼属 Osteochilus | - | 1.83 | 1.97 |
| 无齿𩷶属 Pangasianodon | - | 1.8 | - |
| 单孔鲀属 Pao | - | 1.83 | 1.99 |
| 鮡属 Pareuchiloglanis | 3.11 | - | - |
| 吻孔鲃属 Poropuntius | 2.97 | 2.39 | 2.02 |
| 褶鮡属 Pseudecheneis | 3.23 | - | - |
| 波鱼属 Rasbora | - | 3.17 | 3.1 |
| 南鳅属 Schistura | 2.83 | 3.92 | 2.79 |
| 裂腹鱼属 Schizothorax | 6.25 | - | 2.61 |
| 结鱼属 Tor | 2.68 | - | - |
| 高原鳅属 Triplophysa | 6.18 | - | 2.27 |
| 目 Order | 科 Family | 属 Genus | 贡献率 Contribution (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 源区 Headwaters | 鲤形目 Cypriniformes | 鲤科 Cyprinidae | 裂腹鱼属 Schizothorax | 34.43 |
| 叶须鱼属 Ptychobarbus | 2.04 | |||
| 裸裂尻鱼属 Schizopygopsis | 2.04 | |||
| 条鳅科 Nemacheilidae | 高原鳅属 Triplophysa | 16.11 | ||
| 荷马条鳅属 Homatula | 2.13 | |||
| 爬鳅科 Balitoridae | 拟平鳅属 Pseudohomaloptera | 2.13 | ||
| 鲇形目 Siluriformes | 鮡科 Sisoridae | 纹胸鮡属 Glyptothorax | 9.86 | |
| 鮡属 Pareuchiloglanis | 7.95 | |||
| 褶鮡属 Pseudecheneis | 6.74 | |||
| 异鮡属 Creteuchiloglanis | 4.61 | |||
| 上游 Upper reach | 鲤形目 Cypriniformes | 鲤科 Cyprinidae | 吻孔鲃属 Poropuntius | 7.07 |
| 舟齿鱼属 Scaphiodonichthys | 4.7 | |||
| 结鱼属 Torg | 4.13 | |||
| 高鲮属 Altigena | 3.42 | |||
| 墨头鱼属 Garra | 3.4 | |||
| 东坡墨鱼属 Ageneiogarra | 3.01 | |||
| 条鳅科 Nemacheilidae | 南鳅属 Schistura | 3.91 | ||
| 鲇形目 Siluriformes | 鮡科 Sisoridae | 纹胸鮡属 Glyptothorax | 8.86 | |
| 褶鮡属 Pseudecheneis | 4.1 | |||
| 锡伯鲶科 Ailiidae | 鲱鲶属 Clupisoma | 2.98 | ||
| 中游 Middle reach | 鲤形目 Cypriniformes | 鲤科 Cyprinidae | 长臀鲃属 Mystacoleucus | 4 |
| 圆唇鱼属 Cyclocheilichthys | 2.66 | |||
| 裂峡鲃属 Hampala | 2.48 | |||
| 纹唇鱼属 Osteochilus | 2.7 | |||
| 鱼丹科 Danionidae | 波鱼属 Rasbora | 3.91 | ||
| 真马口波鱼属 Opsarius | 3.74 | |||
| 鲈形目 Perciformes | 鳢科 Channidae | 鳢属 Channa | 3.36 | |
| 合鳃目 Synbranchiformes | 刺鳅科 Mastacembelidae | 刺鳅属 Mastacembelus | 2.3 | |
| 鲇形目 Siluriformes | 鲿科 Bagridae | 鳠属 Mystus | 2.28 | |
| 鲀形目 Tetraodontiformes | 鲀科 Tetraodontidae | 单孔鲀属 Pao | 2.22 |
表3 河源、上游和中游鱼类组成相似性的主要属及其贡献率
Table 3 The genera contributing to similarity of fish composition within headwaters, upper and middle reaches
| 目 Order | 科 Family | 属 Genus | 贡献率 Contribution (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 源区 Headwaters | 鲤形目 Cypriniformes | 鲤科 Cyprinidae | 裂腹鱼属 Schizothorax | 34.43 |
| 叶须鱼属 Ptychobarbus | 2.04 | |||
| 裸裂尻鱼属 Schizopygopsis | 2.04 | |||
| 条鳅科 Nemacheilidae | 高原鳅属 Triplophysa | 16.11 | ||
| 荷马条鳅属 Homatula | 2.13 | |||
| 爬鳅科 Balitoridae | 拟平鳅属 Pseudohomaloptera | 2.13 | ||
| 鲇形目 Siluriformes | 鮡科 Sisoridae | 纹胸鮡属 Glyptothorax | 9.86 | |
| 鮡属 Pareuchiloglanis | 7.95 | |||
| 褶鮡属 Pseudecheneis | 6.74 | |||
| 异鮡属 Creteuchiloglanis | 4.61 | |||
| 上游 Upper reach | 鲤形目 Cypriniformes | 鲤科 Cyprinidae | 吻孔鲃属 Poropuntius | 7.07 |
| 舟齿鱼属 Scaphiodonichthys | 4.7 | |||
| 结鱼属 Torg | 4.13 | |||
| 高鲮属 Altigena | 3.42 | |||
| 墨头鱼属 Garra | 3.4 | |||
| 东坡墨鱼属 Ageneiogarra | 3.01 | |||
| 条鳅科 Nemacheilidae | 南鳅属 Schistura | 3.91 | ||
| 鲇形目 Siluriformes | 鮡科 Sisoridae | 纹胸鮡属 Glyptothorax | 8.86 | |
| 褶鮡属 Pseudecheneis | 4.1 | |||
| 锡伯鲶科 Ailiidae | 鲱鲶属 Clupisoma | 2.98 | ||
| 中游 Middle reach | 鲤形目 Cypriniformes | 鲤科 Cyprinidae | 长臀鲃属 Mystacoleucus | 4 |
| 圆唇鱼属 Cyclocheilichthys | 2.66 | |||
| 裂峡鲃属 Hampala | 2.48 | |||
| 纹唇鱼属 Osteochilus | 2.7 | |||
| 鱼丹科 Danionidae | 波鱼属 Rasbora | 3.91 | ||
| 真马口波鱼属 Opsarius | 3.74 | |||
| 鲈形目 Perciformes | 鳢科 Channidae | 鳢属 Channa | 3.36 | |
| 合鳃目 Synbranchiformes | 刺鳅科 Mastacembelidae | 刺鳅属 Mastacembelus | 2.3 | |
| 鲇形目 Siluriformes | 鲿科 Bagridae | 鳠属 Mystus | 2.28 | |
| 鲀形目 Tetraodontiformes | 鲀科 Tetraodontidae | 单孔鲀属 Pao | 2.22 |
| [1] | Baran E ( 2006) Fish Migration Triggers in the Lower Mekong Basin and Other Tropical Freshwater Systems. MRC Technical Paper No. 14, Mekong River Commission, Vientiane. |
| [2] | Baran E ( 2010) Mekong fisheries and mainstream dams. In: ICEM 2010, pp. 1-145. Mekong River Commission Strategic Environmental Assessment of Hydropower on the Mekong Mainstream, International Centre for Environmental Management, Hanoi, Vietnam. |
| [3] | Chen LH, He DM ( 2000) The ecological impacts of hydropower cascade development in Lancang-Mekong River. Acta Geographica Sinica, 67, 577-586. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 陈丽晖, 何大明 ( 2000) 澜沧江-湄公河水电梯级开发的生态影响. 地理学报, 67, 577-586.] | |
| [4] | Chu XL, Chen YR ( 1989) The Fishes of Yunnan, China Part I. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 褚新洛, 陈银瑞 ( 1989) 云南鱼类志(上册). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [5] | Chu XL, Chen YR ( 1990) The Fishes of Yunnan, China Part II. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 褚新洛, 陈银瑞 ( 1990) 云南鱼类志(下册). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [6] | Clarke KR, Warwick RM ( 1998) A taxonomic distinctness index and its statistical properties. Journal of Applied Ecology, 35, 523-531. |
| [7] | Clarke KR, Warwick RM ( 2001 a) A further biodiversity index applicable to species lists: Variation in taxonomic distinctness. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 216, 265-278. |
| [8] | Clarke KR, Warwick RM ( 2001 b) Change in marine communities: An approach to statistical analysis and interpretation, 2nd edn. Plymouth Marine Laboratory, Plymouth. |
| [9] | Dudgeon D ( 2011) Asian river fishes in the Anthropocene: Threats and conservation challenges in an era of rapid environmental change. Journal of Fish Biology, 79, 1487-1524. |
| [10] | Dudgeon D, Arthington AH, Gessner MO, Kawabata Z, Knowler DJ, Leveque C, Naiman RJ, Prieur RAH, Soto D, Stiassny MLJ, Sullivan CA ( 2006) Freshwater biodiversity: Importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biological Reviews, 81, 163-182. |
| [11] | Eschmeyer WN, Fricke R ( 2019) Catalog of Fishes: Genera, Species, References. |
| [12] | Ge F ( 2008) Modern Ecology, 2nd edn. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [ 戈峰 ( 2008) 现代生态学, 第2版. 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [13] | He DM ( 1995) Analysis of hydrological characteristics in Lancang-Mekong River. Yunnan Geographic Environment Research, 7, 58-74. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 何大明 ( 1995) 澜沧江-湄公河水文特征分析. 云南地理环境研究, 7, 58-74.] | |
| [14] | Hortle KG ( 2009) Chapter 9—Fisheries of the Mekong River Basin. In: The Mekong (ed. Campbell IC), pp. 197-249. Academic Press, San Diego. |
| [15] | Jiang XM, Ding CZ, Brosse S, Pan B, Lu Y, Xie ZC ( 2019) Local rise of phylogenetic diversity due to invasions and extirpations leads to a regional phylogenetic homogenization of fish fauna from Chinese isolated plateau lakes. Ecological Indicators, 101, 388-398. |
| [16] | Jiang ZG, Ji LQ ( 1999) Avian-mammalian species diversity in nine representative sites in China. Chinese Biodiversity, 7, 220-225. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 蒋志刚, 纪力强 ( 1999) 鸟兽物种多样性测度的G-F指数方法. 生物多样性, 7, 220-225.] | |
| [17] | Kang B, He DM, Perrett L, Wang HY, Hu WX, Deng WD, Wu YF ( 2009 a) Fish and fisheries in the upper Mekong: Current assessment of the fish community, threats and conservation. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, 19, 465-480. |
| [18] | Kang B, Perrett L, Li YG, He DM ( 2009 b) Are the fish of the upper and lower Mekong interconnected. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 27, 400-407. |
| [19] | Kano Y, Dudgeon D, Nam S, Samejima H, Watanabe K, Grudpan C, Grudpan J, Magtoon W, Musikasinthorn P, Nguyen PT, Praxaysonbath B, Sato T, Shibukawa K, Shimatani Y, Suvarnaraksha A, Tanaka W, Thach P, Tran DD, Yamashita T, Utsugi K ( 2016) Impacts of dams and global warming on fish biodiversity in the Indo-Burma hotspot. PLoS ONE, 11, e0160151. |
| [20] | MacArthur RH, Wilson EO ( 1967) The Theory of Island Biogeography. Princeton University Press, Princeton. |
| [21] | MRC ( 2003) Mekong Fish Database: A Taxonomic Fish Database for the Mekong Basin. Mekong River Commission, Phnom Penh. |
| [22] | Poulsen AF, Poeu O, Viravong S, Suntornratana U, Tung NT ( 2002) Fish migrations of the Lower Mekong River Basin: Implications for Development, Planning and Environmental Management. MRC Technical Paper No.8, Mekong River Commission, Phnom Penh. |
| [23] | Qu FY, Yu ZS ( 2010) The application of taxonomic diversity in macrobenthic ecology: Taking Yellow Sea for example. Biodiversity Science, 18, 150-155. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 曲方圆, 于子山 ( 2010) 分类多样性在大型底栖动物生态学方面的应用: 以黄海底栖动物为例. 生物多样性, 18, 150-155.] | |
| [24] | Rainboth WJ ( 1996) Fishes of the Cambodian Mekong. FAO Species Identification Field Guide for Fishery Purposes, FAO, Rome. |
| [25] | Rainboth WJ, Vidthayanon C, Mai DY ( 2012) Fishes of the Greater Mekong Ecosystem with Species List and Photographic Atlas. Miscellaneous Publications No. 201, University of Michigan, Museum of Zoology, Ann Arbor. |
| [26] | Sun ZL, Liu YL, Liu J, Zhao ZX, Wang GX, Jin JL, Bao ZX, Liu CS ( 2018) Analysis on the present situation and demand of water utilization in the Lancang-Mekong River Basin. Journal of Water Resources & Water Engineering, 29(4), 70-76. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 孙周亮, 刘艳丽, 刘冀, 赵志轩, 王高旭, 金君良, 鲍振鑫, 刘翠善 ( 2018) 澜沧江-湄公河流域水资源利用现状与需求分析. 水资源与水工程学报, 29(4), 70-76.] | |
| [27] | Tang ZY, Wang ZH, Fang JY ( 2009) Historical hypothesis in explaining spatial patterns of species richness. Biodiversity Science, 17, 635-643. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 唐志尧, 王志恒, 方精云 ( 2009) 生物多样性分布格局的地史成因假说. 生物多样性, 17, 635-643.] | |
| [28] | Valbo-Jørgensen J, Coates D, Hortle KG ( 2009) Chapter 8—Fish diversity in the Mekong River basin. In: The Mekong (ed. Campbell IC), pp. 161-196. Academic Press, San Diego. |
| [29] | Warwick RM, Clarke KR ( 2001) Practical measures of marine biodiversity based on relatedness of species. Oceanography and Marine Biology: An Annual Review, 39, 207-231. |
| [30] | Wei FW, Nie YG, Miao HX, Lu H, Hu YB ( 2014) Advancements of the researches on biodiversity loss mechanisms. Chinese Science Bulletin, 59, 430-437. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 魏辅文, 聂永刚, 苗海霞, 路浩, 胡义波 ( 2014) 生物多样性丧失机制研究进展. 科学通报, 59, 430-437.] | |
| [31] | Xu BD, Jin XS, Liang ZL ( 2005) Calculation of hierarchical diversity of fish in the Huanghai and Bohai Seas. Periodical of Ocean University of China (Natural Science), 35, 25-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 徐宾铎, 金显仕, 梁振林 ( 2005) 对黄、渤海鱼类等级多样性的推算. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 35, 25-28.] | |
| [32] | You Z, Feng ZM, Jiang LG, Yang YZ ( 2014) Population distribution and its spatial relationship with terrain elements in Lancang-Mekong River Basin. Mountain Research, 32, 21-29. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [ 游珍, 封志明, 姜鲁光, 杨艳昭 ( 2014) 澜沧江-湄公河流域人口分布及其与地形的关系. 山地学报, 32, 21-29.] | |
| [33] | Zhang C, Ding L, Ding C, Chen L, Sun J, Jiang X ( 2018) Responses of species and phylogenetic diversity of fish communities in the Lancang River to hydropower development and exotic invasions. Ecological Indicators, 90, 261-279. |
| [34] | Ziv G, Baran E, Nam S, Rodríguez-Iturbe I, Levin SA ( 2012) Trading-off fish biodiversity, food security, and hydropower in the Mekong River Basin. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 109, 5609-5614. |
| [1] | 许佳, 崔小娟, 张翼飞, 吴昌, 孙远东. 南岭地区鱼类多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 23482-. |
| [2] | 梁伟诺, 胡亮. 中国新石器时代以来淡水及河口鱼类考古遗存的地理分布及其生物地理学意义[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(8): 21471-. |
| [3] | 王子彤, 张鹗. 赣江鱼类物种更新名录[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(9): 1256-1264. |
| [4] | 赵阳, 牛诚祎, 李雪健, 刘海波, 孙光, 罗遵兰, 赵亚辉. 跨流域调水背景下汉江流域洋县段的鱼类多样性及资源现状[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(3): 361-372. |
| [5] | 李雪健,贾佩尧,牛诚祎,邢迎春,李浩林,刘海波,唐文乔,赵亚辉. 新疆阿勒泰地区额尔齐斯河和乌伦古河流域鱼类多样性演变和流域健康评价[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(4): 422-434. |
| [6] | 张家真, 高春蕾, 李艳, 孙萍, 王宗灵. 江阴港口外来船舶压载舱沉积物中甲藻包囊种类及组成[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(2): 144-154. |
| [7] | 赵亚辉, 邢迎春, 吕彬彬, 周传江, 杨文波, 赵凯. 黄河流域淡水鱼类多样性和保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(12): 1496-1510. |
| [8] | 高宇, 林光辉. 典型红树林生态系统藻类多样性及其在生态过程中的作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2018, 26(11): 1223-1235. |
| [9] | 宋小晶, 唐文乔, 张亚. 华东武夷山-仙霞岭地区淡水鱼类区系特征及其动物地理区划[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(12): 1331-1338. |
| [10] | 郦珊, 陈家宽, 王小明. 淡水鱼类入侵种的分布、入侵途径、机制与后果[J]. 生物多样性, 2016, 24(6): 672-685. |
| [11] | 肖琼, 杨志, 唐会元, 段鹏翔, 王晓清, 肖调义, 刘小燕. 乌江下游干流鱼类物种多样性及其资源保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(4): 499-506. |
| [12] | 王太, 张艳萍, 管丽红, 杜岩岩, 娄忠玉, 焦文龙. 甘肃省鱼类资源现状及DNA条形码在鱼类物种鉴定中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2015, 23(3): 306-313. |
| [13] | 崔鹏, 徐海根, 吴军, 丁晖, 曹铭昌, 卢晓强, 雍凡, 陈冰. 中国脊椎动物红色名录指数评估[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(5): 589-595. |
| [14] | 孙柔鑫, 王彦国, 连光山, 林茂. 海南岛西北沿岸海域浮游桡足类的分布及群落特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2014, 22(3): 320-328. |
| [15] | 李凡, 张焕君, 吕振波, 徐炳庆, 郑亮. 莱州湾游泳动物群落种类组成及多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(5): 537-546. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn