



生物多样性 ›› 2018, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (2): 138-148. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017188 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2017188
所属专题: 青藏高原生物多样性与生态安全
武晓宇1,2, 董世魁1,*( ), 刘世梁1, 刘全儒3, 韩雨晖1, 张晓蕾1, 苏旭坤1, 赵海迪1, 冯憬1
), 刘世梁1, 刘全儒3, 韩雨晖1, 张晓蕾1, 苏旭坤1, 赵海迪1, 冯憬1
收稿日期:2017-06-26
接受日期:2017-12-01
出版日期:2018-02-20
发布日期:2018-05-05
通讯作者:
董世魁
作者简介:# 共同第一作者
基金资助:
Xiaoyu Wu1,2, Shikui Dong1,*( ), Shiliang Liu1, Quanru Liu3, Yuhui Han1, Xiaolei Zhang1, Xukun Su1, Haidi Zhao1, Jing Feng1
), Shiliang Liu1, Quanru Liu3, Yuhui Han1, Xiaolei Zhang1, Xukun Su1, Haidi Zhao1, Jing Feng1
Received:2017-06-26
Accepted:2017-12-01
Online:2018-02-20
Published:2018-05-05
Contact:
Dong Shikui
About author:# Co-first authors
摘要:
三江源地处全球生物多样性热点之一的青藏高原腹地, 是高寒草地生物多样性的集中分布区。但过去几十年中, 人为干扰和气候变化等因素导致高寒草地严重退化, 草地生物多样性受到极大威胁。本研究利用最大熵(MaxEnt)模型模拟了三江源区40种濒危保护植物当前及未来气候变化情景下的热点分布区。根据最大熵模型估计结果统计, 目前三江源濒危保护植物的热点区面积89,438 km2, 主要分布于三江源东部和南部, 其中濒危物种大于30种的最热点地区面积485 km2, 主要分布于囊谦县、玉树市、班玛县、久治县和河南县。未来在增温增湿的气候变化情景下, 最大熵模型模拟的三江源区草地濒危保护植物的热点区将向西北部扩大, 有利于植物多样性的维持和提升。然而, 模型模拟还发现, 在囊谦县、玉树市、班玛县、久治县和河南县等县市, 均有濒危保护植物大于25种以上的热点区域未被重点保护区覆盖, 总面积为4,423 km2。这一区域被划分为可开展畜牧生产活动的一般保护区, 受到人为干扰的可能性较大, 应予以更多关注与保护。
武晓宇, 董世魁, 刘世梁, 刘全儒, 韩雨晖, 张晓蕾, 苏旭坤, 赵海迪, 冯憬 (2018) 基于MaxEnt模型的三江源区草地濒危保护植物热点区识别. 生物多样性, 26, 138-148. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017188.
Xiaoyu Wu, Shikui Dong, Shiliang Liu, Quanru Liu, Yuhui Han, Xiaolei Zhang, Xukun Su, Haidi Zhao, Jing Feng (2018) Identifying priority areas for grassland endangered plant species in the Sanjiangyuan Nature Reserve based on the MaxEnt model. Biodiversity Science, 26, 138-148. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2017188.
| 变量 Variable | 描述 Description |
|---|---|
| Bio1 | 年均温 Annual mean temperature |
| Bio2 | 平均温度日较差 Mean diurnal temperature range |
| Bio3 | 等温性 Isothermality |
| Bio4 | 温度季度变化 Temperature seasonality |
| Bio5 | 最热月最高温 Max temperature of warmest month |
| Bio6 | 最冷月最低温 Min temperature of coldest month |
| Bio7 | 年温度变化范围 Temperature annual range |
| Bio8 | 最湿季度均温 Mean temperature of wettest quarter |
| Bio9 | 最干季度均温 Mean temperature of driest quarter |
| Bio10 | 最暖季度均温 Mean temperature of warmest quarter |
| Bio11 | 最冷季度均温 Mean temperature of coldest quarter |
| Bio12 | 年平均降水量 Annual precipitation |
| Bio13 | 最湿月降水量 Precipitation of wettest month |
| Bio14 | 最干月降水量 Precipitation of driest month |
| Bio15 | 降水量变异系数 Precipitation seasonality (coefficient of variation) |
| Bio16 | 最湿季度降水量 Precipitation of wettest quarter |
| Bio17 | 最干季度降水量 Precipitation of driest quarter |
| Bio18 | 最暖季度降水量 Precipitation of warmest quarter |
| Bio19 | 最冷季度降水量 Precipitation of coldest quarter |
表1 19个生物气候环境因子及其描述
Table 1 19 bioclimatic variables and their descriptions
| 变量 Variable | 描述 Description |
|---|---|
| Bio1 | 年均温 Annual mean temperature |
| Bio2 | 平均温度日较差 Mean diurnal temperature range |
| Bio3 | 等温性 Isothermality |
| Bio4 | 温度季度变化 Temperature seasonality |
| Bio5 | 最热月最高温 Max temperature of warmest month |
| Bio6 | 最冷月最低温 Min temperature of coldest month |
| Bio7 | 年温度变化范围 Temperature annual range |
| Bio8 | 最湿季度均温 Mean temperature of wettest quarter |
| Bio9 | 最干季度均温 Mean temperature of driest quarter |
| Bio10 | 最暖季度均温 Mean temperature of warmest quarter |
| Bio11 | 最冷季度均温 Mean temperature of coldest quarter |
| Bio12 | 年平均降水量 Annual precipitation |
| Bio13 | 最湿月降水量 Precipitation of wettest month |
| Bio14 | 最干月降水量 Precipitation of driest month |
| Bio15 | 降水量变异系数 Precipitation seasonality (coefficient of variation) |
| Bio16 | 最湿季度降水量 Precipitation of wettest quarter |
| Bio17 | 最干季度降水量 Precipitation of driest quarter |
| Bio18 | 最暖季度降水量 Precipitation of warmest quarter |
| Bio19 | 最冷季度降水量 Precipitation of coldest quarter |
| 物种 Species | AUC值 AUC value | 物种 Species | AUC值 AUC value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 褐紫乌头 Aconitum brunneum | 0.969 | 广布红门兰 Orchis chusua | 0.910 |
| 八宿雪灵芝 Arenaria baxoiensis | 0.969 | 宽叶红门兰 Orchis latifolia | 0.919 |
| 三刺草 Aristida triseta | 0.978 | 河北红门兰 Orchis tschiliensis | 0.995 |
| 华雀麦 Bromus sinensis | 0.962 | 青海固沙草 Orinus kokonorica | 0.982 |
| 凹舌兰 Coeloglossum viride | 0.948 | 川赤芍 Paeonia veitchii | 1.000 |
| 毛杓兰 Cypripedium franchetii | 0.997 | 羽叶点地梅 Pomatosace filicula | 0.833 |
| 黑紫披碱草 Elymus atratus | 0.867 | 小丛红景天 Rhodiola dumulosa | 0.992 |
| 短芒披碱草 Elymus breviaristatus | 0.884 | 喜马红景天 Rhodiola himalensis | 0.876 |
| 矮麻黄 Ephedra minuta | 0.930 | 圆丛红景天 Rhodiola juparensis | 0.830 |
| 单子麻黄 Ephedra monosperma | 0.839 | 狭叶红景天 Rhodiola kirilowii | 0.911 |
| 中华羊茅 Festuca sinensis | 0.915 | 四裂红景天 Rhodiola quadrifida | 0.844 |
| 南山龙胆 Gentiana grumii | 0.880 | 粗茎红景天 Rhodiola wallichiana | 0.844 |
| 西南手参 Gymnadenia orchidis | 0.942 | 短颖鹅观草 Roegneria breviglumis | 0.906 |
| 落地金钱 Habenaria aitchisonii | 0.981 | 短柄鹅观草 Roegneria brevipes | 0.953 |
| 裂瓣角盘兰 Herminium alaschanicum | 0.984 | 青海鹅观草 Roegneria kokonorica | 0.980 |
| 角盘兰 Herminium monorchis | 0.981 | 云状雪兔子 Saussurea aster | 0.818 |
| 沼兰 Malaxis monophyllos | 0.983 | 苞叶雪莲 Saussurea obvallata | 0.927 |
| 红花绿绒蒿 Meconopsis punicea | 0.921 | 红叶雪兔子 Saussurea paxiana | 0.855 |
| 颈果草 Metaeritrichium microuloides | 0.873 | 羌塘雪兔子 Saussurea wellbyi | 0.916 |
| 羌活 Notopterygium incisum | 0.940 | 华福花 Sinadoxa corydalifolia | 0.993 |
表2 MaxEnt模型模拟三江源自然保护区濒危植物当前分布的模型预测准确性(AUC值)
Table 2 The AUC value of predicted distribution of endangered plant species in Sanjiangyuan Nature Reserve based on MaxEnt model
| 物种 Species | AUC值 AUC value | 物种 Species | AUC值 AUC value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 褐紫乌头 Aconitum brunneum | 0.969 | 广布红门兰 Orchis chusua | 0.910 |
| 八宿雪灵芝 Arenaria baxoiensis | 0.969 | 宽叶红门兰 Orchis latifolia | 0.919 |
| 三刺草 Aristida triseta | 0.978 | 河北红门兰 Orchis tschiliensis | 0.995 |
| 华雀麦 Bromus sinensis | 0.962 | 青海固沙草 Orinus kokonorica | 0.982 |
| 凹舌兰 Coeloglossum viride | 0.948 | 川赤芍 Paeonia veitchii | 1.000 |
| 毛杓兰 Cypripedium franchetii | 0.997 | 羽叶点地梅 Pomatosace filicula | 0.833 |
| 黑紫披碱草 Elymus atratus | 0.867 | 小丛红景天 Rhodiola dumulosa | 0.992 |
| 短芒披碱草 Elymus breviaristatus | 0.884 | 喜马红景天 Rhodiola himalensis | 0.876 |
| 矮麻黄 Ephedra minuta | 0.930 | 圆丛红景天 Rhodiola juparensis | 0.830 |
| 单子麻黄 Ephedra monosperma | 0.839 | 狭叶红景天 Rhodiola kirilowii | 0.911 |
| 中华羊茅 Festuca sinensis | 0.915 | 四裂红景天 Rhodiola quadrifida | 0.844 |
| 南山龙胆 Gentiana grumii | 0.880 | 粗茎红景天 Rhodiola wallichiana | 0.844 |
| 西南手参 Gymnadenia orchidis | 0.942 | 短颖鹅观草 Roegneria breviglumis | 0.906 |
| 落地金钱 Habenaria aitchisonii | 0.981 | 短柄鹅观草 Roegneria brevipes | 0.953 |
| 裂瓣角盘兰 Herminium alaschanicum | 0.984 | 青海鹅观草 Roegneria kokonorica | 0.980 |
| 角盘兰 Herminium monorchis | 0.981 | 云状雪兔子 Saussurea aster | 0.818 |
| 沼兰 Malaxis monophyllos | 0.983 | 苞叶雪莲 Saussurea obvallata | 0.927 |
| 红花绿绒蒿 Meconopsis punicea | 0.921 | 红叶雪兔子 Saussurea paxiana | 0.855 |
| 颈果草 Metaeritrichium microuloides | 0.873 | 羌塘雪兔子 Saussurea wellbyi | 0.916 |
| 羌活 Notopterygium incisum | 0.940 | 华福花 Sinadoxa corydalifolia | 0.993 |
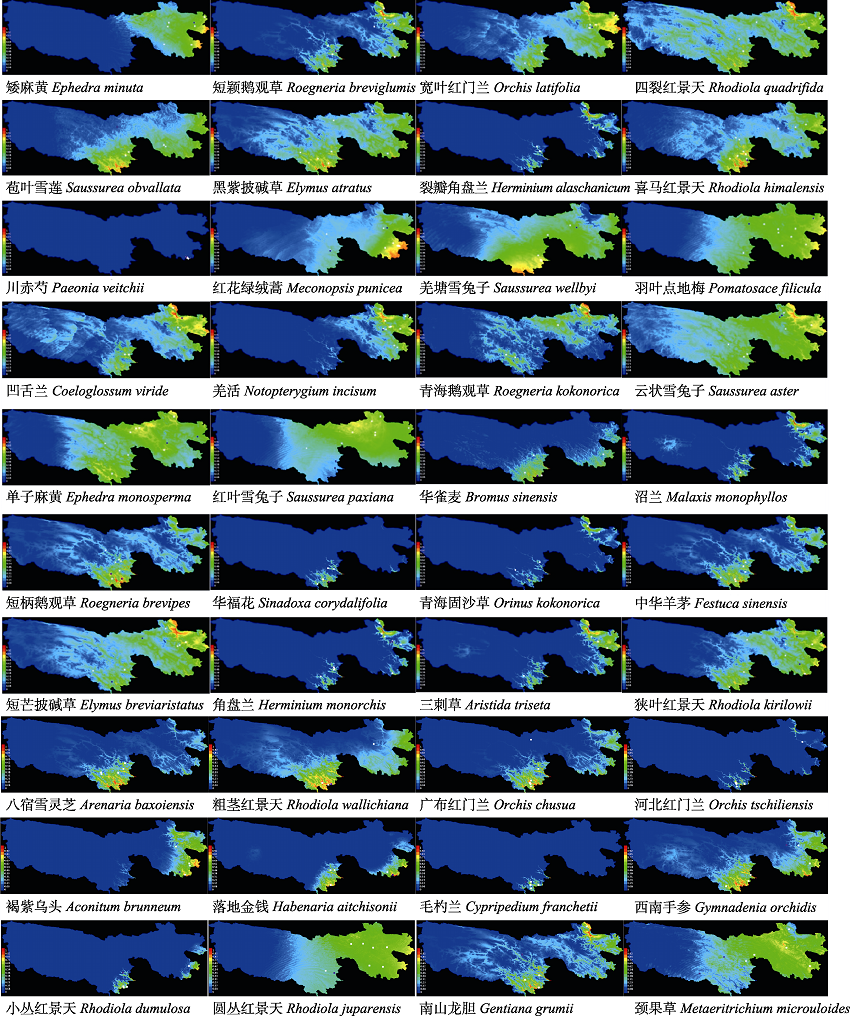
图2 基于MaxEnt模型的三江源自然保护区草地濒危植物当前分布概率图。物种存在概率为0-1, 暖色为物种存在概率高的区域, 最高为红色, 依次下降为橙色、黄色、绿色、青色、淡青色, 深蓝色为最低。
Fig. 2 The probability graph of current distribution of the grassland endangered plant species in Sanjiangyuan Nature Reserve based on MaxEnt models. The species existing probability range from 0 to 1. Warmer colors show areas with higher predicted probability, red is the highest, followed by orange, yellow, green, cyan, light cyan and dark blue.
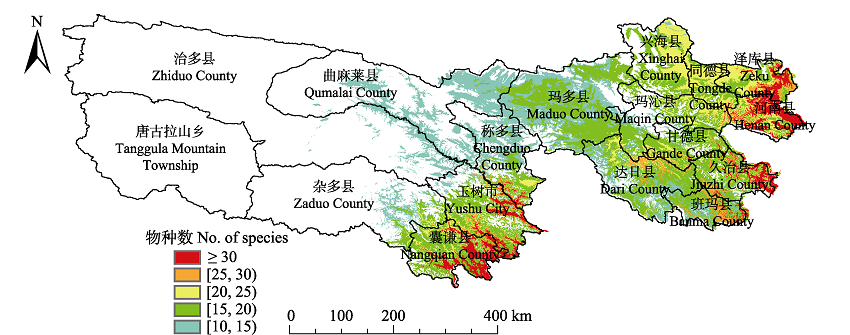
图4 气候变化RCP2.6情景下2070年三江源自然保护区草地濒危保护植物多样性热点分布图
Fig. 4 The distribution map of the grassland endangered plant species hotspots in Sanjiangyuan Nature Reserve under RCP2.6 of climate change in 2070
| [1] | Bai WQ, Zhang YL, Xie GD, Shen ZX (2012) Analysis of formation causes of grassland degradation in Maduo County in the source region of Yellow River. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 13, 823-826. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [摆万奇, 张镱锂, 谢高地, 沈振西 (2012) 黄河源区玛多县草地退化成因分析. 应用生态学报, 13, 823-826.] | |
| [2] | Beaumont L, Pitman A, Poulsen M, Hughes L (2007) Where will species go? Incorporating new advances in climate modelling into projections of species distributions. Global Change Biology, 13, 1368-1385. |
| [3] | Canton Y, Barrio GD, Sole-Benet A, Lazaro R (2004) Topog¬raphic controls on the spatial distribution of ground cover in the Tabernas badlands of SE Spain. Catena, 55, 341-365. |
| [4] | Chi XL, Zhang ZJ, Xu XT, Zhang XB, Zhao ZP, Liu YN, Wang QG, Wang H, Li Y, Yang G, Guo LP, Tang ZY, Huang LQ (2017) Threatened medicinal plants in China: Distributions and conservation priorities. Biological Con¬servation, 210, 89-95. |
| [5] | Costanza R, Groot RD, Farberk S, Grasso M, Hannon B, Lim¬burg KE, Naeem S, Paruelo JM, Raskin RG, Suttonkk P, Belt MVD (1997) The value of the world’s ecosystem ser¬vices and natural capital. Nature, 386, 253-260. |
| [6] | Dalton R (2000) Biodiversity cash aimed at hotspots. Nature, 406, 818. |
| [7] | Dong SK, Wen L, Zhu L, Li XY (2010) Implication of coupled natural and human systems in sustainable rangeland ecosystem management in HKH region. Frontiers of Earth Science in China, 4, 42-50. |
| [8] | Goberville E, Beaugrand G, Hautekeete N, Piquot Y, Luczak C (2015) Uncertainties in the projection of species distribu¬tions related to general circulation models. Ecology and Evolution, 5, 1100-1116. |
| [9] | Guo YL Wei HY, Lu CY, Zhang HL, Gu W (2014) Predictions of potential geographical distribution of Sinopodophyllum hexandrum under climate change. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 38, 249-261. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [郭彦龙, 卫海燕, 路春燕, 张海龙, 顾蔚 (2014) 气候变化下桃儿七潜在地理分布的预测. 植物生态学报, 38, 249-261.] | |
| [10] | Gould S, Beeton N, Harris R, Hutchinson M, Lechner A, Porfirio L, Mackey B (2014) A tool for simulating and communicating uncertainty when modelling species distributions under future climates. Ecology and Evolution, 4, 4798-4811. |
| [11] | Hijmans RJ, Cameron SE, Parra JL, Jones PG, Jarvis A (2005) Very high resolution interpolated climate surfaces for global land areas. International Journal of Climatology, 25, 1965-1978. |
| [12] | IPCC(2013) Climate change 2013: The physical science basis. In: Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (eds Stocker TF, Qin D, Plattner GK, Tignor M, Allen SK, Boschung J, Nauels A, Xia Y, Bex V, Midgley PM). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge and New York. |
| [13] | Jiang C, Zhang LB (2015) Climate change and its impact on the eco-environment of the Three-Rivers Headwater Region on the Tibetan Plateau, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 12, 12057-12081. |
| [14] | Jiang ZG, Fan EY (2003) Exploring the endangered species criteria: Rethinking the IUCN Red List Criteria. Biodiversity Science, 11, 382-392. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [蒋志刚, 樊恩源 (2003) 关于物种濒危等级标准之探讨——对IUCN物种濒危等级的思考. 生物多样性, 11, 382-392.] | |
| [15] | John R, Dalling JW, Harms KE Yavitt JB, Stallard RF, Mirabello M, Hubbell SP, Valencia R, Navarrete H, Vallejo M, Foster RB (2007) Soil nutrients influence spatial distributions of tropical tree species. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 104, 864-869. |
| [16] | Liana NJ, Richard FM, Hugh PP (2008) Optimal allocation of resources among threatened species: A project prioritization protocol. Conservation Biology, 23, 328-338. |
| [17] | Liu JY, Xu XL, Shao QQ (2008) The spatial and temporal characteristics of grassland degradation in the Three-River Headwaters region in Qinghai Province. Acta Geographica Sinica, 63, 364-376. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘纪远, 徐新良, 邵全琴 (2008) 近30年来青海三江源地区草地退化的时空特征. 地理学报, 63, 364-376.] | |
| [18] | Liu MC, Li DQ, Wen YM, Luan XF (2006) Assessment of the priorities of species diversity conservation in Sanjiangyuan region by GIS. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 20(4), 51-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘敏超, 李迪强, 温琰茂, 栾晓峰 (2006) 基于GIS的三江源地区物种多样性保护优先性分析. 干旱区资源与环境, 20(4), 51-54.] | |
| [19] | Liu ZS, Gao H, Teng LW, Su Y, Wang XQ, Kong FY (2013) Habitat suitability assessment of blue sheep in Helan Mountain based on MaxEnt modeling. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33, 7243-7249. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [刘振生, 高惠, 滕丽微, 苏云, 王晓勤, 孔芳毅 (2013) 基于MaxEnt模型的贺兰山岩羊生境适宜性评价. 生态学报, 33, 7243-7249.] | |
| [20] | Ma KP, Qian YQ (1998) Biodiversity conservation and its research progress. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 4, 95-99. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [马克平, 钱迎倩 (1998) 生物多样性保护及其研究进展. 应用与环境生物学报, 4, 95-99.] | |
| [21] | Ma LZ, Pan JB (2012) Floristic study of rare and endangered plants and national key protected plants in Qinghai Province. Journal of Northwest Normal University, 48(1), 78-85. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [马莉贞, 潘建斌 (2012) 青海省珍稀濒危植物的区系研究. 西北师范大学学报, 48(1), 78-85.] | |
| [22] | Meehl GA, Stocker TF, Collins WD, Friedlingstein P, Gaye AT, Gregory JM, Kitoh A, Knutti R, Murphy JM, Noda A, Raper SCB, Watterson IG, Weaver AJ, Zhao Z (2007) Global climate projections. In: Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (eds Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M, Chen Z, Marquis M, Averyt KB, Tignor M, Miller HL).Cambridge University Press, Cambridge and New York. |
| [23] | Murray-Smith C, Brummitt NA, Oliverira-Filho AT, Bachman S, Moat J, Lughadha EMN, Lucas EJ (2009) Plant diversity hotspots in the Atlantic coastal forests of Brazil. Conservation Biology, 23, 151-163. |
| [24] | Myers N, Mittermeier RA, Mittermeier CG, Fonseca GABD, Kent J (2000) Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature, 403, 853-859. |
| [25] | Orme CD, Davies RG, Burgess M, Rigenbrod F, Pickup N, Olson VA, Webster AJ, Ding TS, Rasmussen PC, Ridgely RS, Stattersfield AJ, Bennett PM, Blackburn TM, Gaston KJ, Owens IP (2005) Global hotspots of species richness are not congruent with endemism or threat. Nature, 436, 1016-1019. |
| [26] | Pearson RG, Raxworthy CJ, Nakamura M, Peterson AT (2007) Predicting species distributions from small numbers of occurrence records: A test case using cryptic geckos in Madagascar. Journal of Biogeography, 34, 102-117. |
| [27] | Phillips S, Anderson RI, Schapille RE (2006) Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distribution. Ecological Modeling, 190, 231-259. |
| [28] | Shao QQ, Liu JY, Huang L, Fan JW, Xu XL, Wang JB (2013) Integrated assessment on the effectiveness of ecological conservation in Sanjiangyuan National Nature Reserve. Geographical Research, 32, 1645-1656. (in Chinese with abstract) |
| [邵全琴, 刘纪远, 黄麟, 樊江文, 徐新良, 王军邦 (2013) 2005-2009年三江源自然保护区生态保护和建设工程生态成效综合评估. 地理研究, 32, 1645-1656.] | |
| [29] | State Environmental Protection Administration, Institute of Botany of the Chinese Academy of Sciences(1987) China Rare and Endangered Plant Species List, Vol I. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [国家环境保护局, 中国科学院植物所(1987) 中国珍稀濒危保护植物名录(第一册). 科学出版社, 北京.] | |
| [30] | Sun HQ, Shi HX, Ma L (2013) Floristic study on Sanjiangyuan National Nature Reserve. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 35(3), 85-91. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孙海群, 石红霄, 马雷 (2013) 三江源自然保护区种子植物区系分析. 中国草地学报, 35(3), 85-91.] | |
| [31] | Swets JA (1988) Measuring the accuracy of diagnostic systems. Science, 240, 1285-1293. |
| [32] | Wang S, Xie Y (2004) China Species Red List, Vol I: Red List. Higher Education Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) |
| [汪松, 解焱 (2004) 中国物种红色名录, 第一卷: 红色名录. 高等教育出版社, 北京.] | |
| [33] | Wilson KA, Mcbride MF, Bode MF Possingham HP (2006) Prioritizing global conservation efforts. Nature, 440, 337-340. |
| [34] | Wu YH (2006) The Endemic Species of Seed Plants and Their Eco-geographic Distribution in Qinghai. Acta Botanica Yunnanica, 28, 327-336. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [吴玉虎 (2006) 青海种子植物特有种及其生态地理分布. 云南植物研究, 28, 327-336.] | |
| [35] | Wulff AS, Hollingsworth PM, Ahrends A, Jaffre T, Veillon JM, Huillier LL, Fogliani B (2013) Conservation priorities in a biodiversity hotspot: Analysis of narrow endemic plant species in New Caledonia. PLoS ONE, 8, e73371. |
| [36] | Zhang L, Guo HD, Ji L, Lei LP, Wang CZ, Yan DM, Li B, Li J (2013) Vegetation greenness trend (2000 to 2009) and the climate controls in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 7, 1-17. |
| [37] | Zhang L, Ouyang ZY, Xu WH (2015) Theory, work frame and hot issues of systematic conservation planning. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35,1284-1295. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张路, 欧阳志云, 徐卫华 (2015) 系统保护规划的理论、方法及关键问题. 生态学报, 35, 1284-1295.] |
| [1] | 干靓 刘巷序 鲁雪茗 岳星. 全球生物多样性热点地区大城市的保护政策与优化方向[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24529-. |
| [2] | 曾子轩 杨锐 黄越 陈路遥. 清华大学校园鸟类多样性特征与环境关联[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24373-. |
| [3] | 臧明月, 刘立, 马月, 徐徐, 胡飞龙, 卢晓强, 李佳琦, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 《昆明-蒙特利尔全球生物多样性框架》下的中国城市生物多样性保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24482-. |
| [4] | 祝晓雨, 王晨灏, 王忠君, 张玉钧. 城市绿地生物多样性研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 25027-. |
| [5] | 袁琳, 王思琦, 侯静轩. 大都市地区的自然留野:趋势与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24481-. |
| [6] | 胡敏, 李彬彬, Coraline Goron. 只绿是不够的: 一个生物多样性友好的城市公园管理框架[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24483-. |
| [7] | 王欣, 鲍风宇. 基于鸟类多样性提升的南滇池国家湿地公园生态修复效果分析[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24531-. |
| [8] | 明玥, 郝培尧, 谭铃千, 郑曦. 基于城市绿色高质量发展理念的中国城市生物多样性保护与提升研究[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24524-. |
| [9] | 谢淦, 宣晶, 付其迪, 魏泽, 薛凯, 雒海瑞, 高吉喜, 李敏. 草地植物多样性无人机调查的物种智能识别模型构建[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24236-. |
| [10] | 褚晓琳, 张全国. 演化速率假说的实验验证研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25019-. |
| [11] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [12] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [13] | 农荞伊, 曹军, 程文达, 彭艳琼. 不同方法对蜜蜂总科昆虫资源与多样性监测效果的比较[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 25057-. |
| [14] | 郭雨桐, 李素萃, 王智, 解焱, 杨雪, 周广金, 尤春赫, 朱萨宁, 高吉喜. 全国自然保护地对国家重点保护野生物种的覆盖度及其分布状况[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24423-. |
| [15] | 赵维洋, 王伟, 马冰然. 其他有效的区域保护措施(OECMs)研究进展与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24525-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2026 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn
![]()