



生物多样性 ›› 2018, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (11): 1147-1157. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018135 cstr: 32101.14.biods.2018135
蔡军奇1, 刘大鹏2, 张淑媛1, 宗国1, 刘佳1, 白雪娇1,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2018-05-04
接受日期:2018-08-18
出版日期:2018-11-20
发布日期:2019-01-08
通讯作者:
白雪娇
作者简介:# 共同第一作者
基金资助:
Junqi Cai1, Dapeng Liu2, Shuyuan Zhang1, Guo Zong1, Jia Liu1, Xuejiao Bai1,3,*( )
)
Received:2018-05-04
Accepted:2018-08-18
Online:2018-11-20
Published:2019-01-08
Contact:
Bai Xuejiao
About author:# Co-first authors
摘要:
为了解辽东山区次生林乔木幼苗组成及其年际动态, 本文以4 ha动态监测样地为平台, 对样地内1,600个 5 m × 5 m样方进行监测。依据2014-2016年连续3年的调查, 对样地内乔木幼苗的组成、高度分布、新增和死亡年际动态、空间分布格局等进行分析。结果表明: (1)调查期间共记录到22种乔木幼苗, 3年间幼苗组成没有发生变化, 但各个样方间出现极大差异, 并且幼苗优势树种组成与样地内优势树种成分保持着一定的相似性。(2)幼苗数量在不同树种和年际间表现出较大的差异: 花曲柳(Fraxinus rhynchophylla)、色木槭(Acer mono)、胡桃楸(Juglans mandshurica)在3年间幼苗数量最多, 占幼苗总数的75.6%; 花曲柳和胡桃楸幼苗数量表现出较明显的年际波动, 其他树种波动较小, 不同树种的幼苗密度差异很大。(3)幼苗新增和死亡存在明显的种间和年际差异: 2014-2015年间幼苗的新增数量(3,888)明显高于2015-2016年间(1,710), 同时2014-2015年间幼苗死亡率(23.7%)也明显高于2015-2016年间(12.7%)。对2015-2016年间新增幼苗和已有幼苗的死亡情况进行比较可以发现, 新增幼苗总体死亡率(18.8%)明显高于已有幼苗(8.1%)。(4)对比幼苗和大树的空间分布可以发现, 样地内优势幼苗都表现出集群分布的特征。在空间分布上, 幼苗与母树保持一定的相似性。
蔡军奇, 刘大鹏, 张淑媛, 宗国, 刘佳, 白雪娇 (2018) 辽东山区次生林乔木幼苗组成及其年际动态. 生物多样性, 26, 1147-1157. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018135.
Junqi Cai, Dapeng Liu, Shuyuan Zhang, Guo Zong, Jia Liu, Xuejiao Bai (2018) Composition and interannual dynamics of tree seedlings in a secondary forest in montane region of eastern Liaoning Province, China. Biodiversity Science, 26, 1147-1157. DOI: 10.17520/biods.2018135.
 |
表1 不同年份幼苗树种组成、死亡率和更新率及其各新生幼苗出现的样方数
Table 1 Species composition, mortality and recruitment rates of seedings, and the number of quadrats presented with recruited seedlings across different years
 |
| 树种 Species | 幼苗数量 No. of seedlings | 幼苗密度 Seedling density (mean ± SE, n = 1,600) | 幼苗密度变异系数 CV of seedling density (%) | 相对多度 Relative abundance | 相对频度 Relative frequency | 重要值 Importance value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 花曲柳 Fraxinus rhynchophylla | 5,189 | 3.685 ± 0.347 | 376.97 | 32.93 | 10.81 | 21.87 | |
| 色木槭 Acer mono | 3,910 | 2.777 ± 0.146 | 209.71 | 24.81 | 17.13 | 20.97 | |
| 胡桃楸 Juglans mandshurica | 1,712 | 1.216 ± 0.040 | 131.52 | 10.86 | 19.53 | 15.20 | |
| 暴马丁香 Syringa amurensis | 827 | 0.587 ± 0.042 | 288.83 | 5.25 | 7.13 | 6.19 | |
| 假色槭 Acer pseudo-sieboldianum | 742 | 0.527 ± 0.044 | 336.29 | 4.71 | 5.53 | 5.12 | |
| 水曲柳 Fraxinus mandshruica | 622 | 0.442 ± 0.042 | 379.44 | 3.95 | 5.42 | 4.69 | |
| 山杨 Populus davidiana | 614 | 0.436 ± 0.046 | 425.41 | 3.90 | 3.17 | 3.54 | |
| 灯台树 Bothrocaryum controversum | 379 | 0.269 ± 0.023 | 348.90 | 2.40 | 4.58 | 3.49 | |
| 裂叶榆 Ulmus laciniata | 291 | 0.207 ± 0.015 | 283.45 | 1.85 | 4.93 | 3.39 | |
| 蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica | 240 | 0.170 ± 0.016 | 386.00 | 1.52 | 3.05 | 2.29 | |
| 青楷槭 Acer tegmentosum | 208 | 0.148 ± 0.014 | 379.95 | 1.32 | 3.01 | 2.17 | |
| 小楷槭 Acer komarovii | 178 | 0.126 ± 0.012 | 383.95 | 1.13 | 2.82 | 1.98 | |
| 怀槐 Maackia amurensis | 180 | 0.128 ± 0.012 | 378.25 | 1.14 | 2.71 | 1.93 | |
| 稠李 Prunus padus | 172 | 0.122 ± 0.013 | 440.27 | 1.09 | 2.55 | 1.82 | |
| 水榆花楸 Sorbus alnifolia | 143 | 0.102 ± 0.010 | 379.01 | 0.91 | 2.57 | 1.74 | |
| 千金榆 Carpinus cordata | 154 | 0.109 ± 0.012 | 434.08 | 0.98 | 2.34 | 1.66 | |
| 紫椴 Tilia amurensis | 86 | 0.061 ± 0.007 | 483.57 | 0.55 | 1.20 | 0.88 | |
| 花楷槭 Acer ukurunduense | 41 | 0.029 ± 0.008 | 1,105.50 | 0.26 | 0.58 | 0.42 | |
| 黄檗 Phellodendron amurense | 33 | 0.023 ± 0.007 | 1,215.70 | 0.21 | 0.42 | 0.32 | |
| 春榆 Ulmus propinqua | 29 | 0.021 ± 0.005 | 1,022.49 | 0.18 | 0.35 | 0.27 | |
| 黄榆 Ulmus macrocarpa | 7 | 0.005 ± 0.002 | 1,415.22 | 0.04 | 0.12 | 0.08 | |
| 三花槭 Acer triflorum | 3 | 0.002 ± 0.001 | 2,164.87 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.05 | |
| 总计 Total | 15,760 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | |||
表2 2014年幼苗组成与数量特征
Table 2 Species composition and quantitative characteristics of tree seedlings in 2014
| 树种 Species | 幼苗数量 No. of seedlings | 幼苗密度 Seedling density (mean ± SE, n = 1,600) | 幼苗密度变异系数 CV of seedling density (%) | 相对多度 Relative abundance | 相对频度 Relative frequency | 重要值 Importance value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 花曲柳 Fraxinus rhynchophylla | 5,189 | 3.685 ± 0.347 | 376.97 | 32.93 | 10.81 | 21.87 | |
| 色木槭 Acer mono | 3,910 | 2.777 ± 0.146 | 209.71 | 24.81 | 17.13 | 20.97 | |
| 胡桃楸 Juglans mandshurica | 1,712 | 1.216 ± 0.040 | 131.52 | 10.86 | 19.53 | 15.20 | |
| 暴马丁香 Syringa amurensis | 827 | 0.587 ± 0.042 | 288.83 | 5.25 | 7.13 | 6.19 | |
| 假色槭 Acer pseudo-sieboldianum | 742 | 0.527 ± 0.044 | 336.29 | 4.71 | 5.53 | 5.12 | |
| 水曲柳 Fraxinus mandshruica | 622 | 0.442 ± 0.042 | 379.44 | 3.95 | 5.42 | 4.69 | |
| 山杨 Populus davidiana | 614 | 0.436 ± 0.046 | 425.41 | 3.90 | 3.17 | 3.54 | |
| 灯台树 Bothrocaryum controversum | 379 | 0.269 ± 0.023 | 348.90 | 2.40 | 4.58 | 3.49 | |
| 裂叶榆 Ulmus laciniata | 291 | 0.207 ± 0.015 | 283.45 | 1.85 | 4.93 | 3.39 | |
| 蒙古栎 Quercus mongolica | 240 | 0.170 ± 0.016 | 386.00 | 1.52 | 3.05 | 2.29 | |
| 青楷槭 Acer tegmentosum | 208 | 0.148 ± 0.014 | 379.95 | 1.32 | 3.01 | 2.17 | |
| 小楷槭 Acer komarovii | 178 | 0.126 ± 0.012 | 383.95 | 1.13 | 2.82 | 1.98 | |
| 怀槐 Maackia amurensis | 180 | 0.128 ± 0.012 | 378.25 | 1.14 | 2.71 | 1.93 | |
| 稠李 Prunus padus | 172 | 0.122 ± 0.013 | 440.27 | 1.09 | 2.55 | 1.82 | |
| 水榆花楸 Sorbus alnifolia | 143 | 0.102 ± 0.010 | 379.01 | 0.91 | 2.57 | 1.74 | |
| 千金榆 Carpinus cordata | 154 | 0.109 ± 0.012 | 434.08 | 0.98 | 2.34 | 1.66 | |
| 紫椴 Tilia amurensis | 86 | 0.061 ± 0.007 | 483.57 | 0.55 | 1.20 | 0.88 | |
| 花楷槭 Acer ukurunduense | 41 | 0.029 ± 0.008 | 1,105.50 | 0.26 | 0.58 | 0.42 | |
| 黄檗 Phellodendron amurense | 33 | 0.023 ± 0.007 | 1,215.70 | 0.21 | 0.42 | 0.32 | |
| 春榆 Ulmus propinqua | 29 | 0.021 ± 0.005 | 1,022.49 | 0.18 | 0.35 | 0.27 | |
| 黄榆 Ulmus macrocarpa | 7 | 0.005 ± 0.002 | 1,415.22 | 0.04 | 0.12 | 0.08 | |
| 三花槭 Acer triflorum | 3 | 0.002 ± 0.001 | 2,164.87 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.05 | |
| 总计 Total | 15,760 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | |||
| 自由度 df | 平方和 SS | 均方和 MS | F | P | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年份 Year | 2 | 343.18 | 171.591 | 4,016.3 | 0.001*** | |
| 残差 Residuals | 4,797 | 204.95 | 0.043 | |||
| 总数 Total | 4,799 | 548.13 | ||||
| 2014 vs. 2015 | 2,674.386 | 0.001 | ||||
| 2014 vs. 2016 | 5,036.132 | 0.001 | ||||
| 2015 vs. 2016 | 7,513.394 | 0.001 | ||||
表3 2014-2016年乔木幼苗的非参数多元方差分析
Table 3 The results of perMANOVA for tree seedlings during 2014-2016
| 自由度 df | 平方和 SS | 均方和 MS | F | P | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年份 Year | 2 | 343.18 | 171.591 | 4,016.3 | 0.001*** | |
| 残差 Residuals | 4,797 | 204.95 | 0.043 | |||
| 总数 Total | 4,799 | 548.13 | ||||
| 2014 vs. 2015 | 2,674.386 | 0.001 | ||||
| 2014 vs. 2016 | 5,036.132 | 0.001 | ||||
| 2015 vs. 2016 | 7,513.394 | 0.001 | ||||
| 自由度 df | 平方和 SS | 均方和 MS | F | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年份 Year | 1 | 166.74 | 166.744 | 2,701.5 | 0.001*** |
| 残差 Residuals | 3,198 | 197.39 | 0.062 | ||
| 总数 Total | 3,198 | 364.13 |
表4 2014-2016年新增乔木幼苗的非参数多元方差分析
Table 4 The results of perMANOVA for recruited tree seedlings during 2014-2016
| 自由度 df | 平方和 SS | 均方和 MS | F | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年份 Year | 1 | 166.74 | 166.744 | 2,701.5 | 0.001*** |
| 残差 Residuals | 3,198 | 197.39 | 0.062 | ||
| 总数 Total | 3,198 | 364.13 |
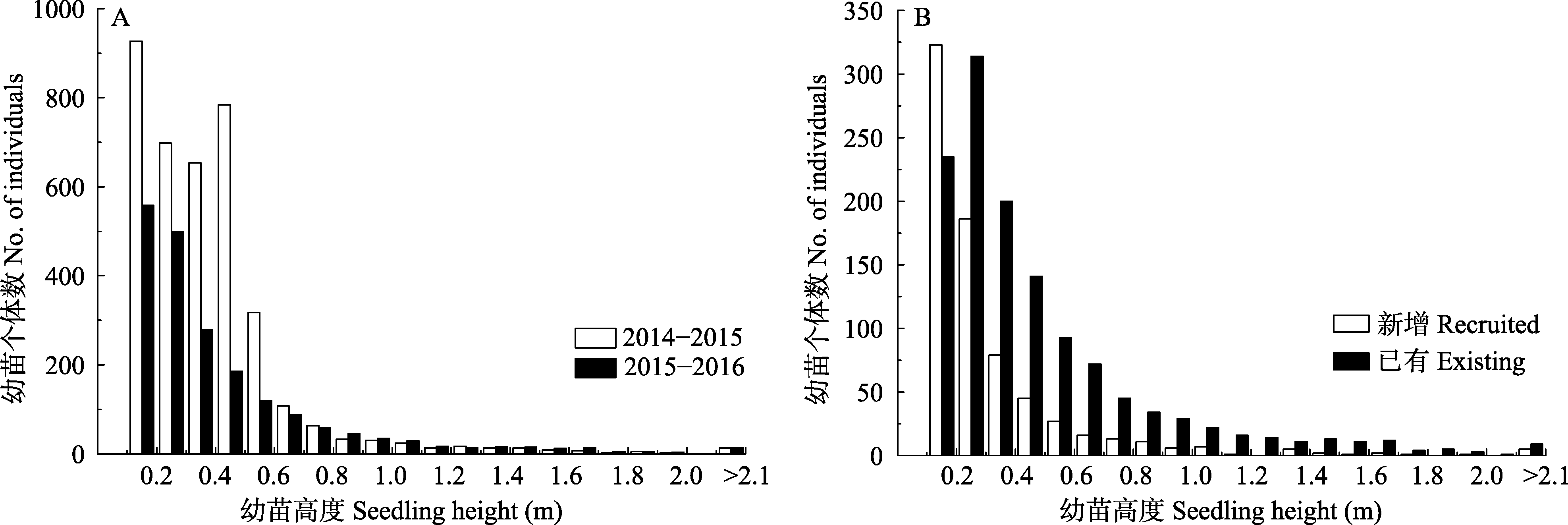
图3 2014-2016年间死亡幼苗高度级分布及2015-2016年间新增和已有死亡幼苗高度级分布
Fig. 3 Height distribution of dead seedlings in 2014-2016 and height distribution of dead recruited and existing seedlings in 2015-2016
| [1] | Anderson MJ (2005) PERMANOVA: A FORTRAN Computer Program for Permutational Multivariate Analysis of Variance. Department of Statistics, University of Auckland, Auckland. |
| [2] | Bagchi R, Gallery RE, Gripenberg S, Gurr SJ, Narayan L, Addis CE, Freckleton RP, Lewis OT (2014) Pathogens and insect herbivores drive rainforest plant diversity and composition. Nature, 506, 85-88. |
| [3] | Bai XJ, Queenborough SA, Wang XG, Zhang J, Li BH, Yuan ZQ, Xing DL, Lin F, Ye J, Hao ZQ (2012) Effects of local biotic neighbors and habitat heterogeneity on tree and shrub seedling survival in an old-growth temperate forest. Oecologia, 170, 755-765. |
| [4] | Bai XJ, Deng LP, Li LL, Niu SS, Han MN, Qin SJ, Zhou YB (2015) Distribution patterns of woody plants in a secondary forest in the montane region of eastern Liaoning Province, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35, 98-105. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [白雪娇, 邓莉萍, 李露露, 牛沙沙, 韩美娜, 秦胜金, 周永斌 (2015) 辽东山区次生林木本植物空间分布. 生态学报, 35, 98-105.] | |
| [5] | Chang-Yang CH, Lu CL, Sun IF, Hsieh CF (2013) Long-term seedling dynamics of tree species in a subtropical rain forest, Taiwan. Taiwania, 58, 35-43. |
| [6] | Clark DA, Clark DB (1984) Spacing dynamics of a tropical rain forest tree: Evaluation of the Janzen-Connell model. The American Naturalist, 124, 769-788. |
| [7] | Collins RJ, Carson WP (2004) The effects of environment and life stage on Quercus abundance in the eastern deciduous forest, USA: Are sapling densities most responsive to environmental gradients? Forest Ecology and Management, 201, 241-258. |
| [8] | Condit R (1995) Research in large, long-term tropical forest plots. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 10, 18-22. |
| [9] | Condit R, Ashton PS, Manokaran N, Lafrankie JV, Hubbell SP, Foster RB (1999) Dynamics of the forest communities at Pasoh and Barro Colorado: Comparing two 50-ha plots. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 354, 1739-1748. |
| [10] | Connell JH (1971) On the role of natural enemies in preventing competitive exclusion in some marine animals and in rain forest trees. Dynamics of Populations, 298, 298-312. |
| [11] | Connell JH, Green PT (2000) Seedling dynamics over thirty-two years in a tropical rain forest tree. Ecology, 81, 568-584. |
| [12] | Ding H, Fang YM, Yang XH, Yuan FY, He LH, Yao JF, Wu J, Chi B, Li Y, Chen SF (2016) Community characteristics of a subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest in Huangshan, Anhui Province, East China. Biodiversity Science, 24, 875-887. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [丁晖, 方炎明, 杨新虎, 袁发银, 何立恒, 姚剑飞, 吴俊, 迟斌, 李垚, 陈水飞 (2016) 黄山亚热带常绿阔叶林的群落特征. 生物多样性, 24, 875-887.] | |
| [13] | Fyllas NM, Politi PI, Galanidis A, Dimitrakopoulos PG, Arianoutsou M (2010) Simulating regeneration and vegetation dynamics in Mediterranean coniferous forests. Ecological Modelling, 221, 1494-1504. |
| [14] | Harms KE, Wright SJ, Calderón O, Hernández A, Herre EA (2000) Pervasive density-dependent recruitment enhances seedling diversity in a tropical forest. Nature, 404, 493-495. |
| [15] | Hu LL, Mao ZH, Zhu JJ, Liu ZG, Chen GH, Zhang LJ (2005) Classification and ordination of secondary forests in montane zone of eastern Liaoning Province. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 25, 2848-2854. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [胡理乐, 毛志宏, 朱教君, 刘足根, 陈广华, 张立君 (2005) 辽东山区天然次生林的数量分类. 生态学报, 25, 2848-2854.] | |
| [16] | Janzen DH (1970) Herbivores and the number of tree species in tropical forests. The American Naturalist, 104, 501-528. |
| [17] | Khurana E, Singh JS (2000) Influence of seed size on seedling growth of Albizia procera, under different soil water levels. Annals of Botany, 86, 1185-1192. |
| [18] | Kong XW, Hu WL, Zhang B, Wang YG (2002) Quantative classification of structural types of present secondary natural forests in eastern Liaoning. Journal of Liaoning Forestry Science and Technology, (3), 14-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [孔祥文, 胡万良, 张冰, 王玉光 (2002) 辽东山区现有次生林结构类型的数量分类. 辽宁林业科技, (3), 14-16.] | |
| [19] | Li JQ, Song XY, Cao M (2016) Response of tree seedlings to altitudinal gradient and its seasonal variation in Ailao Mountain and Yulong Mountain, Yunnan Province, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 27, 3403-3412. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李洁琼, 宋晓阳, 曹敏 (2016) 云南哀牢山和玉龙雪山森林树种幼苗对海拔梯度的响应及其季节性差异. 应用生态学报, 27, 3403-3412.] | |
| [20] | Li XF, Zhu JJ, Wang QL, Liu ZG, Hou CS, Yang HJ (2004) Snow/wind damage in natural secondary forests in Liaodong mountainous regions of Liaoning Province. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 15, 941-946. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李秀芬, 朱教君, 王庆礼, 刘足根, 侯传生, 杨焕君 (2004) 辽东山区天然次生林雪/风灾害成因及分析. 应用生态学报, 15, 941-946.] | |
| [21] | Li XL, Wang H, Zheng Z, Lin LX, Deng XB, Cao M (2009) Composition, spatial distribution and survival during the dry season of tree seedlings in a tropical forest in Xishuangbanna, SW China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 33, 658-671. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [李晓亮, 王洪, 郑征, 林露湘, 邓晓保, 曹敏 (2009) 西双版纳热带森林树种幼苗的组成、空间分布和旱季存活. 植物生态学报, 33, 658-671.] | |
| [22] | Lin F, Comita LS, Wang XG, Bai XJ, Yuan ZQ, Xing DL, Hao ZQ (2014) The contribution of understory light availability and biotic neighborhood to seedling survival in secondary versus old-growth temperate forest. Plant Ecology, 215, 795-807. |
| [23] | Lu J, Johnson DJ, Qiao X, Lu Z, Wang Q, Jiang M (2015) Density dependence and habitat preference shape seedling survival in a subtropical forest in central China. Journal of Plant Ecology, 8, 568-577. |
| [24] | Maher EL, Germino MJ (2006) Microsite differentiation among conifer species during seedling establishment at alpine treeline. Ecoscience, 13, 334-341. |
| [25] | Markl JS, Schleuning M, Forget PM, Jordano P, Lambert JE, Traveset A, Wright SJ, Böhning-Gaese K (2012) Meta-analysis of the effects of human disturbance on seed dispersal by animals. Conservation Biology, 26, 1072-1081. |
| [26] | Metz MR, Comita LS, Chen YY, Norden N, Condit R, Hubbell SP, Sun IF, Noor NSBM, Wright SJ (2008) Temporal and spatial variability in seedling dynamics: A cross-site comparison in four lowland tropical forests. Journal of Tropical Ecology, 24, 9-18. |
| [27] | Metz MR, Sousa WP, Valencia R (2010) Widespread density-dependent seedling mortality promotes species coexistence in a highly diverse Amazonian rain forest. Ecology, 91, 3675-3685. |
| [28] | Minami Y, Oba M, Kojima S (2015) Distribution pattern of coniferous seedlings after a partial harvest along a creek in a Canadian Pacific northwest forest. Journal of Forest Research, 20, 328-336. |
| [29] | Muhamed H, Maalouf JP, Michalet R (2013) Summer drought and canopy opening increase the strength of the oak seedlings-shrub spatial association. Annual of Forest Science, 70, 345-355. |
| [30] | Norden N, Chave J, Caubère A, Châtelet P, Ferroni N, Forget PM, Thébaud C (2007) Is temporal variation of seedling communities determined by environment or by seed arrival? A test in a neotropical forest. Journal of Ecology, 95, 507-516. |
| [31] | Peng SJ, Huang ZL, Peng SL, Ouyang XJ, Xu GL (2004) Factors influencing mortality of seed and seedling in plant nature regeneration process. Guihaia, 24, 113-121. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [彭闪江, 黄忠良, 彭少麟, 欧阳学军, 徐国良 (2004) 植物天然更新过程中种子和幼苗死亡的影响因素. 广西植物, 24, 113-121.] | |
| [32] | Shimono Y, Kudo G (2003) Intraspecific variations in seedling emergence and survival of Potentilla matsumurae (Rosaceae) between alpine fellfield and snowbed habitats. Annals of Botany, 91, 21-29. |
| [33] | Simões CG, Marques M (2010) The role of sprouts in the restoration of Atlantic rainforest in southern Brazil. Restoration Ecology, 15, 53-59. |
| [34] | Su Y, Jiao JY, Wang ZJ (2014) Characteristics of seedling survival in habitats of hill and gully slopes in hill-gully Loess Plateau region of northern Shaanxi. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 38, 694-709. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [苏嫄, 焦菊英, 王志杰 (2014) 陕北黄土丘陵沟壑区坡沟立地环境下幼苗的存活特征. 植物生态学报, 38, 694-709.] | |
| [35] | Swamy V, Terborgh J, Dexter KG, Best BD, Alvarez P, Cornejo F (2011) Are all seeds equal? Spatially explicit comparisons of seed fall and sapling recruitment in a tropical forest. Ecology Letters, 14, 195-201. |
| [36] | Tan YB, Zhan CA, Xiao ZX, Yang HD, Peng JH, Wu KS (2010) Population structure and dynamic characteristics of Machilus chinensis in Nan’ao Island, Guangdong Province. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 29, 1901-1906. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [谭一波, 詹潮安, 肖泽鑫, 杨海东, 彭剑华, 吴凯胜 (2010) 广东南澳岛中华楠种群结构及动态特征. 生态学杂志, 29, 1901-1906.] | |
| [37] | Uriarte M, Canham CJ, Zimmerman J, Brokaw N (2005) Seedling recruitment in a hurricane-driven tropical forest: Light limitation, density-dependence and the spatial distribution of parent trees. Journal of Ecology, 93, 291-304. |
| [38] | Wang M, Tao DL (1998) Drought-tolerance of main tree species in Changbai Mountain. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 9, 7-10. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [王淼, 陶大立 (1998) 长白山主要树种耐旱性的研究. 应用生态学报, 9, 7-10.] | |
| [39] | Wright SJ, Mullerlandau HC, Calderón O, Hernandéz A (2005) Annual and spatial variation in seedfall and seedling recruitment in a neotropical forest. Ecology, 86, 848-860. |
| [40] | Xi ZJ, Wang XJ, Song HJ, Zhao BQ, Hao J, Guo DG (2017) Short-term dynamics of the main trees seedings death and its relationship with topographic factors in a Pinus tabulaeformis forest in the Lingkong Mountain, Shanxi. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences, 45, 978-982. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [席朝骏, 王晓军, 宋厚娟, 赵冰清, 郝婧, 郭东罡 (2017) 山西灵空山油松林主要乔木幼苗短期死亡动态及其与地形因子的关系. 山西农业科学, 45, 978-982.] | |
| [41] | Xu ZB, Dai LM, Chen JQ, Wang Z, Dai HC, Li X (2001) Natural regeneration condition in Pinus koraiensis broad-leaved mixed forest. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 21, 1413-1420. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [徐振邦, 代力民, 陈吉泉, 王战, 戴洪才, 李昕 (2001) 长白山红松阔叶混交林森林天然更新条件的研究. 生态学报, 21, 1413-1420.] | |
| [42] | Yan Y, Zhang XN, Yao J, Zhang CY, Zhao XH (2016) Composition and temporal dynamics of tree seedlings at different successional stages of conifer and broad-leaved mixed forests in Jiaohe, Jilin Province, China. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 40, 127-139. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [闫琰, 张新娜, 姚杰, 张春雨, 赵秀海 (2016) 吉林蛟河不同演替阶段针阔混交林乔木幼苗数量组成及其时间动态. 植物生态学报, 40, 127-139.] | |
| [43] | Zeng XQ, Chen LZ, Tan FY, Huang JH, Xu HL, Lin GH (2008) Seedling emergence and dispersal pattern of the introduced Sonneratia caseolaris in Shenzhen Bay, China. Biodiversity Science, 16, 236-244. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [曾雪琴, 陈鹭真, 谭凤仪, 黄建辉, 徐华林, 林光辉 (2008) 深圳湾引种红树植物海桑的幼苗发生和扩散格局的生态响应. 生物多样性, 16, 236-244.] | |
| [44] | Zhang GS, Wang Z, Wang LH, Hao YL, Wen GS (2006) Regenerative seedlings dynamics of natural Sabina vulgaris community in Mu Us sandland. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 42(5), 62-67. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张国盛, 王哲, 王林和, 郝云龙, 温国胜 (2006) 毛乌素沙地天然臭柏居群有性更新幼苗动态研究. 林业科学, 42(5), 62-67.] | |
| [45] | Zhang J, Li BH, Bai XJ, Yuan ZQ, Wang XG, Ye J, Hao ZQ (2009) Composition and interannual dynamics of tree seedlings in broad-leaved Korean pine (Pinus koraiensis) mixed forest in Changbai Mountain. Biodiversity Science, 17, 385-396. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [张健, 李步杭, 白雪娇, 原作强, 王绪高, 叶吉, 郝占庆 (2009) 长白山阔叶红松林乔木树种幼苗组成及其年际动态. 生物多样性, 17, 385-396.] | |
| [46] | Zong G, Bai XJ, Zhang SY, Cai JQ (2018) Spatial pattern and interspecific spatial association of tree seedlings in a secondary forest in montane region of eastern Liaoning Province, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 29, 18-24. (in Chinese with English abstract) |
| [宗国, 白雪娇, 张淑媛, 蔡军奇 (2018) 辽东山区次生林乔木幼苗分布格局与种间空间关联性. 应用生态学报, 29, 18-24.] |
| [1] | 贾贞妮, 张意岑, 杜彦君, 任海保. 干扰对中亚热带森林群落物种多样性演替动态的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24078-. |
| [2] | 马文俊, 刘思嘉, 李柯懋, 简生龙, 薛长安, 韩庆祥, 魏金良, 陈生学, 牛依萌, 崔洲平, 隋瑞臣, 田菲, 赵凯. 青海省长江源区鱼类分布及多样性格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24494-. |
| [3] | 李艳朋, 陈洁, 卢春洋, 许涵. 海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林64 ha次生林动态监测样地群落结构特征[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24445-. |
| [4] | 何泽嵘, 叶鹏, 王舒婷, 关永鑫, 闫淑君, 洪心茹. 中国城市草坪的杂草优势种组成及空间分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24133-. |
| [5] | 舒为杰, 何花, 曾罗, 谷志容, 谭敦炎, 杨晓琛. 雌雄异株物种一把伞南星雌雄株空间分布及性别二态性[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24084-. |
| [6] | 吴芳芳, 刘娜, 何春梅, 原作强, 郝占庆, 尹秋龙. 秦岭山地木本植物群落结构及多样性的海拔梯度格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24239-. |
| [7] | 陈明苗, 张楚然, 邓云, 李生发, 李逢昌, 唐志忠, 魏兆喆, 张彩彩, 林露湘. 地形因子对亚热带半湿润常绿阔叶林木本植物萌生特征的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24282-. |
| [8] | 杨俊毅, 关潇, 李俊生, 刘晶晶, 郝颢晶, 王槐睿. 乌江流域生物多样性与生态系统服务的空间格局及相互关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 23061-. |
| [9] | 林木青, 张应明, 欧阳芳, 束祖飞, 朱朝东, 肖治术. 广东车八岭国家级自然保护区独栖性胡蜂多样性空间分布特征及其对环境因子的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(2): 22310-. |
| [10] | 崔家鹤, 李智勇, 王宇池, 孙蔷, 莎娜, 李紫晶, 武艳涛, 史亚博, 韩瀛, 李明乐, 王立新, 赵利清, 梁存柱. 垫状驼绒藜群落特征及地理分布数据集[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(10): 23172-. |
| [11] | 杨润明, 中村彰宏. 巢居蚂蚁更倾向于在人造光源附近定居繁殖[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(8): 22067-. |
| [12] | 王雅婷, 张定海, 张志山. 古尔班通古特沙漠固定沙丘上白梭梭和梭梭的空间分布及种间关联性[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(3): 21280-. |
| [13] | 王定一, 倪祥银, 岳楷, 张潇月, 康自佳, 朱玲, 吴福忠. 白蚁活动对中亚热带次生林和人工林的危害差异[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(3): 21324-. |
| [14] | 王重阳, 赵联军, 孟世勇. 王朗国家级自然保护区滑坡体兰科植物分布格局及其保护策略[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(2): 21313-. |
| [15] | 刘璐, 迟瑶, 吴朝宁, 钱天陆, 王结臣. 陆栖哺乳动物的地理隔离研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(8): 1134-1145. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
备案号:京ICP备16067583号-7
Copyright © 2022 版权所有 《生物多样性》编辑部
地址: 北京香山南辛村20号, 邮编:100093
电话: 010-62836137, 62836665 E-mail: biodiversity@ibcas.ac.cn